Abstract
Fast-food chains are everywhere and every day millions of people choose to have a break in a fast-food outlet. However, in recent years some local hamburger foodservice chains outside of the well-known international fast-food chains have found success by leveraging products linked with their territory. How do consumers value the service received in an international, rather than a local, fast-food outlet? This aspect is under-investigated in the literature, but is relevant in order to capture the main and most important differences between the two systems. Through a structured survey, consumers’ perceptions of both international and local hamburger foodservice outlets in the Turin Metropolitan area (Italy) were measured and analysed. The results indicate that consumers generally have a break in an international fast-food restaurant, but the value assigned to local fast-food chains is higher than that assigned to international ones. Specifically, local fast-food chains are appreciated for particular aspects related to the supply chain (animal welfare, ethical and social aspects, the origin of the raw materials, and some other characteristics of the food). The findings contribute to a more in-depth understanding of consumer behaviour, and give an insight into the relevance of the local aspects as opposed to the international ones.
1. Introduction
Fast food is not an invention of the 20th century: the fast-food phenomenon exists everywhere and at all times (Pitte 1997). Street food is central in many geographical areas such as North America, Latin America, the Middle East and Africa (Abrahale et al. 2019; Bellia et al. 2016; Hill et al. 2016; Sezgin and Şanlıer 2016). From this point of view, Italy is a country rich in typical fast-food products, such as piadina, farinata, arancini, and focaccia (Barone and Pellerito 2020), but the need for a quick meal was also present centuries ago, in the Roman Empire (Grossi 2012) or in Bourbon Naples (Parente 2007), for example. For a long time, traditional street food and hamburgers underlined the distinction between an artisanal product and an industrial product, provoking conflicting opinions. Indeed, fast-food chains are a symbol of globalisation, exploiting an industrial and standardised production system, low prices, and speed of service, while on the other side there is the culture of food that seeks health, tradition, and ethical standards (Ritzer and Rainò 1997; Poulain 2017). Today, consumers are attracted by the authenticity of products and raw materials and the concept of ‘tradition’ (Guerrero et al. 2010); indeed, in recent decades, giants such as McDonald’s or Subway started to pay attention to these aspects in what they offer (Crawford et al. 2015; Mathur 2017; Simi and Matusitz 2017).
Currently, the increasing attention paid to health and raw materials has been leading to various transformations in the fast-food offer, in terms of both ingredients and service: this is also possible due the increasing success of local products and their recognition by customers (De Bernardi 2015; Kowitt 2014).
The literature focusing on the role of consumers and their loyalty, on the prediction of purchasing behaviour, and on managerial strategies provides a core of theoretical and empirical tools (Churchill and Surprenant 1982; Dahlgaard-Park 2012). The fundamental concept of consumer satisfaction measures the gap between the expectation and the perception of a service (Ciavolino and Dahlgaard 2007; Hemple 1977; Tse and Wilton 1988). Some studies focus on buy again and the attitude towards buying new products as a consequence of consumer satisfaction (Cardozo 1965; Yip et al. 2011); others highlight the psychological aspects and the concept of perceived value (Howard and Sheth 1969), and underline that consumer satisfaction is characterised by evaluative experience (Churchill and Surprenant 1982).
Many conceptual models have been proposed in the literature to measure the quality of a service; however, to the best of these authors’ knowledge, consumers’ perceptions of the quality of service received in international and well-known hamburger restaurants (fast-food outlets) and in local hamburger restaurants has not yet been investigated.
In this context, a multidimensional and hierarchical model is used to describe the quality of service (Brady and Cronin 2001; Dabholkar et al. 1996; Wu and Mohi 2015). A service is implemented to respond better to the needs of the consumer (Liu et al. 2017), reducing the gap between expectations and perception as much as possible. The aim is to increase re-purchase margins, the purchase of new products, and the impact of word of mouth on the acquisition of new customers (Yu et al. 2007), thus acting on the operating result. Specifically, the analysis is conducted on burger outlets in the city of Turin. We chose the expression ‘hamburger foodservice’ instead of the more generic ‘fast food’ to describe the nature of the gastronomic offer of the research area. Indeed, in addition to what we define as the International Hamburger Foodservice (IHF) of McDonald’s and Burger King, which is distinctly fast-food, this study takes into consideration what we define as the Local Hamburger Foodservice (LHF) of M** Bun and L’Hamburgheria di Eataly, which do not have this feature as their main characteristic. The business of these two latter companies is serving hamburgers with particular characteristics in terms of tradition, authenticity, and origin of the raw materials.
The paper is structured as follows: the first section is dedicated to a literature review, which has a particular focus on the evolution of the fast-food industry and on the role of the traditions linked to a territory. The second section is about our materials and methods, and includes the main details about the area being analysed: the IHF and LHF industries. Here, the methods are explained. In the third section, the main results are presented and discussed, while the last section contains the conclusion.
