Preventive Preservation of Rammed Earth Historical Heritage Through Continuous Monitoring, Architectural Inspections, and Data Fusion
Abstract
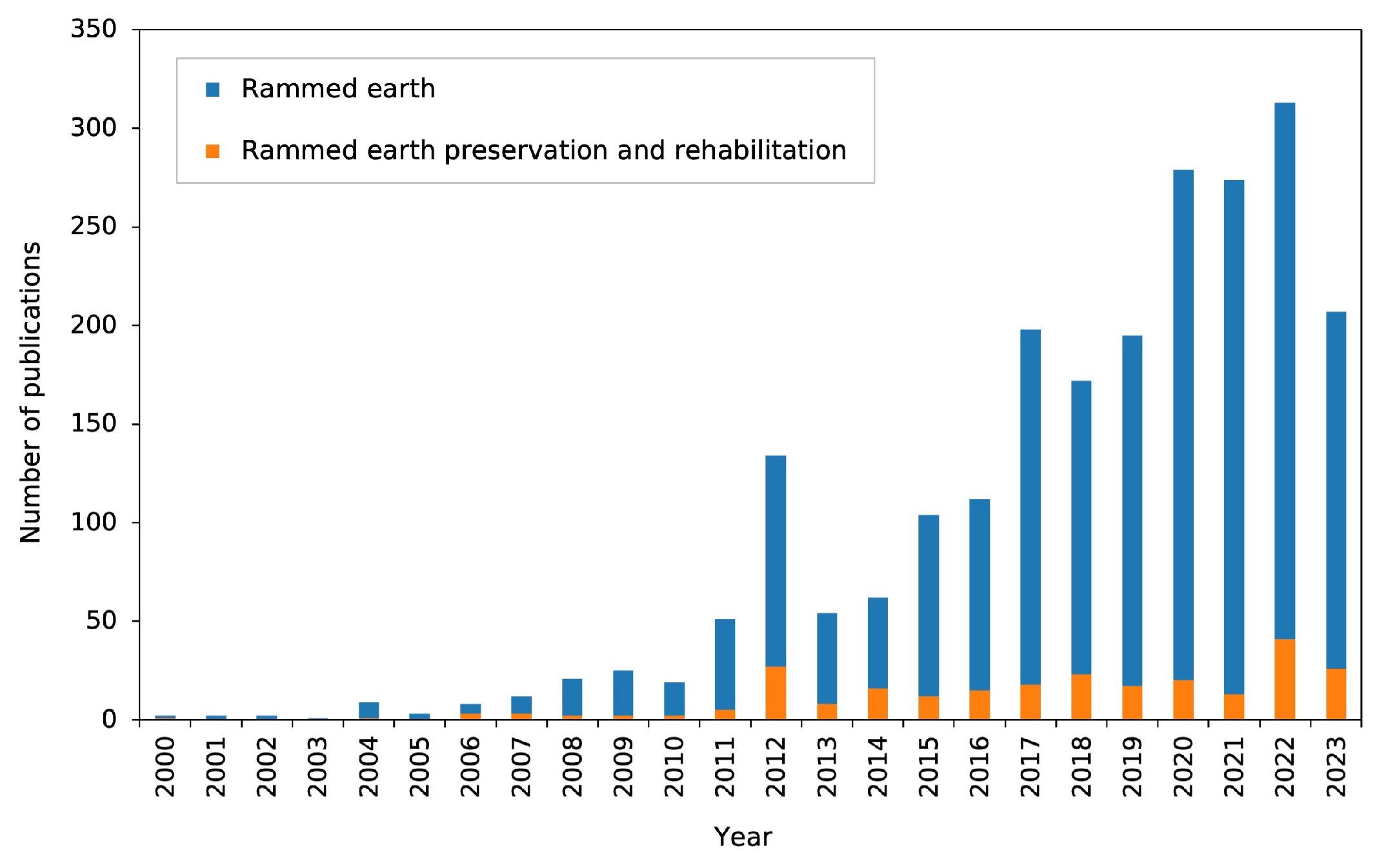
1. Introduction and Background
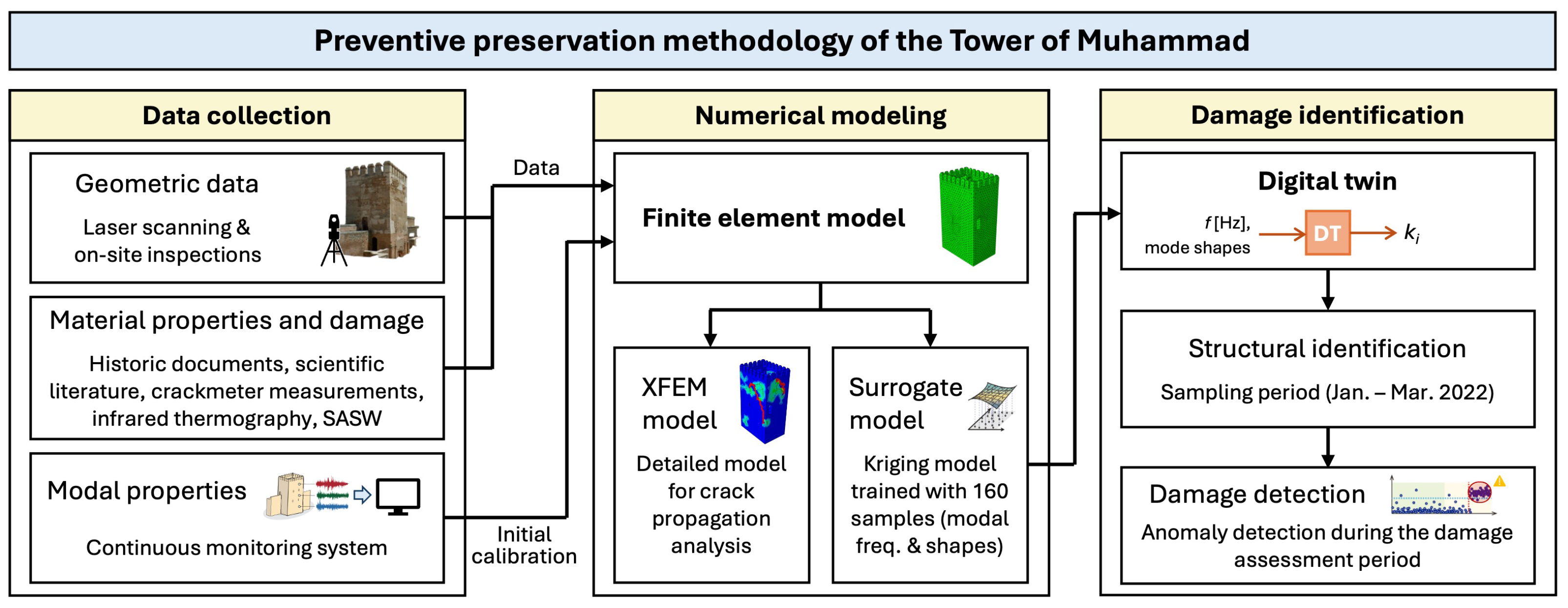
2. Methodology for the Vulnerability Assessment of Historical RE Buildings
- Existing data collection;
- Periodic inspections;
- Continuous monitoring;
- Numerical modeling and digital twin creation;
- Damage identification and vulnerability assessment.
