Abstract
We compare the association between educational attainment and housework participation among single and married women in Japan and the US. Using the cross-sectional time-use diaries from the 2006 American Time Use Survey (ATUS) and the 2006 Japanese Survey on Time Use and Leisure Activities (STULA) and unconditional quantile regressions (UQR), we test whether educational attainment is associated with less time spent on housework in Japan compared to the US. We find that this assumption stands only for American women and non-married Japanese women. However, married Japanese women are unlikely to reduce participation in housework with an increase in their educational level. Married Japanese women are more likely to do more housework proportionately to the level of their education. The findings reveal the presence of a marriage penalty among highly educated Japanese women. In Japan, the institute of marriage places higher expectations regarding women’s housework participation on married women with higher levels of education, thereby penalising Japanese women with higher educational attainments. Our findings illustrate that the tenets of the resource-based and gender-centred frameworks developed based on the empirical findings in Western countries cannot always directly apply to the patterns observed in East Asia.
1. Introduction
Global societies are moving towards an equal division of labour (Altintas and Sullivan 2017; Kan et al. 2011; Marshall 2011; Sullivan et al. 2018) but the gains for women have been relatively slow (Treas and Lui 2013). Many triumphs in gender equality have been ascribed to women’s increased participation in the labour market and their successes in the educational system. Thus, the overall trends demonstrate that women with higher levels of educational attainment engage in housework less than women who have lower levels of education (Altintas and Sullivan 2017; Álvarez and Miles 2003; Chesters 2011; Evertsson and Nermo 2007; Fuwa and Cohen 2007; Gupta 2007; Ruppanner 2010), partially because they have better skills to negotiate housework responsibilities and mature in more egalitarian educational environments, with the normalised expectations of an equal division of housework labour at home (Altintas and Sullivan 2017).
The present study contributes to this issue by testing the association of education with housework participation in Japan, compared to the US. The paper challenges the conventional theoretical explanations of the resource-based and gender-centred frameworks in housework literature (Becker 1981; Brines 1994; Chesters 2011; Davis and Greenstein 2009; Gupta 2007; Killewald and Gough 2010; West and Zimmerman 1987). Notably, it calls for the consideration of cultural contexts where women’s educational attainments do not open enough career opportunities due to persistent structural barriers (Ruppanner 2009) and where higher levels of education do not necessarily relate to a more gender-egalitarian ideology. For women in such contexts, higher levels of education, as a resource facilitated by an espoused gender ideology, might not be associated with lower levels of housework participation. For instance, a positive association between educational attainment and housework was observed in Ueda (2005) but only noted as an anomaly without an exhaustive discussion. Earlier studies have also established that in East Asia, the likelihood of employment among highly educated women plummets after childbirth (Brinton and Oh 2019), but housework is shared more equitably among higher-educated couples on weekends (Kan and Laurie 2018).
Another contribution of the present study is establishing that education produces a differential effect on housework participation among women depending on the levels of housework participation. Education may matter at average levels of housework division but might have only subtler effects on the lower or higher levels of housework participation. Higher levels of housework participation are more likely to be over-represented by women who are not in the labour market and are stay-at-home housewives with care responsibilities. Conversely, lower levels of housework participation might be populated by women who have to work long hours, such as women on the two different sides of the earnings spectrum: professionals and the working poor.
Moreover, the present paper discusses the association of education with housework participation at different life-course stages, mainly focusing on marriage and parenthood. These stages are the major milestones of adult life and affect how much educational attainment ameliorates the necessity to do housework. Life-course stages have been studied extensively in relation to paid work and earnings. For instance, Budig et al. (2012) analysed the motherhood penalty on women’s earnings across European and North American countries and found that the penalty was significant even after controlling for individual and cultural variation. In unpaid work, previous housework literature echoes the literature on paid work, asserting that, on top of the penalties in paid work, transitions into marriage and parenthood aggravate women’s housework responsibilities (Blair and Lichter 1991; Cowan and Cowan 1992; South and Spitze 1994). Between marriage and parenthood, the latter is more strongly associated with a decrease in paid work and an increase in unpaid work than marriage (Budig and Hodges 2014; Cooke and Hook 2018).
In the present paper, we reconcile the three directions identified in the previous research by (1) examining cross-national variations, (2) differentiating by level of housework participation, and (3) analysing the association between education and housework participation on different life-course transitions. We use the unconditional quantile regression (UQR) (Firpo et al. 2009) on the American Time Use Survey (ATUS) and the Japanese Survey of Time Use and Leisure Activities (STULA) to test whether educational level produces differences in the allocation of time to housework at different levels of housework participation among non-married and married Japanese women in the same way as it does in the US.
2. The Role of Education in the Division of Housework
Education plays a vital role in the two main approaches to the explanation of the gender differences in housework participation. On the one hand, education works as an individual resource, and thus, its association with housework participation can rely on the rational choice theory. On the other hand, education plays a major part in gendering processes through the educational system. Imbued with dissimilar gendering experiences, people develop different gender practices, including those related to housework participation. Accordingly, the association between education and housework participation can also depend on the gendering processes of the educational socialisation.
