Abstract
Dredged sludge usually has high water content and poor engineering properties, which would be unfavorable for its rapid resource utilization. Meanwhile, straw fiber is an environmentally friendly material for improving the mechanical behavior of soil. In this research, a series of shrinkage tests were conducted to investigate the straw fiber effects on the shrinkage behavior of dredged sludge with high water content. Four initial water contents and straw fiber amounts were designed. The water content and crack development were recorded throughout the test. According to the test results, a reduction in water content regarding drying time can be divided into three stages: the constant-rate stage, the falling-rate stage, and the residual stage. At the falling-rate stage, water evaporation is affected significantly by straw fiber. Compared with the sample without straw fiber, the influence of straw fiber on the water evaporation of dredged sludge depends upon the initial water content and the straw fiber content. The straw fiber shows an overall inhibitory effect on the initiation and development of cracks for the tested samples. Moreover, the influence of straw fiber on the shrinkage behavior of dredged sludge depends upon the initial water content and fiber content.
1. Introduction
Dredging works are carried out every year to guarantee the navigational capacity and eco-environment of rivers, lakes, and coastal water systems, which produce a large amount of dredged sludge with high water content in China [1,2]. Dredged sludge usually has poor engineering properties and cannot be reused directly [3,4,5]. So, it is often first disposed of in areas such as low-lying land and fish ponds. With the progress of natural drainage, consolidation, and evaporation, its water content is decreased [6,7,8]. Due to the common hydraulic dredging methods in China, dredged sludge exhibits a high initial water content, low strength, and poor permeability.The disposal progress of dredged sludge is time-consuming, up to several years, which leads to the prolonged occupation of large land resources, and the treatment cost is greatly increased. Over time, the dredged sludge would inevitably suffer desiccation shrinkage, which is unfavorable for further utilization of dredged sludge (e.g., land application, engineered backfilling, and so on) [9,10,11,12]. Currently, there is insufficient research and practical experience in the application of eco-environmental methods for the treatment of dredged sludge with high water content, including enhancing its consolidation, accelerating the dehydration processes, as well as increasing the load-bearing capacity necessary for mechanical cultivation.
On the other hand, there is a great amount of straw produced in China annually via agricultural production [13]. It is usually costly to store straw. So, a significant amount of straw is burned or casually discarded, which inevitably causes ecological environment pollution [14,15,16]. Meanwhile, since the resource reuse of straw has obvious environmental and economic benefits, straw has been widely used in aspects of practical engineering, like housing construction, straw–cement composites, building material production, and so on [17,18,19]. Furthermore, because straw has a certain amount of tensile strength and ductility, it has been used to improve the mechanical and deformation behavior of soils. For example, straw fiber can be used to increase the mechanical properties of clayey soil [20], shorten curing time, and improve compressive strength [21,22]. El kefafy et al. found that using rice straw fiber on the slope of sand soil can increase the soil stress and friction angle [23]. Chai et al. found that straw can increase soil cohesion and shear strength as the axial strain of the reinforced soil reached a threshold [24,25,26,27]. Moreover, straw has also been used to attenuate the cracking ratio and improve the crack morphology [7]. Jianbin et al. found that straw can limit soil deformation and crack development, and the strength of the sample is affected by the length and content of straw. It should be noted that the water content of soils used in previous research is often low.
At present, the research on straw-stabilized soil has mainly focused on clay with relatively low water content. However, the water content plays an important role in the crack initiation and development of soil [28,29,30]. In compacted clayey soil, the higher water content accelerates the development of desiccation cracks, resulting in a decrease in the surface crack ratio, total crack length, and average crack width [31]. A crack does not usually propagate in those areas of the clay layer with low water content [32]. Therefore, it is vital to clarify the effect of straw fibers on the dry shrinkage characteristics of dredged sludge with high water content. In addition, straw will degrade under the dredge sludge environment, which increases the content of organic matter, carbon (C), nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) [29,33]. But, the fibrous main structure of the straw still exists, which can reinforce the sludge and improve its strength [34]. Therefore, it is vital to clarify the effect of straw fibers on the dry shrinkage characteristics of dredged sludge with high water content.
