Isolation and Characterization of Kingella bonacorsii sp. nov., A Novel Kingella Species Detected in a Stable Periodontitis Subject
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Strain Isolation and Phenotypic Characteristics
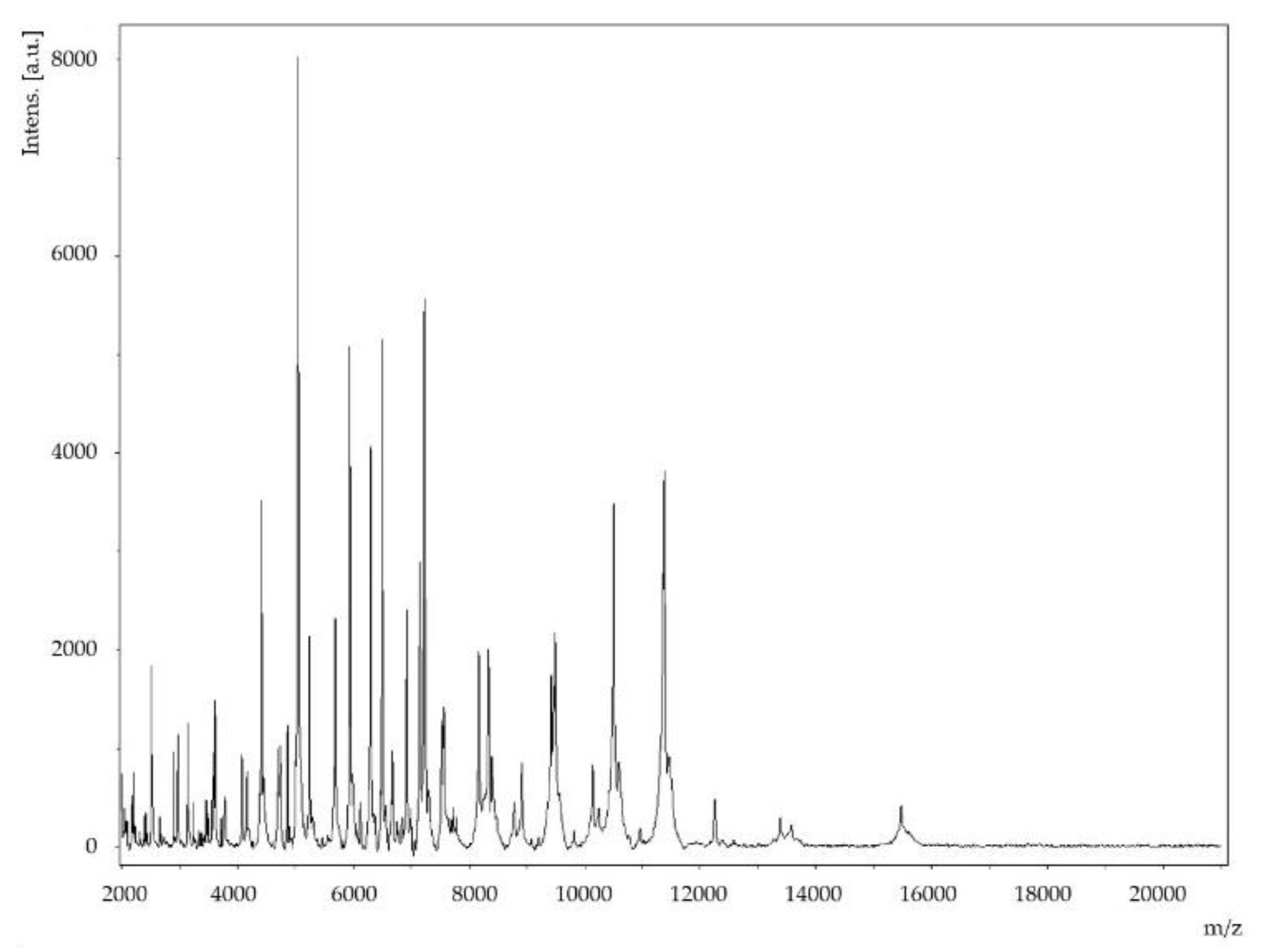
2.2. Genome Sequencing Information and Genome Properties
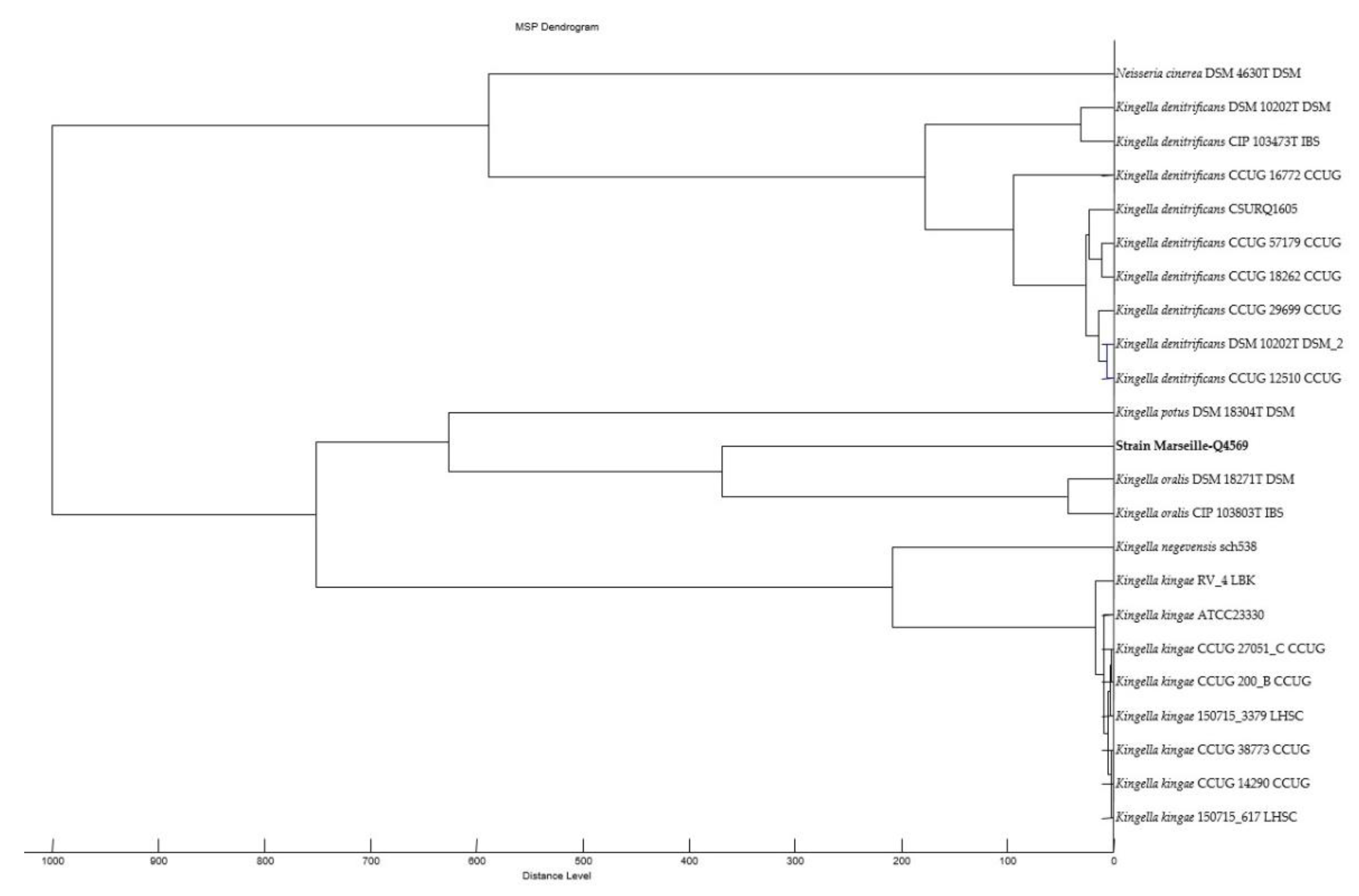
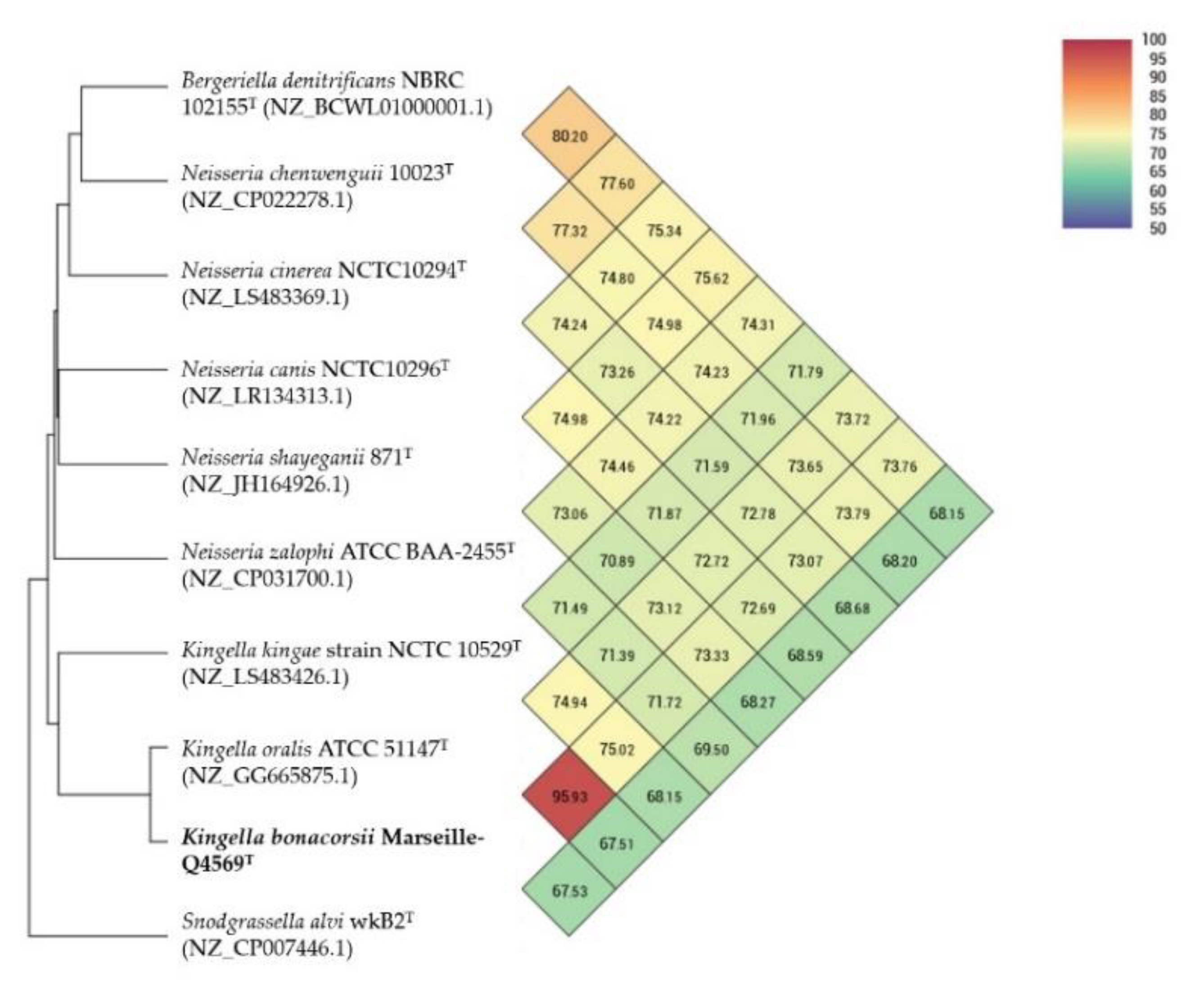
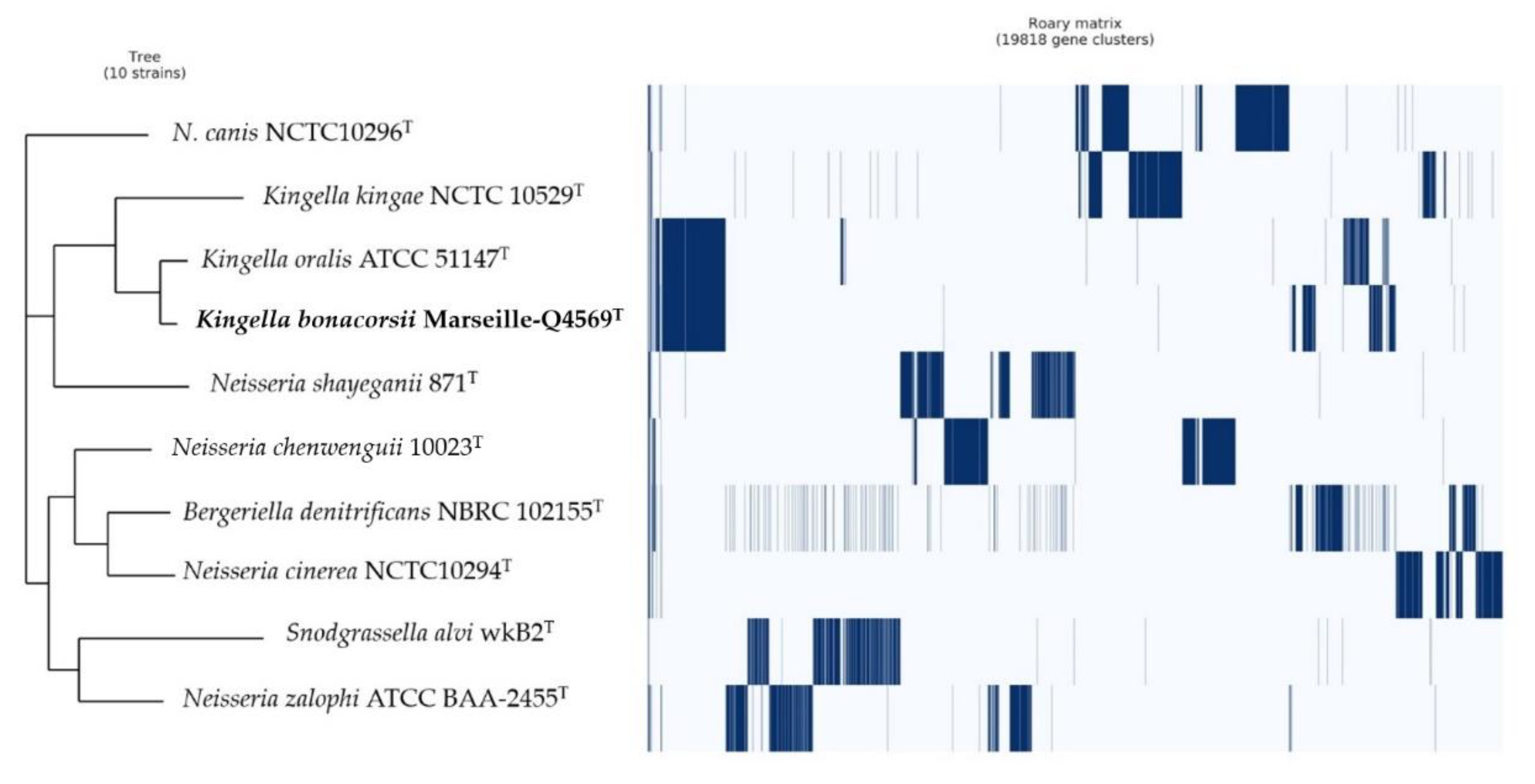
2.3. Comparison with Closely Related Bacterial Strains
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Strain Isolation and Phenotypic Tests
4.2. Extraction and Genome Sequencing
4.3. Assembly and Annotation of Genome Sequence
4.4. Phylogenetic Analysis and Genome Comparison
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tonetti, M.S.; Greenwell, H.; Kornman, K.S. Staging and grading of periodontitis: Framework and proposal of a new classification and case definition. J. Periodontol. 2018, 89, S159–S172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapple, I.L.C.; Mealey, B.L.; Van Dyke, T.E.; Bartold, P.M.; Dommisch, H.; Eickholz, P.; Geisinger, M.L.; Genco, R.J.; Glogauer, M.; Goldstein, M.; et al. Periodontal health and gingival diseases and conditions on an intact and a reduced periodontium: Consensus report of workgroup 1 of the 2017 World Workshop on the Classification of Periodontal and Peri-Implant Diseases and Conditions. J. Periodontol. 2018, 89, S74–S84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz, P.I.; Hoare, A.; Hong, B.-Y. Subgingival Microbiome Shifts and Community Dynamics in Periodontal Diseases. J. Calif. Dent. Assoc. 2016, 44, 421–435. [Google Scholar]
