Immune Monitoring of Paediatric Patients Infected with Rickettsia rickettsii, Ehrlichia canis and Coinfected
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Subjects and Inclusion Criteria
2.2. Statement of Ethics
2.3. Haematological and Serum Biochemistry
2.4. DNA Isolation, PCR Protocol, and Sequencing
2.5. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.6. Cytokine and Chemokine Profiles
2.7. T-Cell Immunophenotype
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
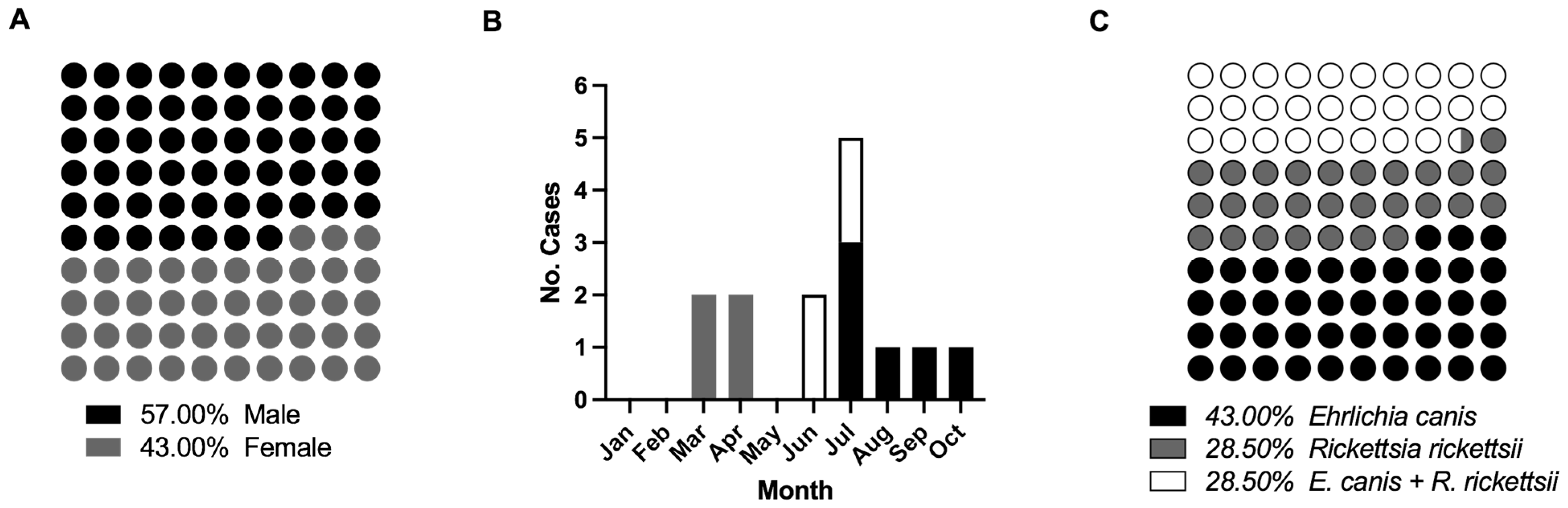
3.1. Overview of Subjects, Molecular Diagnosis, and Detection of Monoinfection and Coinfection
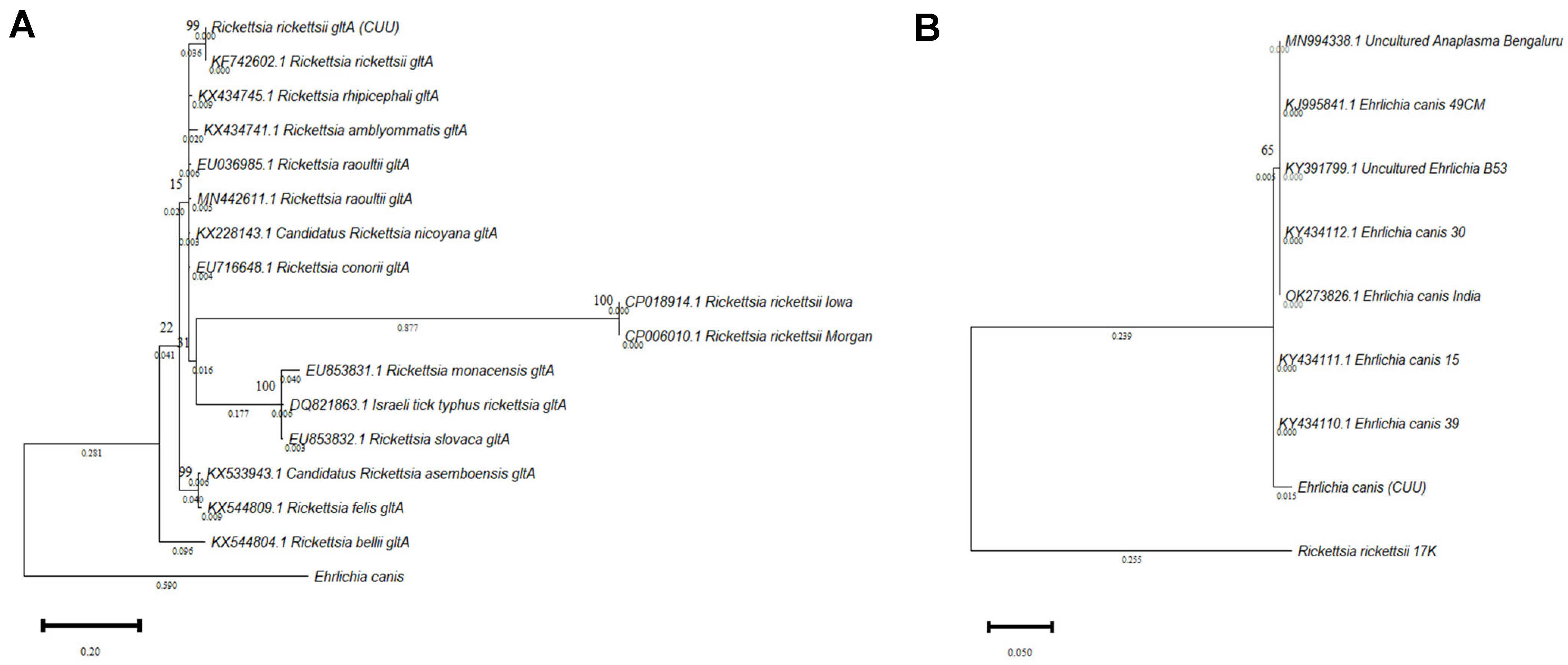
3.2. Phylogenetic Analysis
3.3. Laboratory Panel Tests
3.4. Cytokine Profiles
3.5. Chemokine Profiles
3.6. Immunophenotyping CD4+ T Cells
3.7. Immunophenotyping CD8+ T Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sistema Único de Información Boletín Epidemiológico—Sistema Nacional de Vigilancia Epidemiológica Sistema Único de Información. 2021, Vigilancia Epidemiológica Número 52|Volumen 38|Semana 52|del 26 de Diciembre del 2021 al 1 de Enero del 2022. Secretaria de Salud. Available online: https://www.gob.mx/salud/documentos/boletinepidemiologico-sistema-nacional-de-vigilancia-epidemiologica-sistema-unico-de-informacion-2021 (accessed on 16 September 2022).
