Markers of Infection-Mediated Cardiac Damage in Influenza and COVID-19
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
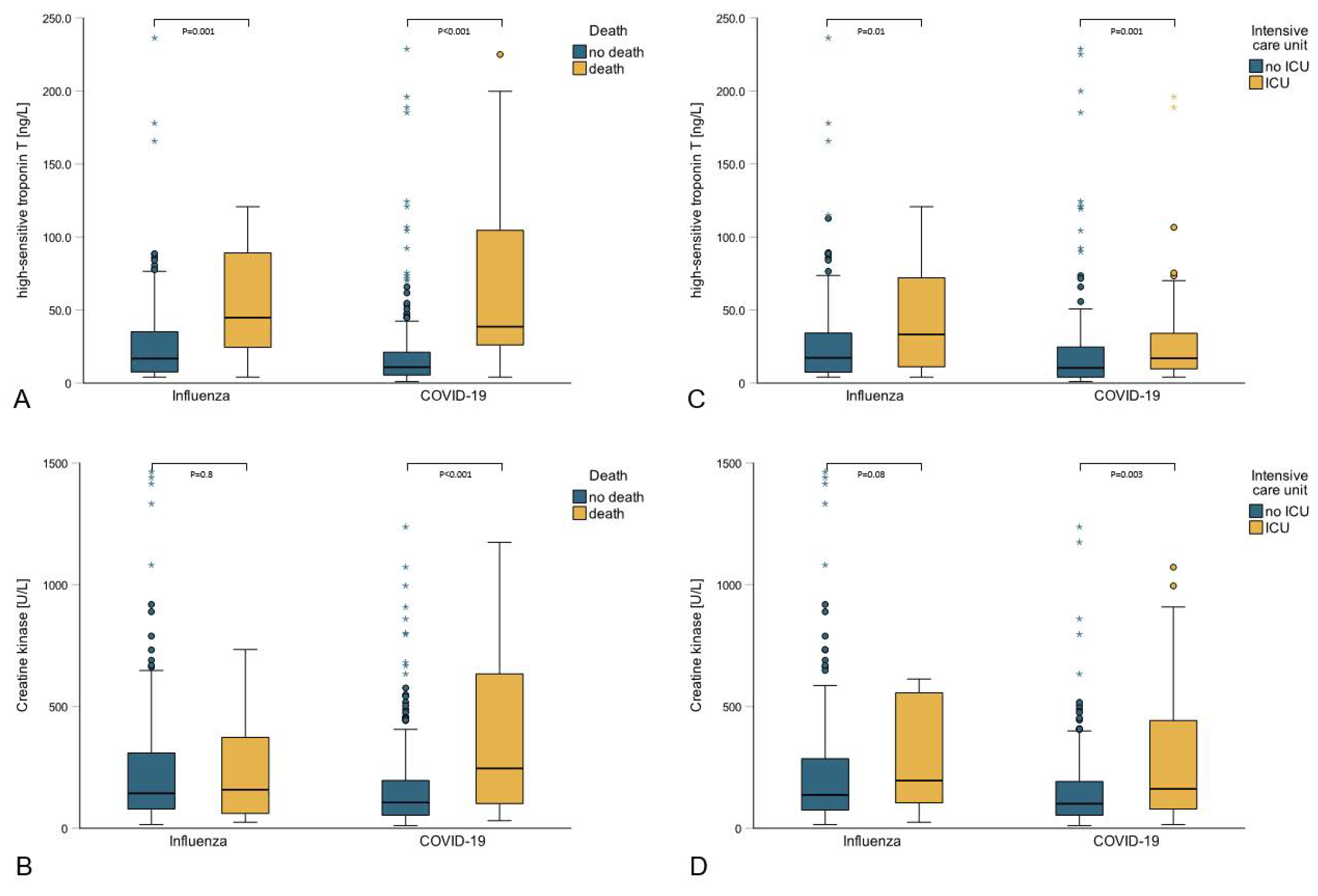
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Institute of Medicine. The Threat of Pandemic Influenza: Are We Ready? Workshop Summary; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; p. 430. [Google Scholar]
- Saunders-Hastings, P.R.; Krewski, D. Reviewing the History of Pandemic Influenza: Understanding Patterns of Emergence and Transmission. Pathogens 2016, 5, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, T.; Lozano, J.E.; Meerhoff, T.; Snacken, R.; Beauté, J.; Jorgensen, P.; Ortiz de Lejarazu, R.; Domegan, L.; Mossong, J.; Nielsen, J.; et al. Influenza surveillance in Europe: Comparing intensity levels calculated using the moving epidemic method. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 2015, 9, 234–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webster, R.G.; Bean, W.J.; Gorman, O.T.; Chambers, T.M.; Kawaoka, Y. Evolution and ecology of influenza A viruses. Microbiol. Rev. 1992, 56, 152–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webby, R.J.; Swenson, S.L.; Krauss, S.L.; Gerrish, P.J.; Goyal, S.M.; Webster, R.G. Evolution of swine H3N2 influenza viruses in the United States. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 8243–8251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghebrehewet, S.; MacPherson, P.; Ho, A. Influenza. BMJ 2016, 355, i6258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, A.; Soldevila, N.; Romero-Tamarit, A.; Torner, N.; Godoy, P.; Rius, C.; Jané, M.; Domínguez, À. Surveillance of Hospitalized Cases of Severe Influenza in Catalonia Working, G. Risk factors associated with severe outcomes in adult hospitalized patients according to influenza type and subtype. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0210353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rößler, S.; Ankert, J.; Baier, M.; Pletz, M.W.; Hagel, S. Influenza-associated in-hospital mortality during the 2017/2018 influenza season: A retrospective multicentre cohort study in central Germany. Infection 2021, 49, 149–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellers, S.A.; Hagan, R.S.; Hayden, F.G.; Fischer, W.A., 2nd. The hidden burden of influenza: A review of the extra-pulmonary complications of influenza infection. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 2017, 11, 372–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estabragh, Z.R.; Mamas, M.A. The cardiovascular manifestations of influenza: A systematic review. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 167, 2397–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwong, J.C.; Schwartz, K.L.; Campitelli, M.A.; Chung, H.; Crowcroft, N.S.; Karnauchow, T.; Katz, K.; Ko, D.T.; McGeer, A.J.; McNally, D.; et al. Acute Myocardial Infarction after Laboratory-Confirmed Influenza Infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukhdeo, S.; Lee, N. Influenza: Clinical aspects, diagnosis, and treatment. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2022, 28, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belongia, E.A.; Simpson, M.D.; King, J.P.; Sundaram, M.E.; Kelley, N.S.; Osterholm, M.T.; McLean, H.Q. Variable influenza vaccine effectiveness by subtype: A systematic review and meta-analysis of test-negative design studies. Lancet. Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 942–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möst, J.; Weiss, G. Consecutive Infections With Influenza A and B Virus in Children During the 2014–2015 Seasonal Influenza Epidemic. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 214, 1139–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Möst, J.; Redlberger-Fritz, M.; Weiss, G. Multiple Influenza Virus Infections in 4 Consecutive Epidemiological Seasons: A Retrospective Study in Children and Adolescents. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2019, 6, ofz195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, O.; Birrell, F.A.; Mifsud, E.J.; Sullivan, S.G. Epidemiology of repeat influenza infection in Queensland, Australia, 2005–2017. Epidemiol. Infect. 2022, 150, e144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenjie, T.; Zhao, X.; Ma, X.; Wang, W.; Niu, P.; Xu, W.; Gao, G.; Wu, G. A Novel Coronavirus Genome Identified in a Cluster of Pneumonia Cases—Wuhan, China 2019−2020. China CDC Wkly. 2020, 2, 61–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fan, G.; Xu, J.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 2020, 395, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, A.M.; Wysocki, J.; Batlle, D. Interaction of SARS-CoV-2 and Other Coronavirus with ACE (Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme)-2 as Their Main Receptor: Therapeutic Implications. Hypertension 2020, 76, 1339–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burkert, F.R.; Lanser, L.; Bellmann-Weiler, R.; Weiss, G. Coronavirus Disease 2019: Clinics, Treatment, and Prevention. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 761887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oberfeld, B.; Achanta, A.; Carpenter, K.; Chen, P.; Gilette, N.M.; Langat, P.; Said, J.T.; Schiff, A.E.; Zhou, A.S.; Barczak, A.K.; et al. SnapShot: COVID-19. Cell 2020, 181, 954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solís Arce, J.S.; Warren, S.S.; Meriggi, N.F.; Scacco, A.; McMurry, N.; Voors, M.; Syunyaev, G.; Malik, A.A.; Aboutajdine, S.; Adeojo, O.; et al. COVID-19 vaccine acceptance and hesitancy in low- and middle-income countries. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1385–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamming, I.; Timens, W.; Bulthuis, M.L.; Lely, A.T.; Navis, G.; van Goor, H. Tissue distribution of ACE2 protein, the functional receptor for SARS coronavirus. A first step in understanding SARS pathogenesis. J. Pathol. 2004, 203, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; McGoogan, J.M. Characteristics of and Important Lessons From the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Outbreak in China: Summary of a Report of 72 314 Cases From the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. JAMA 2020, 323, 1239–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basu-Ray, I.; Almaddah, N.K.; Adeboye, A.; Soos, M.P. Cardiac Manifestations Of Coronavirus (COVID-19). In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing LLC: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Lodigiani, C.; Iapichino, G.; Carenzo, L.; Cecconi, M.; Ferrazzi, P.; Sebastian, T.; Kucher, N.; Studt, J.D.; Sacco, C.; Bertuzzi, A.; et al. Venous and arterial thromboembolic complications in COVID-19 patients admitted to an academic hospital in Milan, Italy. Thromb. Res. 2020, 191, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, W.; Kang, J.