This research aims to study the straw fiber effects on the desiccation shrinkage behavior of dredged sludge with high water content. A series of shrinkage tests were conducted on samples with different initial water contents and straw fiber contents under natural atmosphere conditions. The sample mass, the volumetric shrinkage, and the desiccation crack development were measured throughout the test. Based on the test results, the straw fiber effects on the shrinkage characteristics of dredged sludge with high water content were first explored. Then, the mechanisms responsible for the alteration in the crack initiation and development of dredged sludge amended by straw fiber were explored. Finally, the appropriate amount of straw fiber for improving the shrinkage characteristics was also discussed.
2. Testing Program
2.1. Materials
The dredged sludge used in this study was obtained from the Huai River Estuary waterway in Funing County, Jiangsu Province, China. Some of the physical properties are shown in Table 1. According to the liquid limit (53.8%) and plastic limit (24.7%), the sludge is a high-plasticity clay per the Unified Soil Classification System [35].

Table 1.
Physical properties of the sludge.
The straw used in this research was obtained from Yancheng City, Jiangsu Province, China. After natural air-drying, the straw was crushed using a grinder and sieved. The straw fiber with the size of 0.075 to 0.6 mm exhibited good dispersibility and was easily mixed uniformly. So, the straw fiber within the range of 0.075 mm to 0.6 mm was used for preparing tested samples (Figure 1). The chemical composition of straw fiber is mainly hemicellulose, cellulose, and lignin, and is rich in nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and some trace elements [36]. The straw fiber used in the test was detected as 21.2% hemicellulose, 32.9% cellulose, and 20.7% lignin. Before the experiment, the straw fiber was placed in an oven and dried at 65 °C for 24 h to prevent the water in the straw affecting the test results.

Figure 1.
Straw fiber.
2.2. Shrinkage Tests
The water content of the dredged sludge is about 2.0 to 3.0 times the liquid limit after sediment [32]. Hence, four initial water contents w0 (=80.7%, 107.6%, 134.5%, and 161.4%) were designed for tested samples. Meanwhile, four straw fiber contents Cs (Table 2), which is defined as the ratio of the straw mass to the mass of soil particle, were also selected to study the variations in shrinkage characteristics with straw content for dredged sludge.

Table 2.
Program of shrinkage tests.
The dredged sludge was first stirred evenly and its initial water content determined. Then, the additional amount of water was calculated according to the target water content in Table 2, added to the dredged sludge, and subsequently stirred to obtain even sludge. After that, the quantity of additional straw fiber required was calculated based on the target straw fiber content and then added to the sludge several times in small amounts while being stirred with a mixer. The homogeneous mixture was filled into the test molds (405 mm × 320 mm × 25 mm) and shaken to remove air bubbles (Figure 2). At last, the surface of the sample was leveled, and each sample was labeled with a number (Table 2). Note that the bottom and side walls of each mold are treated with a thin layer of Vaseline to minimize the impact of friction.
Figure 2.
Tested sample.
All samples were placed in the laboratory under natural atmosphere conditions to simulate the drying process in practical engineering. During the test, the sample was weighed to obtain its water content, which is defined as the ratio of the mass of water to the mass of soil particle. Meanwhile, surface images were also taken to monitor the development of cracks. When the sample mass change between two adjacent measurements was less than 1 g and the difference in water content was less than 0.1% during continued measurement, the test was ended. Throughout the experiment, the average daily temperature was 27 °C, and the average relative humidity was 75%.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Water Content
Since the water content is an important factor affecting the shrinkage characteristics of clay, the variations in water content during the desiccation process were studied at first. Figure 3 depicts the changes in the water content (w) with drying time (t) for dredged sludge with and without straw fibers at the same initial water content. The changes in water content vary with the drying time during the test process, which can basically be divided into three stages, i.e., the constant-rate stage, the falling-rate stage, and the residual stage. At the constant-rate stage, the water content decreases rapidly with drying time. There is a linear relationship between water content and drying time. However, the water content of samples with different straw fiber content is almost the same at the same drying time. This may be because there is sufficient free water at the surface of the samples to evaporate [11], and the duration of this stage is short, which limits the effect of straw fibers on water evaporation. In addition, as this stage usually lasts for a short time, the overall reduction in water content is relatively small compared to the falling-rate stage and increases with the initial water content of the samples; e.g., for the samples with the w0 of 80.7%, the water content decreases by about 19%, whereas the reduction in water content is approximately 38% for those samples with the w0 of 134.5%.
