Morphometrics of Amblyomma mixtum in the State of Veracruz, Mexico
Abstract
1. Introduction
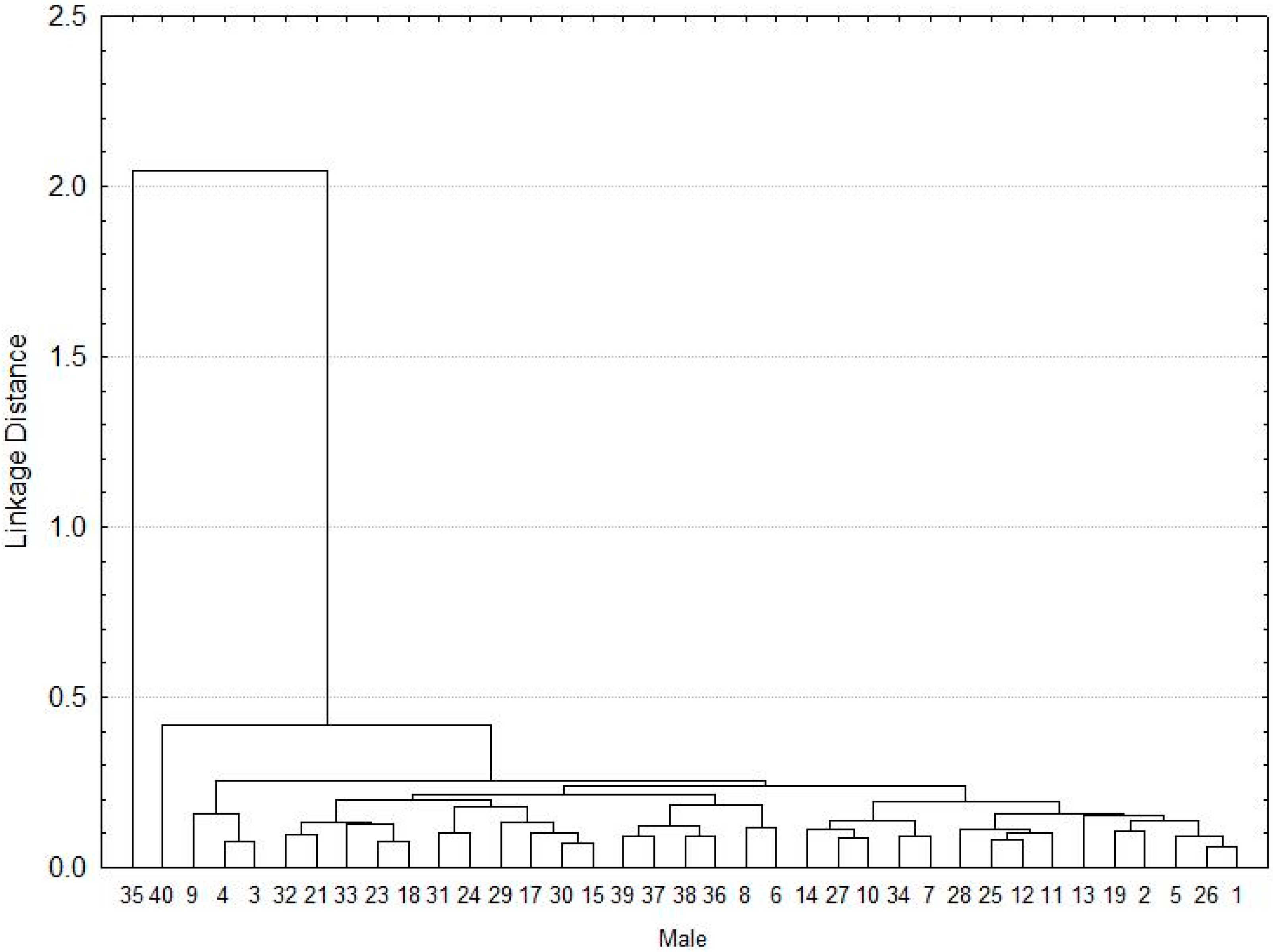
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
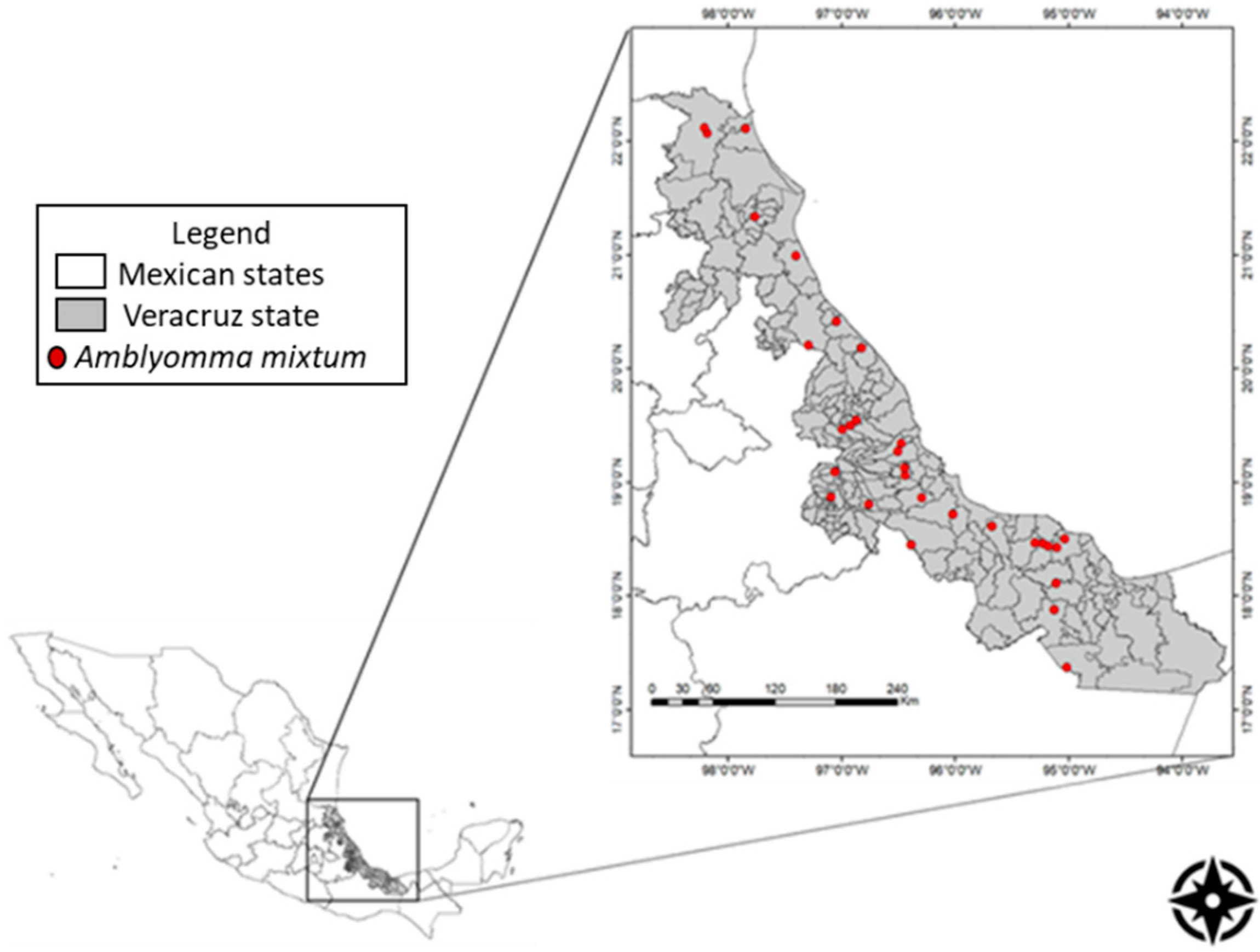
4.1. Study Area
4.2. Sampling
4.3. Tick Collection from Infested Livestock
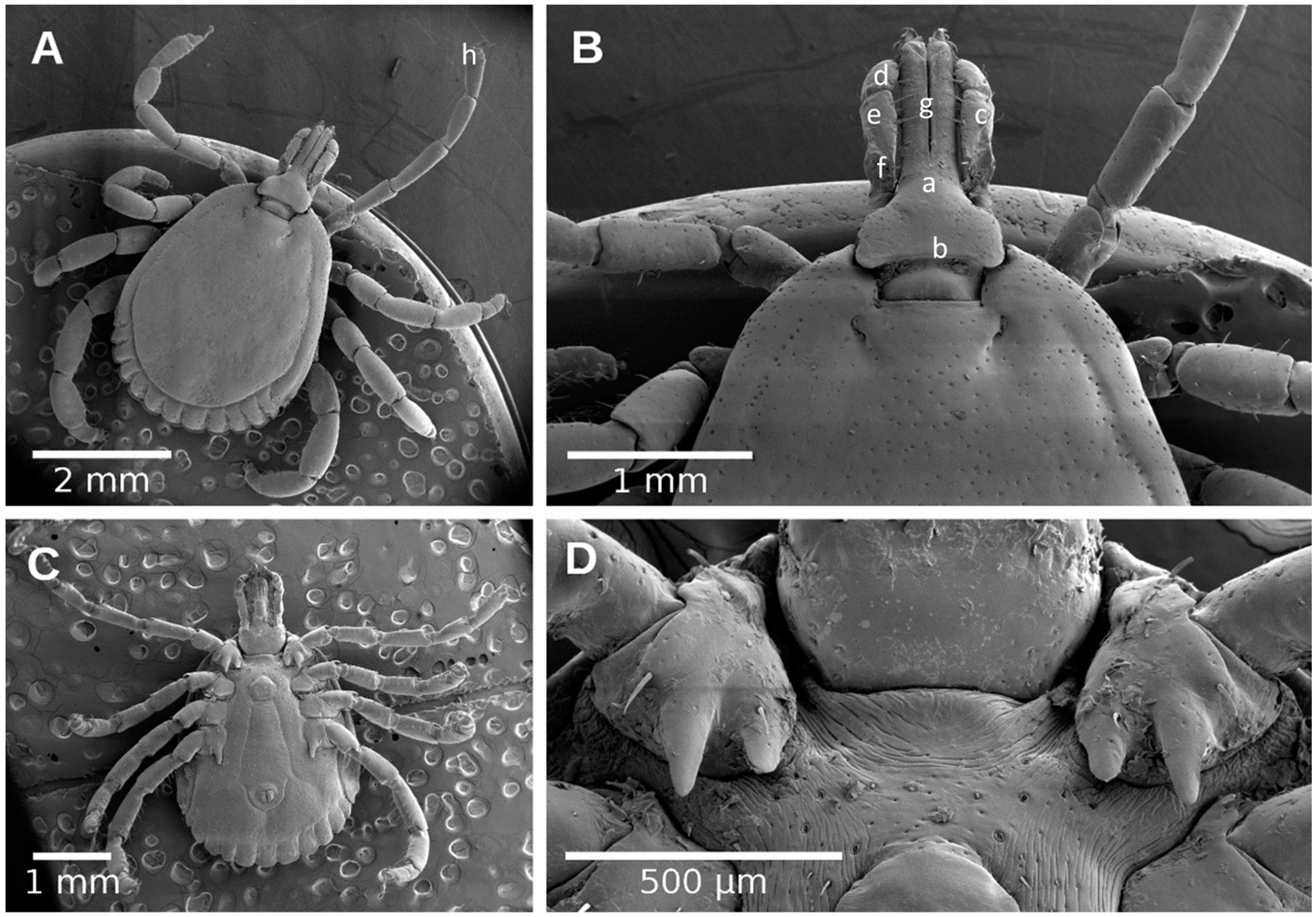
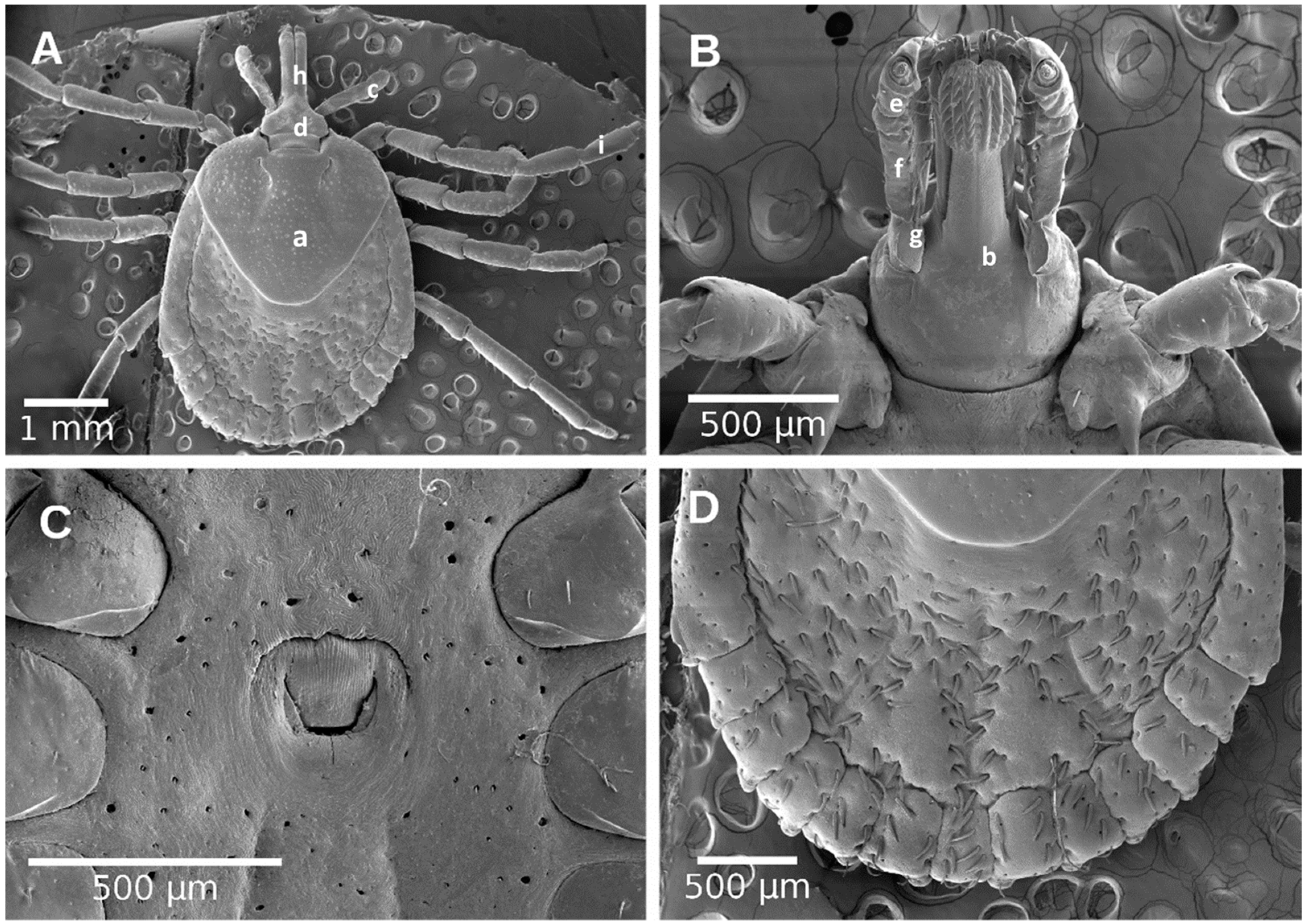
4.4. Morphological Identification of Ticks
4.5. Scanning Electron Microscopic Analysis
4.6. Morphometrics
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Estrada-Peña, A. Ticks as vectors: Taxonomy, biology and ecology. Rev. Sci. Tech. 2015, 34, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adalberto, A.; Pérez de León, R.D.; Mitchell-Miller, R.; Lohmeyer, K. Advances in integrated tick Management research for area-wide mitigation of tick-borne disease Burden. In Area-Wide Integrated Pest Management. Development and Field Application, 1st ed.; Hendrichs, J., Pereira, R., Vreysen, M.J.B., Eds.; Routledge and CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2021; pp. 251–274. [Google Scholar]
- Gondard, M.; Cabezas-Cruz, A.; Charles, R.A.; Vayssier-Taussat, M.; Albina, E.; Moutailler, S. Ticks and Tick-Borne Pathogens of the Caribbean: Current Understanding and Future Directions for More Comprehensive Surveillance. