Analyzing Sociodemographic Factors Influencing Citizen Participation: The Case of Infrastructure Planning in Khon Kaen, Thailand
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Sociodemographic Factors for Citizen Participation
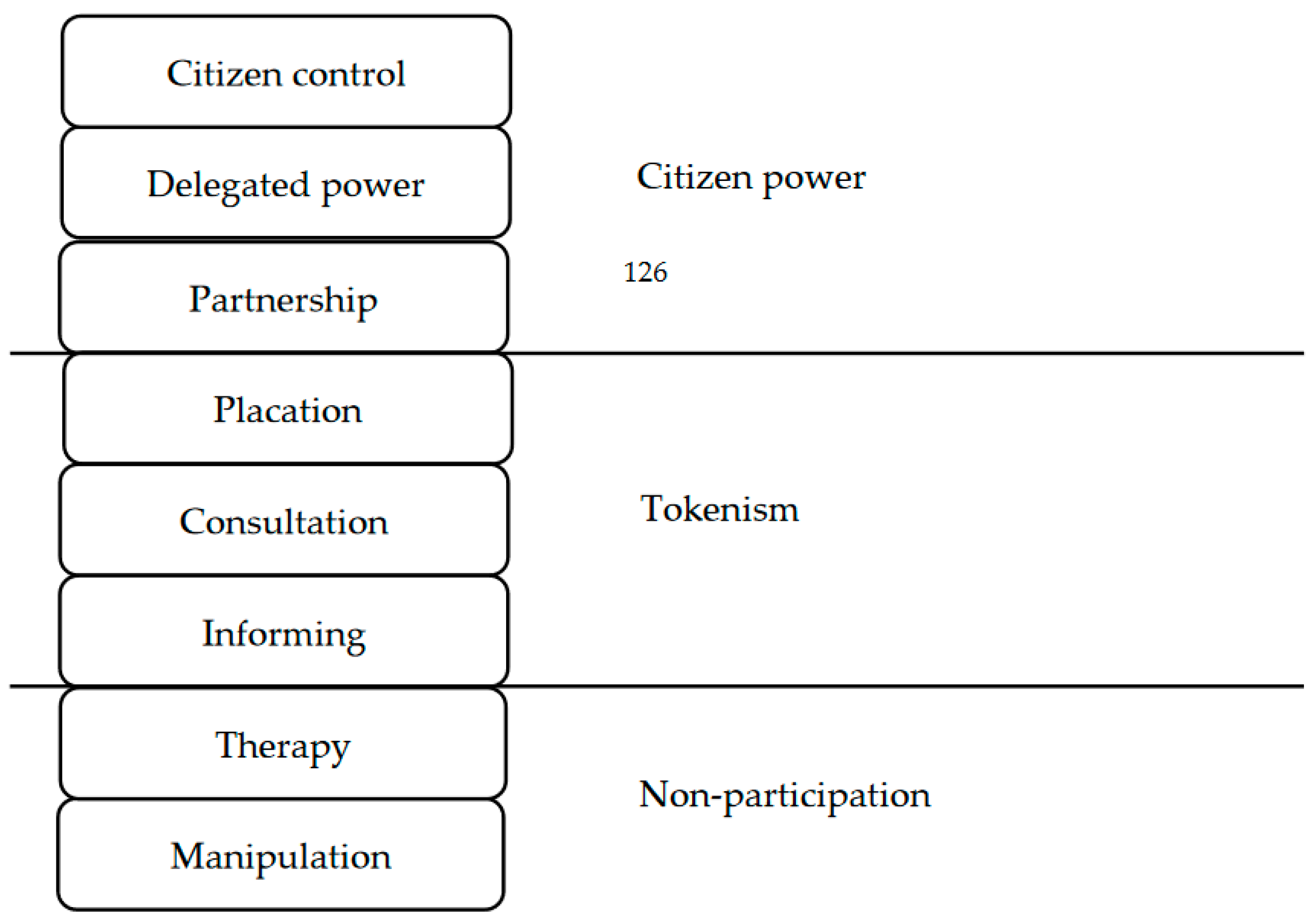
2.2. Typology of Citizen Participation
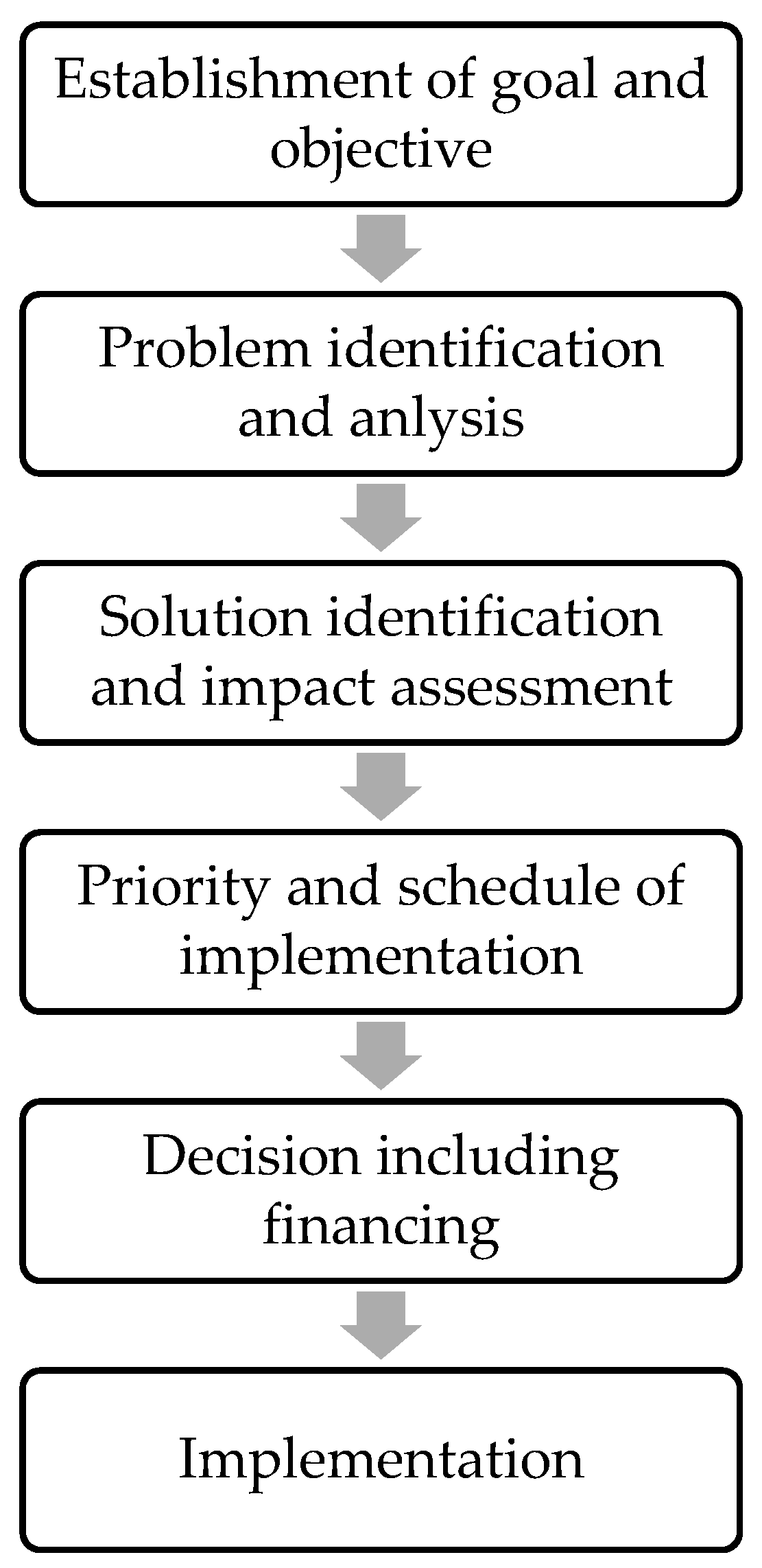
2.3. Infrastructure Planning Process
3. Materials and Methods
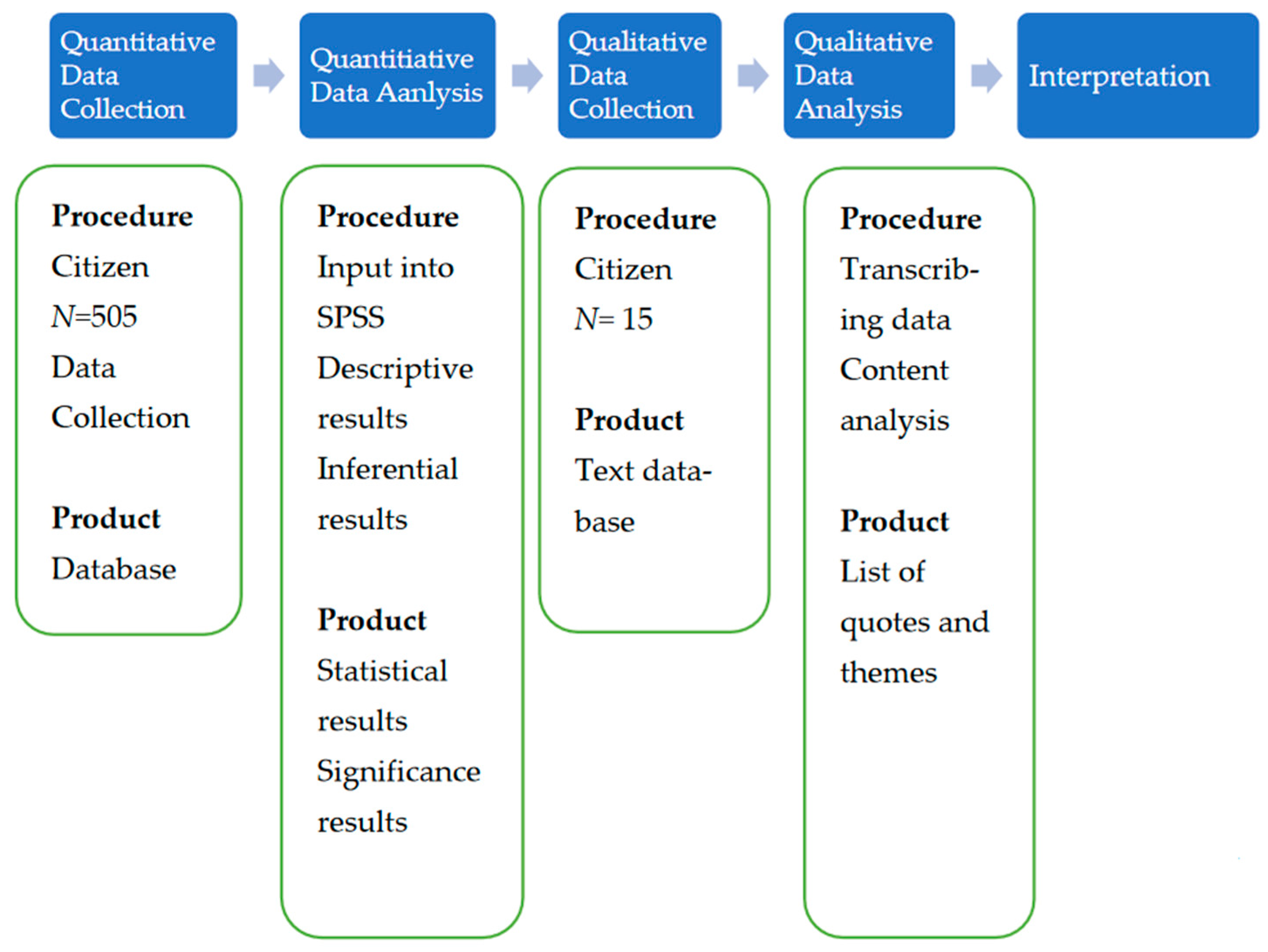
3.1. Research Design
3.2. Study Area and LRT Project Background
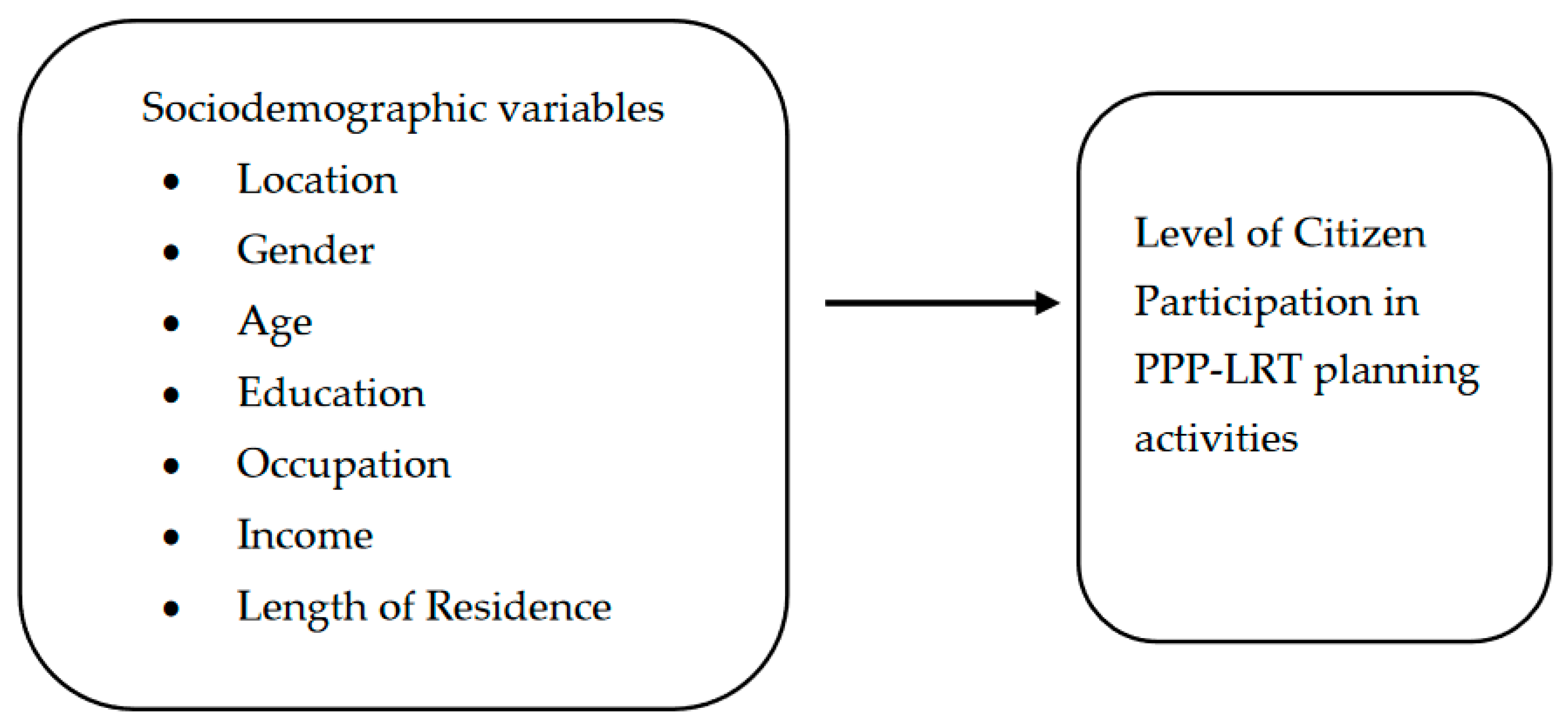
3.3. Variables
3.4. Sampling and Data Collection
3.5. Analytical Methods
4. Empirical Results
4.1. Sociodemographic Characteristics of the Respondents
4.2. Participation Patterns
4.3. Factors Influencing Citizen Participation
4.4. Urban and Peri-Urban Participation Experiences
5. Discussions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Indicator | Participation Pattern | Typology by Arnstein |
|---|---|---|
| The stakeholders initiate or propose topics of discussion and may share decisions with authority. | 8. Citizen control | Citizen Power |
| The stakeholders may direct and co-facilitate PP activities. The issues and topics are well-explained prior to the activities. | 7. Delegate power | |
| The stakeholders are part of a working group or committee involved with project development from design to implementation. | 6. Partnership | |
| The stakeholders can advise and even plan, but it is the power-holder that finally decides whether to even take these ideas into account or not. | 5. Involvement | Tokenism |
