The Potential Role of an Aberrant Mucosal Immune Response to SARS-CoV-2 in the Pathogenesis of IgA Nephropathy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
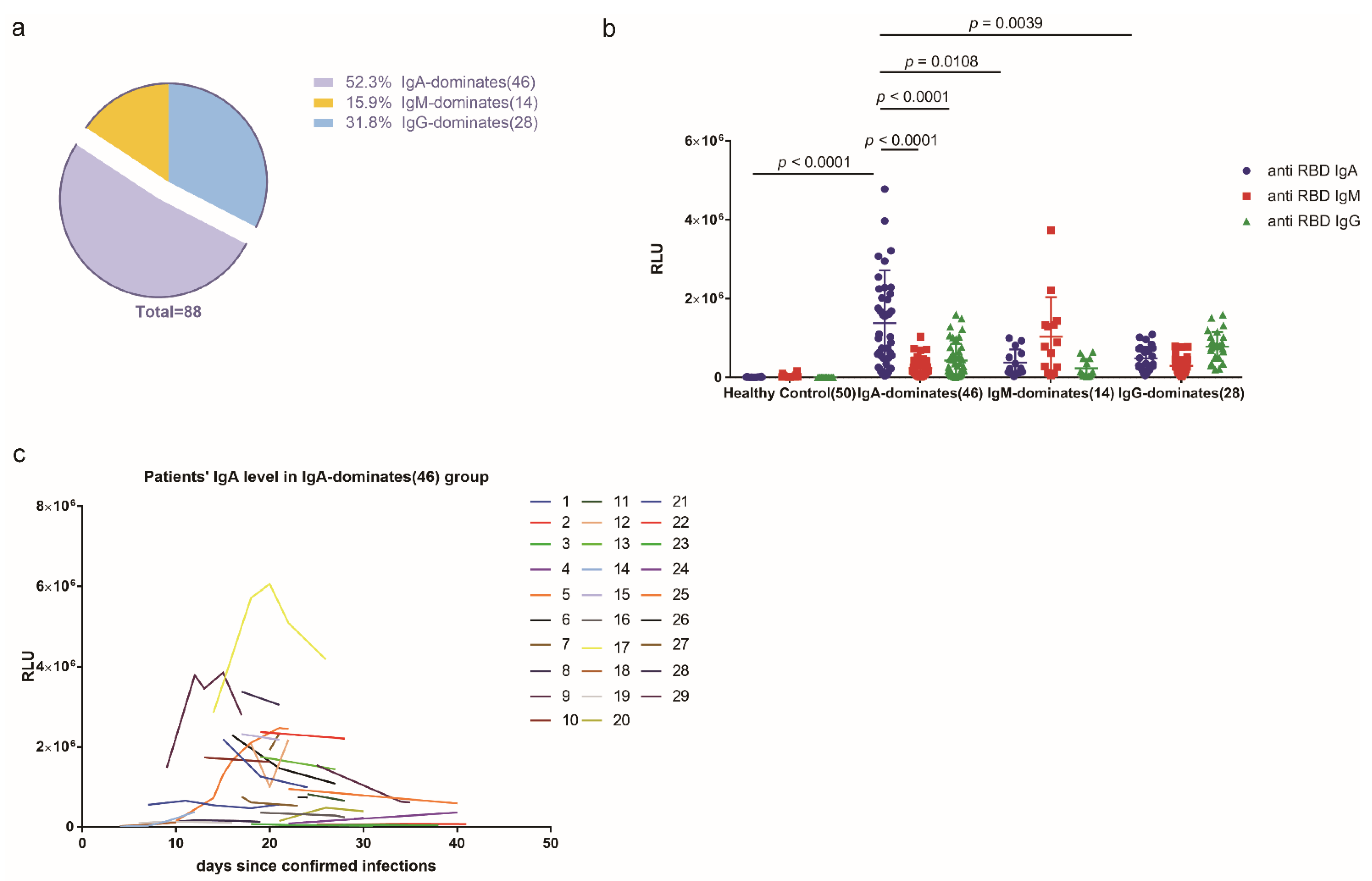
2.1. More Than Half of the COVID-19 Cohort Produced More Anti-SARS-CoV-2 RBD IgA Than IgG or IgM during SARS-CoV-2 Infection
2.2. A Patient with IgA-Dominant COVID-19 and Concurrent IgAN Exhibited Reduced Renal Function during and after Infection
2.3. Intestinal Dysbiosis and Inflammation Were Observed in the COVID-19 IgAN Case
3. Discussion
4. Patients and Methods
4.1. Patient Cohort
4.2. Measurement of Serum Immunoglobin Levels
4.3. Measurement of Total IgA and IL-18 Concentrations
4.4. Flow Cytometric Analysis of Fecal IgA
4.5. 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing
4.6. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hoffmann, M.; Kleine-Weber, H.; Schroeder, S.; Kruger, N.; Herrler, T.; Erichsen, S.; Schiergens, T.S.; Herrler, G.; Wu, N.H.; Nitsche, A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor. Cell 2020, 181, 271–280.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Penninger, J.M.; Li, Y.; Zhong, N.; Slutsky, A.S. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) as a SARS-CoV-2 receptor: Molecular mechanisms and potential therapeutic target. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 46, 586–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, M.Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X. Expression of the SARS-CoV-2 cell receptor gene ACE2 in a wide variety of human tissues. Infect Dis. Poverty 2020, 9, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hikmet, F.; Mear, L.; Edvinsson, A.; Micke, P.; Uhlen, M.; Lindskog, C. The protein expression profile of ACE2 in human tissues. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2020, 16, e9610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, R.M.; Killerby, M.E.; Newton, S.; Ashworth, C.E.; Berns, A.L.; Brennan, S.; Bressler, J.M.; Bye, E.; Crawford, R.; Morano, L.H.; et al. Symptom Profiles of a Convenience Sample of Patients with COVID-19. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2020, 69, 904–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavriatopoulou, M.; Korompoki, E.; Fotiou, D.; Ntanasis-Stathopoulos, I.; Psaltopoulou, T.; Kastritis, E.; Terpos, E.; Dimopoulos, M.A. Organ-specific manifestations of COVID-19 infection. Clin. Exp. Med. 2020, 20, 493–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fan, G.; Xu, J.; Gu, X. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 2020, 395, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, D.; Hu, B.; Hu, C.; Zhu, F.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, B.; Xiang, H.; Cheng, Z.; Xiong, Y. Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus–infected pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA 2020, 323, 1061–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, B.E.; Ong, S.W.X.; Kalimuddin, S.; Low, J.G.; Tan, S.Y.; Loh, J.; Ng, O.T.; Marimuthu, K.; Ang, L.W.; Mak, T.M.; et al. Epidemiologic Features and Clinical Course of Patients Infected With SARS-CoV-2 in Singapore. JAMA 2020, 323, 1488–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, F.; Yu, T.; Du, R.; Fan, G.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xiang, J.; Wang, Y.; Song, B.; Gu, X. Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: A retrospective cohort study. Lancet 2020, 395, 1054–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, K.S.; Hung, I.F.N.; Chan, P.P.Y.; Lung, K.C.; Tso, E.; Liu, R.; Ng, Y.Y.; Chu, M.Y.; Chung, T.W.H.; Tam, A.R.; et al. Gastrointestinal Manifestations of SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Virus Load in Fecal Samples From a Hong Kong Cohort: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Gastroenterology 2020, 159, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Amico, F.; Baumgart, D.C.; Danese, S.