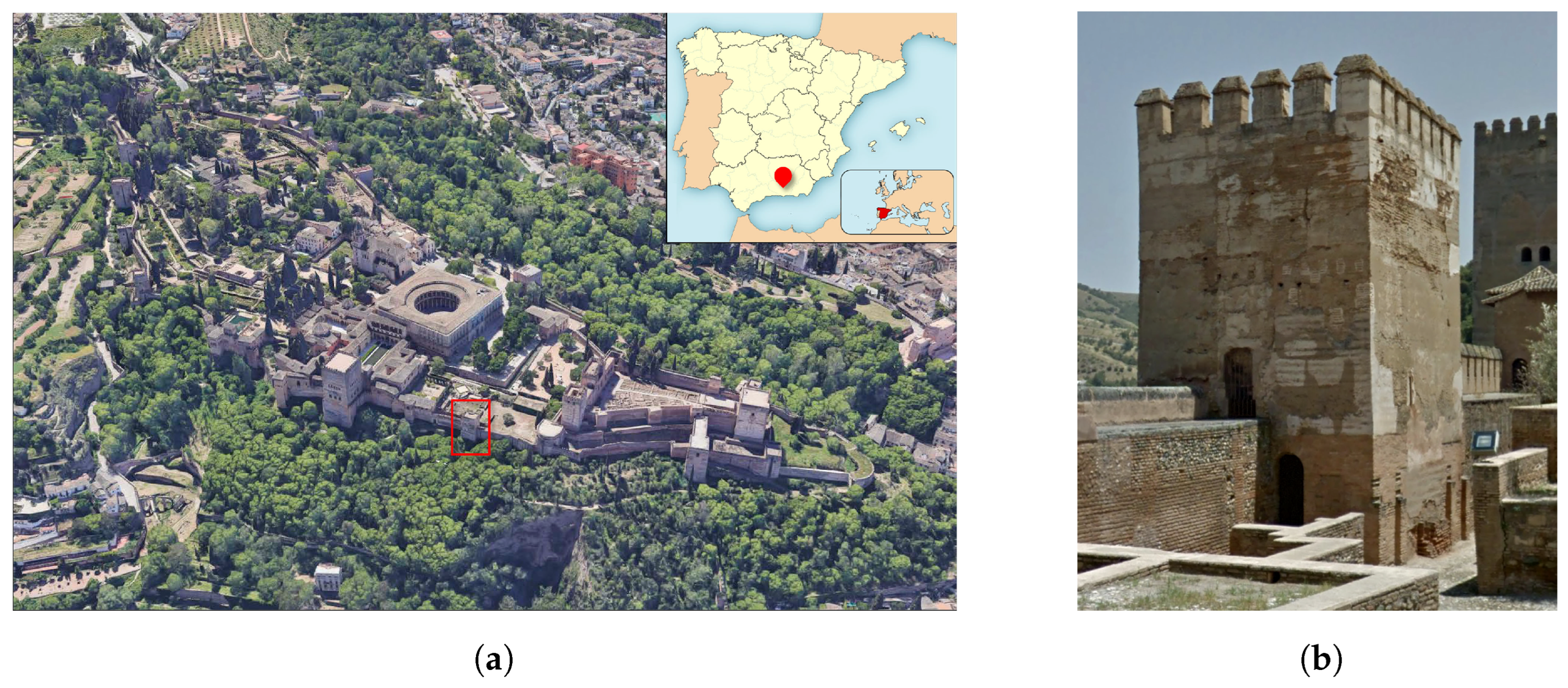
3. Experiences in the Tower of Muhammad
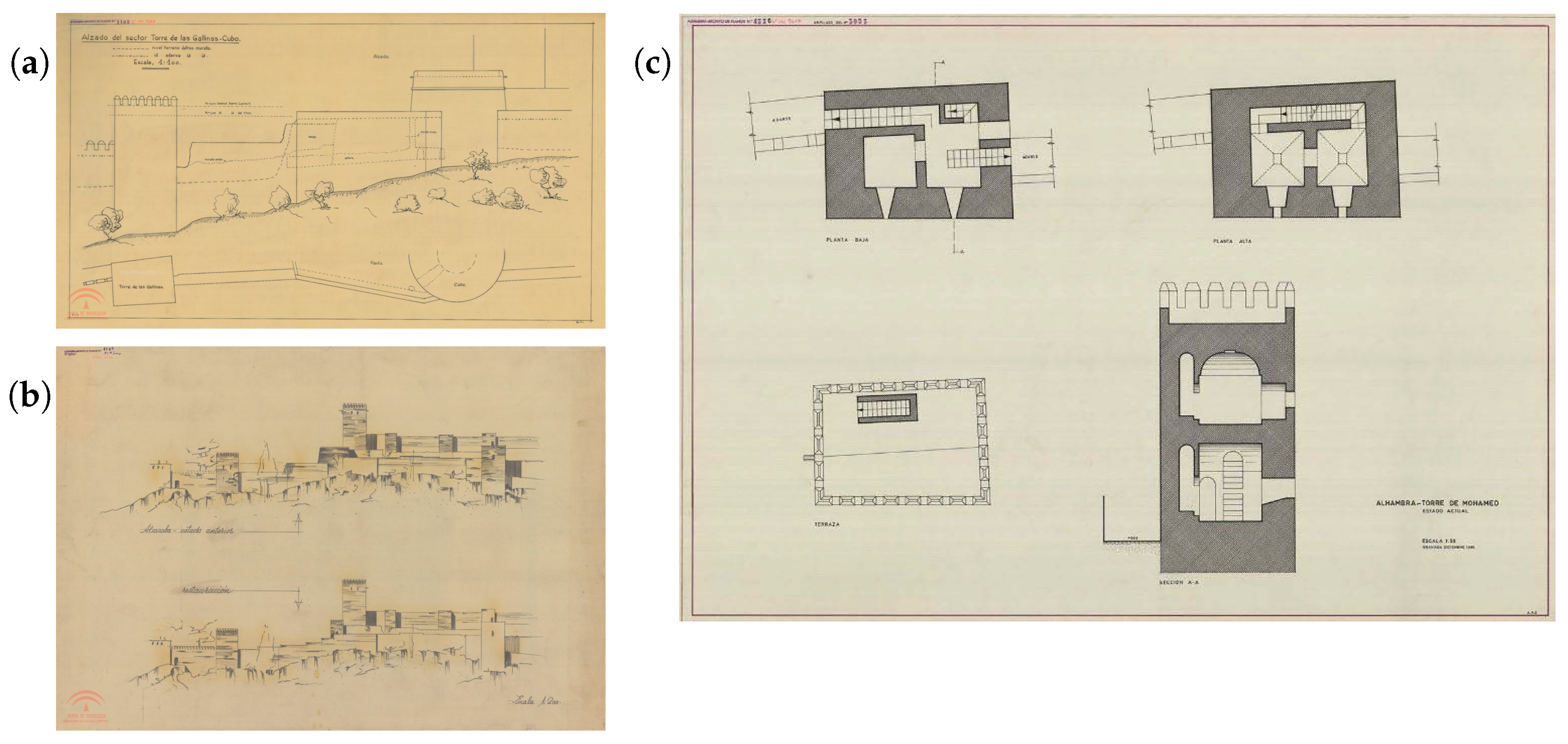
3.1. Architectural and Geometrical Characterization
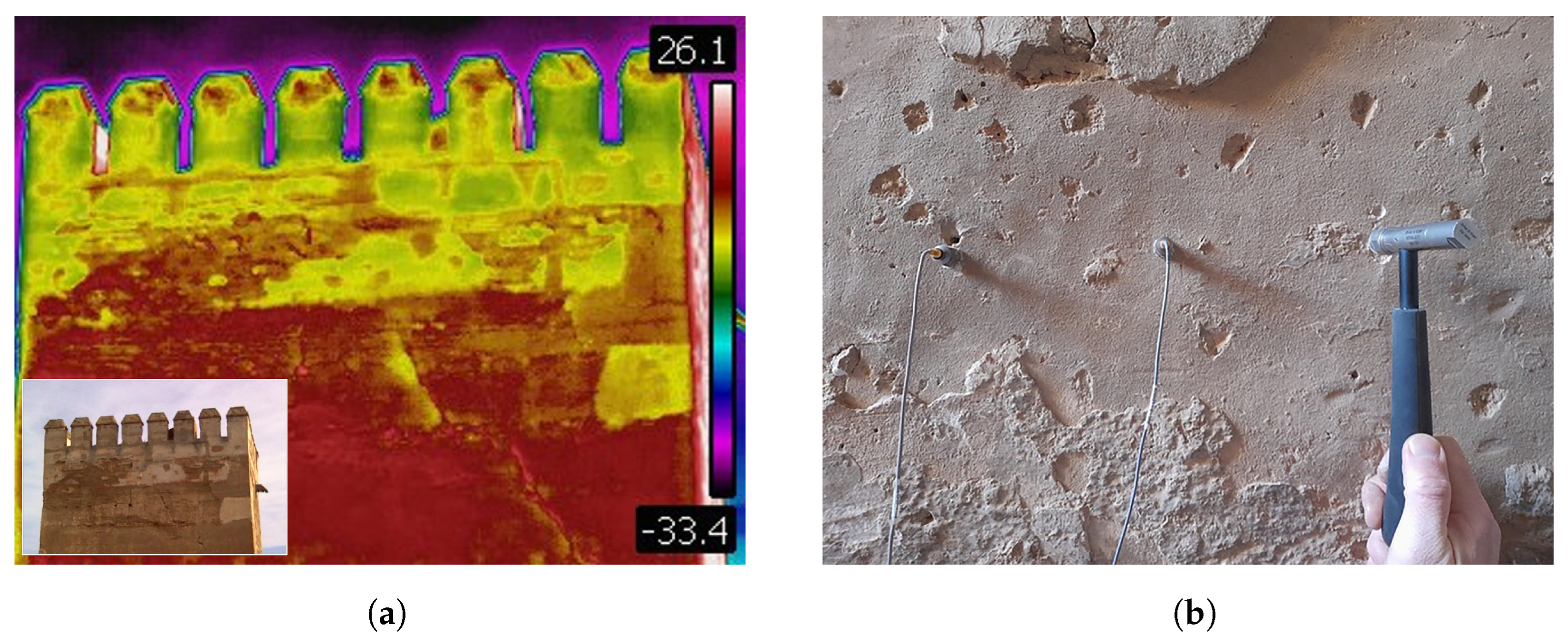
3.2. Inspections and Nondestructive Testing
- Humidity causing salt efflorescence.
