1. Introduction
Shape memory alloys (SMAs) are novel materials which can recover the original shape after being heated to a determined temperature. They are able to “remember” their previous shape, i.e., return to the shape in which they were before a certain deformation. That is why they are called shape memory alloys, and the phenomenon is called shape memory effect (SME) [
1].
The first SME was detected in gold–cadmium alloy in 1932, but the effect was not widely studied until 1971, when in Naval Ordnance Laboratories, USA, a nickel–titanium (mostly abbreviated as NiTi, but also Ni-Ti) alloy showed the possibility of considerable amounts of recoverable deformation. Since then, different alloy systems have been proposed as SMAs. Nevertheless, only NiTi, Cu-based and Fe-based SMAs have achieved a relevant commercial impact. Cu-based alloys include the Cu-Zn-Al and Cu-Al-Ni (also denoted as CuZnAl and CuAlNi) alloy systems [
2].
Several shape memory alloys have been extensively studied and are available in many now almost everyday life applications, such as eyeglass frames, orthodontic wires and coronary stents [
3]. These alloys are composed of nickel and titanium, which is why they have adequate biocompatibility as well. Besides medical applications, SMAs may nowadays be found in automotive applications, aeronautical applications and architecture [
4].
Smart materials such as SMAs may be used in civil engineering for health monitoring of civil infrastructures, assessment of damage or integrity, structural control, maintenance and repair. Bedsides improving the reliability and durability, potential benefits include increased safety towards vibrations and natural hazards, such as earthquakes, wind blows, ocean waves, etc. Nowadays, the concept of self-sensing concrete is studied in the fields of smart concrete for self-healing, self-adjusting and self-heating. The stress or strain detection in concrete is studied by integrating concrete with optical fibers, piezoelectric ceramics and electrical resistance strain gauges. Carbon fiber-reinforced polymer composites have been studied as well, since they have very good electrical conductivity. SMAs may be used for monitoring deformations and estimation of cracks [
5].
Since the 1990s, an increasing number of studies of application of SMAs as novel materials for seismic protection have been concluded. Currently, the construction industry is not commonly using SMAs because of the information gap between material science and practical civil engineering. Some of the recent successful applications of NiTi SMAs as seismic energy dissipaters include, for example, the retrofitting of the bell tower of the St. Giorgio Martire church in Trignano, RE, Italy, whose 18.5 m high tower was significantly damaged in the 1996 earthquake of 4.8 Richter magnitude. After retrofitting with SMA energy-dissipation devices, the bell tower successfully endured the next 4.5 Richter magnitude earthquake in 2000. Following this success, several other churches in Italy, as well as bridges in seismic-active areas of the USA, have been retrofitted in the same way [
6].
Recent studies of possible application of nickel–titanium (NiTi) SMAs instead of steel to reinforce novel bridge columns offers long-term column durability and excellent seismic resistance [
7]. One of the more economic SMAs which could be used instead of NiTi are Cu-Zn-Al SMAs, nowadays commercially available. For example, vibration damping of the steel frame engineering structures with Cu-Zn-Al SMA damping elements installed can be significantly reduced, up to 10 times, for both austenitic or martensitic structures [
8]. SMAs improve the ability of concrete columns to withstand strong seismic excitations when used for confining concrete cylinders [
9]. For the dissipation of earthquake energy, adequate curvature ductility is needed in critical areas of the construction where inelastic flexural deformations arise, so hysteretic behavior is necessary [
10]. For preventing the collapse from strong earthquakes, buildings and bridge columns have to be designed with as high ductility as possible. Adequate transverse reinforcement of the plastic hinge regions in columns made from reinforced concrete may be provided either by hoops or spirals of a ductile material, typically steel, in order to avoid shear failure of the column [
11]. Plastic hinges of reinforced concrete elements made out of hybrid SMA/steel have excellent effects against permanent deformation of the building after a seismic event, the so-called residual drift. Studies have shown that coupling of SMA with fiber-reinforced composite instead of steel additionally improves corrosion resistance [
12]. Corrosion of the SMA itself may also occur, thus possibly lowering the shape memory effect. Chemical corrosion of the copper-based shape memory alloys is only recently being studied, for example, in solutions which simulate the marine environment, acid rain in the urban environment and acid rain in the industrial environment, where the shape memory effect was maintained, although corrosion products were made part of the porous corrosion layer [
13].
