Structural Characterization of Haemophilus influenzae Enolase and Its Interaction with Human Plasminogen by In Silico and In Vitro Assays
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
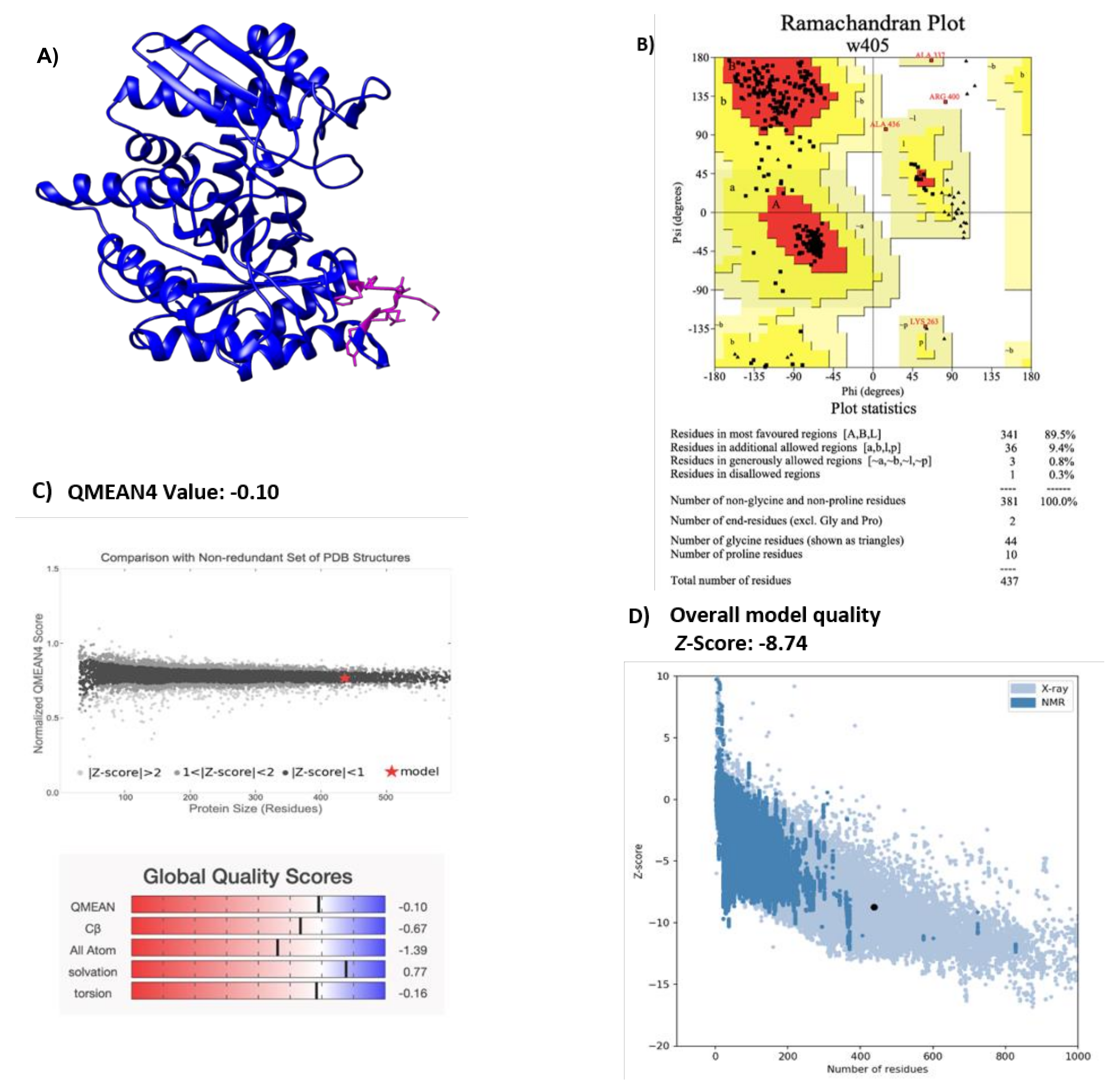
2.1. Modeling H. influenzae Enolase Structure
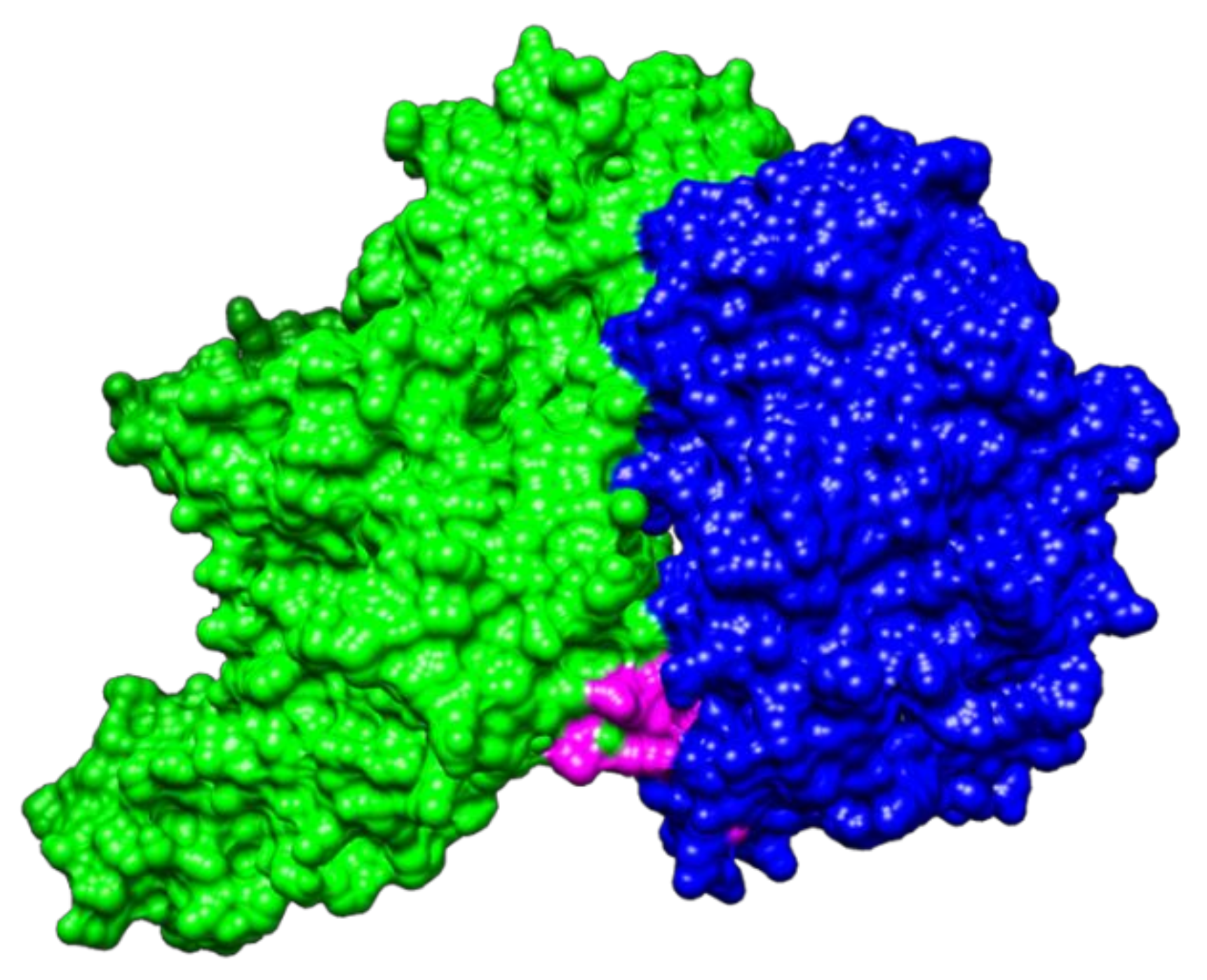
2.2. Molecular Docking between NTHiENO and Plg
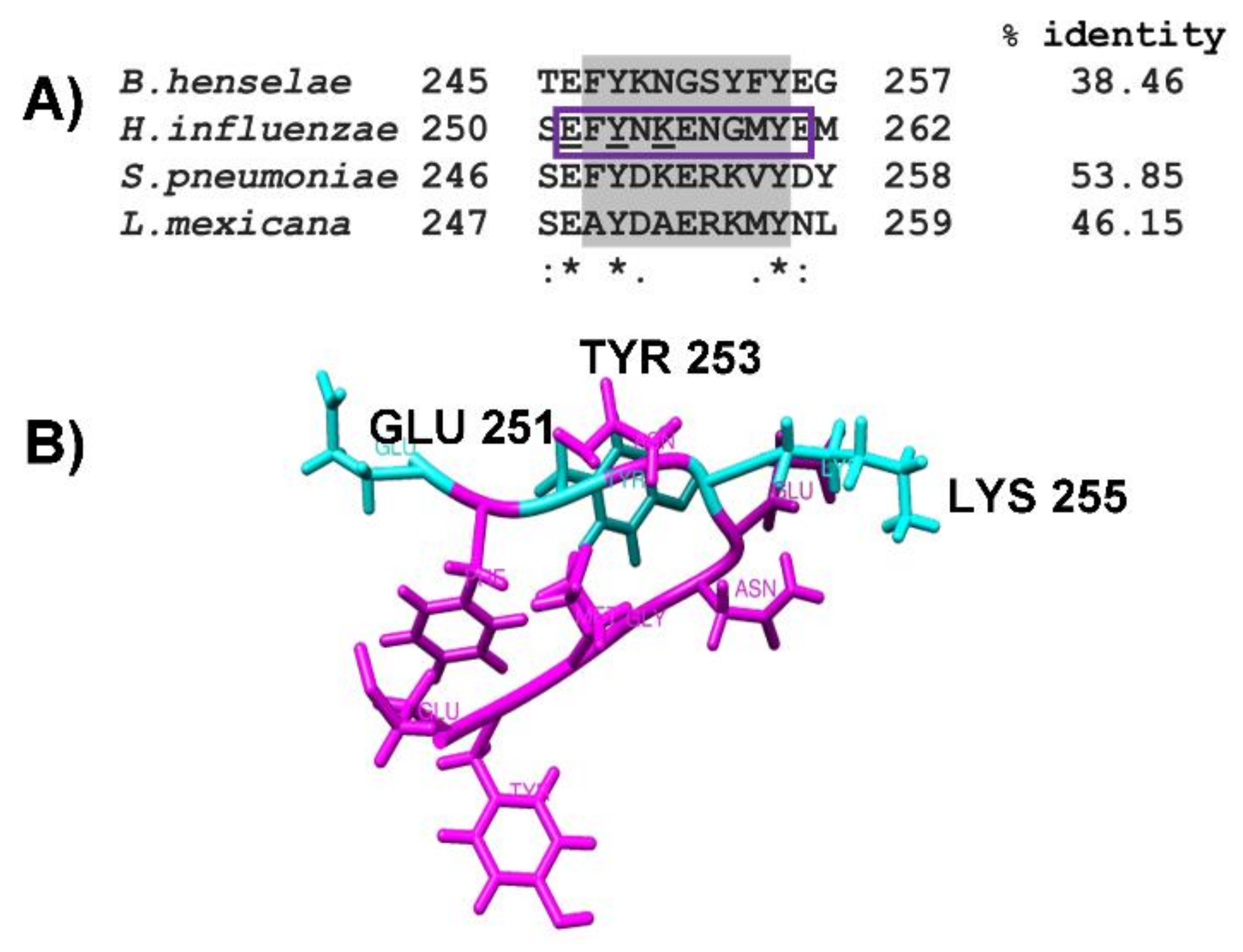
2.3. Identification of Putative Plasminogen-Binding Domain in NTHiENO
2.4. Obtention of pbmHiENO Peptide
2.5. pbmHiENO–Plasminogen Interaction
2.6. Docking Analysis in Positive Controls
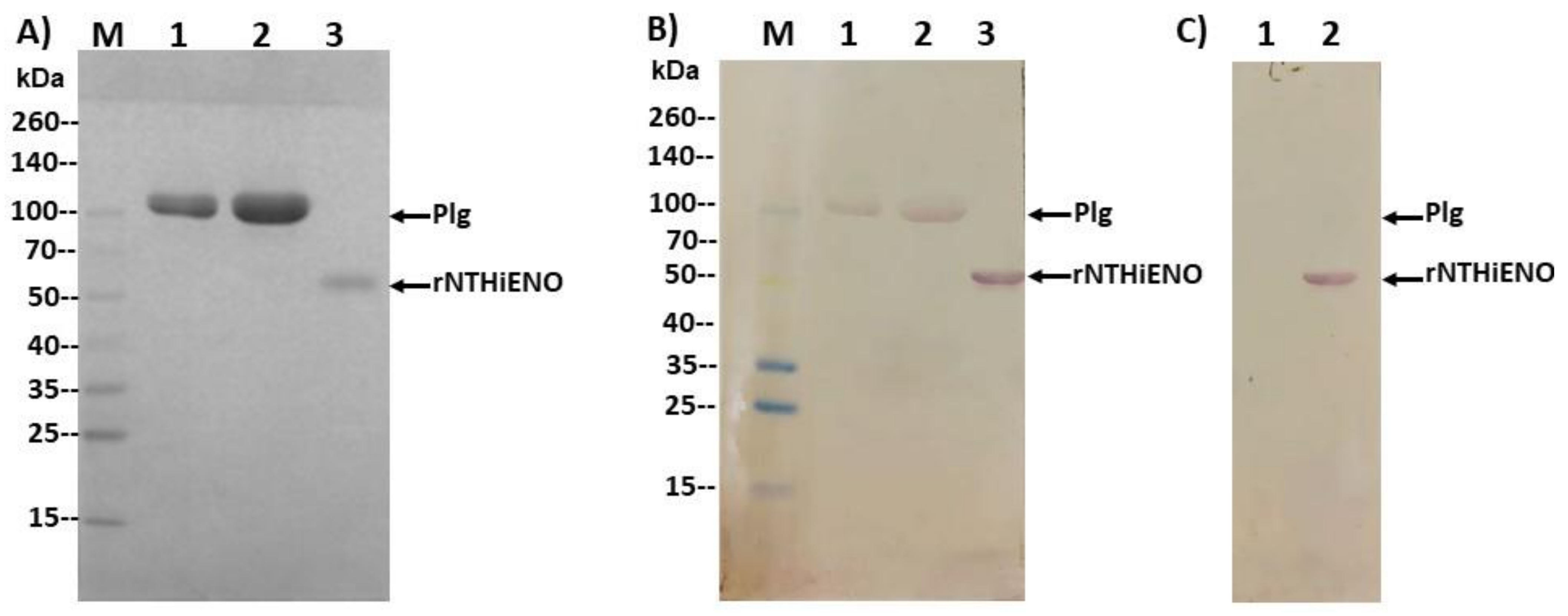
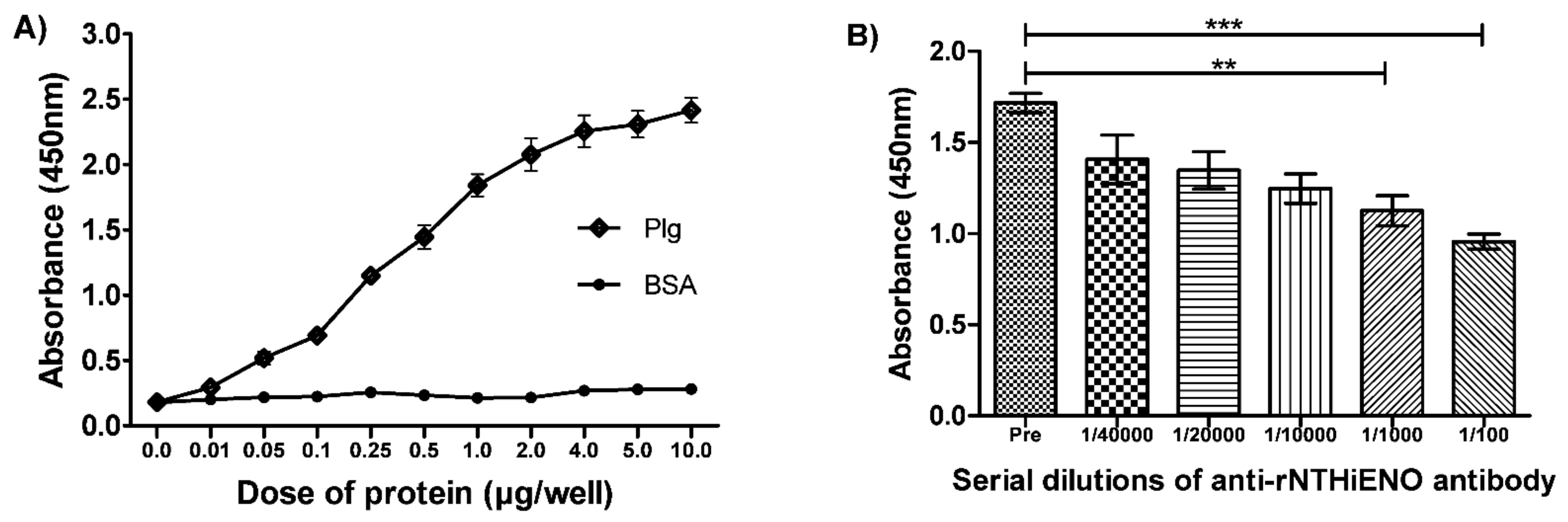
2.7. Experimental Detection of Non-Typeable H. influenzae Enolase–Plasminogen Interaction
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Enolase Sequences and Alignments
4.2. Analyses of Protein–Protein Docking
4.3. Obtaining the Internal Binding Motif to Plg (pbmHiENO)
4.4. Blind Docking pbmHiENO–Plg
4.5. Docking Positive Controls
4.6. Plasminogen-Binding Assay by Far-Western Blot
4.7. Detection of Interactions of rNTHiENO with Plasminogen by ELISA
4.8. Generation of Anti-Plg Polyclonal Antibodies
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Langereis, J.D.; de Jonge, M.I. Invasive Disease Caused by Nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 1711–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegstad, K.; Mylvaganam, H.; Janice, J.; Josefsen, E.; Sivertsen, A.; Skaare, D. Role of Horizontal Gene Transfer in the Development of Multidrug Resistance in Haemophilus influenzae. mSphere 2020, 5, e00969-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zarei, A.E.; Almehdar, H.A.; Redwan, E.M. Hib Vaccines: Past, Present, and Future Perspectives. J. Immunol. Res. 2016, 2016, 7203587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Eldere, J.; Slack, M.P.; Ladhani, S.; Cripps, A.W. Non-typeable Haemophilus influenzae, an under-recognised pathogen. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 1281–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rao, V.K.; Krasan, G.P.; Hendrixson, D.R.; Dawid, S.; St Geme, J.W., III. Molecular determinants of the pathogenesis of disease due to non-typable Haemophilus influenzae. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 1999, 23, 99–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, H.; Wu, S.; Song, Q.; Zhang, J.; Sang, F.; Sun, X.; Xu, T.