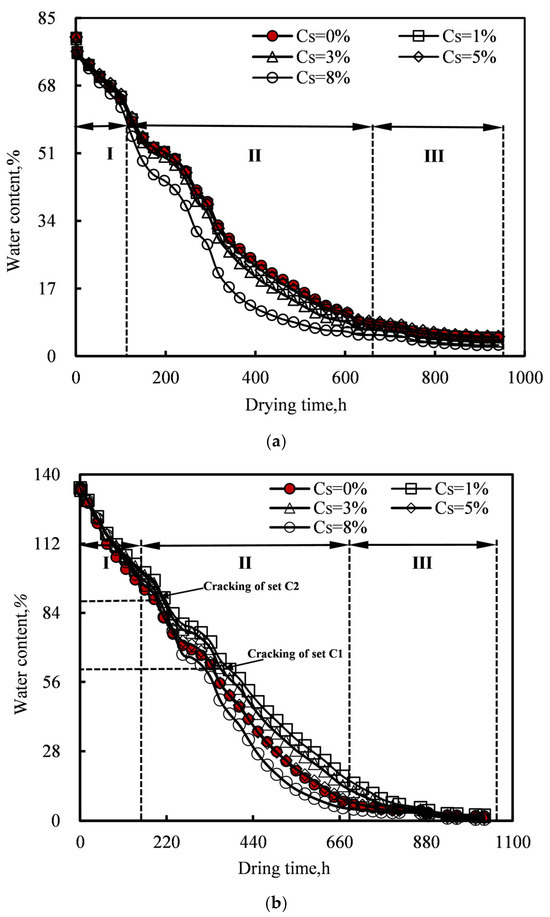
Figure 3.
Changes in water content with drying time. (a) w0 = 80.7%. (b) w0 = 134.5%.
During the falling-rate stage, a significant decrease in water content is observed. Because the straw fiber would provide additional pathways for water movement, the water evaporation is greatly affected by the straw fiber content, as shown in Figure 3. Meanwhile, for those samples with higher w0, the fibrous straw absorbs more water due to the higher evaporate content, thus affecting the desiccation development [37]. Hence, the influence of straw fiber on the water evaporation at this stage depends upon the initial water content. For samples with lower initial water content (w0 = 80.7%) (Figure 3a), the sample with higher straw fiber often has lower water content at the same drying time; i.e., the straw fiber is favorable for water evaporation. This is consistent with the reduction in water content increasing from 57% to 61% when the straw fiber content increases from 0 to 8%. However, for samples with higher initial water content (w0 = 134.5%) (Figure 3b), the reduction in water content increases initially and then decreases with increasing straw fiber content. This may be attributed to the enhanced water adsorption by the exposed hydrophilic functional groups of straw due to degradation under high water content [29]. Therefore, the water content of samples with 1% and 3% straw fiber is more than that of the samples without straw. When the straw fiber increases to 5% and 8%, the water content begins to decrease. The addition of straw fiber changes the porosity and pore structure of dredged sludge, providing more pathways for water movement, leading to the evaporation of water being more than its adsorption.
As the desiccation procedure continues, the variation in the water content enters the residual stage. At this stage, the water content first decreases and then reaches stabilization as the drying time increases. Compared with the sample without straw fiber, the addition of straw fiber reduced the water content of the tested samples with low initial water content.
