Abstract
A tapered concrete-filled double-skin steel tubular (TCFDST) structure has been used as the main framework in transmission towers, offshore facility platforms, and turbine towers owing to its excellent mechanical properties. In order to solve the difficulties of calculating the axial compressive capacity of TCFDST members due to the variations in cross-section, this paper applied heuristic optimization algorithms such as Genetic Algorithms (GAs), Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO), Simulated Annealing (SA), and Ant Colony Optimization (ACO) to enhance a Backpropagation Neural Network (BPNN) model. A predictive model incorporating both global and local optimization strategies for the axial compressive capacity of a TCFDST structure is proposed. A comprehensive axial database for TCFDST members, comprising 1327 sets of experimental and finite element analysis results, was established, with ten types of component dimensions and material parameters selected as input variables and compressive bearing capacity as the output variable. This study developed and assessed four BPNN models, each optimized by a different heuristic algorithm, against various machine learning algorithms and standards. The heuristic-algorithm-optimized BPNN models demonstrated superior accuracy in predicting the axial compressive capacity of TCFDST members. Through parametric analysis, this study identified the relationship between the model’s bearing capacity predictions and each input parameter, confirming the model’s broad applicability. The optimized BPNN model, refined with heuristic algorithms, provides a significant reference for addressing the computational challenges associated with the load-bearing capacity of TCFDST structures and facilitating their application.
1. Introduction
Concrete-filled double-skin steel tubular (CFDST) structures are widely recognized for their superior axial compression, bending, torsion, fire, and impact resistance. These characteristics make CFDST structures ideal for various applications, including long-span structures, bridge piers, underground constructions, and high-rise or super-high-rise buildings, where safety and stability are critically important [1,2]. In wind power generation, both offshore and onshore, CFDST columns provide a more reliable alternative to traditional single-layer steel towers, especially for turbines exceeding 12 MW. As tower heights reach up to 220 m, the enhanced load-bearing capacity of CFDST columns is crucial for supporting the axial and eccentric forces from the nacelle and blades, ensuring safe and long-term operation [3,4]. CFDST columns also play a key role in high-rise construction, where they efficiently manage vertical and lateral loads [5]. Additionally, their inherent fire resistance makes them particularly suitable for high-rise buildings where fire safety is a concern [1,6]. CFDST structures’ energy absorption capabilities make them highly effective in seismic-resistant designs, contributing to their use in earthquake-prone regions [7,8,9]. The strength and resilience of CFDST structures also suit bridge piers and underground structures, where they withstand compressive and impact forces [8,10]. The following example serves to further demonstrate the versatility of CFDST in modern infrastructure, as illustrated Figure 1.

Figure 1.
Engineering application of tapered CFDST structure in modern infrastructure: building columns, bridge support columns, wind turbine towers, and platform support structures. The outer steel tube exerts an inward confining effect on the interlayer concrete (blue arrows), while the inner steel tube provides an outward supporting effect (green arrows).
A tapered concrete-filled double-skin steel tubular (TCFDST) structure is developed based on the traditional CFDST structure [11,12]. Compared to ordinary CFDST columns, the gradually increasing section of a TCFDST structure from bottom to top accommodates the gradually increasing bending moment along the column direction due to horizontal loads, thereby reducing the structural weight [13,14]. However, its variable section design also makes it difficult for designers to accurately apply existing CFDST design codes to select calculation sections and accurately calculate structural bearing capacity [15,16]. Therefore, determining how to accurately predict the axial compression bearing capacity of TCFDST components and reduce structural redundancy design rates holds significant value in promoting and applying TCFDST components as the primary support structure in architectural design.
In recent years, domestic and international scholars have conducted extensive experimental research on the axial compression performance of concrete-filled double-skin steel tubular (CFDST) members [17,18,19]. Based on this research, they have established formulas for calculating axial compression capacity through linear and nonlinear regression methods, incorporating the confinement theory, unified theory, and superposition theory [20,21,22]. Apart from the axial compression capacity formulas based on mechanical principles, with the gradual maturity of machine learning algorithms, applying deep learning algorithms to the field of engineering design to solve structural design problems has become a new approach in building structural design and performance analysis [23,24,25]. Wang et al. [23] trained three methods, including support vector machines (SVMs), random forest regression (RFR), and neural networks (NNs), on a database of CFST eccentric compression test samples, and established a machine learning model with dimensional and material parameters as the input layer and flexural capacity as the output layer. Hong et al. [25] compared various machine learning algorithms with normative capacity calculation formulas and concluded that the K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN) algorithm exhibits high accuracy in predicting the axial compressive capacity of CFDST members. Nguyen et al. [26] utilized three heuristic optimization algorithms (SCSO, GWO_WOA, and ARO) to tune the hyperparameters of the gradient boosting regression (GBR) algorithm and analyzed the prediction accuracy of different optimization algorithms for the axial compressive capacity of CFDST columns. Chandramouli et al. [27] predicted the axial compressive capacity of CFDST members using six machine learning models and provided the optimal calculation model applicable to various fiber composite materials and steel-confined core concrete. Zhao et al. [28] conducted a comparative analysis of the predictive effectiveness of standard backpropagation neural network (BPNN) and PSO-BPNN models for the axial compressive capacity of CFDST members and recommended a member capacity prediction model based on domestic and international standards.
In literature research, it has been observed that both domestic and international standards predominantly employ conservative calculations for determining the bearing capacity of TCFDST members [29]. These calculations primarily utilize the minimum top section and corrected length, which often leads to substantial errors in the computed bearing capacity [30,31]. Consequently, scholars globally are progressively shifting their focus towards utilizing machine learning algorithms for predicting the bearing capacity of CFDST members [32]. Nonetheless, there remains a notable lack of machine learning prediction models for TCFDST members with taper and varying hollowness ratios.
Based on a data-driven strategy, this paper established an analytical database consisting of axial compressive test data from 192 CFDST and TCFDST members, as well as numerical simulation data from 1135 TCFDST members, corresponding to their axial compressive capacities. By integrating optimization algorithms such as the Genetic Algorithm (GA), Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO), Simulated Annealing (SA), and Ant Colony Optimization (ACO), this paper optimized the Backpropagation Neural Network (BPNN) model for predicting the axial compressive capacity of TCFDST members. The feasibility of the model was analyzed, and the advantages of the heuristic-algorithm-optimized model were examined in comparison with various commonly used machine learning algorithms and normative formulas for capacity calculation. Additionally, through parametric analysis, the variation patterns between the predicted capacity of the model and the input variables were presented.
2. Testing Database
2.1. Experiment Database
To implement a machine learning algorithm for predicting the axial compressive capacity of TCFDST members using a data-driven approach, it is necessary to establish an axial compression database by experiment. This database consists of measured axial compression data from 182 CFDST and TCFDST members. These experimental results form the foundation for training the machine learning model and ensuring its accuracy in predicting the load-bearing capacity of TCFDST components. The sample parameters and axial compressive capacities of the experimentally tested members are presented in Table 1; more detailed information is presented in Appendix A.

Table 1.
Source and summary of the TCFDST member database by experiment.
2.2. Finite Element Database
In this study, a simulation model of axial compression for TCFDST members using the general finite element program ABAQUS is presented. The stress–strain relationship of the inner and outer steel tubes is calculated using a five-stage bilinear plastic flow constitutive model, and its tensile behavior can be represented by Equation (1) [14]. The steel stress–strain relationship is shown in Figure 2.
where the parameters of , , , , ,, , , and can be derived from the literature [14].
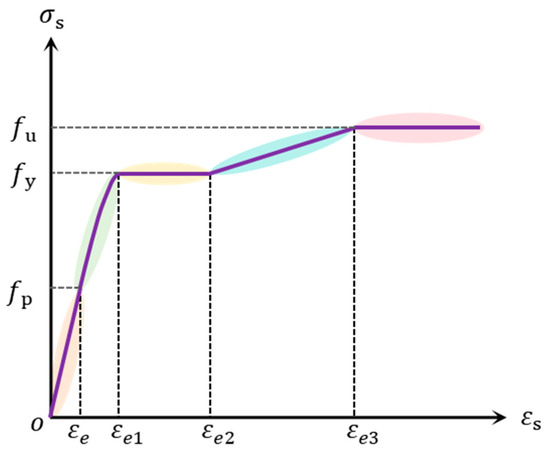
Figure 2.
Steel stress–strain relationship of five-stage bilinear plastic flow model.
The stress–strain relationship of the sandwich concrete using the concrete damage plasticity (CDP) model and its compressive behavior can be represented by Equation (2) [19,33].
where is the dimensionless compressive strain and is the dimensionless compressive stress. The peak strain and coefficient are given as follows. The compressive stress–strain relationship of sandwich concrete is shown in Figure 3a.
where is the confinement factor [54]. The uniaxial tensile stress–strain relationship of the sandwich concrete can be represented by Equation (4) [55].
where is the dimensionless tensile strain and is the dimensionless tensile stress. The peak tensile strain and coefficient are given as follows. The tensile stress–strain relationship of sandwich concrete is shown in Figure 3b.
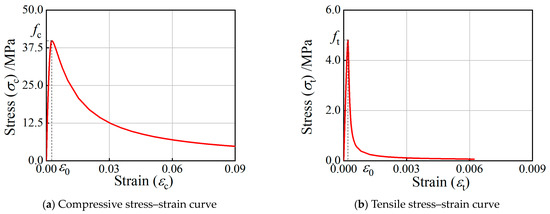
Figure 3.
Stress–strain curves of sandwich concrete under compressive and tensile load.
According to Sidiroff’s energy equivalence principle, the elastic strain energy of an undamaged material is equal to the elastic strain energy of a damaged material under the effect of equivalent stress or equal to the elastic strain energy under the damaged elastic modulus, as shown in Equation (6). The relationship between the damage factors for concrete under compression and tension with strain is shown in Figure 4.
where is the damage factor, represents the true stress of the concrete, denotes the true strain of the concrete, and is the initial elastic modulus of the concrete.
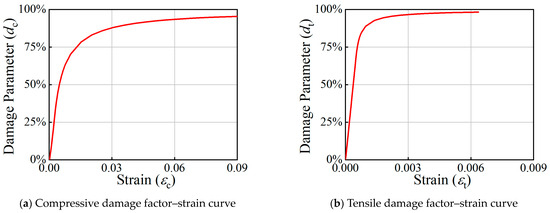
Figure 4.
Damage factor–strain curves of sandwich concrete under compressive and tensile load.
In the simulation model, the S4R shell element is employed for both the inner and outer steel tubes, while the C3D8R solid element is utilized for the sandwiched concrete. A surface-to-surface contact relationship is established between the inner and outer steel tubes and the sandwiched concrete. Normal and tangential behaviors are simulated using the hard contact and Coulomb friction models, respectively, with a friction coefficient set at 0.6 [13,18,19]. At both the loading and fixed ends, MPC beams are utilized to couple the inner and outer steel tubes and the sandwiched concrete to a reference point located at the center of the section. The fixed end constrains translational degrees of freedom in the x-, y-, and z-directions, while the loading end applies a load in the y-direction and constrains translational degrees of freedom in the x- and z-directions. Based on research findings from the literature, TCFDST members exhibit robust plastic deformation capacity under axial compression in the z-direction, and the impact of residual stresses on the peak bearing capacity of the members is insignificant [56,57]. Therefore, the influence of defects such as residual stresses on the axial compression performance of the members is disregarded in this study. The numerical model of TCDFST is shown in Figure 5.
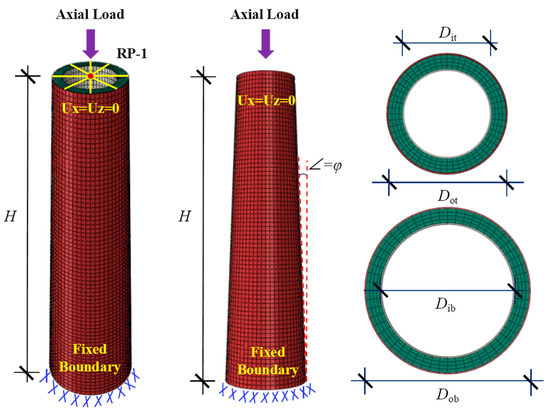

Figure 5.
Numerical modeling of TCFDST members under axial load.
A total of eight axial compression test data for TCFDST components were selected for model validation, and the test specimen information is presented in Table 2. The consistency between the experimentally measured and numerically simulated axial load–displacement curves and failure modes verifies the effectiveness and accuracy of the numerical model in calculating the axial compression loading of TCFDST components. Straight test specimen C1-1 exhibited failure at the middle section of the components under axial compression; tapered test specimens C3-1, CT3-1, CT4-1, CT5-1, and CT6-1 exhibited failure at the top section of the components under axial compression, with the outer steel tube showing noticeable buckling. In the tapered numerical model, the top sections of the outer steel tubes in each specimen reached yield strength, displaying significant local bulging, consistent with the observed failure modes in the experiments.

Table 2.
Detailed information of validation specimens.
Additionally, the axial load–displacement curves obtained from both the experiments and numerical simulations indicate good agreement in terms of axial stiffness, peak load, and the descending branch of the load–displacement curve. This further confirms the reliability of the numerical model. Based on these findings, the numerical model can be confidently used to establish a simulation database for further analysis in the subsequent sections. The test results of the load–displacement curves and failure modes from the numerical simulations are shown in Figure 6 and Figure 7.
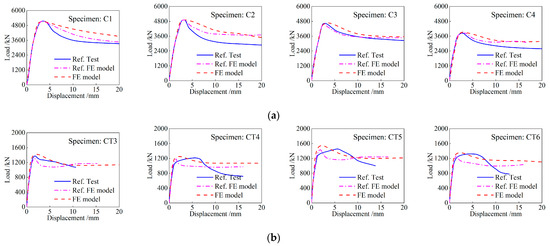
Figure 6.
Verification through compression load–displacement curves: (a) comparison with test result in Ref. [33]; (b) comparison with test result in Ref. [19].
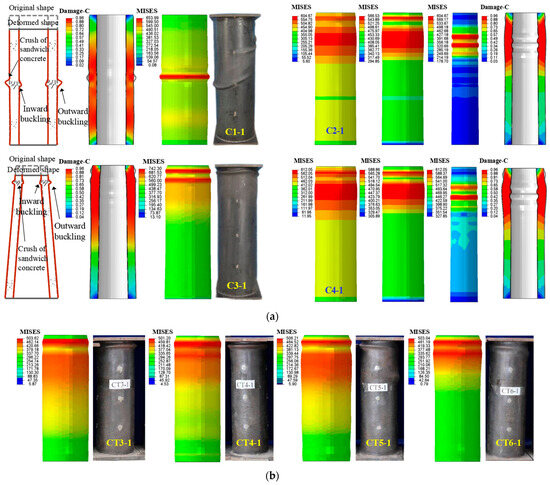
Figure 7.
Model validation by axial loading failure pattern: (a) comparison with failure patterns in Ref. [33]; (b) comparison with failure patterns in Ref. [19].
In addition to the experimental data, validated finite element simulation data from 1180 TCFDST members were incorporated into the database, as shown in Table 3. The purpose of using simulation data alongside experimental results is to expand the database, allowing for a more comprehensive exploration of the parameter space. Simulated data provide additional insights into the behavior of TCFDST members under various conditions that may not be fully covered by physical experiments due to practical limitations. This larger and more diverse database enables the machine learning model to capture complex patterns and interactions between the parameters, leading to improved predictive accuracy and robustness.