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L. Diarrhea During COVID-19 Infection: Pathogenesis, Epidemiology, Prevention, and Management. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol 2020, 18, 1663–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Madhavan, M.V.; Sehgal, K.; Nair, N.; Mahajan, S.; Sehrawat, T.S.; Bikdeli, B.; Ahluwalia, N.; Ausiello, J.C.; Wan, E.Y.; et al. Extrapulmonary manifestations of COVID-19. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1017–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Tang, M.; Zheng, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Shan, H. Evidence for Gastrointestinal Infection of SARS-CoV-2. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1831–1833.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, W.; Wang, X.; Zhang, G.; Guo, M.; Ma, H.; Zhao, D.; Sun, Y.; He, J.; Liu, L.; Zhang, K.; et al. Re-detectable positive SARS-CoV-2 RNA tests in patients who recovered from COVID-19 with intestinal infection. Protein Cell 2020, 12, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.J.; Dong, X.; Cao, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yan, Y.; Akdis, C.; Gao, Y. Clinical characteristics of 140 patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 in Wuhan, China. Allergy 2020, 75, 1730–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Gao, Y.; Wang, G.; Song, G.; Liu, S.; Sun, D.; Xu, Y.; Tian, Z. Functional exhaustion of antiviral lymphocytes in COVID-19 patients. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2020, 17, 533–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, N.; Zhou, M.; Dong, X.; Qu, J.; Gong, F.; Han, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Wei, Y.; et al. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: A descriptive study. Lancet 2020, 395, 507–513.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zuo, T.; Zhang, F.; Lui, G.; Yeoh, Y.; Li, A.; Zhan, H.; Wan, Y.; Chung, A.; Cheung, C.; Chen, N.; et al. Alterations in Gut Microbiota of Patients With COVID-19 During Time of Hospitalization. Gastroenterology 2020, 159, 944–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Gao, H.; Lv, L.; Guo, F.; Zhang, X.; Luo, R.; Huang, C.; et al. Alterations of the Gut Microbiota in Patients with COVID-19 or H1N1 Influenza. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 2669–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, W.; Zhang, G.; Wang, X.; Guo, M.; Zeng, W.; Xu, Z.; Cao, D.; Pan, A.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, K.; et al. Analysis of the intestinal microbiota in COVID-19 patients and its correlation with the inflammatory factor IL-18. Med. Microecol. 2020, 5, 100023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerutti, A.; Chen, K.; Chorny, A. Immunoglobulin responses at the mucosal interface. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 29, 273–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Caselli, E.; Soffritti, I.; Lamberti, G.; D’Accolti, M.; Franco, F.; Demaria, D.; Contoli, M.; Passaro, A.; Contini, C.; Perri, P. Anti-SARS-Cov-2 IgA Response in Tears of COVID-19 Patients. Biology 2020, 9, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejemel, M.; Li, Q.; Hou, S.; Schiller, Z.A.; Tree, J.A.; Wallace, A.; Amcheslavsky, A.; Kurt Yilmaz, N.; Buttigieg, K.R.; Elmore, M.J.; et al. A cross-reactive human IgA monoclonal antibody blocks SARS-CoV-2 spike-ACE2 interaction. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterlin, D.; Mathian, A.; Miyara, M.; Mohr, A.; Anna, F.; Claër, L.; Quentric, P.; Fadlallah, J.; Devilliers, H.; Ghillani, P.; et al. IgA dominates the early neutralizing antibody response to SARS-CoV-2. Sci. Transl. Med. 2020, 13, eabd2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaebler, C.; Wang, Z.; Lorenzi, J.C.C.; Muecksch, F.; Finkin, S.; Tokuyama, M.; Cho, A.; Jankovic, M.; Schaefer-Babajew, D.; Oliveira, T.Y.; et al. Evolution of antibody immunity to SARS-CoV-2. Nature 2021, 591, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.; Li, X.K. The Role of Immune Modulation in Pathogenesis of IgA Nephropathy. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Breedveld, A.; van Egmond, M. IgA and FcalphaRI: Pathological Roles and Therapeutic Opportunities. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suso, A.S.; Mon, C.; . Alonso, I.O.; Romo, K.G.; Juarez, R.C.; Ramirez, C.L.; Sanchez, M.S.; Valdivia, V.M.; Librero, M.O.; Pala, A.O.; et al. IgA Vasculitis with Nephritis (Henoch-Schonlein purpura) in a COVID-19 patient. Kidney Int. Rep. 2020, 5, 2074–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdoni, L.; Mazza, A.; Gervasoni, A.; Martelli, L.; Ruggeri, M.; Ciuffreda, M.; Bonanomi, E.; D’Antiga, L. An outbreak of severe Kawasaki-like disease at the Italian epicentre of the SARS-CoV-2 epidemic: An observational cohort study. Lancet 2020, 395, 1771–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakumar, P.V.; Westrich, G.M.; Kanaly, S.; Garka, K.; Born, T.L.; Derry, J.M.J.; Viney, J.L. Interleukin 18 is a primary mediator of the inflammation associated with dextran sulphate sodium induced colitis: Blocking interleukin 18 attenuates intestinal damage. Gut 2002, 50, 812–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suzuki, H.; Kiryluk, K.; Novak, J.; Moldoveanu, Z.; Herr, A.B.; Renfrow, M.B.; Wyatt, R.J.; Scolari, F.; Mestecky, J.; Gharavi, A.G.; et al. The pathophysiology of IgA nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 22, 1795–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barratt, J.; Feehally, J. IgA nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2005, 16, 2088–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, Y.; Hara, M. Glomerular IgA deposition in pulmonary diseases. Kidney Int. 1986, 29, 557–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, Y.; Chen, X.; Nishi, S.; Narita, I.; Gejyo, F. Relationship between tonsils and IgA nephropathy as well as indications of tonsillectomy. Kidney Int. 2004, 65, 1135–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, Y.; Nishi, S.; Ueno, M.; Imai, N.; Sakatsume, M.; Narita, I.; Suzuki, Y.; Akazawa, K.; Shimada, H.; Arakawa, M.; et al. The efficacy of tonsillectomy on long-term renal survival in patients with IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2003, 63, 1861–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.Y.; Chen, D.; Chen, L.; Liu, J.; Vaziri, N.; Guo, Y.; Zhao, Y. Microbiome-metabolome reveals the contribution of gut-kidney axis on kidney disease. J. Transl. Med. 2019, 17, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Angelis, M.; Montemurno, E.; Piccolo, M.; Vannini, L.; Lauriero, G.; Maranzano, V.; Gozzi, G.; Serrazanetti, D.; Dalfino, G.; Gobbetti, M.; et al. Microbiota and metabolome associated with immunoglobulin A nephropathy (IgAN). PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mahmoodpoor, F.; Rahbar Saadat, Y.; Barzegari, A.; Ardalan, M.; Vahed, S.Z. The impact of gut microbiota on kidney function and pathogenesis. Biomed Pharm. 2017, 93, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fellström, B.C.; Barratt, J.; Cook, H.; Coppo, R.; Feehally, J.; de Fijter, J.W.; Floege, J.; Hetzel, G.; Jardine, A.G.; Locatelli, F.; et al. Targeted-release budesonide versus placebo in patients with IgA nephropathy (NEFIGAN): A double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 2b trial. Lancet 2017, 389, 2117–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zuo, T.