Molecular Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Human and Food Samples in Northern Algeria
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Ethical Statement
2.3. Isolation of Staphylococcus spp.
2.4. MALDI-TOF MS Identification
2.5. Molecular Identification of Staphylococcus spp.
2.6. DNA Microarray Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lindsay, J.A.; Holden, M.T. Understanding the rise of the superbug: Investigation of the evolution and genomic variation of Staphylococcus aureus. Funct Integr Genom. 2006, 6, 186–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tristan, A.; Rasigade, J.P.; Ruizendaal, E.; Laurent, F.; Bes, M.; Meugnier, H.; Lina, G.; Etienne, J.; Celard, M.; Tattevin, P.; et al. Rise of CC398 lineage of Staphylococcus aureus among Infective endocarditis isolates revealed by two consecutive population-based studies in France. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Le Loir, Y.; Baron, F.; Gautier, M. Staphylococcus aureus and food poisoning. Genet. Mol. Res. 2003, 2, 63–76. [Google Scholar]
- Foster, T.J.; Geoghegan, J.A.; Ganesh, V.K.; Hook, M. Adhesion, invasion and evasion: The many functions of the surface proteins of Staphylococcus aureus. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 12, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Otto, M. Staphylococcus aureus toxins. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2014, 17, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palavecino, E.L. Clinical, epidemiologic, and laboratory aspects of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 661–664. [Google Scholar]
- Bosch, T.; Pluister, G.N.; van Luit, M.; Landman, F.; van Santen-Verheuvel, M.; Schot, C.; Witteveen, S.; van der Zwaluw, K.; Heck, M.E.; Schouls, L.M. Multiple-locus variable number tandem repeat analysis is superior to spa typing and sufficient to characterize MRSA for surveillance purposes. Future Microbiol. 2015, 10, 1155–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Adawy, H.; Ahmed, M.; Hotzel, H.; Monecke, S.; Schulz, J.; Hartung, J.; Ehricht, R.; Neubauer, H.; Hafez, H.M. Characterization of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolated from healthy turkeys and broilers using DNA microarrays. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMillan, K.; Moore, S.C.; McAuley, C.M.; Fegan, N.; Fox, E.M. Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from raw milk sources in Victoria, Australia. BMC Microbiol. 2016, 16, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monecke, S.; Kuhnert, P.; Hotzel, H.; Slickers, P.; Ehricht, R. Microarray based study on virulence-associated genes and resistance determinants of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from cattle. Vet. Microbiol. 2007, 125, 128–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefani, S.; Chung, D.R.; Lindsay, J.A.; Friedrich, A.W.; Kearns, A.M.; Westh, H.; Mackenzie, F.M. Meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA): Global epidemiology and harmonisation of typing methods. Int J. Antimicrob Agents. 2012, 39, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, S.S.; Otto, M. Improved understanding of factors driving methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus epidemic waves. Clin. Epidemiol. 2013, 5, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Armand-Lefevre, L.; Ruimy, R.; Andremont, A. Clonal comparison of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from healthy pig farmers, human controls, and pigs. Emerg Infect. Dis. 2005, 11, 711–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.C.; Pearson, N. The emergence of Staphylococcus aureus ST398. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2011, 11, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djoudi, F.; Bonura, C.; Benallaoua, S.; Touati, A.; Touati, D.; Aleo, A.; Cala, C.; Fasciana, T.; Mammina, C. Panton-Valentine leukocidin positive sequence type 80 methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus carrying a staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec type IVc is dominant in neonates and children in an Algiers hospital. New Microbiol. 2013, 36, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Enany, S.; Yaoita, E.; Yoshida, Y.; Enany, M.; Yamamoto, T. Molecular characterization of Panton-Valentine leukocidin-positive community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates in Egypt. Microbiol Res. 2010, 165, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariem, B.J.; Ito, T.; Zhang, M.; Jin, J.; Li, S.; Ilhem, B.B.; Adnan, H.; Han, X.; Hiramatsu, K. Molecular characterization of methicillin-resistant Panton-valentine leukocidin positive Staphylococcus aureus clones disseminating in Tunisian hospitals and in the community. BMC Microbiol. 2013, 13, 1471–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tenover, F.C.; McDougal, L.K.; Goering, R.V.; Killgore, G.; Projan, S.J.; Patel, J.B.; Dunman, P.M. Characterization of a strain of community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus widely disseminated in the United States. