Investigation of an Autochthonous Outbreak of Bovine Besnoitiosis in Northwestern Sicily
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Farm A
2.1.1. Serological Findings
2.1.2. Clinical Signs
2.2. Farm B
2.2.1. Serological Findings
2.2.2. Clinical Signs
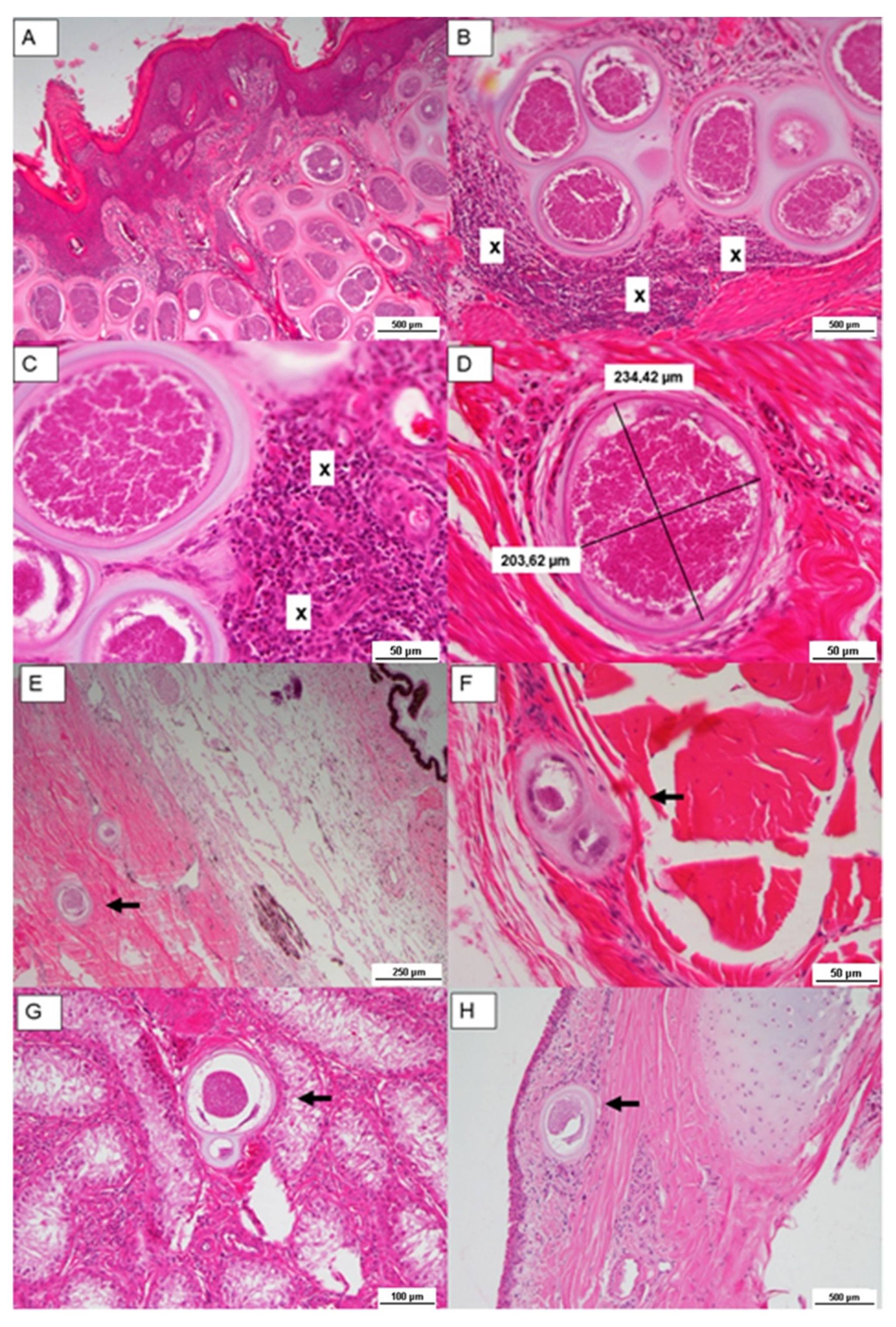
2.2.3. Histological Findings
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Characterization of Farms
4.1.1. Farm A
4.1.2. Farm B
4.2. ELISA
4.3. Histological Examination
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Olias, P.; Schade, B.; Mehlhorn, H. Molecular Pathology, Taxonomy and Epidemiology of Besnotia Species (Protozoa: Sarcocystidae). Infec. Genet. Evol. 2011, 11, 1564–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, S.V.; Cerqueira-Cézar, C.K.; Murata, F.H.A.; Lovallo, M.J.; Rosenthal, B.M.; Dubey, J.P. Bobcats (Lynx rufus) are natural definitive host of Besnoitia darlingi. Vet. Parasitol. 2017, 248, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez-García, G.; Frey, C.F.; Mora, L.M.O.; Schares, G. A century of Bovine Besnoitiosis: An Unknown Disease Re-Emerging in Europe. Trends Parasitol. 2013, 29, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pols, J.W.; Alexander, R.A.; Clark, R.; Louw, J.G.; De Kock, V.E. Studies on Bovine besnoitiosis with special reference to the aetiology. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 1960, 8, 266–334. [Google Scholar]
- Bigalke, R.D. New concepts on the epidemiological features of bovine besnoitiosis as determined by laboratory and field investigations. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 1968, 35, 3–137. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Langenmayer, M.C.; Gollnick, N.S.; Majzoub-Altweck, M.; Scharr, J.C.; Schares, G.; Hermanns, W. Naturally Acquired Bovine Besnoitiosis: Histological and Immunohistochemical Findings in Acute, Subacute, and Chronic Disease. Vet. Pathol. 2015, 52, 476–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frey, C.F.; Regidor-Cerrillo, J.; Marreros, N.; García-Lunar, P.; Gutiérrez-Expósito, D.; Schares, G.; Dubey, J.P.; Gentile, A.; Jacquiet, P.; Shkap, V.; et al. Besnoitia Besnoiti Lytic Cycle in Vitro and Differences in Invasion and Intracellular Proliferation among Isolates. Parasit Vectors 2016, 9, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Basson, P.A.; McCully, R.M.; Bigalke, R.D. Observations on the pathogenesis of bovine and antelope strains of Besnoitia besnoiti (Marotel, 1912) infection in cattle and rabbits. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 1970, 37, 105–126. [Google Scholar]
- Bigalke, R.D.; Prozesky, L. Besnoitiosis. In Infectious Diseases of Livestock, 2nd ed.; Coetzer, J.A., Tustin, R.C., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Cape Town, South Africa, 2004; Volume 1, pp. 351–359. [Google Scholar]