| The stakeholder provides opinions on issues and simple consulting on the decision process. The issues and decision process are not explained in advance. | 4. Consultation | |
| The stakeholders are informed and aware of the project goals. It is a two-way communication process. The citizen learns from the officers and the officers learn from the citizen. | 3. Inform | |
| The local officers lead activities with the main goal of disseminating information to stakeholders. Stakeholders are part of the events without any input and not much understanding about the issues. | 2. Passive participation | Non-participation |
| Stakeholders who affected by the project; however, they do not attend the public participation activity. | 1. Non-attendance |
| X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | Tolerance | 0.97 | 0.57 | 0.86 | 0.91 | 0.94 | 0.57 |
| VIF | 1.04 | 1.77 | 1.16 | 1.1 | 1.07 | 1.76 | |
| X2 | Tolerance | 0.54 | 0.86 | 0.92 | 0.9 | 0.5 | |
| VIF | 1.86 | 1.16 | 1.09 | 1.12 | 2.02 | ||
| X3 | Tolerance | 0.87 | 0.96 | 0.89 | 0.8 | ||
| VIF | 1.16 | 1.05 | 1.13 | 1.25 | |||
| X4 | Tolerance | 0.91 | 0.92 | 0.51 | |||
| VIF | 1.1 | 1.08 | 1.96 | ||||
| X5 | Tolerance | 0.89 | 0.49 | ||||
| VIF | 1.13 | 2.03 | |||||
| X6 | Tolerance | 0.49 | |||||
| VIF | 2.03 | ||||||
| X7 | Tolerance | ||||||
| VIF |
References
- Aijaz, Rumi. 2019. India’s Peri-Urban Regions: The Need for Policy and the Challenges of Governance. ORF Issue Brief (Observer Research Foundation) 285. Available online: https://www.orfonline.org/research/india-peri-urban-regions-need-policy-challenges-governance-49274/ (accessed on 1 February 2023).
