Clinical Evaluation of Three Commercial RT-PCR Kits for Routine COVID-19 Diagnosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population and Ethical Consideration
2.2. Specimen Collection
2.3. COVID-19 Diagnosis by RT-PCR
2.4. Aridia® COVID-19 Real-Time PCR Test
2.5. AllplexTM 2019-nCoV Assay (Seegene Inc.)
2.6. Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) Nucleic Acid Detection Kit (Sansure Biotech)
2.7. Lower Limit of Detection (LLOD), Linearity and Assay Reproducibility
2.8. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. RT-qPCR Results
3.2. Performance of Aridia® COVID-19 Real-Time PCR Test
3.3. Performance of AllplexTM 2019-nCoV Assay
3.4. Performance of Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) Nucleic Acid Detection Kit, Sansure Biotech
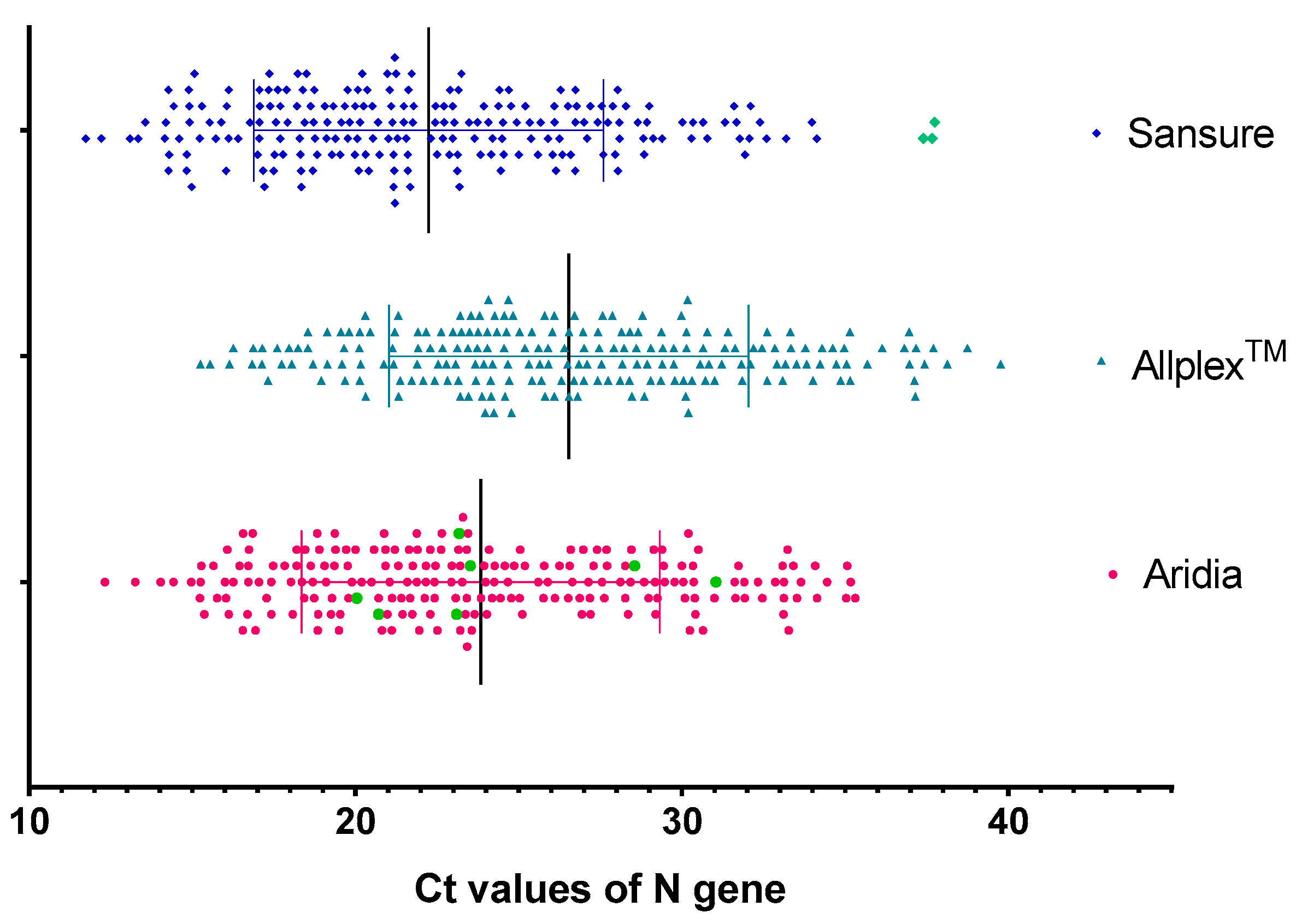
3.5. Sensitivity in Detection of N Gene
3.6. Sensitivity in Detection of E Gene
3.7. Sensitivity in Detection of ORF1ab Gene
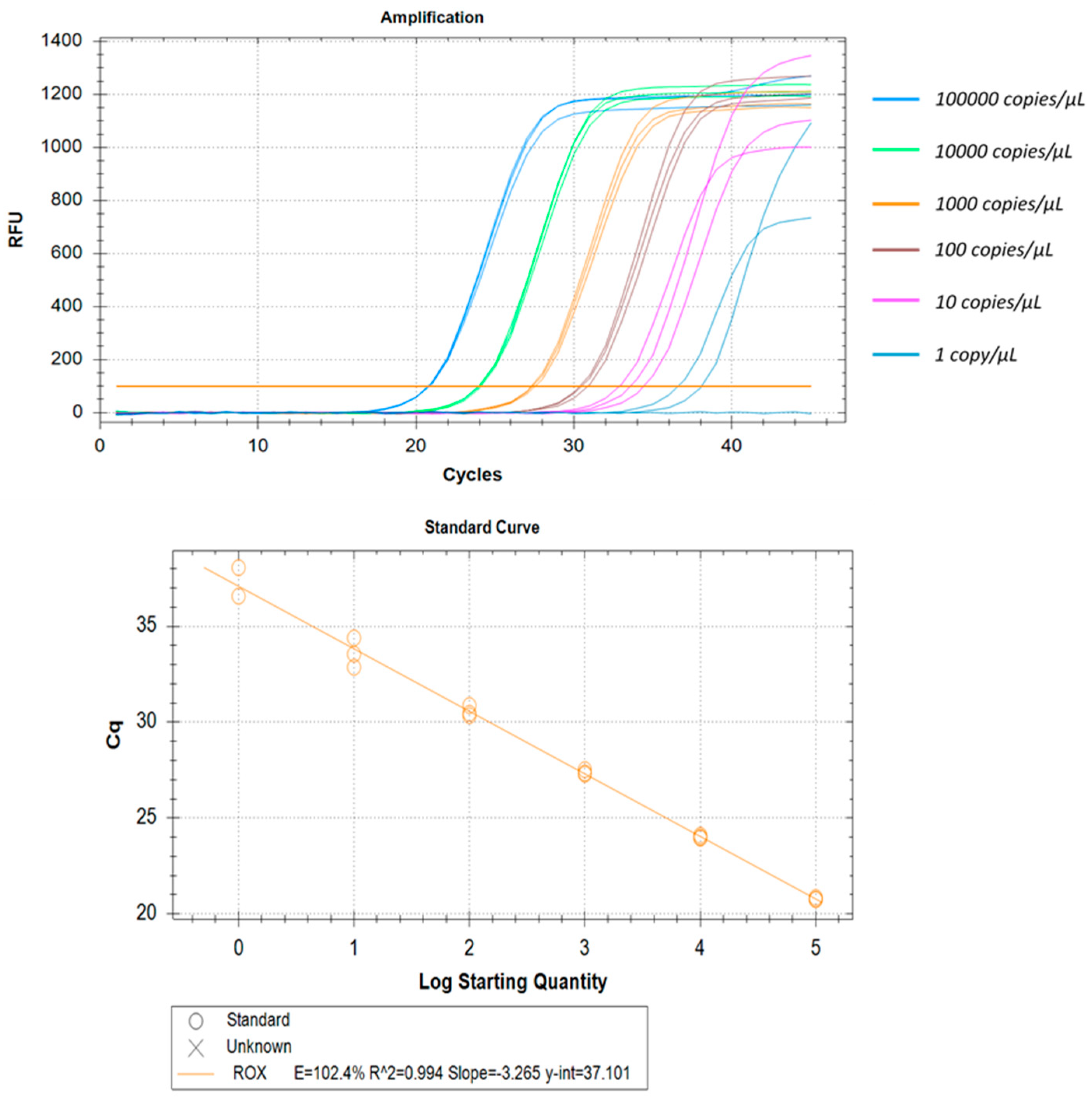
3.8. LLOD, Linearity, and Reproducibility
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization (WHO). Coronavirus COVID-19 Dashboard. Available online: https://covid19.who.int (accessed on 8 December 2021).
