Optimization of Natural Ventilation via Computational Fluid Dynamics Simulation and Hybrid Beetle Antennae Search and Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm for Yungang Grottoes, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
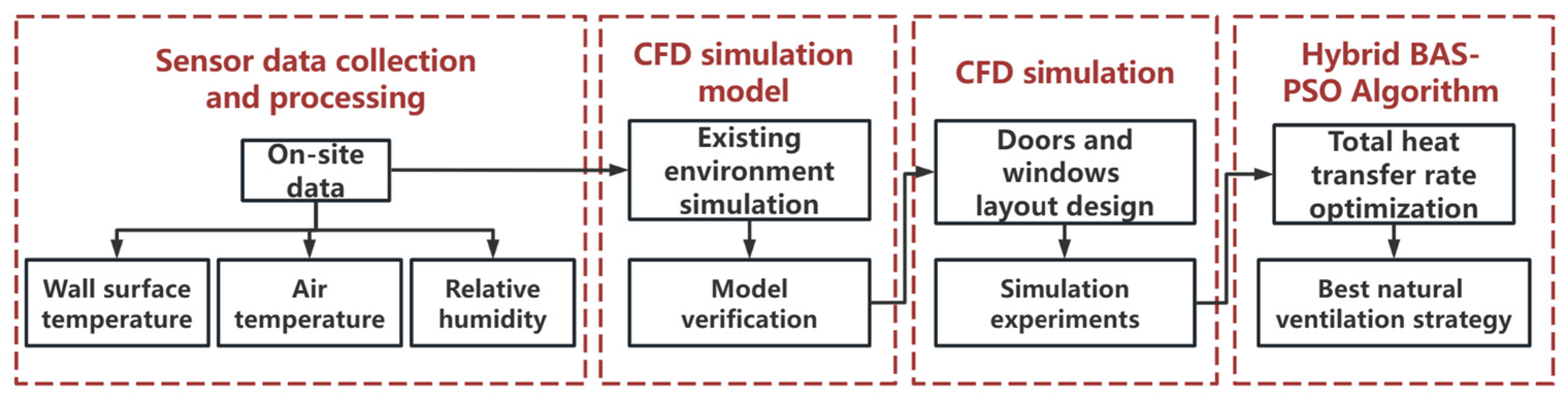
2. Methods and Procedures
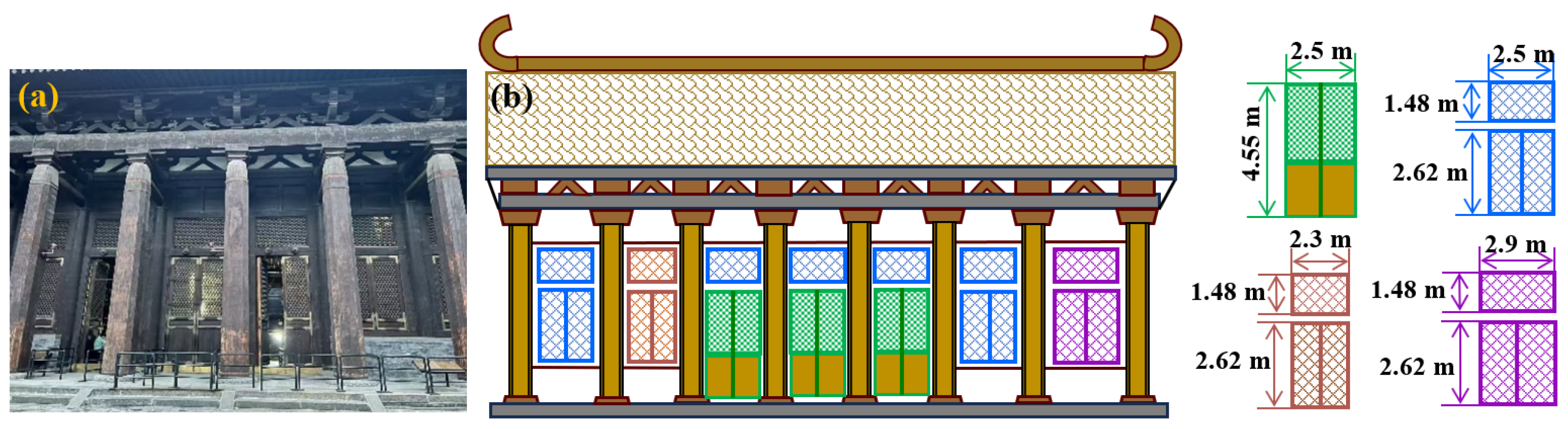
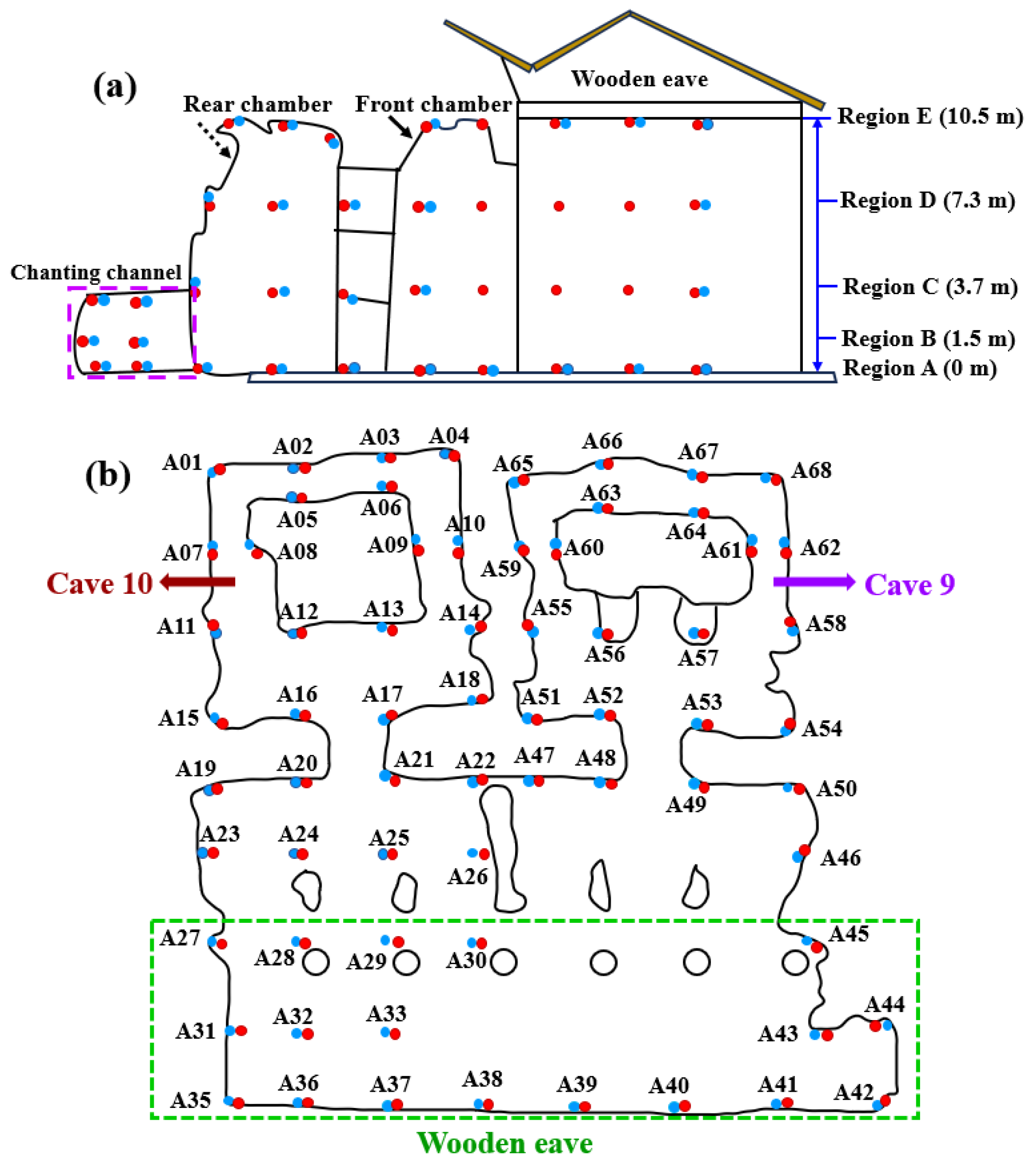