- Dubey, J.P.; Van Wilpe, E.; Blignaut, D.J.C.; Schares, G.; Williams, H.J. Development of Early Tissue Cysts and Associated Pathology of Besnoitia Besnoiti in a Naturally Infected Bull (Bos Taurus) from South Africa. J. Parasitol. 2013, 99, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquiet, P.; Liénard, E.; Franc, M. Bovine Besnoitiosis: Epidemiological and Clinical Aspects. Vet. Parasitol. 2010, 174, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentile, A.; Militerno, G.; Schares, G.; Nanni, A.; Testoni, S.; Bassi, P.; Gollnick, N.S. Evidence for Bovine Besnoitiosis Being Endemic in Italy—First in Vitro Isolation of Besnoitia Besnoiti from Cattle Born in Italy. Vet. Parasitol. 2012, 184, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortes, H.; Leitão, A.; Gottstein, B.; Hemphill, A. A Review on Bovine Besnoitiosis: A Disease with Economic Impact in Herd Health Management, Caused by Besnoitia besnoiti (Franco and Borges, 1916). Parasitology 2014, 141, 1406–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gazzonis, A.L.; Alvarez-Garcia, G.; Maggioni, A.; Zanzani, S.A.; Oliveri, E.; Compiani, R.; Sirioni, G.; Ortega-Mora, L.M.; Manfredi, M.T. Serological Dynamics and Risk Factors of Besnoitia Besnoiti Infection in Breeding Bulls from an Endemically Infected Purebred Beef Herd. Parasitol. Res. 2017, 116, 1383–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Food Safety Authority. Bovine Besnoitiosis: An Emerging Disease in Europe. EFSA J. 2010, 8, 1499–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Garcia, A.; Risco-Castillo, V.; Pedrasa-Diaz, S.; Aguado-Martinez, A.; Alvarez-Garcia, G.; Gomez-Bautista, M. First isolation of Besnoitia besnoiti from a chronically infected cow in Spain. J. Parasitol. 2009, 95, 474–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanhoudt, A.; Pardon, B.; De Schutter, P.; Bosseler, L.; Sarre, C.; Vercruysse, J.; Deprez, P. First Confirmed Case of Bovine Besnoitiosis in an Imported Bull in Belgium. Vlaams Diergeneeskund. Tijdschr. 2015, 84, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agosti, M.; Belloli, A.; Morini, M.; Vacirca, G. Report of an Outbreak of Besnoitiosis in Imported Beef Cattle. Prax. Vet. 1994, 15, 5–6. [Google Scholar]
- Mutinelli, F.; Schiavon, E.; Ceglie, L.; Fasolato, M.; Natale, A.; Rampin, F.; Carminato, A. Bovine Besnoitiosis in Imported Cattle in Italy. Vet. Parasitol. 2011, 178, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Marco, V.; Amato, B.; Mignacca, S.A.; Spuria, L.; Lastra, A.; Agnello, S.; Capucchio, M.T.; Biasibetti, E. One Case of Besnoitiosis in a Young Beef Cattle in Sicily; SISVet: Palermo, Italy, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Napoli, E.; Remesar, S.; Mendoza-Roldan, J.; De Benedetto, G.; Di Giorgio, S.; Sfacteria, A.; Marino, G.; Arfuso, F.; Catone, G.; Brianti, E. Bovine Besnoitiosis in a Cattle Herd in Sicily: An Isolated Outbreak or the Acknowledgment of an Endemicity? Parasitol. Res. 2021, 2021, 3547–3553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardiner, C.H.; Fayer, R.; Dubey, J.P. An Atlas of Protozoan Parasites on Animal Tissues, 2nd ed.; Armed Forces Institute of Pathology, American Registry of Pathology: Washington, DC, USA, 1998; pp. 49–53. [Google Scholar]