3.2. Residual Water Content
To further clarify the influence of straw fiber on the shrinkage characteristics of dredged sludge, the residual water content (wr) of the samples was determined as shown in Figure 4, which is defined as the water content at the end of the residual stage. For those samples with the same initial water content, the value of wr of the samples with 1% straw fiber is similar to that of the 0% straw fiber sample, and then it generally decreases as Cs increases. For example, the residual water content reduces from 5.2% to 3.2% for those samples with the w0 of 80.7% due to the straw fiber addition. Moreover, the straw fiber affects the residual water content more pronouncedly until the straw fiber content is greater than 3%. Furthermore, the residual water content gradually decreases with the increasing w0 for the tested samples. In addition, the samples with high water content and low straw fiber content (Cs = 1%, 3%) incur penetrating cracks. For example, in the sample with the w0 of 161.4%, the samples with 1% and 3% straw fiber cracked, and the drying process was faster than in the other samples in the same group, indicating that the straw fiber and cracks increased the pathway for water movement, accelerating water evaporation. The wr of the dredged sludge with 3% straw fiber was significantly lower than that of the other samples with the same w0.
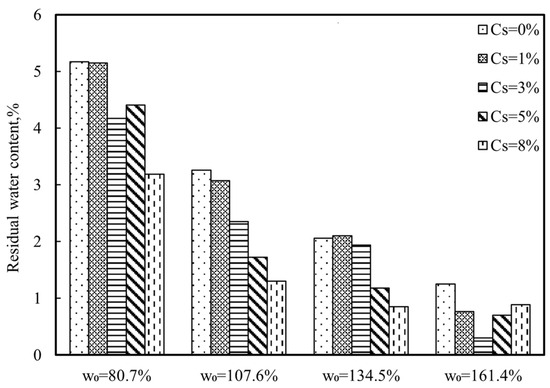
Figure 4.
Variations in residual water content.
3.3. Shrinkage Development
During the desiccation process, volumetric shrinkage and crack development were captured using a digital camera. For the tested samples, the shrinkage of the samples developed in two ways, i.e., overall shrinkage (pattern I) and desiccation cracks (pattern II).
The samples initially shrink in all directions. Vertical deformation is dominant, with the thickness of the samples decreasing continuously. Then, they detach from the walls of the mold and horizontal shrinkage accelerates [38,39,40].
Figure 5 shows the typical development of pattern I shrinkage. At the early stage of evaporation, the height of the sample decreases, and the sample is simultaneously separated from the side walls of the mold (Figure 5a). Then, as the desiccation continues, the suction among the soil particles increases, resulting in numerous small cracks on the surface of the sample (Figure 6a). The samples further converge towards the center, forming a relatively regular rectangular block shape (Figure 5b). At the end of the test, there are only small cracks distributed on the surface of the sample (Figure 6a), and no crack propagates through the entire depth, which is found at the surface defects of a tiny pit (Figure 6b). Hence, the sample is whole after the desiccation test (Figure 5c). From the side of the sample, the overall bending of the sample is not large, and the thickness is approximately uniform (Figure 6c). In addition, because the straw fiber provided additional pathways for water movement, the sample with 8% straw fiber shrunk faster than the others with the same w0.
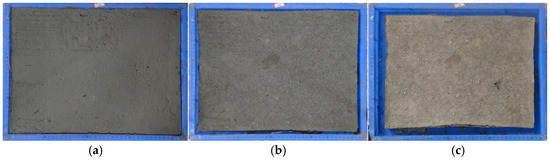
Figure 5.
Shrinkage process of sample A4 (w0 = 80.7% and Cs = 8%). (a) 80 h; (b) 171 h; (c) 991 h.

Figure 6.
Surface cracks of sample A4 (w0 = 80.7% and Cs = 8%). (a) Surface cracks; (b) cracks at the tiny pit; (c) side view of the sample.
