Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Membrane Vesicles Inhibit the Proliferation and Induce the Apoptosis of Epithelial Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Isolates and Molecular Typing
2.2. Isolation and Analysis of MRSA MVs
2.3. Cell Culture, CCK-8 Assay, and Flow Cytometry
2.4. qPCR Array and Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR)
2.5. Western Blotting
2.6. Statistical Analysis
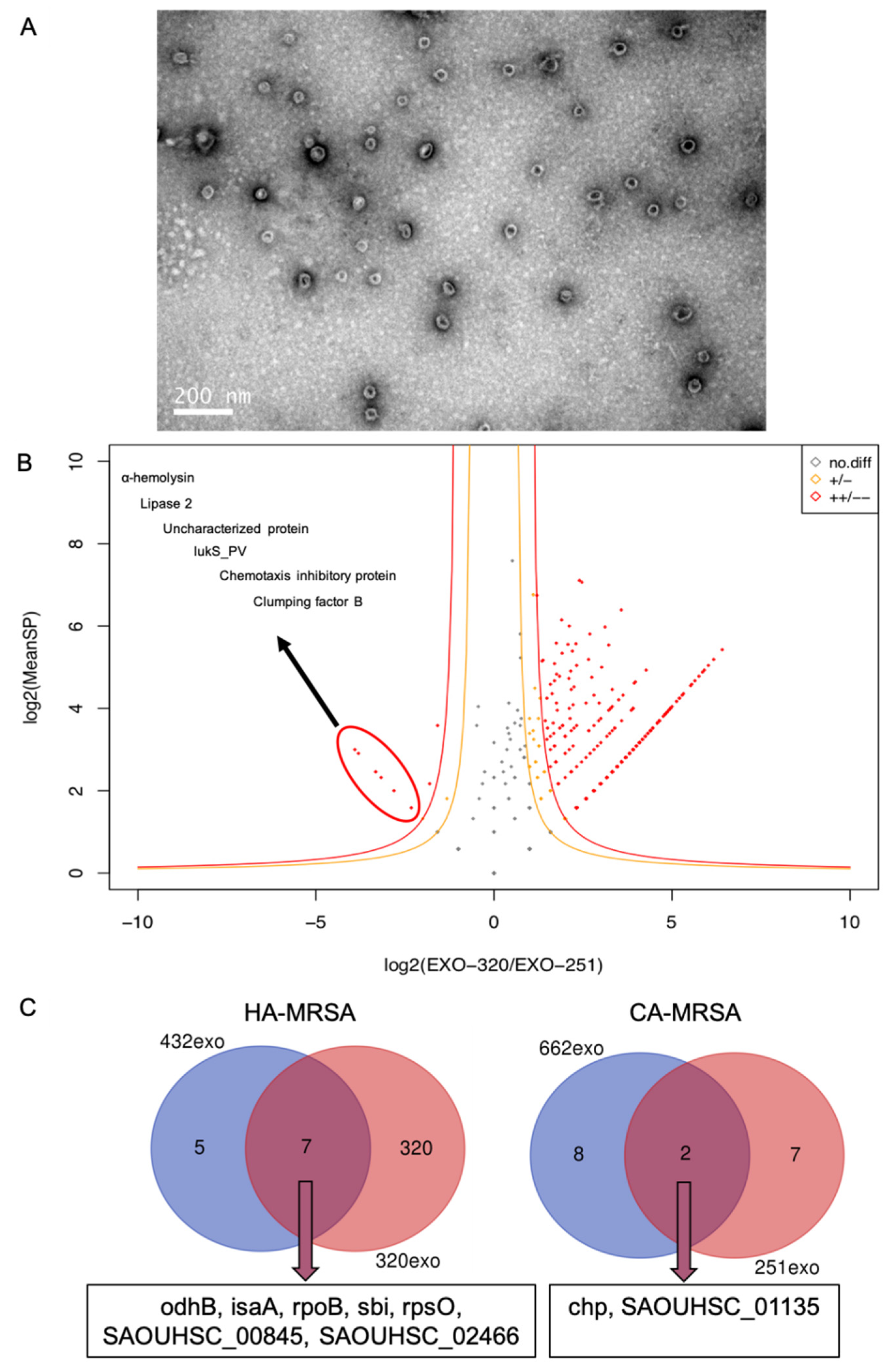
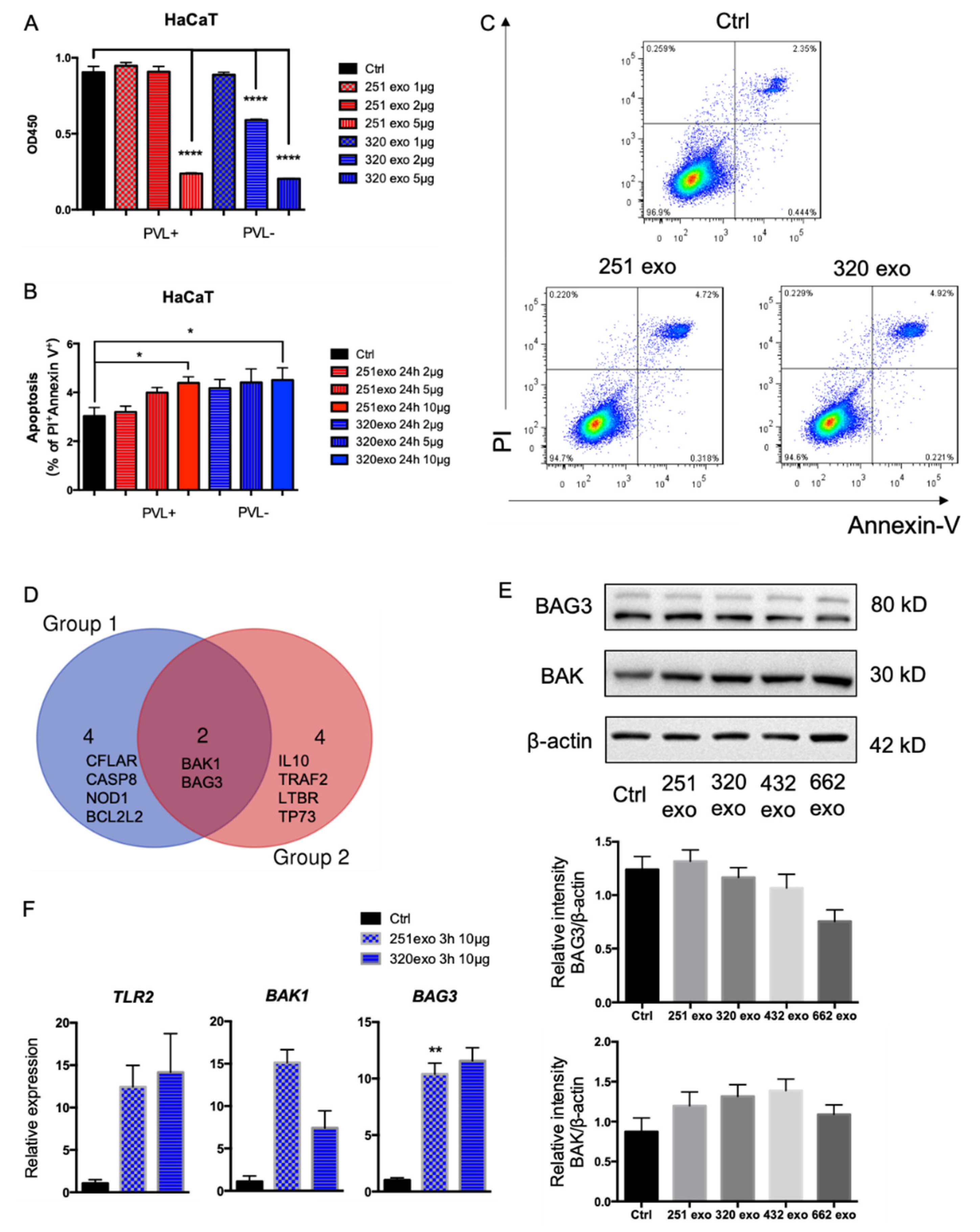
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, A.S.; de Lencastre, H.; Garau, J.; Kluytmans, J.; Malhotra-Kumar, S.; Peschel, A.; Harbarth, S. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2018, 4, 18033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kallen, A.J.; Mu, Y.; Bulens, S.; Reingold, A.; Petit, S.; Gershman, K.; Ray, S.M.; Harrison, L.H.; Lynfield, R.; Dumyati, G.; et al. Health care-associated invasive MRSA infections, 2005–2008. JAMA 2010, 304, 641–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang, Y.Y.; Huang, Y.C. Molecular epidemiology of community-associated meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Asia. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2013, 13, 698–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Du, X.; Villaruz, A.E.; Diep, B.A.; Wang, D.; Song, Y.; Tian, Y.; Hu, J.; Yu, F.; Lu, Y.; et al. MRSA epidemic linked to a quickly spreading colonization and virulence determinant. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 816–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Sun, K.; Luo, Q.; Duan, Y.; Chen, F. Emergence and spread of pvl-positive genotypic CA-MRSA ST59 with increased adhesion capacity from wounds in hospitals. J. Infect. 2019, 79, 612–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouyos, R.; Klein, E.; Grenfell, B. Hospital-community interactions foster coexistence between methicillin-resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kateete, D.P.; Bwanga, F.; Seni, J.; Mayanja, R.; Kigozi, E.; Mujuni, B.; Ashaba, F.K.; Baluku, H.; Najjuka, C.F.; Källander, K.; et al. CA-MRSA and HA-MRSA coexist in community and hospital settings in Uganda. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2019, 8, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briaud, P.; Carroll, R.K. Extracellular Vesicle Biogenesis and Functions in Gram-Positive Bacteria. Infect. Immun. 