- Manuali, E.; Lepri, E.; Salamida, S.; D’Avino, N.; Mangili, P.; Vitellozzi, G.; Grelloni, V.; Filippini, G. An Outbreak of Bovine Besnoitiosis in Beef Cattle Born in Central Italy: Bovine Besnoitiosis in Central Italy. Transboundary Emerg. Dis. 2011, 58, 464–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Militerno, G.; Bassi, P.; Mandrioli, L.; Morandi, F.; Arcangelo, G. Besnoitiosi bovina (Besnotia besnoiti) in Italia: Quadri Anatomo-cito-Istopatologici ed Ultrastrutturali; AIPVet: Padova, Italy, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Rinaldi, L.; Maurelli, M.P.; Musella, V.; Bosco, A.; Cortes, H.; Cringoli, G. First Cross-Sectional Serological Survey on Besnoitia Besnoiti in Cattle in Italy. Parasitol. Res. 2013, 112, 1805–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gollnick, N.S.; Gentile, A.; Schares, G. Diagnosis of Bovine Besnoitiosis in a Bull Born in Italy. Vet. Rec. 2010, 166, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lepri, E.; Filippini, G.; Brachelente, C.; Di Matteo, I.; Sforna, M.; D’Avino, N.; Mangili, P.; Manuali, E.; Agostini, R.; Mechelli, L.; et al. Besnoitiosi Bovina: Descrizione Di Un Nuovo Focolaio in Italia Centrale. Large Anim. Rev. 2011, 17, 145–150. [Google Scholar]
- Diezma-Díaz, C.; Ferre, I.; Saldias, B.; Blanco-Murcia, J.; Ortega-Mora, L.M.; Álvarez-García, G. Added Value of IgM Detection and Low Avidity Index as Markers of Acute Bovine Besnoitiosis. Vet. Parasitol. 2020, 277, 109012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basso, W.; Schares, G.; Gollnick, N.S.; Rütten, M.; Deplazes, P. Exploring the Life Cycle of Besnoitia Besnoiti—Experimental Infection of Putative Definitive and Intermediate Host Species. Vet. Parasitol. 2011, 178, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diesing, L.; Heydorn, A.O.; Matuschka, F.R.; Bauer, C.; Pipano, E.; de Waal, D.T.; Potgieter, F.T. Besnoitia Besnoiti: Studies on the Definitive Host and Experimental Infections in Cattle. Parasitol. Res. 1988, 75, 114–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostaher, A.; Mueller, R.S.; Majzoub, M.; Schares, G.; Gollnick, N.S. Bovine Besnoitiosis in Germany. Vet. Dermatol. 