- Arnstein, Sherry R. 1969. A Ladder Of Citizen Participation. Journal of the American Institute of Planners 35: 216–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baum, Frances E., Robert A. Bush, Carolyn C. Modra, Charlie J. Murray, Eva M. Cox, Kathy M. Alexander, and Robert C. Potter. 2000. Epidemiology of participation: An Australian community study. Journal of Epidemiology & Community Health 54: 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown-Iannuzzi, Jazmin L., Kristjen B. Lundberg, and Stephanie McKee. 2017. The politics of socioeconomic status: How socioeconomic status may influence. Current Opinion in Psychology 18: 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaisomphob, Taweep, Jaturong Sa-nguanmanasak, and Kanokporn Swangjang. 2015. Role of Public Participation in Planning Power Plant Project in Thailand. Thammasat International Journal of Science and Technology 9: 67–73. [Google Scholar]
- Chutarat, Chompunth. 2017. Role of public participaiton in environmental impact assessent in Thailand. International Journal of GEOMATE 12: 109–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creswell, John W. 2015. A Concise Introduction to Mixed Methods Research, 2nd ed. New York: SAGE. [Google Scholar]
- Creswell, John, and Amanda Garrett. 2008. The “movement” of mixed methods research and the role of educators. South African Journal of Education 28: 321–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, Kristie. 2015. Goal 11—Cities Will Play an Important Role in Achieving the SDGs. United Nation. Apr. Available online: https://www.un.org/en/chronicle/article/goal-11-cities-will-play-important-role-achieving-sdgs (accessed on 1 February 2023).