Table 3.
Source and summary of the TCFDST member database by finite element analysis.
2.3. Database Processing
Different literature sources have presented concrete specimen tests conducted using dimensional information specified by various standards to obtain the compressive strength of concrete. Since multiple concrete strengths do not exhibit statistical characteristics, this paper refers to Formula (7) presented in a reference to convert them to (standard cylinder compressive strength) [23].
where represents the compressive strength of a concrete cylinder with a diameter of 150 mm; represents the compressive strength of a concrete cylinder with a diameter of 100 mm; represents the compressive strength of a concrete cube with a diameter of 150 mm; the compressive strength of a concrete cube with a diameter of 100 mm.
The distribution of the input parameters is presented in the data distribution plot. The probability plot exhibits a bell-shaped curve, indicating a balanced and symmetrical distribution of the data, as shown in Figure 8. To visually analyze whether there was a strong correlation between the input and output parameters, the Pearson, Spearman, and Kendall methods were employed to calculate the correlation coefficients between the input and output parameters, as illustrated in Figure 9.
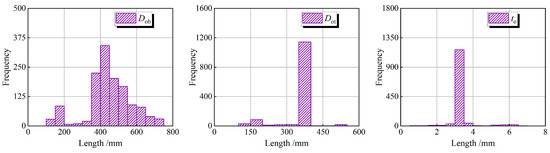
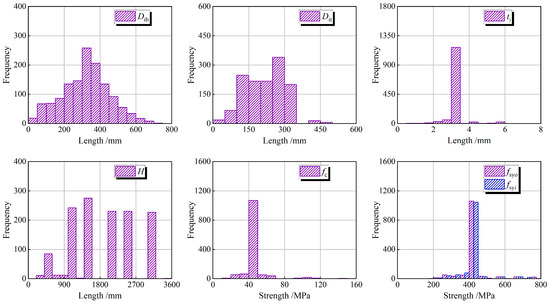
Figure 8.
Parametric distribution of input parameters of the TCFDST member database under compression.
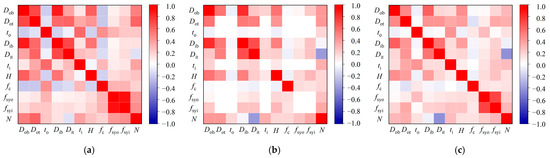
Figure 9.
Correlation coefficient between input parameters and output parameters: (a) Pearson; (b) Spearman; (c) Kendall.
3. Prediction of Axial Compressive Capacity Based on BPNN
3.1. Standard BP Neural Network
The Backpropagation Neural Network (BPNN) model encompasses two primary processes: forward propagation and backpropagation. During forward propagation, input data are passed through hidden layers to the output layer, where the output of each node is determined by a weighted sum followed by an activation function, as shown in Figure 10. In backpropagation, the difference between the output and the desired output is propagated backward through the network. This error is used to adjust the weights and thresholds, thereby minimizing the error [58].
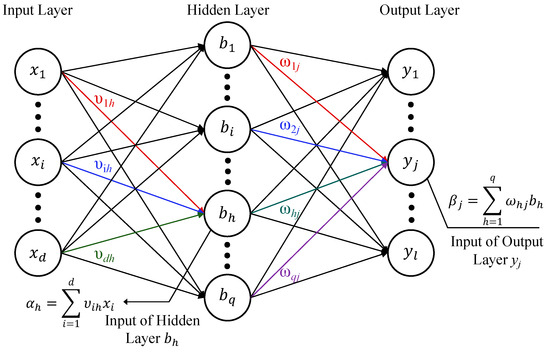
Figure 10.
Schematic diagram of the BPNN.
The central idea of the Backpropagation Neural Network (BPNN) algorithm is to iteratively adjust the network’s weights and thresholds based on the output error, with the goal of making the network’s output as close as possible to the desired value. This adjustment process is driven by backpropagation, where the error is propagated backward through the network to update each weight and threshold.
At the start of training, weights and thresholds are usually initialized randomly, and the choice of these initial values can significantly impact the training process. Poor initialization may lead to slow convergence or cause the network to become stuck in local minima, resulting in suboptimal performance. In contrast, well-chosen initial values help the network converge faster and achieve better accuracy. Thus, selecting optimal initial weights and thresholds is crucial for effective training, as it enhances the likelihood of the network reaching a global solution and improves overall performance.
3.2. Optimizing BPNN with Genetic Algorithm (GA-BPNN)
3.2.1. Advantages and Specific Contributions of GA
The Genetic Algorithm (GA) is a population-based optimization technique inspired by natural selection and genetic mechanisms. One of its primary advantages in BPNN optimization is its ability to explore the global solution space efficiently, thereby mitigating the risk of the model becoming trapped in local optima. The advantages of the Genetic Algorithm are as follows:
- (1)
- Global exploration: GA maintains a diverse population of solutions, encouraging exploration and preventing premature convergence.
- (2)
- Robustness to nonlinear surfaces: GA operates independently of gradient information, making it suitable for handling the complex, nonlinear error surfaces typically associated with BPNN.
- (3)
- Crossover and mutation: These genetic operations allow GA to combine and alter solutions, promoting diversity in the search space.
- (4)
- Role in optimization: GA is particularly effective in the initial stages of optimization, where broad exploration of the solution space is essential. By simulating evolutionary processes, GA efficiently identifies promising regions in the search space, balancing exploration and exploitation of the network weights and thresholds.
3.2.2. Detailed Steps for Optimizing BPNN Using GA
Genetic Algorithms (GAs) are search optimization algorithms that simulate natural selection and genetic mechanisms. These algorithms emulate the principle of “survival of the fittest” from Darwinian evolutionary theory through operations such as selection, crossover (hybridization), and mutation to identify optimal solutions [59].
Genetic Algorithms operate within the global space of variables by executing population selection, crossover, and mutation, thus avoiding the pitfalls of local optima that can occur with random value assignments in gradient descent methods. The core concept of GA-BPNN includes the following steps; the structure is shown in Figure 11.
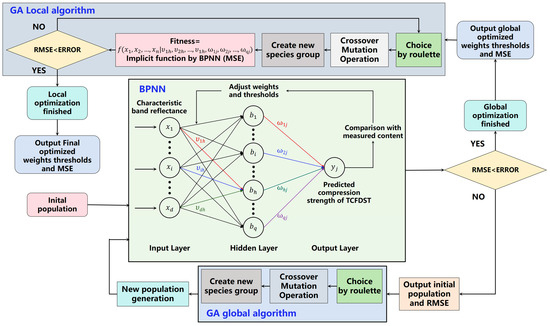
Figure 11.
The structure of Genetic-Algorithm-optimized BPNN (GA-BPNN).
- (1)
- The optimization process for the GA-BPNN begins with the initialization of the population, where random weights and thresholds for the BPNN are generated as chromosomes. Each chromosome represents a potential solution with encoded weights and thresholds. The BPNN is then trained using these initial weights, and the Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) is calculated between the predicted and actual values. Based on this RMSE, the fitness of each chromosome is evaluated. If the error does not meet the precision requirements, the Genetic Algorithm (GA) is applied to optimize the weights and thresholds.
- (2)
- During the GA process, parameters such as selection rate, crossover probability, and mutation rate are set to guide the optimization. The selection rate controls the proportion of individuals chosen to form the next generation, balancing the trade-off between intensifying the search around high-fitness solutions and maintaining population diversity. A higher selection rate favors the exploitation of fitter individuals, while a lower rate preserves genetic diversity. The crossover probability determines the likelihood of combining two parent solutions to explore new areas of the solution space, while the mutation rate introduces random changes to genes (weights and thresholds), preventing premature convergence to local minima. Through these genetic operations, the population is iteratively updated, minimizing RMSE and generating new sets of weights and thresholds. This updated population then serves as the initial population for the next generation.
- (3)
- Once the global optimization through GA achieves the desired accuracy, the process moves into the local optimization phase. The final optimized weights and thresholds from the GA are used as inputs for the BPNN, and the BPNN is employed as a prediction tool (without additional training) to further fine-tune the weights and thresholds. During this phase, GA continues to refine the solution by adjusting the weights and thresholds through additional selection, crossover, and mutation processes. This continues until the RMSE satisfies the predefined accuracy requirements, resulting in the final set of optimized weights, thresholds, and minimal error.
3.3. Optimizing BPNN with Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm (PSO-BPNN)
3.3.1. Advantages and Specific Contributions of PSO
Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) is another population-based algorithm, modeled on the social behavior of swarms. PSO excels in both local and global search processes by adjusting the position of particles (candidate solutions) based on their own experience and that of their neighbors. The advantages of the particle swarm algorithm are as follows:
- (1)
- Balance of exploration and exploitation: PSO strikes a balance between exploration and exploitation by allowing particles to move toward better-known solutions while exploring new areas of the solution space.
- (2)
- Faster convergence: Compared to GA, PSO tends to converge more quickly, as it directly updates the solutions based on the experience of the best particles.
- (3)
- Simplicity: PSO requires fewer parameters to tune, making it simpler to implement and computationally efficient.
Role in optimization: PSO is particularly advantageous in the later stages of optimization when fine-tuning is required. Its rapid convergence helps to quickly identify high-quality solutions after the initial global exploration.
3.3.2. Detailed Steps for Optimizing BPNN Using PSO
Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) is a population-based optimization algorithm inspired by the foraging behavior of birds. In the PSO algorithm, each solution in the solution space is represented as a particle, endowed with its own position and velocity. The algorithm simulates the flight of each particle (solution) through the solution space to locate the optimal solution [60].
The particle swarm algorithm dynamically adjusts and searches within the global space of variables by continually updating the velocity and position of each particle. This process aims to find the weight and threshold configurations that minimize the error in a BPNN model. The core concept of PSO-BPNN includes the following steps; the structure is shown in Figure 12.
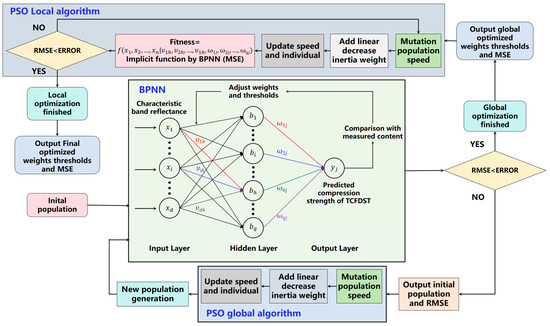
Figure 12.
The structure of particle-swarm-optimized BPNN (PSO-BPNN).
- (1)
- The optimization process begins with the initialization of the population, where initial weights and thresholds for the BPNN are randomly set. Subsequently, the BPNN is trained, and the Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) between the predicted and actual values is calculated. Based on this error, the algorithm determines whether the error tolerance is met. If the error does not meet the precision requirements, the initial population along with the calculated RMSE is fed into the PSO (Particle Swarm Optimization) algorithm for further optimization.
- (2)
- During the PSO process, parameters such as the inertia weight, cognitive (personal) learning coefficient, and social (global) learning coefficient are set to guide the optimization. The inertia weight controls the impact of the previous velocity on the current velocity, which balances the trade-off between exploration (global search) and exploitation (local search). A higher inertia weight favors exploration, while a lower one favors exploitation. The cognitive coefficient encourages each particle to return to its personal best-known position, while the social coefficient leads the particles towards the global best-known position found by the entire swarm. Through these updates, the particles’ velocities and positions are adjusted iteratively to minimize the RMSE, ultimately generating a new set of weights and thresholds. This updated population is then used as the initial population for the next generation.
- (3)
- Once the global optimization reaches the desired accuracy, the process transitions into the local optimization phase. The final optimized weights and thresholds from the global optimization step are used as inputs for the PSO algorithm, with BPNN functioning as a prediction tool in this stage (no additional training is performed). The net generated by BPNN, viewed as a function, is continuously fine-tuned by PSO to further optimize the weights and thresholds. This iterative process continues until the RMSE meets the predefined precision requirement, yielding the final set of weights, thresholds, and RMSE that minimizes the error between predicted and actual values.
3.4. Optimizing BPNN with Simulated Annealing Algorithm (SA-BPNN)
3.4.1. Advantages and Specific Contributions of SA
Simulated Annealing (SA) is an optimization method inspired by the annealing process in metallurgy, where a material is gradually cooled to remove defects. In the context of BPNN optimization, SA mimics this process by accepting both better and occasionally worse solutions, depending on a probability function that decreases over time. The advantages of the Simulated Annealing algorithm are as follows:
- (1)
- Escaping local optima: SA’s acceptance of worse solutions early in the process allows it to escape local minima, an important feature when optimizing complex error surfaces like those in BPNN.
- (2)
- Gradual refinement: SA reduces the probability of accepting worse solutions as the algorithm progresses, allowing it to transition from exploration to exploitation.
- (3)
- Simplicity: SA is relatively easy to implement and requires minimal parameter adjustments.
- (4)
- Role in optimization: SA is well suited for fine-tuning weights and thresholds; its ability to escape local minima makes it a robust tool for refining solutions and ensuring that the final weights and thresholds are near-optimal.
3.4.2. Detailed Steps for Optimizing BPNN Using SA
Simulated Annealing (SA) is a probabilistic search algorithm based on the material annealing process. During annealing, a material is heated and then cooled slowly. Its internal structure becomes disordered during heating, but as it cools slowly, atoms gradually move to a state of lower energy, eventually reaching a more stable structure [61].
The Simulated Annealing algorithm mimics this process by determining the probability of accepting new solutions as the system cools from a high to a low temperature. It effectively searches the global space of variables by setting random perturbations, aiming to find the global optimum. The core concept of SA-BPNN includes the following steps; the structure is shown in Figure 13.
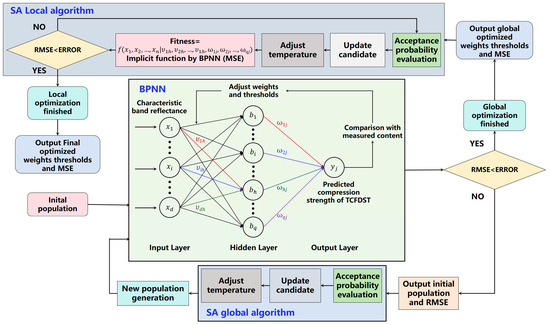
Figure 13.
The structure of Simulated-Annealing-optimized BPNN (SA-BPNN).
- (1)
- The optimization process begins with the initialization of weights and thresholds for the BPNN, which are set randomly. The BPNN is then trained, and the Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) between the predicted and actual values is calculated. If the error does not meet the predefined precision requirements, the Simulated Annealing (SA) algorithm is applied to optimize the weights and thresholds further.
- (2)
- During the SA process, key parameters such as the initial temperature, cooling schedule, and acceptance probability are defined. The initial temperature controls the likelihood of accepting worse solutions, enabling the algorithm to explore a wider range of potential solutions. As the temperature decreases according to the cooling schedule, the algorithm gradually shifts from exploration to exploitation, focusing more on refining the current solution. The acceptance probability allows the algorithm to occasionally accept solutions with higher RMSE, preventing it from becoming stuck in local minima and encouraging exploration of the solution space. By iteratively perturbing the weights and thresholds and accepting or rejecting changes based on the temperature and acceptance probability, the SA process minimizes RMSE.