2020, 88, e00433-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rumbo, C.; Fernández-Moreira, E.; Merino, M.; Poza, M.; Mendez, J.A.; Soares, N.C.; Mosquera, A.; Chaves, F.; Bou, G. Horizontal transfer of the OXA-24 carbapenemase gene via outer membrane vesicles: A new mechanism of dissemination of carbapenem resistance genes in Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 3084–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Lin, H. Characterization and function of membrane vesicles in Gram-positive bacteria. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 1795–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Lee, E.-Y.; Kim, S.-H.; Kim, D.-K.; Park, K.-S.; Kim, K.P.; Kim, Y.-K.; Roh, T.-Y.; Gho, Y.S. Staphylococcus aureus extracellular vesicles carry biologically active β-lactamase. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 2589–2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Thompson, C.D.; Weidenmaier, C.; Lee, J.C. Release of Staphylococcus aureus extracellular vesicles and their application as a vaccine platform. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Eagen, W.J.; Lee, J.C. Orchestration of human macrophage NLRP3 inflammasome activation by Staphylococcus aureus extracellular vesicles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 3174–3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bitto, N.J.; Cheng, L.; Johnston, E.L.; Pathirana, R.; Phan, T.K.; Poon, I.K.H.; O’Brien-Simpson, N.M.; Hill, A.F.; Stinear, T.P.; Kaparakis-Liaskos, M. Staphylococcus aureus membrane vesicles contain immunostimulatory DNA, RNA and peptidoglycan that activate innate immune receptors and induce autophagy. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2021, 10, e12080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Q.; Cheng, H.; Yuan, W.; Zeng, F.; Shang, W.; Tang, D.; Xue, W.; Fu, J.; Zhou, R.; Zhu, J.; et al. Panton-Valentine leukocidin (PVL)-positive health care-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates are associated with skin and soft tissue infections and colonized mainly by infective PVL-encoding bacteriophages. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Wang, W.-K.; Han, L.-Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Tang, J.; Liu, Q.-Z.; Huangfu, Y.-C.; Ni, Y.