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coombs, G.W.; Goering, R.V.; Chua, K.Y.L.; Monecke, S.; Howden, B.P.; Stinear, T.P.; Ehricht, R.; O’Brien, F.G.; Christiansen, K.J. The molecular epidemiology of the highly virulent ST93 Australian community Staphylococcus aureus strain. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cuny, C.; Friedrich, A.; Kozytska, S.; Layer, F.; Nubel, U.; Ohlsen, K.; Strommenger, B.; Walther, B.; Wieler, L.; Witte, W. Emergence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in different animal species. Int J. Med. Microbiol. 2010, 300, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, J.M.; Lloyd, D.H.; Lindsay, J.A. Staphylococcus aureus host specificity: Comparative genomics of human versus animal isolates by multi-strain microarray. Microbiol. 2008, 154, 1949–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Voss, A.; Loeffen, F.; Bakker, J.; Klaassen, C.; Wulf, M. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in pig farming. Emerg Infect. Dis. 2005, 11, 1965–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandenesch, F.; Naimi, T.; Enright, M.C.; Lina, G.; Nimmo, G.R.; Heffernan, H.; Liassine, N.; Bes, M.; Greenland, T.; Reverdy, M.E.; et al. Community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus carrying Panton-Valentine leukocidin genes: Worldwide emergence. Emerg Infect. Dis. 2003, 9, 978–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, L.G.; Perdreau-Remington, F.; Rieg, G.; Mehdi, S.; Perlroth, J.; Bayer, A.S.; Tang, A.W.; Phung, T.O.; Spellberg, B. Necrotizing fasciitis caused by community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Los Angeles. N Engl J. Med. 2005, 352, 1445–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Antri, K.; Rouzic, N.; Dauwalder, O.; Boubekri, I.; Bes, M.; Lina, G.; Vandenesch, F.; Tazir, M.; Ramdani-Bouguessa, N.; Etienne, J. High prevalence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus clone ST80-IV in hospital and community settings in Algiers. Clin. Microbiol Infect. 2011, 17, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wangai, F.K.; Masika, M.M.; Maritim, M.C.; Seaton, R.A. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in East Africa: Red alert or red herring? BMC Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conceição, T.; Santos Silva, I.; de Lencastre, H.; Aires-de-Sousa, M. Staphylococcus aureus nasal carriage among patients and health care workers in São Tomé and Príncipe. Microb Drug Resist. 2014, 20, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egyir, B.; Guardabassi, L.; Sørum, M.; Nielsen, S.S.; Kolekang, A.; Frimpong, E.; Addo, K.K.; Newman, M.J.; Larsen, A.R. Molecular epidemiology and antimicrobial susceptibility of clinical Staphylococcus aureus from healthcare institutions in Ghana. PloS one. 2014, 9, e89716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shittu, A.O.; Oyedara, O.; Abegunrin, F.; Okon, K.; Raji, A.; Taiwo, S.; Ogunsola, F.; Onyedibe, K.; Elisha, G. Characterization of methicillin-susceptible and -resistant staphylococci in the clinical setting: A multicentre study in Nigeria. BMC Infect. Dis. 2012, 12, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oosthuysen, W.F.; Orth, H.; Lombard, C.; Sinha, B.; Wasserman, E. In vitro characterization of representative clinical South African Staphylococcus aureus isolates from various clonal lineages. New Microbe New Infect. 2014, 2, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdulgader, S.M.; Shittu, A.O.; Nicol, M.P.; Kaba, M. Molecular epidemiology of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Africa: A systematic review. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozano, C.; Gharsa, H.; Ben Slama, K.; Zarazaga, M.; Torres, C. Staphylococcus aureus in animals and food: Methicillin resistance, prevalence and population structure. A Review in the African Continent. Microorganisms. 2016, 4, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gharsa, H.; Ben Slama, K.; Lozano, C.; Gómez-Sanz, E.; Klibi, N.; Ben Sallem, R.; Gómez, P.; Zarazaga, M.; Boudabous, A.; Torres, C. Prevalence, antibiotic resistance, virulence traits and genetic lineages of Staphylococcus aureus in healthy sheep in Tunisia. Vet. Microbiol. 2012, 156, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaumburg, F.; Pauly, M.; Anoh, E.; Mossoun, A.; Wiersma, L.; Schubert, G.; Flammen, A.; Alabi, A.S.; Muyembe-Tamfum, J.J.; Grobusch, M.P.; et al. Staphylococcus aureus complex from animals and humans in three remote African regions. Clin. Microbiol Infect. 2015, 21, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agabou, A.; Ouchenane, Z.; Ngba Essebe, C.; Khemissi, S.; Chehboub, M.T.E.; Chehboub, I.B.; Sotto, A.; Dunyach-Remy, C.; Lavigne, J.P. Emergence of nasal carriage of ST80 and ST152 PVL+ Staphylococcus aureus isolates from livestock in Algeria. Toxins. 