- (3)
- Once the global optimization phase reaches the desired accuracy, the process transitions into the local optimization phase. In this stage, the final optimized weights and thresholds from the global optimization step are used as inputs, and BPNN acts as a prediction tool (without further training). The net generated by BPNN is fine-tuned through additional iterations of SA, where further adjustments to the weights and thresholds are made to minimize RMSE further. The iterative process continues until the RMSE satisfies the predefined precision requirement, yielding the final optimized set of weights, thresholds, and RMSE that minimizes the error between the predicted and actual values.
3.5. Optimizing BPNN with Ant Colony Optimization Algorithm (ACO-BPNN)
3.5.1. Advantages and Specific Contributions of ACO
Ant Colony Optimization (ACO) is a probabilistic technique inspired by the foraging behavior of ants. In optimization, it uses artificial pheromone trails to guide the search process, with successful solutions reinforcing their probability of being selected in future iterations. The advantages of the Ant Colony Optimization algorithm are as follows:
- (1)
- Efficient combinatorial search: ACO excels in solving combinatorial optimization problems and efficiently explores combinations of weights and thresholds in BPNN.
- (2)
- Positive feedback mechanism: Successful solutions increase their selection probability through pheromone updates, guiding the search toward optimal areas in the solution space.
- (3)
- Adaptability: ACO dynamically adjusts its search strategy based on feedback, making it responsive to changes in the optimization landscape.
- (4)
- Role in optimization: ACO is particularly effective for identifying optimal or near-optimal combinations of weights and thresholds in complex, multi-dimensional optimization problems like BPNN. Its iterative refinement helps to focus the search on the most promising solutions.
3.5.2. Detailed Steps for Optimizing BPNN Using ACO
Ant Colony Optimization (ACO) is a heuristic algorithm that simulates the foraging behavior of ants in nature, primarily utilized for solving path optimization problems such as the Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP) and Vehicle Routing Problem (VRP). The algorithm leverages the mechanism of pheromone deposition by ants to mark paths, allowing other ants to choose paths based on the concentration of pheromone residue [62]. The core concept of ACO-BPNN includes the following steps; the structure is shown in Figure 14.
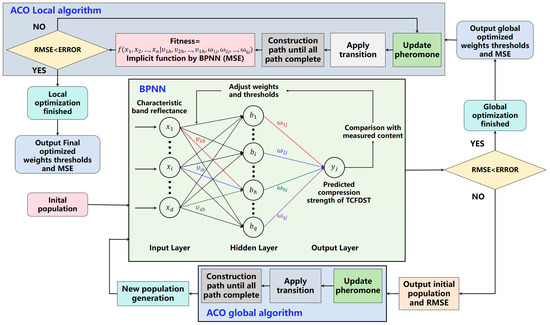
Figure 14.
The structure of simulated ant-colony-optimized BPNN (ACO-BPNN).
- (1)
- The optimization process begins with the initialization of the population, where the initial weights and thresholds for the BPNN are randomly set. The BPNN is trained using these initial weights, and the Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) between the predicted and actual values is calculated. If the error does not meet the predefined precision requirement, the Ant Colony Optimization (ACO) algorithm is applied to optimize the weights and thresholds further.
- (2)
- During the ACO process, key parameters such as the number of ants, pheromone evaporation rate, and influence of pheromone trails are defined to guide the search for optimal solutions. Ants represent individual solutions (sets of weights and thresholds), and each ant constructs a solution based on probabilistic rules that are influenced by the pheromone trails left by previous solutions and heuristic information. As ants explore the solution space, pheromone is deposited on paths that lead to better solutions (lower RMSE), making those paths more likely to be followed by subsequent ants. A pheromone evaporation rate is applied to prevent the algorithm from converging too quickly to local minima by reducing the influence of older paths. This process continues iteratively as ants adjust their paths (weights and thresholds) to explore the search space effectively, minimizing RMSE.
- (3)
- Once the global optimization through ACO reaches the desired accuracy, the process transitions into the local optimization phase. In this phase, the final optimized weights and thresholds obtained from the global ACO optimization are used as inputs for further fine-tuning. BPNN functions as a prediction tool during this stage (without additional training). The net generated by BPNN is continuously refined through additional iterations of ACO, further optimizing the weights and thresholds until the RMSE satisfies the precision requirement. This iterative process continues until the final set of weights, thresholds, and RMSE is obtained, minimizing the error between predicted and actual values.
The optimization process of the BPNN model using the four heuristic algorithms is outlined in Figure 15. Initially, the Levenberg–Marquardt (L-M) method is utilized to train the network on database samples to compute the predictive model’s weights and thresholds. Subsequently, heuristic algorithms are employed to select the initial weights and thresholds of the BPNN network. During this phase, the heuristic algorithms continuously optimize the weights and thresholds within the initial value range until the iteration that achieves the minimum RMSE, thereby accomplishing global optimization. In the subsequent phase, the computed weights and thresholds undergo a secondary tuning using heuristic algorithms without further training via the L-M method. Instead, based on the prediction errors, the heuristic algorithms adjust the weights and thresholds, constituting local optimization. To prevent model overfitting, the heuristic algorithms are designed for optimization based on the reduction of errors in both the training and validation sets. Overall, the integrated strategies of global and local optimization enhance the accuracy and generalizability of the BPNN model.
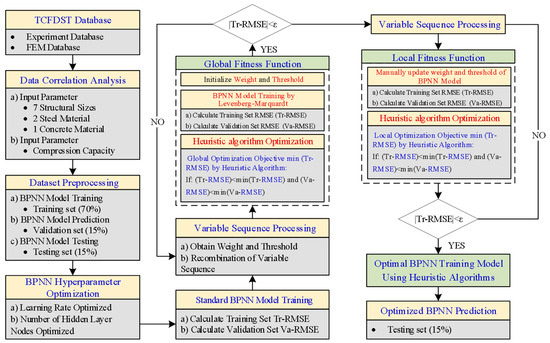
Figure 15.
Structure description of BPNN based on optimization algorithm.
3.6. Model Evaluation Metrics
When employing machine learning algorithms for predicting the load-bearing capacity of axles, the accuracy and reliability of the predictions are commonly assessed using the following metrics:
- (1)
- Root Mean Square Error (RMSE): This metric represents the square root of the average of the squares of the differences between predicted and actual values. It is used to measure the variation between the predictions and the actual observations.
- (2)
- Mean Absolute Error (MAE): MAE is the average of the absolute differences between the predicted values and the actual values. It evaluates the degree of deviation in the prediction results.
- (3)
- Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE): MAPE measures the average of the absolute differences between the predicted and actual values divided by the actual values, typically expressed as a percentage. It provides an insight into the prediction accuracy in relative terms.
- (4)
- Coefficient of Determination (R2): R2 indicates the degree of fit between the predicted values and the actual values. A value of R2 lies in the range [0, 1], where 1 indicates perfect prediction accuracy.
These metrics enable a comprehensive evaluation of the model’s performance. The formulas are provided as follows:
where represents the model’s predicted values, denotes the actual values, is the mean of the actual values, and n is the number of test samples.
3.7. Hyperparameter Tuning
The hyperparameters of the BPNN model include the number of nodes in the hidden layers and the learning rate. The range for the number of hidden layer nodes is calculated using Equation (12), and the search range for the learning rate is set between 0.005 and 0.145. By setting these hyperparameters, an error matrix corresponding to the number of hidden nodes and learning rate is established. The training and validation datasets undergo 50 training iterations using these settings. The resulting hyperparameters and their corresponding average error values on the validation set are depicted in a heatmap, as shown in Figure 16.
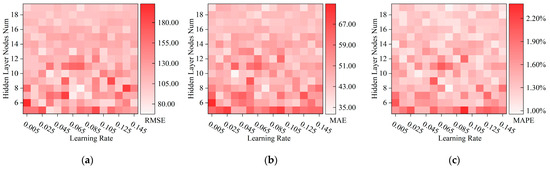
Figure 16.
Error optimization heatmap under the influence of the number of hidden layer nodes and learning rate: (a) RMSE; (b) MAE; (c) MAPE.
This study selects the parameters corresponding to the smallest average RMSE as the benchmark hyperparameters for the BPNN network. Table 4 lists the recommended hyperparameters for the BPNN network to be used in prediction.
where nhidden represents the number of nodes in the hidden layer, ninput denotes the number of nodes in the input layer, noutput denotes the number of nodes in the output layer, and α is an integer within the range [1, 10].

Table 4.
Recommended network hyperparameters for BPNN.
When the initial values of weights and thresholds in BPNN are tuned using different optimization algorithms, the size of the initial population significantly impacts the accuracy of the final model error. Generally, a larger population size enhances the global search capability of the optimization algorithm but also increases the computational duration. Therefore, this paper has selected three different initial population sizes to compute the model, as shown in Figure 17. When the initial population size , all four optimization models achieve better global optima with a moderate duration.
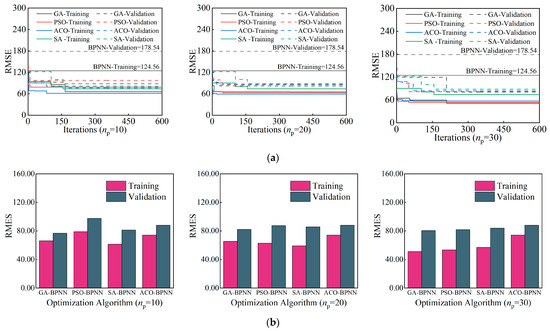
Figure 17.
Error between training set and validation set under different initial populations: (a) RMSE–iterations curve; (b) RMSE.
4. Comparison of Optimization Effects
4.1. Comparison of Model Performance Metrics
Based on the hyperparameter optimization results and the recommended initial population size, the error metrics for both the standard BPNN model and four heuristic-algorithm-optimized BPNN models on the training and validation sets were calculated, as shown in Table 5.

Table 5.
Characteristic parameters for multiple machine learning models for predicting compression bearing capacity.
As illustrated in Figure 18a, compared to the standard BPNN model, the GA-BPNN model shows a reduction in RMSE by 58.03%, MAE by 56.07%, and MAPE by 59.02% on the training set, with the coefficient of determination R2 increasing to 0.9992. On the validation set, RMSE decreased by 36.74%, MAE by 42.27%, MAPE by 43.99%, and R2 improved to 0.9959. The strong performance of the GA-BPNN model is largely due to the Genetic Algorithm’s ability to efficiently explore the global solution space and avoid local minima, allowing for better optimization of weights and thresholds. However, the model may exhibit higher computational costs due to the iterative nature of GA, especially for larger datasets, and may be sensitive to hyperparameter settings such as mutation rates and population size, which influence its convergence behavior.
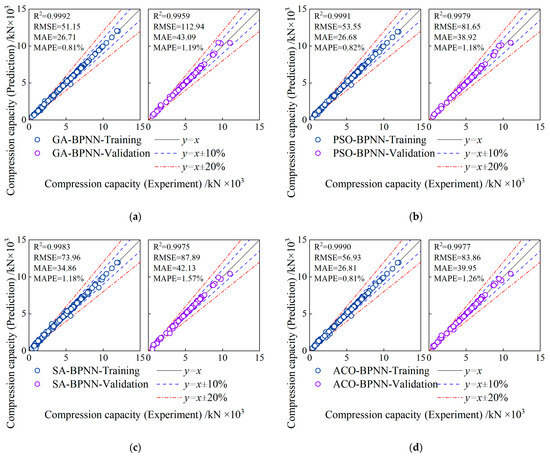
Figure 18.
Heuristic algorithm optimization of BPNN model to obtain predicted bearing capacity measured bearing capacity distribution: (a) GA-BPNN; (b) PSO-BPNN; (c) SA-BPNN; (d) ACO-BPNN.
Figure 18b shows that, compared to the standard BPNN model, the PSO-BPNN model achieved a training set RMSE reduction of 57.01%, MAE reduction of 56.12%, MAPE reduction of 58.67%, and an increase in R2 to 0.9991. On the validation set, RMSE decreased by 54.27%, MAE by 47.83%, MAPE by 44.22%, and R2 improved to 0.9979. The PSO-BPNN model demonstrates rapid convergence, which explains its strong performance across both training and validation sets. The model benefits from the swarm’s ability to share information among particles, but it can sometimes converge prematurely to suboptimal solutions if the diversity of the swarm is not maintained. Sensitivity to initial conditions and the choice of the inertia weight parameter can also influence performance, making it important to fine-tune these aspects to avoid premature convergence.
As depicted in Figure 18c, compared to the standard BPNN model, the SA-BPNN model shows a reduction in RMSE by 40.62%, MAE by 42.67%, and MAPE by 40.47% on the training set, with R2 increasing to 0.9983. On the validation set, RMSE decreased by 50.77%, MAE by 43.54%, MAPE by 25.89%, and R2 improved to 0.9975. The performance of the SA-BPNN model is likely due to Simulated Annealing’s ability to escape local minima by occasionally accepting worse solutions during optimization. This capability is useful for refining solutions after initial exploration, but the slower convergence rate compared to GA and PSO can limit the model’s efficiency, especially when the search space is large. The cooling schedule and the choice of initial temperature greatly affect the performance, requiring careful tuning to balance exploration and exploitation.
Figure 18d illustrates that the ACO-BPNN model, compared to the standard BPNN model, exhibits a training set RMSE reduction of 54.29%, MAE reduction of 55.91%, MAPE reduction of 59.38%, and an increase in R2 to 0.9990. On the validation set, RMSE decreased by 53.03%, MAE by 46.46%, MAPE by 40.74%, and R2 improved to 0.9977. ACO-BPNN performs well due to its ability to iteratively explore and reinforce successful pathways, which is advantageous when searching for optimal combinations of weights and thresholds. However, ACO’s convergence can be slower compared to PSO and GA due to the pheromone update process, and the model may be sensitive to the tuning of parameters such as the pheromone evaporation rate and heuristic factor, which impact its balance between exploration and exploitation.
Among the models tested, the GA-BPNN model showed a reduction in test set error metrics with RMSE decreasing by 31.73%, MAE by 38.03%, and MAPE by 42.63%, and the coefficient of determination R2 improved to 0.991. The PSO-BPNN model demonstrated reductions in RMSE by 21.24%, MAE by 33.45%, and MAPE by 41.05%, with R2 increasing to 0.994. For the SA-BPNN model, test set error metrics showed a decrease in RMSE by 46.31%, MAE by 39.11%, and MAPE by 40.53%, with R2 improving to 0.996. The ACO-BPNN model exhibited reductions in RMSE by 37.48%, MAE by 32.82%, and MAPE by 41.58%, with R2 improving to 0.996.
While all heuristic algorithms significantly improve the predictive accuracy of the BPNN model, their performance varies depending on the nature of the optimization problem and the input parameters. Models like PSO and GA excel in global search efficiency but can be sensitive to premature convergence or computational demands. Simulated Annealing and ACO, while robust in escaping local optima, can be slower to converge, particularly when the number of parameters or data complexity increases.