-S.; Wang, Q.; Kim, T.-E. Cardiac biomarkers and COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Infect. Public Health 2021, 14, 1191–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwaenepoel, B.; Dhont, S.; Hoste, E.; Gevaert, S.; Schaubroeck, H. The Prognostic Value of Cardiac Biomarkers and Echocardiography in Critical COVID-19. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 752237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.-S.; Pan, N.-N.; Chen, R.-D.; Zeng, L.-C.; Yang, H.-K.; Li, H. Cardiac Biomarker Levels and Their Prognostic Values in COVID-19 Patients With or Without Concomitant Cardiac Disease. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 7, 599096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Rasool, S.T.; Ahmed, S.I. Role of Cardiac Biomarkers in COVID-19: What Recent Investigations Tell Us? Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2021, 46, 100842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonagh, T.A.; Metra, M.; Adamo, M.; Gardner, R.S.; Baumbach, A.; Böhm, M.; Burri, H.; Butler, J.; Čelutkienė, J.; Chioncel, O.; et al. 2021 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 3599–3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, M.; Heywood, A.E.; Mahimbo, A.; Rahman, B.; Newall, A.T.; Macintyre, C.R. Acute myocardial infarction and influenza: A meta-analysis of case-control studies. Heart 2015, 101, 1738–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzini, A.; Burkert, F.; Theurl, I.; Weiss, G.; Bellmann-Weiler, R. Prognostic impact of high sensitive Troponin T in patients with influenza virus infection: A retrospective analysis. Heart Lung J. Crit. Care 2020, 49, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, B.; Brady, W.J.; Koyfman, A.; Gottlieb, M. Cardiovascular complications in COVID-19. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2020, 38, 1504–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Booth, A.; Reed, A.B.; Ponzo, S.; Yassaee, A.; Aral, M.; Plans, D.; Labrique, A.; Mohan, D. Population risk factors for severe disease and mortality in COVID-19: A global systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0247461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahmy, O.H.; Daas, F.M.; Salunkhe, V.; Petrey, J.L.; Cosar, E.F.; Ramirez, J.; Akca, O. Is Microthrombosis the Main Pathology in Coronavirus Disease 2019 Severity?-A Systematic Review of the Postmortem Pathologic Findings. Crit. Care Explor. 2021, 3, e0427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burkert, F.R.; Niederreiter, L.; Dichtl, W.; Mayr, A.; Virgolini, I.; Klauser, A.; Weiss, G.; Bellmann-Weiler, R. Case report of a COVID-19-associated myocardial infarction with no obstructive coronary arteries: The mystery of the phantom embolus or local endothelitis. Eur. Heart J. Case Rep. 2021, 5, ytaa521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maccio, U.; Zinkernagel, A.S.; Shambat, S.M.; Zeng, X.; Cathomas, G.; Ruschitzka, F.; Schuepbach, R.A.; Moch, H.; Varga, Z. SARS-CoV-2 leads to a small vessel endotheliitis in the heart. eBioMedicine 2021, 63, 103182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Chen, T.; Mui, D.; Ferrari, V.; Jagasia, D.; Scherrer-Crosbie, M.; Chen, Y.; Han, Y. Cardiovascular manifestations and treatment considerations in