The development of pattern II shrinkage is presented in Figure 7. Crack formation includes three stages according to the process characteristics [41,42]. At the early development stage, the first crack comes into being on the sample surface of a tiny pit (Figure 7a). As the drying continues, the small crack develops into a primary crack, which forms in samples with relatively higher water content (Figure 7b). Then, the crack development enters the development stage. During this stage, the secondary cracks first generate from the primary crack (Figure 7c), and then the third cracks generate from the secondary cracks (Figure 7d). The cracking network composed of desiccation cracks finally divides the sample into blocks (Figure 7e). When the water is further evaporated, the shrinkage enters the stable stage. During this process, the existing cracks gradually widen, and no new cracks are formed. Hence, the shapes of the divided blocks remain unchanged, with the area decreasing (Figure 7f). It should be noted that the widths and lengths of the cracks formed later at relatively low water content values are smaller in comparison with the primary crack. Overall, the structure of the cracking network is simple, and the amount of soil blocks is limited. It may be due to the friction resistance provided by straw fiber, which would restrain the formation of small cracks. Moreover, it is observed that nearly all new cracks tend to intersect with the original ones at 90°, and this can be explained by the crack propagation criterion and maximum stress release criterion [42,43].
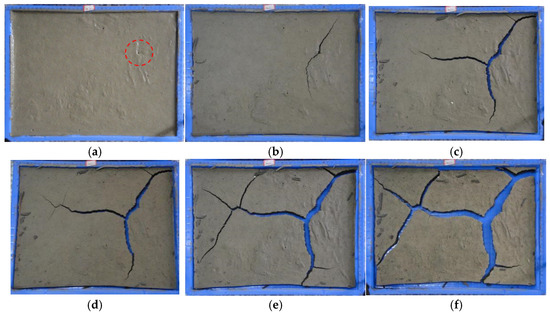
Figure 7.
Crack development of sample C2 (w0 = 161.4% and Cs = 3%). (a) 92 h; (b) 312 h; (c) 356 h; (d) 387 h; (e) 432 h; (f) 572 h.
To further clarify the straw fiber effect on the development of cracks, the profile images of samples with different straw fiber contents under the same water content were taken, as shown in Figure 8. For those samples with the w0 = 161.4%, the first crack of sample D1 (Cs = 1%) formed at 308 h, while D2 (Cs = 3%) formed at 356 h. However, as the straw fiber content increased, no desiccation cracks were found in samples D3 (Cs = 5%) and D4 (Cs = 8%). The profiles of the pits where the first cracks occurred in samples D1 and D2 are presented in Figure 8a,b); the amount of straw fiber in the upper soil layer of the crack is less than that in the lower layer. In contrast, after breaking the uncracked sample D3, the profile displays a homogeneous distribution of straw fibers (Figure 8c). This indicates that straw fiber has certain inhibition on the formation of cracks.
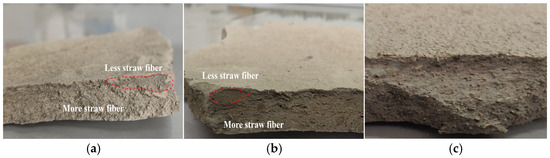
Figure 8.
Typical images of profiles of samples (w0 = 161.4%). (a) Cracked profile of D1; (b) cracked profile of D2; (c) uncracked profile of D3.
3.4. Final Crack Patterns
According to the foregoing analysis, the final crack pattern of the tested samples varied with their straw fiber content and initial water content. All the final crack patterns of the tested samples are provided in Table 3. For those samples with low initial water content (w0 = 80.7% and 107.6%), they produce overall shrinkage. The bonding and frictional forces among the fibers and soil particles are greater than the tensile stress among the particles due to desiccation, which would restrain the propagation of the initial small cracks. Hence, there are only small cracks on the sample surface. This is consistent with the findings reported by Gui et al. [44]. At the end of the experiment, the samples exist in the form of a whole, and the soil particles are compact. In addition, the sample is overall shrunk, with little difference in the overall thickness because the rate of water evaporation is relatively low under 27 °C.

Table 3.
Final shrinkage and crack patterns of tested samples.
On the other hand, when the initial water content is higher (w0 = 134.5% and 161.4%), the tensile stress among the soil particles due to evaporation exceeds the bonding and frictional forces at the soil particle–fiber interface. Hence, the crack initiation first occurs at positions of concentrated stress and eventually propagates through the entire soil layer. Since the addition of straw fiber provides certain resistance to the formation of small cracks, the crack network is generally simpler than that in the study of Tang, et al. [42]. In addition, no crack propagates through the sample when the straw fiber content increases to 5%. It may be ascribed to the higher resistance force provided by a large amount of straw fiber, which would prevent further propagation of small cracks.
