Antiviral Activity of Oligonucleotides Targeting the SARS-CoV-2 Genomic RNA Stem-Loop Sequences within the 3′-End of the ORF1b
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells and Viruses
2.2. Phosphorothioate Deoxyoligonucleotide Synthesis
2.3. SARS-CoV-2 S-ON Inhibitory Assay
2.4. Cell Cytotoxicity Assay
2.5. RNA Extraction, Reverse Transcription, and Real-Time PCR of the Viral Genomic Positive and Negative Strand
2.6. Immunofluorescence Investigation
3. Results
3.1. Antiviral Activity of S-ON from the SL1 and SL2 Sequence in the 3′ End of the ORF1b against SARS-CoV-2
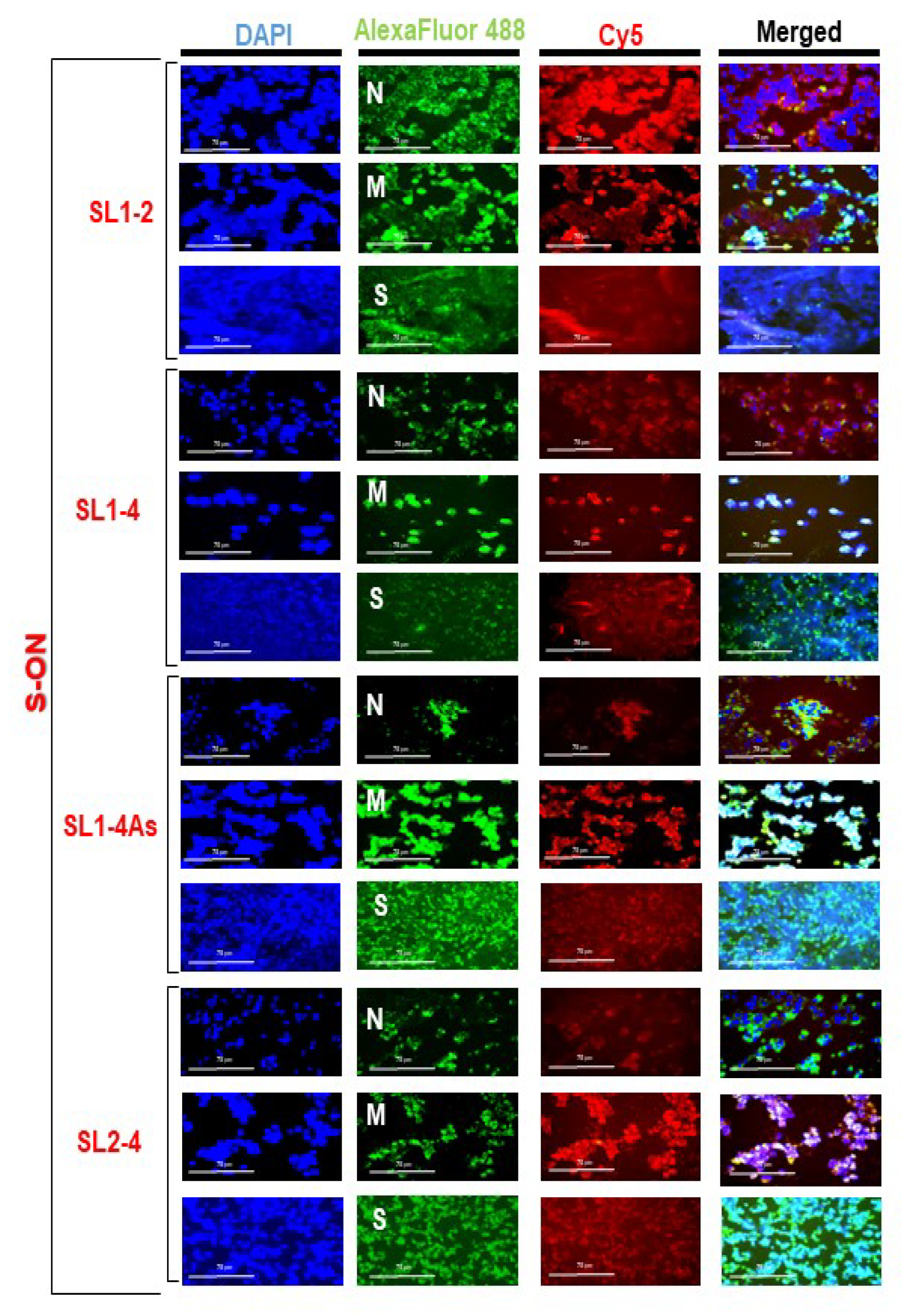
3.2. Localization of S-ONs within Infected Cells
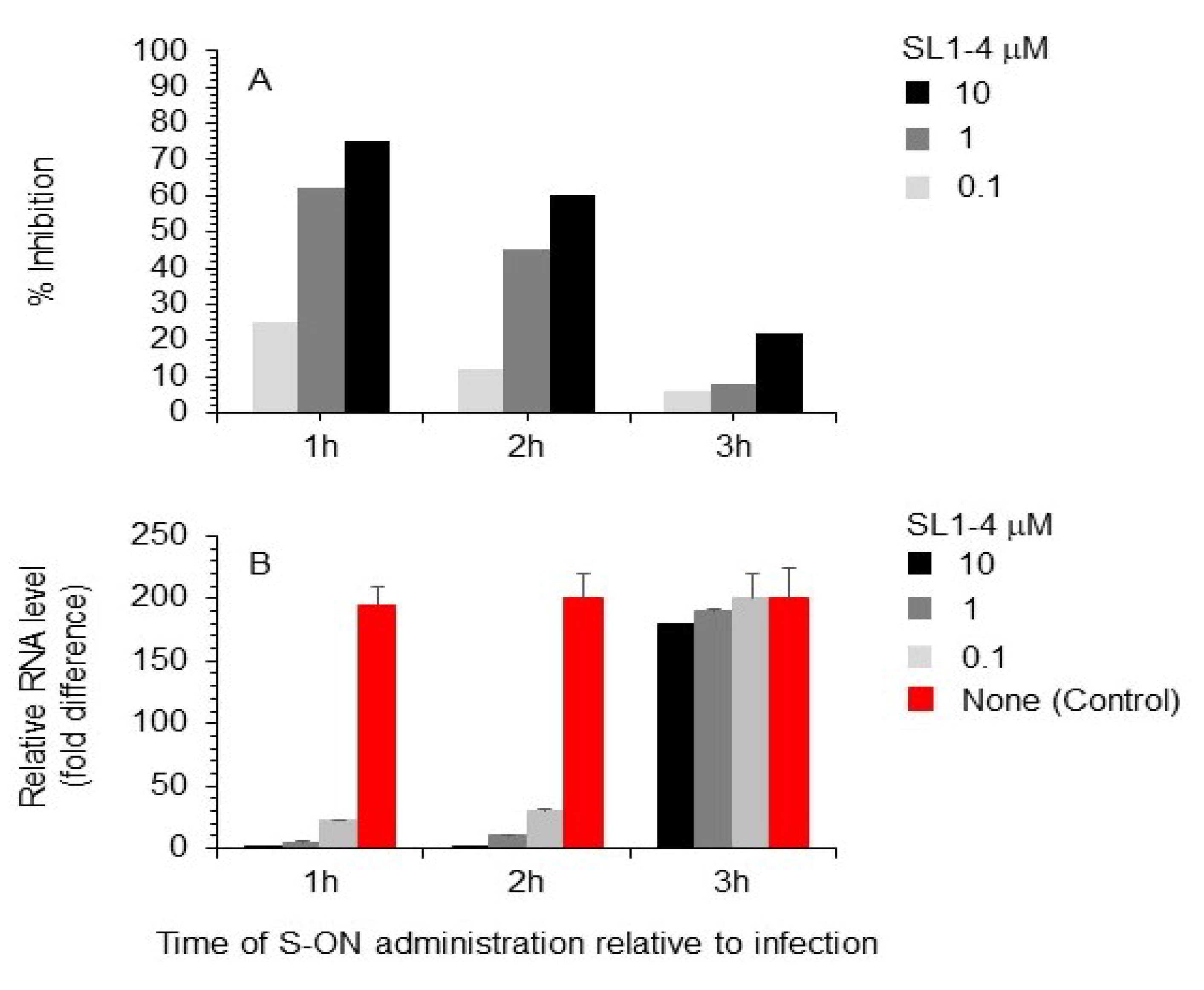
3.3. Effect of Varying the Time of S-ON Treatment on Virus Inhibition
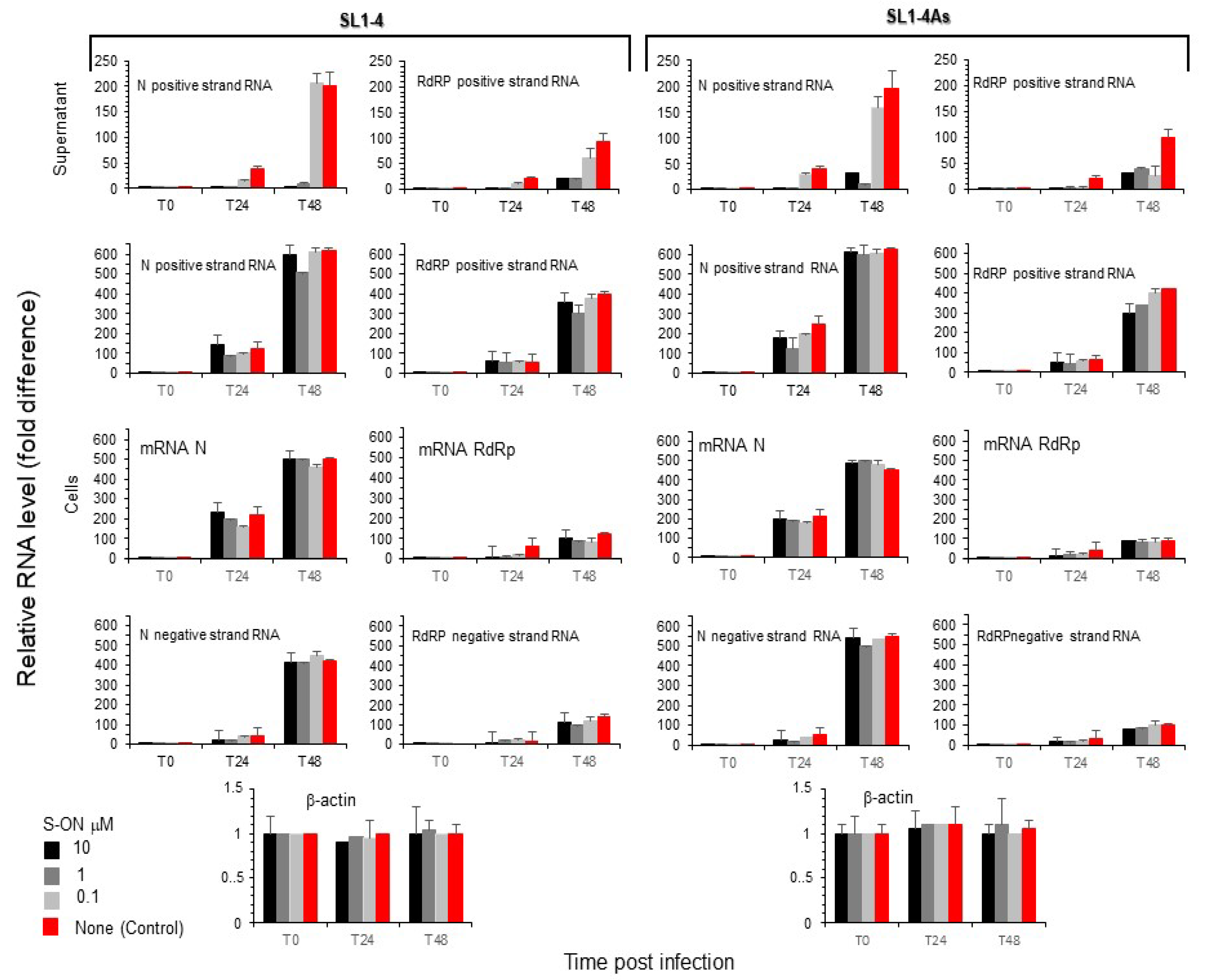
3.4. Effect of S-ON Treatment on Viral RNA Replication and M, N Protein Expression at Different Times of Infection
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, P.; Yang, X.L.; Wang, X.G.; Hu, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Si, H.R.; Zhu, Y.; Li, B.; Huang, C.L.; et al. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature 2020, 579, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fan, G.; Xu, J.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 2020, 395, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- WHO. Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Pandemic WHO. 2020. Available online: https://covid19.who.int (accessed on 15 September 2022).