In terms of input sensitivity, parameters such as the concrete strength, steel tube yield strength, and component dimensions (e.g., wall thickness, diameter) exert considerable influence on model performance. For instance, variations in concrete strength can lead to more significant error in certain models if the parameter is not well represented in the training data. Similarly, models may exhibit higher sensitivity to geometric features such as tube diameter or wall thickness.
Correlation analysis of the test and validation datasets reveals that heuristic optimization algorithms enhance the BPNN model’s learning effectiveness on the training set and reduce the prediction errors on the validation set. Since the heuristic algorithms incorporate validation set errors as the fitness function for optimization, it is necessary to test the optimized network using entirely new data. Therefore, 200 new sample data points were selected to test the final optimized model.
In summary, the BPNN models optimized with algorithms such as GA, PSO, SA, and ACO not only achieve high fitting accuracy on the training set for the original sample data but also ensure effective validation on the validation set and superior predictive accuracy on the final test set. The global and local optimization strategy of heuristic algorithms effectively enhances the learning efficiency of the BPNN network for training samples by utilizing validation set errors to guide the optimization. This approach strategically reduces errors in both the training and validation sets, ensuring the predictive accuracy of the final model and mitigating the risks of overfitting and underfitting to some extent.
4.2. Comparison of Other Machine Learning Methods
To analyze and compare the advantages and disadvantages of BPNN models optimized with four heuristic algorithms against other common machine learning methods, this study selected four widely used machine learning algorithms: Random Forest (RF), K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN), Support Vector Regression (SVR), and Radial Basis Function Neural Network (RBFNN). The same training, validation, and test datasets were used to evaluate the learning and predictive performance of these algorithms, with the feature calculation parameters presented in Table 5.
As shown in Figure 19, among the common machine learning algorithms, the Random Forest (RF) algorithm exhibited the highest prediction errors across the training, validation, and test sets, followed by the Support Vector Regression (SVR) algorithm. The K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN) algorithm demonstrated improved prediction errors compared to the aforementioned two algorithms, while the Radial Basis Function Neural Network (RBFNN) showed prediction errors similar to the standard BPNN algorithm. Overall, compared to common machine learning algorithms, the proposed prediction model yielded superior error metrics (RMSE, R2, MAPE, MAE) across the training, validation, and test sets.
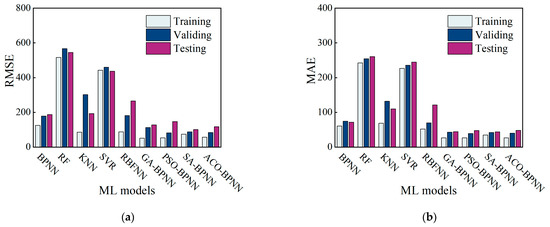
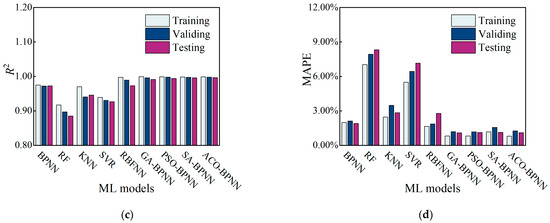
Figure 19.
Error index of different machine learning models: (a) RMSE; (b) MAE; (c) R2; (d) MAPE.
5. Comparison of Design Code Results
To address the issue of calculating the axial load-bearing capacity of TCFDST components, current methods often use the calculation formulas for straight CFDST components by substituting the dimensions of the top section of the tapered components for an approximate calculation of the TCFDST axial load-bearing capacity. Since the ACI 318-19 [63], AISC360-22 [64], EC4 [65], and GB 50936-2014 [66] standards are only applicable to the design of CFST (Concrete-Filled Steel Tubular) components, scholars have provided modified formulas based on these standards that are suitable for calculating the load-bearing capacity of CFDST components.
The commonly used formulas for calculating the axial load-bearing capacity of a CFDST component include the modified ACI 318-19 Method, modified AISC 360-22 Method, modified EC4 Method, T/CCES 7-2020 [67] Method, and modified GB 50936-2014 Method. The specific expressions of the formulas from various standards are provided in Equations (7)–(27).
5.1. Modified ACI 318-19 Method
According to design standard ACI 318-19, the formula for calculating the axial compression bearing capacity of a CFDST component is given by the following type:
5.2. Modified AISC 360-22 Method
According to design standard AISC 360-22, the formula for calculating the axial compression bearing capacity of a CFDST component is given by the following type:
where is the axial compression bearing capacity contributed by the inner steel tube and is the axial compression bearing capacity contributed by the outer steel tube; the two parameters can be determined as follows:
where is the critical buckling stress of the inner steel tube; is the axial load-bearing capacity contributed by the composite section of the outer steel tube and the sandwich concrete; is the critical buckling load of the composite section of the outer steel tube and the sandwich concrete. The coefficients in Equations (15) and (16) are given as follows:
5.3. Modified EC4 Method
According to design standard EC4, the formula for calculating the axial compression bearing capacity of a CFDST component is given by the following type:
where ηa and ηc are calculation coefficients, given as follows:
where is the non-dimensional slenderness ratio, given as follows:
where = 0.6 is a coefficient factor.
5.4. T/CCES 7-2020 Method
According to design standard T/CCES 7-2020, the formula for calculating the axial compression bearing capacity of a CFDST component is given by the following type:
where is the design value of the axial compressive strength of the composite section of the outer steel tube and the sandwich concrete; is the stability coefficient for axially compressed members. The coefficients in Equation (29) are given as follows:
where and are calculation coefficients; is the confinement factor.
5.5. Modified GB 50936-2014 Method
According to design standard GB 50936-2014, the formula for calculating the axial compression bearing capacity of a CFDST component is given by the following type:
where is the axial compressive strength of the composite section, taking into account the confinement effect of the outer steel tube on the sandwich concrete; is the equivalent compressive area of the composite section consisting of the outer steel tube and the sandwich concrete, given as follows:
where and are calculation coefficients.
As shown in Figure 20a, the modified ACI 318-19 method considers the axial load-bearing capacity of the component as the sum of the contributions from the outer steel tube, inner steel tube, and infill concrete. Additionally, a reduction factor is applied to conservatively calculate the axial load-bearing capacity contributed by the sandwich concrete. As a result, the calculated load-bearing capacity for the test set is lower than the measured values.
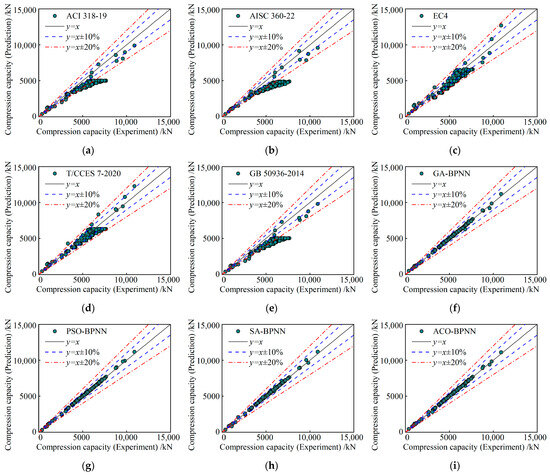
Figure 20.
Optimizing the predicted–experiment bearing capacity relationship of different specifications and heuristic-algorithm-optimized BPNN models: (a) ACI 318-19; (b) AISC 360-22; (c) EC4; (d) T/CCES 7-2020; (e) GB 50936-2014; (f) GA-BPNN; (g) PSO-BPNN; (h) SA-BPNN; (i) ACO-BPNN.
As shown in Figure 20b, the modified AISC 360-22 formula considers the axial load-bearing capacity of the component as the sum of the contributions from the inner steel tube and the composite section of the outer steel tube and sandwich concrete. The combined section’s load-bearing capacity is calculated as the sum of the reduced contributions of the outer steel tube and sandwich concrete, with the confining effect of the outer steel tube considered only when calculating the composite section’s buckling capacity. As a result, the calculated load-bearing capacity for the test set is lower than the measured values.
As shown in Figure 20c, the modified EC4 formula treats the axial load-bearing capacity as the sum of the contributions from the infill concrete and the composite section of the outer and inner steel tubes. It simultaneously accounts for the reduction in strength of the outer and inner steel tubes and the enhancement of the sandwich concrete strength due to the combined action. Consequently, the error in the calculated load-bearing capacity for the test set is generally less than 20%.
As shown in Figure 20d, the T/CCES 7-2020 standard considers the axial load-bearing capacity as the sum of the contributions from the composite section of the outer steel tube and sandwich concrete and the inner steel tube. The enhancement of the infill concrete strength due to the confinement by the outer steel tube is accounted for using parameters such as steel content ratio, nominal steel content ratio, and hoop coefficient. As a result, the error in the calculated load-bearing capacity for the test set is generally less than 20%.
As shown in Figure 20e, the modified GB 50936-2014 formula considers the axial load-bearing capacity as the sum of the contributions from the composite section of the outer steel tube and sandwich concrete and the inner steel tube. The composite section’s axial load-bearing capacity is calculated by multiplying the compressive strength of the composite section by the equivalent sectional area. Consequently, the error in the calculated load-bearing capacity for the test set is generally less than the predicted value.
As shown in Figure 20f–i and Figure 21, the axial load-bearing capacity predictions obtained from the four heuristic-algorithm-optimized BPNN models exhibit higher fitting accuracy compared to the standard formulas. Additionally, these models demonstrate significantly improved predictive performance on both the training and test sets compared to the standard BPNN model, with all error metrics showing better results. The predictive performance of the five standard formulas and the four optimized models is summarized in Table 6.
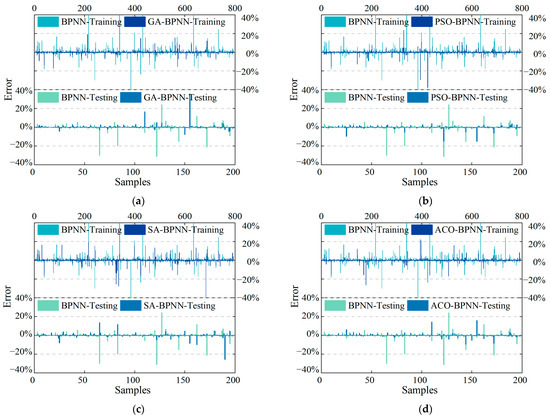
Figure 21.
Error of heuristic-algorithm-optimized BPNN models for the training and testing sets: (a) GA-BPNN; (b) PSO-BPNN; (c) SA-BPNN; (d) ACO-BPNN.

Table 6.
Comparison of design code and heuristic-algorithm-optimized BPNN model evaluation metrics.
6. Parametric Analysis of Predictive Models
The results of the axial load-bearing capacity predictions for TCFDST structures using the aforementioned machine-learning-based methods and standard formulas demonstrate the effectiveness of the four heuristic-algorithm-optimized BPNN networks in improving model prediction accuracy. However, because machine learning algorithms construct complex implicit nonlinear mappings between input parameters and output parameters, it is challenging to intuitively analyze the variable–load-bearing capacity relationship established by the predictive models. Therefore, based on the single-variable sample data from the axial load database, an interpolation method was used to establish a test set with a single variable as the control parameter. Using the predictive models, single-variable load-bearing capacity curves (for selected input parameters) were plotted and compared with the prediction results of the standard formulas.
As shown in Figure 22a, increasing the bottom diameter of the outer steel tube, while keeping the hollowness ratio constant, leads to an upward trend in the axial load-bearing capacity of the test samples. This is due to a reduction in the slenderness ratio and an increase in the effective compressive area. The four predictive models accurately captured this trend. The standard formulas, which conservatively calculate load capacity based on the minimum top cross-section and adjust for taper, also showed a slight increase in predicted capacity as Dob increased, due to the shorter calculated length.
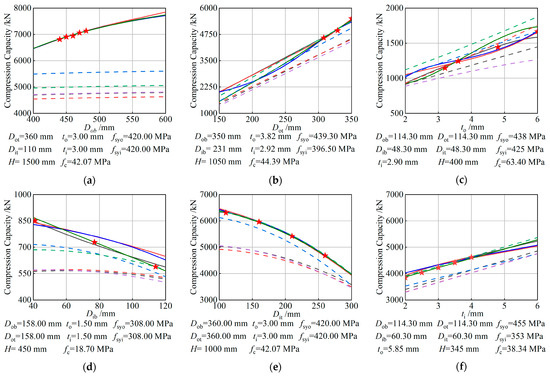
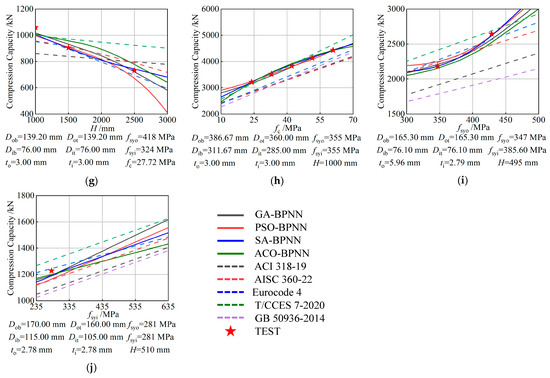
Figure 22.
Parameter analysis of heuristic-algorithm-optimized BPNN models: (a) ; (b) ; (c) ; (d) ; (e) ; (f) ; (g) ; (h) ; (i) ; (j) .
As shown in Figure 22b, under the condition that the hollowness ratio of the top section of the component remains constant, continuously increasing the diameter Dot of the top section of the outer steel tube leads to an upward trend in the axial load-bearing capacity of the test samples. This is because the increase in the effective compressive area of the component plays a dominant role in enhancing the load-bearing capacity. Both the four predictive models and the standard formulas exhibit this upward trend.
As shown in Figure 22c,f, increasing the thickness of the outer steel tube () or the thickness of the inner steel tube () results in an upward trend in the compression bearing capacity of the test samples. This is because the effective compressive area of the outer (or inner) steel tube increases, and the confinement (supporting) effect on the sandwich concrete is enhanced. Both the four predictive models and the standard formulas exhibit this upward trend.
As illustrated in Figure 22d,e, under the condition that the taper of the component remains constant, continuously increasing the bottom diameter (top diameter) of the inner steel tube results in a downward trend in the compression bearing capacity of the test samples. This is due to the increase in the hollowness ratio of the section as the diameter of the inner steel tube (either top or bottom) increases, which reduces the effective compressive area of the component. Both the four predictive models and the standard formulas reflect the same downward trend.
As depicted in Figure 22g, as the height of the component increases, the compression bearing capacity of the test samples decreases. This is due to the increase in the slenderness ratio with the height, which reduces the stability coefficient. Both the four predictive models and the standard formulas reflect the same downward trend.
As shown in Figure 22h, as the strength of the sandwich concrete increases, the compression bearing capacity of the test samples increases. This is because the strength of the composite section of the component increases, leading to a higher compression capacity. However, as the strength of the sandwich concrete continues to increase, the confinement effect of the outer steel tube diminishes, causing the rate of increase in compression capacity to gradually decline. Both the four predictive models and the standard formulas closely match the observed trend in load-bearing capacity changes.
As shown in Figure 22i, as the strength of the outer steel tube increases, the axial compression bearing capacity of the test specimens also increases. This increase is attributed to the enhanced confinement effect of the outer steel tube on the sandwich concrete. Both the four heuristic algorithm prediction models and the standard formulas capture the same trend in bearing capacity changes.