- Degradation of the lime plaster with material loss (Figure 6a).
- Biodeterioration due to the growth of parasitic vegetation, leading to cracking and partial loss of the lime plaster (Figure 6b).
- Pollution and other anthropogenic factors.
- Inadequate restorations.
- Fissures and surface cracks, without the separation of parts (Figure 6c).
- Deep cracks, with the separation of parts.
- Exfoliation, the separation of layers.
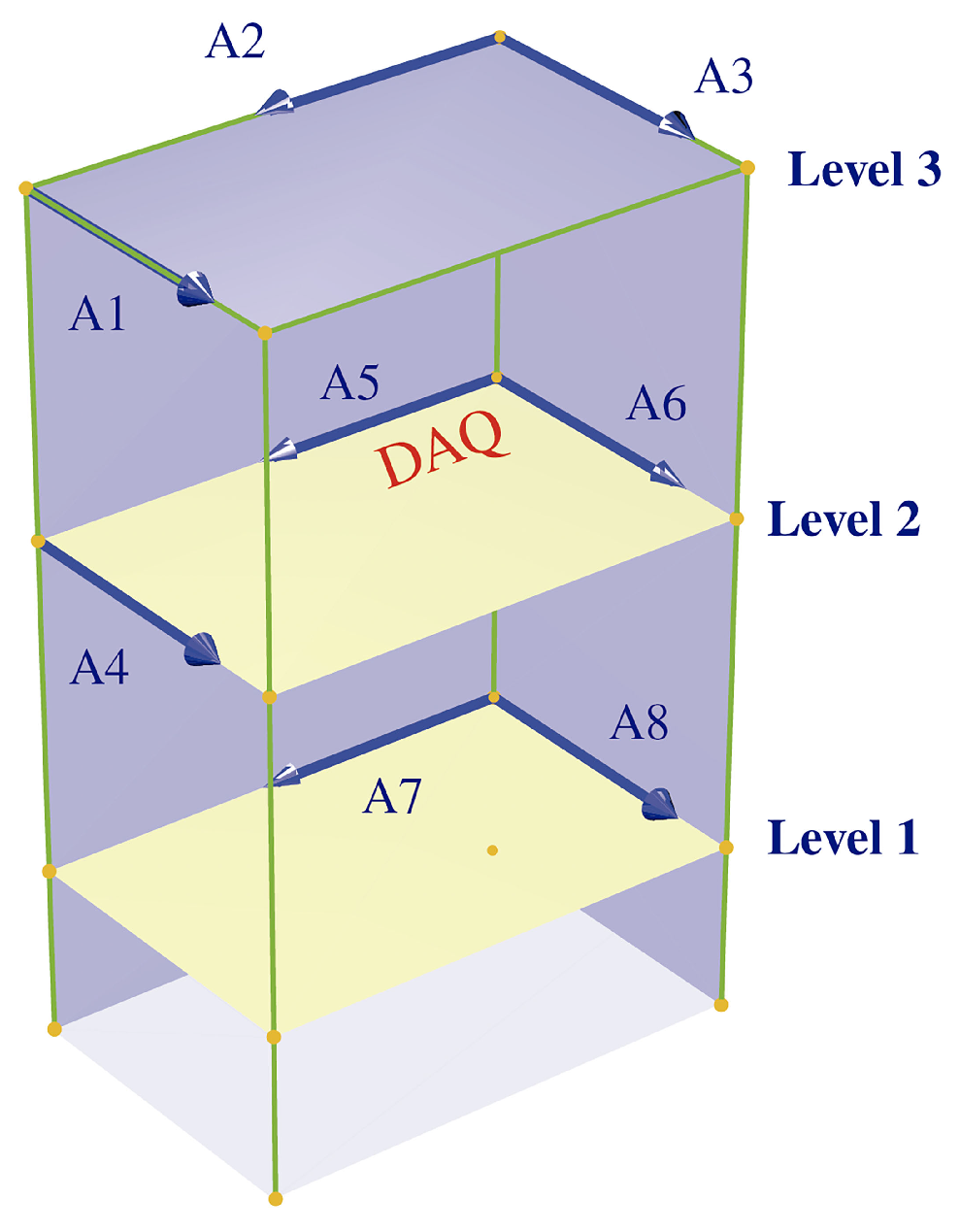
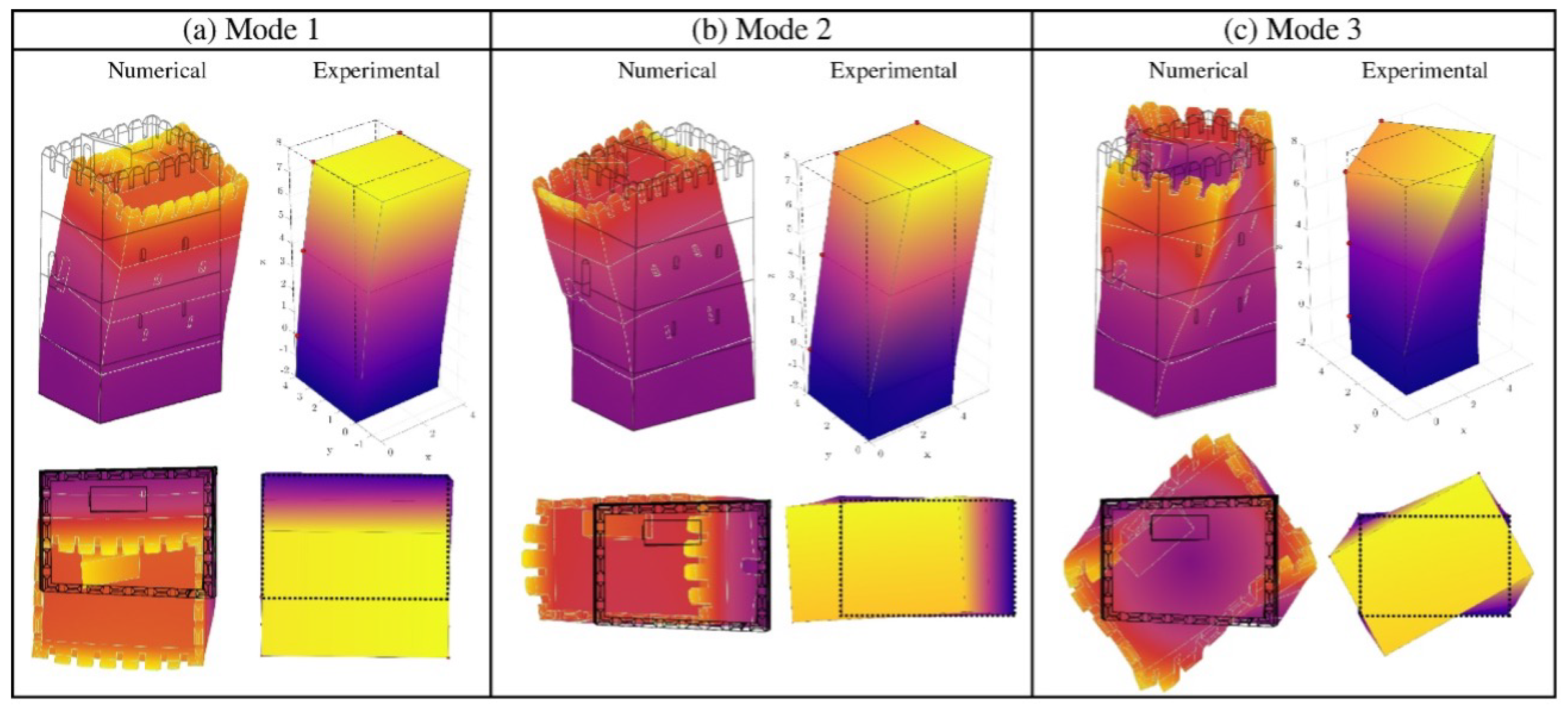
3.3. Operational Modal Analysis
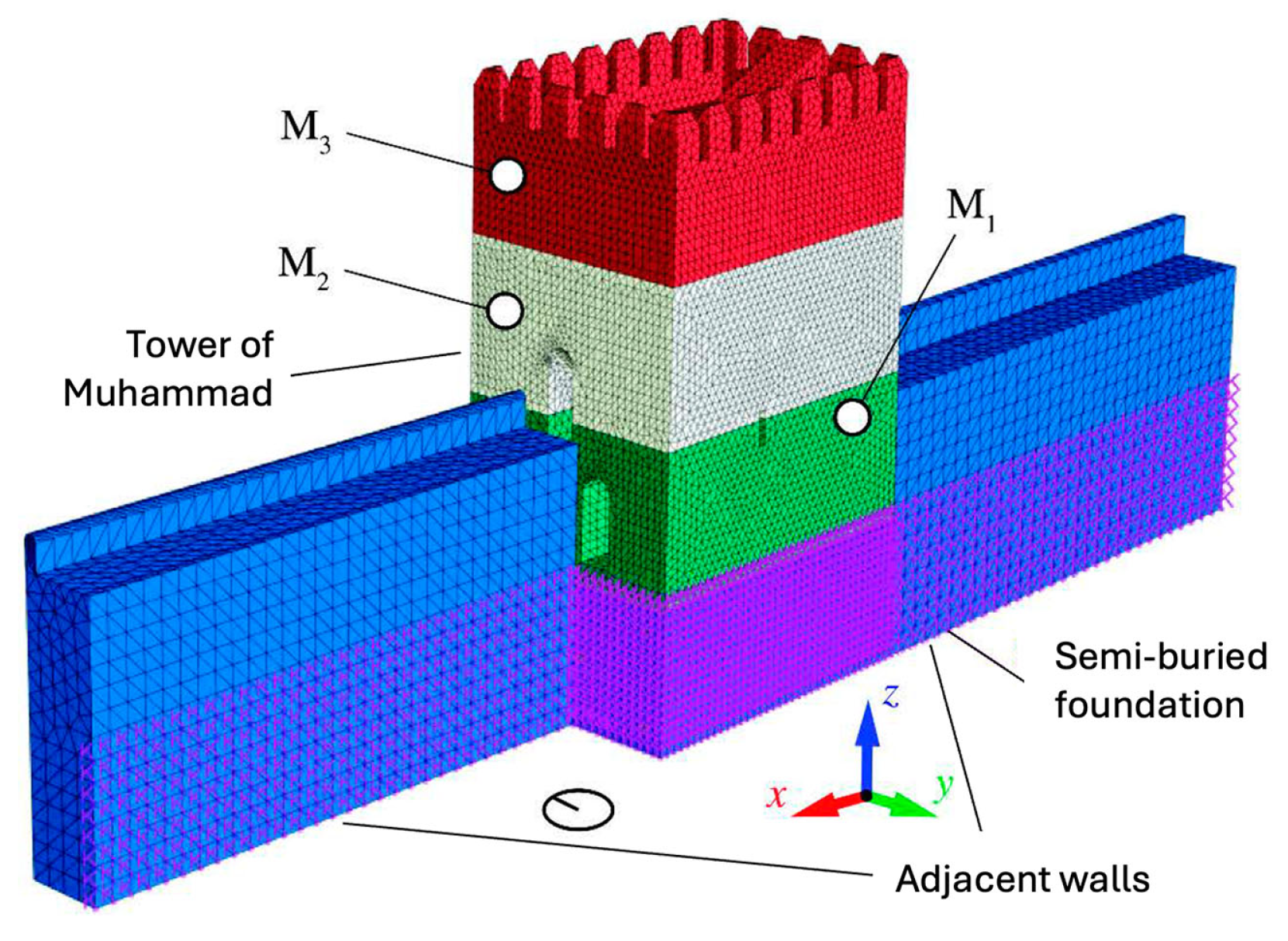
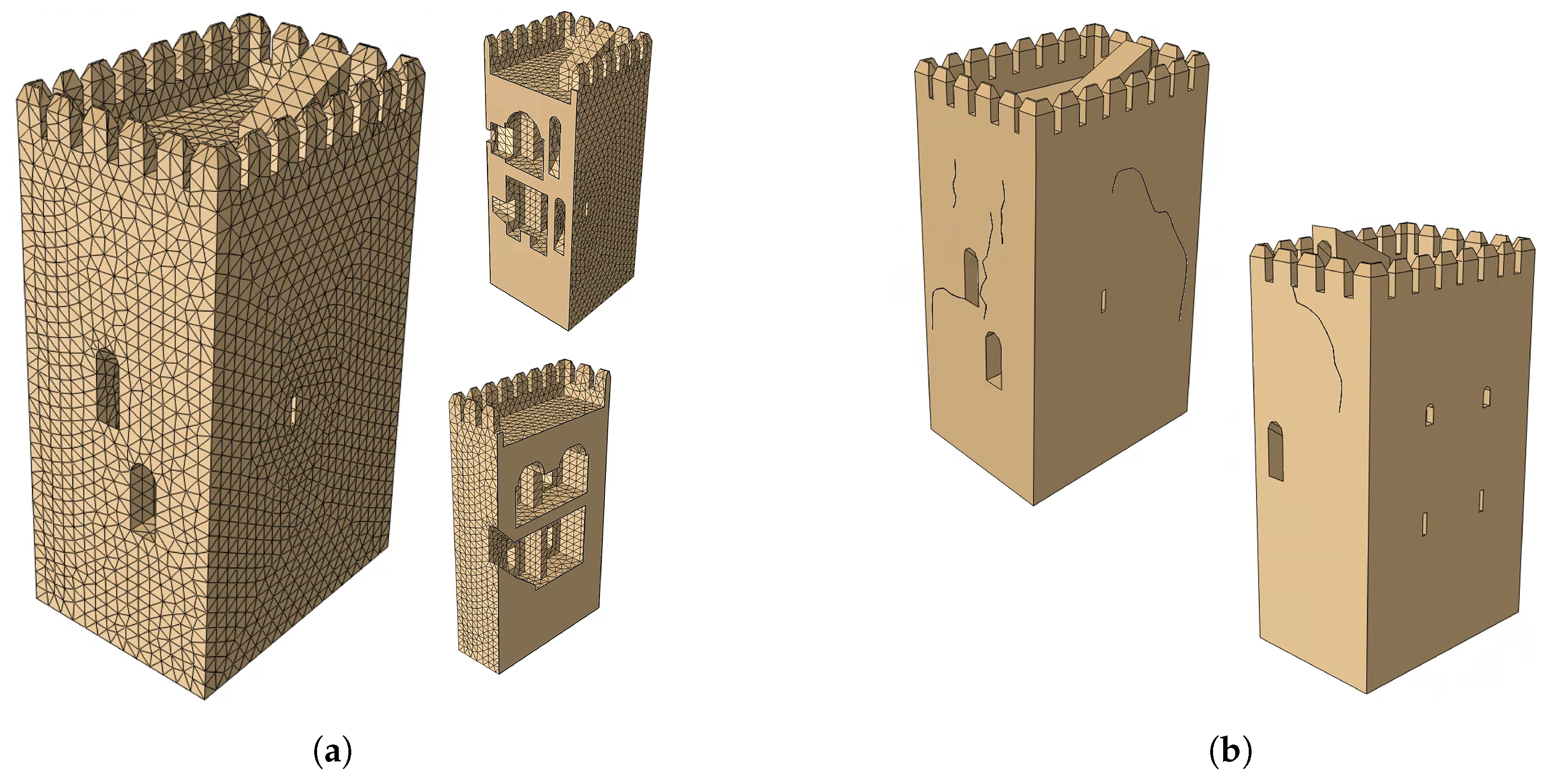
3.4. FEM Modeling and Vibration-Based Damage Identification