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, B. Cloning and identification of Bartonella alpha-enolase as a plasminogen-binding protein. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 135, 103651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pancholi, V. Multifunctional alpha-enolase: Its role in diseases. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2001, 58, 902–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, K.; Chen, D.; Geng, Y.; Huang, X.; He, Y.; Ji, L.; Liu, T.; Wang, E.; Yang, Q.; et al. Cloning and Characterization of Surface-Localized alpha-Enolase of Streptococcus iniae, an Effective Protective Antigen in Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 14490–14510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kainulainen, V.; Korhonen, T.K. Dancing to another tune-adhesive moonlighting proteins in bacteria. Biology 2014, 3, 178–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diaz-Ramos, A.; Roig-Borrellas, A.; Garcia-Melero, A.; Lopez-Alemany, R. α-Enolase, a multifunctional protein: Its role on pathophysiological situations. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2012, 2012, 156795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boel, G.; Pichereau, V.; Mijakovic, I.; Maze, A.; Poncet, S.; Gillet, S.; Giard, J.C.; Hartke, A.; Auffray, Y.; Deutscher, J. Is 2-phosphoglycerate-dependent automodification of bacterial enolases implicated in their export? J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 337, 485–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Zao, Y.J.; Yan, S.W.; Song, Y.Y.; Yang, D.M.; Dai, L.Y.; Liu, R.D.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.Q.; Cui, J. Molecular characterization of a Trichinella spiralis enolase and its interaction with the host’s plasminogen. Vet. Res. 2019, 50, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ayon-Nunez, D.A.; Fragoso, G.; Bobes, R.J.; Laclette, J.P. Plasminogen-binding proteins as an evasion mechanism of the host’s innate immunity in infectious diseases. Biosci. Rep. 2018, 38, BSR20180705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nogueira, S.V.; Backstedt, B.T.; Smith, A.A.; Qin, J.H.; Wunder, E.A., Jr.; Ko, A.; Pal, U. Leptospira interrogans enolase is secreted extracellularly and interacts with plasminogen. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, S.; Wild, D.; Diekmann, O.; Frank, R.; Bracht, D.; Chhatwal, G.S.; Hammerschmidt, S. Identification of a novel plasmin(ogen)-binding motif in surface displayed alpha-enolase of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Mol. Microbiol. 2003, 49, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehinger, S.; Schubert, W.D.; Bergmann, S.; Hammerschmidt, S.; Heinz, D.W. Plasmin(ogen)-binding alpha-enolase from Streptococcus pneumoniae: Crystal structure and evaluation of plasmin(ogen)-binding sites. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 343, 997–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanegas, G.; Quinones, W.; Carrasco-Lopez, C.; Concepcion, J.L.; Albericio, F.; Avilan, L. Enolase as a plasminogen binding protein in Leishmania mexicana. Parasitol. Res. 2007, 101, 1511–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, A.K.; Coppens, I.; Gardsvoll, H.; Ploug, M.; Jacobs-Lorena, M. Plasmodium ookinetes coopt mammalian plasminogen to invade the mosquito midgut. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 17153–17158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mutlu, O.; Yakarsonmez, S.; Sariyer, E.; Danis, O.; Yuce-Dursun, B.; Topuzogullari, M.; Akbulut, E.; Turgut-Balik, D. Comprehensive structural analysis of the open and closed conformations of Theileria annulata enolase by molecular modelling and docking. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2016, 64, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osorio-Aguilar, Y.; Gonzalez-Vazquez, M.C.; Lozano-Zarain, P.; Martinez-Laguna, Y.; Carabarin-Lima, A.; Del Carmen Rocha-Gracia, R. Cloning and Characterization of Immunological Properties of Haemophilus influenzae Enolase. J. Immunol. Res. 2021, 2021, 6629824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelley, L.A.; Mezulis, S.; Yates, C.M.; Wass, M.N.; Sternberg, M.J. The Phyre2 web portal for protein modeling, prediction and analysis. Nat. Protoc. 2015, 10, 845–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera—A visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chandran, V.; Luisi, B.F. Recognition of enolase in the Escherichia coli RNA degradosome. J. Mol. Biol. 2006, 358, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watts, S.C.; Holt, K.E. hicap: In Silico Serotyping of the Haemophilus influenzae Capsule Locus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2019, 57, e00190-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Takeuchi, N.; Segawa, S.; Ishiwada, N.; Ohkusu, M.; Tsuchida, S.; Satoh, M.; Matsushita, K.; Nomura, F. Capsular serotyping of Haemophilus influenzae by using matrix-associated laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry. J. Infect. Chemother. 