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enríquez, S.; Guerrero, R.; Arrivillaga-Henríquez, J.; Araujo, P.; Villacrés, E.; Enríquez, A.; Benítez-Ortíz, W. New records of ticks of genus Amblyomma Koch, 1844 (Acari: Ixodidae) for Ecuador. Acta Parasitol. 2020, 65, 430–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molaei, G.; Karpathy, S.E.; Andreadis, T.G. First Report of the Introduction of an Exotic Tick, Amblyomma coelebs (Acari: Ixodidae), Feeding on a Human Traveler Returning to the United States from Central America. J. Parasitol. 2019, 105, 571–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascoe, E.L.; Marcantonio, M.; Caminade, C.; Foley, J.E. Modeling Potential Habitat for Amblyomma Tick Species in California. Insects 2019, 10, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nava, S.; Beati, L.; Labruna, M.B.; Cáceres, A.G.; Mangold, A.J.; Guglielmone, A.A. Reassessment of the taxonomic status of Amblyomma cajen-nense (Fabricius, 1787) with the description of three new species, Amblyomma tonelliae n. sp., Amblyomma interandinum n. sp. and Amblyomma patinoi n. sp., and reinstatement of Amblyomma mixtum Koch, 1844, and Amblyomma sculptum Berlese, 1888 (Ixodida: Ixodidae). Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2014, 5, 252–276. [Google Scholar]