2.1. Education as an Individual Resource
Similar to earnings and wealth, education represents an individual resource. From the household specialisation perspective (Becker 1981), education signals partners’ accumulation of advantage through time investment into knowledge acquisition and skills development. According to this perspective, superior skills work as a basis for a partner to specialise in the market activities, whereas their spouse, with comparatively lower levels of education, specialises in unpaid work and household production activities.
From the bargaining perspective in housework research (Blood and Wolfe 1960; Coverman 1985; Hook 2004; Kubo 2009; Nakagawa 2009), higher levels of education can be individuals’ bargaining chips in the division of household labour and can also help them to be more eloquent when negotiating. Consequently, education becomes a skill that affects the bargaining outcomes of the partners’ division of household labour. These mechanisms based on resources work in both Western countries and East Asia. In Japan, researchers found that in heterosexual households where women have higher bargaining power and relative resources, men participate more actively in housework and childcare activities than in households, where women cannot contribute to the family income (Kubo 2009; Nakagawa 2009).
Education also represents the absolute resources of an individual. According to the absolute resources perspective (Gupta 2007; Killewald and Gough 2010), education is a resource that can be used to accumulate monetary resources to be able to outsource housework to hired labour, without having to negotiate with one’s partner.
On the whole, in all resource-based perspectives—specialisation, relative-resources, and absolute-resources perspectives—on par with individual monetary resources and time, education is central to the explanation of the gendered division of domestic labour.
2.2. Education as a Gendering Process
The societal expectations about traditional gender performances are higher in Japan than in Western countries. Out of 149 countries, Japan was ranked 110, below the world average in the Global Gender Gap Report 2018 (World Economic Forum 2018). The long work hours in Japan prevent women with children to remain in the workforce after childbirth. The full-time employment among Japanese women has followed what is called the “M-curve” when women quit their full-time employment in their 20s and 30s because of childcare responsibilities and return into the workforce after their children grow up. Some demographers have reported that the “M-curve” has been disappearing in recent decades, arguing that the labour market opportunities for Japanese women have improved over time (Ato and Tsuya 2018). However, more recent research shows that the M-curve in women’s employment did not weaken; its dispersal is the result of the delayed birth among some Japanese women (Brinton and Oh 2019). Thus, women still quit their full-time jobs at the time of childbirth, only at different ages rather than at the uniform time as before (Brinton and Oh 2019).
A study of gender inequality in the medical profession reveals that upon childbearing, Japanese women experience a work-life strain because of an inadequate child support system, harassment at the workplace, and social sanctions for violating stereotypical gender role expectations (Izumi et al. 2013; Nomura et al. 2015). Harassment, reported by women in Nomura et al. (2015), referred to criticisms and discrimination endured by mothers from their male and female colleagues because of the widespread belief that longer leaves by mothers due to childrearing responsibilities would increase the workload of others, who have to cover for the new mothers, and because there is no temporary staff to cover the resulting labour force shortages.
Although powerful as an individual resource, education can also be a socialisation tool. People learn gender scripts and socially accepted gender performances in their families and from society through a process referred to as socialisation. One important socialisation institution is the educational system. In the system, people acquire their gender behaviours (Brines 1994; Kan and Laurie 2018; Kolpashnikova 2018; Thébaud et al. 2019; West and Zimmerman 1987) and espouse gender ideologies (Davis and Greenstein 2009; Ishii-Kuntz and Coltrane 1992; Ishii-Kuntz 2009). Although socialisation processes can be traced in most societies, they are also unique in the sense that the scripts related to gender performances and internalised gender ideology are often dependent on the local culture or even the school. Although the existence of cultural idiosyncrasies in the socialisation process is not contested, the previous literature asserts that education is more conducive to gender-egalitarian ideology within most cultural contexts, and thus works in East Asia in the same general direction as in Western countries (Ishii-Kuntz 2005; Ishii-Kuntz 2009). Still, the contradicting results on the association between education and housework participation are present in the literature on Japanese women but have not been discussed theoretically (Kan et al. 2019; Ueda 2005).
Overall, from the gender perspectives in housework research, educational institutions are one of the main catalysts through which women and men acquire gender scripts and identities. Education reflects the processes of socialisation in educational institutions, which are often bounded within a culture and a smaller geographic area. The gender ideology transferred within the educational system may vary across different contexts. Some of the resulting educational socialisation differences between East Asia and the US can be due to the methods through which students learn and the ways of how gender scripts are acquired. For example, Azuma (1994) points out that socialisation in schools in Japan and the US occurs through different methods. In the US, verbal teaching is more common, whereas in Japan students learn more through osmosis—imitation and conformity.
2.3. Education’s Effects on Housework at Life-Course Stages and by Gender
We should expect differences in the effects of educational attainment on housework participation not only depending on cultural processes but also on the life-course stage. Previous literature shows that married women spend more time on housework than single, separated, or divorced women (Baxter et al. 2008; Baxter et al. 2010; Gupta 2007). On the one hand, according to the resource-based arguments in housework research, this effect of marriage on women’s housework is due to the fact that a family of two or more needs more housework done in total compared to single people, and women usually shoulder most housework responsibilities because of patriarchal hegemonic structures common to most modern societies. According to the resource-based explanations, because the amount of housework increases, while the social power of women does not, the amount of housework that married women do ends up being more than what the single women must do for themselves.
