Isolation and Characterization of Capnocytophaga bilenii sp. nov., a Novel Capnocytophaga Species Detected in a Gingivitis Subject
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
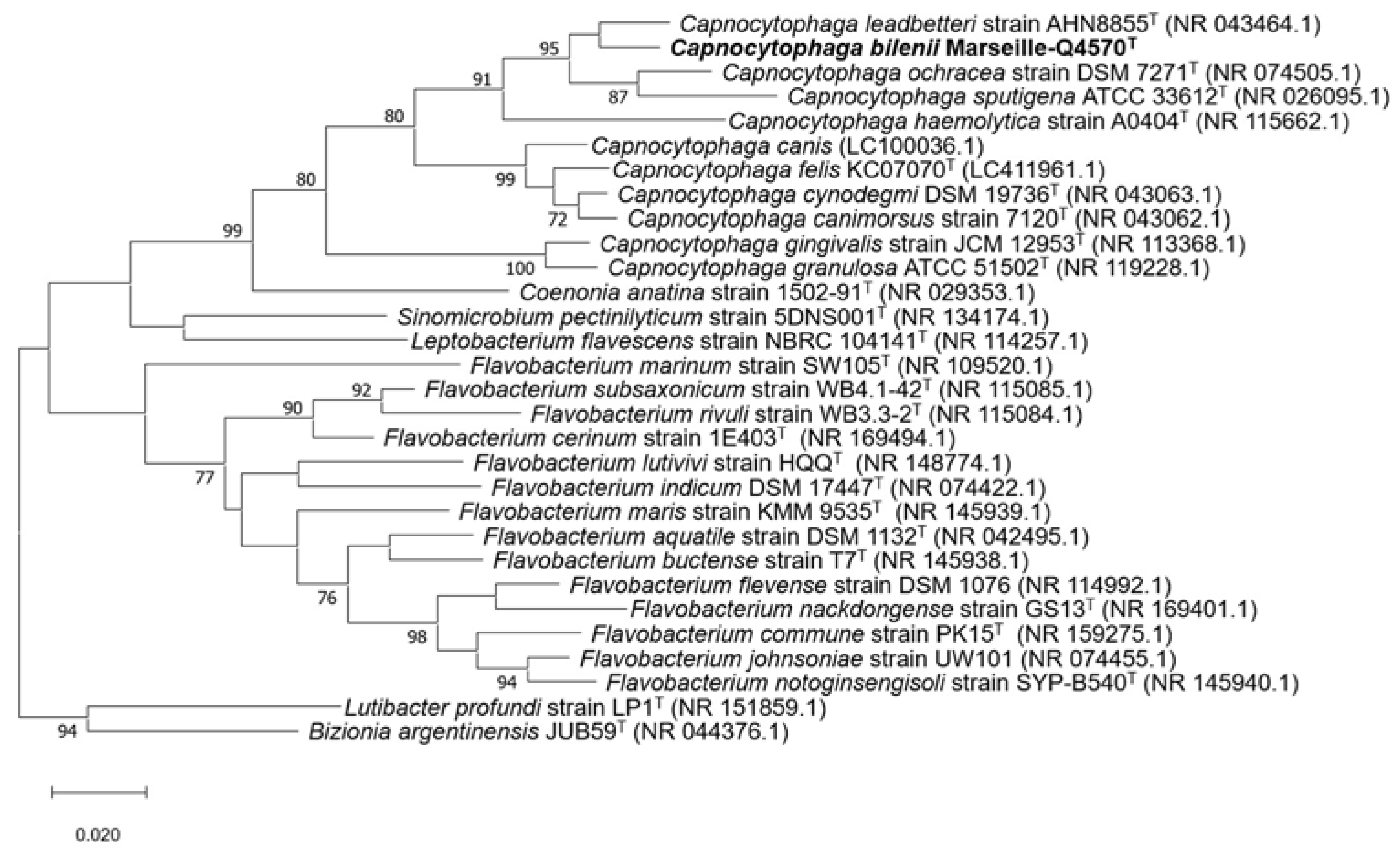
2.1. Strain Identification and Classification
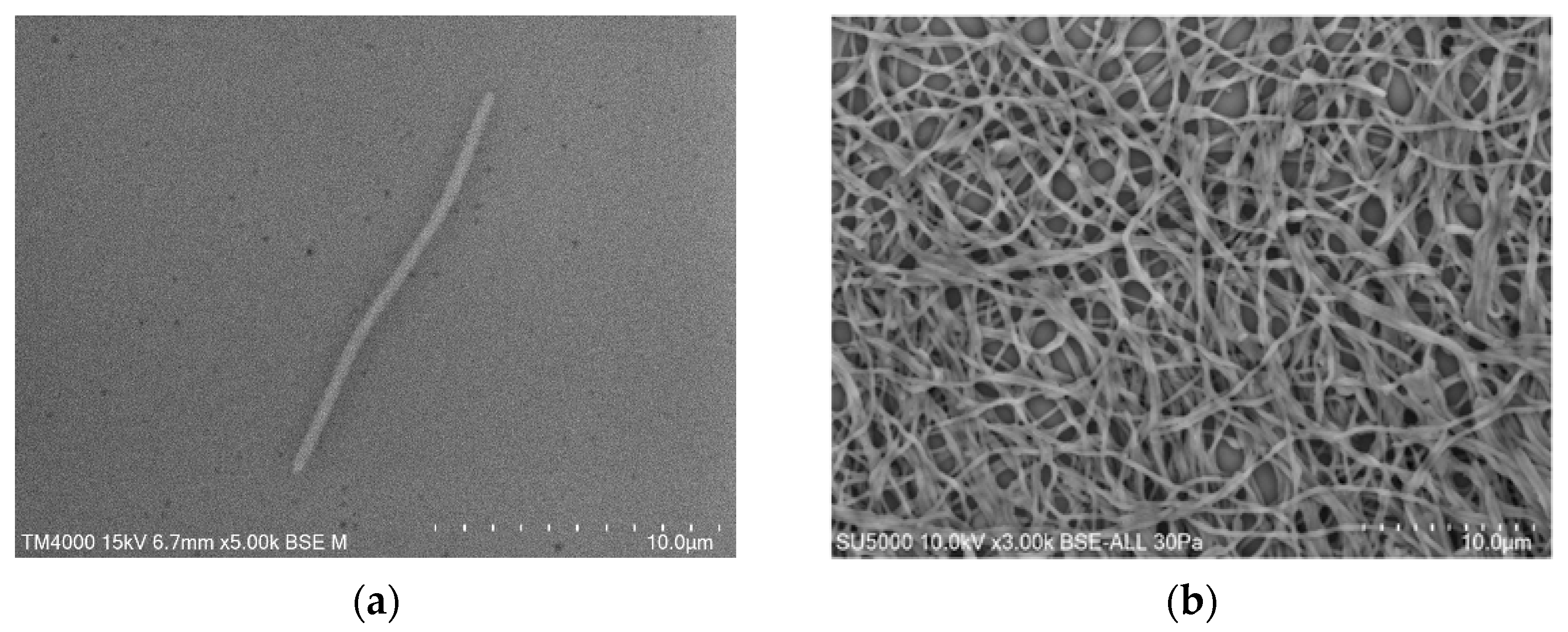
2.2. Phenotypic Characteristics
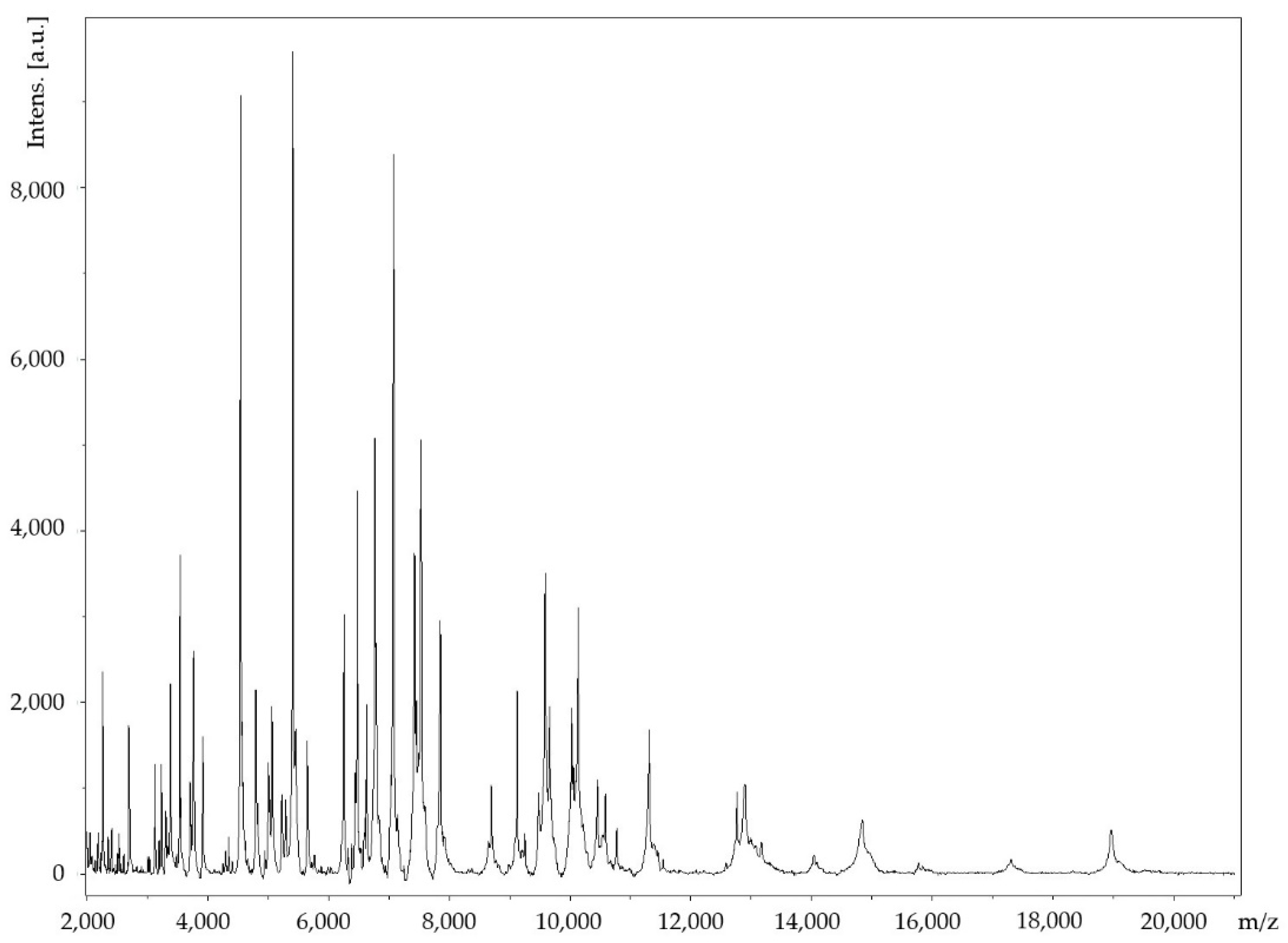
2.3. Genome Sequencing Information and Genome Properties
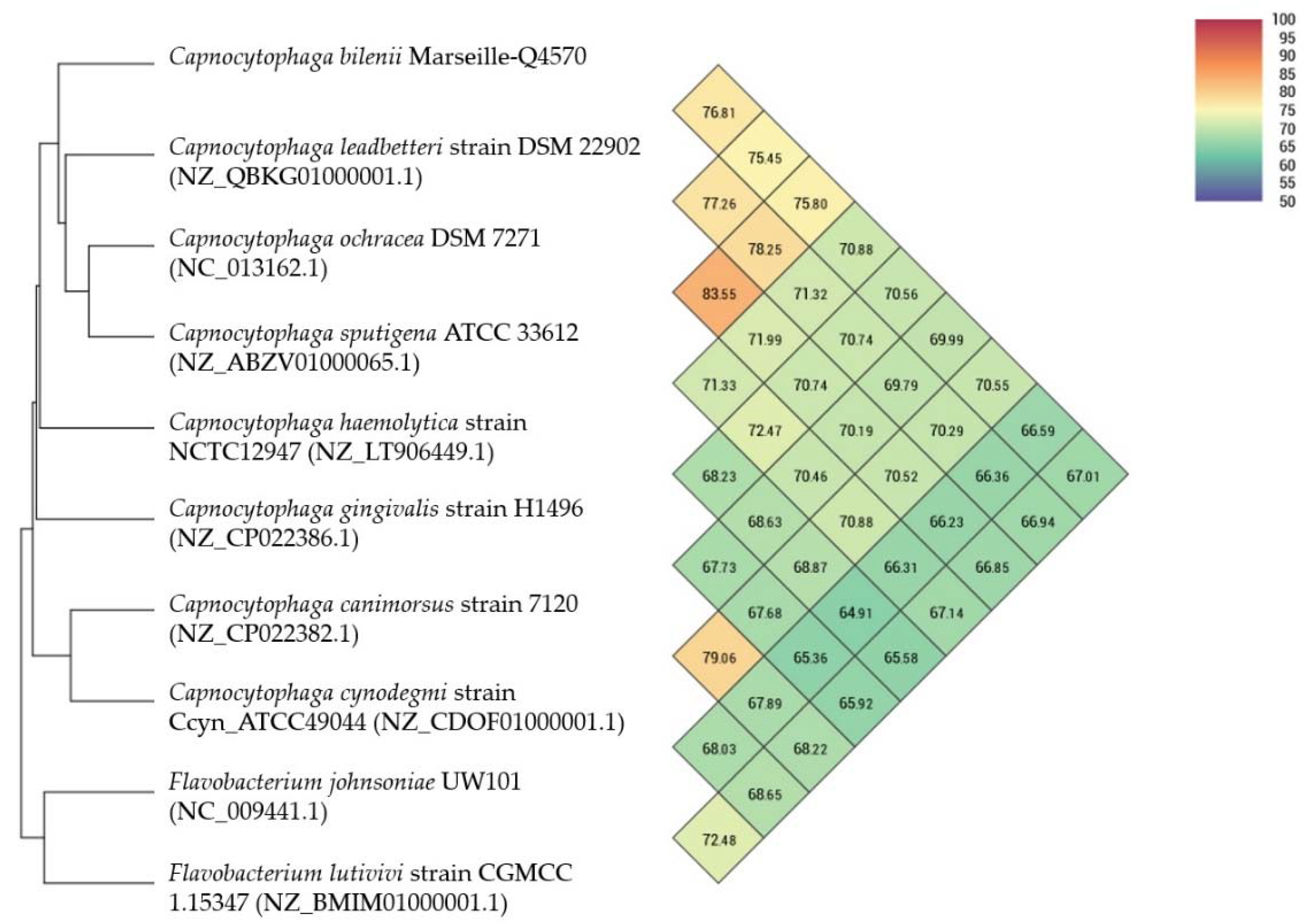
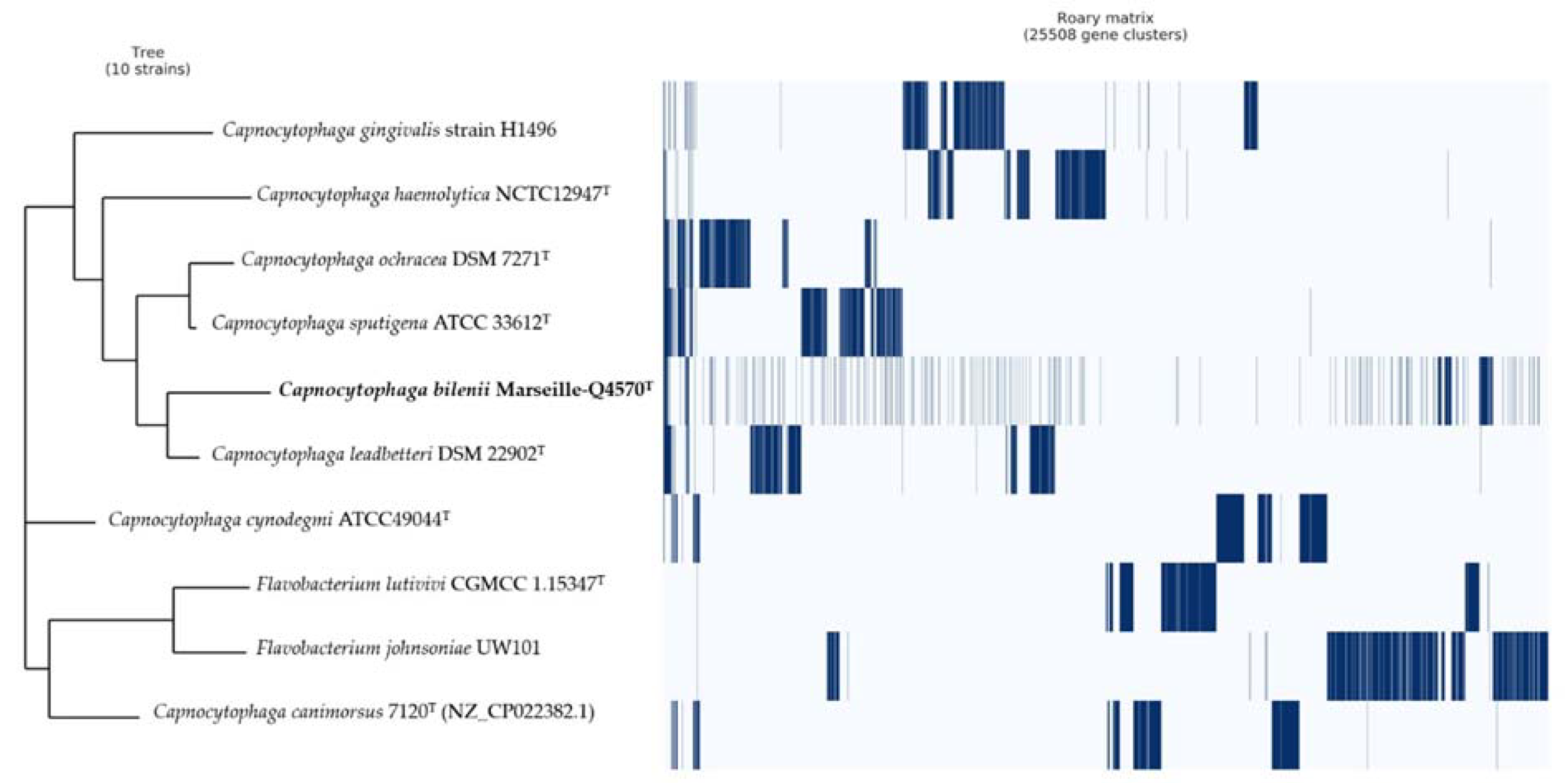
2.4. Comparison to Closely Related Bacterial Strains
2.5. Description of Capnocytophaga bilenii nov. sp.
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Strain Isolation and Phenotypic Tests
4.2. Extraction and Genome Sequencing
4.3. Assembly and Annotation of the Genome Sequence
4.4. Phylogenetic Analysis and Genome Comparison
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leadbetter, E.R.; Holt, S.C.; Socransky, S.S. Capnocytophaga: New genus of gram-negative gliding bacteria. I. General characteristics, taxonomic considerations and significance. Arch. Microbiol. 1979, 122, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hundertmark, M.; Williams, T.; Vogel, A.; Moritz, M.; Bramlage, P.; Pagonas, N.; Ritter, O.; Sasko, B. Capnocytophaga canimorsus as Cause of Fatal Sepsis. Case Rep. Infect. Dis. 2019, 2019, 3537507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, F.R.; Bruniera, F.R.; Schmidt, J.; Cury, A.P.; Rizeck, C.; Higashino, H.; Oliveira, F.N.; Rossi, F.; Rocha, V.; Costa, S.F. Capnocytophaga sputigena bloodstream infection in hematopoietic stem cell transplantations: Two cases report and review of the literature. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. Sao Paulo 2020, 62, e48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bello, A.; Castaneda, A.; Vakil, A.; Varon, J.; Surani, S. Capnocytophaga Induced Acute Necrotizing and Exudative Pericarditis with Abscess Formation. Case Rep. Infect. Dis. 2018, 2018, 6437928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daigle, P.; Lee, M.