- Piña, F.T.B.; Rodrigues, V.D.S.; Higa, L.D.O.S.; Garcia, M.V.; Barros, J.C.; De León, A.A.P.; Andreotti, R. Life cycle of Amblyomma mixtum (Acari: Ixodidae) parasitizing different hosts under laboratory conditions. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2017, 73, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almazan, C.; Tipacamu, G.A.; Rodriguez, S.; Mosqueda, J.; Perez de Leon, A. Immunological control of ticks and tick-borne diseases that impact cattle health and production. Front. Biosci. 2018, 23, 1535–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Vivas, R.; Apanaskevich, D.; Ojeda-Chi, M.; Trinidad-Martínez, I.; Reyes-Novelo, E.; Esteve-Gassent, M.; de León, A.P. Ticks collected from humans, domestic animals, and wildlife in Yucatan, Mexico. Veter. Parasitol. 2016, 215, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán-Cornejo, C.; Robbins, R.; Guglielmone, A.A.; Montiel-Parra, G.; Pérez, T.M. The Amblyomma (Acari: Ixodidae) of Mexico: Identification keys, distribution and hosts. Zootaxa. 2011, 2998, 16–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Dominguez, M.; Romero-Salas, D.; Sánchez-Montes, S.; Barradas-Piña, F.; Rosas, G.; Cruz-Romero, A.; Ibarra-Priego, N.; Becker, I.; Lohmeyer, K.H.; de León, A.P. Ocurrence of Amblyomma mixtum on the water buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) in Mexico. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2018, 7, 405–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez, C.; Zavaleta, L. Traditional livestock of the north of the state of Veracruz. Nacameh 2019, 13, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higa, L.D.O.S.; Piña, F.T.B.; Rodrigues, V.D.S.; Garcia, M.V.; Salas, D.R.; Miller, R.J.; de Leon, A.P.; Barros, J.C.; Andreotti, R. Evidence of acaricide resistance in different life stages of Amblyomma mixtum and Rhipicephalus microplus (Acari: Ixodidae) collected from the same farm in the state of Veracruz, Mexico. Prev. Veter. Med. 2020, 174, 104837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Domínguez, M.; Sánchez-Montes, S.; Esteve-Gassent, M.D.; Barrientos-Salcedo, C.; de León, A.P.; Romero-Salas, D. Genetic structure analysis of Amblyomma mixtum populations in Veracruz State, Mexico. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2019, 10, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balinandi, S.; Mugisha, L.; Bbira, J.; Kabasa, W.; Nakayiki, T.; Bakkes, D.K.; Lutwama, J.J.; Chitimia-Dobler, L.; Malmberg, M. General and Local Morphological Anomalies in Amblyomma lepidum (Acari: Ixodidae) and Rhipicephalus decoloratus Infesting Cattle in Uganda. J. Med. Èntomol. 