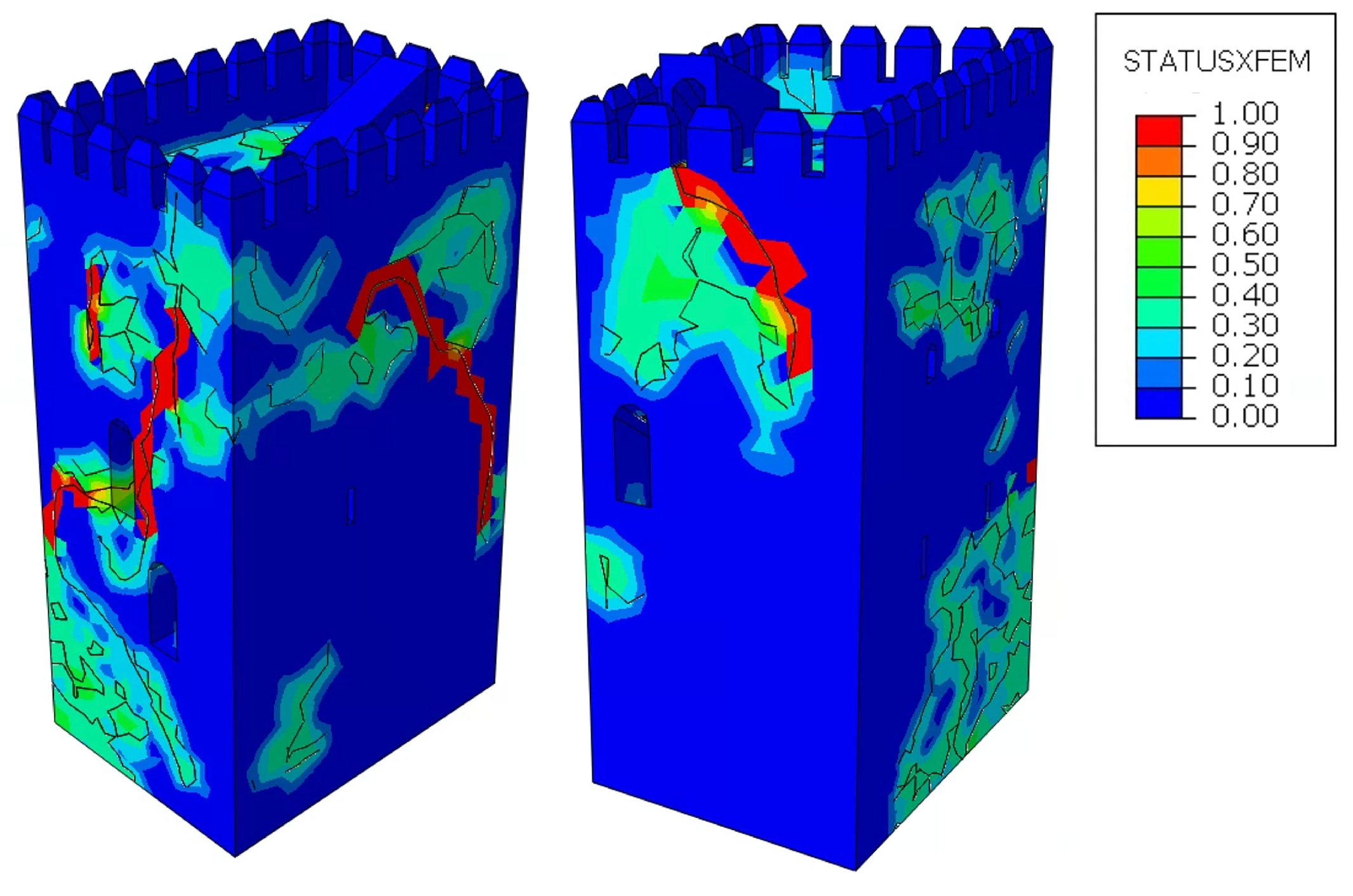
3.5. Finite Element Analysis of Crack Propagation Damage
4. Conclusions
- Develop digital twins using Bayesian model updating to quantify uncertainties in the calibration parameters.
- Incorporate aging degradation models to predict the expected lifespan.
- Periodically update the digital twins based on the results of regular on-site inspections and nondestructive evaluations.
- Emphasize the importance of pattern recognition models for filtering out environmental effects.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Cov-SSI | Covariance-driven stochastic subspace identification |
| DT | Digital twin |
| FEM | Finite element method |
| GPR | Ground-penetrating radar |
| HBIM | Heritage building information model |
| LiDAR | Light detection and ranging |
| MAC | Modal assurance criterion |
| NDT | Nondestructive testing |
| OMA | Operational modal analysis |
| RE | Rammed earth |
| SASW | Spectral analysis of surface waves |
| SHM | Structural health monitoring |
| UPV | Ultrasonic pulse velocity |
| URE | Unstabilized rammed earth |
| XFEM | Extended finite element method |
References
- Council conclusions of 21 May 2014 on cultural heritage as a strategic resource for a sustainable Europe (2014/C 183/08). Off. J. Eur. Union 2014, 183, 36–38.