2. Literature Review
In the last decade, the big fast-food chains have increased the levels of attention they pay to this area by implementing continuous updates. Some typical elements of a restaurant’s setting, such as the care given to the interior (a studied mixture of furnishings and colours, correct and sufficient lighting, and background music that suits the tastes of the expected target) and the design of the menu, can affect the satisfaction of the consumer (Hultén 2011; Ifeanyichukwu and Peter 2018). The experience proposed to the consumer involves all the senses and exploits the power of the response to unconscious stimuli: sensory marketing is widely used to build strategies suitable for the fast-food industry (Grow and Schwartz 2014; Joe et al. 2020; Lewis et al. 2020; Thaichon et al. 2019). In this way, when a commonly frequented fast-food restaurant is quite crowded and noisy, for example, the sensory marketing choices take into consideration the most effective background music for an environment in the middle of such a flow of customers (Ifeanyichukwu and Peter 2018). The products are re-worked and the range of the offer is modified and adapted to the target and the geographical area, by means of menus that vary over time, offering local foods and seasonal news, according to glocalisation strategies (Crawford et al. 2015; Mathur 2017; Simi and Matusitz 2017). In order to attract as many consumers as possible, some large fast-food chains have started to introduce vegetarian menus, organic products, and calorie indicators in their menus (Besson et al. 2020; Petimar et al. 2019). The classic strategies based on discounts, free meals, and collectible items, together with speed of service (which is, of course, an essential feature of international foodservice burgers), do not seem to be enough (Gheribi 2017; Lee and Lambert 2017; Mathur 2017). The menus have a proportion of fixed products, which are identifiable as the company’s standard products, and a proportion of variable products (Crawford et al. 2015). Moreover, in the years of the economic crisis, the decrease in consumption linked to foodstuffs also affected fast-food giants such as McDonald’s and Burger King (De Bernardi 2015; Kowitt 2014). This situation was accentuated by some ‘scandals’ related to the use of unhealthy products, which, undoubtedly, influenced demand to some extent (Zhu et al. 2017).
However, in the last two decades, the hamburger foodservice has developed new dimensions of product services. The LHF has proposed a different offer compared to the IHF and has emphasised the importance of the origin and provenance of raw materials and produces. The LHF is founded on local food production and, generally, on food sustainable systems. In this context, the LHF has absorbed the main principles of the Alternative Food Networks (AFNs) philosophy that has been proposed as an alternative to the dominant agro-industrial system, which is perceived as being unsustainable on an environmental level, a catalyst for social disparities, and characterised by economic hyper-centralisation to the detriment of local realities. Indeed, the AFN aims to reconnect productivity and nature, as well as producers and consumers, by means of increased product quality, the creation of short supply chains, and respect for local production and nature (Morgan 2015; Renting et al. 2003). Themes such as the wholesomeness of food, the well-being of workers and animals, and forgotten natural criteria (such as, for example, seasonality) are shown concretely through very different solutions (Forno et al. 2013; Morgan 2009). In particular, this phenomenon began with the Slow Food Movement, which was born as a result of the Braidese ferments of the 1970s and the 1987 ‘Slow Food Manifesto’ (Petrini 2003; Andrews 2008) with a cultural revolution that introduced the concepts of tradition as innovation and that also takes into account the ethical aspects of the food supply chain (Burnier et al. 2021; Carbone 2018; García-Gudiño et al. 2021; Gross et al. 2021; Mastronardi et al. 2019; Sajdakowska et al. 2018).
Currently, in Italy and in other countries, it is possible to find organic agriculture, farmers’ markets, the Slow Food movement (Petrini 2013), so-called Solidarity Purchase Groups (Schifani and Migliore 2011), consumer cooperatives, the use of crowdfunding, economic solidarity networks, factory outlets, and other circuits that are part of Alternative Food Networks (Carzedda et al. 2018; Cappella et al. 2015; Renting et al. 2003; Tregear 2011). The LHF phenomenon has followed these initiatives and has been developed in parallel with IHF.
These phenomena seem to fully demonstrate the growing possibilities and capacities for consumers to select producers and products. The introduction of short supply chains, the selection of natural and controlled raw materials, and the use of recipes and processing procedures linked to tradition and territory according to the principle of sustainability, contribute to local realities, guaranteeing a more stable profit for farmers, for example (Bonadonna et al. 2020).
The growing interest of consumers in traditional products has also been confirmed in the academic field by the scientific contributions dedicated to the topic, which significantly increased during the 2000s (Guerrero et al. 2010; Kumpulainen et al. 2018; Petrescu et al. 2020; Pícha et al. 2018). As emerged from the studies of the last 20 years, numerous definitions of traditional foods have been given in the literature (Trichopoulou et al. 2007; Weichselbaum et al. 2009), but they are mainly from the point of view of those employed in this sector, while it is essential to investigate the image that is formed in the minds of consumers (Guerrero et al. 2010). It has been highlighted that ‘traditional’ is a subjective concept, and therefore that the pool of ‘traditional’ food products is continuously transformed (Nosi and Zanni 2004). Finally, the definition of traditional can be influenced by the media, marketing, and the different opinions of consumers who are in touch with each other (Almli et al. 2011).
The important socio-cultural trends that have developed in recent decades have made consumers more aware, attentive, and oriented, and managers have to take this into account (Arcese et al. 2015). These aspects strongly influence consumers’ expectations and cannot be excluded from the set of variables used in research that aims to provide a reliable approximation of the quality of service. Moreover, consumer perceptions also depend on other elements: the importance attributed by the public to certain elements such as the design, the furnishings, the background music, the decorations, and the communication methods of the serving employees are of increasing importance, and are influenced by cultural dynamics.
On the one hand, part of the literature is focused on the relationship between consumers and IHF, highlighting the importance of service methods, menus, staff, and promotions as aspects influencing the frequency of return, establishment of relationships of trust with retailers, and environmental characteristics (Dastane and Fazlin 2017; Farahiyan et al. 2015; Jaini et al. 2015; Saghaian and Mohammadi 2018; Siddiqua and Shaw Alem 2018; Yarimoglu and Satana 2016). On the other hand, there is a lack of studies dedicated to the relationship between consumers and LHF. Starting from this consideration, we analysed the consumers’ perceptions about the quality of service in international and well-known hamburger restaurants (IHFs) and in local hamburger restaurants (LHFs). In particular, we formulated the following research questions:
RQ1: How do consumers perceive the quality of service in international and local hamburger foodservices?
RQ2: Are there differences in terms of consumers’ perceptions of the quality of service between international and local hamburger foodservices?