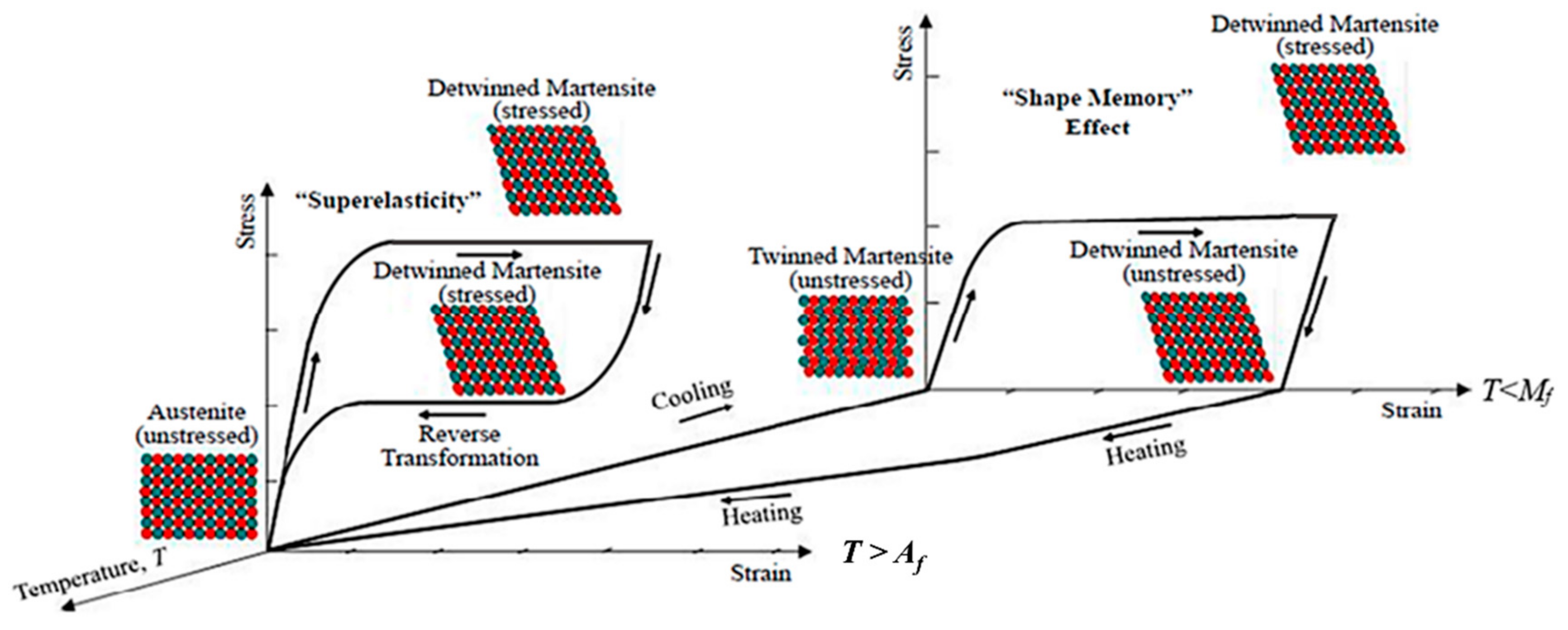
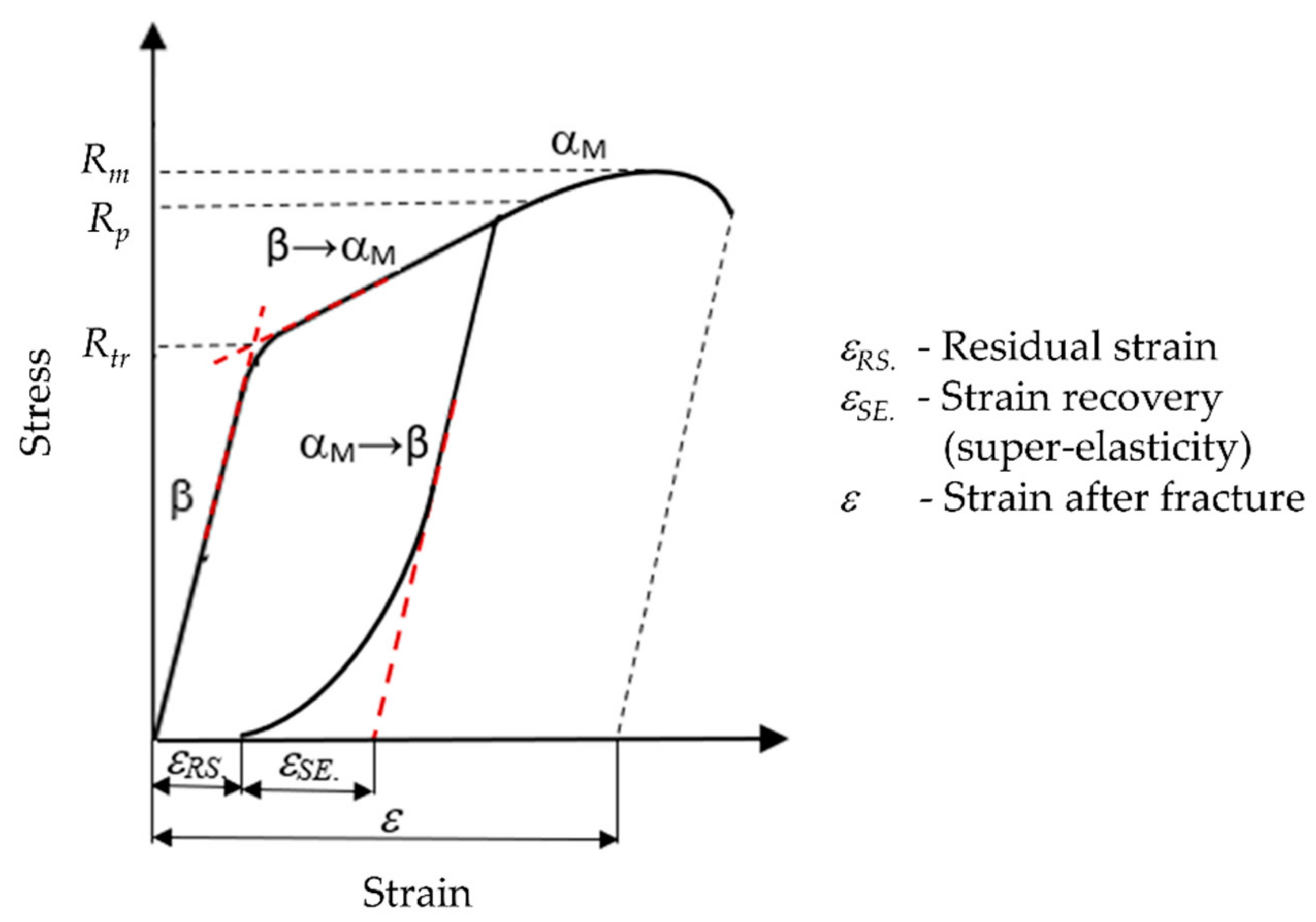
The specific behavior of SMA’s recovery to the original shape by heating or unloading is based on the presence of a reversible crystallographic austenite–martensite transformation. In general, there are two variants of martensite phase in alloys: twinned and detwinned martensite. Twinned or thermal martensite is formed when the alloy starts to cool below the temperature at which the martensitic transformation starts, i.e., below martensite start temperature (
Ms), without any stress applied to the material. This martensite is called twinned because of twin domains in one martensite grain, which have the same crystallographic characteristics, except for the local orientation. On the other hand, there is the variant of the detwinned or stress martensite: this martensite is formed when stress, either tensile or compressive, is present. In the detwinned martensite, all domains are aligned according to the direction of the applied stress. The term detwinning originates from the crystallographic reorientation, which happens in the grain, leaving it without any twin variants. The applied stress has to be above a defined level for this phenomenon to occur, while the alloy shows an exemplary large deformation, which looks like typical plastic deformation observed in alloys in general [
14].
