Zoonotic Genotypes of Enterocytozoon bieneusi in Wild Living Invasive and Native Carnivores in Poland
Abstract
:1. Introduction
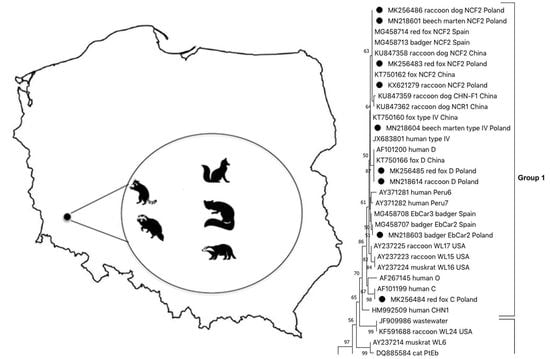
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Areas and Specimen Collection
4.2. Molecular and Phylogenetic Analyses
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Didier, E.S.; Weiss, L.M. Microsporidiosis: Current status. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2006, 19, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Didier, E.S.; Weiss, L.M. Microsporidiosis: Not just in AIDS patients. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 24, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Feng, Y.; Santin, M. Host specificity of enterocytozoon bieneusi and public health implications. Trends Parasitol. 2019, 35, 436–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Xiao, L. Ecological and public health significance of Enterocytozoon bieneusi. One Health 2021, 12, 100209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duscher, G.G.; Leschnik, M.; Fuehrer, H.P.; Joachim, A. Wildlife reservoirs for vector-borne canine, feline and zoonotic infections in Austria. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2015, 4, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waindok, P.; Raue, K.; Grilo, M.L.; Siebert, U.; Strube, C. Predators in northern Germany are reservoirs for parasites of One Health concern. Parasitol. Res. 2021, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauhala, K.; Kowalczyk, R. Invasion of the raccoon dog Nyctereutes procyonides in Europe: History of colonization, features behind its success, and threats to native fauna. Curr. Zool. 2011, 57, 584–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Biedrzycka, A.; Zalewski, A.; Bartoszewicz, M.; Okarma, H.; Jędrzejewska, E. The genetic structure of raccoon introduced in Central Europe reflects multiple invasion pathways. Biol. Invasions 2014, 16, 1611–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gross, J.; Elvinger, F.; Hungerford, L.L.; Gehrt, S.D. Raccoon use of the urban matrix in the Baltimore Metropolitan Area, Maryland. Urban Ecosyst. 2012, 15, 667–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beltrán-Beck, B.; García, F.J.; Gortázar, C. Raccoons in Europe: Disease hazards due to the establishment of an invasive species. Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2011, 58, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutor, A.; Schwarz, S.; Conraths, F.J. The biological potential of the raccoon dog (Nyctereutes procyonoides, Gray 1834) as an invasive species in Europe—new risks for disease spread? Acta Thériol. 2014, 59, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoszewicz, M.; Okarma, H.; Zalewski, A.; Szczęsna, J. Ecology of the raccoon (Procyon lotor) from western Poland. Ann. Zool. Fenn. 2008, 45, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leśniańska, K.; Perec-Matysiak, A.; Hildebrand, J.; Buńkowska-Gawlik, K.; Piróg, A.; Popiołek, M. Cryptosporidium spp. and Enterocytozoon bieneusi in introduced raccoons (Procyon lotor)—first evidence from Poland and Germany. Parasitol. Res. 2016, 115, 4535–4541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heddergott, M.; Frantz, A.C.; Pohl, D.; Osten-Sacken, N.; Steinbach, P. Detection of cryptosporidium spp. Infection in wild raccoons (Procyon lotor) from Luxembourg using an ELISA approach. Acta Parasitol. 2020, 65, 985–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popiołek, M.; Szczęsna-Staśkiewicz, J.; Bartoszewicz, M.; Okarma, H.; Smalec, B.; Zalewski, A. Helminth Parasites of an introduced invasive carnivore species, the raccoon (Procyon lotor L.), from the Warta Mouth National Park (Poland). J. Parasitol. 2011, 97, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildebrand, J.; Buńkowska-Gawlik, K.; Adamczyk, M.; Gajda, E.; Merta, D.; Popiołek, M.; Perec-Matysiak, A. The occurrence of Anaplasmataceae in European populations of invasive carnivores. Ticks Tick-borne Dis. 2018, 9, 934–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helle, E.; Kauhala, K. Distribution history and present status of the raccoon dog in Finland. Ecography 1991, 14, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurimaa, L.; Moks, E.; Soe, E.; Valdmann, H.; Saarma, U. Echinococcus multilocularis and other zoonotic parasites in red foxes in Estonia. Parasitology 2016, 143, 1450–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasanen-Mortensen, M.; Pyykönen, M.; Elmhagen, B. Where lynx prevail, foxes will fail-limitation of a mesopredator in Eurasia. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2013, 22, 868–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šálek, M.; Drahníková, L.; Tkadlec, E. Changes in home range sizes and population densities of carnivore species along the natural to urban habitat gradient. Mammal Rev. 2015, 45, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, I.M.; Fayer, R.; Lal, A.A.; Trout, J.M.; Schaefer, F.W., 3rd; Xiao, L. Molecular characterization of microsporidia indicates that wild mammals harbor host-adapted Enterocytozoon spp. as well as human-pathogenic Enterocytozoon bieneusi. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 4495–4501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, Y.; Alderisio, K.A.; Yang, W.; Cama, V.; Feng, Y.; Xiao, L. Host specificity and source of Enterocytozoon bieneusi genotypes in a drinking source watershed. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhang, S.; Tao, W.; Wan, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Li, W. Widespread presence of human-pathogenic Enterocytozoon bieneusi genotype D in farmed foxes (Vulpes vulpes) and raccoon dogs (Nyctereutes procyonoides) in China: First identification and zoonotic concern. Parasitol. Res. 2015, 114, 4341–4348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Zhang, W.; Yang, Z.; Liu, A.; Zhang, L.; Yang, F.; Wang, R.; Ling, H. Genotyping of Enterocytozoon bieneusi in farmed blue foxes (Alopex lagopus) and raccoon dogs (Nyctereutes procyonoides) in China. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143992. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.-X.; Cong, W.; Lou, Z.-L.; Ma, J.-G.; Zheng, W.-B.; Yao, Q.-X.; Zhao, Q.; Zhu, X.-Q. Prevalence, risk factors and multilocus genotyping of Enterocytozoon bieneusi in farmed foxes (Vulpes lagopus), Northern China. Parasites Vectors 2016, 9, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, C.; Ma, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.X.; Zhao, J.P.; Ba, H.X.; Du, R.; Xing, X.M.; Wang, Q.K.; Zhao, Q. Prevalence, risk factors and molecular characterization of Enterocytozoon bieneusi in raccoon dogs (Nyctereutes procyonoides) in five provinces of Northern China. Acta Trop. 2016, 161, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amer, S.; Kim, S.; Han, J.I.; Na, K.J. Prevalence and genotypes of Enterocytozoon bieneusi in wildlife in Korea: A public health concern. Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.Y.; Ma, Y.T.; Nie, L.B.; Li, T.S.; Peng, J.J.; Cong, W.; Zou, Y.; Zhu, X.Q. Prevalence and genotype distribution of Enterocytozoon bieneusi in farmed raccoon dogs (Nyctereutes procyonoides) in Shandong Province, eastern China. Parasitol. Res. 2020, 119, 1873–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xin, L.; Zhao, A.; Xu, C.; Wang, T.; Jing, B.; Qi, M. Molecular detection and genotypes of Enterocytozoon bieneusi in farmed mink (Neovison vison), blue foxes (Alopex lagopus), and raccoon dogs (Nyctereutes procyonoides) in Xinjiang, China. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2021, 14, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galván-Díaz, A.L.; Magnet, A.; Fenoy, S.; Henriques-Gil, N.; Haro, M.; Gordo, F.P.; Millán, J.; Miró, G.; del Águila, C.; Izquierdo, F. Microsporidia detection and genotyping study of human pathogenic Enterocytozoon bieneusi in animals from Spain. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santín, M.; Calero-Bernal, R.; Carmena, D.; Mateo, M.; Balseiro, A.; Barral, M.; Lima Barbero, J.F.; Habela, M.Á. Molecular characterization of Enterocytozoon bieneusi in wild carnivores in Spain. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2018, 65, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wandeler, P.; Funk, S.M.; Largiadèr, C.R.; Gloor, S.; Breitenmoser, U. The city-fox phenomenon: Genetic consequences of a recent colonization of urban habitat. Mol. Ecol. 2003, 12, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauhala, K.; Holmala, K.; Lammers, W.; Schregel, J. Home ranges and densities of medium-sized carnivores in south-east Finland, with special reference to rabies spread. Acta Thériol. 