- Stefanelli, P.; Rezza, G. COVID-19 Vaccination Strategies and Their Adaptation to the Emergence of SARS-CoV-2 Variants. Vaccines 2022, 10, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, K.; Tzou, P.L.; Nouhin, J.; Bonilla, H.; Jagannathan, P.; Shafer, R.W. SARS-CoV-2 Antiviral Therapy. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2021, 34, e0010921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero-López, C.; Berzal-Herranz, A. Unmasking the information encoded as structural motifs of viral RNA genomes: A potential antiviral target. Rev. Med. Virol. 2013, 23, 340–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, A.M.; Choi, Y.H.; Tu, M.J. RNA drugs and RNA targets for small molecules: Principles, progress, and challenges. Pharmacol. Rev. 2020, 72, 862–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, S.M.; Aartsma-Rus, A.; Alves, S.; Borgos, S.E.; Buijsen, R.A.M.; Collin, R.W.J.; Covello, G.; Denti, M.A.; Desviat, L.R.; Echevarría, L.; et al. Delivery of oligonucleotide-based therapeutics: Challenges and opportunities. EMBO Mol. Med. 2021, 13, e13243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crooke, S.T.; Witztum, J.L.; Bennett, C.F.; Baker, B.F. RNA-Targeted Therapeutics. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 714–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le, T.K.; Paris, C.; Khan, K.S.; Robson, F.; Ng, W.L.; Rocchi, P. Nucleic acid-based technologies targeting Coronaviruses. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2021, 46, 351–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wimmer, E.; Paul, A.V. Cis-acting RNA elements in human and animal plus-strand RNA viruses. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1789, 495–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, T. Selective genome packaging mechanisms of Influenza A viruses. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2021, 11, a038497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, T.; Kawaoka, Y. Structure of influenza virus ribonucleoprotein complexes and their packaging into virions. Rev. Med. Virol. 2010, 20, 380–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavazzi, C.; Yver, M.; Isel, C.; Smyth, R.P.; Rosa-Calatrava, M.; Lina, B.; Moules, V.; Marquet, R. A functional sequence-specific interaction between influenza A virus genomic RNA segments. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 16604–16609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miyamoto, S.; Muramoto, Y.; Shindo, K.; Fujita-Fujiharu, Y.; Morikawa, T.; Tamura, R.; Gilmore, J.L.; Nakano, M.; Noda, T. Contribution of RNA-RNA Interactions Mediated by the Genome Packaging Signals for the Selective Genome Packaging of Influenza A Virus. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e0164121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, E.C.; von Kirchbach, J.C.; Gog, J.R.; Digard, P. Genome packagingin influenza A virus. J. Gen. Virol. 