- Gaber, John. 2020. Building “A Ladder of Citizen Participation”. In Learning from Arnstein’s Ladder From Citizen Participation to Public Engagement. New York: Routledge. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, Roger A. 1979. Children’s Participation from Tokenism to Citizenship. New Brunswick: Elise Boulding. [Google Scholar]
- Hingels, Anders, Andrea Saltelli, Anna Rita Manca, Massimiliano Mascherini, and Bryony Hoskins. 2009. Growing Cohesive Societies: The Characterization of Active Citizenship. In The 3rd OECD World Forum on “Statistics, Knowledge and Policy" Charting Progress, Building Visions, Improving Life. Busan: OECD. Available online: https://www.oecd.org/site/progresskorea/44120679.pdf (accessed on 1 February 2023).
- Huang, Zhengdong. 2003. Data Integration For Urban Transport Planning. Utrecht: Utrecht University. [Google Scholar]
- International Finance Corporation—Worldbank Grou. 2019. A Guide to Community Engagement for Public-Private Partnership. Draft for Discussion. Washington DC: Worldbank. [Google Scholar]
- Jennings, Ray Salvatore. 2000. Participatory Development as the New Paradigm: The Transition of Development Professionalism. In Community Based Reintegration and Rehabilitation in Post-Conflict Settings. Washington, DC: USAID, pp. 20–21. [Google Scholar]
- Kamnuansilpa, Peerasit, Sirisak Laochankham, Charles David Crumpton, and John Draper. 2020. Citizen Awareness of the Smart City: A Study of Khon Kaen, Thailand. The Journal of Asian Finance, Economics and Business [Internet], 497–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Naewon, and Nojin Kwak. 2003. A Multilevel Approach to Civic Participation: Individual Length of Residence, Neighborhood Residential Stability, and Their Interactive Effects With Media Use. Communication Research 30: 80–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantamaturapoj, Kanang, Ganda Piyajun, and Suwit Wibulpolprasert. 2020. Comparison of Public Participation in Environmental and Health Impact Assessment between Thailand and other countries. Journal of Politics and Governance 10: 108–26. [Google Scholar]
- Khon Kaen City Development Co., Ltd. n.d. Khon Kaen Smart City Project. Available online: https://www.khonkaenthinktank.com/project.php (accessed on 10 January 2020).
- Lao, Rattana, Thomas I Parks, and Charn Sangvirojkul. 2019. Thailand’s Inequality: Myths & Reality of ISAN. Bangkok: The Asia Foundation. [Google Scholar]
- Litman, Todd Alexander. 2022. Introduction to Multi-Modal Transportation Planning. Victoria Transport Policy Institute, 6–19. Available online: https://www.vtpi.org/multimodal_planning.pdf (accessed on 28 February 2023).
- Litman, Todd Alexander. 2011. Measuring transportation: Traffic, mobility and accessibility. Social Research in Transport (SORT) Clearinghouse 73. Available online: https://www.vtpi.org/measure.pdf (accessed on 28 February 2023).
- Maarseveen, Raoul Van. 2021. The urban rural-education gap: Do cities indeed make us smarter? Journal of Economic Geography 21: 683–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, Richard. 2021. Introduction: The Khon Kaen Model and Light Rail Transit. waymagazine.org. May 13. Available online: https://waymagazine.org/conjuring-the-people-entrepreneurial-localism-and-the-case-of-the-khon-kaen-model/ (accessed on 28 February 2022.).
- Macrotrends. 2023. Khon-Kaen, Thailand Metro Area Population 1950–2023. Available online: https://www.macrotrends.net/cities/22620/khon-kaen/population (accessed on 5 January 2023).
- Manowong, Ektewan, and Stephen O. Ogunlana. 2023. Public hearings in Thailand’s infrastructure projects: Effective participations? Engineering, Construction and Architectural Management 13: 343–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, Jennifer. 2006. Mixing methods in a qualitatively driven way. Qualitative Research, 9–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurice, Nyarangaa, Hao Chen, and Hongo Duncan. 2021. The Role of Public Participation in Governance towards Achieving Sustainable Development. Part 1. RUDN Journal of Public Administration 8: 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbithi, Antony, Damiana Ndambuki, and Fredrick Juma. 2018. Determinants of Public Participation in Kenya County Governments. Journal of Asian and African Studies 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modeni, Sibanda, and Liezel Lues. 2021. Public participation power dynamics in strategic development planning in a metropolitan municipality: Eastern Cape Province. Journal of Local Government Research and Innovation 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Centre for Research Method. n.d. 5.3 Key Assumptions of Ordinal Regression. Available online: https://www.restore.ac.uk/srme/www/fac/soc/wie/research-new/srme/modules/mod5/3/index.html#:~:text=The%20key%20assumption%20in%20ordinal,but%20it’s%20the%20same%20thing (accessed on 9 November 2022).
- Ng, S. T., J. M. W. Wong, and K. K. W. Wong. 2010. Public participation in public private partnership projects - The way forward. The Sustainable World 142: 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, Thomas, Terry Li, and James Wong. 2012. Rethinking public participation in infrastructure projects. Municipal Engineer 165: 101–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NordNordWest. 2009. Thailand Khon Kaen Locator map.svg. Available online: https://th.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E0%B9%84%E0%B8%9F%E0%B8%A5%E0%B9%8C:Thailand_Khon_Kaen_locator_map.svg (accessed on 1 February 2022).
- Nyama, Vellim, and Geofrey Mukwada. 2022. Factors Affecting Citizen Participation in Local Development Planning in Murewa District, Zimbabwe. Journal of Asian and African Studies. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pancho, Quita. 2014. Infrastructure Planning and Management. Lecture. July 11. Available online: https://www.slideserve.com/ghita/infrastructure-planning-and-management (accessed on 9 November 2022).
- Papaoikonomou, Antonis. 2021. An ordinal logistic regression model on civic education usefulness in Greece: Empirical research in a sample of university students. HuSS International Journal of Research in Humanities and Social Sciences 9: 18–25. [Google Scholar]
- Quick, Kathryn S. 2018. The Narrative Production of Stakeholder Engagement Processes. Journal of Planning Education and Research 41: 326–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintelier, Ellen. 2007. Differences in political participation between young and old people. Contemporary Politics 13: 165–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Read, Geoffrey. n.d. Disaster Risk Management in East Asia and the Pacific. The World Bank. Washington, DC: EAP DRM KnowledgeNote. Available online: https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/bitstream/handle/10986/10129/529390BRI0REVI10BOX353820B01PUBLIC1.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y (accessed on 9 November 2022).