- Henriksen, S.D.; Bovre, K. Transfer of Moraxella kingae Henriksen and Bøvre to the Genus Kingella gen. nov. in the Family Neisseriaceae. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1976, 26, 447–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagupsky, P. Kingella kingae: From medical rarity to an emerging paediatric pathogen. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2004, 4, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grevich, S.; Lee, P.; Leroux, B.; Ringold, S.; Darveau, R.; Henstorf, G.; Berg, J.; Kim, A.; Velan, E.; Kelly, J.; et al. Oral health and plaque microbial profile in juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Pediatr. Rheumatol. Online J. 2019, 17, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Kamel, A.; Baraniya, D.; Al-Hajj, W.A.; Halboub, E.; Abdulrab, S.; Chen, T.; Al-Hebshi, N.N. Subgingival microbiome of experimental gingivitis: Shifts associated with the use of chlorhexidine and N-acetyl cysteine mouthwashes. J. Oral Microbiol. 2019, 11, 1608141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amado, P.P.P.; Kawamoto, D.; Albuquerque-Souza, E.; Franco, D.C.; Saraiva, L.; Casarin, R.C.V.; Horliana, A.C.R.T.; Mayer, M.P.A. Oral and Fecal Microbiome in Molar-Incisor Pattern Periodontitis. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 583761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Houmami, N.; Bakour, S.; Bzdrenga, J.; Rathored, J.; Seligmann, H.; Robert, C.; Armstrong, N.; Schrenzel, J.; Raoult, D.; Yagupsky, P.; et al. Isolation and characterization of Kingella negevensis sp. nov., a novel Kingella species detected in a healthy paediatric population. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 2370–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snell, J.J.S.; Lapage, S.P. Transfer of Some Saccharolytic Moraxella Species to Kingella Henriksen and Bovre 1976, with Descriptions of Kingella indologenes sp. nov. and Kingella denitrificans sp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1976, 26, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewhirst, F.E.; Chen, C.