The gender-centred explanation, on the other hand, assigns more explanatory value to the fact that heterosexual partnerships lay heightened expectations of traditional gender performances on women, meaning that in marriage, women are expected to do more housework and are sanctioned more harshly than men if they do not (Ruppanner and Treas 2015; Thébaud et al. 2019). Therefore, the institute of heterosexual marriage is one of the “gender factories” and life-course stages where women are expected to perform their traditional gender (Baxter et al. 2008; Berk 1985; West and Zimmerman 1987). They reaffirm their gender identity by engaging in more traditionally feminine activities such as housework. Thus, gender scholars argued that married women were more likely to perform their gender via housework activities than other women (Berk 1985; Bittman et al. 2003).
3. Previous Research in Japan and the US
Overall, studies report similar patterns of paid work, education, and housework over the recent decades among women in Japan and the US (Álvarez and Miles 2003; Chesters 2011; Evertsson and Nermo 2007; Fuwa and Cohen 2007; Guppy et al. 2019; Gupta 2007; Ruppanner 2010). A higher proportion of women participates in the labour market now than in the past in Western countries (Guppy et al. 2019; Qian and Sayer 2016), and the educational attainment of women reached and even exceeded the average level for men (DiPrete and Buchmann 2013). Substantial progress has been made to enact equal opportunities legislation in the labour market in both the US and Japan. Nevertheless, in both countries, most housework is still performed by women (Inaba 1998; Ishii-Kuntz 2009; Kan et al. 2019; Matsuda 2001; Nishioka and Yamauchi 2017; Tsuya 2000). In the US, Sayer (2010) demonstrates that the trends in housework consistently show that the amount of housework decreased for women and increased for men between 1970s and 2000s. In Japan, Kolpashnikova et al. (2019) showed that the amount of housework for Japanese women decreased between 2011 and 2016; using the raw data from the Statistical Bureau of Japan.
The two societies differ in the level of severity of gendered barriers in the labour market. On the one hand, in Japan, the traditional gender-specialisation model with men-breadwinners and women-homemakers remains dominant (Brinton and Oh 2019; Kan and Hertog 2017; Lee and Ono 2008). Men are expected to focus their time on paid work, whereas most Japanese women quit their jobs after nuptials (Brinton and Oh 2019). Brinton and Oh (2019) show that the “M-curve” of the life-course progression through employment has flattened for Japanese women, and the labour force participation rate by age group in Japan is now similar to the US. However, the flattening of the “M-curve” in Japan, as Brinton and Oh (2019) argue, is misleading, because it includes both married and non-married women. Considering the increase in the delay in marriage and childbirth among Japanese women, the flattening might simply be the artefact of changing marriage and fertility patterns. Studies overall show that in the US, the dual-earner household model is more prevalent (Brinton and Oh 2019). Even after marriage, most American women and men keep a paid job.
These contextual differences in structural barriers are also embodied in how gender expectations are socialised across different life-course stages depending on the cultural and political context (Hook 2010; Knudsen and Wærness 2007; Stier and Lewin-Epstein 2007). Every life-course stage represents a unique set of normative expectations and social identities, all of which are also context-dependent (Elder 1998). For example, Rothbaum et al. (2000) argue that there are specific motivational values associated with each life-course transition, and those in Japan are different from those in the US. The nuances in motivational values across different cultural and political contexts influence the resulting behaviour and the allocation of time to various activities, including unpaid work.
4. Hypotheses
Both from the resource-based and gender-centred perspectives, women with higher educational attainment are more likely to engage in paid work compared to women with lower educational attainments (England et al. 2004; Rubery et al. 1999). Consequently, they have less time to spare on housework and other unpaid work (Killewald and Gough 2010; Qian and Sayer 2016; Sayer 2010). Following the main theoretical frameworks of housework research, including both economic and gender perspectives, we expect that:
Hypothesis 1a (H1a).
The effects of education are negative on housework participation of both Japanese and American women, regardless of the level of housework participation.
Considering the profound differences in gender roles and expectations in Japan, compared to Western countries including the US, we can also expect that the effects of education on housework time to be absent or even contrary to those expected in Western countries. The gendered character of the institute of marriage in Japan lays out expectations on women to quit (temporarily or permanently) the workforce. Such expectations are less pronounced in the US. Therefore, the alternative hypothesis is:
Hypothesis 1b (H1b).
The effects of education are non-existent or positive on housework participation among Japanese women.
We can also expect some variability among women at different life-course stages. Life-course transitions, such as the transition to a partnered union, are expected to affect housework participation. For example, Gupta (1999) and South and Spitze (1994) found that married women and men are more involved in housework activities compared to single people. However, Baxter et al. (2008) found that the effects, leading to an increase of the housework time upon marriage, apply to women but not to men. Overall, the previous research suggests that there is a change in the amount of housework done on each life-course stage among women, but there is not likely to be a change in the association between education and housework participation regardless of the life-course stage.
However, the country differences should be observed in the amount of housework time but not in the association between education and housework (Inaba 1998; Ishii-Kuntz 2009; Kan et al. 2019; Matsuda 2001; Nishioka and Yamauchi 2017; Tsuya 2000). Thus, we expect the following:
Hypothesis 2 (H2).
The amount of housework performed differs for women at different life-course stages (marriage and childbirth).