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, F.; Lui, G.; Tso, E.; Yeoh, Y.; Chen, Z.; Boon, S.; Chan, F.; Chan, P.; et al. Depicting SARS-CoV-2 faecal viral activity in association with gut microbiota composition in patients with COVID-19. Gut 2021, 70, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascoal, L.B.; Rodrigues, P.B.; Genaro, L.M.; Gomes, A.; Toledo-Teixeira, D.A.; Parise, P.L.; Bispo-Dos-Santos, K.; Simeoni, C.L.; Guimaraes, P.V.; Buscaratti, L.I.; et al. Microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids do not interfere with SARS-CoV-2 infection of human colonic samples. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumas, A.; Bernard, L.; Poquet, Y.; Lugo-Villarino, G.; Neyrolles, O. The role of the lung microbiota and the gut-lung axis in respiratory infectious diseases. Cell Microbiol. 2018, 20, e12966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quast, I.; Tarlinton, D. B cell memory: Understanding COVID-19. Immunity 2021, 54, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Zeng, W.; He, H.; Zhao, D.; Jiang, D.; Zhou, P.; Cheng, L.; Li, Y.; Ma, X.; Jin, T. Serum IgA, IgM, and IgG responses in COVID-19. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2020, 17, 773–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, W.; Ma, H.; Ding, C.; Yang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Huang, X.; He, W.; Xiang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Jin, T. Characterization of SARS-CoV-2-specific antibodies in COVID-19 patients reveals highly potent neutralizing IgA. Signal. Transduct Target Ther. 2021, 6, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Clinical Characteristics | COVID-19 IgAN Case |
|---|---|
| Age, years | 39 |
| Sex | Female |
| Cause of kidney failure | IgAN |
| Kidney failure vintage, years | 14 |
| Signs and symptoms of SARS-CoV-2 infection | |
| Fever | Yes |
| Dry cough | Yes |
| Dyspnea | Yes |
| Fatigue | Yes |
| Nausea | No |
| Vomiting | No |
| Diarrhea | No |
| Gross hematuria | No |
| Laboratory Characteristics | |
| White blood cell count, ×109/L | 4.2 (reference: 3.5~9.5) |
| Neutrophil count, ×109/L | 3.2 (reference: 1.8~6.3) |
| Lymphocyte count, ×109/L | 0.6 (reference: 1.1~3.2) |
| CD4+ cell, cells/μL | 186 (reference: 404~1612) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Z.; Zhang, G.; Guo, M.; Tao, W.; Liu, X.; Wei, H.; Jin, T.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, S. The Potential Role of an Aberrant Mucosal Immune Response to SARS-CoV-2 in the Pathogenesis of IgA Nephropathy. Pathogens 2021, 10, 881. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10070881
Zhang Z, Zhang G, Guo M, Tao W, Liu X, Wei H, Jin T, Zhang Y, Zhu S. The Potential Role of an Aberrant Mucosal Immune Response to SARS-CoV-2 in the Pathogenesis of IgA Nephropathy. Pathogens. 2021; 10(7):881. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10070881
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Zhao, Guorong Zhang, Meng Guo, Wanyin Tao, Xingzi Liu, Haiming Wei, Tengchuan Jin, Yuemiao Zhang, and Shu Zhu. 2021. "The Potential Role of an Aberrant Mucosal Immune Response to SARS-CoV-2 in the Pathogenesis of IgA Nephropathy" Pathogens 10, no. 7: 881. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10070881
APA StyleZhang, Z., Zhang, G., Guo, M., Tao, W., Liu, X., Wei, H., Jin, T., Zhang, Y., & Zhu, S. (2021). The Potential Role of an Aberrant Mucosal Immune Response to SARS-CoV-2 in the Pathogenesis of IgA Nephropathy. Pathogens, 10(7), 881. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10070881