The initial structure of shape memory alloys is the high-temperature austenite phase, usually denoted as beta (β), which transforms into the low-temperature martensitic phase, typically marked with alpha (α
M) [
1,
15,
16]. β and α
M represent two different crystal structures, i.e., solid phase constituents of the Cu-Zn-Al alloy. β-phase is thermodynamically stable (i.e., will not change over a long period of time) at high temperatures, while α
M is stable at low temperatures. Both are solid solutions, where β has the body-centered cubic (BCC) unit cell or lattice and α
M has the cubic close packing (CCP) unit. During this transformation, the diffusion rate is negligible, as well as the atomic mobility, because the transformation takes place at relatively low temperatures. In the course of transformation, atoms move simultaneously and there is not any individual atom movement present. Rather, atoms are redistributed by a homogeneous shear, which occurs at levels lower than the parameter of the unit cell. This phenomenon is observed by a change in shape and dimensions of shape memory alloys, and is commonly known as the super elasticity (SE) or the shape memory effect (SME) [
17,
18,
19]. The super elasticity effect may be induced by applying external mechanical stress, either with a temperature change or without it. In SE, the material returns to its previous shape after the load that has induced a large deformation is removed. On the other hand, the shape memory effect is connected to reversing to the original shape by applying heat,
Figure 1 [
20,
21,
22,
23].
SMAs manifest the shape memory effect below the martensite finish temperature (
Mf),
Figure 1, where the alloys consist of the martensitic phase. The martensite is able to take in a lot of plastic deformation at low and highlighted stress plateau, which is a result of the stress-induced phase transformation from twinned to detwinned martensite. The induced deformation remains after the stress is removed. Residual strain starts to disappear when the SMAs are reheated. This shape recovery process is initialized by heating the SMAs above the austenite finish temperature (
Af). During heating, the detwinned martensitic phase changes back into the initial austenitic phase, i.e., it is a thermally induced reversible transformation. The twinned martensitic phase is reinstalled after cooling, by which the whole phase transformation cycle is completed, thanks to the shape memory effect [
24].
The other phenomenon characteristic for SMAs is super elasticity, which appears at a temperature greater than the austenite finish temperature (
Af). Super elasticity is marked by the typical flag-shaped loop of hysteresis in the stress–strain diagram,
Figure 1. Similar to the shape memory effect, the stress induces a considerable amount of reversible deformation by phase transformation, but now it is the transformation from austenite into detwinned martensite that occurs.
The austenitic phase of a SMA is able to fully recover to the original shape without any residual deformation. As indicated in
Figure 1, austenitic SMAs have higher values of stress for the slip plateau than the martensitic SMAs.
The properties of SMAs are influenced by various factors, such as the temperature, chemical composition, crystal structure (polycrystal or monocrystal) and orientation, grain size, the presence of precipitate phase, heat treatment, etc. Sun et al. studied the super elasticity and the shape memory effect of polycrystalline SMAs and noticed that the thermomechanical response of SMAs shows a distinct grain size effect [
25]. The polycrystal SMAs with smaller grain size shows lower capacity for shape memory and a narrower temperature interval for hysteresis, as well as higher hardening response for super elasticity. They also found that the crystal orientation has a clear influence on the stress-induced martensite transformation. Chen and Schuh studied the size of the super-elastic effect in CuAlNi microwires with a bamboo grain structure by conducting the tensile test and thermal cycling. The stress and temperature hysteresis were found to increase with the decrease in grain size [
26]. Using the molecular dynamics method for the simulation of a single crystal NiTi alloy, thermomechanical response in adiabatic conditions, it was calculated that there is a significant temperature change of the SMA during both martensite and reverse transformation processes. For example, when the strain increased to 8%, the calculated temperature increased by 41.75 °C [
27]. Similarly, the molecular dynamics method was used to reveal in detail the evolution of the microstructure of different NiTi compositions of SMAs. Several microstructural features obtained by simulation confirmed good agreement with literature reports and even new microstructural features were discovered [
28].