-H.; Flores, M.; Campisi, P.; DeAngelis, D. Capnocytophaga sputigena as a cause of severe orbital cellulitis and subperiosteal abscess in a child. Can. J. Ophthalmol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duong, M.; Besancenot, J.F.; Neuwirth, C.; Buisson, M.; Chavanet, P.; Portier, H. Vertebral Osteomyelitis Due to Capnocytophaga Species in Immunocompetent Patients: Report of Two Cases and Review. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1996, 22, 1099–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fossé, Q.; Flateau, C.; Gomart, C.; Decousser, J.W.; Gallien, S. Severe community-acquired Capnocytophaga leadbetteri pneumonia in a HIV-infected patient. Med. Mal. Infect. 2018, 48, 155–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mekouar, H.; Voortman, G.; Bernard, P.; Hutchings, G.; Boeras, A.; Rodriguez-Villalobos, H. Capnocytophaga species and perinatal infections: Case report and review of the literature. Acta Clin. Belg. 2012, 67, 42–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mager, D.L.; Haffajee, A.D.; Devlin, P.M.; Norris, C.M.; Posner, M.R.; Goodson, J.M. The salivary microbiota as a diagnostic indicator of oral cancer: A descriptive, non-randomized study of cancer-free and oral squamous cell carcinoma subjects. J. Transl. Med. 2005, 3, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpiński, T.M. Role of Oral Microbiota in Cancer Development. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Yang, M.; Liu, J.; Gao, R.; Hu, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Shi, Y.; Guo, H.; Cheng, J.; et al. Discovery and validation of potential bacterial biomarkers for lung cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2015, 5, 3111–3122. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gajardo, M.; Silva, N.; Gómez, L.; León, R.; Parra, B.; Contreras, A.; Gamonal, J. Prevalence of Periodontopathic Bacteria in Aggressive Periodontitis Patients in a Chilean Population. J. Periodontol. 2005, 76, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciantar, M.; Gilthorpe, M.S.; Hurel, S.J.; Newman, H.N.; Wilson, M.; Spratt, D.A. Capnocytophaga spp. in Periodontitis Patients Manifesting Diabetes Mellitus. J. Periodontol. 2005, 76, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonnenmacher, C.; Mutters, R.; de Jacoby, L.F. Microbiological characteristics of subgingival microbiota in adult periodontitis, localized juvenile periodontitis and rapidly progressive periodontitis subjects. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2001, 7, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papapanou, P.N.; Sanz, M.; Buduneli, N.; Dietrich, T.; Feres, M.; Fine, D.H.; Flemmig, T.F.; Garcia, R.; Giannobile, W.V.; Graziani, F.; et al. Periodontitis: Consensus report of workgroup 2 of the 2017 World Workshop on the Classification of Periodontal and Peri-Implant Diseases and Conditions: Classification and case definitions for periodontitis. J. Periodontol. 2018, 89, S173–S182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, O.-J.; Yi, H.; Jeon, J.; Kang, S.-S.; Koo, K.-T.; Kum, K.-Y.; Chun, J.; Yun, C.-H.; Han, S. Pyrosequencing Analysis of Subgingival Microbiota in Distinct Periodontal Conditions. J. Dent. Res. 2015, 94, 921–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acharya, A.; Chen, T.; Chan, Y.; Watt, R.M.; Jin, L.; Mattheos, N. Species-Level Salivary Microbial Indicators of Well-Resolved Periodontitis: A Preliminary Investigation. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrmann, E.; Handal, T.; Tamanai-Shacoori, Z.; Bonnaure-Mallet, M.; Fosse, T. High prevalence of -lactam and macrolide resistance genes in human oral Capnocytophaga species. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2014, 69, 381–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Oh, H.-S.; Park, S.-C.; Chun, J. Towards a taxonomic coherence between average nucleotide identity and 16S rRNA gene sequence similarity for species demarcation of prokaryotes. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2014, 64, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across Computing Platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frandsen, E.V.G.; Poulsen, K.; Kononen, E.; Kilian, M. Diversity of Capnocytophaga species in children and description of Capnocytophaga leadbetteri sp. nov. and Capnocytophaga genospecies AHN8471. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2008, 58, 324–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Culture Collection University of Gothenburg (CCUG); Curators of the CCUG; CCUG 9716. Available online: www.ccug.se/strain?id=9716 (accessed on 15 March 2021).