At present, two mechanisms were proposed to explain the strengthened mechanical behaviors of straw-reinforced soil: the increase in friction force between soil and straw and the spatial constraints generated by soil–straw networks [13], but the research on these aspects is still limited. According to the SEM images of the straw fiber [45], it is evident that the edge around the straw fiber is very rough, which is because the straw is crushed by the grinder before use, resulting in its surface structure being broken. The modified structure strengthens the connection between the straw fiber and soil particles, providing more tensile stress. In addition, the straw fibers are randomly distributed and interwoven in the dredged sludge, which has a spatial constraint effect on the soil particles, which improves the deformation resistance of the sample and inhibits the formation of cracks.
4. Conclusions
A series of shrinkage tests were carried out to investigate the straw fiber effects on the shrinkage characteristics of dredged sludge with high water content. According to the test results, some conclusions were obtained as follows:
The water content of dredged sludge with and without straw fiber decreases with drying time. The influence of straw fiber on water evaporation depends upon the fiber content, the drying time, and the initial water content of the dredged sludge. In addition, the evaporation of water during the shrinkage test can be divided into three stages, i.e., the constant-rate stage, the falling-rate stage, and the residual stage.
At the constant-rate stage, water content decreases rapidly with drying time. The overall reduction in the water content is relatively small. There is little difference in the water content at the same drying time for samples with different straw fiber content. However, the water content reduces significantly at the falling-rate stage. For samples with lower initial water content (w0 = 80.7% and 107.6%), the water content decreases with the increasing straw fiber content at the same drying time. Meanwhile, for samples with higher initial water content (w0 = 134.5% and 161.4%), the reduction in the water content increases initially and then decreases with increasing straw fiber content. Unlike the constant-rate and falling-rate stages, the water content first decreases and then reaches stabilization as the drying time increases at the residual stage. Compared with the sample without straw fiber, the addition of straw fiber would reduce the residual water content of the tested samples.
For dredged sludge with low initial water content (w0 = 80.7% and 107.6%), the water evaporation only induces small cracks on the sample surface. Meanwhile, when the initial water content is higher (w0 = 134.5% and 161.4%), small cracks first occur at positions of concentrated stress and eventually propagate through the entire soil layer for samples with low straw fiber content. The crack network is generally simple as the addition of straw fiber provides certain resistance to the formation of small cracks. In addition, no cracks propagate through the sample when the straw fiber content increases to 5%. Overall, straw fiber would restrain the initiation and development of cracks during the desiccation process.
Adding straw fiber to dredged sludge is an environmentally friendly reinforcement method, which can improve its mechanical properties, increase its strength, and reduce the occurrence of shrinkage cracks when the dredged sludge is cultivated in situ or used as engineering backfill, etc. In future studies, it is proposed to further research the mechanism of straw fiber inhibiting crack development and water transfer in soil.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.X.; Methodology, G.X.; Validation, H.Q.; Formal analysis, H.Q.; Investigation, C.Q.; Resources, M.S.; Data curation, M.S.; Writing—original draft, H.Q.; Writing—review & editing, M.S.; Project administration, C.Q.; Funding acquisition, M.S. and G.X. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grants No. 52078449 and 52008363).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author/s.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Song, D.B.; Chen, W.B.; Yin, Z.Y.; Song, S.X.; Yin, J.H. Recycling dredged mud slurry using vacuum-solidification combined method with sustainable alkali-activated binder. Geotext. Geomembr. 2023, 51, 104–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Abriak, N.E.; Zentar, R. Dredged marine sediments used as novel supply of filling materials for road construction. Mar. Georesour. Geotechnol. 2017, 35, 472–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Ding, J. Sedimentation Behavior of Four Dredged Slurries in China. Mar. Georesour. Geotechnol. 2012, 30, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.-L.; Hong, Z.