- ICOMOS. Charter—Principles for the Analysis, Conservation and Structural Restoration of Architectural Heritage. In Proceedings of the ICOMOS 14th General Assembly, Vicoria Falls, Zimbabwe, 27–31 October 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Council of Europe—Committee of Minister. Recommendation No. R (93) 9 of the Committee of Ministers to Member States on the Protection of the Architectural Heritage Against Natural Disasters; Council of Europe: Strasbourg, France, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- The United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction (UNISDR). Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction 2015–2030; UNISDR: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ávila, F.; Puertas, E.; Gallego, R. Characterization of the mechanical and physical properties of stabilized rammed earth: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 325, 126693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ávila, F.; Puertas, E.; Gallego, R. Characterization of the mechanical and physical properties of unstabilized rammed earth: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 270, 121435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ávila, F. Mechanical, Structural and Seismic Behavior of Rammed Earth Constructions. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Granada, Granada, Spain, University of Florence, Firenze, Italy, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Cid, J.; Mazarrón, F.R.; Cañas, I. Las normativas de construcción con tierra en el mundo. Inf. Constr. 2011, 63, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Font, F.; Hidalgo, P. Rammed earth in Spain: Current techniques and examples. Inf. Constr. 2011, 63, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kianfar, E.; Toufigh, V. Reliability analysis of rammed earth structures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 127, 884–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamin Lacouture, L.E.; Phillips Bernal, C.; Reyes Ortiz, J.C.; Ruiz Valencia, D. Seismic vulnerability studies, renovation and reinforcement of houses built with adobe brick and rammed earth. J. Cult. Herit. Stud. 2007, 20, 286–303. [Google Scholar]
- Ávila, F.; Puertas, E.; Torrús, C.; Gallego, R. Influence of crack propagation on the seismic behavior of historic rammed earth buildings: The Tower of Muhammad in the Alhambra (Spain). Eng. Struct. 2024, 301, 117365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.A.; Jaquin, P.; Oliveira, D.V.; Miranda, T.F.; Schueremans, L.; Cristelo, N. Conservation and New Construction Solutions in Rammed Earth. In Structural Rehabilitation of Old Buildings; Costa, A., Guedes, J.M., Varum, H., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 77–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foerster, E.; Krien, Y.; Dandoulaki, M.; Priest, S.; Tapsell, S.; Delmonaco, G.; Margottini, C.; Bonadonna, C. Methodologies to Assess Vulnerability of Structural Systems (ENSURE—Del. 1.1.1). 2009. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/257342955_Methodologies_to_assess_vulnerability_of_structural_systems (accessed on 15 October 2024).
- Zizi, M.; Rouhi, J.; Chisari, C.; Cacace, D.; De Matteis, G. Seismic Vulnerability Assessment for Masonry Churches: An Overview on Existing Methodologies. Buildings 2021, 11, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabani, A.; Kioumarsi, M.; Plevris, V.; Stamatopoulos, H. Structural Vulnerability Assessment of Heritage Timber Buildings: A Methodological Proposal. Forests 2020, 11, 881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canivell, J. Characterization methodology to efficiently manage the conservation of historical rammed-earth buildings. In Rammed Earth Conservation, 1st ed.; Mileto, C., Vegas, F., Cristini, V., Eds.; CRC Press: London, UK, 2012; pp. 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arto, I.; Garrido, J.; Gutiérrez-Carrillo, M.L. Seismic vulnerability analysis of medieval rammed earth fortifications in southeastern Spain. Bull. Earthq. Eng. 2020, 18, 5827–5858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Gupta, R.; Garg, M. Determining material characteristics of “Rammed Earth” using Non-Destructive Test methods for structural design. Structures 2019, 20, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, R.; Hota, G.; Lei, Y.; Li, Y.; Stanislawski, D.; Jiang, Y. Nondestructive Evaluation of Historic Hakka Rammed Earth Structures. Sustainability 2013, 5, 298–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ávila, F.; Puertas, E.; Gallego, R. Mechanical characterization of lime-stabilized rammed earth: Lime content and strength development. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 350, 128871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arto, I.; Gallego, R.; Cifuentes, H.; Puertas, E.; Gutiérrez-Carrillo, M.L. Fracture behavior of rammed earth in historic buildings. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 289, 123167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canivell, J.; Martin-del Rio, J.J.; Alejandre, F.J.; García-Heras, J.; Jimenez-Aguilar, A. Considerations on the physical and mechanical properties of lime-stabilized rammed earth walls and their evaluation by ultrasonic pulse velocity testing. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 191, 826–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-del Rio, J.J.; Canivell, J.; Falcón, R.M. The use of non-destructive testing to evaluate the compressive strength of a lime-stabilised rammed-earth wall: Rebound index and ultrasonic pulse velocity. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 242, 118060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.S.; Seo, W.S.; Lee, K.M. IE-SASW method for nondestructive evaluation of concrete structure. NDT E Int. 2006, 39, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Soto, F.; Ávila, F.; Puertas, E.; Gallego, R. FFRC and SASW nondestructive evaluation of concrete strength from early ages. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 76, 107093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Soto, F.; Ávila, F.; Puertas, E.; Gallego, R. Spectral analysis of surface waves for non-destructive evaluation of historic masonry buildings. J. Cult. Herit. 2021, 52, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosyidi, S.A.P.; Yusoff, N.I.M.; Ismail, N.N.; Yazid, M.R.M. Integrated time-frequency wavelet analysis and impulse response filtering on SASW test for rigid pavement stiffness prediction. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2021, 12, 367–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, L.M.S.; Rodrigues, H.; Gaspar, F. Nondestructive Techniques for the Assessment and Preservation of Historic Structures; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solla, M.; Lorenzo, H.; Rial, F.; Novo, A. Ground-penetrating radar for the structural evaluation of masonry bridges: Results and interpretational tools. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 29, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Macías, E.; Ubertini, F. MOVA/MOSS: Two integrated software solutions for comprehensive Structural Health Monitoring of structures. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2020, 143, 106830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Macías, E.; Ierimonti, L.; Venanzi, I.; Ubertini, F. An Innovative Methodology for Online Surrogate-Based Model Updating of Historic Buildings Using Monitoring Data. Int. J. Archit. Herit. 2021, 15, 92–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, M. Machine learning techniques for structural health monitoring of heritage buildings: A state-of-the-art review and case studies. J. Cult. Herit. 2021, 47, 227–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Macías, E.; Hernández-González, I.A.; Puertas, E.; Gallego, R.; Castro-Triguero, R.; Ubertini, F. Meta-Model Assisted Continuous Vibration-Based Damage Identification of a Historical Rammed Earth Tower in the Alhambra Complex. Int. J. Archit. Herit. 2024, 18, 427–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrar, C.R.; Worden, K. An introduction to structural health monitoring. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2007, 365, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrar, C.R.; Worden, K. Structural Health Monitoring; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rytter, A. Vibrational Based Inspection of Civil Engineering Structures. Ph.D. Thesis, Aalborg University, Aalborg East, Denmark, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- García-Macías, E.; Ubertini, F. Integrated SHM Systems: Damage Detection Through Unsupervised Learning and Data Fusion. In Structural Health Monitoring Based on Data Science Techniques. Structural Integrity, Vol 21; Cury, A., Ribeiro, D., Ubertini, F., Todd, M.D., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 247–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoen, E.; De Roeck, G.; Lombaert, G. Dealing with uncertainty in model updating for damage assessment: A review. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2015, 56–57, 123–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ierimonti, L.; Cavalagli, N.; Venanzi, I.; García-Macías, E.; Ubertini, F. A Bayesian-based inspection-monitoring data fusion approach for historical buildings and its post-earthquake application to a monumental masonry palace. Bull. Earthq. Eng. 2023, 21, 1139–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Yin, S.; Li, K.; Luo, H.; Kaynak, O. Industrial applications of digital twins. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2021, 379, 20200360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angjeliu, G.; Coronelli, D.; Cardani, G. Development of the simulation model for Digital Twin applications in historical masonry buildings: The integration between numerical and experimental reality. Comput. Struct. 2020, 238, 106282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kita, A.; Cavalagli, N.; Venanzi, I.; Ubertini, F. A new method for earthquake-induced damage identification in historic masonry towers combining OMA and IDA. Bull. Earthq. Eng. 2021, 19, 5307–5337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loverdos, D.; Sarhosis, V. Geometrical digital twins of masonry structures for documentation and structural assessment using machine learning. Eng. Struct. 2023, 275, 115256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Nabouch, R.; Bui, Q.B.; Perrotin, P.; Plé, O.; Plassiard, J.P. Numerical modeling of rammed earth constructions: Analysis and recommendations. In Proceedings of the First Conference on Bio-Based Building Materials, Clermont-Ferrand, France, 22–24 June 2015; pp. 21–24. [Google Scholar]
- Suresh, A.; Anand, K.B. Strength and Durability of Rammed Earth for Walling. J. Archit. Eng. 2017, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, S.; De Fino, M.; Fatiguso, F. Historic Building Information Modelling: Performance assessment for diagnosis-aided information modelling and management. Autom. Constr. 2018, 86, 256–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Historic England. BIM for Heritage: Developing a Historic Building Information Model; Historic England: Swindon, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, X.; Hucks, R.G. Preserving our heritage: A photogrammetry-based digital twin framework for monitoring deteriorations of historic structures. Autom. Constr. 2023, 152, 104928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yiğit, A.Y.; Uysal, M. Automatic crack detection and structural inspection of cultural heritage buildings using UAV photogrammetry and digital twin technology. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 94, 109952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleymani, A.; Jahangir, H.; Nehdi, M.L. Damage detection and monitoring in heritage masonry structures: Systematic review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 397, 132402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehgal, S.; Kumar, H. Damage and Damping Identification in a Structure Through Novel Damped Updating Method. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. Civ. Eng. 2021, 45, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avci, O.; Abdeljaber, O.; Kiranyaz, S.; Hussein, M.; Gabbouj, M.; Inman, D.J. A review of vibration-based damage detection in civil structures: From traditional methods to Machine Learning and Deep Learning applications. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2021, 147, 107077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehgal, S.; Kumar, H. Experimental damage identification by applying structural dynamic model updating. J. Theor. Appl. Mech. 2019, 49, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Kosasih, E.; Zhang, J.; Brintrup, A.; Calinescu, A. Digital Twins: State of the art theory and practice, challenges, and open research questions. J. Ind. Inf. Integr. 2022, 30, 100383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrar, C.R.; Doebling, S.W.; Nix, D.A. Vibration–based structural damage identification. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. London. Ser. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2001, 359, 131–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Macías, E.; Ubertini, F. Least Angle Regression for early-stage identification of earthquake-induced damage in a monumental masonry palace: Palazzo dei Consoli. Eng. Struct. 2022, 259, 114119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabanelas Rodríguez, D. The Alhambra: An Introduction. In Al-Andalus Art Islam. Spain; Dodds, J.D., Ed.; Metropolitan Museum of Art: New York, NY, USA, 1992; pp. 127–134. [Google Scholar]
- Vilar Sánchez, J.A. Murallas, Torres y Dependencias de la Alhambra, 1st ed.; Editorial Comares S.L., 2016; Available online: https://www.comares.com/libro/murallas-torres-y-dependencias-de-la-alhambra_115971/ (accessed on 15 October 2024).
- González Limón, T.; Álvarez de Buergo, M.; de las Casas Gómez, A. Estudio de los materiales y de las fábricas de la Torre de Comares de la Alhambra. Cuad. Alhambra 1997, 33–34, 95–104. [Google Scholar]
- Torres Balbás, L. Proyecto de Obras Complementarias de la Torre de Comares; Archivo del Patronato de la Alhambra y Generalife: Granada, Spain, 1932. [Google Scholar]
- Valverde-Espinosa, I.; Ontiveros-Ortega, E.; Sebastián-Pardo, E. El tapial de las murallas de Granada. Re. Rev. Edif. 1997, 26, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orihuela Uzal, A. Casas y Palacios Nazaríes. Siglos XIII-XV; Fundación El Legado Andalusí: Granada, Spain, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- UNE 83312:1990; Concrete Tests. Hardened Concrete. Determination of the Density; CTN 83-Hormigón. AENOR: Madrid, Spain, 1990.
- UNE 83304:1984; Tests of Concrete. Compression Failure; CTN 83-Hormigón. AENOR: Madrid, Spain, 1984.
- Astiz, M.Á. Estudio de la seguridad estructural de la Torre de Comares. Cuad. Alhambra 1997, 33–34, 115–132. [Google Scholar]
- Astiz, M. The importance of earthquake - The case of the Comares tower in the Alhambra palace of Granada. In Proceedings of the Structural Analysis of Historical Constructions II. Possibilities of Numerical and Experimental Techniques, Barcelona, Spain, 4–6 November 1998; Roca, P., Gonzáles, J.L., Oñate, E., Lourenço, P.B., Eds.; pp. 19–37. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez, J.; Ávila, F.; Puertas, E.; Burgos, A.; Gallego, R. Historical and architectural study for the numerical modeling of heritage buildings: The Tower of Comares of the Alhambra (Granada, Spain). Inf. Constr. 2022, 74, e429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Instituto Andaluz de Geofísica. Terremotos de Julio de 1431 en Atarfe y Granada; Instituto Andaluz de Geofísica: Granada, Spain, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Viñes Millet, C. Aspectos de la significación militar de la Alhambra en el siglo XIX: El informe de 1834. Cuad. Alhambra 1983, 19, 213–232. [Google Scholar]
- Velázquez Bosco, R. Plan de Conservación de la Alhambra; Archivo del Patronato de la Alhambra y Generalife: Granada, Spain, 1917. [Google Scholar]
- Torres Balbás, L. Libro Diario de Obras y Reparos de la Alhambra; Technical Report; Patronato de la Alhambra y el Generalife: Granada, Spain, 1936. [Google Scholar]
- Romero Gallardo, A. Prieto-Moreno, Arquitecto Conservador de la Alhambra (1936–1978): Razón y Sentimiento; Patronato de la Alhambra y Generalife: Granada, Spain, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- López Osorio, J.M. Proyecto de Urgencia técnica para la Consolidación de Merlones y Paramentos de la Torre de Las Gallinas—I. Memoria. Technical Report, Patronato de la Alhambra y Generalife; Junta de Andalucía: Granada, Spain, 2021.
- López Díaz de la Guardia, F. P-001266. Plaza de los Aljibes. Alzado del sector Torre de las Gallinas o Mohamed al Cubo. 1954. Available online: https://www.alhambra-patronato.es/ria/handle/10514/1271?show=full (accessed on 15 October 2024).
- Prieto-Moreno, F. P-006116. Alcazaba. Alzado Desde Torre de las Gallinas a Torre de las Armas. Estado Anterior y Restauración de Murallas. 1957. Available online: https://www.alhambra-patronato.es/ria/handle/10514/5456 (accessed on 15 October 2024).