- Relph, Edward. 2008. Place and Placelessness, Relph, Edward. Toronto: SAGE Publications Ltd. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, Elizabeth M. 1997. A Ladder of Empowerment. Journal of Planning Education and Research 17: 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shea, Daniel M. 2015. Young Voters, Declining Trust and the Limits of “Service Politics”. The Forum 13: 459–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinclair, A John, and P Alan Diduck. 2017. Reconceptualizing Public Participation In Environmental Assessment As EA Civics. Environmental Impact Assessment Review 62: 174–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siroros, Patcharee, and Kenneth J Haller. 2015. Thai Public Hearings: Smokescreen or Ceremony? TU Review 5: 147–64. [Google Scholar]
- STATISTICS HELP. n.d. STATISTICS HELP. Available online: https://www.stathelp.se/en/dummy_en.html (accessed on 2 December 2022).
- Sudhipongpracha, Tatchalerm, and Bharat Dahiya. 2019. City Profile: Khon Kaen, Thailand. Environment and Urbanization ASIA 10: 271–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sustainable World. 2019. Demographic Characteristics: An Important Part of Science. July 13. Available online: https://worldsustainable.org/demographic-characteristics/ (accessed on 27 June 2022).
- The Analysis Factor. n.d. How to Decide between Multinomial and Ordinal Logistic Regression Models. Available online: https://www.theanalysisfactor.com/decide-between-multinomial-and-ordinal-logistic-regression-models/ (accessed on 10 November 2022).
- Thananithichot, Stithorn. 2012. Political engagement and participation of Thai citizens: The rural–urban disparity. Contemporary Politics 18: 87–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toruńczyk-Ruiz, Sabina, and Borja Martinović. 2020. The bright and dark sides of length of residence in the neighbourhood: Consequences for local participation and openness to newcomers. Journal of Environmental Psychology 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tupmongkol, Piyamart, and Achakorn Wongpreedee. 2022. Public and private partnership in khon kaen urban development as a smart city: A case study of light rail transit (lrt) construction project. Journal of Graduate Studies Valaya Alongkron Rajabhat University 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UKEssays. 2018. Transportation Planning And Urban Form Environmental Sciences Essay. Available online: https://www.ukessays.com/essays/essays/environmental-sciences/transportation-planning-and-urban-form-environmental-sciences-essay.php?vref=1 (accessed on 29 June 2022).