2018, 24, 510–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, S.; Feng, D.; Chen, D.; Yang, L.; Xu, Z. Molecular epidemiology and evolution of Haemophilus influenzae. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2020, 80, 104205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruce, M.G.; Deeks, S.L.; Zulz, T.; Navarro, C.; Palacios, C.; Case, C.; Hemsley, C.; Hennessy, T.; Corriveau, A.; Larke, B.; et al. Epidemiology of Haemophilus influenzae serotype a, North American Arctic, 2000–2005. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behrouzi, A.; Vaziri, F.; Rahimi-Jamnani, F.; Afrough, P.; Rahbar, M.; Satarian, F.; Siadat, S.D. Vaccine Candidates against Nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae: A Review. Iran. Biomed. J. 2017, 21, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adderson, E.E.; Byington, C.L.; Spencer, L.; Kimball, A.; Hindiyeh, M.; Carroll, K.; Mottice, S.; Korgenski, E.K.; Christenson, J.C.; Pavia, A.T. Invasive serotype a Haemophilus influenzae infections with a virulence genotype resembling Haemophilus influenzae type b: Emerging pathogen in the vaccine era? Pediatrics 2001, 108, E18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agarwal, S.; Kulshreshtha, P.; Bambah Mukku, D.; Bhatnagar, R. Alpha-Enolase binds to human plasminogen on the surface of Bacillus anthracis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1784, 986–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kornblatt, M.J.; Kornblatt, J.A.; Hancock, M.A. The interaction of canine plasminogen with Streptococcus pyogenes enolase: They bind to one another but what is the nature of the structures involved? PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Benkert, P.; Tosatto, S.C.; Schomburg, D. QMEAN: A comprehensive scoring function for model quality assessment. Proteins 2008, 71, 261–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derbise, A.; Song, Y.P.; Parikh, S.; Fischetti, V.A.; Pancholi, V. Role of the C-terminal lysine residues of streptococcal surface enolase in Glu- and Lys-plasminogen-binding activities of group A streptococci. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lahteenmaki, K.; Kuusela, P.; Korhonen, T.K. Bacterial plasminogen activators and receptors. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2001, 25, 531–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menhart, N.; McCance, S.G.; Sehl, L.C.; Castellino, F.J. Functional independence of the kringle 4 and kringle 5 regions of human plasminogen. Biochemistry 1993, 32, 8799–8806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marti, D.N.; Schaller, J.; Llinas, M. Solution structure and dynamics of the plasminogen kringle 2-AMCHA complex: 3(1)-helix in homologous domains. Biochemistry 1999, 38, 15741–15755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellino, F.J.; Ploplis, V.A. Structure and function of the plasminogen/plasmin system. Thromb. Haemost. 2005, 93, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, S.; Ploplis, V.A.; Castellino, F.J. Bacterial plasminogen receptors utilize host plasminogen system for effective invasion and dissemination. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2012, 2012, 482096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rahi, A.; Dhiman, A.; Singh, D.; Lynn, A.M.; Rehan, M.; Bhatnagar, R. Exploring the interaction between Mycobacterium tuberculosis enolase and human plasminogen using computational methods and experimental techniques. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 2408–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Candela, M.; Bergmann, S.; Vici, M.; Vitali, B.; Turroni, S.; Eikmanns, B.J.; Hammerschmidt, S.; Brigidi, P. Binding of human plasminogen to Bifidobacterium. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 5929–5936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Candela, M.; Biagi, E.; Centanni, M.; Turroni, S.; Vici, M.; Musiani, F.; Vitali, B.; Bergmann, S.; Hammerschmidt, S.; Brigidi, P. Bifidobacterial enolase, a cell surface receptor for human plasminogen involved in the interaction with the host. Microbiology 2009, 155, 3294–3303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Satala, D.; Satala, G.; Karkowska-Kuleta, J.; Bukowski, M.; Kluza, A.; Rapala-Kozik, M.; Kozik, A. Structural Insights into the Interactions of Candidal Enolase with Human Vitronectin, Fibronectin and Plasminogen. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguayo-Ortiz, R.; Meza-Cervantez, P.; Castillo, R.; Hernandez-Campos, A.; Dominguez, L.; Yepez-Mulia, L. Insights into the Giardia intestinalis enolase and human plasminogen interaction. Mol. Biosyst. 2017, 13, 2015–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pancholi, V.; Fischetti, V.A. Alpha-enolase, a novel strong plasmin(ogen) binding protein on the surface of pathogenic streptococci. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 14503–14515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mundodi, V.; Kucknoor, A.S.; Alderete, J.F. Immunogenic and plasminogen-binding surface-associated alpha-enolase of Trichomonas vaginalis. Infect. Immun. 2008, 76, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chumchua, V.; Pornputtapong, N.; Thammarongtham, C.; Meksuriyen, D. Homology modeling of Mycoplasma pneumoniae enolase and its molecular interaction with human plasminogen. Bioinformation 2008, 3, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lottenberg, R.; Minning-Wenz, D.; Boyle, M.D. Capturing host plasmin(ogen): A common mechanism for invasive pathogens? Trends Microbiol. 1994, 2, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulde, M.; Steinert, M.; Bergmann, S. Interaction of streptococcal plasminogen binding proteins with the host fibrinolytic system. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2013, 3, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laskowski, R.A.; MacArthur, M.W.; Moss, D.S.; Thornton, J.M. PROCHECK: A program to check the stereochemical quality of protein structures. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1993, 26, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiederstein, M.; Sippl, M.J. ProSA-web: Interactive web service for the recognition of errors in three-dimensional structures of proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, W407–W410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schneidman-Duhovny, D.; Inbar, Y.; Nussinov, R.; Wolfson, H.J. PatchDock and SymmDock: Servers for rigid and symmetric docking. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, W363–W367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Duhovny, D.; Nussinov, R.; Wolfson, H.J. Efficient unbound docking of rigid molecules. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Algorithms in Bioinformatics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002; pp. 185–200. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, L.C.; Rodrigues, J.P.; Kastritis, P.L.; Bonvin, A.M.; Vangone, A. PRODIGY: A web server for predicting the binding affinity of protein-protein complexes. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 3676–3678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, A.; Holder, A. Gauss View 5.0, User’s Reference; Gaussian Inc.: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey, W.; Dalke, A.; Schulten, K. VMD: Visual molecular dynamics. J. Mol. Graph. 1996, 14, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, R.H.P.; Wu, G.; Leung, E.W.W.; Hidaka, K.; Quek, A.J.; Caradoc-Davies, T.T.; Jeevarajah, D.; Conroy, P.J.; Kirby, N.M.; Norton, R.S.; et al. X-ray crystal structure of plasmin with tranexamic acid-derived active site inhibitors. Blood Adv. 2017, 1, 766–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tabernero, L.; Chang, C.Y.; Ohringer, S.L.; Lau, W.F.; Iwanowicz, E.J.; Han, W.C.; Wang, T.C.; Seiler, S.M.; Roberts, D.G.; Sack, J.S. Structure of a retro-binding peptide inhibitor complexed with human alpha-thrombin. J. Mol. Biol. 1995, 246, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matter, H.; Defossa, E.; Heinelt, U.; Blohm, P.M.; Schneider, D.; Muller, A.; Herok, S.; Schreuder, H.; Liesum, A.; Brachvogel, V.; et al. Design and quantitative structure-activity relationship of 3-amidinobenzyl-1H-indole-2-carboxamides as potent, nonchiral, and selective inhibitors of blood coagulation factor Xa. J. Med. Chem. 2002, 45, 2749–2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guex, N.; Peitsch, M.C. SWISS-MODEL and the Swiss-PdbViewer: An environment for comparative protein modeling. Electrophoresis 1997, 18, 2714–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, R.A. Studying protein-protein interactions via blot overlay/far western blot. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1278, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
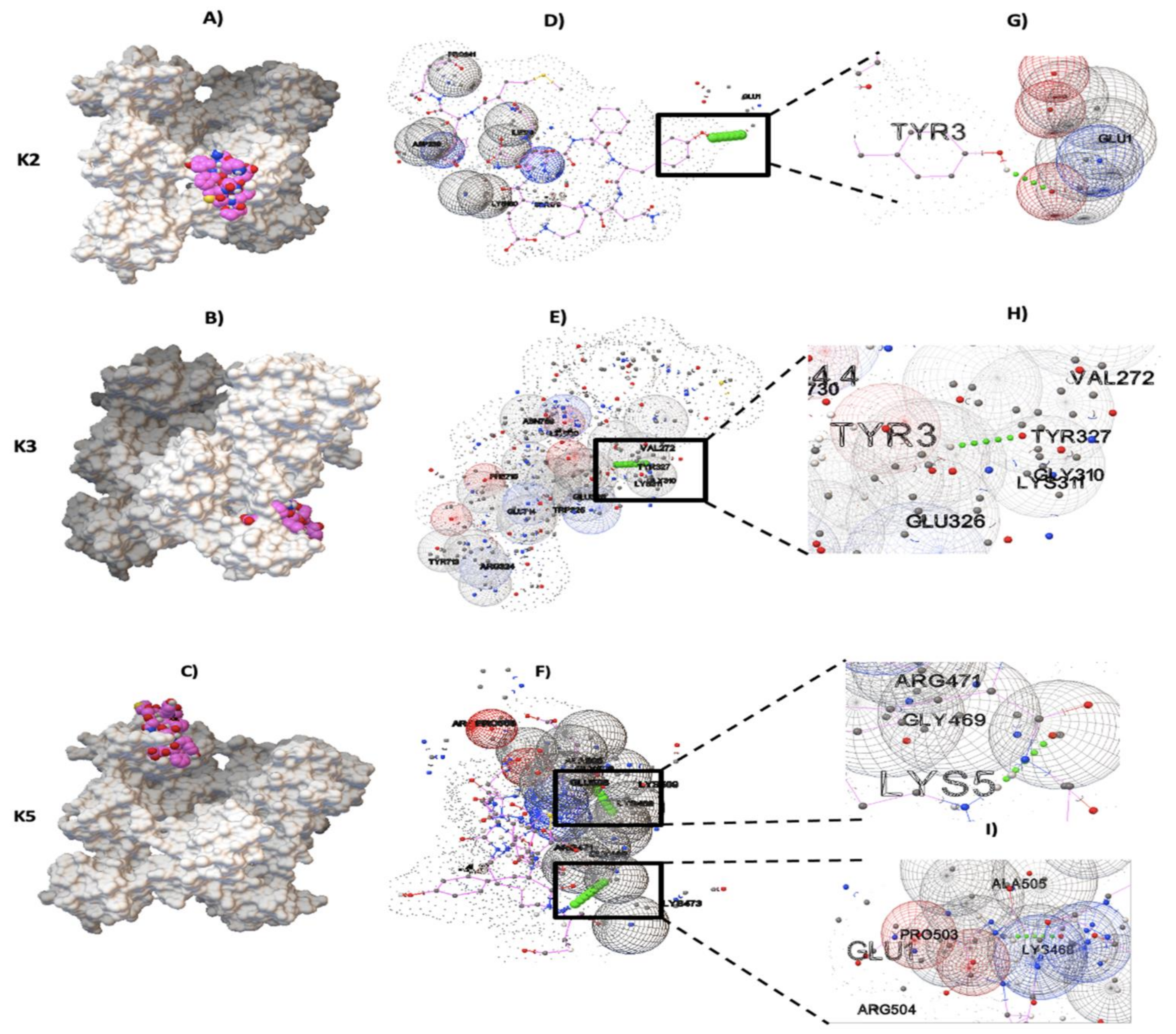
| Target Kringle Plg Domain | Residue in NTHiENO | Residue in pbmHiENO | Residue Plg | Hydrogen Bonding Interactions | Binding Energy (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K2 | TYR253 | TYR3 | GLU1 | 1 | -3.9 |
| K3 | TYR253 | TYR3 | GLY310 | 1 | -4.4 |
| K5 | LYS255 GLU251 | LYS5 GLU1 | ARG471 LYS468 | 2 | -4.8 |