Several alloying systems show the shape memory and super-elastic effects. For example, copper-based shape memory alloys were studied a lot over time [
29]. Cu-based SMAs, such as Cu-Al, Cu-Al-Mn, Cu-Al-Ni and Cu-Zn-Al, have attracted a lot of scientific attention thanks to their satisfactory shape memory capacity. Compared to NiTi-based SMAs, Cu-based SMAs have a more limited transformation temperature interval, but are more easily produced, and hence have lower costs. On the other hand, polycrystalline copper-based SMAs are less tough, i.e., more brittle, which makes them harder to work than NiTi alloys. The brittleness comes as a result of a larger degree of order of the native austenitic β-phase, as well as a consequence of the elevated elastic anisotropy of the β-phase [
30]. Copper-based SMAs are typically used for sensors and actuators, since they possess good mechanical properties at a comparably low price compared to NiTi SMAs [
31,
32]. Although NiTi SMAs possess higher super elasticity, better shape memory effect, higher tensile strength and better corrosion resistance than other SMAs, their main disadvantage is high cost. High costs arise from energy-intensive smelting of the alloying elements (primarily nickel and titanium) and a complex melting process which requires either vacuum melting or melting under an inert atmosphere. Therefore, where biocompatibility is not a primary requirement, the use of copper-based SMAs is preferred.
Copper-based SMAs may be heat-treated in order to modify yield and tensile strength and hardness, as specified by a distinct application. The desired properties are met through a change in microstructure or by introducing lattice defects to the crystal structure. The transformation interface propagation and the nucleation process may be altered using vacancies, dislocations, grain boundaries, solute chemical elements or precipitated particles [
33,
34]. For NiTi SMAs fabricated from powders by Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS), subsequent heat treatment at temperatures from 600 to 700 °C with slow cooling was found to be necessary to obtain good ductility [
35].
The City of Zagreb, which is the Capital of Croatia, was hardly struck by the 5.5 Richter magnitude earthquake in March 2020. Currently, there is a need of an extensive retrofitting of several infrastructural facilities, as well as cultural and historic objects of national value. Although NiTi SMAs have been successfully applied in recent years in more developed countries for retrofitting of valuable civic building, their cost is very high. Research conducted by Si et al. indicated the possibility of using cheaper damping elements made of heat-treated (homogenized and quenched) Cu-Zn-Al SMAs with monophase austenitic or martensitic structure and super-elastic capacity around of 2% [
8]. Therefore, the presented research is focused on using the thermomechanical treatment, which includes hot rolling at the homogenization temperature, for improving the properties (primarily, the super elasticity) of the Cu-Zn-Al SMA. This has already been proved successful on the example of the NiTi alloy, where Hornbogen et al., in their study, found that defects introduced by ausforming were related to strengthening of the austenite, super-elastic capability and the consequent shift to lower temperatures of the transformation cycle [
36].
The primary objective of this study is to determine the influence of the ausforming processing on the SMA’s microstructure, phase transformation temperatures, static mechanical properties and the recovery of deformation by the super elasticity effect. Thus, this study aims at improving the specific properties of copper-based SMAs by studying the capabilities and constraints of the ausforming processing.