2010, 21, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez-Expósito, D.; Esteban-Gil, A.; Ortega-Mora, L.M.; García-Lunar, P.; Castillo, J.A.; Marcén, J.M.; Alvarez-García, G. Prevalence of Besnoitia Besnoiti Infection in Beef Cattle from the Spanish Pyrenees. Vet. J. 2014, 200, 468–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, L.; Gazzonis, A.L.; Zanzani, S.A.; Perlotti, C.; Sironi, G.; Manfredi, M.T. Bovine Besnoitiosis in an Endemically Infected Dairy Cattle Herd in Italy: Serological and Clinical Observations, Risk Factors, and Effects on Reproductive and Productive Performances. Parasitol. Res. 2019, 118, 3459–3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Lunar, P.; Ortega-Mora, L.M.; Shares, N.S.; Gollnick, N.S.; Jacquiet, P.; Grisez, C.; Prevot, F.; Frey, C.F.; Gottstein, B.; Alvarez-Garcia, G. An Inter-Laboratory Comparative Study of Serological Tools Employed in the Diagnosis of Besnoitia Besnoiti Infection in Bovines. Transbound Emerg. Dis. 2013, 60, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamilla, A.; Messina, A.; Condorelli, L.; Licitra, F.; Antoci, F.; Lanza, M.; Loria, G.R.; Cascone, G.; Puleio, R. Morphological and Immunohistochemical Examination of Lymphoproliferative Lesions Caused by Marek’s Disease Virus in Breeder Chickens. Animals 2020, 10, 1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Category | Age Class | Number of Positive Animals | Antibodies Values (S/P) 1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calves (male) | <12 months | 1 | 53.32 |
| Females | 1–4 years | 4 | 94.08 |
| Females | 4–6 years | 3 | 193.71 |
| Adult females | 7–11 years | 3 | 115.04 |
| Category | Age Class | Number of Positive Animals | Antibodies Values (S/P) 1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calves (males) | <12 months | 3 | 59.74 |
| Females and males | 1–2 years | 22 and 1 | 104.72 and 200.09 |
| Females | 3–6 years | 10 | 105.03 |
| Adult females | 7–13 years | 21 | 124.11 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Neve, V.C.; Coltraro, M.; Stamilla, A.; Spadola, F.; Puleio, R.; Loria, G.R.; Antoci, F.; Cascone, G.; Salina, F. Investigation of an Autochthonous Outbreak of Bovine Besnoitiosis in Northwestern Sicily. Pathogens 2022, 11, 122. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11020122
Neve VC, Coltraro M, Stamilla A, Spadola F, Puleio R, Loria GR, Antoci F, Cascone G, Salina F. Investigation of an Autochthonous Outbreak of Bovine Besnoitiosis in Northwestern Sicily. Pathogens. 2022; 11(2):122. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11020122
Chicago/Turabian StyleNeve, Veronica Cristina, Miriana Coltraro, Alessandro Stamilla, Filippo Spadola, Roberto Puleio, Guido Ruggero Loria, Francesco Antoci, Giuseppe Cascone, and Felice Salina. 2022. "Investigation of an Autochthonous Outbreak of Bovine Besnoitiosis in Northwestern Sicily" Pathogens 11, no. 2: 122. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11020122
APA StyleNeve, V. C., Coltraro, M., Stamilla, A., Spadola, F., Puleio, R., Loria, G. R., Antoci, F., Cascone, G., & Salina, F. (2022). Investigation of an Autochthonous Outbreak of Bovine Besnoitiosis in Northwestern Sicily. Pathogens, 11(2), 122. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11020122