- Randriamahazo, T.R.; Andrianarivelo, A.M.; Rakotoarivo, A.T.; Raheritiana, T.M.; Rakotovao, L.A.; Randriamanantany, Z.A.; Alson, A.O.R.; Rasamindrakotroka, A. Evaluation of antigen-based rapid detection test for the diagnosis of SARS CoV-2 in low-income countries. J. Virol. Methods 2021, 300, 114409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Balda, S.; Apreja, M.; Kataria, K.; Capalash, N.; Sharma, P. COVID-19 Diagnosis: Current and Future Techniques. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 193, 1835–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yüce, M.; Filiztekin, E.; Özkaya, K.G. COVID-19 diagnosis—A review of current methods. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 172, 112752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apostolopoulos, I.D.; Mpesiana, T.A. Covid-19: Automatic detection from X-ray images utilizing transfer learning with convolutional neural networks. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 2020, 43, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Verma, J.; Mishra, A.S. COVID-19 infection: Disease detection and mobile technology. PeerJ 2020, 8, e10345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sazed, S.A.; Kibria, M.G.; Hossain, M.S.; Zamil, F.; Adhikary, P.C.; Hossain, M.E.; Ahmed, D.; Haque, R.; Alam, M.S. Clinical Evaluation of a New Antigen-Based COVID-19 Rapid Diagnostic Test from Symptomatic Patients. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torretta, S.; Zuccotti, G.; Cristofaro, V.; Ettori, J.; Solimeno, L.; Battilocchi, L.; D’Onghia, A.; Bonsembiante, A.; Pignataro, L.; Marchisio, P.; et al. Diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 by RT-PCR using different sample sources: Review of the literature. Ear Nose Throat J. 2021, 100 (Suppl. 2), 131S–138S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, A.; Ghoshal, U.; Patel, S.S.; Singh, D.V.; Arya, A.K.; Vasanth, S.; Pandey, A.; Srivastava, N. Evaluation of seven commercial RT-PCR kits for COVID-19 testing in pooled clinical specimens. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 93, 2281–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Guo, H.; Zhou, P.; Shi, Z.L. Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Kasteren, P.B.; van Der Veer, B.; van den Brink, S.; Wijsman, L.; de Jonge, J.; van den Brandt, A.; Molenkamp, R.; Reusken, C.B.; Meijer, A. Comparison of seven commercial RT-PCR diagnostic kits for COVID-19. J. Clin. Virol. 2020, 128, 104412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sisay, A.; Abera, A.; Dufera, B.; Endrias, T.; Tasew, G.; Tesfaye, A.; Hartnack, S.; Beyene, D.; Desta, A.F. Diagnostic accuracy of three commercially available one step RT-PCR assays for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 in resource limited settings. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0262178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, E.; Israelow, B.; Vogels, C.B.; Lu, P.; Wyllie, A.L.; Tokuyama, M.; Venkataraman, A.; Brackney, D.E.; Ott, I.M.; Petrone, M.E.; et al. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA by multiplex RT-qPCR. PLoS Biol. 2020, 18, e3000867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umunnakwe, C.N.; Makatini, Z.N.; Maphanga, M.; Mdunyelwa, A.; Mlambo, K.M.; Manyaka, P.; Nijhuis, M.; Wensing, A.; Tempelman, H.A. Evaluation of a commercial SARS-CoV-2 multiplex PCR genotyping assay for variant identification in resource-scarce settings. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0269071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire-Paspuel, B. and Garcia-Bereguiain, M.A. Clinical Performance and Analytical Sensitivity of Three SARS-CoV-2 Nucleic Acid Diagnostic Tests. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2021, 104, 1516–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sazed, S.; Kibria, M.; Alam, M. An Optimized Real-Time qPCR Method for the Effective Detection of Human Malaria Infections. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čretnik, T.Ž.; Retelj, M.; Janežič, S.; Mahnič, A.; Tesovnik, T.; Šket, R.; Bizjan, B.J.; Jeverica, S.; Ravnik, M.; Rak, M.; et al. Accuracy of Allplex SARS-CoV-2 assay amplification curve analysis for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 variant Alpha. Future Microbiol. 2022, 17, 1125–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caza, M.; Hogan, C.A.; Jassem, A.; Prystajecky, N.; Hadzic, A.; Wilmer, A. Evaluation of the clinical and analytical performance of the Seegene allplex™ SARS-CoV-2 variants I assay for the detection of variants of concern (VOC) and variants of interests (VOI). J. Clin. Virol. 2021, 144, 104996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.Y.; Chong, Y.M.; Sam, I.C.; Chan, Y.F. SARS-CoV-2 multiplex RT-PCR to detect variants of concern (VOCs) in Malaysia, between January to May 2021. J. Virol. Methods 2022, 301, 114462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banko, A.; Petrovic, G.; Miljanovic, D.; Loncar, A.; Vukcevic, M.; Despot, D.; Cirkovic, A. Comparison and Sensitivity Evaluation of Three Different Commercial Real-Time Quantitative PCR Kits for SARS-CoV-2 Detection. Viruses 2021, 13, 1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Li, L.; Ren, S.; Liu, X.; Zhang, L.; Li, W.; Yu, H. Comparison of the diagnostic efficacy between two PCR test kits for SARS-CoV-2 nucleic acid detection. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2020, 34, e23554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, D.; Yang, S.; Li, G.; Xuan, Q.; Guo, W.; Wu, W. Sample-to-Answer and Routine Real-Time RT-PCR: A Comparison of Different Platforms for SARS-CoV-2 Detection. J. Mol. Diagn. 2021, 23, 665–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morecchiato, F.; Coppi, M.; Baccani, I.; Maggini, N.; Ciccone, N.; Antonelli, A.; Rossolini, G.M. Evaluation of extraction-free RT-PCR methods for faster and cheaper detection of SARS-CoV-2 using two commercial systems. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 112, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Parameter | Aridia® | AllplexTM | Sansure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | 100 (95% CI: 98.3% to 100%) | 98.1% (95% CI: 95.2% to 99.5% ) | 98.6% (95% CI: 95.9% to 99.7%) |
| Specificity | 100.00% (95% CI: 96.9% to 100%) | 100% (95% CI: 96.9% to 100%) | 95.7% (95% CI: 90.3% to 98.6%) |
| AUC (Area Under Curve) | 1 (95% CI: 0.99 to 1.0) | 0.99 (95% CI: 0.97 to 0.99) | 0.971 (95% CI: 0.95 to 0.99) |
| Positive Predictive Value | 100 % | 100.00% | 97.6% (95% CI: 94.6% to 98.9%) |
| Negative Predictive Value | 100 % | 99.90% (95% CI: 99.7% to 99.9%) | 99.9% (95% CI: 99.8% to 99.9%) |
| Accuracy | 100.00% (98.9% to 100%) | 99.90% (95% CI: 98.7% to 100%) | 95.87% (95% CI: 93.1% to 97.8%) |
| κ | 1.0 | 0.97 | 0.95 |
| Ct Values | Aridia® | AllplexTM | Sansure |
|---|---|---|---|
| <25 | 128 (61.2%) | 89 (43.6%) | 147 (70.3%) |
| 25–30 | 44 (21.2%) | 59 (28.9%) | 42 (20.1%) |
| 30–35 | 33 (15.8%) | 40 (19.6%) | 17 (8.1%) |
| >35 | 4 (1.9%) | 16 (7.8%) | 0 (0%) |
| Total samples | 209 | 204 ** | 206 |
| Ct Values | Aridia® Kit, n (%) | AllplexTM Kit, n (%) |
|---|---|---|
| <25 | 136 (65.1%) | 117 (57.6%) |
| 25–30 | 39 (18.7%) | 53 (26.1%) |
| 30–35 | 31 (14.8%) | 28 (13.8%) |
| >35 | 03 (1.4%) | 05 (2.5%) |
| Total samples | 209 | 203 *** |