- Wangwongwatana, Supat, Daisuke Sano, and Peter Noel King. 2015. Assessing Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) in Thailand: Implementation Challenges and Opportunities for Sustainable Development Planning (Working Paper), Asian Environmental Compliance and Enforcement Network (AECEN) Working Paper Asian Environmental. Hayama: Institute for Global Environmental Strategies. [Google Scholar]
- Wiyaboon, Saowanee. 2019. Community Participation in Local Development Projects. Journal Of International Buddhist Studies College (JIBSC) 4: 18–24. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Yuze, and Lin Ye. 2020. Peri-Urban Development. Oxford Bibliographies in Urban Studies. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
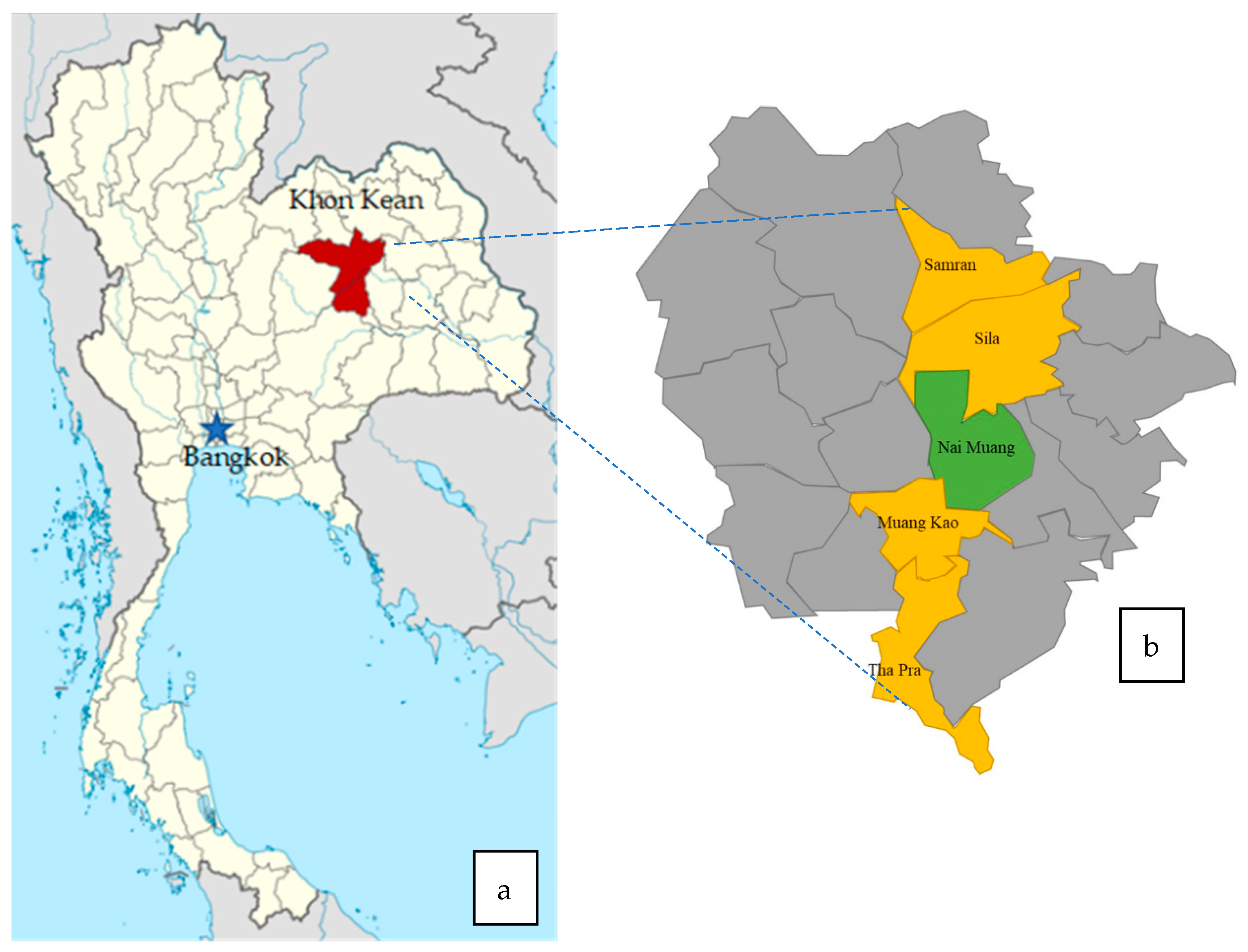
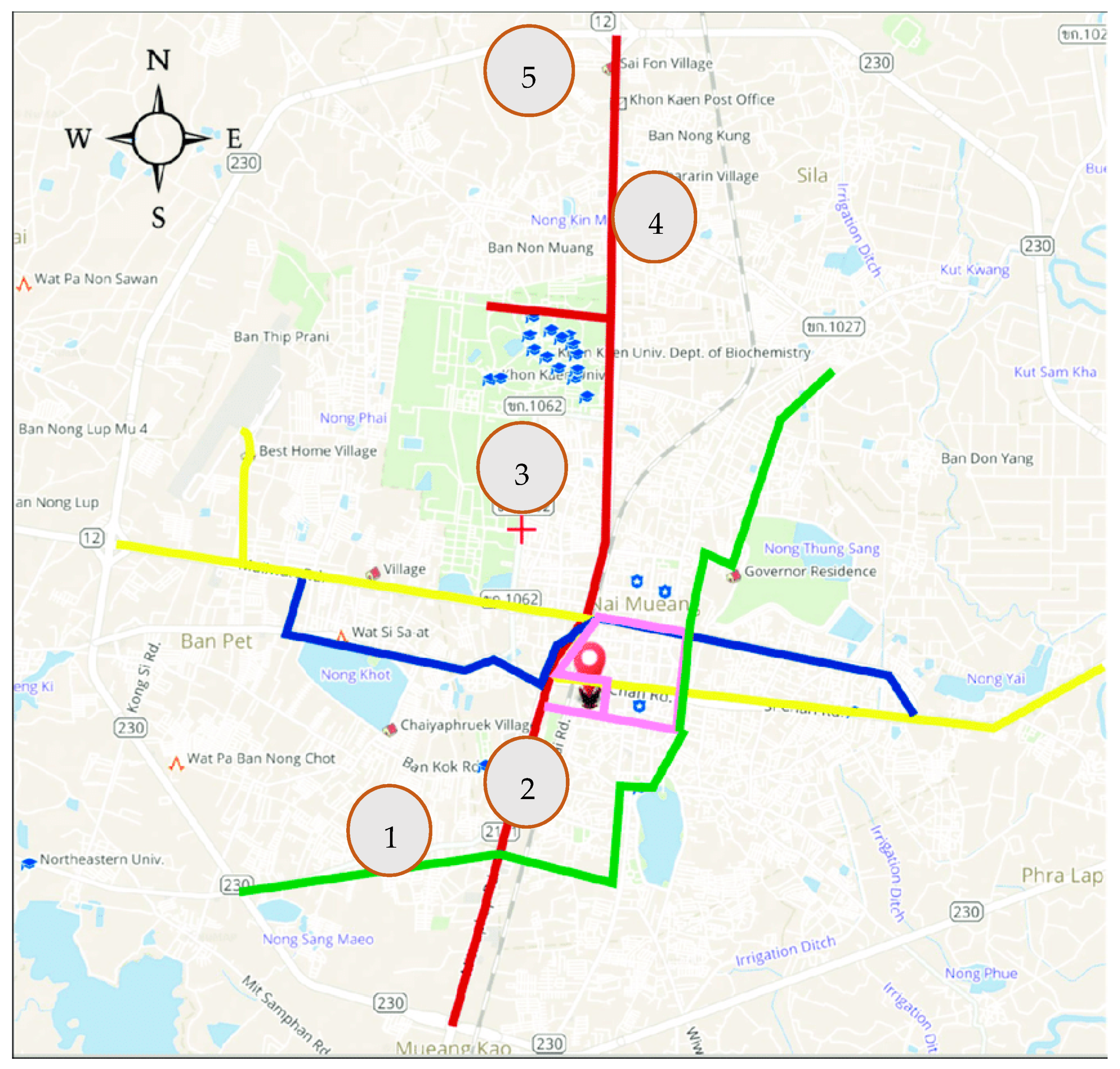
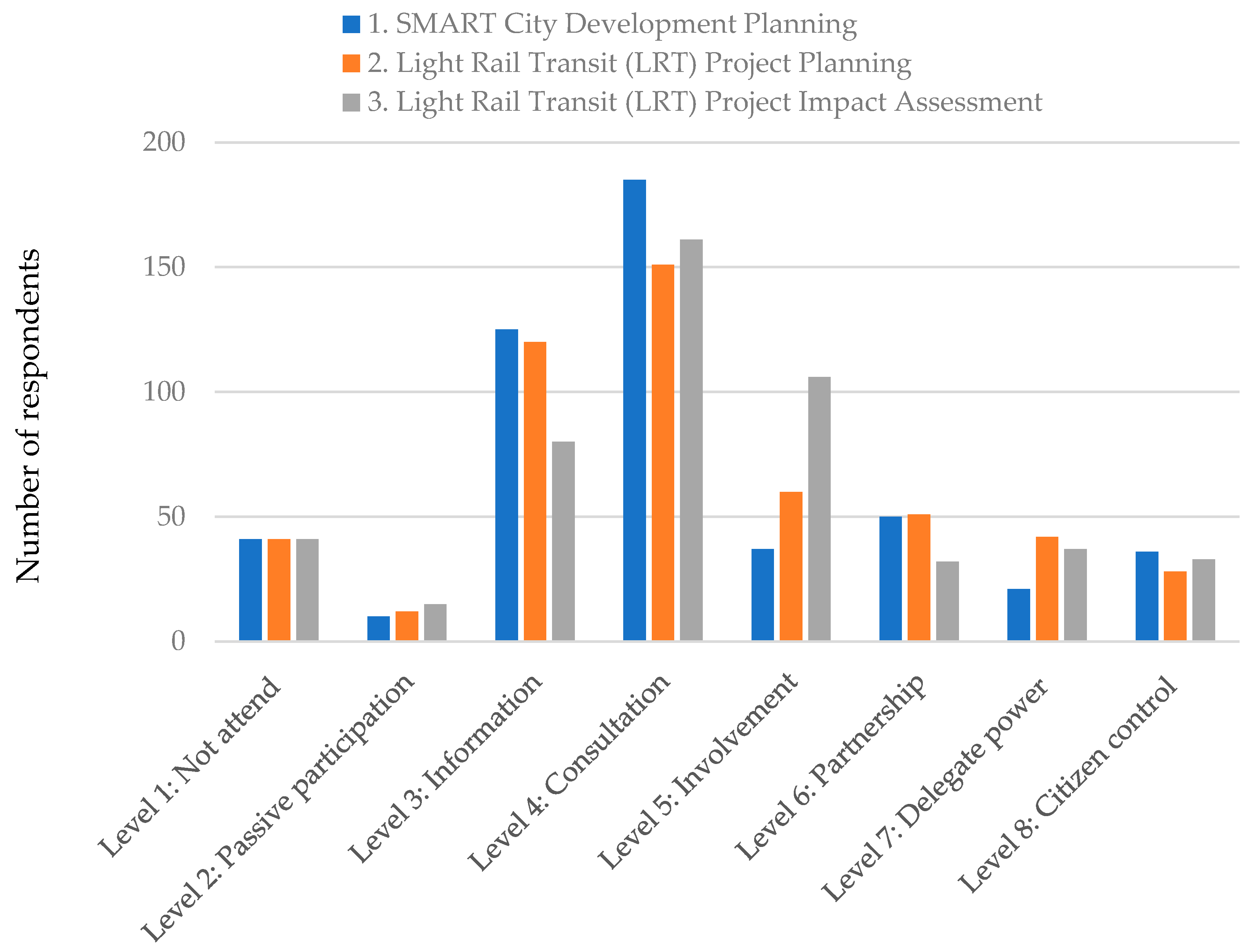
| Urban (%) | Peri-Urban (%) | (p-Value) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 44.0 | 56.0 | ||
| Gender | Male | 18.8 | 24.2 | 0.157 |
| Female | 25.2 | 31.9 | ||
| Age (years) | 18–24 | 6.9 | 6.3 | 0.295 |
| 25–34 | 7.5 | 10.3 | ||
| 35–44 | 5.9 | 10.9 | ||
| 45–54 | 12.5 | 15.8 | ||
| >54 | 11.1 | 12.7 | ||
| Education level | Less than high school | 5.9 | 9.1 | 0.001 |
| High school | 12.3 | 27.7 | ||
| Bachelor or above | 25.7 | 19.2 | ||
| Occupation | Student | 4.8 | 4.0 | 0.001 |
| Unemployed | 5.7 | 10.9 | ||
| Gov. officer | 8.7 | 5.0 | ||
| Employee | 10.9 | 14.3 | ||
| Retiree | 7.9 | 10.1 | ||
| Other | 5.9 | 11.9 | ||
| Income (THB per month) | ≤7000 | 13.5 | 24.2 | 0.001 |
| 7001–30,000 | 25.7 | 28.7 | ||
| >30,000 | 4.8 | 3.2 | ||
| Duration of residence (years) | ≤10 | 3.6 | 7.9 | 0.920 |
| 11–30 | 15.8 | 14.1 | ||
| 31–50 | 14.3 | 20.0 | ||
| >50 | 10.3 | 14.1 |
| Municipality | No. of Villages | Population | Proportion of Population | Number of Respondents |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nai Muang | - | 118,203 | 55% | 218 |
| Sam Ran | 13 | 9637 | 4% | 18 |
| Tha Phra | 20 | 19,197 | 9% | 35 |
| Muang Kao | 17 | 24,840 | 11% | 46 |
| Sila | 28 | 44,194 | 20% | 82 |
| 216,071 | 100% | 399 |
| Overall | Urban | Peri-Urban | p-Value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |||
| SMART City Development Planning | ||||||||
| Citizen Power | Citizen control | 4.00 | 0.58 | 3.79 | 0.149 | 3.96 | 0.14 | ≤0.001 |
| Delegate power | 3.48 | 0.17 | 3.26 | 0.178 | 3.60 | 0.16 | ≤0.001 | |
| Partnership | 3.00 | 0.49 | 2.81 | 0.173 | 3.22 | 0.14 | ≤0.001 | |
| Total | 3.49 | 0.33 | 3.29 | 0.167 | 3.59 | 0.10 | ≤0.001 | |
| Tokenism | Involvement | 2.67 | 0.18 | 2.60 | 0.158 | 2.70 | 0.12 | 1.000 |
| Consultation | 2.17 | 0.17 | 2.16 | 0.167 | 2.22 | 0.16 | 0.250 | |
| Informed | 1.67 | 0.12 | 1.71 | 0.128 | 1.80 | 0.11 | 1.000 | |
| Total | 2.17 | 0.33 | 2.16 | 0.151 | 2.24 | 0.13 | 0.087 | |