2019, 56, 873–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beati, L.; Nava, S.; Burkman, E.J.; Barros-Battesti, D.M.; Labruna, M.B.; A Guglielmone, A.; Cáceres, A.G.; Guzmán-Cornejo, C.M.; León, R.; A Durden, L.; et al. Amblyomma cajennense (Fabricius, 1787) (Acari: Ixodidae), the Cayenne tick: Phylogeography and evidence for allopatric speciation. BMC Evol. Biol. 2013, 13, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera-Páez, F.A.; Labruna, M.B.; Martins, T.F.; Perez, J.E.; Castaño-Villa, G.J.; Ossa-López, P.A.; Gil, C.A.; Sampieri, B.R.; Aricapa-Giraldo, H.J.; Camargo-Mathias, M.I. Contributions to the knowledge of hard ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) in Colombia. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2018, 9, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Illoldi-Rangel, P.; Rivaldi, C.-L.; Sissel, B.; Fryxell, R.T.; Gordillo-Pérez, G.; Rodríguez-Moreno, A.; Williamson, P.; Montiel-Parra, G.; Sánchez-Cordero, V.; Sarkar, S. Species Distribution Models and Ecological Suitability Analysis for Potential Tick Vectors of Lyme Disease in Mexico. J. Trop. Med. 2012, 2012, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosa-Gutierrez, C.G.; Vargas-Sandoval, M.; Torres, J.; Gordillo-Pérez, G. Tick-borne rickettsial pathogens in questing ticks, removed from humans and animals in Mexico. J. Veter. Sci. 2016, 17, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Salas, D.; Mira, A.; Mosqueda, J.; García-Vázquez, Z.; Hidalgo-Ruiz, M.; Vela, N.A.O.; de León, A.A.P.; Florin-Christensen, M.; Schnittger, L. Molecular and serological detection of Babesia bovis- and Babesia bigemina-infection in bovines and water buffaloes raised jointly in an endemic field. Veter. Parasitol. 2016, 217, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso-Díaz, M.; Fernández-Salas, A.; Martínez-Ibáñez, F.; Osorio-Miranda, J. Amblyomma cajennense (Acari: Ixodidae) tick populations susceptible or resistant to acaricides in the Mexican Tropics. Veter. Parasitol. 2013, 197, 326–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almazán, C.; Torres-Torres, A.; Torres-Rodríguez, L.; Soberanes-Céspedes, N.; Ortiz-Estrada, M. Aspectos biológicos de Amblyomma mixtum (Koch, 1844) en el noreste de México. Quehacer Científico en Chiapas 2016, 2, 10–19. [Google Scholar]
- Coronel-Benedett, K.C.; Ojeda-Robertos, N.F.; González-Garduño, R.; Ibañez, F.M.; Rodríguez-Vivas, R.I. Prevalence, intensity and population dynamics of hard ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) on sheep in the humid tropics of Mexico. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2018, 74, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- INEGI, Censo de Población y vivienda. Available online: https://www.inegi.org.mx/ (accessed on 25 April 2019).
- INAFED Instituto para el Federalismo y el Desarrollo Municipal. Available online: https://www.gob.mx/inafed (accessed on 3 April 2019).