COVID-19. Heart 2020, 106, 1132–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welty, F.K.; Rajai, N.; Amangurbanova, M. Comprehensive Review of Cardiovascular Complications of Coronavirus Disease 2019 and Beneficial Treatments. Cardiol. Rev. 2022, 30, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegers, J.Y.; Novakovic, B.; Hulme, K.D.; Marshall, R.J.; Bloxham, C.J.; Thomas, W.G.; Reichelt, M.E.; Leijten, L.; van Run, P.; Knox, K.; et al. A High-Fat Diet Increases Influenza A Virus-Associated Cardiovascular Damage. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 222, 820–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnweber, T.; Sahanic, S.; Pizzini, A.; Luger, A.; Schwabl, C.; Sonnweber, B.; Kurz, K.; Koppelstätter, S.; Haschka, D.; Petzer, V.; et al. Cardiopulmonary recovery after COVID-19-an observational prospective multi-center trial. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 57, 2003481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Overall | Influenza | COVID-19 | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | 616 | 250 | 366 | |
| Patient age, years (mean (SD)) | 64.43 (18.00) | 65.92 (18.49) | 63.41 (17.61) | 0.089 |
| Age over 65 (%) | 347 (56.3) | 160 (64.0) | 187 (51.1) | 0.002 |
| Patient sex = woman (%) | 253 (41.1) | 114 (45.6) | 139 (38.1) | 0.063 |
| Creatinine, mg/dL (median [IQR]) | 0.98 [0.80, 1.21] | 1.01 [0.83, 1.22] | 0.94 [0.79, 1.19] | 0.156 |
| EGFR, mL/min (mean (SD)) | 70.91 (29.81) | 68.08 (27.72) | 73.20 (31.27) | 0.046 |
| Hs-TnT, ng/L (median [IQR]) | 15.20 [6.60, 32.88] | 17.60 [8.00, 38.05] | 11.80 [5.90, 27.80] | 0.003 |
| Hs-TnT over 14 ng/L (%) | 267 (51.9) | 140 (58.6) | 127 (46.2) | 0.005 |
| Δhs-TnT, ng/L (median [IQR]) | 4.90 [2.08, 18.05] | 8.00 [2.85, 31.25] | 3.60 [2.00, 10.80] | 0.001 |
| Creatine kinase, U/L (median [IQR]) | 126.00 [64.50, 269.00] | 144.00 [76.00, 309.00] | 111.50 [55.25, 222.75] | 0.001 |
| In-hospital mortality (%) | 58 (9.4) | 19 (7.6) | 39 (10.7) | 0.202 |
| ICU admittance (%) | 122 (19.8) | 35 (14.0) | 87 (23.8) | 0.003 |
| Chronic heart disease (%) | 134 (24.6) | 92 (36.8) | 42 (14.3) | <0.001 |
| Overall | Hs-TnT under 14 ng/L | Hs-TnT over 14 ng/L | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | 514 | 247 | 267 | |
| Patient age, years (mean (SD)) | 64.49 (18.17) | 54.54 (17.31) | 73.72 (13.49) | <0.001 |
| Patient sex = woman (%) | 218 (42.4) | 117 (47.4) | 101 (37.8) | 0.029 |
| Creatinine, mg/dL (median [IQR]) | 0.96 [0.79, 1.22] | 0.87 [0.73, 1.00] | 1.12 [0.89, 1.54] | <0.001 |
| EGFR, mL/min (mean (SD)) | 71.21 (30.13) | 85.64 (27.41) | 57.92 (26.18) | <0.001 |
| Hs-TnT, ng/L (median [IQR]) | 15.20 [6.60, 32.88] | 6.50 [4.00, 9.55] | 31.90 [20.15, 55.60] | <0.001 |
| Creatine kinase, U/L (median [IQR]) | 127.00 [67.00, 272.00] | 109.00 [63.00, 181.00] | 154.00 [76.00, 406.00] | <0.001 |
| In-hospital mortality (%) | 46 (8.9) | 5 (2.0) | 41 (15.6) | <0.001 |
| ICU admittance (%) | 112 (21.8) | 43 (17.4) | 69 (25.8) | 0.021 |
| Chronic heart disease (%) | 122 (26.6) | 34 (15.5) | 88 (36.8) | <0.001 |
| Overall | Influenza | COVID-19 | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | 267 | 140 | 127 | |
| Patient age, years (mean (SD)) | 73.72 (13.49) | 72.87 (14.73) | 74.67 (11.95) | 0.279 |
| Patient sex = woman (%) | 101 (37.8) | 64 (45.7) | 37 (29.1) | 0.005 |
| Creatinine, mg/dL (median [IQR]) | 1.12 [0.89, 1.54] | 1.07 [0.90, 1.44] | 1.16 [0.88, 1.65] | 0.341 |