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Hamburger Foodservice in Turin Area
Companies operating in the food sector are looking for new solutions that can answer the new needs of the market, and they have already taken certain measures. However, they are still living in a period of transition: consumption patterns are constantly changing, costs are high, and competition is growing. Several changes have already been introduced to renew the commercial offer, but the unstable revenues of the sector inform the actors involved that the offer is only partially meeting consumers’ expectations. Therefore, the fast-food sector is facing a reduction in consumption caused by the economic crisis and consumers’ reduced ability to spend money. In parallel with the lower spending capacity, there is a cultural ferment linked to ethical issues, higher quality standards, and the desire for new solutions.
The research was conducted in the Turin metropolitan area where, over the past 15 years, the traditional large multinational chains have been joined by a number of local hamburger sellers. The stores that record the highest consumption in this geographical area belong to four hamburger foodservice chains: McDonald’s, Burger King, M** Bun and L’Hamburgheria di Eataly. McDonald’s and Burger King have an international profile, a number of retailers in the area under consideration and a standardised service. M** Bun and L’Hamburgheria di Eataly represent the first LHF outlets with more than one store in the metropolitan area of Turin. These four companies have tried to adapt their offers to the new trends of the last few years, and have diversified their commercial propositions to meet the expectations of the market.
McDonald’s and Burger King offer conventional products that are typical of IHF (hamburgers, chips, soft drinks). In the case of McDonald’s, some local/typical products have been introduced, such as Piedmontese beef, Chianina meat, Calabrian red onion from Tropea PGI, and Provolone Valpadana DOP, while Burger King has chosen to update its menu from time to time with high quality products and new recipes. McDonald’s is mainly chosen by consumers who want a meal in the shortest possible time: the waiting time is between two and six minutes, while the average waiting time at Burger King is eight minutes, in line with an assemble-to-order production model. As for the price, a McDonald’s meal ranges from €4.90 to €8.90, while for Burger King the price range is €3.99 to €10.
On the other hand, M** Bun and L’Hamburgheria di Eataly are configured as LHF outlets, and base their commercial offers on raw materials, local ingredients, and local recipes, combined with traditional processing methods and the use of the short supply chain. Indeed, the main raw materials (beef, pork, and vegetables) are produced about 60 km from the metropolitan area of Turin, near the province of Cuneo. The price of a meal ranges from €11.50 to €14 for M** Bun, and from €13.30 to €18 for L’Hamburgheria di Eataly. The average waiting times are 15–25 min in the first case and 15–20 min in the second case, depending on the time required for the preparation of the meal on site (a make-to-order production model) (Bonadonna et al. 2019, 2020).
3.2. Methodology
Some studies (Brady and Cronin 2001; Wu and Mohi 2015) have taken into consideration the following primary dimensions: interaction quality, quality of the environment, and quality of the result. The ‘quality of interaction’ dimension was divided into three sub-dimensions: interpersonal interaction, problem solving, and professionalism. The ‘quality of the environment’ dimension was divided into the following sub-dimensions: aesthetics, atmosphere and degree of comfort of the internal environment, cleanliness in the restaurant, architecture and car park, and menu design. The third dimension, ‘quality of the result’, was structured in three sub-dimensions: waiting time and desired/expected experience, food quality/supply chain, and diversity and originality of the menu. Finally, in addition to the three primary dimensions used, the quality dimension of the product/market system (QP/M) was included in this study (Peri 2006).
Indeed, for an analysis that concerns Italian fast food, the data on the quality/price ratio could be useful, as there are considerable differences in the quality of the food (e.g., hamburgers, chips, draft drinks) served in different fast-food restaurants and, consequently, there are price differences that are not always in proportion to the qualitative variation of the food. The quality perceived by consumers, however, can confirm whether this gap in the quality or price is justified. Therefore, the primary dimension ‘quality of the product/market system’ is measured as a single sub-dimension. The objective of this variable is to investigate the relationship between the perceived quality and the price paid, in relation to the quality of the staff service, the raw materials, the food, and the overall quality of the product/service.
A questionnaire was built that covered some of the dimensions and sub-dimensions of the quality of service. For each sub-dimension, different items were identified. The specific questions about the quality of the service were preceded by general questions that allowed the authors to identify the general characteristics of the consumers, such as their gender, age, employment status, preferred fast food, and frequency of going to the restaurant for a break. As regards the questions corresponding to the items of the model, a Likert scale with values from 1 to 7 was used; the respondents could also select ‘NA’ if they were unable to answer the specific question.
The questionnaire was administered online at the beginning of 2019 (it was closed after one week) with a virtual referral sampling technique. According to the objective of the paper, just the answers of individuals used to go to hamburger foodservice were taken into consideration (n. 227 questionnaires). Among the respondents, it was possible to identify those who had visited each of the four foodservice chains selected. Therefore, a statistical analysis was carried out and a separate analysis was conducted for each of the four groups of responses (pertaining to each of the chains identified). The questionnaire, as mentioned, presented some preliminary qualitative variables. Regarding the sample overall, by processing the answers to these questions, descriptive analysis was performed on both the qualitative and quantitative variables using the R software. Multivariate analysis (PCA) was also carried out on the overall sample. Furthermore, descriptive statistical analysis was performed separately for each group containing the responses for each foodservice chain identified.
4. Results and Discussion
The majority of the sample was composed of women (representing 73.57% of the sample); the respondents were mostly students and workers (respectively 56.39% and 39.21%), and were generally young individuals with an average age of 27 years. The results indicate that 94.27% of the sample liked hamburger foodservice. The most popular hamburger restaurant was McDonald’s (52.86%), followed by M** Bun (15.42%), Burger King (14.10%), and L’Hamburgheria di Eataly (3.52%). The majority of young people and students preferred McDonald’s, while young workers chose L’Hamburgheria di Eataly. The respondents who indicated that they preferred Burger King or M** Bun had a slightly higher average age (29.31 and 29.03 years, respectively).
Regarding the frequency of visits, 48.9% of the respondents went to hamburger restaurants three or four times per year, 30.84% went monthly, 6.61% went weekly, 3.52% went once per year, and 6.17% went with other frequencies. Moreover, M** Bun and L’Hamburgheria di Eataly show a clear prevalence of a visit frequency of three to four times a year (Table 1).