2.1. The Locations of Sensors
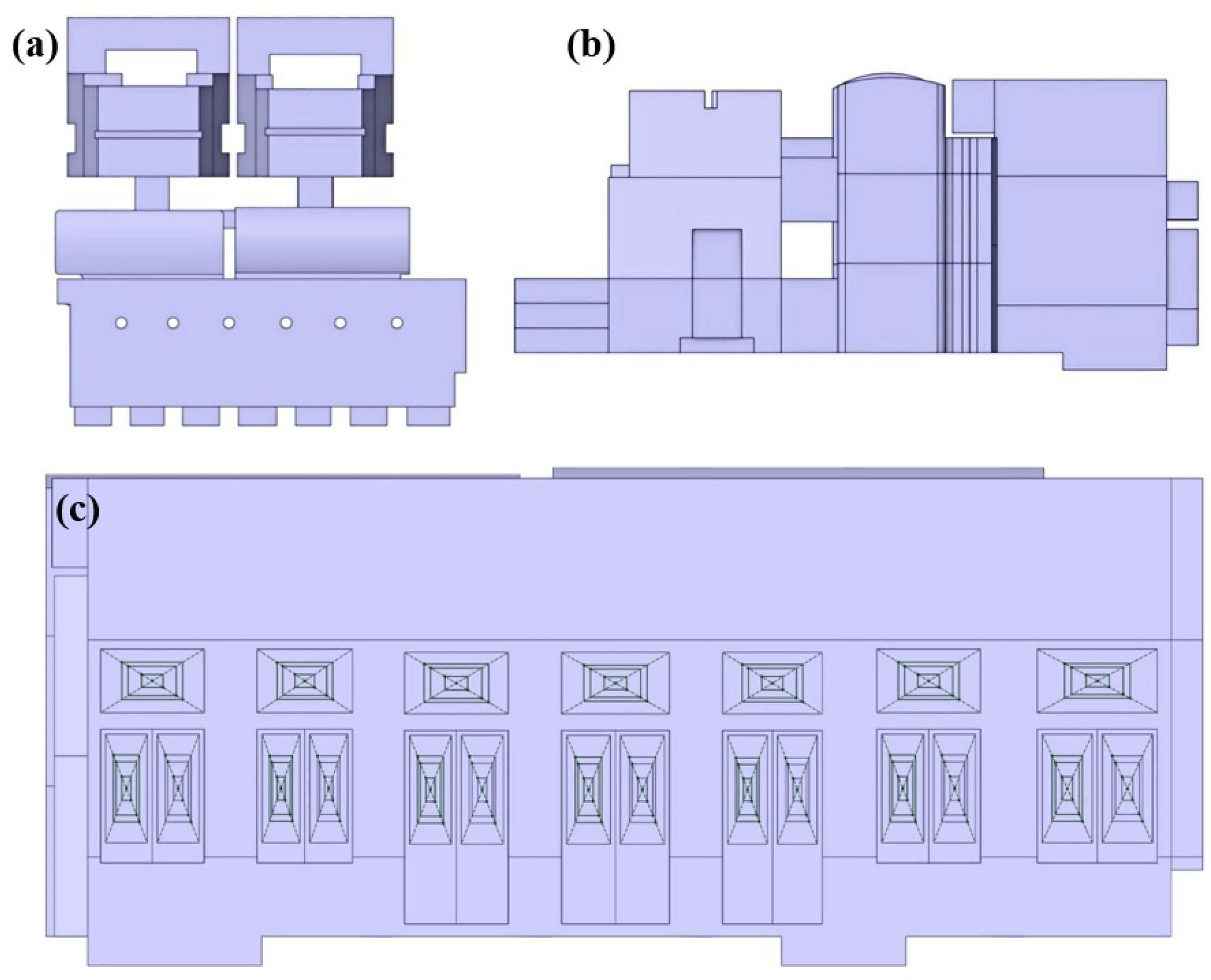
2.2. Simulation Model
2.3. Orthogonal Experimental Design
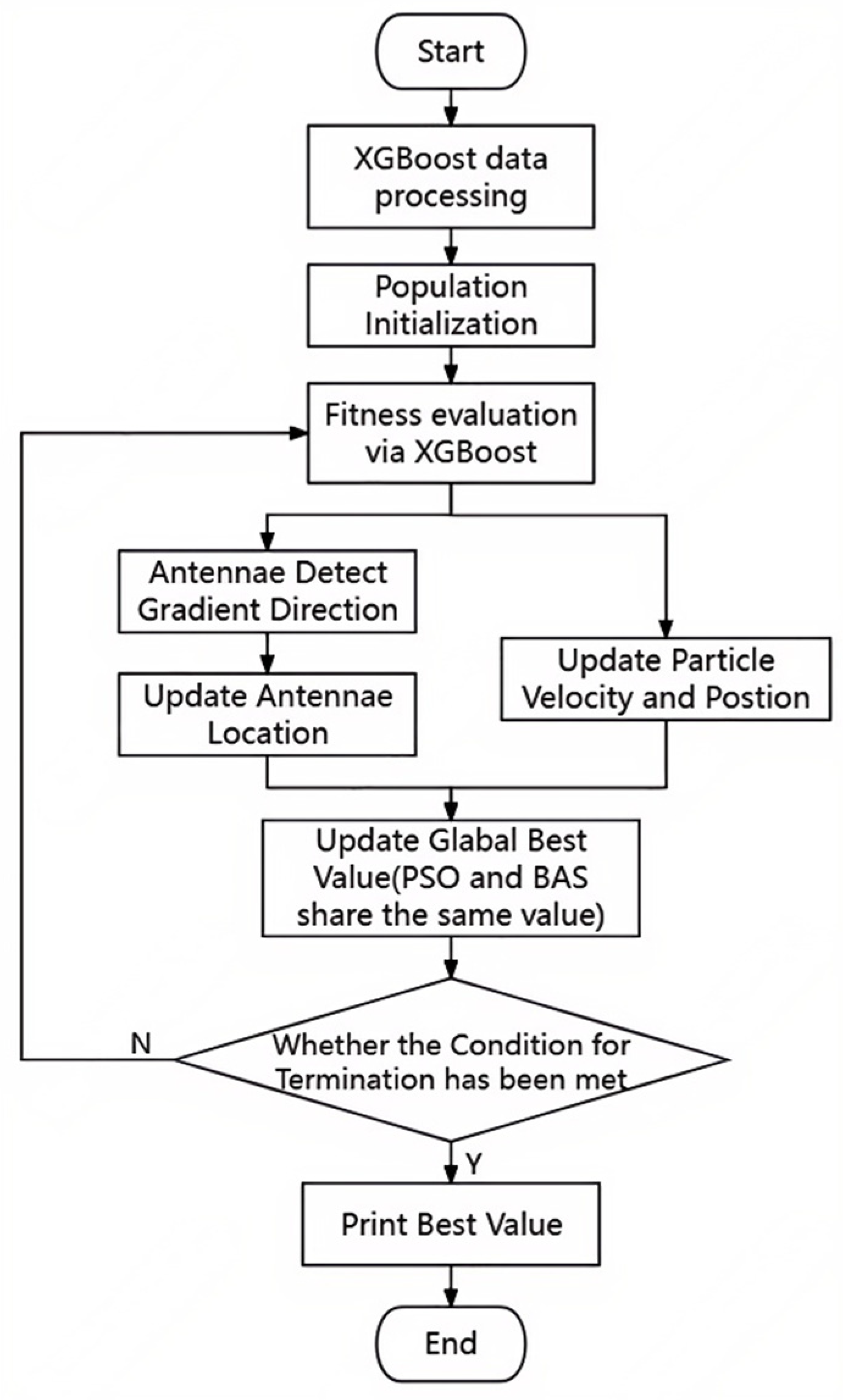
2.4. Intelligent Hybrid Algorithm
3. Results
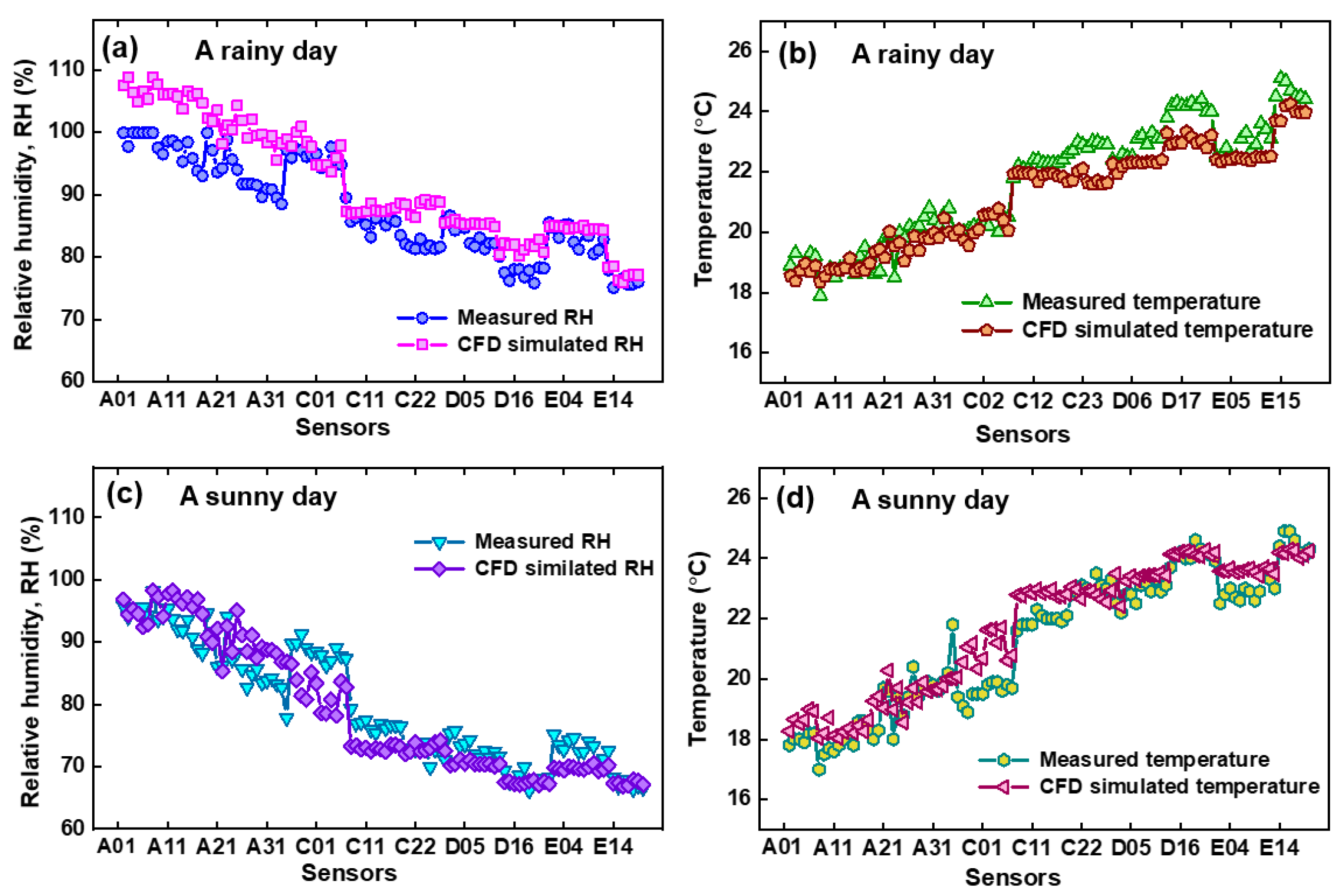
3.1. Model Validation
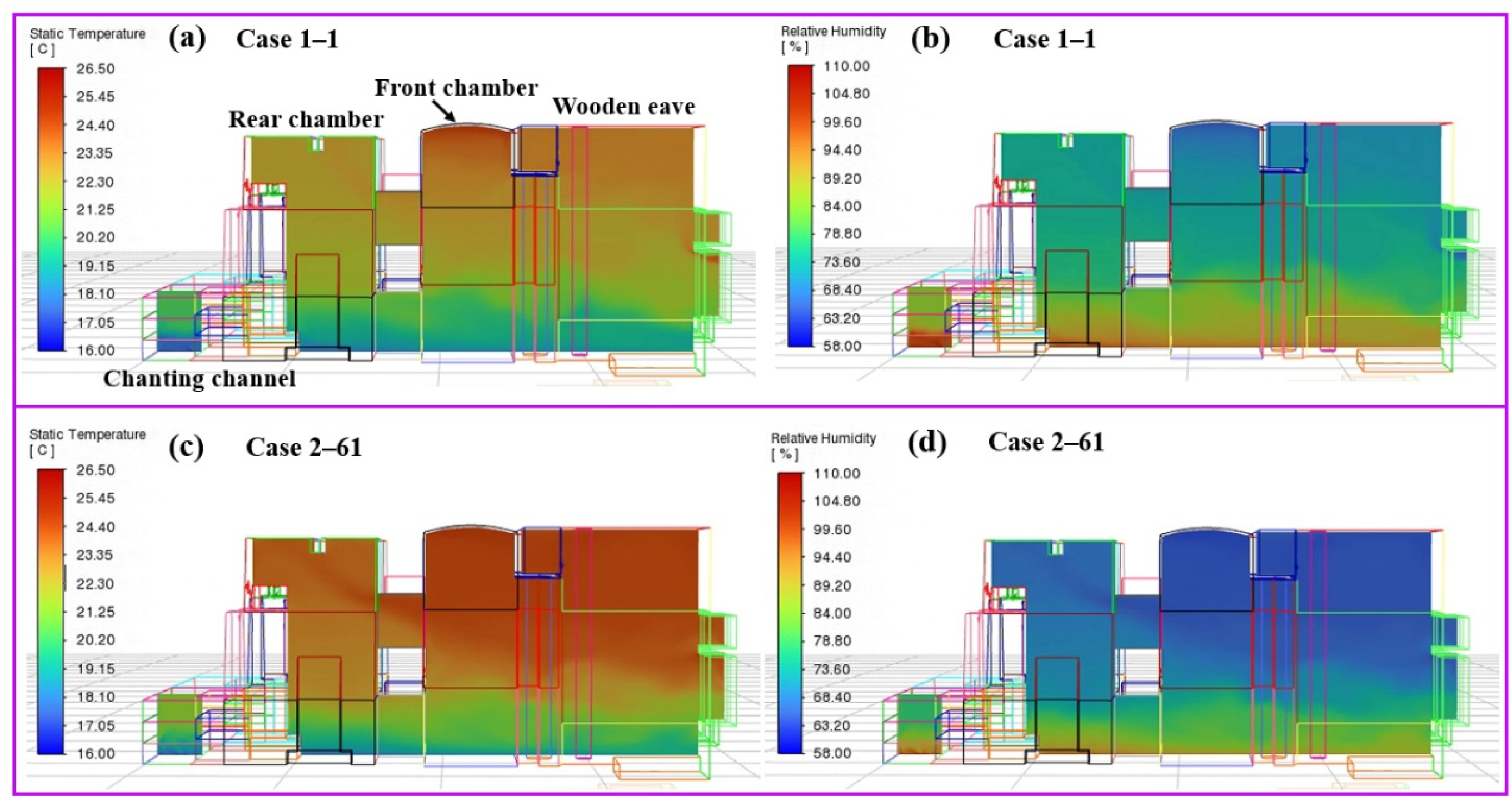
3.2. CFD Simulation