- Yamamoto, T.; Kajiura, S.; Hirai, Y.; Watanabe, T. Capnocytophaga haemolytica sp. nov. and Capnocytophaga granulosa sp. nov., from Human Dental Plaque. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1994, 44, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culture Collection University of Gothenburg (CCUG); Curators of the CCUG; CCUG 14446. Available online: www.ccug.se/strain?id=14446 (accessed on 15 March 2021).
- Culture Collection University of Gothenburg (CCUG); Curators of the CCUG; CCUG 54501. Available online: www.ccug.se/strain?id=54501 (accessed on 15 March 2021).
- Brenner, D.J.; Hollis, D.G.; Fanning, G.R.; Weaver, R.E. Capnocytophaga canimorsus sp. nov. (formerly CDC group DF-2), a cause of septicemia following dog bite, and C. cynodegmi sp. nov., a cause of localized wound infection following dog bite. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1989, 27, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culture Collection University of Gothenburg (CCUG); Curators of the CCUG; CCUG 53895. Available online: www.ccug.se/strain?id=53895 (accessed on 15 March 2021).
- Culture Collection University of Gothenburg (CCUG); Curators of the CCUG; CCUG 64133. Available online: www.ccug.se/strain?id=64133 (accessed on 15 March 2021).
- Culture Collection University of Gothenburg (CCUG); Curators of the CCUG; CCUG 30012. Available online: www.ccug.se/strain?id=30012 (accessed on 15 March 2021).
- Dees, S.B.; Karr, D.E.; Hollis, D.; Moss, C.W. Cellular fatty acids of Capnocytophaga species. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1982, 16, 779–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stothard, P.; Wishart, D.S. Circular genome visualization and exploration using CGView. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 537–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier-Kolthoff, J.P.; Auch, A.F.; Klenk, H.-P.; Göker, M. Genome sequence-based species delimitation with confidence intervals and improved distance functions. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jolivet-Gougeon, A.; Bonnaure-Mallet, M. Screening for prevalence and abundance of Capnocytophaga spp. by analyzing NGS data: A scoping review. Oral Dis. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, H.J.; Zhang, C.P. The Oral Microbiota May Have Influence on Oral Cancer. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 9, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Xiang, C.; Zhang, C.; Xu, B.; Wu, J.; Wang, R.; Yang, Y.; Shi, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhan, Z. Microbial biomarkers of common tongue coatings in patients with gastric cancer. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 127, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonetti, M.S.; Greenwell, H.; Kornman, K.S. Staging and grading of periodontitis: Framework and proposal of a new classification and case definition. J. Periodontol. 2018, 89, S159–S172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerbino, D.R.; Birney, E. Velvet: Algorithms for de novo short read assembly using de Bruijn graphs. Genome Res. 2008, 18, 821–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A New Genome Assembly Algorithm and Its Applications to Single-Cell Sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, R.; Liu, B.; Xie, Y.; Li, Z.; Huang, W.; Yuan, J.; He, G.; Chen, Y.; Pan, Q.; Liu, Y.; et al. SOAPdenovo2: An empirically improved memory-efficient short-read de novo assembler. GigaScience 2012, 1, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyatt, D.; Chen, G.-L.; LoCascio, P.F.; Land, M.L.; Larimer, F.W.; Hauser, L.J. Prodigal: Prokaryotic gene recognition and translation initiation site identification. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, K.; Karsch-Mizrachi, I.; Lipman, D.J.; Ostell, J.; Sayers, E.W. GenBank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D67–D72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seemann, T. Prokka: Rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuccuru, G.; Orsini, M.; Pinna, A.; Sbardellati, A.; Soranzo, N.; Travaglione, A.; Uva, P.; Zanetti, G.; Fotia, G. Orione, a web-based framework for NGS analysis in microbiology. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1928–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, I.; Ouk Kim, Y.; Park, S.-C.; Chun, J. OrthoANI: An improved algorithm and software for calculating average nucleotide identity. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 1100–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, A.J.; Cummins, C.A.; Hunt, M.; Wong, V.K.; Reuter, S.; Holden, M.T.G.; Fookes, M.; Falush, D.; Keane, J.A.; Parkhill, J. Roary: Rapid large-scale prokaryote pan genome analysis. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3691–3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Characteristics | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oxidase activity | − | − | − | − | − | + | + | − | − |
| Catalase activity | − | − | − | − | − | + | + | − | − |
| Fermentation of: | |||||||||
| Amygdalin | w | − | + | w | − | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| Cellobiose | w | − | + | − | − | + | − | ND | ND |
| Fructose | + | − | + | − | + | + | − | + | ND |
| Galactose | + | w | + | + | + | + | + | ND | ND |
| Glucose | + | w | + | + | + | + | + | + | ND |
| Lactose | + | w | + | + | + | + | + | ND | ND |
| Raffinose | + | − | + | + | w | + | − | ND | ND |
| API ZYM | |||||||||
| Alkaline phosphatase | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| C4 esterase | + | w | − | − | + | + | + | + | + |
| C8 esterase lipase | + | w | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| C14 lipase | − | ND | − | ND | − | − | − | − | − |
| Leucine arylamidase | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Valine arylamidase | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Cystine arylamidase | + | + | + | − | + | − | − | + | + |
| Trypsin | + | − | − | + | − | + | + | − | + |
| α−Chymotrypsin | + | w | − | w | − | − | − | − | + |
| Acid phosphatase | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Naphthol−AS−BI−Phosphohydrolase | + | ND | + | ND | + | + | + | + | + |
| α−Galactosidase | − | ND | − | ND | − | − | − | − | − |
| β−Galactosidase | − | + | + | w | + | − | − | + | − |
| β−Glucuronidase | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| α−Glucosidase | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| β−Glucosidase | − | − | − | − | + | − | − | − | + |
| N−Acetyl−β−Glucosaminidase | + | + | + | + | − | + | + | + | − |
| α−Mannosidase | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| α−Fucosidase | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | − | − |
| Fatty Acid | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C13:0 | TR | ND | ND | ND |