| EGFR, mL/min (mean (SD)) | 57.92 (26.18) | 58.23 (25.08) | 57.58 (27.44) | 0.841 |
| Hs-TnT, ng/L (median [IQR]) | 31.90 [20.15, 55.60] | 33.55 [21.95, 58.35] | 29.40 [19.20, 53.30] | 0.343 |
| Creatine kinase, U/L (median [IQR]) | 154.00 [76.00, 406.00] | 157.00 [86.00, 455.00] | 150.50 [63.50, 384.00] | 0.239 |
| In-hospital mortality (%) | 41 (15.4) | 15 (10.7) | 26 (20.5) | 0.027 |
| ICU admittance (%) | 69 (25.8) | 23 (16.4) | 46 (36.2) | <0.001 |
| Chronic heart disease (%) | 88 (36.8) | 64 (45.7) | 24 (24.2) | 0.001 |
| Overall | Survival | Death | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | 616 | 558 | 58 | |
| Patient age, years (mean (SD)) | 64.43 (18.00) | 63.07 (17.94) | 77.52 (12.58) | <0.001 |
| Creatinine, mg/dL (median [IQR]) | 0.98 [0.80, 1.21] | 0.95 [0.79, 1.16] | 1.30 [0.96, 1.65] | <0.001 |
| EGFR, mL/min (mean (SD)) | 70.91 (29.81) | 72.51 (29.48) | 55.38 (28.82) | <0.001 |
| Hs-TnT, ng/L (median [IQR]) | 15.20 [6.60, 32.88] | 12.75 [6.30, 27.80] | 40.25 [24.60, 89.73] | <0.001 |
| Δhs-TnT, ng/L (median [IQR]) | 4.90 [2.08, 18.05] | 4.25 [2.00, 13.78] | 25.70 [7.50, 51.75] | <0.001 |
| Creatine kinase, U/L (median [IQR]) | 126.00 [64.50, 269.00] | 123.00 [64.25, 241.25] | 206.00 [67.00, 525.00] | 0.012 |
| ICU admittance (%) | 122 (19.8) | 103 (18.5) | 19 (32.8) | 0.009 |
| Chronic heart disease (%) | 134 (24.6) | 118 (23.8) | 16 (33.3) | 0.143 |
| Overall | No ICU Admission | ICU Admission | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | 616 | 494 | 122 | |
| Patient age, years (mean (SD)) | 64.43 (18.00) | 65.21 (18.85) | 61.27 (13.70) | 0.03 |
| Creatinine, mg/dL (median [IQR]) | 0.98 [0.80, 1.21] | 0.97 [0.80, 1.16] | 1.00 [0.79, 1.43] | 0.206 |
| EGFR, mL/min (mean (SD)) | 70.91 (29.81) | 71.14 (29.21) | 70.06 (32.08) | 0.729 |
| Hs-TnT, ng/L (median [IQR]) | 15.20 [6.60, 32.88] | 13.00 [6.00, 29.40] | 18.35 [10.05, 53.50] | 0.001 |
| Δhs-TnT, ng/L (median [IQR]) | 4.90 [2.08, 18.05] | 3.30 [1.75, 10.80] | 10.00 [3.90, 40.10] | <0.001 |
| Creatine kinase, U/L (median [IQR]) | 126.00 [64.50, 269.00] | 117.00 [64.00, 226.00] | 164.50 [80.75, 458.50] | 0.004 |
| In-hospital mortality (%) | 58 (9.4) | 39 (7.9) | 19 (15.6) | 0.009 |
| Chronic heart disease (%) | 134 (24.6) | 118 (26.5) | 16 (16.2) | 0.031 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Burkert, F.R.; Lanser, L.; Pizzini, A.; Bellmann-Weiler, R.; Weiss, G. Markers of Infection-Mediated Cardiac Damage in Influenza and COVID-19. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1191. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11101191
Burkert FR, Lanser L, Pizzini A, Bellmann-Weiler R, Weiss G. Markers of Infection-Mediated Cardiac Damage in Influenza and COVID-19. Pathogens. 2022; 11(10):1191. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11101191
Chicago/Turabian StyleBurkert, Francesco Robert, Lukas Lanser, Alex Pizzini, Rosa Bellmann-Weiler, and Günter Weiss. 2022. "Markers of Infection-Mediated Cardiac Damage in Influenza and COVID-19" Pathogens 11, no. 10: 1191. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11101191
APA StyleBurkert, F. R., Lanser, L., Pizzini, A., Bellmann-Weiler, R., & Weiss, G. (2022). Markers of Infection-Mediated Cardiac Damage in Influenza and COVID-19. Pathogens, 11(10), 1191. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11101191