3.3. XGBoost Fitting and Comparative Analysis of Algorithm Performances
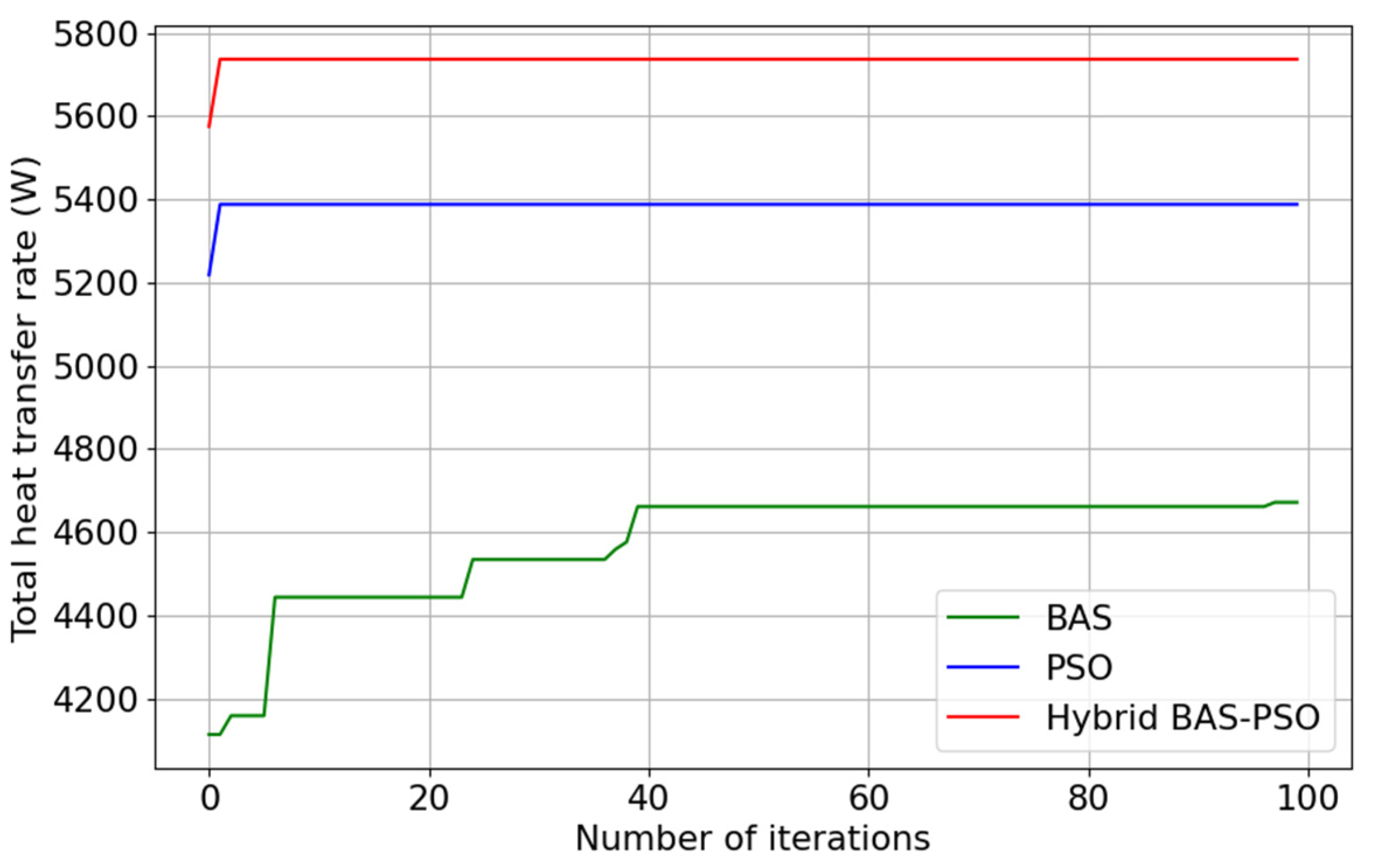
3.4. Optimization of Total Heat Transfer Rate
3.5. On-Site Verification of Natural Ventilation Strategy Efficiency
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- A CFD simulation model for the hygrothermal environment within the grottoes is developed. The accuracy of this model is validated through real-time measured data on site, exhibiting high precision in predicting temperature and relative humidity under various operational conditions.
- (2)
- The natural ventilation efficiency of the grottoes can be effectively enhanced by employing various ventilation rates and different configurations of the doors and windows on the wooden eave of Cave 9 and Cave 10.
- (3)
- XGBoost shows a good fitting performance, with an R2 of 0.9584. The hybrid BAS–PSO algorithm, combined with XGBoost fitting, shows strong performance in optimization, leading to the achievement of the highest Qmax of 5746.74 W. The hybrid BAS–PSO algorithm exhibits superiority in the optimization of natural ventilation over traditional BAS and PSO algorithms.