| C13:0 iso | 1.3 | – | 3 | TR |
| C14:0 | 1.8 | TR | TR | TR |
| C14:0 iso | TR | ND | ND | ND |
| C14:0 3-OH | TR | ND | ND | ND |
| C15:0 | TR | TR | TR | TR |
| C15:0 iso | 75.6 | 61 | 75 | 78 |
| C15:0 3-OH iso | 1.7 | 3 | 2 | 3 |
| C16:0 | 5.8 | 12 | 3 | 4 |
| C16:0 3-OH | 1.7 | 2 | 4 | 4 |
| C17:0 | TR | TR | TR | TR |
| C17:0 iso | TR | ND | ND | ND |
| C17:0 3-OH iso | 4.1 | 2 | 8 | 7 |
| C17:0 anteiso | TR | ND | ND | ND |
| C18:0 | 1.3 | 4 | TR | 2 |
| C18:1n9 | 2.8 | 6 | 2 | TR |
| C18:2n6 | 2.7 | 10 | 3 | 2 |
| Code | Marseille-Q4570T Strain | Description |
|---|---|---|
| [J] | 129 | Translation, ribosomal structure, and biogenesis |
| [A] | 0 | RNA processing and modification |
| [K] | 40 | Transcription |
| [L] | 67 | Replication, recombination, and repair |
| [B] | 1 | Chromatin structure and dynamics |
| [D] | 12 | Cell cycle control, cell division, and chromosome partitioning |
| [Y] | 0 | Nuclear structure |
| [V] | 21 | Defense mechanisms |
| [T] | 15 | Signal transduction mechanisms |
| [M] | 74 | Cell wall/membrane/envelope biogenesis |
| [N] | 2 | Cell motility |
| [Z] | 0 | Cytoskeleton |
| [W] | 0 | Extracellular structures |
| [U] | 20 | Intracellular trafficking, secretion, and vesicular transport |
| [O] | 50 | Posttranslational modification, protein turnover, and chaperones |
| [X] | 0 | Mobilome: prophages, transposons |
| [C] | 63 | Energy production and conversion |
| [G] | 46 | Carbohydrate transport and metabolism |
| [E] | 87 | Amino acid transport and metabolism |
| [F] | 47 | Nucleotide transport and metabolism |
| [H] | 65 | Coenzyme transport and metabolism |
| [I] | 34 | Lipid transport and metabolism |
| [P] | 48 | Inorganic ion transport and metabolism |
| [Q] | 20 | Secondary metabolites biosynthesis, transport, and catabolism |
| [R] | 118 | General function prediction only |
| [S] | 69 | Function unknown |
| Species | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Capnocytophaga bilenii Marseille-Q4570T | 100.00 | 33.5 (31.1–36) | 25.6 (23.3–28.1) | 25.6 (23.3–28.1) | 24.0 (21.7–26.5) | 23.7 (21.4–26.1) | 23.4 (21.1–25.8) | 22.5 (20.2–25) | 22.1 (19.9–24.6) | 21.0 (18.7–23.4) |