Table 1.
Description of the sample.
Table 2 shows the average of the value for each sub-dimension. The results highlight that the means and standard deviations of the sub-dimensions lie, respectively, between 4.12 and 5.45 and between 1.26 and 1.75. The sub-dimension H has a better performance, indicating a general appreciation for waiting time, service time, type of experience, and related expectations (Table 2). In Appendix A (Table A1), further information dedicated to dimensions, sub-dimensions, and items of the quality of service are available.

Table 2.
Mean, standard deviation, and variance by each sub-dimension.
Table 3 shows the average values for each hamburger foodservice identified. The LHF outlets obtained means with values lying between 4.78 and 5.90, while the IHF values lie between 3.86 and 5.41 (Table 3).

Table 3.
Mean of sub-dimensions by each hamburger foodservice.
The findings indicate that the perceived quality reached a medium-high value and, de facto, confirm the expectations for all the hamburger foodservices identified. In more detail, the highest values are scored for C4 (staff speak an understandable language) with 5.839, C5 (staff are able to inform you about something that is not available that day) with 5.364, D6 (lighting of the dining room is adequate) with 5.362, E2 (pre-packaged condiments are available) with 5.635, G1 (menus are easy to read) with 5.32, G2 (menus are easy to understand) with 5.359, G4 (menus reflect the theme, image, and price range of the restaurant) with 5.396, H1 (waiting time) with 5.435, H2 (type of experience) with 5.509, H3 (service on time) with 5.374, and H4 (experience met expectations) with 5.50. Therefore, an appreciation of the service quality seems to be dependent on the professionalism of the staff, hygiene, the atmosphere, the menu design, and expectations about the overall restaurant experience.
The dimension of product/market system, which investigated the perception of the quality/price ratio, shows a satisfactory level for perceived value. In more detail, M1 (quality/price ratio as service used) scored 4.977, M2 (quality/price ratio as to raw materials used) 4.731, M3 (quality/price ratio as to food consumed) 4.864, and M4 (quality/price ratio as to product/service offered) 4.919.
The items with the lowest means are I6 (supply chain meets the needs related to animal welfare), I7 (supply chain satisfies ethical and social needs), I8 (raw materials used are of local origin), I9 (raw materials used are of national origin), L2 (proposed food is one of a kind), and L3 (proposed food cannot be prepared at home), which scored, respectively, 3.663, 3.738, 3.639, 4.052, 3.615, and 3.777. These items—i.e., I6, I7, I8, and I9 belonging to the food quality/supply chain sub-dimension and L2 and L3 belonging to the menu quality sub-dimension—can be identified as areas of improvement for each of the four hamburger foodservices. The lowest ratings were assigned to the nature of the supply chain and therefore to animal welfare, ethical, and social needs. This is an important aspect, since it demonstrates how relevant these elements are for consumers. The lowest values were assigned precisely to ethical (or hedonistic) factors.
Moreover, in the analysis of these aspects for the four foodservices, it became evident that there is a general dissatisfaction with respect to McDonald’s and Burger King, while the values assigned to these variables are definitely satisfactory for M** Bun and L’Hamburgheria di Eataly. More in depth, some evidence emerged from items I8 and i9, i.e., respectively raw materials with local and national origin, where the typicality of food preparation is integrated with the origin of raw materials. Indeed, LHFs propose menus with regional selected ingredients e.g., Piedmontese beef, Toma Piemontese cheese, and mica bread, and promote them to the customers. Only in recent times have IHFs developed systems of valorisation of typicality with national ingredients such as Parmigiano Reggiano PDO or Bresaola della Valtellina PGI, but the respondents seemed to not perceive this improvement (Table 4).

Table 4.
Specific items of food quality/supply chain and menu quality sub-dimensions by each hamburger foodservice.
Lastly, the map of the variable factors, obtained from the Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and carried out on the variables of the entire questionnaire, shows the degree of correlation of the items and the level of cohesion and solidity of the model (Figure 1).
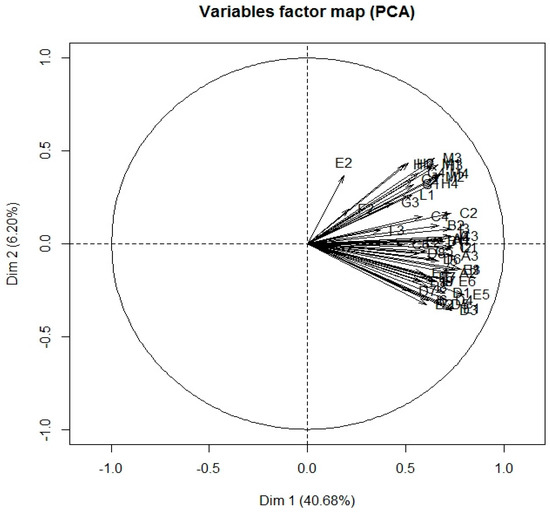
Figure 1.
Variables factor map (PCA).
The map of the variable factors shows a dense group of items, closely related to each other, in which the majority of the variables lie and which is located in the second quadrant and in the lower area of the first. Moreover, in the first quadrant, there is a less numerous thickening of variables amongst the M, G, L, and H groups concerning, respectively, the product/market system, the menus, the waiting time, and the perception of the experience. The single factor E2, concerning the presence of pre-packaged condiments, lies on its own but has a strong correlation with respect to the groups just described. Overall, all the factors can be inscribed in an acute angle, with a new confirmation of the existence of a general correlation between all the variables that make up the dimensions of the model. The two dimensions identified through the PCA, Dim 1, and Dim 2, represent 46.88% of the sample analysed, which can be synthesised in satisfactory proportions.