2010, 91, 313–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannecchini, S.; Clausi, V.; Nosi, D.; Azzi, A. Oligonucleotides derived fromthe packaging signal at the 5end of the viral PB2 segment specifically inhibitinfluenza virus in vitro. Arch. Virol. 2009, 154, 821–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannecchini, S.; Wise, H.M.; Digard, P.; Clausi, V.; Del Poggetto, E.; Vesco, L.; Puzelli, S.; Donatelli, I.; Azzi, A. Packaging signals in the 5-ends of influenzavirus, P.A.; PB1, and PB2 genes as potential targets to develop nucleic-acid basedantiviral molecules. Antiviral Res. 2011, 92, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabat, M.; Lorent, D.; Czapik, T.; Tomaszewska, M.; Kierzek, E.; Kierzek, R. RNA Secondary Structure as a first step for rational design of the oligonucleotides towards Inhibition of Influenza A virus replication. Pathogens 2020, 9, 925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martelli, F.; Salata, C.; Calistri, A.; Parolin, C.; Azzi, A.; Palù, G.; Giannecchini, S. Small RNAs targeting the 5′ end of the viral polymerase gene segments specifically interfere with influenza type A virus replication. J. Biotechnol. 2015, 210, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Xiong, B.; Luo, C.; Guo, Z.M.; Hao, P.; Su, J.; Nan, P.; Feng, Y.; Shi, Y.X.; Yu, X.J.; et al. Identification of probable genomic packaging signal sequence from SARS CoV genome by bioinformatics analysis. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2003, 24, 489–496. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.; Leibowitz, J.L. The structure and functions of coronavirus genomic 3and 5ends. Virus Res. 2015, 206, 120–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rangan, R.; Zheludev, I.N.; Hagey, R.J.; Pham, E.A.; Wayment-Steele, H.K.; Glenn, J.S.; Das, R. RNA genome conservation and secondary structure in SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-related viruses: A first look. RNA 2020, 26, 937–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhatlani, B.Y. In silico identification of conserved cis-acting RNA elements in the SARS-CoV-2 genome. Future Virol. 2020, 15, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masters, P.S. Coronavirus genomic RNA packaging. Virology 2019, 537, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sola, I.; Mateos-Gomez, P.A.; Almazan, F.; Zũniga, S.; Enjuanes, L. RNA-RNA and RNA-protein interactions in coronavirus replication and transcription. RNA Biol. 2011, 8, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ambike, S.; Cheng, C.C.; Feuerherd, M.; Velkov, S.; Baldassi, D.; Afridi, S.Q.; Porras-Gonzalez, D.; Wei, X.; Hagen, P.; Kneidinger, N.; et al. Targeting genomic SARS-CoV-2 RNA with siRNAs allows efficient inhibition of viral replication and spread. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, 333–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vora, S.M.; Fontana, P.; Mao, T.; Leger, V.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, T.M.; Lieberman, J.; Gehrke, L.; Shi, M.; Wang, L.; et al. Targeting stem-loop 1 of the SARS-CoV-2 5′ UTR to suppress viral translation and Nsp1 evasion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2117198119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lulla, V.; Wandel, M.P.; Bandyra, K.J.; Ulferts, R.; Wu, M.; Dendooven, T.; Yang, X.; Doyle, N.; Oerum, S.; Beale, R.; et al. Targeting the Conserved Stem Loop 2 Motif in the SARS-CoV-2 Genome. J. Virol. 2021, 95, e0066321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanner, E.J.; Kirkegaard, K.A.; Weinberger, L.S. Exploiting genetic interference for antiviral therapy. PLoS Genet. 2016, 12, e1005986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alnaji, F.G.; Brooke, C.B. Influenza virus DI particles: Defective interfering or delightfully interesting? PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.; Narayanan, A.; Majowicz, S.A.; Jose, J.; Archetti, M. A synthetic defective interfering SARS-CoV-2. PeerJ 2021, 9, e11686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalamvoki, M.; Norris, V. A Defective Viral Particle Approach to COVID-19. Cells 2022, 11, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuker, M. Mfold web server for nucleic acid folding and hybridization prediction. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3406–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarn, W.Y.; Cheng, Y.; Ko, S.H.; Huang, L.M. Antisense Oligonucleotide-Based Therapy of Viral Infections. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenke, K.; Leventhal, S.; Moulton, H.M.; Hatlevig, S.; Hawman, D.; Feldmann, H.; Stein, D.A. Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 in Vero cell cultures by peptide-conjugated morpholino oligomers. J Antimicrob. Chemother. 2021, 76, 413–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, L.; Liu, M.; Gou, Y.; Yang, Y.; He, B.; Huang, J. Development and application of ribonucleic acid therapy strategies against COVID-19. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 18, 5070–5085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, T.C.; Langer, R.; Wood, M.J.A. Advances in oligonucleotide drug delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2020, 19, 673–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yang, X.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, B.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Li, M. Inhibition of influenza A virus replication by RNA interference targeted against the PB1 subunit of the RNA polymerase gene. Arch. Virol. 