-X. Epidemiological and genetic diversity of Staphylococcus aureus causing bloodstream infection in Shanghai, 2009–2011. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enright, M.C.; Day, N.P.; Davies, C.E.; Peacock, S.J.; Spratt, B.G. Multilocus sequence typing for characterization of methicillin-resistant and methicillin-susceptible clones of Staphylococcus aureus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 1008–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Liu, X.; Luo, Q.; Xu, L.; Chen, F. An efficient method to isolate lemon derived extracellular vesicles for gastric cancer therapy. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 18, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Luo, Q.; Chen, X.; Chen, F. Bitter melon derived extracellular vesicles enhance the therapeutic effects and reduce the drug resistance of 5-fluorouracil on oral squamous cell carcinoma. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Luo, Q.; Ding, J.; Yang, M.; Zhang, R.; Chen, F. Zymosan promotes proliferation, Candida albicans adhesion and IL-1β production of oral squamous cell carcinoma in vitro. Infect. Agents Cancer 2020, 15, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yin, Y.; van Dorp, L.; Shaw, L.P.; Gao, H.; Acman, M.; Yuan, J.; Chen, F.; Sun, S.; Wang, X.; et al. Drivers of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) lineage replacement in China. Genome Med. 2021, 13, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Zhou, W.; Zhan, Q.; Zheng, B.; Chen, Y.; Luo, Q.; Shen, P.; Xiao, Y. Genomic Epidemiology and Characterization of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus from Bloodstream Infections in China. mSystems 2021, 6, e0083721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, B.; Singh, B.; Nadeem, A.; Askarian, F.; Wai, S.N.; Johannessen, M.; Hegstad, K. Transcriptome Profiling of Staphylococcus aureus Associated Extracellular Vesicles Reveals Presence of Small RNA-Cargo. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 566207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, H.; Oh, M.H.; Jun, S.H.; Kim, S.I.; Choi, C.W.; Kwon, H.I.; Na, S.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Nicholas, A.; Selasi, G.N.; et al. Variation among Staphylococcus aureus membrane vesicle proteomes affects cytotoxicity of host cells. Microb. Pathog. 