The variables belonging to the sub-dimension M concerning the product/market system belong to the minor group of factors, with which they are closely related: they are located on the lower margin of this group and are, therefore, also very closely correlated with a consistent part of the largest group of items.
The findings can be compared with some observations that have previously emerged in the literature and that highlight the sensitivity of consumers towards certain topics, such as the speed of service, variety in the menus, the behaviour of the staff (Farahiyan et al. 2015), related promotional initiatives (discounts and gifts), the visual components of the brochures (Yarimoglu and Satana 2016), and the influence of social circles (Siddiqua and Shaw Alem 2018). It should be noted, on the basis of this comparison, that the IHF marketing strategies are particularly incisive for these aspects. In another recent study, however, the impact of certain factors on consumer satisfaction was analysed, and among them the intrinsic quality of the food provided was found to have a significant effect on the frequency of return to the restaurant chain (Saghaian and Mohammadi 2018). Other influential factors concern the characteristics of the environment, the structure itself, and the design of the restaurant chain (Dastane and Fazlin 2017).
The findings show a group of consumers who are sufficiently satisfied with the service time and the staff communication skills. This differs from a 2015 sector study, for example, where different consumers’ opinions emerged, with a low appreciation for these variables (Jaini et al. 2015).
Regarding the comparison between IHF and LHF, the general level of consumer satisfaction was medium-high but some differences emerged for specific items. There was lower satisfaction with McDonald’s and Burger King with regard to the perceived quality of the supply chain, the ethical and animal welfare issues, and the specifically selected food. On the other hand, M** Bun and L’Hamburgheria di Eataly achieved higher scores for the same items. Moreover, the diversification of products/services for LHF also seems to be evident to consumers, in line with what has emerged in other studies (Bonadonna et al. 2019; Bonadonna et al. 2020), and this diversification appears to be effective and highly appreciated by the sample involved. This positive approach highlights a marked sensitivity of consumers towards issues such as the importance of the origin of food (Kumpulainen et al. 2018; Petrescu et al. 2020; Pícha et al. 2018) and the entire supply chain through food innovation, breeding methods, and the satisfaction of ethical and social needs (Burnier et al. 2021; Carbone 2018; Gross et al. 2021; García-Gudiño et al. 2021; Sajdakowska et al. 2018).
5. Conclusions, Limitations, and Future Research
The results show that the younger generations are more inclined to have a break in an IHF restaurant than in an LHF one. However, looking at the level of satisfaction, IHF and LHF obtained very similar results, although there are some differences linked to a number of items considered. The research contributes to the theory giving new insights about the perception of young consumers on hamburger restaurants, presenting a comparison between international and local fast-food chains. Moreover, the study allowed us to reflect on the most important elements taken into consideration by respondents when they decide to have a frugal meal.
The foodservice models presented in this study have distinct characteristics. On the one hand, IHF is characterised by a strategy devoted to maximising efficiency by providing fast, cheap, tasty, and standardised food with small elements of personalisation. On the other hand, LHF provides slower food that is prepared using ingredients linked to the territory and tradition, with high quality standards, and provides relevant information involving the environmental sustainability of decision-making and production processes.
Although the results of the study show that respondents identify, as significant elements, animal welfare, the local origin of raw materials, and ethical and social needs in carrying out activities in the supply chain, at the same time they have a propensity to prefer IHF. This observation highlights several practical implications for fast-food operators, who should concentrate on more interaction with local supply chains for the creation of meals made from high quality raw materials.
However, this study has some limitations because of the data collected and the methodology applied. Indeed, the sample is limited to consumers resident in the study area, mainly belonging to younger generations such as Gen Y and Gen Z, and the sample size is small, mainly because of the survey technique (virtual referral sampling). In this case, the discussion has an explorative intention and compares only the main results obtained to highlight differences among hamburger foodservices. Moreover, the study opens opportunities for some future research.
Future research can go into greater depth by analysing the perception of the quality of service of different generational cohorts, to detect specific elements that are relevant to target. Moreover, it would be interesting to gain more insights into how people evaluate critical issues related to animal welfare and/or ethical aspects.
The relationship between IHF and LHF can also be analysed by looking at the roles of social media and social networks in influencing the common perception of online users. In this case, too, dividing the respondents into different generational cohorts could highlight interesting peculiarities.
Finally, it would be interesting to collect data on the perceptions of consumers in different European countries, to evaluate the critical issues within a wider area and with more socio-cultural nuances.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.G., N.T. and A.B.; methodology, C.G., N.T. and A.B.; validation, C.G., N.T. and A.B.; formal analysis, C.G., N.T. and A.B.; investigation, C.G., N.T. and A.B.; resources, C.G., N.T. and A.B.; data curation, C.G., N.T. and A.B.; writing—original draft preparation, C.G., N.T. and A.B.; writing—review and editing, C.G., N.T. and A.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A

Table A1.
Dimensions, sub-dimensions, and items of the quality of service.
Table A1.
Dimensions, sub-dimensions, and items of the quality of service.