| Ct Values | Aridia® Kit, n (%) | Sansure Kit, n (%) |
|---|---|---|
| <25 | 157 (75.1%) | 137 (65.9%) |
| 25–30 | 38 (18.2%) | 47 (22.6%) |
| 30–35 | 14 (6.7%) | 20 (9.6%) |
| >35 | 00 (0%) | 04 (1.9%) |
| Total samples | 209 | 208 **** |
| Copies/µL | Intra Assay Variation of Ct Values | Inter Assay Variation of Ct Values | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Replicate 1 | Replicate 2 | Replicate 3 | Mean | SD | CV (%) | Assay 1 | Assay 2 | Mean | SD | CV (%) | |
| 100,000 | 22.53 | 22.38 | 22.7 | 22.54 | 0.16 | 0.71 | 22.54 | 22.79 | 22.67 | 0.18 | 0.80 |
| 10,000 | 25.88 | 25.99 | 25.91 | 25.93 | 0.06 | 0.22 | 25.93 | 25.46 | 25.70 | 0.33 | 1.28 |
| 1000 | 29.23 | 29.17 | 29.06 | 29.15 | 0.09 | 0.30 | 29.15 | 28.57 | 28.86 | 0.41 | 1.44 |
| 100 | 32.31 | 32.46 | 32.2 | 32.32 | 0.13 | 0.40 | 32.32 | 31.90 | 32.11 | 0.30 | 0.92 |
| 10 | 36.05 | 35.52 | 35.4 | 35.66 | 0.35 | 0.97 | 35.66 | 35.21 | 35.43 | 0.32 | 0.89 |
| 1 | 38.65 | 38.54 | 38.53 | 38.57 | 0.07 | 0.17 | 38.57 | 39.04 | 38.81 | 0.33 | 0.85 |
| Copies/µL | Intra Assay Variation of Ct Values | Inter Assay Variation of Ct Values | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Replicate 1 | Replicate 2 | Replicate 3 | Mean | SD | CV (%) | Assay 1 | Assay 2 | Mean | SD | CV (%) | |
| 100,000 | 23.22 | 23.13 | 23.26 | 23.20 | 0.07 | 0.29 | 23.20 | 23.18 | 23.19 | 0.02 | 0.07 |
| 10,000 | 26.63 | 26.35 | 26.55 | 26.51 | 0.14 | 0.54 | 26.51 | 26.49 | 26.50 | 0.02 | 0.06 |
| 1000 | 30.1 | 30.06 | 29.88 | 30.01 | 0.12 | 0.39 | 30.01 | 30.01 | 30.01 | 0.00 | 0.02 |
| 100 | 33.56 | 33.35 | 33.33 | 33.41 | 0.13 | 0.38 | 33.41 | 33.34 | 33.38 | 0.05 | 0.16 |
| 10 | 36.52 | 36.76 | 36.66 | 36.65 | 0.12 | 0.33 | 36.65 | 36.59 | 36.62 | 0.04 | 0.10 |
| 1 | 39.66 | 39.55 | 39.76 | 39.66 | 0.11 | 0.26 | 39.66 | 39.30 | 39.48 | 0.25 | 0.63 |
| Copies/µL | Intra ASSAY Variation of Ct Values | Inter Assay Variation of Ct Values | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Replicate 1 | Replicate 2 | Replicate 3 | Mean | SD | CV (%) | Assay 1 | Assay 2 | Mean | SD | CV (%) | |
| 100,000 | 20.86 | 20.76 | 20.74 | 20.79 | 0.06 | 0.31 | 20.79 | 20.68 | 20.74 | 0.07 | 0.35 |
| 10,000 | 24.1 | 23.95 | 24 | 24.02 | 0.08 | 0.32 | 24.02 | 24.00 | 24.01 | 0.01 | 0.04 |
| 1000 | 27.52 | 27.36 | 27.28 | 27.39 | 0.12 | 0.45 | 27.39 | 27.24 | 27.31 | 0.11 | 0.39 |
| 100 | 30.87 | 30.47 | 30.35 | 30.56 | 0.27 | 0.89 | 30.56 | 30.53 | 30.55 | 0.02 | 0.07 |
| 10 | 34.4 | 32.87 | 33.56 | 33.61 | 0.77 | 2.28 | 33.61 | 33.62 | 33.61 | 0.00 | 0.01 |
| 1 | 36.58 | -- | 38.07 | 37.33 | 1.05 | 2.82 | 37.33 | 36.71 | 37.02 | 0.43 | 1.17 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Juthi, R.T.; Sazed, S.A.; Zamil, M.F.; Alam, M.S. Clinical Evaluation of Three Commercial RT-PCR Kits for Routine COVID-19 Diagnosis. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1389. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11111389
Juthi RT, Sazed SA, Zamil MF, Alam MS. Clinical Evaluation of Three Commercial RT-PCR Kits for Routine COVID-19 Diagnosis. Pathogens. 2022; 11(11):1389. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11111389
Chicago/Turabian StyleJuthi, Rifat Tasnim, Saiful Arefeen Sazed, Md Fahad Zamil, and Mohammad Shafiul Alam. 2022. "Clinical Evaluation of Three Commercial RT-PCR Kits for Routine COVID-19 Diagnosis" Pathogens 11, no. 11: 1389. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11111389
APA StyleJuthi, R. T., Sazed, S. A., Zamil, M. F., & Alam, M. S. (2022). Clinical Evaluation of Three Commercial RT-PCR Kits for Routine COVID-19 Diagnosis. Pathogens, 11(11), 1389. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11111389