As shown in Figure 22j, as the strength of the inner steel tube increases, the axial compressive bearing capacity of the test specimens also exhibits an increasing trend. This is because the higher strength of the inner steel tube enables it to withstand greater axial compressive loads, and simultaneously, the inner steel tube provides support to the sandwich concrete. Both the four heuristic algorithm prediction models and the standard formulas can accurately predict the variation in axial compressive bearing capacity with respect to the strength of the inner steel tube.
Following the parametric analysis, linear regression models were employed to describe the relationship between each input parameter and the axial load-bearing capacity. The results are summarized in Table 7, which presents the influence of different input parameters, such as outer steel tube diameter (top and bottom), outer tube thickness, inner steel tube diameter (top and bottom), inner tube thickness, height, sandwich concrete strength, yield strength of the outer tube, and yield strength of the inner tube, on load-bearing capacity. These linear regression equations provide quantitative insights into the impact of each parameter on axial load-bearing capacity, demonstrating the direction and magnitude of change as the input parameters vary. By analyzing these trends, the linear equations offer clear and actionable guidance for structural design, allowing engineers to predict the effect of parameter adjustments on load-bearing performance with greater accuracy and precision.

Table 7.
Fitted equations and standardized importance values for key input parameters in predicting axial load-bearing capacity.
To improve the interpretability of the machine learning models used to predict axial load-bearing capacity, Local Interpretable Model-agnostic Explanations (LIME) was employed. LIME generates locally interpretable linear models by approximating the behavior of complex models around individual predictions. It assigns a coefficient, analogous to a slope, to each input feature, quantifying its contribution to the prediction. These coefficients provide valuable insights into how variations in individual input parameters influence the predicted load-bearing capacity. An analysis of the LIME coefficients allows the influence of key parameters on the model’s predictions to be better understood, thereby enhancing transparency and supporting practical decision-making. The standardized importance formulas are provided in Equations (34), and the value is presented in Table 7.
where is the linear slope of each parameter fitting formula and is the number of key parameters.
7. Conclusions
This paper proposes four heuristic-algorithm-optimized BPNN predictive models for the axial load-bearing capacity of TCFDST components, and these models are optimized through global and local tuning of the initial weights and thresholds. The main conclusions are as follows:
- (1)
- The database established in this study uses the basic dimensions of the components (outer steel tube bottom diameter, outer steel tube top diameter, outer steel tube wall thickness, inner steel tube bottom diameter, inner steel tube top diameter, inner steel tube wall thickness, and component length) and material strengths (concrete strength, outer steel tube yield strength, and inner steel tube yield strength) as input parameters, with the axial load-bearing capacity of TCFDST components as the output variable. The sample distribution of the database exhibits a bell-shaped curve, approximately following a normal distribution, which indicates good characteristics for data analysis.
- (2)
- The heuristic-algorithm-optimized BPNN predictive models for axial load-bearing capacity demonstrate smaller prediction errors across the training, validation, and test sets compared to the standard BPNN, RF, KNN, SVR, and RBFNN models. The goodness of fit for the test set improved after model optimization.
- (3)
- The heuristic-algorithm-optimized BPNN predictive models show better accuracy in predicting axial load-bearing capacity on both the test and training sets compared to the national standard formulas, with the goodness of fit (R2) exceeding 0.99 and the mean absolute percentage error (MAPE) being less than 2%.
- (4)
- The parametric analysis indicates that the heuristic-algorithm-optimized BPNN predictive models can effectively capture the relationship between input variables and axial load-bearing capacity, showing consistency with the results obtained from standard formulas and providing higher accuracy.
- (5)
- To enhance the interpretability of the predictive models, LIME was applied, providing a deeper understanding of the contribution of each input parameter to the model’s predictions. The analysis revealed that key features such as outer steel tube diameter (top and bottom), outer tube thickness, inner steel tube diameter (top and bottom), inner tube thickness, height, sandwich concrete strength, yield strength of the outer tube, and yield strength of the inner tube play significant roles in determining the axial load-bearing capacity. The combination of high accuracy and improved interpretability makes these models highly valuable for practical engineering applications, allowing for more transparent and data-driven decision-making in the design and optimization of TCFDST components.
The promising results of the heuristic-algorithm-optimized BPNN predictive models pave the way for future advancements in predicting the axial load-bearing capacity of TCFDST members. With the simple input of the component dimensions and material parameters, these models can provide highly accurate and precise predictions of axial load-bearing capacity, enhancing design efficiency and safety margins. The practical implementation of these models in real-world structural engineering offers significant potential. Moving forward, these models can be integrated into structural design software and Building Information Modeling (BIM) frameworks, such as the 2024 version of Revit, enabling engineers to input design parameters and receive real-time predictions of load capacity. This will streamline the decision-making process, allowing for rapid evaluation of design alternatives and optimization of material selection and safety considerations. Additionally, the models’ adaptability across various TCFDST configurations makes them flexible tools applicable to diverse projects.
The integration of advanced machine learning techniques, such as deep learning and real-time sensor data, could further refine predictive accuracy. As computational power increases and more real-world data become available, these machine learning models will become crucial tools in advancing structural engineering practices, improving both accuracy and efficiency in modern design processes.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.L. and S.K.D.; methodology, X.L.; validation, X.L., S.K.D., and Z.Y.; formal analysis, X.L. and S.K.D.; investigation, X.L. and Y.S.; resources, X.L. and Z.Y.; writing—original draft preparation, X.L.; writing—review and editing, X.L., S.K.D., and Z.Y.; visualization, X.L. and Y.S.; supervision, Q.S. and J.W.; project administration, Q.S. and J.W.; funding acquisition, Q.S. and J.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 52008228, 51978570) and a project of State Grid Zhejiang Electric Power Co., Ltd. (No. 5211JY220003).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the numerical assistance from the team members of Xi’an Jiaotong University and Xi’an University of Architecture and Technology. Additionally, minor refinements in language, grammar of this manuscript were enhanced with the assistance of AI-based tools.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper. The authors declare that this study received funding from State Grid Zhejiang Electric Power Co., Ltd. The funder assisted in securing high-performance computing resources for the project.
Abbreviations
| TCFDST | tapered concrete-filled double-skin steel tubular |
| CFDST | concrete-filled double-skin steel tubular |
| CFST | concrete-filled steel tubular |
| GA | Genetic Algorithm |
| PSO | Particle Swarm Optimization |
| SA | Simulated Annealing |
| ACO | Ant Colony Optimization |
| SCSO | symbiotic organism search optimization |
| GWO_WOA | grey wolf optimizer and whale optimization algorithm |
| ARO | artificial rabbit optimization |
| GBR | gradient boosting regression |
| SVM | support vector machine |
| RFR | random forest regression |
| NN | neural network |
| KNN | K-Nearest Neighbors |
| tensile strain of steel | |
| tensile stress of steel | |
| elastic model of steel | |
| yield strength of steel | |
| tensile strength of steel | |
| compression strength of concrete cylinder | |
| outer diameter of the outer steel tube at the bottom of the specimen | |
| outer diameter of the outer steel tube at the top of the specimen | |
| thickness of the outer steel tube | |
| yield strength of the outer steel tube | |
| outer diameter of the inner steel tube at the bottom of the specimen | |
| outer diameter of the inner steel tube at the top of the specimen | |
| thickness of the inner steel tube | |
| yield strength of the inner steel tube | |
| height of the specimen | |
| compression bearing capacity | |
| compressive strength of a concrete cylinder with a diameter of 100 mm | |
| compressive strength of a concrete cylinder with a diameter of 150 mm | |
| compressive strength of a concrete cube with a diameter of 100 mm | |
| compressive strength of a concrete cube with a diameter of 150 mm | |
| input parameters of BPNN input layer node i | |
| the weight of input node i corresponding to hidden layer node h | |
| input parameters of BPNN hidden layer node h | |
| output parameters of BPNN hidden layer node h | |
| the weight of hidden layer node h corresponding to output layer node j | |
| input parameters of BPNN output layer node j | |
| output parameters of BPNN output layer node j | |
| area of the outer steel tube | |
| area of the inner steel tube | |
| section moment of inertia of the outer steel tube | |
| section moment of inertia of the sandwich concrete |
Appendix A. Detailed Information of Test 192 Column Under Compression
| Specimen Label | Outer Tube Dimensions (mm) | Inner Tube Dimensions (mm) | /mm | /° | Materials (MPa) | /kN | |||||||
| CFDST-ZY-1A | 360.00 | 338.00 | 3.12 | 300.00 | 278.00 | 3.12 | 1080.00 | 0.58 | 0.84 | 788.00 | 788.00 | 117.74 | 6800.00 |
| CFDST-ZY-2A | 300.00 | 282.00 | 3.12 | 240.00 | 222.00 | 3.12 | 900.00 | 0.57 | 0.81 | 788.00 | 788.00 | 117.74 | 6051.00 |
| CFDST-ZY-3A | 300.00 | 282.00 | 3.12 | 240.00 | 222.00 | 3.97 | 900.00 | 0.57 | 0.81 | 788.00 | 755.00 | 117.74 | 6616.00 |
| CFDST-ZY-4A | 300.00 | 282.00 | 3.97 | 210.00 | 192.00 | 5.97 | 900.00 | 0.57 | 0.70 | 755.00 | 708.00 | 117.74 | 9577.00 |
| CFDST-ZY-5A | 300.00 | 282.00 | 5.97 | 210.00 | 192.00 | 5.97 | 900.00 | 0.57 | 0.71 | 708.00 | 708.00 | 117.74 | 9950.00 |
| C1-1/2 | 350.00 | 350.00 | 3.82 | 231.00 | 231.00 | 2.92 | 1050.00 | 0.00 | 0.67 | 439.30 | 396.50 | 44.39 | 5448.00 |
| C2-1/2 | 350.00 | 329.00 | 3.82 | 231.00 | 210.00 | 2.92 | 1050.00 | 0.57 | 0.65 | 439.30 | 396.50 | 44.39 | 4932.00 |
| C3-1/2 | 350.00 | 308.00 | 3.82 | 231.00 | 189.00 | 2.92 | 1050.00 | 1.15 | 0.63 | 439.30 | 396.50 | 44.39 | 4585.00 |
| C4-1/2 | 300.00 | 282.00 | 3.82 | 198.00 | 180.00 | 2.92 | 900.00 | 0.57 | 0.66 | 439.30 | 396.50 | 44.39 | 3961.00 |
| C5-1/2 | 250.00 | 235.00 | 3.82 | 165.00 | 150.00 | 2.92 | 750.00 | 0.57 | 0.66 | 439.30 | 396.50 | 44.39 | 3103.00 |
| CT1-1 | 170.00 | 160.00 | 2.78 | 115.00 | 105.00 | 2.78 | 510.00 | 0.56 | 0.68 | 281.00 | 281.00 | 52.94 | 1228.00 |
| CT1-2 | 170.00 | 160.00 | 2.78 | 115.00 | 105.00 | 2.78 | 510.00 | 0.56 | 0.68 | 281.00 | 281.00 | 52.94 | 1229.00 |