- Alvarez-Hernandez, G.; Murillo-Benitez, C.; del Carmen Candia-Plata, M.; Moro, M. Clinical Profile and Predictors of Fatal Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever in Children from Sonora, Mexico. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2015, 34, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demma, L.J.; Traeger, M.S.; Nicholson, W.L.; Paddock, C.D.; Blau, D.M.; Eremeeva, M.E.; Dasch, G.A.; Levin, M.L.; Singleton, J.; Zaki, S.R.; et al. Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever from an Unexpected Tick Vector in Arizona. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McQuiston, J.H.; Guerra, M.A.; Watts, M.R.; Lawaczeck, E.; Levy, C.; Nicholson, W.L.; Adjemian, J.; Swerdlow, D.L. Evidence of Exposure to Spotted Fever Group Rickettsiae among Arizona Dogs Outside a Previously Documented Outbreak Area. Zoonoses Public Health 2011, 58, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, J.A.; Dahm, N.M.; Ruiz, M.O.; Brown, W.M. Temporal and Spatial Distribution of Tick-Borne Disease Cases among Humans and Canines in Illinois (2000–2009). Environ. Health Insights 2014, 8, EHI-S16017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Drexler, N.A.; Yaglom, H.; Casal, M.; Fierro, M.; Kriner, P.; Murphy, B.; Kjemtrup, A.; Paddock, C.D. Fatal Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever along the United States–Mexico Border, 2013–2016. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 1621–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Escárcega Ávila, A.M.; Luna Flores, B.S.; De la Mora Covarrubias, A.; Jiménez, F. Análisis exploratorio de enfermedades Rickettsiales transmitidas por garrapatas en perros de Ciudad Juárez, Chihuahua, México. Acta Univ. 2018, 28, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrada, I.; Balagot, C.; Fierro, M.; Kriner, P.; Iniguez-Stevens, E.; Kjemtrup, A.; Foley, J. Spotted fever group rickettsiae canine serosurveillance near the US–Mexico border in California. Zoonoses Public Health 2020, 67, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-López, D.I.; Ochoa-Mora, E.; Nichols Heitman, K.; Binder, A.M.; Álvarez-Hernández, G.; Armstrong, P.A. Epidemiology and Clinical Features of Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever from Enhanced Surveillance, Sonora, Mexico: 2015–2018. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2021, 104, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Tommasi, A.S.; Otranto, D.; Dantas-Torres, F.; Capelli, G.; Breitschwerdt, E.B.; de Caprariis, D. Are vector-borne pathogen co-infections complicating the clinical presentation in dogs? Parasit. Vectors 2013, 6, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jimenez-Coello, M.; Ortega-Pacheco, A.; Guzman-Marin, E.; Guiris-Andrade, D.M.; Martinez-Figueroa, L.; Acosta-Viana, K.Y. Stray Dogs as Reservoirs of the Zoonotic Agents Leptospira interrogans, Trypanosoma cruzi, and Aspergillus spp. in an Urban Area of Chiapas in Southern Mexico. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2010, 10, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otranto, D.; Dantas-Torres, F.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. Managing canine vector-borne diseases of zoonotic concern: Part one. Trends Parasitol. 2009, 25, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otranto, D.; Dantas-Torres, F.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. Managing canine vector-borne diseases of zoonotic concern: Part two. Trends Parasitol. 2009, 25, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez-Hernández, G.; Roldán, J.F.G.; Milan, N.S.H.; Lash, R.R.; Behravesh, C.B.; Paddock, C.D. Rocky Mountain spotted fever in Mexico: Past, present, and future. Lancet. Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, e189–e196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schotthoefer, A.M.; Schrodi, S.J.; Meece, J.K.; Fritsche, T.R.; Shukla, S.K. Pro-inflammatory immune responses are associated with clinical signs and symptoms of human anaplasmosis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gómez-Rivera, N.; Gómez-Jiménez, I.A.; Fonseca-Chon, I. Factores relacionados con la mortalidad en niños con fiebre manchada de las montañas rocosas: Análisis de 14 años en Sonora, México. Rev. Mex. Pediatría 2019, 86, 8–12. [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson, W.L.; Allen, K.E.; McQuiston, J.H.; Breitschwerdt, E.B.; Little, S.E. The increasing recognition of rickettsial pathogens in dogs and people. Trends Parasitol. 2010, 26, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Tommasi, A.S.; Otranto, D.; Furlanello, T.; Tasca, S.; Cantacessi, C.; Breitschwerdt, E.B.; Stanneck, D.; Dantas-Torres, F.; Baneth, G.; Capelli, G.; et al. Evaluation of blood and bone marrow in selected canine vector-borne diseases. Parasit. Vectors 2014, 7, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Medina, M.A.; Padilla-Zamudio, G.; Solís-Gallardo, L.P.; Guevara-Tovar, M. Fiebre manchada de las montañas rocosas. Informe de dos casos. Gac. Med. Mex. 2005, 4, 309–312. [Google Scholar]
- León- Arias, J.J.; Dzul-Rosado, K.R.; Zavala-Velázquez, J.E.; Walker, D.H.; Zavala-Castro, J.E. An Increase in Human Cases of Spotted Fever Rickettsiosis in Yucatan, Mexico, Involving Children. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2008, 79, 907–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, R.N.; Álvarez, H.G.; García, Z.M.G.; Fonseca, C.I.; Villalobos, G.L.; Cano, R.M.A. Fiebre manchada de las Montañas Rocosas en niños: Experiencia hospitalaria. Rev. Mex. Pediatría 2013, 80, 227–231. [Google Scholar]
- Dzul-Rosado, K.R.; Cardenas-Marrufo, M.F.; Lugo-Caballero, C.; Alvarez-Baeza, A.; Mendez-Dominguez, N. Clinical Manifestations in a Fatal Case of Probable Rickettsia and Leptospira Coinfection in Yucatan, Mexico. Pathogens 2021, 10, 914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahni, S.K.; Rydkina, E. Host-cell interactions with pathogenic Rickettsia species. Future Microbiol. 2009, 4, 323–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baltadzhiev, I.G.; Pavlov, P.I. Clinical Investigations. T-Lymphocyte Subset Absolute Counts in the Peripheral Blood of Mediterranean Spotted Fever Patients: Relations to Disease Severity. Folia Med. 2015, 57, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groom, J.R.; Luster, A.D. CXCR3 ligands: Redundant, collaborative and antagonistic functions. Inmunol. Cell Biol. 2011, 89, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Osterloh, A. Immune response against rickettsiae: Lessons from murine infection models. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2017, 206, 403–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tappe, D.; Booken, N.; Boer-Auer, A.; Rauch, J.; Schmiedel, S.; Reich, K. Histology and serum cytokine responses in an imported rickettsia slovaca Infection, Germany. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2018, 98, 248–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rydkina, E.; Turpin, L.C.; Sahni, S.K. Rickettsia rickettsii infection of human macrovascular and microvascular endothelial cells reveals activation of both common and cell type-specific host response mechanisms. Infect. Immun. 2010, 78, 2599–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mansueto, P.; Vitale, G.; Cascio, A.; Seidita, A.; Pepe, I.; Carroccio, A.; Di Rosa, S.; Rini, G.B.; Cillari, E.; Walker, D.H. New insight into immunity and immunopathology of Rickettsial diseases. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2012, 2012, 967852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Påhlson, C.; Lu, X.; Ott, M.; Nilsson, K. Characteristics of in vitro infection of human monocytes, by Rickettsia helvetica. Microbes Infect. 2020, 23, 104776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tizard, I. Veterinary Inmunology, 10th ed.; Elsevier: St. Louis MO, USA, 2013; ISBN 9780323523493. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, D.H.; Dumler, J.S. The role of CD8 T lymphocytes in rickettsial infections. Semin. Immunopathol. 