2017, 9, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- El-Ashker, M.; Gwida, M.; Tomaso, H.; Monecke, S.; Ehricht, R.; El-Gohary, F.; Hotzel, H. Staphylococci in cattle and buffaloes with mastitis in Dakahlia Governorate, Egypt. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 7450–7459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Djahmi, N.; Messad, N.; Nedjai, S.; Moussaoui, A.; Mazouz, D.; Richard, J.L.; Sotto, A.; Lavigne, J.P. Molecular epidemiology of Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from inpatients with infected diabetic foot ulcers in an Algerian University Hospital. Clin. Microbiol Infect. 2013, 19, E369–E404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Achek, R.; El-Adawy, H.; Hotzel, H.; Tomaso, H.; Ehricht, R.; Hamdi, T.M.; Azzi, O.; Monecke, S. Short communication: Diversity of staphylococci isolated from sheep mastitis in northern Algeria. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 890–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akkou, M.; Bentayeb, L.; Ferdji, K.; Medrouh, B.; Bachtarzi, M.A.; Ziane, H.; Kaidi, R.; Tazir, M. Phenotypic characterization of staphylococci causing mastitis in goats and microarray-based genotyping of Staphylococcus aureus isolates. Small Ruminant Res. 2018, 169, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titouche, Y.; Hakem, A.; Houali, K.; Meheut, T.; Vingadassalon, N.; Ruiz-Ripa, L.; Salmi, D.; Chergui, A.; Chenouf, N.; Hennekinne, J.A.; et al. Emergence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) ST8 in raw milk and traditional dairy products in the Tizi Ouzou area of Algeria. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 6876–6884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denis, F.; Ploy, M.C.; Martin, C.; Bingen, E.; Quentin, R. Bactériologie Médicale: Techniques Usuelles, 3rd ed.; Elsevier Masson SAS: Issy-les-Moulineaux, France, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Oliver, S.P.; Gonzalez, R.N.; Hogan, J.S.; Jayarao, M.; Owens, W.E. Microbiological Procedures for the Diagnosis of Bovine Udder Infection and Determination of Milk Quality, 4th ed.; Council, N.M., Ed.; National Mastitis Council NMC Inc.: Verona, MN, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Karmakar, A.; Dua, P.; Ghosh, C. Biochemical and molecular analysis of Staphylococcus aureus clinical isolates from hospitalized patients. Can. J. Infect. Dis Med. Microbiol. 2016, 9041636, 24. [Google Scholar]
- ISO. Microbiology of food and animal feeding stuffs — Horizontal method for the enumeration of coagulase-positive staphylococci (Staphylococcus aureus and other species) — Part 1: Technique using Baird-Parker agar medium; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Bizzini, A.; Greub, G. Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry, a revolution in clinical microbial identification. Clin. Microbiol Infect. 2010, 16, 1614–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.Y.; Kim, S.; Kim, J.; Park, S.D.; Uh, Y.; Lee, H. Multiplex real-time PCR assay for rapid detection of methicillin-resistant staphylococci directly from positive blood cultures. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 1911–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monecke, S.; Ehricht, R. Rapid genotyping of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) isolates using miniaturised oligonucleotide arrays. Clin. Microbiol Infect. 2005, 11, 825–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Strauß, L.; Ruffing, U.; Abdulla, S.; Alabi, A.; Akulenko, R.; Garrine, M.; Germann, A.; Grobusch, M.P.; Helms, V.; Herrmann, M.; et al. Detecting Staphylococcus aureus virulence and resistance genes: A comparison of whole-genome sequencing and DNA microarray technology. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 1008–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monecke, S.; Slickers, P.; Ehricht, R. Assignment of Staphylococcus aureus isolates to clonal complexes based on microarray analysis and pattern recognition. FEMS Immunol Med. Microbiol. 2008, 53, 237–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Krzywinski, M.; Schein, J.; Birol, I.; Connors, J.; Gascoyne, R.; Horsman, D.; Jones, S.J.; Marra, M.A. Circos: An information aesthetic for comparative genomics. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 1639–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lozano, C.; López, M.; Gómez-Sanz, E.; Ruiz-Larrea, F.; Torres, C.; Zarazaga, M. Detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus ST398 in food samples of animal origin in Spain. J. Antimicrob Chemother. 2009, 64, 1325–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mairi, A.; Touati, A.; Pantel, A.; Zenati, K.; Martinez, A.Y.; Dunyach-Remy, C.; Sotto, A.; Lavigne, J.P. Distribution of toxinogenic methicillin-resistant and methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus from different ecological niches in Algeria. Toxins. 