5. Data and Methods
We used the 2006 STULA (Statistics Bureau 2016) and the 2006 ATUS (Bureau of Labor Statistics 2019). STULA data collect time diaries for two consecutive days, allowing their treatment as panel data, where the weekday is used as the time variable. Drawing a sample from the Current Population Survey (CPS), ATUS collects time-use diaries of one respondent per household in all 50 states. We chose the two countries as proxies for testing the current theoretical frameworks in housework for two main reasons. First, there are contextual differences between the two that may highlight our results in a clearer and straight-forward way. Second, both countries have very reliable data, which lend credibility to the results obtained through this analysis.
The analytical sample was restricted to women, aged 20 to 60, who reported doing housework on the diary day. The Japanese sample includes 10,957 non-married women without children, 16,799 married women without children, and 33,453 married women. The American sample is represented by 599 non-married women without children, 492 married women without children, and 1780 married women. We chose only one year from the ATUS to make the results comparable across the two countries.
5.1. Measures
The dependent variable is represented by an aggregate measure of the time spent on routine housework, including cooking, cleaning, and doing laundry. We focus on routine housework rather than non-routine tasks, such as gardening and house repairs, because past studies show that the routine tasks are the core types of housework for bargaining, outsourcing, and gender display (Hook 2017; Kan et al. 2011; Kolpashnikova 2018; Kolpashnikova and Kan 2020a, 2020b). Thus, we restricted housework to indoor routine housework for this study. Housework participation is measured in minutes on the diary day.
The main independent variable—education—is a continuous variable, measured in years spent in education. We included household income as a control variable, which is transformed into a categorical measure by the quartiles of income. The lowest quartile represents the lowest 25% of household income, whereas the top quartile represents the upper 25% of household income.
The age variable is represented by age groups: aged 20–29, 30–39, 40–49, and 50–59. Other control variables include household size, homeownership (dummy variable), employment status (dummy variable), and urban residence (dummy variable).
Table 1 and Table 2 summarise the descriptive estimates of means and proportions for the main variables across the deciles of housework participation in Japan (Table 1) and the US (Table 2). Table 1 and Table 2 show substantial differences between women in the top and the bottom deciles of housework participation. Japanese women in the top decile, on average, spend more than ten times the time that women in the bottom decile spend on housework. As noted in the theoretical part, most women in the lower deciles of housework participation were less likely to be employed than women in the upper deciles.

Table 1.
Pooled descriptive statistics, 20 to 60-year-old women, Japan 2006.

Table 2.
Pooled descriptive statistics, 20 to 60-year-old women, US 2006.
Table 2 shows that American women in the top decile take almost 40 times longer than women in the bottom decile. Unlike in Japan, the household income is higher in the households in the middle deciles of housework participation than on both ends. In Japan, however, household income is higher in households where women are in the upper deciles of housework participation. These numbers reflect the labour markets in the two countries: in Japan, households still depend mostly on a single salary, whereas in the US, two-income households are more common.
5.2. Models
We employed the unconditional quantile regression in our models (Firpo et al. 2009). This method is commonly used in the studies of motherhood premiums (Budig and Hodges 2014; Cooke and Hook 2018; England et al. 2016; Killewald and Bearak 2014). UQR is preferred to the conditional quantile regression because the latter provides more biased results than UQR (Killewald and Bearak 2014).
For the American data, we used the original rifreg program to run the UQR regression models, developed by Firpo et al. (2009). For the Japanese data, in addition to the original rifreg, designed for cross-sectional data, we also used the UQR for panel data (using the seven weekdays as panels). The Stata program for the panel data UQR was developed by Borgen (2016). Additionally, we bootstraped the standard errors of model coefficients, as suggested in Cooke and Hook (2018). The results in estimations for cross-sectional and panel data analysis in Japan do not alter the main findings of this paper. Full output tables are available in the Supplementary Materials.
6. Results and Discussion
Table 3 and Figure 1 summarise the estimates for Japan and the US of the effects of education on routine housework time, i.e., cooking and cleaning. We run separate UQR models on housework participation for non-married (including separated and widowed) women without children, married women without children, and married women with children. Table 3 summarises the outputs for the select deciles (10%, 20%, 50%, 80%, and 90%). Our models try to capture how normative life-course transitions in Japan affect the association between education and housework participation and compare the outcomes to the US.

Table 3.
Summary of unconditional quantile regression (UQR) results for Japanese and American Women Education’s Association with Housework.
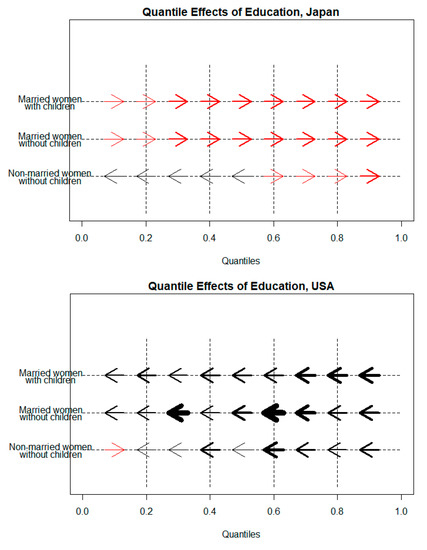
Figure 1.