2015, 37, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jordan, J.M.; Woods, M.E.; Olano, J.; Walker, D.H. The Absence of Toll-Like Receptor 4 Signaling in C3H/HeJ Mice Predisposes Them to Overwhelming Rickettsial Infection and Decreased Protective Th1 Responses. Infect. Immun. 2008, 76, 3717–3724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kokorin, I.N.; Kabanova, E.A.; Shirokova, E.M.; Abrosimova, G.E.; Rybkina, N.N.; Pushkareva, V. I Role of T lymphocytes in Rickettsia conorii infection. Acta Virol. 1982, 26, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ismail, N.; Walker, D.H. Balancing Protective Immunity and Immunopathology: A Unifying Model of Monocytotropic Ehrlichiosis. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2005, 1063, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cillari, E.; Milano, S.; D’Agostino, P.; Arcoleo, F.; Stassi, G.; Galluzzo, A.; Richiusa, P.; Giordano, C.; Quartararo, P.; Colletti, P.; et al. Depression of CD4 T Cell Subsets and Alteration in Cytokine Profile in Boutonneuse Fever. J. Infect. Dis. 1996, 174, 1051–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Herrero-Herrero, J.I.; Ruiz-Beltrán, R.; Cordero, M. T lymphocyte subsets in Mediterranean spotted fever. Acta Trop. 1988, 45, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Escárcega-Ávila, A.M.; de la Mora-Covarrubias, A.; Quezada-Casasola, A.; Jiménez-Vega, F. Occupational risk for personnel working in veterinary clinics through exposure to vectors of rickettsial pathogens. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2019, 10, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inokuma, H.; Raoult, D.; Brouqui, P. Detection of Ehrlichia platys DNA in Brown Dog Ticks (Rhipicephalus sanguineus) in Okinawa Island, Japan. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 4219–4221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghafar, M.W.; Amer, S.A. Prevalence and first molecular characterization of Anaplasma phagocytophilum, the agent of human granulocytic anaplasmosis, in Rhipicephalus sanguineus ticks attached to dogs from Egypt. J. Adv. Res. 2012, 3, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thompson, J. The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: Flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 4876–4882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hughes, A.L. Evolution of the Integrin α and β Protein Families. J. Mol. Evol. 2001, 52, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huhtala, M.; Heino, J.; Casciari, D.; de Luise, A.; Johnson, M.S. Integrin evolution: Insights from ascidian and teleost fish genomes. Matrix Biol. 2005, 24, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega-Morales, A.I.; Nava-Reyna, E.; Ávila-Rodríguez, V.; González-Álvarez, V.H.; Castillo-Martínez, A.; Siller-Rodríguez, Q.K.; Cabezas-Cruz, A.; Dantas-Torres, F.; Almazán, C. Detection of Rickettsia spp. in Rhipicephalus sanguineus (sensu lato) collected from free-roaming dogs in Coahuila state, northern Mexico. Parasit. Vectors 2019, 12, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rojero-Vázquez, E.; Gordillo-Pérez, G.; Weber, M. Infection of Anaplasma phagocytophilum and Ehrlichia spp. in Opossums and Dogs in Campeche, Mexico: The Role of Tick Infestation. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 5, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almazán, C.; González-Álvarez, V.H.; Fernández de Mera, I.G.; Cabezas-Cruz, A.; Rodríguez-Martínez, R.; de la Fuente, J. Molecular identification and characterization of Anaplasma platys and Ehrlichia canis in dogs in Mexico. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2016, 7, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Field Cortázares, J.; Tinoco Gracia, L.; Escárcega Ávila, A.; Castro Corona, M. Seroprevalencia de Borrelia burgdorferi en Ensenada, Baja California, México. Rev. Enferm. Infecc. Pediatría 2019, 32, 1586–1590. [Google Scholar]