2019, 11, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pu, S.; Han, F.; Ge, B. Isolation and characterization of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains from Louisiana retail meats. Appl Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 265–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Olaniyi, R.; Pozzi, C.; Grimaldi, L.; Bagnoli, F. Staphylococcus aureus-associated skin and soft tissue infections: Anatomical localization, epidemiology, therapy and potential prophylaxis. Curr Top. Microbiol Immunol. 2017, 409, 199–227. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Akkou, M.; Bouchiat, C.; Antri, K.; Bes, M.; Tristan, A.; Dauwalder, O.; Martins-Simoes, P.; Rasigade, J.P.; Etienne, J.; Vandenesch, F.; et al. New host shift from human to cows within Staphylococcus aureus involved in bovine mastitis and nasal carriage of animal’s caretakers. Vet. Microbiol. 2018, 223, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hata, E.; Katsuda, K.; Kobayashi, H.; Uchida, I.; Tanaka, K.; Eguchi, M. Genetic variation among Staphylococcus aureus strains from bovine milk and their relevance to methicillin-resistant isolates from humans. Journal of clinical microbiology 2010, 48, 2130–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pantosti, A. Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Associated with Animals and Its Relevance to Human Health. Frontiers in microbiology 2012, 3, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luedicke, C.; Slickers, P.; Ehricht, R.; Monecke, S. Molecular fingerprinting of Staphylococcus aureus from bone and joint infections. Eur J. Clin. Microbiol Infect. Dis. 2010, 29, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monecke, S.; Coombs, G.; Shore, A.C.; Coleman, D.C.; Akpaka, P.; Borg, M.; Chow, H.; Ip, M.; Jatzwauk, L.; Jonas, D.; et al. A field guide to pandemic, epidemic and sporadic clones of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, 0017936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, T.; Kock, M.M.; Ehlers, M.M. Molecular characterization of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from bovine mastitis and close human contacts in South African dairy herds: Genetic diversity and inter-species host transmission. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, S.; Huang, J.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, F.; Yang, X.; Wu, H.; Zeng, H.; Chen, M.; Ding, Y.; et al. Staphylococcus aureus Isolated From Retail Meat and Meat Products in China: Incidence, Antibiotic Resistance and Genetic Diversity. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar-Gal, G.K.; Blum, S.E.; Hadas, L.; Ehricht, R.; Monecke, S.; Leitner, G. Host-specificity of Staphylococcus aureus causing intramammary infections in dairy animals assessed by genotyping and virulence genes. Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 176, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamil, B.; Gawlik, D.; Syed, M.A.; Shah, A.A.; Abbasi, S.A.; Müller, E.; Reißig, A.; Ehricht, R.; Monecke, S. Hospital-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) from Pakistan: Molecular characterisation by microarray technology. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases 2018, 37, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fessler, A.T.; Kadlec, K.; Hassel, M.; Hauschild, T.; Eidam, C.; Ehricht, R.; Monecke, S.; Schwarz, S. Characterization of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates from food and food products of poultry origin in Germany. Appl Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 7151–7157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ogata, K.; Narimatsu, H.; Suzuki, M.; Higuchi, W.; Yamamoto, T.; Taniguchi, H. Commercially distributed meat as a potential vehicle for community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Appl Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 2797–2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petinaki, E.; Spiliopoulou, I. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus among companion and food-chain animals: Impact of human contacts. Clin. Microbiol Infect. 2012, 18, 626–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bekkhoucha, S.N.; Cady, A.; Gautier, P.; Itim, F.; Donnio, P.Y. A portrait of Staphylococcus aureus from the other side of the Mediterranean Sea: Molecular characteristics of isolates from Western Algeria. Eur J. Clin. Microbiol Infect. Dis 2009, 28, 553–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben Nejma, M.; Mastouri, M.; Bel Hadj Jrad, B.; Nour, M. Characterization of ST80 Panton-Valentine leukocidin-positive community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus clone in Tunisia. Diagn Microbiol Infect. Dis. 2013, 77, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udo, E.E.; O’Brien, F.G.; Al-Sweih, N.; Noronha, B.; Matthew, B.; Grubb, W.B. Genetic lineages of community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Kuwait hospitals. J. Clin. Microbiol 2008, 46, 3514–3516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Knight, G.M.; Budd, E.L.; Whitney, L.; Thornley, A.; Al-Ghusein, H.; Planche, T.; Lindsay, J.A. Shift in dominant hospital-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (HA-MRSA) clones over time. J. Antimicrob Chemother. 