| Dimensions | Sub-Dimensions | Items |
|---|---|---|
| Quality of Interaction | A—Interpersonal interaction | A1—Staff has a pleasant demeanor A2—Staff looks nice and well cared for A3—Staff are understanding and reassuring A4—Staff can handle special requests |
| B—Problem solving skills | B1—Staff is skilled in apologising to customers B2—Staff are capable of handling problems and complaints | |
| C—Professional skills | C1—Staff is knowledgeable about the products on offer C2—Staff is skilled in handling requests C3—Staff shows good training and experience C4—Staff speaks an understandable language C5—Staff are able to inform you about something that is not available that day C6—Staff also speaks languages other than Italian | |
| Quality of the Environment | D—General questions as to environment | D1—The wall decorations of the restaurant are pleasant D2—The spaces between the tables are adequate D3—The interior furnishings of the restaurant are pleasant D4—The tables set up for catering are comfortable D5—The seating is comfortable D6—The lighting of the dining room is adequate D7—The background music is pleasant D8—The temperature of the dining room is pleasant |
| E—Cleaning in restaurant | E1—The perceived cleanliness is satisfactory E2—Prepackaged toppings are available E3—The staff seem neat and clean E4—The kitchen (if open) seems to be managed in a hygienically correct way E5—The catering areas are clean and welcoming E6—The toilets are clean and well maintained | |
| F—Layout and design | F1—Parking available near the restaurant F2—The outside of the restaurant has an attractive appearance F3—In the catering rooms can feel a pleasant scent | |
| G—Menu design | G1—Menus are easy to read G2—Menus are easy to understand G3—Menus are written in a foreign language (if any) with explanations G4—Menus reflect the theme, image, and price range of the restaurant | |
| Quality of the Result | H—Restaurant experience | H1—Waiting time to sit down is reasonable H2—The restaurant interprets the type of experience the consumer desires H3—The staff serve the customers on time H4—After consuming the meal, the experience met expectations |
| I—Quality of food/supply chain | I1—The food is fresh and well cooked I2—The food is attractive and tempting I3—The food consumed meets expectations I4—Food satisfies the sensory needs I5—Food satisfies the desired nutritional intake I6—The supply chain meets the needs related to animal welfare I7—The supply chain satisfies the ethical and social needs I8—The raw materials used are of local origin I9—The raw materials used are of national origin | |
| L—Menu quality | L1—The food meets the nutritional needs of consumers L2—The proposed food is one of a kind L3—the proposed food cannot be prepared at home | |
| Quality of the price/quality ratio | M—Quality/price ratio (the primary dimension is not divided into sub-dimensions) | M1—Compared to the service used, the quality-price ratio is adequate M2—Compared to the raw materials used, the quality-price ratio is adequate M3—Compared to the food consumed, the quality-price ratio is adequate M4—Overall, compared to the product/service used, the quality-price ratio is adequate |
References
- Abrahale, K., Sandra Sousa, Gabriela Albuquerque, Patrícia Padrão, and Nuno Lunet. 2019. Street food research worldwide: A scoping review. Journal of Human Nutrition and Dietetics 32: 152–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almli, Valérie Lengard, Wim Verbeke, Filiep Vanhonacker, Tormod Næs, and Margrethe Hersleth. 2011. General image and attribute perceptions of traditional food in six European countries. Food Quality and Preference 22: 129–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, Geoff. 2008. The Slow Food Story: Politics and Pleasure. London: Pluto Press. [Google Scholar]
- Arcese, Gabriella, Serena Flammini, Maria Caludia Lucchetti, and Olimpia Martucci. 2015. Evidence and experience of open sustainability innovation practices in the food sector. Sustainability 7: 8067–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barone, Michele, and Alessandra Pellerito. 2020. The Street Food Culture in Europe. In Sicilian Street Foods and Chemistry. Cham: Springer. [Google Scholar]
- Bellia, Claudio, Manuela Pilato, and Hugues Seraphin. 2016. Street food and food safety: A driver for tourism? Calitatea 17: 20. [Google Scholar]
- Besson, Théo, Hugo Bouxom, and Thibault Jaubert. 2020. Halo it’s meat! The effect of the vegetarian label on calorie perception and food choices. Ecology of Food and Nutrition 59: 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonadonna, Alessandro, Simona Alfiero, Massimo Cane, and Edyta Gheribi. 2019. Eating hamburgers slowly and sustainably: The fast food market in north-west Italy. Agriculture 9: 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonadonna, Alessandro, Chiara Giachino, Francesca Pucciarelli, and Bernardo Bertoldi. 2020. The evolution of fast food in a customer-driven era: Innovation and sustainability for customer needs. In Customer Satisfaction and Sustainability Initiatives in the Fourth Industrial Revolution. Edited by Silvestri Cecilia, Aquilani Barbara and Piccarozzi Michela. Pennsylvania: IGI Global, pp. 251–69. [Google Scholar]
- Brady, Michael K., and J. Joseph Cronin, Jr. 2001. Some new thoughts on conceptualizing perceived service quality: A hierarchical approach. Journal of Marketing 65: 34–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnier, Pedro Carvalho, Eduardo Eugênio Spers, and Marcia Dutra de Barcellos. 2021. Role of sustainability attributes and occasion matters in determining consumers’ beef choice. Food Quality and Preference 88: 104075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappella, Francesco, Paolo Giaccaria, and Giovanni Peira. 2015. La Filiera Della Carne Piemontese: Scenari Possibili. Torino: IRES Piemonte. [Google Scholar]