Quantile Effects of Education on Housework Participation.
The negative coefficients in Table 3, corresponding to the left-pointing arrows in Figure 1, represent the expected sign of the association between education and housework participation when higher levels of educational attainment correspond to lower levels of housework participation for each separate decile. The relative size of an arrow in Figure 1 represents the relative size of the effect of the association.
The results of Table 3 and Figure 1 show that the effects of education on housework participation are different between Japan and the US. The findings for Japan suggest that the association of education with housework participation among married women is positive, which contradicts the theoretical expectations from both the economic and gender perspectives. The effects among married Japanese women are contrary to those in the US or among non-married Japanese women: Japanese married women spend more time on housework with the increase in their educational attainments on all levels of housework participation. Therefore, the results of the present study do not provide support for Hypothesis 1a in Japan. The results indicate that in Japan, the access to advanced educational degrees is not likely to alleviate women’s housework responsibilities when they marry and that there are cultural differences in the effects of education on housework participation between Japan and the US.
Additionally, only non-married Japanese women, who already are in the lower deciles of housework participation, on average, decrease their housework participation with the increase in their educational attainments. The finding refers to women who are in the lower quantiles (below the 6th decile). In contrast, the overall results for American non-married women support Hypothesis 1a. Moreover, we observe that, regardless of their marital status and parenthood, American women lessen their housework time when they have higher levels of education (see the right panel of Figure 1).
These results illustrate how the tenets of the resource-based and gender-centred frameworks developed based on the empirical findings in Western countries cannot always apply to the patterns observed in East Asia.
Predicted Means from the Unconditional Quantile Regression Models
Figure 2 and Figure 3 summarise the estimates of the UQR models for the US and Japan. The solid lines indicate non-married women, the dotted lines indicate married women without children, and the dashed lines refer to married women with children’s association between education and housework time. Although Figure 1 showed that the association in the US is more negative, and the association in Japan is more positive, the predicted housework time by education years in both countries appears flatter, especially in Japan. There is a more explicit negative association between education and housework participation mostly among married American women, who are in the upper deciles of housework participation (see Figure 2).
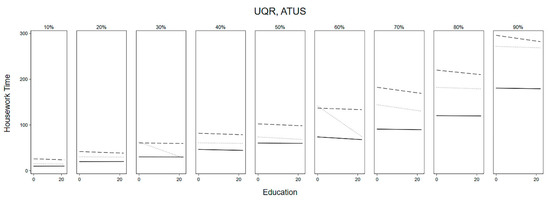
Figure 2.
UQR Predicted Housework Time by Education over Deciles of Housework Participation, US.
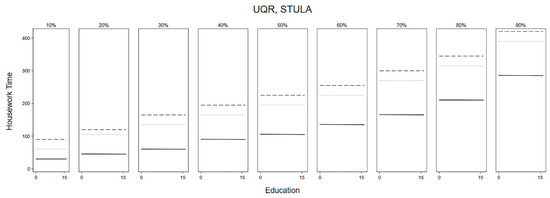
Figure 3.
UQR Predicted Housework Time by Education over Deciles of Housework Participation, Japan.
First, we find support for Hypothesis 2. There is an increase in the amount of housework performed across different life-course stages. Non-married women in the US and Japan do the least amount of housework and married women with children the most. In both countries, the gap is smaller between married women with and without children than between married and non-married women.
The differences between women in different life-course stages are smaller at the lower half of housework participation levels but higher in the upper half. However, the differences by deciles are more pronounced in the US than in Japan. This result indicates that there are more differences by life-course stage among the higher performers of housework than among those in the lower deciles. In Japan, the differences by life-course stages are substantial regardless of the level of housework participation.
Overall, Figure 2 and Figure 3 show that (1) there are differences in how education is associated with housework time in the US compared to Japan; (2) there are differences in how education is associated on different deciles of housework participation and by life-stage course, but only in the US. Japanese women’s participation in housework appears to depend more on the life-course stage, and less on educational level. Additionally, Figure 2 shows that there are stark differences among American women without children in the 3rd and 6th deciles of housework participation depending on their educational level.
7. Conclusions
Both the resource-based and gender-centred explanations of housework participation argue that education is inversely associated with the level of housework participation among women. However, our results reveal that these explanations cannot apply in different cultural contexts. The results of the present study show that even though education is accessible to most Japanese women, married women with higher educational levels will still do more housework than those with lower levels of education. Our findings strongly suggest that there is a marriage penalty among Japanese women with higher levels of educational attainment: the more years of schooling, the more time spent on housework. Thus, in Japan, married women with higher levels of education are more likely to espouse more traditional feminine scripts regarding housework performance because the institute of marriage places higher expectations on married women’s housework participation. Our work supports the arguments in Brinton and Oh (2019) and further confirms that despite recent strides towards gender equality, the mechanisms assumed to help women through education proved to be successful in the West might not be applicable in other contexts, particularly in Japan.