| Non-participation | Passive participation | 1.18 | 0.17 | 1.18 | 0.166 | 1.18 | 0.17 | 0.970 |
| Non-attendance | 1.28 | 0.16 | 1.25 | 0.113 | 1.31 | 0.15 | 0.992 | |
| Total | 1.18 | 0.17 | 1.18 | 0.166 | 1.18 | 0.17 | 0.970 | |
| Overall | 2.28 | 0.28 | 2.21 | 0.161 | 2.34 | 0.13 | ≤0.001 | |
| Light Rail Transit Planning | ||||||||
| Citizen Power | Citizen control | 3.75 | 0.44 | 3.71 | 0.187 | 3.96 | 0.16 | ≤0.001 |
| Delegate power | 3.28 | 0.52 | 3.24 | 0.175 | 3.67 | 0.16 | ≤0.001 | |
| Partnership | 3.12 | 0.59 | 2.98 | 0.172 | 3.22 | 0.18 | ≤0.001 | |
| Total | 3.38 | 0.52 | 3.31 | 0.178 | 3.62 | 0.17 | ≤0.001 | |
| Tokenism | Involvement | 2.62 | 0.37 | 2.69 | 0.182 | 2.38 | 0.12 | 0.397 |
| Consultation | 1.94 | 0.70 | 2.10 | 0.154 | 2.15 | 0.17 | 0.799 | |
| Informed | 1.68 | 0.66 | 1.80 | 0.168 | 1.67 | 0.16 | 0.809 | |
| Total | 2.08 | 0.57 | 2.20 | 0.168 | 2.07 | 0.17 | 0.110 | |
| Non-participation | Passive participation | 1.45 | 0.46 | 1.09 | 0.152 | 1.23 | 0.16 | 0.087 |
| Non-attendance | 1.35 | 0.46 | 1.32 | 0.15 | 1.38 | 0.15 | 0.076 | |
| Total | 1.45 | 0.46 | 1.09 | 0.15 | 1.23 | 0.16 | 0.087 | |
| Overall | 2.30 | 0.52 | 2.20 | 0.17 | 2.30 | 0.18 | ≤0.001 | |
| Light Rail Transit Project Impact Assessment | ||||||||
| Citizen Power | Citizen control | 3.81 | 0.51 | 3.71 | 0.16 | 3.94 | 0.15 | ≤0.001 |
| Delegate power | 3.23 | 0.64 | 3.27 | 0.14 | 3.32 | 0.19 | ≤0.001 | |
| Partnership | 2.86 | 0.25 | 2.87 | 0.18 | 3.21 | 0.13 | ≤0.001 | |
| Total | 3.30 | 0.47 | 3.28 | 0.16 | 3.49 | 0.16 | ≤0.001 | |
| Tokenism | Involvement | 2.64 | 0.64 | 2.67 | 0.13 | 2.48 | 0.14 | 0.634 |
| Consultation | 1.91 | 0.79 | 2.04 | 0.11 | 2.08 | 0.15 | 0.078 | |
| Informed | 1.58 | 0.47 | 1.67 | 0.12 | 1.75 | 0.15 | 0.411 | |
| Total | 2.04 | 0.63 | 2.13 | 0.12 | 2.10 | 0.15 | 0.560 | |
| Non-participation | Passive participation | 1.64 | 0.46 | 1.17 | 0.17 | 1.11 | 0.16 | 0.077 |
| Non-attendance | 1.32 | 0.54 | 1.27 | 0.15 | 1.37 | 0.15 | 0.089 | |
| Total | 1.64 | 0.46 | 1.17 | 0.17 | 1.11 | 0.16 | 0.077 | |
| Overall | 2.33 | 0.52 | 2.19 | 0.15 | 2.23 | 0.15 | ≤0.001 | |
| PO | Variable | Coeff. | Standard Errors | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Citizen Power | ×1 Peri-urban | 27.186 | 52.354 | ≤0.001 |
| ×2 Female | 0.748 | 1.101 | 0.886 | |
| ×3 Age 25–34 | –1.243 | 14.669 | ≤0.001 | |
| ×3 Age 35–44 | –0.058 | 14.683 | ≤0.001 | |
| ×3 Age 45–54 | –1.102 | 14.641 | ≤0.001 | |
| ×3 Age ≥ 54 | 3.343 | 14.827 | 0.972 | |
| ×4 Highschool | 4.244 | 3.763 | 0.459 | |
| ×4 Bachelor or above | 7.495 | 5.144 | 0.520 | |
| ×5 Unemployed | 5.156 | 38.738 | 0.005 | |
| ×5 Gov. officer | 7.440 | 34.767 | ≤0.001 | |
| ×5 Employed | 14.147 | 25.861 | 0.000 | |