-K.C.; Paster, B.J.; Zambon, J.J. Phylogeny of Species in the Family Neisseriaceae Isolated from Human Dental Plaque and Description of Kingella orale sp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1993, 43, 490–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollis, D.G.; Weaver, R.E.; Riley, P.S. Emended description of Kingella denitrificans (Snell and Lapage 1976): Correction of the maltose reaction. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1983, 18, 1174–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, P.A.; Malnick, H.; Collins, M.D.; Shah, J.J.; Chattaway, M.A.; Bendall, R.; Hartley, J.W. Description of Kingella potus sp. nov., an Organism Isolated from a Wound Caused by an Animal Bite. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 3526–3529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stothard, P.; Wishart, D.S. Circular genome visualization and exploration using CGView. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 537–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across Computing Platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier-Kolthoff, J.P.; Auch, A.F.; Klenk, H.-P.; Göker, M. Genome sequence-based species delimitation with confidence intervals and improved distance functions. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Oh, H.-S.; Park, S.-C.; Chun, J. Towards a taxonomic coherence between average nucleotide identity and 16S rRNA gene sequence similarity for species demarcation of prokaryotes. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2014, 64, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.; Ouk Kim, Y.; Park, S.-C.; Chun, J. OrthoANI: An improved algorithm and software for calculating average nucleotide identity. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 1100–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seng, P.; Drancourt, M.; Gouriet, F.; La Scola, B.; Fournier, P.; Rolain, J.M.; Raoult, D. Ongoing Revolution in Bacteriology: Routine Identification of Bacteria by Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 49, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seng, P.; Abat, C.; Rolain, J.M.; Colson, P.; Lagier, J.