A closer analysis based on the UQR models reveals that the housework participation among Japanese women does not depend on the level of education, but on the life-course stage, particularly on marriage. It is in the context of the global north, specifically in the US, that education is associated with a decrease in housework time among married and non-married women alike. In other cultural contexts, such as Japan, we might find the evidence that the cultural meanings of housework are more complex and culturally-bound than the researchers of housework have assumed. Thus, the theoretical frameworks (resource-based and gender-centred) thought to work in Western countries might not work in the same way in others. Education, as a socialisation medium, conveys different values. Moreover, the institution of heterosexual marriage might place higher expectations of housework participation on women in Japan than those expected in the US. These contextual nuances call for the development of more culturally-sensitive housework theories.
One limitation of our work is that we use the 2006 data, as they are the newest STULA dataset available to scholars outside Japan. Although the 2011 and 2016 datasets are available to use in the data centres in Japan, the current pandemic outbreak prevented us from travelling to Japan. Moreover, the turn-out speed on the release of the tables that are created at the data centres remains very slow for the peer review process to be able to accommodate them. However, we are in the process of negotiating with the Japanese government officials the acceleration of the data release process.
Another limitation of the present study is that we are using an unconventional method to analyse housework participation. Although UQR is not explicitly restrictive in its use, it prevented us from including the diaries that did not report housework participation on the diary day. These results and the use of the method should be approached with caution.
Future research can investigate further how the extant theoretical frameworks in unpaid work perform across different cultural contexts.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2076-0760/9/12/235/s1, Table S1: UQR Coefficients, Japanese Non-Married Women without Children, STULA 2006; Table S2: UQR Coefficients, Japanese Married Women without Children, STULA 2006; Table S3: UQR Coefficients, Japanese Married Women with Children, STULA 2006; Table S4: UQR Coefficients, American Non-Married Women without Children, ATUS 2006; Table S5: UQR Coefficients, American Married Women without Children, ATUS 2006; Table S6: UQR Coefficients, American Married Women with Children, ATUS 2006.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation, methodology, formal analysis, investigation, writing, K.K.; supervision, data curation, editing, M.-Y.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This project was funded by the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under the Marie Sklodowska-Curie grant agreement No 892101 (awardee: Kamila Kolpashnikova) and European Research Council Consolidator Grant agreement No 771736 (awardee: Man-Yee Kan), and the Economic and Social Research Council grant No ES/S014098/1 (awardee: Man-Yee Kan). The APC was funded by the Economic and Social Research Council grant No ES/S014098/1 (awardee: Man-Yee Kan). The earlier versions of the manuscript are available as a pre-print on OSF: https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/5qdwy.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Altintas, Evrim, and Oriel Sullivan. 2017. Trends in fathers’ contribution to housework and childcare under different welfare policy regimes. Social Politics 24: 81–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, Begona, and Daniel Miles. 2003. Gender effect on housework allocation: Evidence from Spanish two-earner couples. Journal of Population Economics 16: 227–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ato, Makoto, and Noriko Tsuya. 2018. Aspects of Childless and Aging Society. In Women and Family in the Age of Low Birthrate and Aging Society. Edited by N. Tsuya, M. Ato and H. Nishioka. Tokyo: Keio University Press, pp. 1–55. [Google Scholar]
- Azuma, Hiroshi. 1994. Two modes of cognitive socialization in Japan and the United States. In Cross-Cultural Roots of Minority Child Development. Edited by P.M. Greenfield and R.R. Cocking. Hillsdale: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc, pp. 275–84. [Google Scholar]
- Baxter, Janeed, Belinda Hewitt, and Michele Haynes. 2008. Life course transitions and housework: Marriage, parenthood, and time on housework. Journal of Marriage and Family 70: 259–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxter, Janeen, Michele Haynes, and Belinda Hewitt. 2010. Pathways Into Marriage: Cohabitation and the Domestic Division of Labor. Journal of Family Issues 31: 1507–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, Gary S. 1981. A Treatise on the Family. Cambridge: Harvard University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Berk, Sarah Fenstermaker. 1985. The Gender Factory: The Apportionment of Work in American Households. New York: Plenum. [Google Scholar]
- Bittman, Michael, Paula England, Liana Sayer, Nancy Folbre, and George Matheson. 2003. When does gender trump money? Bargaining and time in household work. American Journal of Sociology 109: 186–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, Sampson Lee, and Daniel T. Lichter. 1991. Measuring the Division of Household Labor: Gender Segregation of Housework Among American Couples. Journal of Family Issues 12: 91–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blood, Robert O., and Donald M. Wolfe. 1960. Husbands and Wives, the Dynamics of Married Living. New York: The Free Press. [Google Scholar]