- Ewing, S.A.; Panciera, R.J. American Canine Hepatozoonosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2003, 16, 688–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tinoco-Gracia, L.; Quiroz-Romero, H.; Quintero-Martínez, M.T.; Rentería-Evangelista, T.B.; González-Medina, Y.; Barreras-Serrano, A.; Hori-Oshima, S.; Moro, M.H.; Vinasco, J. Prevalence of Rhipicephalus sanguineus ticks on dogs in a region on the Mexico-USA border. Vet. Rec. 2009, 164, 59–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dantas-Torres, F. Biology and ecology of the brown dog tick, Rhipicephalus sanguineus. Parasit. Vectors 2010, 3, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delgado-De la Mora, J.; Licona-Enríquez, J.D.; Leyva-Gastélum, M.; Delgado-De la Mora, D.; Rascón-Alcantar, A.; Álvarez-Hernández, G. A fatal case series of Rocky Mountain spotted fever in Sonora, México. Biomédica 2018, 38, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Fatal cases of Rocky Mountain spotted fever in family clusters--three states, 2003. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2004, 53, 407–410. [Google Scholar]
- Gordis, L. Epidemiología, 5th ed.; Elsevier: Barcelona, Spain, 2014; Volume 1, ISBN 978-1-4557-3733-8. [Google Scholar]
- Perez, M.; Bodor, M.; Zhang, C.; Xiong, Q.; Rikihisa, Y. Human Infection with Ehrlichia canis Accompanied by Clinical Signs in Venezuela. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2006, 1078, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, A.B.; Pina Canseco, S.; López Martínez, J.; Pérez-Campos, E. Infección humana asintomática por contacto con perros. Un caso de ehrlichiosis humana. Gac. Med. Mex. 2014, 150, 71–74. [Google Scholar]
- Alcántara-Rodríguez, V.E.; Sánchez-Montes, S.; Contreras, H.; Colunga-Salas, P.; Fierro-Flores, L.; Avalos, S.; Rodríguez-Rangel, F.; Becker, I.; Walker, D.H. Human Monocytic Ehrlichiosis, Mexico City, Mexico. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 3016–3019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Licona-Enríquez, J.D.; Delgado-de la Mora, J.; Álvarez-Hernández, G. Fatal case of co-infected of rickettiosis and dengue virus in Mexico. Rev. Médica Inst. Mex. Seguro Soc. 2018, 56, 320–322. [Google Scholar]
- Paddock, C.D.; Folk, S.M.; Shore, G.M.; Machado, L.J.; Huycke, M.M.; Slater, L.N.; Liddell, A.M.; Buller, R.S.; Storch, G.A.; Monson, T.P.; et al. Infections with Ehrlichia chaffeensis and Ehrlichia ewingii in Persons Coinfected with Human Immunodeficiency Virus. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2001, 33, 1586–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raczniak, G.A.; Regan, J.J.; Mitchell, A.; Levy, C.; Chung, I.H.; Bjork, A.; Austin, A.; Weis, E.; Kato, C.; Maria da Gloria, S.C.; et al. Co-Infection of Rickettsia rickettsii and Streptococcus pyogenes: Is Fatal Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever Underdiagnosed? Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2014, 91, 1154–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carpenter, C.F.; Gandhi, T.K.; Kong, L.K.; Corey, G.R.; Chen, S.; Walker, D.H.; Dumler, J.S.; Breitschwerdt, E.; Hegarty, B.; Sexton, D.J. The Incidence of Ehrlichial and Rickettsial Infection in Patients with Unexplained Fever and Recent History of Tick Bite in Central North Carolina. J. Infect. Dis. 1999, 180, 900–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauch, J.; Sothmann, P.; Aldrich, C.; Hogan, B.; Owusu-Dabo, E.; May, J.; Eibach, D.; Tappe, D. Serum cytokine responses in Rickettsia felis infected febrile children, Ghana. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2018, 207, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rydkina, E.; Silverman, D.J.; Sahni, S.K. Activation of p38 stress-activated protein kinase during Rickettsia rickettsii infection of human endothelial cells: Role in the induction of chemokine response. Cell. Microbiol. 2005, 7, 1519–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rydkina, E.; Sahni, A.; Silverman, D.J.; Sahni, S.K. Comparative analysis of host-cell signalling mechanisms activated in response to infection with Rickettsia conorii and Rickettsia typhi. J. Med. Microbiol. 2007, 56, 896–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bechah, Y.; Capo, C.; Raoult, D.; Mege, J. Infection of Endothelial Cells with Virulent Rickettsia prowazekii Increases the Transmigration of Leukocytes. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 197, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Walker, D.H.; Olano, J.P.; Feng, H.-M. Critical Role of Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes in Immune Clearance of Rickettsial Infection. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 1841–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Bacteria | Target Gene | Primer Sequence | Amplicon Size bp. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ehrlichia spp. | 16S rRNA | F-EHR16SD GGTACCYACAGAAGAAGTCC R-EHR16SR TAGCACTCATCGTTTACAGC | 345 |
| R. rickettsii | 17KDa | F-17K178 GGTGCATTACTTGGAGCAG R-17K452 GGTTGGCGGCATGCATTAC | 274 |
| A. phagocytophilum | 16S rRNA | F-Phago GGCATGTAGGCGGTTTTCGGTAAGTT R-Phago CCCCACATTCAGCACTCATCGTTTA | 262 |
| R. rickettsii | glta | F-Cs78 GCAAGTATCGGTGAGGATGTAAT R-Cs323 GCTTCCTTAAAATTCAATAAATCAGGAT | 401 |
| Nested PCR Ehrlichia spp. | 16S rRNA | F-ECC AGAACGAACGCTGGCGGCAAGC R-ECB CGTATTACCGCGGCTGCTGGCA Nested F-ECAN CAATTATTTATAGCCTCTGGCTATAGGA R-HE3 TATAGGTACCGTCATTATCTTCCCTAT | 483 & 387 |
| Characteristic | Rickettsia (N = 4) | Coinfection Rickettsia + Ehrlichia (N = 4) | Ehrlichia (N = 6) | Control (N = 5) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 4 ± 13 | 2 ± 13 | 1 ± 7 | 7 ± 13 |
| Male sex–No. (%) | 1 (75) | 2 (50) | 2 (33.3) | 2 (40) |
| Course of disease days–Avg. | 3 to 9 (3) | 4 to 5 (2.25) | 2 to 7 (1.5) | N.D. |
| Days on ICU–Avg. | 3 to 7(2.5) | 0 to 18 (4.5) | 0 to 12 (2) | N.D. |
| Days on the wards | 5 to 7 | 3 to 16 | 0 to 7 | N.D. |
| Chronotropic Received/Total | 3/4 | 3/4 | 2/6 | N.D. |
| Disease impact/Total | 2 a/4 | 1 b/4 | 1 a/1 c/6 | N.D. |
| Haematologic Alteration | R. rickettsii | E. canis | Coinfected | Total | % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ELE | 4 | 3 | 4 | 11 | 100 |
| Elevated coagulation times | 4 | 3 | 4 | 11 | 100 |
| Leucocytosis by neutrophilia | 3 | 1 | 2 | 7 | 64 |
| Thrombocytopenia | 1 | 1 | 4 | 6 | 55 |
| Lymphopenia | 0 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 55 |
| Hypoalbuminemia | 2 | 0 | 4 | 6 | 55 |
| Hypoproteinemia | 2 | 0 | 4 | 6 | 55 |
| NNA | 3 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 45 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Garcia-Rosales, L.; Escarcega-Avila, A.; Ramirez-Lopez, M.; Manzanera-Ornelas, D.; Guevara-Macias, E.; Vaquera-Arteaga, M.; Alvarado-Gonzlaez, C.; Estrada, B.E.; Jimenez-Vega, F.; Donis-Maturano, L.; et al. Immune Monitoring of Paediatric Patients Infected with Rickettsia rickettsii, Ehrlichia canis and Coinfected. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1351. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11111351
Garcia-Rosales L, Escarcega-Avila A, Ramirez-Lopez M, Manzanera-Ornelas D, Guevara-Macias E, Vaquera-Arteaga M, Alvarado-Gonzlaez C, Estrada BE, Jimenez-Vega F, Donis-Maturano L, et al. Immune Monitoring of Paediatric Patients Infected with Rickettsia rickettsii, Ehrlichia canis and Coinfected. Pathogens. 2022; 11(11):1351. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11111351
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcia-Rosales, Laura, Angelica Escarcega-Avila, Moises Ramirez-Lopez, Diana Manzanera-Ornelas, Enrique Guevara-Macias, Maribel Vaquera-Arteaga, Carolina Alvarado-Gonzlaez, Blanca Elisa Estrada, Florinda Jimenez-Vega, Luis Donis-Maturano, and et al. 2022. "Immune Monitoring of Paediatric Patients Infected with Rickettsia rickettsii, Ehrlichia canis and Coinfected" Pathogens 11, no. 11: 1351. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11111351
APA StyleGarcia-Rosales, L., Escarcega-Avila, A., Ramirez-Lopez, M., Manzanera-Ornelas, D., Guevara-Macias, E., Vaquera-Arteaga, M., Alvarado-Gonzlaez, C., Estrada, B. E., Jimenez-Vega, F., Donis-Maturano, L., & Espino-Solis, G. P. (2022). Immune Monitoring of Paediatric Patients Infected with Rickettsia rickettsii, Ehrlichia canis and Coinfected. Pathogens, 11(11), 1351. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11111351