- (4)
- The hybrid BAS–PSO algorithm yields the optimal configurations of openings of doors and windows. That is, a 10% ventilation rate is employed for the W2#R, SW1#, SW3#, and SW5# windows, and the other doors and windows remain set at the maximum ventilation rate. It is further validated by CFD simulations, confirming its reliability. The proposed natural ventilation strategy is validated by on-site measured data, indicating that it is effective.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yao, S.S.; Yan, Z.F.; Ma, Q.; Xu, B.K.; Zhang, Z.M.; Bi, W.B.; Zhang, J.J. Analysis of the annual hygrothermal environment in the Maijishan Grottoes by field measurements and numerical simulations. Build. Environ. 2022, 221, 109229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.Z.; Zhang, R.Y.; Luo, Q.Y.; Guo, X.W.; Cao, M.G. Study on optimal design of Grotto-eave system with cable inerter viscous damper for vibration control. Buildings 2022, 12, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, N.; Wang, Y.L.; Wu, X.C.; Duan, Y.F.; Li, P.S.; He, M.C. Real-Time Experimental Monitoring for Water Absorption Evolution Behaviors of Sandstone in Mogao Grottoes, China. Energies 2022, 15, 8504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, H.; Zhang, S.J.; Zhi, J.H.; Zhang, R.P.; Ren, J.G.; Ro, C.U. Acid solution decreases the compressional wave velocity of sandstone from the Yungang Grottoes, Datong, China. Herit. Sci. 2019, 7, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.Y.; Cheng, Y.; Huang, J.Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, H.B. Unsupervised weathering identification of grottoes sandstone via statistical features of acoustic emission signals and graph neural network. Herit. Sci. 2024, 12, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, D.Q.; Wang, X.D.; Meng, J.; Ma, X.M.; Jiang, X.W.; Wan, L.; Yan, H.B.; Fan, Y. Infiltration Assessments on Top of Yungang Grottoes by Time–Lapse Electrical Resistivity Tomography. Hydrology 2022, 9, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.C.; Liu, Y.B.; Ren, W.Z.; Xu, W.H.; Cai, S.M.; Wang, J.X. An adaptive prediction method for mechanical properties deterioration of sandstone under freeze–thaw cycles: A case study of Yungang Grottoes. Herit. Sci. 2021, 9, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.J.; Wang, J.M.; Zhu, C.; He, M.C. Effect of water on long-term strength of column rocks based on creep behavior in Yungang grottoes, China. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2019, 37, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, T.H.; Lu, Y.H.; Zhao, G.Z.; Yang, C.Q.; Ren, J.G.; Shi, Y.L. A synthetic approach to weathering degree classification of stone relics case study of the Yungang Grottoes. Herit. Sci. 2018, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.S.; Wan, L.; Huang, J.Z.; Cao, W.B.; Xu, F.; Dong, P. Variable temperature and moisture conditions in Yungang Grottoes, China, and their impacts on ancient sculptures. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 72, 3079–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, K.Z.; Hou, M.L.; Lyu, S.Q.; Li, L.H. Extraction and restoration of scratched murals based on hyperspectral imaging—A case study of murals in the East Wall of the sixth grotto of Yungang Grottoes, Datong, China. Herit. Sci. 2024, 12, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Y.; Kwok, H.H.L.; Luo, H.; Tong, J.C.K.; Cheng, J.C.P. Automatic relative humidity optimization in underground heritage sites through ventilation system based on digital twins. Build. Environ. 2022, 216, 108999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.L.; Gu, Z.L.; Wang, Z.S.; Tian, W.; Li, K. An independent and simultaneous operational mode of air conditioning systems for visitors and relics in archaeology museum. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2016, 100, 911–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.L.; Huang, X.Y.; Feng, Z.B.; Li, J.; Gu, Z.L. Influence of air inlet/outlet arrangement of displacement ventilation on local environment control for unearthed relics within site museum. Energy Build. 2021, 246, 111116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.L.; Yan, Z.F.; Wang, X.D.; Zhang, Z.M.; Shang, R.H.; Bi, W.B. Experimental research on mechanical ventilation system for Cave 328 in Mogao Grottoes, Dunhuang, China. Energy Build. 2016, 130, 692–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.J.; Yan, Z.F.; Zhang, Z.M.; Bi, W.B.; Yan, S.S. A new correlation for single-sided natural ventilation rate based on full-scale experimental study in Mogao Grottoes, Dunhuang, China. Buildings 2023, 13, 1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wu, W.T.; Norford, L.; Li, N.; Malkawi, A. Model predictive control of short-term winter natural ventilation in a smart building using machine learning algorithms. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 73, 106602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.S.; An, Y.M.; Jeong, J.W. Determinants of manual window control for natural ventilation in homes. Build. Environ. 2023, 244, 110741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bay, E.; Martinez–Molina, A.; Dupont, W.A. Assessment of natural ventilation strategies in historical buildings in a hot and humid climate using energy and CFD simulations. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 51, 104287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, N.; Wei, W.; Ba, J.; Yang, T. Operation parameters study on the performance of PEMFC based orthogonal test method. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2024, 61, 105035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, K.; Ji, F.Z.; Zhao, Z.Q.; Fan, L.M.; Wang, M.S. Optimum design of large–diameter reverse circulation drill bit for drilling rescue wells using orthogonal experimental method and CFD simulation. Energies 2023, 16, 3913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.D.; Jiang, Z.A.; Chen, J.H.; Chen, Y.; Yang, B. Optimization of ventilation and dust removal parameters in plateau extra-long tunnel inclined shaft based on orthogonal numerical simulation test method. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 455, 139131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.K.; Wei, X.B.; Xia, Y.F.; Yu, Y.L.; Zeng, L.J.; Cao, G.Y.; Cao, J. Prompt design of direction air supply using CFD–based proper orthogonal decomposition method considering locally dense sample distribution. Build. Environ. 2023, 244, 110812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.H.; Zhou, C.J.; Su, J.; Jin, G.H.; Shen, R. Injection parameter design to improve the high-speed gear heat dissipation: CFD simulation and regression orthogonal experiment. Simul. Model. Pract. Th. 2023, 128, 102795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharagoz, M.M.; Noureldin, M.; Kim, J. Explainable machine learning (XML) framework for seismic assessment of structures using Extreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost). Eng. Struct. 2025, 327, 119621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, A.; Yates, D.; Blanchard, C.; Islam, M.Z.; Ford, R.; Rehman, S.; Walsh, R. The effect of dataset construction and data pre-processing on the eXtreme Gradient Boosting algorithm applied to head rice yield prediction in Australia. Comput. Electron. Agr. 2024, 219, 108716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.J.; Li, L.; Qiang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, S.Y.; Xu, X.L.; Li, H.J.; Hu, S.C. Sensitivity analysis of slope stability based on eXtreme gradient boosting and SHapley Additive exPlanations: An exploratory study. Heliyon 2024, 10, e35871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.Y.; Li, S. BAS: Beetle antennae search algorithm for optimization problems. Int. J. Robot. Control 2018, 1, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.Z.; Cao, L.; Chen, Y.D.; Chen, B.H.; Yue, Y.G. A comprehensive survey of convergence analysis of beetle antennae search algorithm and its applications. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2024, 57, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, L.F.; Yang, H. A review of beetle antennae search algorithm. Comput. Eng. Appl. 2021, 57, 54–64. [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy, J. The particle swarm: Social adaptation of knowledge. In Proceedings of the 1997 IEEE International Conference on Evolutionary Computation (ICEC ’97), Indianapolis, IN, USA, 13–16 April 1997; pp. 303–308. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.H.; Eberhart, R. A Modified Particle Swarm Optimizer. In Proceedings of the IEEE World Congress on Computational Intelligence, Anchorage, AK, USA, 4–9 May 1998; pp. 69–73. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Liu, S.; Ma, Y.; Lan, H.X. The adaptive algorithm of fuzzy logic system based on modified particle swarm optimization. Comput. Eng. Appl. 2000, 7, 62–63. [Google Scholar]
- Chhokar, C.; Ebadi, M.; Bahrami, M. The total heat transfer rate in the evaporating thin film: A new analytical solution. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2025, 162, 108653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yemalwad, Y.; Aasi, H.K.; Srivastava, A. Dynamic measurements of thermal boundary layer and heat transfer rates along a heated flat plate under the influence of ultrasonic field. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2025, 266, 125734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, Z.R.; Xu, H.L.; Lian, W.H.; Chen, Y.L. Inverse modeling of PM2.5 concentration using a particle swarm optimization XGBoost model. Environ. Sci. 2024, 49, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.; Xu, M.N.; Zhang, H.P.; Wu, W.; Ding, J.M. Numerical simulation of Pantograph-Catenary coupling de-icing based on orthogonal experiment method. Trans. Nanjing Univ. Aeronaut. Astronaut. 2023, 40, 29–41. [Google Scholar]
- Seppänen, O.; Fisk, W.J. Association of ventilation system type with SBS symptoms in office workers. Indoor Air. 2002, 12, 98–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leech, J.A.; Nelson, W.C.; Burnett, R.T.; Aaron, S.; Raizenne, M.E. It’s about time: A comparison of Canadian and American time–activity patterns. J. Expo. Anal. Environ. Epidemiol. 2002, 12, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasche, S.; Bischof, W. Daily time spent indoors in German homes–Baseline data for the assessment of indoor exposure of German occupants. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2005, 208, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Muhieldeen, M.W.; Razman, R.; Ee, J.Y.C. Multi–objective optimization of window configuration and furniture arrangement for the natural ventilation of office buildings using Taguchi-based grey relational analysis. Energy Build. 2023, 296, 113385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyon, D.P. The effects of indoor air quality on performance and productivity. Indoor. Air. 2004, 14, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, G.; Xia, X.; Chen, Y.; Setunge, S.; Shi, L. The impacts of occupant behavior on building energy consumption: A review. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2021, 45, 101212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.L.; Weerasuriya, A.U.; Tse, K.T. CFD simulation of natural ventilation of a generic building in various incident wind directions: Comparison of turbulence modelling, evaluation methods, and ventilation mechanisms. Energy Build. 2020, 229, 110516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.V.; Fuertes, A.; Gregori, E.; Giretti, A. Stochastic behavioural models of occupants’ main bedroom window operation for UK residential buildings. Build. Environ. 2017, 118, 144–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, R.; Fabi, V.; Toftum, J.; Corgnati, S.P.; Olesen, B.W. Window opening behaviour modelled from measurements in Danish dwellings. Build. Environ. 