| Kringle Domain | Plasminogen Amino Acid Residue |
|---|---|
| K2 | GLU1, ILE178, SER179, LYS180, ASP239, and PRO241 |
| K3 | VAL272, GLY310, LYS311, ARG324, TRP325, GLU326, TYR327, TYR713, GLU714, PHE715, LEU730, and ASN769 |
| K5 | LYS468, Gly469, ARG471, LYS473, PRO503, ARG504, ALA505, GLY506, GLU508, and LYS509 |
| Receptor (ID PDB) | Crystalized Ligand (ID PDB) | Binding Energy (kcal/mol) | RMSD Crystallized Ligand/Docked Pose |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmin (5UGG) | 89M | -7.8 | 0.61 Å |
| Alpha-thrombin (1HDT) | 0E7 | -7.2 | 0.65 Å |
| Factor Xa (1LPG) | IMA | -9.1 | 0.68 Å |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Osorio-Aguilar, Y.; Gonzalez-Vazquez, M.C.; Hernandez-Ceron, D.E.; Lozano-Zarain, P.; Martinez-Laguna, Y.; Gonzalez-Bonilla, C.R.; Rocha-Gracia, R.d.C.; Carabarin-Lima, A. Structural Characterization of Haemophilus influenzae Enolase and Its Interaction with Human Plasminogen by In Silico and In Vitro Assays. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1614. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10121614
Osorio-Aguilar Y, Gonzalez-Vazquez MC, Hernandez-Ceron DE, Lozano-Zarain P, Martinez-Laguna Y, Gonzalez-Bonilla CR, Rocha-Gracia RdC, Carabarin-Lima A. Structural Characterization of Haemophilus influenzae Enolase and Its Interaction with Human Plasminogen by In Silico and In Vitro Assays. Pathogens. 2021; 10(12):1614. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10121614
Chicago/Turabian StyleOsorio-Aguilar, Yesenia, Maria Cristina Gonzalez-Vazquez, Diana Elizabeth Hernandez-Ceron, Patricia Lozano-Zarain, Ygnacio Martinez-Laguna, Cesar Raul Gonzalez-Bonilla, Rosa del Carmen Rocha-Gracia, and Alejandro Carabarin-Lima. 2021. "Structural Characterization of Haemophilus influenzae Enolase and Its Interaction with Human Plasminogen by In Silico and In Vitro Assays" Pathogens 10, no. 12: 1614. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10121614
APA StyleOsorio-Aguilar, Y., Gonzalez-Vazquez, M. C., Hernandez-Ceron, D. E., Lozano-Zarain, P., Martinez-Laguna, Y., Gonzalez-Bonilla, C. R., Rocha-Gracia, R. d. C., & Carabarin-Lima, A. (2021). Structural Characterization of Haemophilus influenzae Enolase and Its Interaction with Human Plasminogen by In Silico and In Vitro Assays. Pathogens, 10(12), 1614. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10121614