2012, 67, 2514–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Price, L.B.; Stegger, M.; Hasman, H.; Aziz, M.; Larsen, J.; Andersen, P.S.; Pearson, T.; Waters, A.E.; Foster, J.T.; Schupp, J.; et al. Staphylococcus aureus CC398: Host adaptation and emergence of methicillin resistance in livestock. mBio. 2012, 3, 00305–00311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Witte, W.; Strommenger, B.; Stanek, C.; Cuny, C. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus ST398 in humans and animals, Central Europe. Emerg Infect. Dis 2007, 13, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuny, C.; Wieler, L.H.; Witte, W. Livestock-associated MRSA: The impact on humans. Antibiotics. 2015, 4, 521–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knox, J.; Uhlemann, A.; Lowy, F.D. Staphylococcus aureus infections: Transmission within households and the community. Trends Microbiol. 2015, 23, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Herron-Olson, L.; Fitzgerald, J.R.; Musser, J.M.; Kapur, V. Molecular correlates of host specialization in Staphylococcus aureus. PLoS ONE. 2007, 2, e1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monecke, S.; Luedicke, C.; Slickers, P.; Ehricht, R. Molecular epidemiology of Staphylococcus aureus in asymptomatic carriers. Eur J. Clin. Microbiol Infect. Dis. 2009, 28, 1159–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melles, D.C.; Tenover, F.C.; Kuehnert, M.J.; Witsenboer, H.; Peeters, J.K.; Verbrugh, H.A.; van Belkum, A. Overlapping population structures of nasal isolates of Staphylococcus aureus from healthy Dutch and American individuals. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Basanisi, M.G.; La Bella, G.; Nobili, G.; Franconieri, I.; La Salandra, G. Genotyping of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) isolated from milk and dairy products in South Italy. Food Microbiol. 2017, 62, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Woolhouse, M.; Ward, M.; van Bunnik, B.; Farrar, J. Antimicrobial resistance in humans, livestock and the wider environment. Philos Trans. R Soc. Lond B Biol Sci 2015, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlotter, K.; Ehricht, R.; Hotzel, H.; Monecke, S.; Pfeffer, M.; Donat, K. Leukocidin genes lukF-P83 and lukM are associated with Staphylococcus aureus clonal complexes 151, 479 and 133 isolated from bovine udder infections in Thuringia, Germany. Vet. Res. 2012, 43, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boss, R.; Cosandey, A.; Luini, M.; Artursson, K.; Bardiau, M.; Breitenwieser, F.; Hehenberger, E.; Lam, T.; Mansfeld, M.; Michel, A.; et al. Bovine Staphylococcus aureus: Subtyping, evolution, and zoonotic transfer. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 515–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Käppeli, N.; Morach, M.; Corti, S.; Eicher, C.; Stephan, R.; Johler, S. Staphylococcus aureus related to bovine mastitis in Switzerland: Clonal diversity, virulence gene profiles, and antimicrobial resistance of isolates collected throughout 2017. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 3274–3281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jørgensen, H.J.; Mathisen, T.; Løvseth, A.; Omoe, K.; Qvale, K.S.; Loncarevic, S. An outbreak of staphylococcal food poisoning caused by enterotoxin H in mashed potato made with raw milk. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2005, 252, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dinges, M.M.; Orwin, P.M.; Schlievert, P.M. Exotoxins of Staphylococcus aureus. Clin. Microbiol Rev. 2000, 13, 16–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arciola, C.R.; Campoccia, D.; Ravaioli, S.; Montanaro, L. Polysaccharide intercellular adhesin in biofilm: Structural and regulatory aspects. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2015, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mirani, Z.A.; Aziz, M.; Khan, M.N.; Lal, I.; Hassan, N.U.; Khan, S.I. Biofilm formation and dispersal of Staphylococcus aureus under the influence of oxacillin. Microb Pathog. 2013, 62, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.J.; Oh, D.H.; Song, B.R.; Heo, E.J.; Lim, J.S.; Moon, J.S.; Park, H.J.; Wee, S.H.; Sung, K. Molecular characterization, antibiotic resistance, and virulence factors of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from imported and domestic meat in Korea. Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2015, 12, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parisi, A.; Caruso, M.; Normanno, G.; Latorre, L.; Sottili, R.; Miccolupo, A.; Fraccalvieri, R.; Santagada, G. Prevalence, antimicrobial susceptibility and molecular typing of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in bulk tank milk from southern Italy. Food Microbiol. 