-C.; Gouriet, F.; Fournier, P.E.; Drancourt, M.; La Scola, B.; Raoult, D. Identification of Rare Pathogenic Bacteria in a Clinical Microbiology Laboratory: Impact of Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization-Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 2182–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasser, M. Bacterial Identification by Gas Chromatographic Analysis of Fatty Acid Methyl Esters (GC-FAME); Microbial ID: Newark, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Dione, N.; Sankar, S.A.; Lagier, J.-C.; Khelaifia, S.; Michele, C.; Armstrong, N.; Richez, M.; Abrahão, J.; Raoult, D.; Fournier, P.-E. Genome sequence and description of Anaerosalibacter massiliensis sp. nov. New Microbes New Infect. 2016, 10, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, C.I.; Sankar, S.A.; Fall, B.; Sambe-Ba, B.; Diawara, S.; Gueye, M.W.; Mediannikov, O.; Blanc-Tailleur, C.; Wade, B.; Raoult, D.; et al. High-quality draft genome sequence and description of Haemophilus massiliensis sp. nov. Stand. Genom. Sci. 2016, 11, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zerbino, D.R.; Birney, E. Velvet: Algorithms for de novo short read assembly using de Bruijn graphs. Genome Res. 2008, 18, 821–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A New Genome Assembly Algorithm and Its Applications to Single-Cell Sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, R.; Liu, B.; Xie, Y.; Li, Z.; Huang, W.; Yuan, J.; He, G.; Chen, Y.; Pan, Q.; Liu, Y.; et al. SOAPdenovo2: An empirically improved memory-efficient short-read de novo assembler. GigaSci 2012, 1, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyatt, D.; Chen, G.-L.; LoCascio, P.F.; Land, M.L.; Larimer, F.W.; Hauser, L.J. Prodigal: Prokaryotic gene recognition and translation initiation site identification. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, K.; Karsch-Mizrachi, I.; Lipman, D.J.; Ostell, J.; Sayers, E.W. GenBank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D67–D72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seemann, T. Prokka: Rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuccuru, G.; Orsini, M.; Pinna, A.; Sbardellati, A.; Soranzo, N.; Travaglione, A.; Uva, P.; Zanetti, G.; Fotia, G. Orione, a web-based framework for NGS analysis in microbiology. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1928–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, A.J.; Cummins, C.A.; Hunt, M.; Wong, V.K.; Reuter, S.; Holden, M.T.G.; Fookes, M.; Falush, D.; Keane, J.A.; Parkhill, J. Roary: Rapid large-scale prokaryote pan genome analysis. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3691–3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Characteristics | Strain Marseille-Q4569T | Kingella negevensis Sch538T [9] | Kingella kingae ATCC 23330T [4,9] | Kingella indologenes NCTC 10717T [10] | Kingella denitrificans NCTC 10995T [10,11,12] | Kingella oralis UB-38T [11] | Kingella potus 3/SID/1128T |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rods or coccobacilli | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Pigment | − | − | − | − | − | − | + |
| Catalase | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| Glucose | − | − | + | + | + | + | − |
| Maltose | − | − | + | + | − | − | − |
| Fructose | − | − | − | + | − | − | − |
| Alkaline phosphatase | + | + | ND | ND | ND | + | − |
| C4 esterase | + | − | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| C8 esterase lipase | + | − | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| C14 lipase | − | − | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| Leucine arylamidase | + | + | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| Valine arylamidase | − | − | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| Cystine arylamidase | − | − | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| Trypsin | − | − | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| α-Chymotrypsin | − | − | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| Acid phosphatase | + | + | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| Naphthol-AS-BI-Phosphohydrolase | + | − | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| α-Galactosidase | − | − | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| β-Galactosidase | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| β-Glucuronidase | − | − | ND | ND | ND | ND | − |
| α-Glucosidase | − | − | ND | ND | ND | ND | − |
| β-Glucosidase | − | − | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| N-Acetyl-β-Glucosaminidase | − | − | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| α-Mannosidase | − | − | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| α-Fucosidase | − | − | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| Fatty Acid | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C10:0 3-OH | TR | ND | 3.0 | ND |
| C11:0 | ND | ND | 2.0 | ND |
| C12:0 | 1.9 | 5.6 | 5.2 | 22.5 |
| C12:0 3-OH | 2.3 | 2.3 | 3.6 | 6.5 |
| C14:0 | 4.9 | 40.0 | 2.7 | 37.7 |
| C14:0 3-OH | TR | 1.1 | 3.0 | 4.3 |
| C14:1 | TR | 1.5 | ND | − |
| C14:1n5 | − | TR | ND | 5.7 |
| C15:0 | TR | 1.1 | 2.1 | TR |
| C16:0 | 32.7 | 10.8 | 34.8 | 19.5 |
| C16:1n7 | 21.3 | 25.5 | 14.4 | 18.3 |
| C17:0 | TR | ND | 0.9 | ND |
| C18:0 | 1.7 | 2.2 | 1.0 | 7.1 |
| C18:1n7 | 26.1 | 6.5 | 18.5 | 2.2 |
| C18:1n9 | 3.4 | 1.4 | 2.4 | 7.7 |
| C18:2n6 | 4.2 | TR | ND | 3.7 |
| Code | Strain Marseille-Q4569T | Description |
|---|---|---|
| [J] | 139 | Translation, ribosomal structure and biogenesis |
| [A] | 1 | RNA processing and modification |
| [K] | 60 | Transcription |
| [L] | 109 | Replication, recombination and repair |
| [B] | 0 | Chromatin structure and dynamics |