- Borgen, Nicolai T. 2016. Fixed effects in unconditional quantile regression. The Stata Journal 16: 403–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brines, Julie. 1994. Economic Dependency, Gender, and the Division of Labor at Home. American Journal of Sociology 100: 652–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinton, Mary C., and Eunsil Oh. 2019. Babies, Work, or Both? Highly Educated Women’s Employment and Fertility in East Asia. American Journal of Sociology 125: 105–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budig, Michelle J., and Melissa J. Hodges. 2014. Statistical models and empirical evidence for differences in the motherhood penalty across the earnings distribution. American Sociological Review 79: 358–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budig, Michelle J., Joya Misra, and Irene Boeckmann. 2012. The Motherhood Penalty in Cross-National Perspective: The Importance of Work-Family Policies and Cultural Attitudes. Social Politics: International Studies in Gender, State & Society 19: 163–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bureau of Labor Statistics. 2019. American Time Use Survey. Washington, DC: Bureau of Labor Statistics. [Google Scholar]
- Chesters, Jenny. 2011. Gender convergence in core housework hours: Assessing the relevance of earlier approaches for explaining current trends. Journal of Sociology 49: 78–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, Lynn Prince, and Jennifer L. Hook. 2018. Productivity or Gender? The Impact of Domestic Tasks Across the Wage Distribution. Journal of Marriage and Family 80: 721–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coverman, Shelley. 1985. Explaining Husbands’ Participation in Domestic Labor. The Sociological Quarterly 26: 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowan, Carolyn Pape, and Philip A. Cowan. 1992. When Partners Become Parents: The Big Life Change for Couples. Mahwah: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Publishers. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, Shannon N., and Theodore N. Greenstein. 2009. Gender Ideology: Components, Predictors, and Consequences. Annual Review of Sociology 35: 87–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiPrete, Thomas A., and Claudia Buchmann. 2013. The Rise of Women: The Female Advantage in Education and What it Means for American Schooling. New York: Russell Sage Foundation. [Google Scholar]
- Elder, G.H., Jr. 1998. The life course as developmental theory. Child Development 69: 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- England, Paula, Carmen Garcia-Beaulieu, and Mary Ross. 2004. Women’s employment among blacks, whites, and three groups of Latinas: Do more privileged women have higher employment? Gender & Society 18: 494–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- England, Paula, Jonathan Bearak, Michelle J. Budig, and Melissa J. Hodges. 2016. Do highly paid, highly skilled women experience the largest motherhood penalty? American Sociological Review 81: 1161–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evertsson, Marie, and Magnus Nermo. 2007. Changing resources and the division of housework: A longitudinal study of Swedish couples. European Sociological Review 23: 455–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firpo, Sergio, Nicole M. Fortin, and Thomas Lemieux. 2009. Unconditional quantile regressions. Econometrica 77: 953–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuwa, Makiko, and Philip N. Cohen. 2007. Housework and social policy. Social Science Research 36: 512–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guppy, Neil, Larissa Sakumoto, and Rima Wilkes. 2019. Social Change and the Gendered Division of Household Labor in Canada. Canadian Review of Sociology/Revue Canadienne de Sociologie 56: 178–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, Sanjiv. 1999. The effects of transitions in marital status on men’s performance of housework. Journal of Marriage and the Family 61: 700–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, Sanjiv. 2007. Autonomy, dependence, or display? The relationship between married women’s earnings and housework. Journal of Marriage and Family 69: 399–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hook, Jennifer L. 2004. Reconsidering the Division of Household Labor: Incorporating Volunteer Work and Informal Support. Journal of Marriage and Family 66: 101–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hook, Jennifer L. 2010. Gender inequality in the welfare state: Sex segregation in housework, 1965–2003. American Journal of Sociology 115: 1480–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hook, Jennifer L. 2017. Women’s housework: New tests of time and money. Journal of Marriage and Family 79: 179–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inaba, Akihide. 1998. What sort of men do housework and childcare?: Social class and men’s housework and childcare participation. 1995 SSM Survey Series 15: 1–42. [Google Scholar]
- Ishii-Kuntz, Masako. 2005. Balancing fatherhood and work: Emergence of diverse masculinities in contemporary Japan. In Men and Masculinities in Contemporary JAPAN. Edited by J.E. Roberson and N. Suzuki. London: Routledge, pp. 216–34. [Google Scholar]
- Ishii-Kuntz, Masako. 2009. Father’s Role and Participation in Child-rearing: Present Situation, Regulatory Factors, Impacts on Families. Quarterly Household Economics Study 81: 16–23. [Google Scholar]
- Ishii-Kuntz, Masako, and Scott Coltrane. 1992. Predicting the sharing of household labor: Are parenting and housework distinct? Sociological Perspectives 35: 629–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izumi, Miki, Kyoko Nomura, Yuko Higaki, Yu Akaishi, Masayasu Seki, Shizuko Kobayashi, Takayuki Komoda, and Junji Otaki. 2013. Gender role stereotype and poor working condition pose obstacles for female doctors to stay in full-time employment: Alumnae survey from two private medical schools in Japan. The Tohoku Journal of Experimental Medicine 229: 233–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kan, Man-Yee, and Ekaterina Hertog. 2017. Domestic division of labour and fertility preference in China, Japan, South Korea, and Taiwan. Demographic Research 36: 557–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, Man-Yee, and Heather Laurie. 2018. Who is doing the housework in multicultural Britain? Sociology 52: 55–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kan, Man-Yee, Ekaterina Hertog, and Kamila Kolpashnikova. 2019. Housework share and fertility preference in four East Asian countries in 2006 and 2012. Demographic Research 41: 1021–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, Man-Yee, Oriel Sullivan, and Jonathan Gershuny. 