2011, 156, 1979–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Garcia, G.; Arumugaswami, V.; Guo, F. Structure-based design of antisense oligonucleotides that inhibit SARS-CoV-2 replication. bioRxiv 2021, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagey, R.J.; Elazar, M.; Pham, E.A.; Tian, S.; Ben-Avi, L.; Bernardin-Souibgui, C.; Yee, M.F.; Moreira, F.R.; Rabinovitch, M.V.; Meganck, R.M.; et al. Programmable antivirals targeting critical conserved viral RNA secondary structures from influenza A virus and SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 1944–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Yan, C.; Qin, F.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, X.E. The intraviral protein-protein interaction of SARS-CoV-2 reveals the key role of N protein in virus-like particle assembly. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 3889–3897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, P.K.; Chang, S.C.; Huang, C.C.; Lee, T.T.; Hsiao, C.W.; Kou, Y.H.; Chen, I.Y.; Chang, C.K.; Huang, T.H.; Chang, M.F. Assembly of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus RNA packaging signal into virus-like particles Is nucleocapsid dependent. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 13848–13855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, C.; Lee, J.Y.; Woo, J.Z.; Xu, L.; Nguyenla, X.; Yamashiro, L.H.; Ji, F.; Biering, S.B.; Van Dis, E.; Gonzalez, F.; et al. An intranasal ASO therapeutic targeting SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4503–4515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
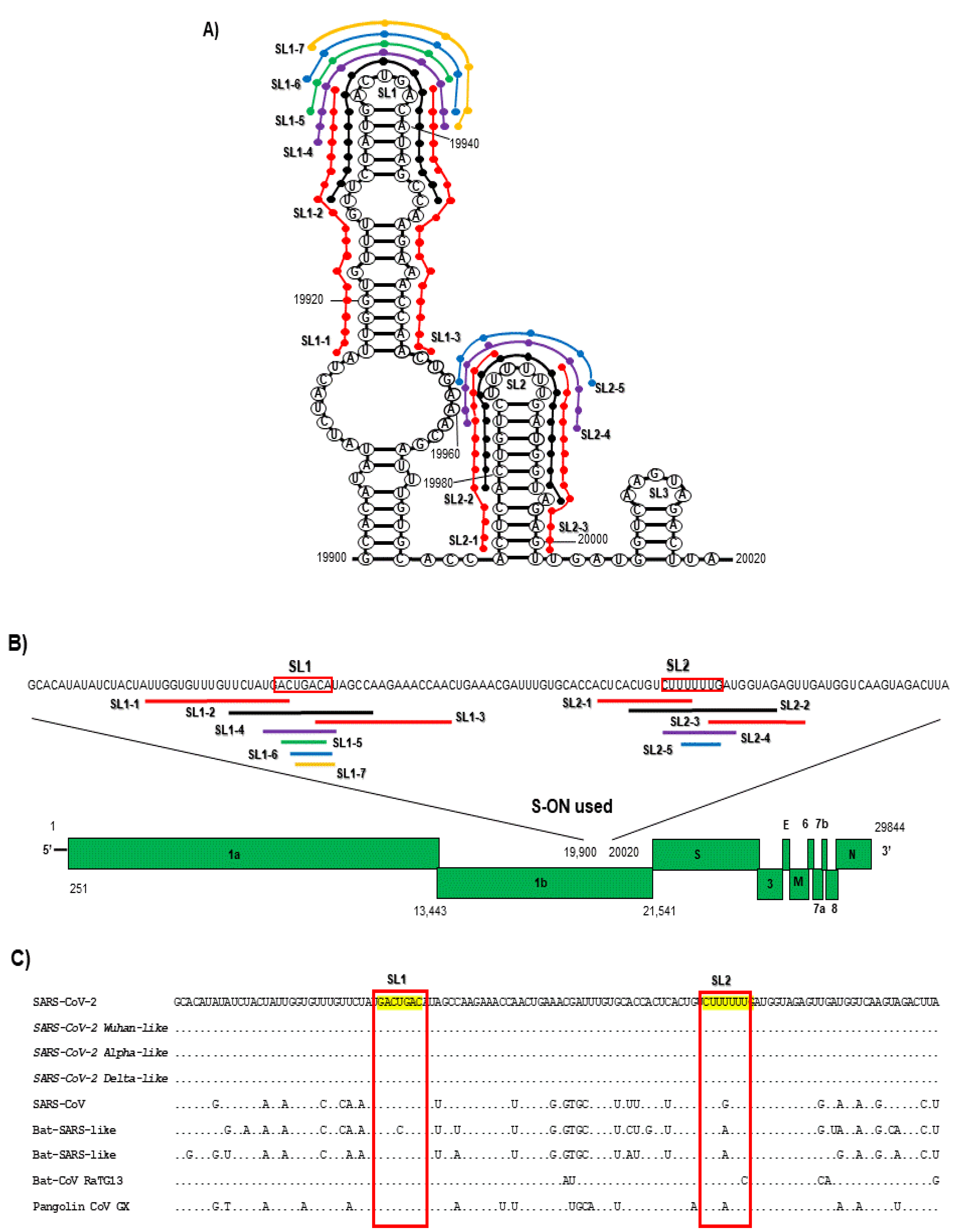

| ID S-ON | Sequence (nt Length) | IC50 μM | CC50 μM | Secondary Structure |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | ||||
| SL1-1 | attggtgtttgttctatga (19 nt) | 5.69 ± 1.20 | >100 | None |
| SL1-1As | taaccacaaacaagatact (19 nt) | 12.21 ± 2.30 | >100 | None |
| SL1-2 | ttctatgactgacatagcc (19 nt) | 0.27 ± 0.18 | >100 |  |
| SL1-2As | aagatactgactgtatcgg (19 nt) | 1.04 ± 0.81 | >100 |  |
| SL1-3 | acatagccaagaaaccaac (19 nt) | 5.80 ± 2.32 | >100 | None |
| SL1-3As | tgtatcggttctttggttg (19 nt) | 2.90 ± 1.23 | >100 |  |
| SL2-1 | actcactgtcttt (13 nt) | 7.23 ± 1.21 | >100 | None |
| SL2-1As | tgagtgacagaaa (13 nt) | 9.90 ± 2.02 | >100 | None |
| SL2-2 | actgtcttttttgatggta (19 nt) | 1.60 + 0.89 | >100 |  |
| SL2-2As | tgacagaaaaaactaccat (19 nt) | 2.60 ± 2.19 | >100 | None |
| SL2-3 | ttgatggtagagt (13 nt) | 4.48 ± 2.34 | >100 | None |
| SL2-3As | aactaccatctca (13 nt) | 1.90 ± 1.20 | >100 | None |
| SL Contr | atttcgatcaagacgctct (19 nt) | >100 | >100 | None |
| ID S-ON | Sequence (nt Length) | IC50 μM | CC50 μM |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | |||
| SL1-4 | atgactgaca (10 nt) | 0.19 ± 0.20 | >100 |
| SL1-4As | tactgactgt (10 nt) | 0.30 ± 0.29 | >100 |