| 2 Capnocytophaga gingivalis | 100.00 | 32.4 (30–34.9) | 35.2 (32.7–37.7) | 20.0 (17.8–22.4) | 30.4 (28–32.9) | 23.4 (21.1–25.9) | 23.5 (21.2–25.9) | 28.0 (25.7–30.5) | 22.9 (20.6–25.4) | |
| 3 Capnocytophaga leadbetteri | 100.00 | 24.8 (22.5–27.3) | 25.4 (23.1–27.9) | 23.7 (21.4–26.1) | 22.0 (19.7–24.4) | 23.7 (21.4–26.2) | 21.5 (19.3–24) | 23.5 (21.2–25.9) | ||
| 4 Capnocytophaga sputigena | 100.00 | 23.3 (21–25.7) | 31.0 (28.6–33.5) | 20.0 (17.8–22.4) | 22.0 (19.7–24.4) | 22.2 (19.9–24.7) | 26.6 (24.3–29.1) | |||
| 5 Flavobacterium lutivivi | 100.00 | 22.0 (19.7–24.4) | 19.1 (16.9–21.5) | 21.6 (19.3–24) | 27.8 (25.4–30.3) | 19.1 (17–21.5) | ||||
| 6 Capnocytophaga ochracea | 100.00 | 23.3 (21–25.8) | 23.4 (21.1–25.9) | 26.6 (24.3–29.1) | 30.1 (27.8–32.7) | |||||
| 7 Capnocytophaga cynodegmi | 100.00 | 44.2 (41.7–46.8) | 22.7 (20.4–25.1) | 24.5 (22.2–27) | ||||||
| 8 Capnocytophaga canimorsus | 100.00 | 24.5 (22.2–27) | 21.2 (18.9–23.6) | |||||||
| 9 Capnocytophaga haemolytica | 100.00 | 29.0 (26.6–31.5) | ||||||||
| 10 Flavobacterium johnsoniae | 100.00 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Antezack, A.; Boxberger, M.; La Scola, B.; Monnet-Corti, V. Isolation and Characterization of Capnocytophaga bilenii sp. nov., a Novel Capnocytophaga Species Detected in a Gingivitis Subject. Pathogens 2021, 10, 547. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10050547
Antezack A, Boxberger M, La Scola B, Monnet-Corti V. Isolation and Characterization of Capnocytophaga bilenii sp. nov., a Novel Capnocytophaga Species Detected in a Gingivitis Subject. Pathogens. 2021; 10(5):547. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10050547
Chicago/Turabian StyleAntezack, Angéline, Manon Boxberger, Bernard La Scola, and Virginie Monnet-Corti. 2021. "Isolation and Characterization of Capnocytophaga bilenii sp. nov., a Novel Capnocytophaga Species Detected in a Gingivitis Subject" Pathogens 10, no. 5: 547. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10050547
APA StyleAntezack, A., Boxberger, M., La Scola, B., & Monnet-Corti, V. (2021). Isolation and Characterization of Capnocytophaga bilenii sp. nov., a Novel Capnocytophaga Species Detected in a Gingivitis Subject. Pathogens, 10(5), 547. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10050547