-S.; Cui, Y.-J. Time-dependent compression behaviour of dredged clays at high water contents in China. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 123, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zheng, Y.; Dong, C.; Zheng, J. Strength behavior of dredged mud slurry treated jointly by cement, flocculant and vacuum preloading. Acta Geotech. 2021, 17, 2581–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crocetti, P.; González-Camejo, J.; Li, K.; Foglia, A.; Eusebi, A.L.; Fatone, F. An overview of operations and processes for circular management of dredged sediments. Waste Manag. 2022, 146, 20–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Fan, S.; Mwiya, R.; Xie, M. Effects of straw incorporation on desiccation cracking patterns and horizontal flow in cracked clay loam. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 182, 130–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Qiao, Y.; Luo, X.; Li, Y. Approaches of Reutilizing Dredged Sediments from Beijing-Hangzhou Grand Canal. E3S Web Conf. 2023, 393, 3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaditager, M.; Sivakugan, N. Influence of Fly Ash–Based Geopolymer Binder on the Sedimentation Behavior of Dredged Mud. J. Waterw. Port Coast. Ocean. Eng. 2017, 143, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oing, K.; Gröngröft, A.; Eschenbach, A. Ripening reduces the shrinkage of processed dredged material. J. Soils Sediments 2020, 20, 571–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, T.D.; Choi, H.; Schroeder, P.R. Settlement of Dredged and Contaminated Material Placement Areas. I: Theory and Use of Primary Consolidation, Secondary Compression, and Desiccation of Dredged Fill. J. Waterw. Port Coast. Ocean Eng. 2005, 131, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Shi, B.; Liu, C.; Zhao, L.; Wang, B. Influencing factors of geometrical structure of surface shrinkage cracks in clayey soils. Eng. Geol. 2008, 101, 204–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Dai, M.; Dai, S.; Dong, X. Current status and environment impact of direct straw return in China’s cropland—A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 159, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Peng, H.; Chen, J.; Wang, X.; Wei, M.; Li, W.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, W.; Mellouki, A. An estimation of CO2 emission via agricultural crop residue open field burning in China from 1996 to 2013. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 2625–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; He, G.; Lau AK, H. Statistical evidence on the impact of agricultural straw burning on urban air quality in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 711, 134633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phuong, P.-T.H.; Nghiem, T.-D.; Thao, P.-T.M.; Pham, C.-T.; Thi, T.-T.; Thanh Dien, N. Impact of rice straw open burning on local air quality in the Mekong Delta of Vietnam. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2021, 12, 101225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Elbashiry, E.M.A.; Yu, T.; Ren, Y.; Guo, Z.; Liu, S. Research progress of wheat straw and rice straw cement-based building materials in China. Mag. Concr. Res. 2018, 70, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Kawai, S.; Umemura, K.; Zhang, M.; Honda, T. Development of high-performance UF-bonded reed and wheat straw medium-density fiberboard. J. Wood Sci. 2001, 47, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Q.; Yu, M.; Ma, X.; Liu, Y.; Yin, X. The Role of Straw Materials in Energy-Efficient Buildings: Current Perspectives and Future Trends. Energies 2023, 16, 3480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Sun, Z. Strength Behavior of Shanghai Clayey Soil Reinforced with Wheat Straw Fibers. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2015, 34, 515–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouhicha, M.; Aouissi, F.; Kenai, S. Performance of composite soil reinforced with barley straw. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2005, 27, 617–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.; Huang, J.; Yao, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H. Unconfined compression strength and mesostructure of reinforced soil with wheat straw. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2021, 80, 9173–9183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El kefafy, S.; Mirdan, A.; Abouelenean, G. Effect of Using Rice Straw Fiber on Slope Stability of sand soil. Port-Said Eng. Res. J. 2015, 19, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, S.X.; Wang, P.; Wang, X.Y. Effect of reinforcing range and cross section of wheat straw on shear strength of reinforced soil. Rock Soil Mech. 2013, 34, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Yamamoto, H.; Cui, J.; Cheng, H. Influence of Load Mode on Particle Crushing Characteristics of Silica Sand at High Stresses. Int. J. Geomech. 