2016, 93, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Yu, W.-W.; Peng, J.; Xu, L.-F.; Zhao, C.-C.; Chang, W.-J.; Ma, X.-L. LukS-PV induces apoptosis in acute myeloid leukemia cells mediated by C5a receptor. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 2474–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Gene | Primer | Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| BAG3 | Forward | AGAGACGGTGTCAGGAAGGTTCAG |
| Reverse | GTTGCTGGGCTGGAGTTCATAGAC | |
| BAK1 | Forward | AGAGATGGTCACCTTACCTCT |
| Reverse | GGTCTGGAACTCTGAGTCATAG | |
| TLR2 | Forward | TGTCTTGTGACCGCAATGGTATCTG |
| Reverse | TGCTAATGTAGGTGATCCTGTTGTTGG | |
| GAPDH | Forward | CCTGCCAAATATGATGACAT |
| Reverse | TCCACCACCCTGTTGCTGTA |
| Isolate | Molecular Characteristics | Category | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| Isolate 251 | pvl-positive t437-ST59-SCCmecIV | CA-MRSA | Pair one |
| Isolate 320 | pvl-negative t030-ST239-SCCmecIII | HA-MRSA | |
| Isolate 432 | pvl-negative t421-ST239-SCCmecIII | HA-MRSA | Pair Two |
| Isolate 662 | pvl-positive t437-ST338-SCCmecV | CA-MRSA |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, X.; Zhang, J.; Yang, M.; Du, G.; Chen, F. Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Membrane Vesicles Inhibit the Proliferation and Induce the Apoptosis of Epithelial Cells. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1429. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11121429
Chen X, Zhang J, Yang M, Du G, Chen F. Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Membrane Vesicles Inhibit the Proliferation and Induce the Apoptosis of Epithelial Cells. Pathogens. 2022; 11(12):1429. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11121429
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Xu, Jingwei Zhang, Meng Yang, Guanhuan Du, and Fuxiang Chen. 2022. "Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Membrane Vesicles Inhibit the Proliferation and Induce the Apoptosis of Epithelial Cells" Pathogens 11, no. 12: 1429. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11121429
APA StyleChen, X., Zhang, J., Yang, M., Du, G., & Chen, F. (2022). Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Membrane Vesicles Inhibit the Proliferation and Induce the Apoptosis of Epithelial Cells. Pathogens, 11(12), 1429. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11121429