| CT2-1 | 170.00 | 160.00 | 2.78 | 131.00 | 121.00 | 2.78 | 510.00 | 0.56 | 0.78 | 281.00 | 281.00 | 52.94 | 1108.00 |
| CT2-2 | 170.00 | 160.00 | 2.78 | 131.00 | 121.00 | 2.78 | 510.00 | 0.56 | 0.78 | 281.00 | 281.00 | 52.94 | 1100.00 |
| CT3-1 | 180.00 | 169.00 | 2.78 | 122.00 | 111.00 | 2.78 | 540.00 | 0.58 | 0.68 | 281.00 | 281.00 | 52.94 | 1320.00 |
| CT3-2 | 180.00 | 169.00 | 2.78 | 122.00 | 111.00 | 2.78 | 540.00 | 0.58 | 0.68 | 281.00 | 281.00 | 52.94 | 1380.00 |
| CT4-1 | 180.00 | 169.00 | 2.78 | 139.00 | 128.00 | 2.78 | 540.00 | 0.58 | 0.78 | 281.00 | 281.00 | 52.94 | 1152.00 |
| CT4-2 | 180.00 | 169.00 | 2.78 | 139.00 | 128.00 | 2.78 | 540.00 | 0.58 | 0.78 | 281.00 | 281.00 | 52.94 | 1170.00 |
| CT5-1 | 190.00 | 179.00 | 2.78 | 129.00 | 118.00 | 2.78 | 570.00 | 0.55 | 0.68 | 281.00 | 281.00 | 52.94 | 1420.00 |
| CT5-2 | 190.00 | 179.00 | 2.78 | 129.00 | 118.00 | 2.78 | 570.00 | 0.55 | 0.68 | 281.00 | 281.00 | 52.94 | 1360.00 |
| CT6-1 | 190.00 | 179.00 | 2.78 | 147.00 | 136.00 | 2.78 | 570.00 | 0.55 | 0.78 | 281.00 | 281.00 | 52.94 | 1240.00 |
| CT6-2 | 190.00 | 179.00 | 2.78 | 147.00 | 136.00 | 2.78 | 570.00 | 0.55 | 0.78 | 281.00 | 281.00 | 52.94 | 1270.00 |
| cc2a | 180.00 | 180.00 | 3.00 | 48.00 | 48.00 | 3.00 | 540.00 | 0.00 | 0.28 | 275.90 | 396.10 | 39.66 | 1790.00 |
| cc3a | 180.00 | 180.00 | 3.00 | 88.00 | 88.00 | 3.00 | 540.00 | 0.00 | 0.51 | 275.90 | 370.20 | 39.66 | 1648.00 |
| cc4a | 180.00 | 180.00 | 3.00 | 140.00 | 140.00 | 3.00 | 540.00 | 0.00 | 0.80 | 275.90 | 342.00 | 39.66 | 1435.00 |
| cc5a | 114.00 | 114.00 | 3.00 | 58.00 | 58.00 | 3.00 | 342.00 | 0.00 | 0.54 | 294.50 | 374.50 | 39.66 | 904.00 |
| cc6a | 240.00 | 240.00 | 3.00 | 114.00 | 114.00 | 3.00 | 720.00 | 0.00 | 0.49 | 275.90 | 294.50 | 39.66 | 2421.00 |
| cc7a | 300.00 | 300.00 | 3.00 | 165.00 | 165.00 | 3.00 | 900.00 | 0.00 | 0.56 | 275.90 | 320.50 | 39.66 | 3331.00 |
| CC-DS-N | 165.00 | 165.00 | 3.54 | 60.00 | 60.00 | 2.85 | 480.00 | 0.00 | 0.38 | 368.00 | 394.00 | 42.53 | 1660.00 |
| Aa-0.8 | 538.00 | 538.00 | 3.76 | 418.00 | 418.00 | 5.63 | 1500.00 | 0.00 | 0.79 | 253.80 | 296.30 | 57.69 | 8949.70 |
| Aa-0.85 | 538.00 | 538.00 | 3.76 | 449.00 | 449.00 | 5.63 | 1500.00 | 0.00 | 0.85 | 253.80 | 296.30 | 57.69 | 7924.70 |
| Aa-0.9 | 538.00 | 538.00 | 3.76 | 477.00 | 477.00 | 5.63 | 1500.00 | 0.00 | 0.90 | 253.80 | 296.30 | 57.69 | 6036.70 |
| Ab-0.8 | 538.00 | 538.00 | 3.76 | 418.00 | 418.00 | 5.63 | 1500.00 | 0.00 | 0.79 | 253.80 | 296.30 | 41.51 | 7896.60 |
| Ab-0.85 | 538.00 | 538.00 | 3.76 | 449.00 | 449.00 | 5.63 | 1500.00 | 0.00 | 0.85 | 253.80 | 296.30 | 41.51 | 6735.20 |
| Ab-0.9 | 538.00 | 538.00 | 3.76 | 477.00 | 477.00 | 5.63 | 1500.00 | 0.00 | 0.90 | 253.80 | 296.30 | 41.51 | 5966.80 |
| Bb-0.8 | 538.00 | 538.00 | 5.63 | 420.00 | 420.00 | 5.63 | 1500.00 | 0.00 | 0.80 | 296.30 | 296.30 | 41.51 | 8864.00 |
| Bb-0.85 | 538.00 | 538.00 | 5.63 | 448.00 | 448.00 | 5.63 | 1500.00 | 0.00 | 0.85 | 296.30 | 296.30 | 41.51 | 8068.00 |
| Bb-0.9 | 538.00 | 538.00 | 5.63 | 473.00 | 473.00 | 5.63 | 1500.00 | 0.00 | 0.90 | 296.30 | 296.30 | 41.51 | 6774.00 |
| C4-46-0.26-3.7-1 | 165.20 | 165.20 | 3.68 | 42.50 | 42.50 | 3.19 | 495.00 | 0.00 | 0.27 | 357.70 | 409.80 | 53.70 | 2060.00 |
| C4-83-0.26-3.7-1 | 165.00 | 165.00 | 3.68 | 42.60 | 42.60 | 3.21 | 495.00 | 0.00 | 0.27 | 357.70 | 409.80 | 90.70 | 2423.00 |
| C4-130-0.26-3.7-1 | 164.80 | 164.80 | 3.69 | 42.60 | 42.60 | 3.20 | 495.00 | 0.00 | 0.27 | 357.70 | 409.80 | 141.00 | 3068.00 |
| C4-46-0.46-3.7-1 | 165.00 | 165.00 | 3.70 | 76.00 | 76.00 | 2.80 | 495.00 | 0.00 | 0.48 | 357.70 | 385.60 | 53.70 | 1831.00 |
| C4-83-0.46-3.7-1 | 165.10 | 165.10 | 3.67 | 76.10 | 76.10 | 2.81 | 495.00 | 0.00 | 0.48 | 357.70 | 385.60 | 90.70 | 2174.00 |
| C4-130-0.46-3.7-1 | 164.80 | 164.80 | 3.68 | 76.30 | 76.30 | 2.80 | 495.00 | 0.00 | 0.48 | 357.70 | 385.60 | 141.00 | 2732.00 |
| C4-46-0.46-6.0-1 | 165.30 | 165.30 | 5.96 | 76.10 | 76.10 | 2.79 | 495.00 | 0.00 | 0.50 | 347.00 | 385.60 | 53.70 | 2183.00 |
| C4-83-0.46-6.0-1 | 164.90 | 164.90 | 6.01 | 75.90 | 75.90 | 2.80 | 495.00 | 0.00 | 0.50 | 347.00 | 385.60 | 90.70 | 2666.00 |
| C4-130-0.46-6.0-1 | 164.90 | 164.90 | 6.01 | 76.00 | 76.00 | 2.81 | 495.00 | 0.00 | 0.50 | 347.00 | 385.60 | 141.00 | 3110.00 |
| C9-46-0.46-6.0-1 | 165.20 | 165.20 | 5.95 | 76.10 | 76.10 | 2.79 | 495.00 | 0.00 | 0.50 | 428.60 | 385.60 | 53.70 | 2645.00 |
| C9-83-0.46-6.0-1 | 165.00 | 165.00 | 5.99 | 75.80 | 75.80 | 2.80 | 495.00 | 0.00 | 0.50 | 428.60 | 385.60 | 90.70 | 2971.00 |
| C9-130-0.46-6.0-1 | 165.10 | 165.10 | 5.94 | 75.90 | 75.90 | 2.80 | 495.00 | 0.00 | 0.50 | 428.60 | 385.60 | 141.00 | 3322.00 |
| C10-375 | 158.00 | 158.00 | 0.90 | 38.00 | 38.00 | 0.90 | 450.00 | 0.00 | 0.24 | 221.00 | 221.00 | 18.70 | 635.00 |
| C10-750 | 159.00 | 159.00 | 0.90 | 76.00 | 76.00 | 0.90 | 450.00 | 0.00 | 0.48 | 221.00 | 221.00 | 18.70 | 540.00 |
| C10-1125 | 159.00 | 159.00 | 0.90 | 114.00 | 114.00 | 0.90 | 450.00 | 0.00 | 0.73 | 221.00 | 221.00 | 18.70 | 378.00 |
| C16-375 | 158.00 | 158.00 | 1.50 | 39.00 | 39.00 | 1.50 | 450.00 | 0.00 | 0.25 | 308.00 | 308.00 | 18.70 | 851.60 |
| C16-750 | 158.00 | 158.00 | 1.50 | 77.00 | 77.00 | 1.50 | 450.00 | 0.00 | 0.50 | 308.00 | 308.00 | 18.70 | 728.10 |
| C16-1125 | 158.00 | 158.00 | 1.50 | 114.00 | 114.00 | 1.50 | 450.00 | 0.00 | 0.74 | 308.00 | 308.00 | 18.70 | 589.00 |
| C23-375 | 158.00 | 158.00 | 2.14 | 40.00 | 40.00 | 2.14 | 450.00 | 0.00 | 0.26 | 286.00 | 286.00 | 18.70 | 968.20 |
| C23-750 | 158.00 | 158.00 | 2.14 | 77.00 | 77.00 | 2.14 | 450.00 | 0.00 | 0.50 | 286.00 | 286.00 | 18.70 | 879.10 |
| C23-1125 | 157.00 | 157.00 | 2.14 | 115.00 | 115.00 | 2.14 | 450.00 | 0.00 | 0.75 | 286.00 | 286.00 | 18.70 | 703.60 |
| C1-1 | 356.00 | 356.00 | 5.50 | 219.00 | 219.00 | 3.30 | 1068.00 | 0.00 | 0.63 | 618.00 | 356.00 | 38.83 | 7242.00 |
| C2-2 | 356.00 | 356.00 | 5.50 | 168.00 | 168.00 | 3.30 | 1068.00 | 0.00 | 0.49 | 618.00 | 356.00 | 38.83 | 8516.00 |
| 1-1-2 | 114.30 | 114.30 | 5.85 | 60.30 | 60.30 | 2.52 | 345.00 | 0.00 | 0.59 | 455.00 | 396.00 | 38.34 | 1421.54 |
| 2-1-2 | 114.30 | 114.30 | 5.85 | 60.30 | 60.30 | 5.77 | 345.00 | 0.00 | 0.59 | 455.00 | 310.00 | 38.34 | 1574.26 |
| 1-1-1 | 114.30 | 114.30 | 2.73 | 60.30 | 60.30 | 2.52 | 345.00 | 0.00 | 0.55 | 285.00 | 396.00 | 38.34 | 734.60 |
| 2-1-1 | 114.30 | 114.30 | 2.73 | 60.30 | 60.30 | 5.77 | 345.00 | 0.00 | 0.55 | 285.00 | 310.00 | 38.34 | 913.07 |
| 1-2-2 | 114.30 | 114.30 | 5.85 | 60.30 | 60.30 | 2.52 | 345.00 | 0.00 | 0.59 | 455.00 | 396.00 | 64.14 | 1505.67 |
| 2-2-2 | 114.30 | 114.30 | 5.85 | 60.30 | 60.30 | 5.77 | 345.00 | 0.00 | 0.59 | 455.00 | 310.00 | 64.14 | 1666.41 |
| 1-2-1 | 114.30 | 114.30 | 2.73 | 60.30 | 60.30 | 2.52 | 345.00 | 0.00 | 0.55 | 285.00 | 396.00 | 64.14 | 899.21 |
| 2-2-1 | 114.30 | 114.30 | 2.73 | 60.30 | 60.30 | 5.77 | 345.00 | 0.00 | 0.55 | 285.00 | 310.00 | 64.14 | 1088.06 |
| C4-36-0.18-5-1 | 190.60 | 190.60 | 5.15 | 34.00 | 34.00 | 3.08 | 570.00 | 0.00 | 0.19 | 346.90 | 348.20 | 37.50 | 2718.00 |
| C4-36-0.31-5-1 | 190.50 | 190.50 | 5.15 | 59.60 | 59.60 | 3.32 | 570.00 | 0.00 | 0.33 | 346.90 | 342.10 | 37.50 | 2718.00 |
| C4-36-0.53-5-1 | 190.70 | 190.70 | 5.11 | 101.60 | 101.60 | 4.03 | 570.00 | 0.00 | 0.56 | 346.90 | 345.80 | 37.50 | 2626.00 |
| C9-36-0.18-5-1 | 188.90 | 188.90 | 5.09 | 33.70 | 33.70 | 3.09 | 570.00 | 0.00 | 0.19 | 464.00 | 348.20 | 37.50 | 3182.00 |
| C9-36-0.31-5-1 | 191.00 | 191.00 | 5.15 | 59.40 | 59.40 | 3.31 | 570.00 | 0.00 | 0.33 | 464.00 | 342.10 | 37.50 | 3286.00 |
| C9-36-0.53-5-1 | 190.70 | 190.70 | 5.15 | 101.10 | 101.10 | 4.10 | 570.00 | 0.00 | 0.56 | 464.00 | 345.80 | 37.50 | 3082.00 |
| C4-24-0.31-5-1 | 190.40 | 190.40 | 5.15 | 59.90 | 59.90 | 3.33 | 570.00 | 0.00 | 0.33 | 346.90 | 342.10 | 29.00 | 2460.00 |
| C4-36-0.31-5-1 | 189.10 | 189.10 | 5.10 | 59.40 | 59.40 | 3.35 | 570.00 | 0.00 | 0.33 | 346.90 | 342.10 | 37.50 | 2623.00 |
| C4-48-0.31-5-1 | 189.90 | 189.90 | 5.12 | 58.90 | 58.90 | 3.31 | 570.00 | 0.00 | 0.33 | 346.90 | 342.10 | 51.00 | 2950.00 |
| C4-36-0.31-4-1 | 190.30 | 190.30 | 4.26 | 59.40 | 59.40 | 3.36 | 570.00 | 0.00 | 0.33 | 336.80 | 342.10 | 37.50 | 2376.00 |
| C4-36-0.31-5-1 | 189.70 | 189.70 | 5.12 | 59.50 | 59.50 | 3.32 | 570.00 | 0.00 | 0.33 | 346.90 | 342.10 | 37.50 | 2611.00 |
| C4-36-0.31-6-1 | 189.10 | 189.10 | 6.77 | 59.70 | 59.70 | 3.34 | 570.00 | 0.00 | 0.34 | 327.30 | 342.10 | 37.50 | 2894.00 |
| C-1 | 398.00 | 340.00 | 3.00 | 332.00 | 274.00 | 2.50 | 1465.00 | 1.13 | 0.82 | 326.67 | 336.67 | 30.74 | 2391.00 |
| C-2 | 398.00 | 300.00 | 3.00 | 332.00 | 234.00 | 2.50 | 1465.00 | 1.92 | 0.80 | 326.67 | 336.67 | 30.74 | 2350.00 |
| C-4 | 398.00 | 340.00 | 3.00 | 312.00 | 254.00 | 2.50 | 1465.00 | 1.13 | 0.76 | 326.67 | 336.67 | 30.74 | 2599.00 |
| C-5 | 398.00 | 340.00 | 3.00 | 292.00 | 234.00 | 2.50 | 1465.00 | 1.13 | 0.70 | 326.67 | 336.67 | 30.74 | 2885.00 |
| C-6 | 398.00 | 340.00 | 3.50 | 332.00 | 274.00 | 3.00 | 1465.00 | 1.13 | 0.82 | 350.00 | 326.67 | 30.74 | 2555.00 |
| C-7 | 398.00 | 340.00 | 2.50 | 332.00 | 274.00 | 2.00 | 1465.00 | 1.13 | 0.82 | 336.67 | 305.00 | 30.74 | 2094.00 |
| S139.2-1.0 | 139.20 | 139.20 | 3.00 | 76.00 | 76.00 | 2.00 | 1000.00 | 0.00 | 0.57 | 418.00 | 324.00 | 27.72 | 1059.20 |
| S139.2-1.5 | 139.20 | 139.20 | 3.00 | 76.00 | 76.00 | 2.00 | 1500.00 | 0.00 | 0.57 | 418.00 | 324.00 | 27.72 | 905.50 |
| S139.2-2.0 | 139.20 | 139.20 | 3.00 | 76.00 | 76.00 | 2.00 | 2000.00 | 0.00 | 0.57 | 418.00 | 324.00 | 27.72 | 831.70 |
| S139.2-2.5 | 139.20 | 139.20 | 3.00 | 76.00 | 76.00 | 2.00 | 2500.00 | 0.00 | 0.57 | 418.00 | 324.00 | 27.72 | 732.10 |
| S152.4-1.0 | 152.40 | 152.40 | 3.00 | 76.00 | 76.00 | 2.00 | 1000.00 | 0.00 | 0.52 | 549.00 | 324.00 | 27.72 | 1263.50 |
| S152.4-1.5 | 152.40 | 152.40 | 3.00 | 76.00 | 76.00 | 2.00 | 1500.00 | 0.00 | 0.52 | 549.00 | 324.00 | 27.72 | 1195.60 |
| S152.4-2.0 | 152.40 | 152.40 | 3.00 | 76.00 | 76.00 | 2.00 | 2000.00 | 0.00 | 0.52 | 549.00 | 324.00 | 27.72 | 1047.30 |
| S152.4-2.5 | 152.40 | 152.40 | 3.00 | 76.00 | 76.00 | 2.00 | 2500.00 | 0.00 | 0.52 | 549.00 | 324.00 | 27.72 | 941.40 |
| S165.1-1.0 | 165.00 | 165.00 | 3.00 | 76.00 | 76.00 | 2.00 | 1000.00 | 0.00 | 0.48 | 516.00 | 324.00 | 27.72 | 1512.30 |
| S165.1-1.5 | 165.00 | 165.00 | 3.00 | 76.00 | 76.00 | 2.00 | 1500.00 | 0.00 | 0.48 | 516.00 | 324.00 | 27.72 | 1286.40 |
| S165.1-2.0 | 165.00 | 165.00 | 3.00 | 76.00 | 76.00 | 2.00 | 2000.00 | 0.00 | 0.48 | 516.00 | 324.00 | 27.72 | 1187.20 |
| S165.1-2.5 | 165.00 | 165.00 | 3.00 | 76.00 | 76.00 | 2.00 | 2500.00 | 0.00 | 0.48 | 516.00 | 324.00 | 27.72 | 1028.00 |
| S193.7-1.0 | 193.70 | 193.70 | 3.50 | 76.00 | 76.00 | 2.00 | 1000.00 | 0.00 | 0.41 | 391.00 | 324.00 | 27.72 | 2010.00 |
| S193.7-1.5 | 193.70 | 193.70 | 3.50 | 76.00 | 76.00 | 2.00 | 1500.00 | 0.00 | 0.41 | 391.00 | 324.00 | 27.72 | 1730.00 |
| S193.7-2.0 | 193.70 | 193.70 | 3.50 | 76.00 | 76.00 | 2.00 | 2000.00 | 0.00 | 0.41 | 391.00 | 324.00 | 27.72 | 1581.60 |
| S193.7-2.5 | 193.70 | 193.70 | 3.50 | 76.00 | 76.00 | 2.00 | 2500.00 | 0.00 | 0.41 | 391.00 | 324.00 | 27.72 | 1451.40 |
| CFT-A1 | 140.00 | 140.00 | 3.00 | 48.00 | 48.00 | 5.00 | 500.00 | 0.00 | 0.36 | 285.00 | 290.00 | 37.82 | 1232.40 |
| CFT-A2 | 140.00 | 140.00 | 3.00 | 58.00 | 58.00 | 5.00 | 500.00 | 0.00 | 0.43 | 285.00 | 290.00 | 37.82 | 1223.70 |
| CFT-A3 | 140.00 | 140.00 | 5.00 | 68.00 | 68.00 | 3.00 | 500.00 | 0.00 | 0.52 | 290.00 | 285.00 | 37.82 | 1347.00 |
| CFT-A4 | 140.00 | 140.00 | 5.00 | 78.00 | 78.00 | 3.00 | 500.00 | 0.00 | 0.60 | 290.00 | 285.00 | 37.82 | 1334.30 |
| CFT-B1 | 180.00 | 180.00 | 3.00 | 48.00 | 48.00 | 5.00 | 500.00 | 0.00 | 0.28 | 300.00 | 320.00 | 37.82 | 1852.20 |
| CFT-B2 | 180.00 | 180.00 | 3.00 | 58.00 | 58.00 | 5.00 | 500.00 | 0.00 | 0.33 | 300.00 | 320.00 | 37.82 | 1841.40 |
| CFT-B3 | 180.00 | 180.00 | 5.00 | 68.00 | 68.00 | 3.00 | 500.00 | 0.00 | 0.40 | 320.00 | 300.00 | 37.82 | 2057.50 |
| CFT-B4 | 180.00 | 180.00 | 5.00 | 78.00 | 78.00 | 3.00 | 500.00 | 0.00 | 0.46 | 320.00 | 300.00 | 37.82 | 2043.30 |