2006, 51, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Němejc, K.; Sak, B.; Květoňová, D.; Hanzal, V.; Janiszewski, P.; Forejtek, P.; Rajský, D.; Kotková, M.; Ravaszová, P.; McEvoy, J.; et al. Prevalence and diversity of Encephalitozoon spp. and Enterocytozoon bieneusi in wild boars (Sus scrofa) in Central Europe. Parasitol. Res. 2014, 113, 761–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torchin, M.E.; Mitchell, C.E. Parasites, pathogens and invasions by plants and animals. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2004, 2, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santín, M.; Fayer, R. Microsporidiosis: Enterocytozoon bieneusi in domesticated and wild animals. Res. Vet. Sci. 2011, 90, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckholt, M.A.; Lee, J.H.; Tzipori, S. Prevalence of Enterocytozoon bieneusi in swine: An 18-month survey at a slaughterhouse in Massachusetts. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 2595–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K.; Mega, X. MEGA X: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Carnivore Species | Collection Country | No. Examined/ No. Positive (%) | E. bieneusi Genotypes | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raccoon Procyon lotor | USA–native | 55/15 (27.3) | D (1), WL1 (4), WL2 (2), WL3 (1), WL15 [syn. WL16] (4), EbpC [syn. WL17] (3) | Sulaiman et al., 2003 [21] |
| USA–native | 22/18 (81.8) | WL4 (8), WW6 (7), Peru11 (1), WL24 (1), WL26 (1) | Guo et al., 2014 [22] | |
| Germany–invasive (wild) | 17/0 | - | Leśniańska et al., 2016 [13] | |
| Poland–invasive (wild) | 32/2 (6.3) | NCF2 (2) | Leśniańska et al., 2016 [13] | |
| Poland–invasive (wild) | 65/15 (23) | D (4), NCF2 (11) | This study | |
| Raccoon dog Nyctereutes procyonoides | China–native (farmed) | 39/1 (2.6) | EbpA (1) | Zhang et al., 2021 [29] |
| China–native (farmed) | 305/68 (22.3) | D (9), CHN-DC1 (9), NCF2 (32), CHN-F1 (3), NCR2 (5), NCR1 (2) | Xu et al., 2016 [26] | |
| China–native (farmed) | 49/2 (4.1) | D (1), CHN-R1 (1) | Zhao et al., 2015 [24] | |
| China–native (farmed) | 162/17 (10.5) | CHN-DC1 (2), D (14), WildBoar3 (1) | Yang et al., 2015 [23] | |
| China–native (farmed) | 356/23 (6.5) | CHG1 (1), D (8), Peru8 (3), Type IV (11) | Ma et al., 2020 [28] | |
| Korea–native (wildlife center) | 48/17 (35.4) | Korea-WL1 (8), Korea-WL2 (6), Korea-WL3 (1), Korea-D (6) | Amer et al., 2019 [27] | |
| Poland–invasive (wild) | 86/35 (40.2) | NCF2 (35) | This study | |
| Red fox Vulpes vulpes | USA (wild) | 67/9 (13.4) | D (2), WL11 (1), EbpC [syn. WL13] (3), WL15 (3) | Sulaiman et al., 2003 [21] |
| Spain (wild) | 7/1 (14.3) | D (1) | Galván-Díaz et al., 2014 [30] | |
| Spain (wild) | 87/8 (9.2) | NCF2 (6), EbCar4 (1), S9 (1) | Santin et al., 2018 [31] | |
| China (farmed) | 191/53 (27.7) | D (53) | Yang et al., 2015 [23] | |
| Poland (wild) | 50/15 (30) | NCF2 (12), D (2), C (1) | This study | |
| European badger Meles meles | Spain (wild) | 69/16 (23.2) | PtEbIX (1), EbCar2 (5), NCF2 (4), S5 (5), EbCar3 (1), | Santin et al., 2018 [31] |
| Poland (wild) | 45/12 (26.7) | EbCar2 (12) | This study | |
| Pine marten Martes martes | Poland (wild) | 24/4 (16.7) | NCF2 (4) | This study |
| Beech marten Martes foina | Spain (wild) | 9/1 (11.1) | EbCar 1 (1) | Santin et al., 2018 [31] |
| Poland (wild) | 51/7 (13.7) | NCF2 (5), Type IV (2) | This study |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Perec-Matysiak, A.; Leśniańska, K.; Buńkowska-Gawlik, K.; Merta, D.; Popiołek, M.; Hildebrand, J. Zoonotic Genotypes of Enterocytozoon bieneusi in Wild Living Invasive and Native Carnivores in Poland. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1478. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10111478
Perec-Matysiak A, Leśniańska K, Buńkowska-Gawlik K, Merta D, Popiołek M, Hildebrand J. Zoonotic Genotypes of Enterocytozoon bieneusi in Wild Living Invasive and Native Carnivores in Poland. Pathogens. 2021; 10(11):1478. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10111478
Chicago/Turabian StylePerec-Matysiak, Agnieszka, Kinga Leśniańska, Katarzyna Buńkowska-Gawlik, Dorota Merta, Marcin Popiołek, and Joanna Hildebrand. 2021. "Zoonotic Genotypes of Enterocytozoon bieneusi in Wild Living Invasive and Native Carnivores in Poland" Pathogens 10, no. 11: 1478. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10111478
APA StylePerec-Matysiak, A., Leśniańska, K., Buńkowska-Gawlik, K., Merta, D., Popiołek, M., & Hildebrand, J. (2021). Zoonotic Genotypes of Enterocytozoon bieneusi in Wild Living Invasive and Native Carnivores in Poland. Pathogens, 10(11), 1478. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10111478