2013, 69, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tahmasebi, F.; Cooper, E.; Stamp, S.; Chalabi, Z.; Burman, E.; Mumovic, D. Exploring the relationship between window operation behavior and thermal and air quality factors: A case study of UK residential buildings. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 48, 103997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, B.; Jeong, J.W.; Park, J.S. Occupant behavior regarding the manual control of windows in residential buildings. Energy Build. 2016, 127, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, M.; Zhao, B. Factors affecting occupants’ interactions with windows in residential buildings in Beijing, China. Procedia Eng. 2017, 205, 3428–3434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Level | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Factor | |||||
| W1#L | 10% | 50% | 80% | 100% | |
| W1#R | 10% | 50% | 80% | 100% | |
| W2#L | 10% | 50% | 80% | 100% | |
| W2#R | 10% | 50% | 80% | 100% | |
| W3#L | 10% | 50% | 80% | 100% | |
| W3#R | 10% | 50% | 80% | 100% | |
| W4#L | 10% | 50% | 80% | 100% | |
| W4#R | 10% | 50% | 80% | 100% | |
| D1#L | 10% | 50% | 80% | 100% | |
| D1#R | 10% | 50% | 80% | 100% | |
| D2#L | 10% | 50% | 80% | 100% | |
| D2#R | 10% | 50% | 80% | 100% | |
| D3#L | 10% | 50% | 80% | 100% | |
| D3#R | 10% | 50% | 80% | 100% | |
| SW1# | 0% | 10% | 50% | 80% | |
| SW2# | 0% | 10% | 50% | 80% | |
| SW3# | 0% | 10% | 50% | 80% | |
| SW4# | 0% | 10% | 50% | 80% | |
| SW5# | 0% | 10% | 50% | 80% | |
| SW6# | 0% | 10% | 50% | 80% | |
| SW7# | 0% | 10% | 50% | 80% | |
| Scenario | Time | Temperature (MRE) | Temperature (RMSE) | RH (MRE) | RH (RMSE) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scenario (1) | 12:00 am, 11 August 2023 | 2.71% | 0.80 | 4.96% | 5.69 |
| Scenario (2) | 10:00 am, 15 August 2023 | 2.99% | 0.77 | 3.92% | 3.98 |
| Scenario | Training Group | Testing Group | All |
|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | 0.9992 | 0.8442 | 0.9584 |
| Factor | K1 | K2 | K3 | K4 | R | Best Levels |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W1#L | 4282.59 | 4341.61 | 4375.59 | 4456.55 | 173.96 | (W1#L)4 |
| W1#R | 4306.37 | 4343.95 | 4361.20 | 4444.82 | 138.44 | (W1#R)4 |
| W2#L | 4312.57 | 4332.25 | 4354.38 | 4457.14 | 144.57 | (W2#L)4 |
| W2#R | 4158.52 | 4380.35 | 4438.56 | 4478.91 | 320.39 | (W2#R)4 |
| W3#L | 4286.88 | 4317.03 | 4378.22 | 4474.22 | 187.34 | (W3#L)4 |
| W3#R | 4271.44 | 4397.95 | 4399.03 | 4387.92 | 127.59 | (W3#R)3 |
| W4#L | 4267.26 | 4361.61 | 4347.93 | 4479.55 | 212.28 | (W4#L)4 |
| W4#R | 4156.38 | 4374.97 | 4416.97 | 4508.03 | 351.66 | (W4#R)4 |
| D1#L | 4193.90 | 4288.52 | 4242.57 | 4731.35 | 537.45 | (D1#L)4 |
| D1#R | 4158.66 | 4307.94 | 4310.58 | 4679.16 | 520.50 | (D1#R)4 |
| D2#L | 4151.51 | 4293.84 | 4330.63 | 4680.37 | 528.86 | (D2#L)4 |
| D2#R | 4242.37 | 4281.34 | 4304.20 | 4628.43 | 386.05 | (D2#R)4 |
| D3#L | 4214.34 | 4290.04 | 4288.49 | 4663.47 | 449.13 | (D3#L)4 |
| D3#R | 4212.61 | 4296.50 | 4305.85 | 4641.38 | 428.77 | (D3#R)4 |
| SW1# | 4376.10 | 4312.80 | 4383.45 | 4383.99 | 71.20 | (SW1#)4 |
| SW2# | 4360.14 | 4402.95 | 4329.31 | 4363.95 | 73.63 | (SW2#)2 |
| SW3# | 4332.46 | 4261.43 | 4409.45 | 4453.00 | 191.56 | (SW3#)4 |
| SW4# | 4229.56 | 4419.18 | 4435.11 | 4372.49 | 205.55 | (SW4#)3 |
| SW5# | 4332.06 | 4350.51 | 4356.43 | 4417.34 | 85.29 | (SW5#)4 |
| SW6# | 4303.00 | 4360.72 | 4382.42 | 4410.20 | 107.21 | (SW6#)4 |
| SW7# | 4364.00 | 4309.23 | 4390.98 | 4392.14 | 82.91 | (SW7#)4 |
| Methods | Orthogonal Experiment | Range Analysis | Hybrid Algorithm | Simulation Verification of Algorithm Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qmax | 5358.35 W | 5578.59 W | 5746.74 W | 5730.67 W |
| Orthogonal Experiments Result | Range Analysis Result | Hybrid Algorithm Result |
|---|---|---|
| (W1#L)4 | (W1#L)4 | (W1#L)4 |
| (W1#R)4 | (W1#R)4 | (W1#R)4 |
| (W2#L)4 | (W2#L)4 | (W2#L)4 |
| (W2#R)1 | (W2#R)4 | (W2#R)1 |
| (W3#L)4 | (W3#L)4 | (W3#L)4 |
| (W3#R)4 | (W3#R)3 | (W3#R)4 |
| (W4#L)4 | (W4#L)4 | (W4#L)4 |
| (W4#R)1 | (W4#R)4 | (W4#R)4 |
| (D1#L)4 | (D1#L)4 | (D1#L)4 |
| (D1#R)1 | (D1#R)4 | (D1#R)4 |
| (D2#L)1 | (D2#L)4 | (D2#L)4 |
| (D2#R)4 | (D2#R)4 | (D2#R)4 |
| (D3#L)4 | (D3#L)4 | (D3#L)4 |
| (D3#R)4 | (D3#R)4 | (D3#R)4 |
| (SW1#)4 | (SW1#)4 | (SW1#)1 |
| (SW2#)4 | (SW2#)2 | (SW2#)4 |
| (SW3#)4 | (SW3#)4 | (SW3#)1 |
| (SW4#)1 | (SW4#)3 | (SW4#)4 |
| (SW5#)4 | (SW5#)4 | (SW5#)1 |
| (SW6#)4 | (SW6#)4 | (SW6#)4 |
| (SW7#)4 | (SW7#)4 | (SW7#)4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, X.; Yan, H.; Huang, J.; Liu, T. Optimization of Natural Ventilation via Computational Fluid Dynamics Simulation and Hybrid Beetle Antennae Search and Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm for Yungang Grottoes, China. Buildings 2025, 15, 937. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15060937
Xu X, Yan H, Huang J, Liu T. Optimization of Natural Ventilation via Computational Fluid Dynamics Simulation and Hybrid Beetle Antennae Search and Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm for Yungang Grottoes, China. Buildings. 2025; 15(6):937. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15060937
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Xinrui, Hongbin Yan, Jizhong Huang, and Tingzhang Liu. 2025. "Optimization of Natural Ventilation via Computational Fluid Dynamics Simulation and Hybrid Beetle Antennae Search and Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm for Yungang Grottoes, China" Buildings 15, no. 6: 937. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15060937
APA StyleXu, X., Yan, H., Huang, J., & Liu, T. (2025). Optimization of Natural Ventilation via Computational Fluid Dynamics Simulation and Hybrid Beetle Antennae Search and Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm for Yungang Grottoes, China. Buildings, 15(6), 937. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15060937