- Carbone, Anna. 2018. Foods and places: Comparing different supply chains. Agriculture 8: 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardozo, Richard N. 1965. An Experimental Study of Customer Effort, Expectation, and Satisfaction. Journal of Marketing Research 2: 244–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carzedda, Matteo, Francesco Marangon, Federico Nassivera, and Stefania Troiano. 2018. Consumer satisfaction in Alternative Food Networks (AFNs): Evidence from Northern Italy. Journal of Rural Studies 64: 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churchill, Gilbert A., and Carol Surprenant. 1982. An Investigation into the Determinants of Customer Satisfaction. Journal of Marketing Research 19: 491–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciavolino, Enrico, and Jens J. Dahlgaard. 2007. ECSI—Customer satisfaction modelling and analysis: A case study. Total Quality Management & Business Excellence 18: 545–54. [Google Scholar]
- Crawford, Alice, Sarah A. Humphries, and Margaret M. Geddy. 2015. McDonald’s: A Case Study in Glocalization. Journal of Global Business Issues 9: 11. [Google Scholar]
- Dabholkar, Pratibha A., Dayle I. Thorpe, and Joseph O. Rentz. 1996. A measure of service quality for retail stores: Scale development and validation. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science 24: 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlgaard-Park, Su Mi. 2012. Core values—The entrance to human satisfaction and commitment. Total Quality Management & Business Excellence 23: 125–40. [Google Scholar]
- Dastane, Omkar, and Intan Fazlin. 2017. Re-investigating key factors of customer satisfaction affecting customer retention for fast food industry. International Journal of Management, Accounting and Economics 4: 379–400. [Google Scholar]
- De Bernardi, Alberto. 2015. I consumi alimentari in Italia: Uno specchio del cambiamento. In L’Italia e le Sue Regioni. L’età Repubblicana. Edited by Salvati Mariuccia and Sciolla Loredana. Milano: Treccani. [Google Scholar]
- Farahiyan, Leila, Sanjay S. Kaptan, and S. U. Jadhavar. 2015. An exploratory study of fast food restaurant selection criteria amongst college students through conjoint analysis. Journal of Commerce and Management Thought 6: 487–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forno, Francesca, Cristina Grasseni, and Silvana Signori. 2013. Oltre la spesa. I Gruppi di Acquisto Solidale come laboratori di cittadinanza e palestre di democrazia. Sociologia del Lavoro 132: 127–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Gudiño, Javier, Isabel Blanco-Penedo, Marina Gispert, Albert Brun, José Perea, and Maria Font-i-Furnols. 2021. Understanding consumers’ perceptions towards Iberian pig production and animal welfare. Meat Science 172: 108317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheribi, Edyta. 2017. Corporate social responsibility in gastronomy business in Poland on selected example. European Journal of Service Management 23: 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gross, Sabine, Megan E. Waldrop, and Jutta Roosen. 2021. How does animal welfare taste? Combining sensory and choice experiments to evaluate willingness to pay for animal welfare pork. Food Quality and Preference 87: 104055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossi, Federica. 2012. Bar, fast food e tavole calde: Nomi e funzioni dei locali di ristoro nelle città romane dell’Impero. LANX. Rivista della Scuola di Specializzazione in Archeologia-Università degli Studi di Milano, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grow, H. Mollie, and Marlene B. Schwartz. 2014. Food marketing to youth: Serious business. JAMA Journal of the American Medical Association 312: 1918–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, Luis, Anna Claret, Wim Verbeke, Geraldine Enderli, Sylwia Zakowska-Biemans, Filiep Vanhonacker, Sylvie Issanchou, Marta Sajdakowska, Britt Signe Granli, Luisa Scalvedi, and et al. 2010. Perception of traditional food products in six European regions using free word association. Food Quality and Preference 21: 225–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemple, Donald J. 1977. Consumer satisfaction with the home buying process: Conceptualization and measurement. In The Conceptualization of Consumer Satisfaction and Dissatisfaction. Edited by Keith Hunt. Cambridge: Marketing Science Institute. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, Jillian, Zandile Mchiza, Jean Fourie, Thandi Puoane, and Nelia Steyn. 2016. Consumption patterns of street food consumers in Cape Town. Journal of Consumer Sciences 1: 25–35. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, John A., and Jagdish N. Sheth. 1969. The Theory of Buyer Behavior. New York. 63. Available online: https://books.google.it/books?hl=it&lr=&id=HLuo1sawoAYC&oi=fnd&pg=PA81&dq=%22A+Theory+of+Buyer+Behavior%22&ots=IfkCaT7tTw&sig=wH59w8l0-IvldFQWUYhlUJ8QdZ8&redir_esc=y#v=onepage&q=%22A%20Theory%20of%20Buyer%20Behavior%22&f=false (accessed on 1 July 2021).
- Hultén, Bertil. 2011. Sensory marketing: The multi-sensory brand-experience concept. European Business Review 23: 256–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ifeanyichukwu, Chioma, and Abude Peter. 2018. The Role of Sensory Marketing in Achieving Customer Patronage in Fast Food Restaurants in Awka. International Research Journal of Management, IT & Social Sciences 5: 155–63. [Google Scholar]
- Jaini, Azila, Nor Asma Ahmad, and Siti Zamanira Mat Zaib. 2015. Determinant factors that influence customers’ experience in fast food restaurants in Sungai Petani, Kedah. Journal of Entrepreneurship and Business 3: 60–71. [Google Scholar]
- Joe, Meeyoung, Seoki Lee, and Sunny Ham. 2020. Which brand should be more nervous about nutritional information disclosure: McDonald’s or Subway? Appetite 155: 104805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowitt, Beth. 2014. Fallen Arches: Can McDonald’s Get Its Mojo Back. Available online: https://fortune.com/2014/11/12/can-mcdonalds-get-its-mojo-back/ (accessed on 17 September 2020).