2016, 58, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesah, C.; Ben Redjeb, S.; Odugbemi, T.O.; Boye, C.S.; Dosso, M.; Ndinya Achola, J.O.; Koulla-Shiro, S.; Benbachir, M.; Rahal, K.; Borg, M. Prevalence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in eight African hospitals and Malta. Clin. Microbiol Infect. 2003, 9, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alioua, M.A.; Labid, A.; Amoura, K.; Bertine, M.; Gacemi-Kirane, D.; Dekhil, M. Emergence of the European ST80 clone of community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus as a cause of healthcare-associated infections in Eastern Algeria. Med. Mal. Infect. 2014, 44, 180–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouchenane, Z.; Smati, F.; Rolain, J.M.; Raoult, D. Molecular characterization of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates in Algeria. Pathologie Biologie 2011, 59, e129–e132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebiahi, S.A.; Abdelouahid, D.E.; Rahmoun, M.; Abdelali, S.; Azzaoui, H. Emergence of vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus identified in the Tlemcen university hospital (North-West Algeria). Med. Mal. Infect. 2011, 41, 646–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barour, D.; Berghiche, A.; Boulebda, N. Antimicrobial resistance of Escherichia coli isolates from cattle in Eastern Algeria. Vet. World. 2019, 12, 1195–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benrabia, I.; Hamdi, T.M.; Shehata, A.A.; Neubauer, H.; Wareth, G. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in poultry species in Algeria: Long-term study on prevalence and antimicrobial resistance. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dermota, U.; Jurca, T.; Harlander, T.; Košir, M.; Zajc, U.; Golob, M.; Zdovc, I.; Košnik, I.G. Infections caused by community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus European clone (ST80) in Slovenia between 2006 And 2013. Zdr Varst. 2016, 55, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Larsen, A.R.; Böcher, S.; Stegger, M.; Goering, R.; Pallesen, L.V.; Skov, R. Epidemiology of european community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus clonal complex 80 type IV strains isolated in Denmark from 1993 to 2004. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
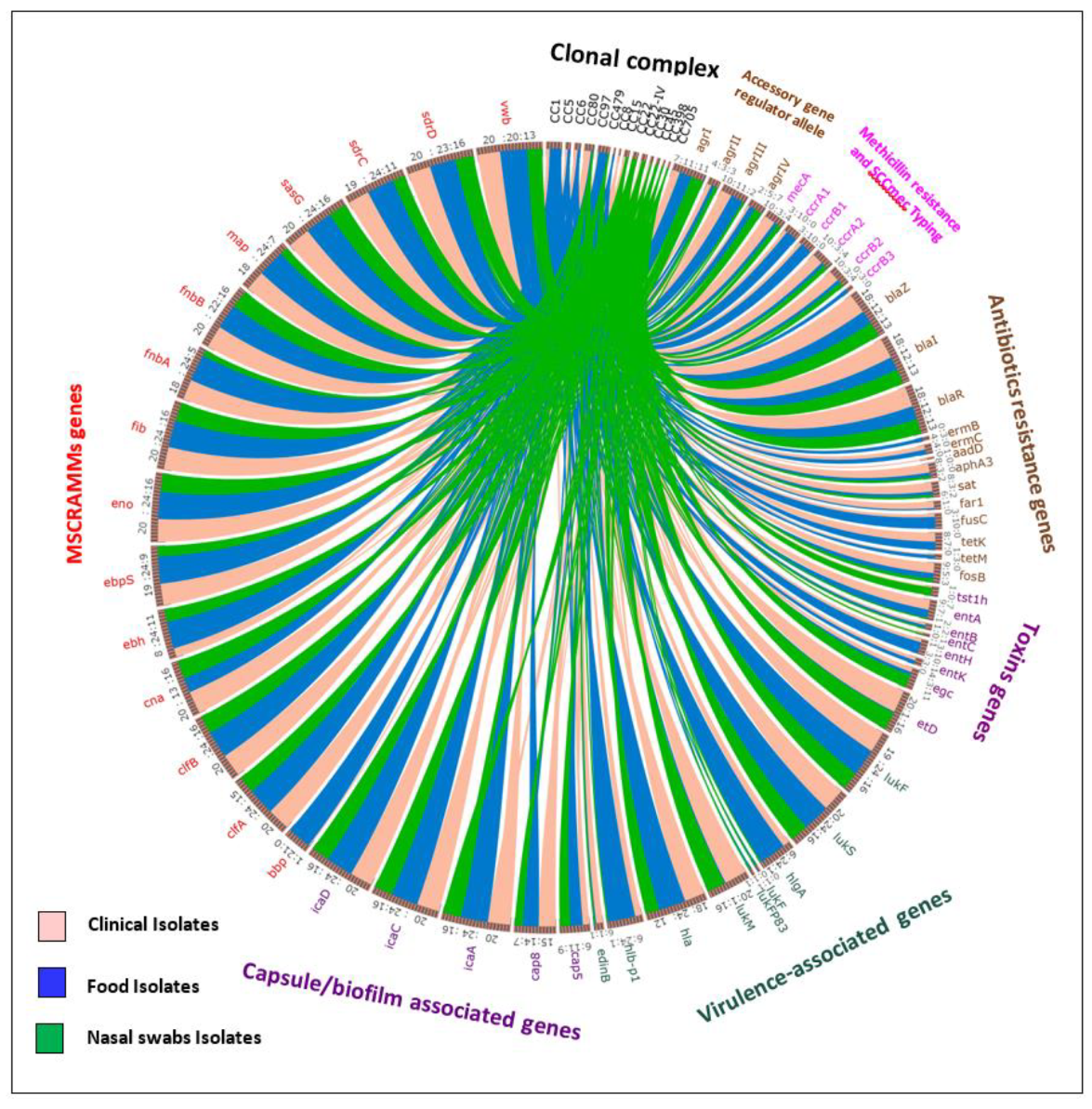
| Clonal Complex | Source of Isolates | Total CC | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Samples | Food Samples | Nasal Swabs | |||||||
| Source | Isolates Number | Total | Source | Isolates Number | Total | Isolates Number | Total | ||
| CC1-MSSA | Blood culture | 1 | 3 | Raw milk | 4 | 10 | - | - | 13 |
| Pus | 1 | Chicken meat | 1 | ||||||
| Surgical wound | 1 | Minced beef meat | 4 | ||||||
| Sausages | 1 | ||||||||
| CC5-MSSA | Urine | 1 | 2 | Minced beef meat | 2 | 2 | - | - | 4 |
| Vaginal discharge | 1 | ||||||||
| CC6-MRSA IV | Catheter | 2 | 3 | Minced beef meat | 2 | 2 | - | - | 5 |
| Pus | 1 | ||||||||
| CC80-MRSA IV | Sperm | 1 | 6 | Minced beef meat | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 8 |
| Pus | 4 | ||||||||
| Urine | 1 | ||||||||
| CC97-MSSA | Throat fluid | 1 | 1 | Creamy cake | 2 | 8 | 1 | 1 | 10 |
| Raw milk | 5 | ||||||||
| Minced beef meat | 1 | ||||||||
| CC15-MSSA | Pus | 2 | 2 | - | - | - | 2 | 2 | 4 |
| CC22-MRSA-IV | Pus | 1 | 1 | - | - | - | 3 | 3 | 4 |
| CC30-MSSA | Pus | 1 | 1 | - | - | - | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| CC8-MSSA | Urine | 1 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | 1 |
| CC479-MSSA | - | - | - | Raw milk | 1 | 1 | - | - | 1 |
| CC22-MSSA | - | - | - | - | - | - | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| CC398-MSSA | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| CC45-MSSA | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| CC705-MSSA | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Total | 20 | 24 | 16 | 60 | |||||
| Clonal Complex (n) | Origin * (n) | agr Group (n) | Virulence-Associated Genes | Capsule/Biofilm-Associated Genes | Toxin Genes | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| lukFS-PV | lukF-PV (P83) | luk-M | lukF-hlg | lukS-hlg | hlgA | hla | hlb | edinB | cap5 | cap8 | icaACD | sea | seb | sec | seh | sek | egc | tst1 | etD | |||
| CC1-MSSA (13) | C (3) | agr III (3) | - | - | - | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | - | - | 3 | 3 | 3 | 1 | - | 3 | 3 | - | - | - |
| F (10) | agr III (10) | - | - | - | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | - | - | 10 | 10 | 3 | - | - | 10 | 3 | - | - | - | |
| CC5-MSSA (4) | C (2) | agr III (2) | - | - | - | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | - | 2 | - | 2 | 2 | - | - | - | - | 2 | - | - |