| [D] | 26 | Cell cycle control, cell division, chromosome partitioning |
| [Y] | 0 | Nuclear structure |
| [V] | 18 | Defense mechanisms |
| [T] | 22 | Signal transduction mechanisms |
| [M] | 99 | Cell wall/membrane/envelope biogenesis |
| [N] | 1 | Cell motility |
| [Z] | 0 | Cytoskeleton |
| [W] | 0 | Extracellular structures |
| [U] | 26 | Intracellular trafficking, secretion and vesicular transport |
| [O] | 54 | Posttranslational modification, protein turnover, chaperones |
| [X] | 0 | Mobilome: prophages, transposons |
| [C] | 86 | Energy production and conversion |
| [G] | 47 | Carbohydrate transport and metabolism |
| [E] | 107 | Amino acid transport and metabolism |
| [F] | 43 | Nucleotide transport and metabolism |
| [H] | 65 | Coenzyme transport and metabolism |
| [I] | 42 | Lipid transport and metabolism |
| [P] | 67 | Inorganic ion transport and metabolism |
| [Q] | 11 | Secondary metabolites biosynthesis, transport and catabolism |
| [R] | 165 | General function prediction only |
| [S] | 165 | Function unknown |
| Species | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Kingella bonacorsii Marseille-Q4569T | 100.00 | 63.6 [60.7–66.4] | 33.3 [30.9–35.8] | 24.0 [21.7–26.5] | 23.2 [20.9–25.6] | 22.9 [20.6–25.4] | 22.5 [20.2–24.9] | 22.4 [20.1–24.9] | 22.3 [20–24.7] | 22.2 [19.9–24.6] |
| 2 Kingella oralis ATCC 51147T (NZ_GG665875.1) | 100.00 | 30.8 [28.4–33.3] | 23.6 [21.3–26.1] | 22.4 [20.1–24.8] | 22.2 [19.9–24.6] | 21.5 [19.2–23.9] | 21.7 [19.5–24.1] | 21.9 [19.6–24.3] | 21.8 [19.5–24.2] | |
| 3 Snodgrassella alvi wkB2T (NZ_CP007446.1) | 100.00 | 25.7 [23.4–28.2] | 23.1 [20.8–25.6] | 25.1 [22.8–27.6] | 22.9 [20.6–25.4] | 26.8 [24.4–29.3] | 25.2 [22.8–27.6] | 22.8 [20.5–25.2] | ||
| 4 Neisseria cinerea NCTC10294T (NZ_LS483369.1) | 100.00 | 23.0 [20.8–25.5] | 24.0 [21.6–26.4] | 24.1 [21.8–26.6] | 23.7 [21.4–26.1] | 23.3 [21–25.8] | 23.2 [20.9–25.7] | |||