| O1I1 | 114.30 | 114.30 | 6.00 | 48.30 | 48.30 | 2.90 | 400.00 | 0.00 | 0.47 | 454.00 | 425.00 | 63.40 | 1665.00 |
| O2I1 | 114.30 | 114.30 | 4.80 | 48.30 | 48.30 | 2.90 | 400.00 | 0.00 | 0.46 | 416.00 | 425.00 | 63.40 | 1441.00 |
| O3I1 | 114.30 | 114.30 | 3.60 | 48.30 | 48.30 | 2.90 | 400.00 | 0.00 | 0.45 | 453.00 | 425.00 | 63.40 | 1243.00 |
| O4I1 | 114.30 | 114.30 | 3.20 | 48.30 | 48.30 | 2.90 | 400.00 | 0.00 | 0.45 | 430.00 | 425.00 | 63.40 | 1145.00 |
| O5I2 | 165.10 | 165.10 | 3.50 | 101.60 | 101.60 | 3.30 | 500.00 | 0.00 | 0.64 | 433.00 | 394.00 | 63.40 | 1629.00 |
| O6I2 | 165.10 | 165.10 | 3.00 | 101.60 | 101.60 | 3.20 | 500.00 | 0.00 | 0.64 | 395.00 | 394.00 | 63.40 | 1613.00 |
| O7I2 | 163.80 | 163.80 | 2.35 | 101.60 | 101.60 | 3.20 | 500.00 | 0.00 | 0.64 | 395.00 | 394.00 | 63.40 | 1487.00 |
| O8I2 | 163.00 | 163.00 | 1.95 | 101.60 | 101.60 | 3.20 | 500.00 | 0.00 | 0.64 | 395.00 | 394.00 | 63.40 | 1328.00 |
| O9I2 | 162.50 | 162.50 | 1.70 | 101.60 | 101.60 | 3.20 | 500.00 | 0.00 | 0.64 | 395.00 | 394.00 | 63.40 | 1236.00 |
| CA-0.8-a | 538.00 | 538.00 | 3.76 | 418.00 | 418.00 | 5.63 | 1507.00 | 0.00 | 0.79 | 253.80 | 296.30 | 57.69 | 8949.70 |
| CA-0.85-a | 538.00 | 538.00 | 3.76 | 449.00 | 449.00 | 5.63 | 1507.00 | 0.00 | 0.85 | 253.80 | 296.30 | 57.69 | 7924.70 |
| CA-0.9-a | 538.00 | 538.00 | 3.76 | 477.00 | 477.00 | 5.63 | 1507.00 | 0.00 | 0.90 | 253.80 | 296.30 | 57.69 | 6036.70 |
| CA-0.8-b | 538.00 | 538.00 | 3.76 | 418.00 | 418.00 | 5.63 | 1507.00 | 0.00 | 0.79 | 253.80 | 296.30 | 41.51 | 7896.60 |
| CA-0.85-b | 538.00 | 538.00 | 3.76 | 449.00 | 449.00 | 5.63 | 1507.00 | 0.00 | 0.85 | 253.80 | 296.30 | 41.51 | 6735.20 |
| CA-0.9-b | 538.00 | 538.00 | 3.76 | 477.00 | 477.00 | 5.63 | 1507.00 | 0.00 | 0.90 | 253.80 | 296.30 | 41.51 | 5966.80 |
| CB-0.8-b | 538.00 | 538.00 | 5.63 | 420.00 | 420.00 | 5.63 | 1507.00 | 0.00 | 0.80 | 296.30 | 296.30 | 41.51 | 8864.00 |
| CB-0.85-b | 538.00 | 538.00 | 5.63 | 448.00 | 448.00 | 5.63 | 1507.00 | 0.00 | 0.85 | 296.30 | 296.30 | 41.51 | 8068.00 |
| CB-0.9-b | 538.00 | 538.00 | 5.63 | 473.00 | 473.00 | 5.63 | 1507.00 | 0.00 | 0.90 | 296.30 | 296.30 | 41.51 | 6774.00 |
| 1 | 160.00 | 160.00 | 1.00 | 37.00 | 37.00 | 1.00 | 400.00 | 0.00 | 0.23 | 220.00 | 220.00 | 23.60 | 635.00 |
| 2 | 160.00 | 160.00 | 1.00 | 75.00 | 75.00 | 1.00 | 400.00 | 0.00 | 0.47 | 220.00 | 220.00 | 23.60 | 540.00 |
| 3 | 160.00 | 160.00 | 1.00 | 112.00 | 112.00 | 1.00 | 400.00 | 0.00 | 0.71 | 220.00 | 220.00 | 23.60 | 378.00 |
| 4 | 160.00 | 160.00 | 1.50 | 37.00 | 37.00 | 1.50 | 400.00 | 0.00 | 0.24 | 255.00 | 255.00 | 23.60 | 851.00 |
| 5 | 160.00 | 160.00 | 1.50 | 75.00 | 75.00 | 1.50 | 400.00 | 0.00 | 0.48 | 255.00 | 255.00 | 23.60 | 728.00 |
| 6 | 160.00 | 160.00 | 1.50 | 112.00 | 112.00 | 1.50 | 400.00 | 0.00 | 0.71 | 255.00 | 255.00 | 23.60 | 589.00 |
| 7 | 160.00 | 160.00 | 2.10 | 37.00 | 37.00 | 2.10 | 400.00 | 0.00 | 0.24 | 300.00 | 300.00 | 23.60 | 968.00 |
| 8 | 160.00 | 160.00 | 2.10 | 75.00 | 75.00 | 2.10 | 400.00 | 0.00 | 0.48 | 300.00 | 300.00 | 23.60 | 879.00 |
| 9 | 160.00 | 160.00 | 2.10 | 112.00 | 112.00 | 2.10 | 400.00 | 0.00 | 0.72 | 300.00 | 300.00 | 23.60 | 703.00 |
| CDCS400-3-1000 | 400.20 | 400.20 | 3.01 | 241.20 | 241.20 | 3.01 | 1002.00 | 0.00 | 0.61 | 366.00 | 366.00 | 28.36 | 3423.00 |
| CDCS400-3-2000 | 400.60 | 400.60 | 3.02 | 240.50 | 240.50 | 3.00 | 2003.00 | 0.00 | 0.61 | 366.00 | 366.00 | 28.36 | 3013.00 |
| CDCS400-3-2500 | 398.20 | 398.20 | 3.00 | 239.80 | 239.80 | 3.00 | 2501.00 | 0.00 | 0.61 | 366.00 | 366.00 | 28.36 | 3256.50 |
| CDCS400-3-3500 | 398.60 | 398.60 | 3.00 | 239.60 | 239.60 | 3.02 | 3502.00 | 0.00 | 0.61 | 366.00 | 366.00 | 28.36 | 2923.00 |
| 1-W0-0 | 114.30 | 114.30 | 2.73 | 60.30 | 60.30 | 2.56 | 343.00 | 0.00 | 0.55 | 285.00 | 380.00 | 37.80 | 758.61 |
| 2-W0-0 | 114.30 | 114.30 | 5.85 | 60.30 | 60.30 | 4.71 | 343.00 | 0.00 | 0.59 | 455.00 | 435.00 | 37.80 | 1622.25 |
| R-1 | 160.00 | 160.00 | 2.99 | 60.00 | 60.00 | 2.00 | 420.00 | 0.00 | 0.39 | 371.00 | 369.00 | 53.23 | 1487.00 |
| R-2 | 160.00 | 160.00 | 2.99 | 60.00 | 60.00 | 2.00 | 420.00 | 0.00 | 0.39 | 371.00 | 369.00 | 53.23 | 1542.00 |
| R-3 | 160.00 | 160.00 | 2.99 | 60.00 | 60.00 | 2.00 | 420.00 | 0.00 | 0.39 | 371.00 | 369.00 | 53.23 | 1538.00 |
| GC1-1 | 140.00 | 140.00 | 2.50 | 114.00 | 114.00 | 2.00 | 420.00 | 0.00 | 0.84 | 307.00 | 321.00 | 45.99 | 755.00 |
| CG1-2 | 140.00 | 140.00 | 2.50 | 114.00 | 114.00 | 2.00 | 420.00 | 0.00 | 0.84 | 307.00 | 321.00 | 45.99 | 701.30 |
| GC2-1 | 140.00 | 140.00 | 2.50 | 76.00 | 76.00 | 1.60 | 420.00 | 0.00 | 0.56 | 307.00 | 429.00 | 45.99 | 941.70 |
| GC2-2 | 140.00 | 140.00 | 2.50 | 76.00 | 76.00 | 1.60 | 420.00 | 0.00 | 0.56 | 307.00 | 429.00 | 45.99 | 928.10 |
| GCL-1 | 450.00 | 450.00 | 8.00 | 400.00 | 400.00 | 8.00 | 700.00 | 0.00 | 0.92 | 365.00 | 365.00 | 49.32 | 8906.00 |
| GCL-2 | 450.00 | 450.00 | 8.00 | 400.00 | 400.00 | 8.00 | 700.00 | 0.00 | 0.92 | 365.00 | 365.00 | 49.32 | 8773.70 |
| C203-4-76 | 203.00 | 203.00 | 4.00 | 76.00 | 76.00 | 4.00 | 600.00 | 0.00 | 0.39 | 711.20 | 450.00 | 97.10 | 5572.10 |
| C203-4-114 | 203.00 | 203.00 | 4.00 | 114.00 | 114.00 | 4.00 | 600.00 | 0.00 | 0.58 | 711.20 | 378.00 | 106.90 | 4751.40 |
| C203-6-114 | 203.00 | 203.00 | 6.00 | 114.00 | 114.00 | 4.00 | 600.00 | 0.00 | 0.60 | 770.50 | 378.00 | 106.70 | 6081.50 |
| C300-6-203A | 300.00 | 300.00 | 6.00 | 203.00 | 203.00 | 4.00 | 900.00 | 0.00 | 0.70 | 770.50 | 711.20 | 106.70 | 9783.80 |
| C300-6-203B | 300.00 | 300.00 | 6.00 | 203.00 | 203.00 | 4.00 | 900.00 | 0.00 | 0.70 | 770.50 | 711.20 | 97.10 | 9438.30 |
| CFDST-ZY-1 | 320.00 | 290.00 | 6.00 | 170.00 | 140.00 | 4.00 | 1500.00 | 0.57 | 0.50 | 763.00 | 748.00 | 102.83 | 10438.10 |
| CFDST-ZY-2 | 320.00 | 290.00 | 6.00 | 200.00 | 170.00 | 4.00 | 1500.00 | 0.57 | 0.61 | 763.00 | 748.00 | 102.83 | 9815.20 |
| CFDST-ZY-3 | 270.00 | 240.00 | 6.00 | 170.00 | 140.00 | 4.00 | 1500.00 | 0.57 | 0.61 | 763.00 | 748.00 | 102.83 | 8027.13 |
| CFDST-ZY-4 | 320.00 | 260.00 | 6.00 | 170.00 | 110.00 | 4.00 | 3000.00 | 0.57 | 0.44 | 763.00 | 748.00 | 102.83 | 9645.80 |
| CFDST-ZY-5 | 320.00 | 290.00 | 6.00 | 170.00 | 140.00 | 4.00 | 1500.00 | 0.57 | 0.50 | 763.00 | 748.00 | 102.56 | 11016.61 |
| CFDST-ZY-6 | 320.00 | 290.00 | 6.00 | 200.00 | 170.00 | 4.00 | 1500.00 | 0.57 | 0.61 | 763.00 | 748.00 | 102.56 | 9836.21 |
| CFDST-ZY-7 | 270.00 | 240.00 | 6.00 | 170.00 | 140.00 | 4.00 | 1500.00 | 0.57 | 0.61 | 763.00 | 748.00 | 102.56 | 8112.20 |
| CFDST-ZY-8 | 320.00 | 260.00 | 6.00 | 320.00 | 110.00 | 4.00 | 3000.00 | 0.57 | 0.44 | 763.00 | 748.00 | 102.56 | 9413.20 |
| CFDST-ZY-1 | 300.00 | 300.00 | 6.00 | 135.00 | 135.00 | 4.00 | 1500.00 | 0.00 | 0.47 | 763.00 | 748.00 | 102.83 | 10897.00 |
| CFDST-ZY-2 | 300.00 | 300.00 | 6.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 4.00 | 1500.00 | 0.00 | 0.35 | 763.00 | 748.00 | 102.83 | 12015.00 |
| CFDST-ZY-3 | 250.00 | 250.00 | 6.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 4.00 | 1500.00 | 0.00 | 0.42 | 763.00 | 748.00 | 102.83 | 8748.00 |
| CFDST-ZY-4 | 300.00 | 300.00 | 6.00 | 135.00 | 135.00 | 4.00 | 1500.00 | 0.00 | 0.47 | 763.00 | 748.00 | 102.56 | 11179.00 |
| CFDST-ZY-5 | 300.00 | 300.00 | 6.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 4.00 | 1500.00 | 0.00 | 0.35 | 763.00 | 748.00 | 102.56 | 11867.00 |
| CFDST-ZY-6 | 250.00 | 250.00 | 6.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 4.00 | 1500.00 | 0.00 | 0.42 | 763.00 | 748.00 | 102.56 | 8628.00 |
| C-C-1 | 165.00 | 165.00 | 2.78 | 89.00 | 89.00 | 2.68 | 495.00 | 0.00 | 0.56 | 200.00 | 193.30 | 119.34 | 2040.00 |
| C-C-2 | 165.00 | 165.00 | 2.78 | 114.00 | 114.00 | 2.76 | 495.00 | 0.00 | 0.72 | 200.00 | 193.30 | 110.43 | 1900.00 |
| C-C-3 | 165.00 | 165.00 | 2.78 | 140.00 | 140.00 | 3.00 | 495.00 | 0.00 | 0.88 | 200.00 | 208.30 | 113.04 | 1320.00 |
| C-C-4 | 219.00 | 219.00 | 2.45 | 114.00 | 114.00 | 2.76 | 657.00 | 0.00 | 0.53 | 225.00 | 193.30 | 106.92 | 3414.00 |
| C-C-5 | 219.00 | 219.00 | 2.45 | 140.00 | 140.00 | 3.00 | 657.00 | 0.00 | 0.65 | 225.00 | 208.30 | 113.22 | 2852.00 |
| C-C-6 | 219.00 | 219.00 | 2.45 | 165.00 | 165.00 | 2.78 | 657.00 | 0.00 | 0.77 | 225.00 | 200.00 | 103.86 | 2150.00 |
| C-C-7 | 273.00 | 273.00 | 2.67 | 140.00 | 140.00 | 3.00 | 819.00 | 0.00 | 0.52 | 235.00 | 208.30 | 91.89 | 4845.00 |
| C-C-8 | 273.00 | 273.00 | 2.67 | 165.00 | 165.00 | 2.78 | 819.00 | 0.00 | 0.62 | 235.00 | 200.00 | 91.89 | 4150.00 |
| dc1-1 | 120.00 | 120.00 | 1.96 | 60.00 | 60.00 | 1.96 | 1324.00 | 0.00 | 0.52 | 311.00 | 380.00 | 32.24 | 578.00 |
| dc2-1 | 120.00 | 120.00 | 1.96 | 60.00 | 60.00 | 1.96 | 1324.00 | 0.00 | 0.52 | 311.00 | 380.00 | 57.50 | 715.00 |
References
- Xiong, M.X.; Hu, Q.D.; Liu, B.Y.; Lin, J. Experimental study on fire behavior of high strength double-skin concrete-filled steel tubular columns. Eng. Mech. 2022, 39, 177–185. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, X.F.; Hao, J.P.; Zhao, Y.G. Study on axial compressive behavior of concrete-filled double skin steel tubular short columns considering effective concrete strength. Eng. Mech. 2024, 11, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwin, H.E.; Orlando, L.D.; Jose, B.R.O.; Andres, L.L.; Perla, Y.S.C.; Bianca, Y.P.S.; Jose, R.D.P. Considerations for the structural analysis and design of wind turbine towers: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 137, 110447. [Google Scholar]
- Chou, J.S.; Ou, Y.C.; Lin, K.Y.; Wang, Z.J. Structural failure simulation of onshore wind turbines impacted by strong winds. Eng. Struct. 2018, 162, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schurgacz, P.; Knobloch, M. Concrete-filled hollow section composite columns for multi-storey buildings—innovation and design. Stahlbau 2023, 92, 155–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahman, A.H.A.; Ghannam, M.; Lotfy, S.; AlHamaydeh, M. Heat transfer in ultra-high-performance concrete-filled double-skin tubes under fire conditions. Fire Technol. 2023, 59, 1519–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; Fu, M.; Lian, Y.; Zhong, H.; Wang, W. Experimental study on the seismic performance of a steel slag CFDST T-Joint. Sustainability 2023, 15, 7991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Li, Y.; Zong, Z.; Bi, K.; Xing, K.; Li, Y. Numerical study of seismic performance of steel-concrete composite rigid-frame bridge with precast segmental CFDST piers crossing fault-rupture zones. Structures 2023, 56, 105039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, W. Seismic performance and damage assessment of CFDST frames with SBYC damper. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2023, 206, 107906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Xing, K.; Zong, Z.; Li, M.; Bi, K.; Li, Y. Experimental study of posttensioned precast segmental CFDST columns under cyclic loading. J. Bridge Eng. 2023, 28, 04023006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernardos, S.; Gantes, C. Experimental behavior of concrete-filled double-skin steel tubular (CFDST) stub members under axial compression: A comparative review. Structures 2019, 22, 383–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Tan, H.; Ge, S.; Qin, J.; Wang, Y. Comprehensive experimental database and analysis of circular concrete-filled double-skin tube stub columns: A review. Front. Struct. Civ. Eng. 2023, 17, 1830–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-T.; Liu, X.-H.; Sun, Q.; Li, Y.-W. Analytical behavior and bearing capacity research on out-of-code tapered CFDST members under pure torsion and compression-torsion combination. Ocean Eng. 2023, 284, 115324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.T.; Liu, X.H.; Sun, Q.; Li, Y.W. Compressive-flexural failure mechanism and bearing capacity calculation of over-ranging tapered CFDST members for support structures of offshore wind turbines. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, R.; Zhou, X.-H.; Ji, W.-D.; Li, R.-F.; Zheng, S.-Q.; Wang, Y.-H. Coupled behaviour and strength prediction of tapered CFDST columns with large hollow ratios for wind turbine towers. Eng. Struct. 2023, 289, 116287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.F.; Wang, X.-T.; Lv, B.-H.; Yan, X.-F.; Yan, C.-Z. Experimental study on torsional behavior of tapered high strength thin-walled concrete-filled double-skin steel tubular columns. Structures 2023, 55, 1823–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.D.; Zhang, C.F.; Wang, J.X.; Zheng, L. Analysis on mechanical behavior of tapered concrete-filled double steel tubular short columns under axial compression. J. Archit. Civ. Eng. 2019, 36, 37–45. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.F.; Fu, F.; Bie, X.M.; Dai, X.H. Axial compressive behaviour of CFDST stub columns with large void ratio. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2021, 186, 106892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.L.; Ji, S.H.; Wang, W.D.; Xian, W.; Fan, J.H. Axial compressive behaviour of tapered CFDST stub columns with large void ratio. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2022, 191, 107206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayough, P.; Sulong, N.H.R.; Ibrahim, Z. Analysis and review of concrete-filled double skin steel tubes under compression. Thin Walled Struct. 2020, 148, 106495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.L. Axial Compressive Behavior of CFDST Stub Columns with Large Hollow Ratio. Ph.D. Thesis, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, X.F.; Zhao, Y.G.; Lin, S.Q. Compressive behaviour of circular CFDST short columns with high- and ultrahigh-strength concrete. Thin Walled Struct. 2021, 164, 107898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chan, T.M. Machine learning (ML) based models for predicting the ultimate strength of rectangular concrete-filled steel tube (CFST) columns under eccentric loading. Eng. Struct. 2023, 276, 115392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.R.; Dang, S.C.; Zhu, Y.F.; Yao, Y. A machine learning based interaction model to predict robustness of concrete-filled double skin steel tubular columns under fire condition. Structures 2023, 57, 105332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Z.T.; Wang, W.D.; Zheng, L.; Shi, Y.L. Machine learning models for predicting axial compressive capacity of circular CFDST columns. Structures 2023, 57, 105285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.A.; Ly, H.B. Predicting axial compression capacity of CFDST columns and design optimization using advanced machine learning techniques. Structures 2024, 59, 105724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandramouli, P.; Jayaseelan, R.; Pandulu, G.; Kumar, V.S.; Murali, G.; Vatin, N.I. Estimating the axial compression capacity of concrete-filled double-skin tubular columns with metallic and non-metallic composite materials. Materials 2022, 15, 3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.H.; Hua, L.W.; Wang, Y. Study on axial compression load capacity of hollow sandwich steel pipe concrete columns based on particle swarm optimization bp neural network. Prog. Steel Build. Struct. 2024, 26, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.-S.; Pang, Y.-H.; Kong, L.; Li, B.-F.; An, N.; Wang, X.-T. Experimental study on high strength tapered thin walled concrete-filled double skin steel tubular stub columns under axial compression. J. Xi’an Univ. Archit. Technol. 2022, 54, 306–316. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, A.; Bhat, J.A. Behavior of partial-length stiffened and full-length stiffened CFDST columns under axial load. World J. Eng. 2024, 21, 455–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.-F.; Lin, S.; He, M. Comparative study on behavior of circular axially loaded CFDST short columns under different loading arrangements. Buildings 2023, 13, 2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajjar, Y.P.; Patel, A.J. Computer Aid for Designing Circular Concrete Filled Double Skinned Tube (C-CFDST) Composite Column; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2023; pp. 81–92. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Ren, Q.X.; Han, L.H.; Zhao, X.L. Behaviour of tapered concrete-filled double skin steel tubular (CFDST) stub columns. Thin Walled Struct. 2012, 57, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Z.; Han, L.H.; Zhao, X.L. Behaviour of concrete-filled double skin (CHS inner and CHS outer) steel tubular stub columns and beam-columns. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2004, 60, 1129–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Guo, X.Y.; Chen, M.C.; Xu, K.C. Comparative experimental research on concrete-filled steel tubular columns subjected to axial compression. J. Guangxi Univ. 2015, 40, 806–814. [Google Scholar]
- Uenaka, K.; Kitoh, H.; Sonoda, K. Concrete filled double skin circular stub columns under compression. Thin Walled Struct. 2010, 48, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Cai, Y.X. Performance of CFDST stub columns using high-strength steel subjected to axial compression. Thin Walled Struct. 2019, 141, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekmekyapar, T.; Ghanim Hasan, H. The influence of the inner steel tube on the compression behaviour of the concrete filled double skin steel tube (CFDST) columns. Mar. Struct. 2019, 66, 197–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.F.; Zhao, Y.G. Compressive strength of axially loaded circular concrete-filled double-skin steel tubular short columns. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2020, 170, 106114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.L.; Li, W.; Fu, K.; Li, T.H.; Deng, R.; Wang, Y.H. Ultimate compressive capacity of tapered concrete-filled double skin steel tubular stub columns with large hollow ratio. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2022, 196, 107356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essopjee, Y.; Dundu, M. Performance of concrete-filled double-skin circular tubes in compression. Compos. Struct. 2015, 133, 1276–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwary, A.K. Experimental investigation into mild steel circular concrete-filled double skin steel tube columns. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2022, 198, 107527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.L.; Tong, L.W.; Wang, X.Y. CFDST stub columns subjected to large deformation axial loading. Eng. Struct. 2010, 32, 692–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Hai, Y. Research on bearing capacity of short concrete filled double skin steel tubes columns under axial compression. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 168, 2154–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Ni, Y.Y.; Jin, W.L. Column tests of dodecagonal section double skin concrete-filled steel tubes. Thin Walled Struct. 2015, 88, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, H.G.; Ekmekyapar, T. Mechanical performance of stiffened concrete filled double skin steel tubular stub columns under axial compression. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2019, 23, 2281–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Han, L.H.; Zhao, X.L. Behavior of CFDST stub columns under preload, sustained load and chloride corrosion. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2015, 107, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, D.; Han, L.H. Behaviour of grout-filled double skin steel tubes under compression and bending: Experiments. Thin Walled Struct. 2017, 116, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Shen, L.; Chen, K.; Feng, C.; Lin, X.C.; Elchalakani, M.; Xu, S.Q. Mechanical performance of circular ultrahigh-performance concrete–filled double skin high-strength steel tubular stub columns under axial compression. J. Struct. Eng. 2022, 148, 04021298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.Y. Experimental Study and Theoretical Analysis the Behavior of Tapered Ultra-High Performance Concrete-Filled Double Skin Steel Tubular under Axial Compression. Ph.D. Thesis, Xi’an University of Architecture & Technology, Xi’an, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.C.; Liang, X.D.; Zhu, P.H.; Wang, X.T.; Pang, Y.H.; Meng, F.D.; Wu, J.L. Study on the axial compression behavior of circular high strength concrete-filled double skin steel tubular members. J. Xi’an Univ. Archit. Technol. 2021, 53, 366–378. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.; Qi, B.H.; Wang, H.Z.; Fang, X. Axial compressive behavior of ultra-high performance concrete short columns with large hollow ratio circular hollow sandwich steel tube. Prog. Steel Build. Struct. 2022, 24, 24–31,46. [Google Scholar]
- LI, Y.J.; Liao, F.Y. Mechanical performance of compressive-bending component with self-compacting concrete filled double skin steel tubes. J. Lanzhou Univ. Technol. 2012, 38, 118–122. [Google Scholar]
- Pagoulatou, M.; Sheehan, T.; Dai, X.H.; Lam, D. Finite element analysis on the capacity of circular concrete-filled double-skin steel tubular (CFDST) stub columns. Eng. Struct. 2014, 72, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Young, B.; Gardner, L. Compressive testing and numerical modelling of concrete-filled double skin CHS with austenitic stainless steel outer tubes. Thin Walled Struct. 2019, 141, 345–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, S.S. Study on Compressive Behavior of Confined Concrete-Filled Double-Skin Steel Tube Stub Columns. Ph.D. Thesis, Xihua University, Chengdu, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, K.Y.; Zhou, X.H.; Wen, H.; Deng, R.; Li, R.F.; Wang, Y.H. Compressive behaviour of stiffened thin-walled CFDST columns with large hollow ratio. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2023, 205, 107886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.L.; Ding, H.; Fan, L.F. Research on mesoscopic parameters calibration of geopolymer concrete upon bp neural network. Eng. Mech. 2023, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, S.F.; Su, C.Y.; Yu, J.Z. An optimizing BP neural network algorithm based on genetic algorithm. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2011, 36, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.D.; Wang, S.H.; Ji, G.L.; Dong, Z.C. An MR brain images classifier system via particle swarm optimization and kernel support vector machine. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 130134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.W.; Zhu, K.J.; Diao, F.Q. A dynamic all parameters adaptive BP neural networks model and its application on oil reservoir prediction. Appl. Math. Comput. 2008, 195, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.Z.; Lv, X.M.; Qian, L.; Liu, X.Y. An optimal bp neural network track prediction method based on a ga-aco hybrid algorithm. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ACI 318-19; Building Code Requirements for Structural Concrete and Commentary. American Concrete Institute: Farmington Hills, MI, USA, 2019.
- ANSI/AISC 360-22; Specification for Structural Steel Buildings. American Institute of Steel Construction: Chicago, IL, USA, 2022.
- BS EN 1994-1-1; Eurocode 4: Design of Composite Steel and Concrete Structures (Part 1-1: General Rules and Rules for Buildings). European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 1994.
- GB 50936-2014; Technical Code for Concrete Filled Steel Tubular Structures. Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2014.
- T/CCES 7-2020; Technical Specification for Concrete-Filled Double Skin Steel Tubular Structures. China Civil Engineering Society: Beijing, China, 2020.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).