2020, 20, 04019194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.W.; Huang, Z.H.; Fu, Q.; Xie, W.F.; Huang, Z.H.; Wu, Y. Effect of complex-grain-size curves on shear modulus degradation of calcareous sand. Mar. Georesources Geotechnol. 2024, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Cui, J.; Huang, J.; Zhang, W.; Yoshimoto, N.; Wen, L. Correlation of critical state strength properties with particle shape and surface fractal dimension of clinker ash. Int. J. Geomech. 2021, 21, 04021071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.; Liu, S.; Wang, Y.; Xu, G. Synergistic influence of lime and straw on dredged sludge reinforcement under vacuum preloading. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 421, 135642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, C.; Xu, L.; Geng, W.; Xu, G.; Zhang, D. Evolutionary Behaviors of Straw-Reinforced Slurry for Sustainable Management of Dredging Sediment: Rheological and Fertility Properties. Waste Biomass Valorization 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.-H.; Wang, H.; Song, M.-M.; Qiu, C.-C.; Weng, J.-X.; Wang, E.-W. Investigation on strength behavior of cemented dredged clay with straw at various curing stages. Mar. Georesour. Geotechnol. 2024, 42, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, B.-G.; Cheng, Q.; Tang, C.-S.; Zeng, H.; Xu, J.; Shi, B. Effects of compaction state on desiccation cracking behaviour of a clayey soil subjected to wetting-drying cycles. Eng. Geol. 2022, 302, 106650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roderick, N.T. Experimental Investigation on the Desiccation and Fracturing of Clay; Delft University of Technology: Delft, The Netherlands, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, L.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L. Sustainable Reuse of Dredged Soil as a Substrate Material by Improvement with Polyacrylamide, Straw, and Superabsorbent Polymer. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2021, 1, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Gu, J.; Wang, Y.; Ni, J. Influence of straw degradation on consolidation of dredged sludge under vacuum preloading. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng.-Geotech. Eng. 2024, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D2487-17e1; Standard Practice for Classification of Soils for Engineering Purposes (Unified Soil Classification System). ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2011.
- Sun, D.; Ge, Y.; Zhou, Y. Punishing and rewarding: How do policy measures affect crop straw use by farmers? An empirical analysis of Jiangsu Province of China. Energy Policy 2019, 134, 110882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Zhou, Z.; Jiang, M.; Xu, X.; Wang, Z.; Hui, D. Cellulosic fibers from rice straw and bamboo used as reinforcement of cement-based composites for remarkably improving mechanical properties. Compos. Part B Eng. 2015, 78, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, K.M.; Bui, H.H.; Sánchez, M.; Kodikara, J. A DEM approach to study desiccation processes in slurry soils. Comput Geotech. 2020, 120, 103448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pak, A.; Samimi, S. Three-dimensional desiccation modeling of very soft soils. In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering: The Academia and Practice of Geotechnical Engineering, Alexandria, Egypt, 5–9 October 2009; Volume 1, pp. 421–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khouchkar, M.; Özçoban, M.Ş.; Özaydin, I.K. Crust Formation in Disposed Dredgings. Soft Ground Technol. 2001, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, B.A.; Benson, C.H. Effect of Desiccation on Compacted Natural Clays. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2001, 127, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.-S.; Shi, B.; Liu, C.; Suo, W.-B.; Gao, L. Experimental characterization of shrinkage and desiccation cracking in thin clay layer. Appl. Clay Sci. 2011, 52, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, P.H.; Graham, J.; Williams, D.J. Cracking in drying soils. Can. Geotech. J. 1992, 29, 263–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiyao, W.; Linchuan SH, A.; Wengui CA, O.; Yongjie, Z.; Qiansong, T. An experiment study of cracking properties of rice straw reinforced soil with different ratios. Hydrogeol. Eng. Geol. 2017, 44, 52–58. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Xu, G.; Luo, F.; Chen, X.; Li, S. Study on the Organic Matter and Nutrients of Dredged Mud after Treated by Vacuum Preloading Combined with Straw Drainage Body. China Rural Water Hydropower 2023, 4, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).