- Alfonso Gallardo, A. P-005617 Alhambra—Torre de Mohamed—Plantas y sección. Arch. Patron. Alhambra Gen. 1985. submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández-González, I.A. Damage Identification of Large-Scale Structures Using Surrogate Kriging Models and Particle Swarm Algorithms. Master’s Thesis, University of Granada, Granada, Spain, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zini, G.; Betti, M.; Bartoli, G. A quality-based automated procedure for operational modal analysis. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2022, 164, 108173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
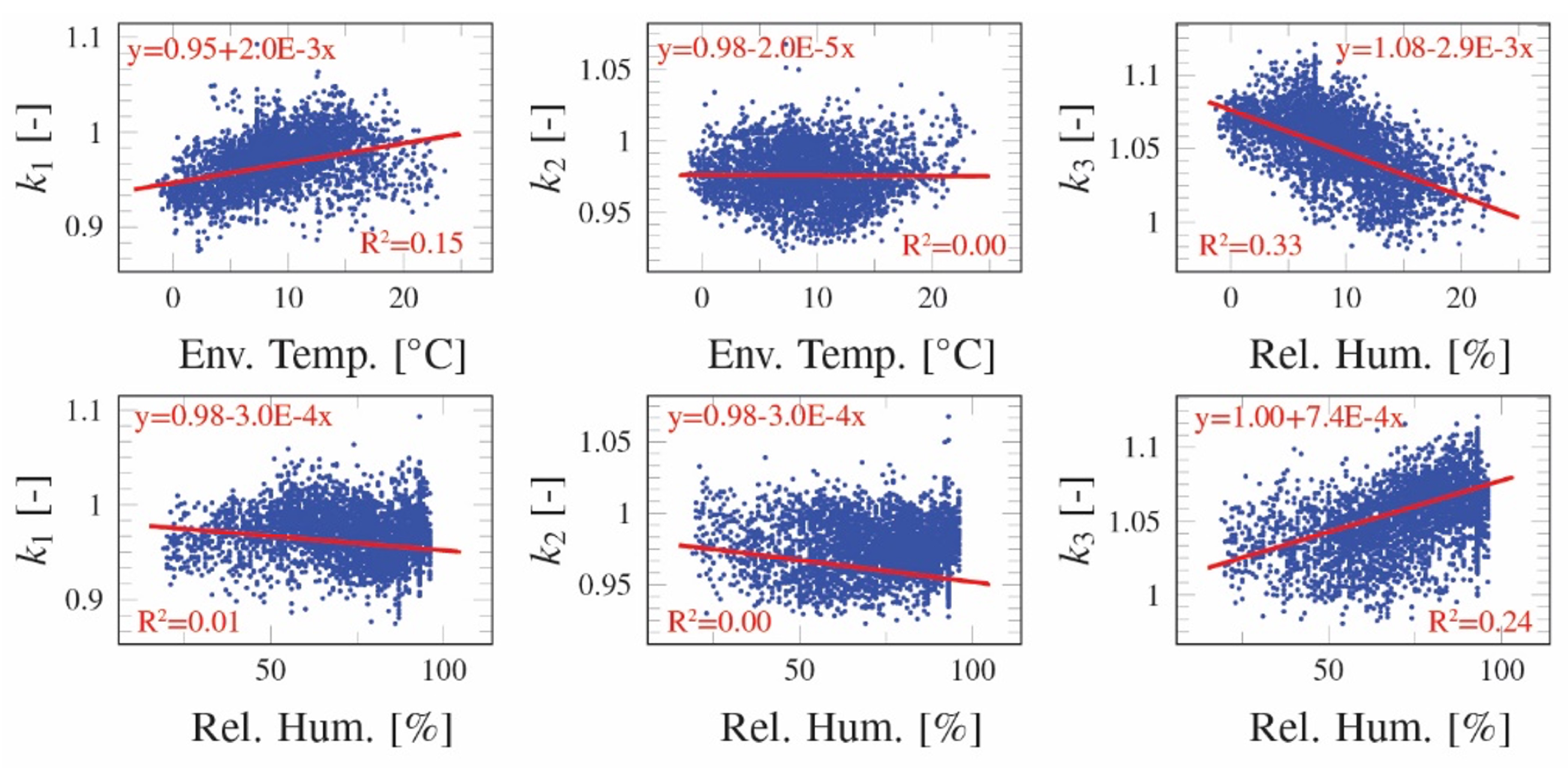
- Keshmiry, A.; Hassani, S.; Mousavi, M.; Dackermann, U. Effects of Environmental and Operational Conditions on Structural Health Monitoring and Non-Destructive Testing: A Systematic Review. Buildings 2023, 13, 918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, D.; Yi, T.; Zhang, G.; Han, J. Eliminating environmental and operational effects on structural modal frequency: A comprehensive review. Struct. Control. Health Monit. 2022, 29, e3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belytschko, T.; Black, T. Elastic crack growth in finite elements with minimal remeshing. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 1999, 45, 601–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curiel-Sosa, J.; Brighenti, R.; Serna Moreno, M.; Barbieri, E. Computational techniques for simulation of damage and failure in composite materials. In Structural Integrity and Durability of Advanced Composites; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 199–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Cheng, B.; Liao, J. Fundamental Concept and Formula of X-FEM. In Extended Finite Element Method; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 51–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López Osorio, J.M. Proyecto MURALH: Fábricas Históricas del Recinto Amurallado de la Alhambra. Technical Report, Patronato de la Alhambra y el Generalife; Universidad de Málaga: Malaga, Spain, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ministerio de Fomento (Spain). NCSE-02. Norma de Construcción Sismorresistente: Parte General y Edificación; Ministerio de Fomento: Madrid, Spain, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Justo, J.L.; Castro, D.; Azañón, J.M.; Saura, J.; Durand, P.; Romero, E.; Vázquez-Carretero, N.; Morales-Esteban, A.; Vázquez-Boza, M.; Justo, E. Environmental and mechanical aspects of an anchored mesh for stabilisation of a cliff at La Alhambra. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2014, 73, 667–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellazzi, G.; D’Altri, A.M.; de Miranda, S.; Ubertini, F. An innovative numerical modeling strategy for the structural analysis of historical monumental buildings. Eng. Struct. 2017, 132, 229–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordano, E.; Clementi, F.; Nespeca, A.; Lenci, S. Damage assessment by numerical modeling of Sant’Agostino’s Sanctuary in Offida during the Central Italy 2016–2017 seismic sequence. Front. Built Environ. 2019, 4, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, Q.B.; Bui, T.T.; Limam, A. Assessing the seismic performance of rammed earth walls by using discrete elements. Cogent. Eng. 2016, 3, 1200835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Nabouch, R.; Bui, Q.B.; Plé, O.; Perrotin, P. Assessing the in-plane seismic performance of rammed earth walls by using horizontal loading tests. Eng. Struct. 2017, 145, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riyono, W.A.; Vincens, E.; Plassiard, J.P. A hierarchical elasto-plastic constitutive model for rammed earth. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 160, 351–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN 1998-1; Eurocode 8: Design of Structures for Earthquake Resistance—Part 1: General Rules, Seismic Actions and Rules for Buildings. European Committee for Standardization (CEN): Milano, Italy, 2004.




| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Density | 2250 |
| Compressive strength | 2.45 MPa |
| Tensile strength | 0.30 MPa |
| Elastic modulus | 0.92 GPa |
| Poisson’s ratio | 0.30 |
| Mode | Frequency [Hz] | Damping Ratio [%] |
|---|---|---|
| 1 () | 4.44 (±4.07%) | 4.49 (±31.67%) |
| 2 () | 7.38 (±4.42%) | 4.39 (±47.46%) |
| 3 () | 9.95 (±6.19%) | 2.46 (±92.11%) |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Density | 2420 |
| Compressive strength | 2.45 MPa |
| Tensile strength | 0.30 MPa |
| Elastic modulus | 1.97 GPa |
| Poisson’s ratio | 0.30 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Puertas, E.; Ávila, F.; García-Macías, E.; Gallego, R. Preventive Preservation of Rammed Earth Historical Heritage Through Continuous Monitoring, Architectural Inspections, and Data Fusion. Buildings 2024, 14, 3294. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14103294
Puertas E, Ávila F, García-Macías E, Gallego R. Preventive Preservation of Rammed Earth Historical Heritage Through Continuous Monitoring, Architectural Inspections, and Data Fusion. Buildings. 2024; 14(10):3294. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14103294
Chicago/Turabian StylePuertas, Esther, Fernando Ávila, Enrique García-Macías, and Rafael Gallego. 2024. "Preventive Preservation of Rammed Earth Historical Heritage Through Continuous Monitoring, Architectural Inspections, and Data Fusion" Buildings 14, no. 10: 3294. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14103294
APA StylePuertas, E., Ávila, F., García-Macías, E., & Gallego, R. (2024). Preventive Preservation of Rammed Earth Historical Heritage Through Continuous Monitoring, Architectural Inspections, and Data Fusion. Buildings, 14(10), 3294. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14103294