| SL1-5 | gactga (6 nt) | 2.1 ± 1.23 | >100 |
| SL1-6 | actgac (6 nt) | 9.80 ± 10.11 | >100 |
| SL1-7 | ctgaca (6 nt) | 2.80 ± 1.70 | >100 |
| SL1-4mut | atggggggca (10 nt) | >100 | >100 |
| SL1-4Asmut | tagggggggt (10 nt) | >100 | >100 |
| SL2-4 | tcttttttga (10 nt) | 2.87 ± 2.30 | >100 |
| SL2-4As | agaaaaaact (10 nt) | 0.93 ± 0.12 | >100 |
| SL2-5 | tttttt (6 nt) | 31.12 ± 9.05 | >100 |
| SL2-4mut | tcggggggga (10 nt) | >100 | >100 |
| SL2-4Asmut | agggggggct (10 nt) | >100 | >100 |
| ID S-ON | Sequence (nt Length) | IC50 μM | CC50 μM |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | |||
| Wild type-like | |||
| SL1-4 | atgactgaca (10 nt) | 4.12 ± 2.23 | >100 |
| SL1-4As | tactgactgt (10 nt) | 2.10 ± 2.09 | >100 |
| SL2-4 | tcttttttga (10 nt) | 1.50 ± 1.20 | >100 |
| SL2-4As | agaaaaaact (10 nt) | 0.65 ± 0.45 | >100 |
| Alpha-like variant | |||
| SL1-4 | atgactgaca (10 nt) | 1.23 ± 0.87 | >100 |
| SL1-4As | tactgactgt (10 nt) | 2.10 ± 1.09 | >100 |
| SL2-4 | tcttttttga (10 nt) | 2.34 ± 1.11 | >100 |
| SL2-4As | agaaaaaact (10 nt) | 1.90 ± 0.88 | >100 |
| Delta-like variant | |||
| SL1-4 | atgactgaca (10 nt) | 5.61 ± 2.34 | >100 |
| SL1-4As | tactgactgt (10 nt) | 4.64 ± 1.24 | >100 |
| SL2-4 | tcttttttga (10 nt) | 5.43 ± 3.32 | >100 |
| SL2-4As | agaaaaaact (10 nt) | 1.88 ± 0.98 | >100 |
| A/Firenze/02/2019 H1N1pmd | |||
| SL1-4 | atgactgaca (10 nt) | >100 | >100 |
| SL1-4As | tactgactgt (10 nt) | >100 | >100 |
| SL2-4 | tcttttttga (10 nt) | >100 | >100 |
| SL2-4As | agaaaaaact (10 nt) | >100 | >100 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stincarelli, M.A.; Rocca, A.; Antonelli, A.; Rossolini, G.M.; Giannecchini, S. Antiviral Activity of Oligonucleotides Targeting the SARS-CoV-2 Genomic RNA Stem-Loop Sequences within the 3′-End of the ORF1b. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1286. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11111286
Stincarelli MA, Rocca A, Antonelli A, Rossolini GM, Giannecchini S. Antiviral Activity of Oligonucleotides Targeting the SARS-CoV-2 Genomic RNA Stem-Loop Sequences within the 3′-End of the ORF1b. Pathogens. 2022; 11(11):1286. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11111286
Chicago/Turabian StyleStincarelli, Maria Alfreda, Arianna Rocca, Alberto Antonelli, Gian Maria Rossolini, and Simone Giannecchini. 2022. "Antiviral Activity of Oligonucleotides Targeting the SARS-CoV-2 Genomic RNA Stem-Loop Sequences within the 3′-End of the ORF1b" Pathogens 11, no. 11: 1286. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11111286
APA StyleStincarelli, M. A., Rocca, A., Antonelli, A., Rossolini, G. M., & Giannecchini, S. (2022). Antiviral Activity of Oligonucleotides Targeting the SARS-CoV-2 Genomic RNA Stem-Loop Sequences within the 3′-End of the ORF1b. Pathogens, 11(11), 1286. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11111286