2011. Gender convergence in domestic work: Discerning the effects of interactional and institutional barriers from large-scale data. Sociology 45: 234–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Killewald, Alexandra, and Jonathan Bearak. 2014. Is the motherhood penalty larger for low-wage women? A comment on quantile regression. American Sociological Review 79: 350–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Killewald, Alexandra, and Margaret Gough. 2010. Money isn’t everything: Wives’ earnings and housework time. Social Science Research 39: 987–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knudsen, Knud, and Kari Wærness. 2007. National context and spouses’ housework in 34 countries. European Sociological Review 24: 97–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolpashnikova, Kamila. 2018. American Househusbands: New Time Use Evidence of Gender Display, 2003–2016. Social Indicators Research 140: 1259–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolpashnikova, Kamila, and Man-Yee Kan. 2020a. Gender Gap in Housework: Couples’ Data Analysis in Kyrgyzstan. Journal of Comparative Family Studies 51: 154–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolpashnikova, Kamila, and Man-Yee Kan. 2020b. Hebdomadal Patterns of Compensatory Behaviour: Weekday and Weekend Housework Participation in Canada, 1986–2010. Work, Employment and Society 32: 174–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolpashnikova, Kamila, Man-Yee Kan, and K. Shirakawa. 2019. Marriage and Housework: Analyzing the Effects of Education Using the 2011 and 2016 Japanese Survey on Time Use and Leisure Activities. IER Discussion Paper Series 696: 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Kubo, Keiko. 2009. Full-time dual-income couples’ sharing of housework and sex role awareness. Bulletin of Educational Studies, Chiba University 57: 275–82. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Kristen Schultz, and Hiroshi Ono. 2008. Specialization and happiness in marriage: A US–Japan comparison. Social Science Research 37: 1216–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, Katherine. 2011. Generational change in paid and unpaid work. Canadian Social Trends 11: 11–24. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda, Shigeki. 2001. Determinants of sharing housework and child rearing among married couples in contemporary Japanese relationships. Epidemiological Science Research Fund Basic Research (A) Nationwide Survey Report on Family 92: 167–84. [Google Scholar]
- Nakagawa, Mari. 2009. Wife’s encouragement and her husband’s childcare and housework in dual-earner couples. Human Culture Creation Science Review Volume 12: 305–13. [Google Scholar]
- Nishioka, Hachiro, and Masakazu Yamauchi. 2017. Has the frequency of husbands’ housework and child care increased? Analysis on full-time employed husbands with children under 3 years old. Journal of Population Problems 73: 97–111. [Google Scholar]
- Nomura, Kyoko, Yuka Yamazaki, Larry D Gruppen, Saki Horie, Masumi Takeuchi, and Jan Illing. 2015. The difficulty of professional continuation among female doctors in Japan: A qualitative study of alumnae of 13 medical schools in Japan. BMJ Open 5: e005845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Yue, and Liana C. Sayer. 2016. Division of labor, gender ideology, and marital satisfaction in East Asia. Journal of Marriage and Family 78: 383–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothbaum, Fred, Martha Pott, Hiroshi Azuma, Kazuo Miyake, and John Weisz. 2000. The Development of Close Relationships in Japan and the United States: Paths of Symbiotic Harmony and Generative Tension. Child Development 71: 1121–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubery, Jill, Mark Smith, and Colette Fagan. 1999. Women’s Employment in Europe: Trends and Prospects. New York: Routledge. [Google Scholar]
- Ruppanner, Leah. 2009. Conflict and housework: Does country context matter? European Sociological Review 26: 557–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruppanner, Leah, and Judith Treas. 2015. Working weekends: Changing European time regimes and gender inequality in household labor. Journal of Family Issues 36: 1782–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruppanner, Leah. 2010. Cross-national reports of housework: An investigation of the gender empowerment measure. Social Science Research 39: 963–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayer, Liana C. 2010. Trends in Housework. In Dividing the Domestic: Men, Women, and Household Work in Cross-National Perspective. Edited by J. Treas and S. Drobnic. Stanford: Stanford University Press, pp. 19–38. [Google Scholar]
- South, Scott J., and Glenna Spitze. 1994. Housework in Marital and Nonmarital Households. American Sociological Review 59: 327–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statistics Bureau. 2016. Survey on Time Use and Leisure Activities. Tokyo: Statistics Bureau. [Google Scholar]
- Stier, Haya, and Noah Lewin-Epstein. 2007. Policy effects on the division of housework. Journal of Comparative Policy Analysis 9: 235–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, Oriel, Jonathan Gershuny, and John P. Robinson. 2018. Stalled or Uneven Gender Revolution? A Long-Term Processual Framework for Understanding Why Change Is Slow. Journal of Family Theory & Review 10: 263–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thébaud, Sarah, Sabino Kornrich, and Leah Ruppanner. 2019. Good Housekeeping, Great Expectations: Gender and Housework Norms. Sociological Methods & Research. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treas, Judith, and Jonathan Lui. 2013. Studying Housework Across Nations. Journal of Family Theory & Review 5: 135–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuya, Noriko. 2000. Work and housework from the gender perspective. Comparison between Japan, Korea and the United States. Journal of Population Problems 56: 25–48. [Google Scholar]
- Ueda, Atsuko. 2005. Intrafamily time allocation of housework: Evidence from Japan. Journal of the Japanese and International Economies 19: 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, Candace, and Don H. Zimmerman. 1987. Doing Gender. Gender & Society 1: 125–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Economic Forum. 2018. The Global Gender Gap Report 2018. Geneva: World Economic Forum. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).