| ×5 Retired | 14.172 | 25.329 | 0.001 | |
| ×5 Other | 32.310 | 25.087 | ≤0.001 | |
| ×6 Income 7001–30,000 | –3.804 | 6.352 | 0.005 | |
| ×6 Income ≥ 30,001 | 2.612 | 13.547 | 0.001 | |
| ×7 Residence 11–30 years | 0.865 | 0.570 | 0.988 | |
| ×7 Residence 31–50 years | 4.393 | 1.373 | 0.925 | |
| ×7 Residence ≤ 50 years | 2.136 | 1.052 | 0.933 | |
| Intercept | 17.024 | 51.614 | 0.925 | |
| Tokenism | ×1 Peri-urban | 5.317 | 0.564 | 0.975 |
| ×2 Female | –0.201 | 0.319 | 0.999 | |
| ×3 Age 25–34 | 3.040 | 0.799 | 0.002 | |
| ×3 Age 35–44 | 2.351 | 0.740 | ≤0.001 | |
| ×3 Age 45–54 | 1.058 | 0.624 | 0.953 | |
| ×3 Age ≥ 54 | –0.434 | 0.586 | ≤0.001 | |
| ×4 Highschool | –0.393 | 0.542 | 0.963 | |
| ×4 Bachelor or above | 0.335 | 0.519 | 0.953 | |
| ×5 Unemployed | 1.238 | 0.504 | 0.959 | |
| ×5 Gov. officer | 1.757 | 0.409 | ≤0.001 | |
| ×5 Employed | 0.332 | 0.388 | ≤0.001 | |
| ×5 Retired | 0.479 | 0.467 | 0.948 | |
| ×5 Other | 2.142 | 0.651 | 0.949 | |
| ×6 Income 7001–30,000 | 3.992 | 1.053 | 0.951 | |
| ×6 Income ≥ 30,001 | 2.835 | 0.959 | 0.975 | |
| ×7 Residence 11–30 years | 4.918 | 1.439 | 0.747 | |
| ×7 Residence 31–50 years | 2.317 | 0.609 | 0.945 | |
| ×7 Residence ≤ 50 years | 1.304 | 0.568 | 0.942 | |
| Intercept | 6.189 | 3.406 | 0.937 | |
| LR test (d.f. = 54) = 804.699 (p = 0.000). Pseudo R2 = Nagelkerke: 0.980; McFadden: 0.949; Cox and Snell: 0.797 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Panyavaranant, P.; Lai Nguyen, T.P.; San Santoso, D.; Nitivattananon, V.; Tsusaka, T.W. Analyzing Sociodemographic Factors Influencing Citizen Participation: The Case of Infrastructure Planning in Khon Kaen, Thailand. Soc. Sci. 2023, 12, 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/socsci12040225
Panyavaranant P, Lai Nguyen TP, San Santoso D, Nitivattananon V, Tsusaka TW. Analyzing Sociodemographic Factors Influencing Citizen Participation: The Case of Infrastructure Planning in Khon Kaen, Thailand. Social Sciences. 2023; 12(4):225. https://doi.org/10.3390/socsci12040225
Chicago/Turabian StylePanyavaranant, Peeranun, Thi Phuoc Lai Nguyen, Djoen San Santoso, Vilas Nitivattananon, and Takuji W. Tsusaka. 2023. "Analyzing Sociodemographic Factors Influencing Citizen Participation: The Case of Infrastructure Planning in Khon Kaen, Thailand" Social Sciences 12, no. 4: 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/socsci12040225
APA StylePanyavaranant, P., Lai Nguyen, T. P., San Santoso, D., Nitivattananon, V., & Tsusaka, T. W. (2023). Analyzing Sociodemographic Factors Influencing Citizen Participation: The Case of Infrastructure Planning in Khon Kaen, Thailand. Social Sciences, 12(4), 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/socsci12040225