- Álvarez, C.V.; Bonilla, M. Adultos y ninfas de la garrapata Amblyomma cajennense fabricius (acari: Ixodidae) en equinos y bovinos. Agronomía Costarricense. 2007, 31, 61–69. [Google Scholar]
- Martins, T.F.; Onofrio, V.C.; Barros-Battesti, D.M.; Labruna, M.B. Nymphs of the genus Amblyomma (Acari: Ixodidae) of Brazil: Descriptions, redescriptions, and identification key. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2010, 1, 75–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Sex | Statistic | CB | CL | VL | TL | LSI | LSII | LSIII | WSI | WSII | WSIII | HL | HW | TaL | TW | SL | SW |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ♀ | Mean | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.7 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.7 | 0.2 | 0.7 | 0.2 | ||
| SD | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.1 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.01 | |||
| ♂ | Mean | 0.7 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.9 | 0.1 | 0.6 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.9 | 0.3 | 0.9 | 0.2 | 1.9 | 1.9 |
| SD | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.2 | 0.1 |
| Number of Ticks | Livestock Host | Municipality | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ♂ | ♀ | ||
| 2 | 2 | Bos taurus | Pánuco |
| 1 | 2 | Equus caballus | Pánuco |
| 1 | Equus caballus | Tampico Alto | |
| 2 | 2 | Bos taurus | Tuxpam |
| 2 | 2 | Equus caballus | Naranjos Amatlán |
| 2 | 2 | Bos taurus | Gutiérrez Zamora |
| 2 | 1 | Equus caballus | Gutiérrez Zamora |
| 1 | Equus caballus | Papantla | |
| 2 | 2 | Bos taurus | Nautla |
| 2 | 2 | Equus caballus | Nautla |
| 2 | 2 | Bos taurus | Xalapa |
| 2 | 1 | Equus caballus | Xalapa |
| 1 | Equus caballus | Coatepec | |
| 2 | Bos taurus | Yanga | |
| 1 | Equus caballus | Yanga | |
| 1 | Bos taurus | Orizaba | |
| 2 | 1 | Equus caballus | Coscomatepec |
| 1 | Bos taurus | Coscomatepec | |
| 1 | 1 | Bos taurus | Puente Nacional |
| 1 | Equus caballus | Puente Nacional | |
| 1 | Bos taurus | Medellín | |
| 1 | Bos taurus | Soledad de Doblado | |
| 1 | Equus caballus | Soledad de Doblado | |
| 1 | Equus caballus | Paso de Ovejas | |
| 2 | Bos taurus | Tlacotalpan | |
| 1 | 1 | Equus caballus | Tlacotalpan |
| 1 | Bos taurus | Tierra Blanca | |
| 1 | Equus caballus | Tierra Blanca | |
| 1 | Bos taurus | Ignacio de la Llave | |
| 1 | Equus caballus | Ignacio de la Llave | |
| 1 | 2 | Bos taurus | San Andrés |
| 1 | Equus caballus | San Andrés | |
| 1 | Bos taurus | Catemaco | |
| 2 | Equus caballus | Catemaco | |
| 1 | Equus caballus | Santiago Tuxtla | |
| 1 | 1 | Bos taurus | Acayucan |
| 1 | 1 | Equus caballus | Acayucan |
| 1 | 1 | Bos taurus | San Juan Evangelista |
| 1 | Equus caballus | San Juan Evangelista | |
| 1 | Equus caballus | Jesús Carranza | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aguilar-Domínguez, M.; Romero-Salas, D.; Sánchez-Montes, S.; Serna-Lagunes, R.; Rosas-Saito, G.; Cruz-Romero, A.; Pérez de León, A.A. Morphometrics of Amblyomma mixtum in the State of Veracruz, Mexico. Pathogens 2021, 10, 533. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10050533
Aguilar-Domínguez M, Romero-Salas D, Sánchez-Montes S, Serna-Lagunes R, Rosas-Saito G, Cruz-Romero A, Pérez de León AA. Morphometrics of Amblyomma mixtum in the State of Veracruz, Mexico. Pathogens. 2021; 10(5):533. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10050533
Chicago/Turabian StyleAguilar-Domínguez, Mariel, Dora Romero-Salas, Sokani Sánchez-Montes, Ricardo Serna-Lagunes, Greta Rosas-Saito, Anabel Cruz-Romero, and Adalberto A. Pérez de León. 2021. "Morphometrics of Amblyomma mixtum in the State of Veracruz, Mexico" Pathogens 10, no. 5: 533. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10050533
APA StyleAguilar-Domínguez, M., Romero-Salas, D., Sánchez-Montes, S., Serna-Lagunes, R., Rosas-Saito, G., Cruz-Romero, A., & Pérez de León, A. A. (2021). Morphometrics of Amblyomma mixtum in the State of Veracruz, Mexico. Pathogens, 10(5), 533. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10050533