- Kumpulainen, Tommi, Annukka Vainio, Mari Sandell, and Anu Hopia. 2018. How young people in Finland respond to information about the origin of food products: The role of value orientations and product type. Food Quality and Preference 68: 173–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Alvin, and Claire Lambert. 2017. Corporate social responsibility in McDonald’s Australia. Asian Case Research Journal 21: 393–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, Nicole, Qiushi Huang, Patrick Merkel, Dong Keun Rhee, and Allison C. Sylvetsky. 2020. Differences in the sugar content of fast-food products across three countries. Public Health Nutrition. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Weng-Kun, Yueh-Shian Lee, and Li-Mei Hung. 2017. The interrelationships among service quality, customer satisfaction, and customer loyalty: Examination of the fast-food industry. Journal of Foodservice Business Research 20: 146–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastronardi, Luigi, Luca Romagnoli, Giampiero Mazzocchi, Vincenzo Giaccio, and Davide Marino. 2019. Understanding consumer’s motivations and behaviour in alternative food networks. British Food Journal 121: 2102–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, Surbhi. 2017. Glocalization in Fast Food Chains: A Case Study of McDonald’s. In Strategic Marketing Management and Tactics in the Service Industry. Pennsylvania: IGI Global. [Google Scholar]
- Morgan, Kevin. 2009. Feeding the city: The challenge of urban food planning. International Planning Studies 14: 341–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, Kevin. 2015. Nourishing the city: The rise of the urban food question in the Global North. Urban Studies 52: 1379–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosi, Costanza, and Lorenzo Zanni. 2004. Moving from “typical products” to “food-related services”. The Slow Food case as a new business paradigm. British Food Journal 106: 779–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parente, Giuseppe. 2007. Cibo veloce e cibo di strada. Le tradizioni artigianali del fast-food in Italia alla prova della globalizzazione. Storicamente 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peri, Claudio. 2006. The universe of food quality. Food Quality and Preference 17: 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petimar, Joshua, Maricelle Ramirez, Sheryl L. Rifas-Shiman, Stephanie Linakis, Jewel Mullen, Christina A. Roberto, and Jason P. Block. 2019. Evaluation of the impact of calorie labeling on McDonald’s restaurant menus: A natural experiment. International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity 16: 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrescu, Dacinia Crina, Iris Vermeir, and Ruxandra Malina Petrescu-Mag. 2020. Consumer understanding of food quality, healthiness, and environmental impact: A cross-national perspective. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17: 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrini, Carlo. 2003. Slow Food: The Case for Taste. New York: Columbia University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Petrini, Carlo. 2013. Slow Food Nation: Why Our Food Should Be Good, Clean, and Fair. Milano: Rizzoli Publications. [Google Scholar]
- Pícha, Kamil, Josef Navrátil, and Roman Švec. 2018. Preference to local food vs. preference to “national” and regional food. Journal of Food Products Marketing 24: 125–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitte, Jean-Robert. 1997. Nascita e diffusione dei ristoranti. In Storia Dell’alimentazione. Edited by Jean-Louis Flandrin and Massimo Montanari. Bari: Laterza. [Google Scholar]
- Poulain, Jean-Pierre. 2017. The Sociology of Food. Eating and the Place of Food in Society. London: Bloomsbury. [Google Scholar]
- Renting, Henk, Terry K. Marsden, and Jo Banks. 2003. Understanding alternative food networks: Exploring the role of short food supply chains in rural development. Environment and Planning A 35: 393–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritzer, George, and Nicola Rainò. 1997. Il Mondo alla McDonald’s. Bologna: Il Mulino. [Google Scholar]
- Saghaian, Sayed, and Hosein Mohammadi. 2018. Factors affecting frequency of fast food consumption. Journal of Food Distribution Research 49: 22–29. [Google Scholar]
- Sajdakowska, Marta, Paweł Jankowski, Krystyna Gutkowska, Dominika Guzek, Sylwia Żakowska-Biemans, and Irena Ozimek. 2018. Consumer acceptance of innovations in food: A survey among Polish consumers. Journal of Consumer Behaviour 17: 253–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schifani, Giorgio, and Giuseppina Migliore. 2011. Solidarity Purchase Groups and the new critical and ethical consumer trends: First results of a direct study in Sicily. New Medit 3: 26–33. [Google Scholar]
- Sezgin, Aybuke Ceyhun, and Nevin Şanlıer. 2016. Street food consumption in terms of the food safety and health. Journal of Human Sciences 13: 4072–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqua, A. Ayesha, and I. Mohamed Shaw Alem. 2018. Impact of situational factors in students’ preference of fast food—An empirical study. Clear International Journal of Research in Commerce & Management 9: 9–11. [Google Scholar]
- Simi, Demi, and Jonathan Matusitz. 2017. Glocalization of Subway in India: How a US Giant Has Adapted in the Asian Subcontinent. Journal of Asian and African Studies 52: 573–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaichon, Park, Sara Quach, and Jiraporn Surachartkumtonkun. 2019. Intention to purchase at a fast food store: Excitement, performance and threshold attributes. Asian Journal of Business Research 9: 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tregear, Angela. 2011. Progressing knowledge in alternative and local food networks: Critical reflections and a research agenda. Journal of Rural Studies 27: 419–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trichopoulou, Antonia, Stavroula Soukara, and Effie Vasilopoulou. 2007. Traditional foods: A science and society perspective. Trends in Food Science & Technology 18: 420–27. [Google Scholar]
- Tse, David K., and Peter C. Wilton. 1988. Models of consumer satisfaction formation: An extension. Journal of Marketing 52: 204–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weichselbaum, Elisabeth, Bridget Benelam, and H. Soares Costa. 2009. Traditional Foods in Europe. Norwich: EuroFIR Project. Available online: https://www.eurofir.org/wp-admin/wp-content/uploads/EuroFIR%20synthesis%20reports/Synthesis%20Report%206_Traditional%20Foods%20in%20Europe.pdf (accessed on 2 August 2020).
- Wu, Hung-Che, and Zurinawati Mohi. 2015. Assessment of service quality in the fast-food restaurant. Journal of Foodservice Business Research 18: 358–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarimoglu, Emel Kursunluoglu, and Aylin Banu Satana. 2016. Students’ insights regarding sales promotion tools: A preliminary study of the fast food industry. ASBBS Proceedings 23: 561. [Google Scholar]
- Yip, Joanne, Heidi HT Chan, Bonny Kwan, and Derry Law. 2011. Influence of appearance orientation, BI and purchase intention on customer expectations of service quality in Hong Kong intimate apparel retailing. Total Quality Management & Business Excellence 22: 1105–18. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Jong Pil, Payal Kaishap Dutta, and Dawn Thorndike Pysarchik. 2007. The impact of reference groups and product familiarity on Indian consumers’ product purchases. Journal of Global Academy of Marketing Science 17: 75–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Lin, Deepa Anagondahalli, and Ai Zhang. 2017. Social media and culture in crisis communication: McDonald’s and KFC crises management in China. Public Relations Review 43: 487–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).