| 5 Neisseria zalophi ATCC BAA-2455T (NZ_CP031700.1) | 100.00 | 22.4 [20.1–24.8] | 21.9 [19.7–24.4] | 24.8 [22.5–27.3] | 23.9 [21.6–26.3] | 22.8 [20.5–25.3] | ||||
| 6 Neisseria chenwenguii 10023T (NZ_CP022278.1) | 100.00 | 20.9 [22.8–27.6] | 22.9 [20.7–25.4] | 22.2 [19.9–24.6] | 23.2 [21–25.7] | |||||
| 7 Bergeriella denitrificans NBRC 102155T (NZ_BCWL01000001.1) | 100.00 | 22.4 [20.2–24.9] | 22.4 [20.1–24.8] | 23.7 [21.4–26.2] | ||||||
| 8 Neisseria shayeganii 871T (NZ_JH164926.1) | 100.00 | 23.5 [21.2–26] | 26.7 [24.4–29.2] | |||||||
| 9. Kingella kingae strain NCTC 10529T (NZ_LS483426.1) | 100.00 | 22.3 [20–24.7] | ||||||||
| 10 Neisseria canis NCTC10296T (NZ_LR134313.1) | 100.00 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Antezack, A.; Boxberger, M.; Rolland, C.; Monnet-Corti, V.; La Scola, B. Isolation and Characterization of Kingella bonacorsii sp. nov., A Novel Kingella Species Detected in a Stable Periodontitis Subject. Pathogens 2021, 10, 240. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10020240
Antezack A, Boxberger M, Rolland C, Monnet-Corti V, La Scola B. Isolation and Characterization of Kingella bonacorsii sp. nov., A Novel Kingella Species Detected in a Stable Periodontitis Subject. Pathogens. 2021; 10(2):240. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10020240
Chicago/Turabian StyleAntezack, Angéline, Manon Boxberger, Clara Rolland, Virginie Monnet-Corti, and Bernard La Scola. 2021. "Isolation and Characterization of Kingella bonacorsii sp. nov., A Novel Kingella Species Detected in a Stable Periodontitis Subject" Pathogens 10, no. 2: 240. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10020240
APA StyleAntezack, A., Boxberger, M., Rolland, C., Monnet-Corti, V., & La Scola, B. (2021). Isolation and Characterization of Kingella bonacorsii sp. nov., A Novel Kingella Species Detected in a Stable Periodontitis Subject. Pathogens, 10(2), 240. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10020240