| F (2) | agr III (2) | - | - | - | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | - | 2 | - | 2 | 2 | - | - | - | - | 2 | - | - | |
| CC6-MRSA IV | C (3) | agr I (3) | - | - | - | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | - | - | 3 | 3 | 3 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| F (2) | agr I (2) | - | - | - | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | - | - | 2 | 2 | 2 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| CC8-MSSA (1) | C (1) | agr I (1) | - | - | - | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | - | 1 | - | 1 | 1 | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - |
| CC15-MSSA (4) | C (2) | agr II (2) | - | - | - | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | - | - | - | 2 | 2 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| N (2) | agr II (2) | - | - | - | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | - | - | - | 2 | 2 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| CC22-MSSA (4) | N (4) | agr I (4) | - | - | - | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | - | 4 | - | 4 | - | - | - | - | - | 4 | 4 § | - |
| CC22-MRSA- IV (4) | C (1) | agr I (1) | - | - | - | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | - | 1 | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | 1 § | - |
| N (3) | agr I (3) | - | - | - | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 3 | - | 3 | - | 3 | - | - | - | - | - | 3 | 3 § | - | |
| CC30-MSSA(2) | C (1) | agr III (1) | - | - | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | - | - | - | 1 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | |
| N(1) | agr III (1) | - | - | - | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | - | - | 1 | 1 | 1 | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | |
| CC45-MSSA (2) | N(2) | agr I (2) | - | - | - | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | - | - | - | 2 | 2 | - | - | 1 | - | - | 2 | - | - |
| CC80-MRSA- IV (8) | C (6) | agr III (6) | 6 | - | - | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | - | 6 | 6 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 6 |
| N (1) | agr III (1) | 1 | - | - | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | - | 1 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | |
| F (1) | agr III (1) | 1 | - | - | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | - | 1 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | |
| CC97-MSSA (10) | C (1) | agr I (1) | - | - | - | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | - | 1 | - | 1 | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| N (1) | agr I (1) | - | - | - | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | - | 1 | - | 1 | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| F (8) | agr I (8) | - | - | - | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | - | 8 | - | 8 | - | 2 | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| CC398-MSSA (1) | N (1) | agr I (1) | - | - | - | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | - | 1 | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| CC479- MSSA | F (1) | agr II (1) | - | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | - | - | 1 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | 1 |
| CC705-MSSA | N (1) | agr II (1) | - | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | - | - | 1 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | - |
| Clonal Complex (n) | Origin * (n) | agr Group (n) | MSCRAMM Genes | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| bbp | clfA/B | cna | ebh | epbs | Eno | fib | fnbA | fnbB | map | sasG | sdrC | sdrD | vwb | |||
| CC1-MSSA (13) | C (3) | agr III (3) | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| F (10) | agr III (10) | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 9 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | |
| CC5-MSSA (4) | C (2) | agr III (2) | 2 | 2 | - | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| F (2) | agr III (2) | 2 | 2 | - | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | |
| CC6-MRSA IV (5) | C (3) | agr I (3) | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| F (2) | agr I (2) | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | |
| CC8-MSSA (1) | C (1) | agr I (1) | 1 | 1 | - | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| CC15-MSSA (4) | C (2) | agr II (2) | 2 | 2 | - | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| N (2) | agr II (2) | 2 | 2 | - | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | |
| CC22-MSSA (4) | N (4) | agr I (4) | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | - | 4 | - | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| CC22-MRSA- IV (4) | C (1) | agr I (1) | 1 | 1 | 1 | - | 1 | 1 | - | 1 | - | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| N (3) | agr I (3) | 3 | 3 | 3 | - | 3 | 3 | - | 3 | - | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | |
| CC30-MSSA (2) | C (1) | agr III (1) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | - | 1 | - | 1 | - | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| N(1) | agr III (1) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | - | 1 | - | 1 | - | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| CC45-MSSA (2) | N(2) | agr I (2) | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | - | 2 | 2 | 2 | - | 2 | - | 2 |
| CC80-MRSA- IV (8) | C (6) | agr III (6) | 6 | 6 | - | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| N (1) | agr III (1) | 1 | 1 | - | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| F (1) | agr III (1) | 1 | 1 | - | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| CC97-MSSA (10) | C (1) | agr I (1) | 1 | 1 | - | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| N (1) | agr I (1) | 1 | 1 | - | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| F (8) | agr I (8) | 6 | 8 | - | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 7 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | |
| CC398-MSSA (1) | N (1) | agr I (1) | - | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | - | 1 | 1 | 1 | - | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| CC479- MSSA (1) | F (1) | agr II (1) | - | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | - | 1 |
| CC705-MSSA (1) | N (1) | agr II (1) | 1 | 1 | - | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | - | 1 | - | 1 | - | 1 |
| Clonal Complex (n) * | Origin (n) * | Antimicrobial Resistance Genes (n) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mecA | SCCmec | blaZ | ermB | ermC | aphA3 | aadD | sat | fusC | far1 | tetM | tetK | fosB | ||
| CC1-MSSA (13) | F (10) | - | ccrAB1 (10) | 3 | - | - | 1 | - | 1 | 10 | - | - | - | - |
| C (3) | - | ccrAB1 (3) | 2 | - | - | - | - | - | 3 | - | 1 | 1 | - | |
| CC5-MSSA (4) | C (2) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2 |
| F (2) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2 | |
| CC6-MRSA IV (5) | C (3) | 3 | ccrAB2 (3) | 3 | - | 3 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 3 |
| F (2) | 2 | ccrAB2 (2) | 1 | - | 2 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2 | |
| CC8-MSSA (1) | C (1) | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | 1 |
| CC15-MSSA (4) | C (2) | - | - | 2 | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | 2 | 2 |
| N (2) | - | - | 2 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2 | |
| CC22-MSSA (4) | N (4) | - | - | 4 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| CC22-MRSA- IV (4) | C (1) | 1 | ccrAB2 (1) | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| N (3) | 4 | ccrAB2 (3) | 3 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| CC30-MSSA (2) | C (1) | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 |
| N (1) | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | |
| CC45-MSSA (2) | N (2) | - | - | 2 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| CC80-MRSA- IV (8) | C (6) | 6 | ccrAB2 (6) | 6 | - | 1 | 6 | - | 6 | - | 6 | - | 6 | - |
| N (1) | 1 | ccrAB2 (1) | - | - | - | 1 | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| F (1) | 1 | ccrAB2 (1) | 1 | - | 1 | 1 | - | 1 | - | 1 | - | 1 | - | |
| CC97-MSSA (10) | C (1) | - | - | 1 | - | - | 1 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| N (1) | - | - | 1 | - | - | 1 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| F (8) | - | - | 8 | 2 | - | 2 | 2 | - | - | 1 | 4 | - | ||
| CC398-MSSA (1) | N (1) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| CC479-MSSA (1) | F (1) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - |
| CC705-MSSA (1) | N (1) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Achek, R.; El-Adawy, H.; Hotzel, H.; Hendam, A.; Tomaso, H.; Ehricht, R.; Neubauer, H.; Nabi, I.; Hamdi, T.M.; Monecke, S. Molecular Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Human and Food Samples in Northern Algeria. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1276. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10101276
Achek R, El-Adawy H, Hotzel H, Hendam A, Tomaso H, Ehricht R, Neubauer H, Nabi I, Hamdi TM, Monecke S. Molecular Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Human and Food Samples in Northern Algeria. Pathogens. 2021; 10(10):1276. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10101276
Chicago/Turabian StyleAchek, Rachid, Hosny El-Adawy, Helmut Hotzel, Ashraf Hendam, Herbert Tomaso, Ralf Ehricht, Heinrich Neubauer, Ibrahim Nabi, Taha Mossadak Hamdi, and Stefan Monecke. 2021. "Molecular Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Human and Food Samples in Northern Algeria" Pathogens 10, no. 10: 1276. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10101276
APA StyleAchek, R., El-Adawy, H., Hotzel, H., Hendam, A., Tomaso, H., Ehricht, R., Neubauer, H., Nabi, I., Hamdi, T. M., & Monecke, S. (2021). Molecular Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Human and Food Samples in Northern Algeria. Pathogens, 10(10), 1276. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10101276