2. Materials and Methods
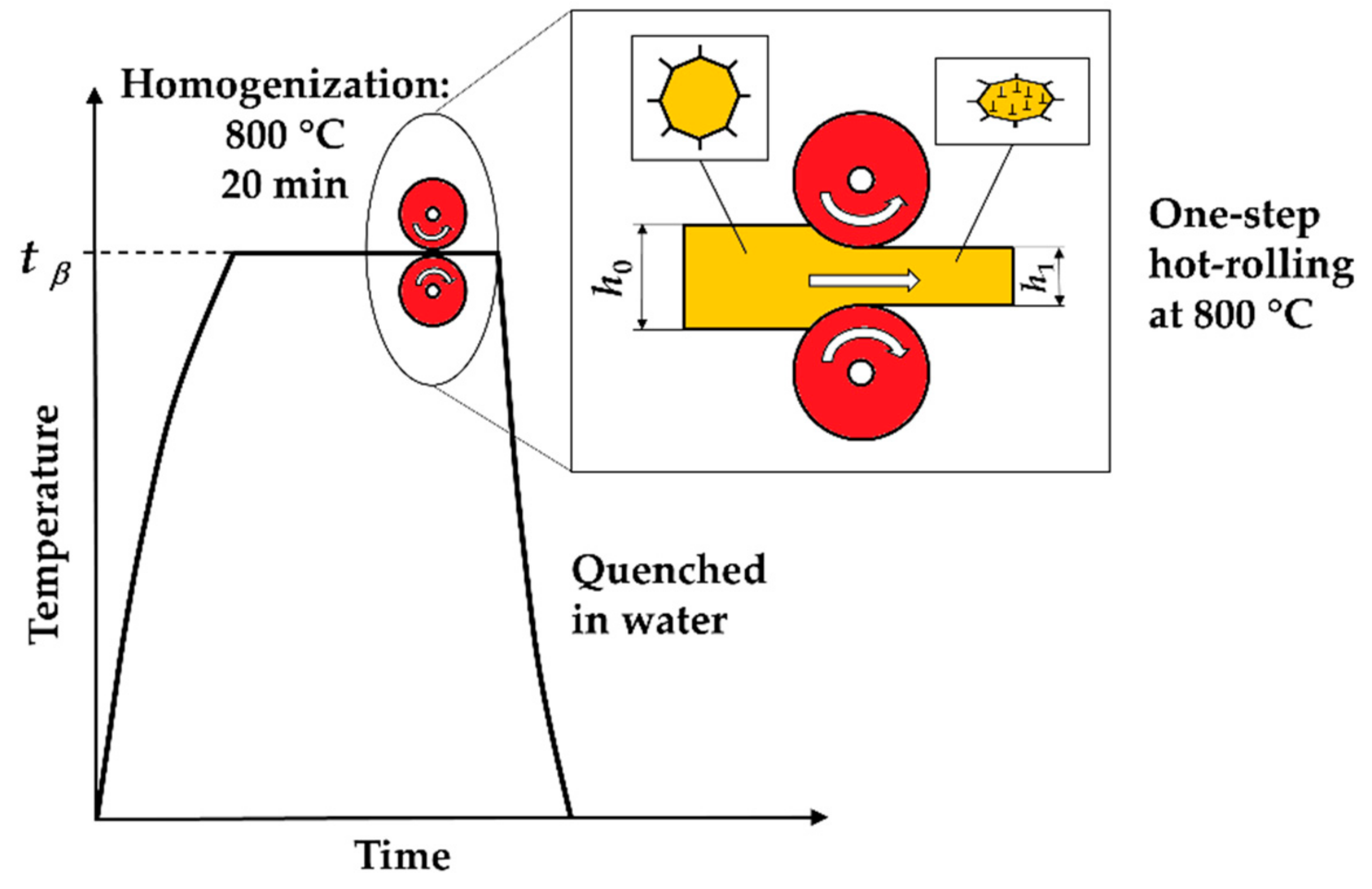
The ternary Cu-Zn-Al shape memory alloy with chemical composition of Cu-26.38%Zn-3.72%Al (hereinafter Cu-26Zn-4Al) was prepared using high-purity copper (99.999 wt.%), zinc (99.99 wt.%) and aluminum (99.99 wt.%) by induction-melting furnace with argon atmosphere at Wieland-Werke A.G., Ulm, Germany, specialized in Cu-Zn-Al shape memory alloys. The studied alloy was cast into cylindrical bars of 50 mm diameter and the bars were cut in four pieces each of 18 mm thickness. Samples were cut in small pieces suitable for thermomechanical treatment. The ausforming heat treatment process, as described in [
37], included β-phase homogenization, i.e., heating of the prepared alloy to form a β-phase homogeneous solid solution, at 800 °C for 20 min, followed by a one-step hot rolling process at 800 °C and finally quenching using water at room temperature,
Figure 2.
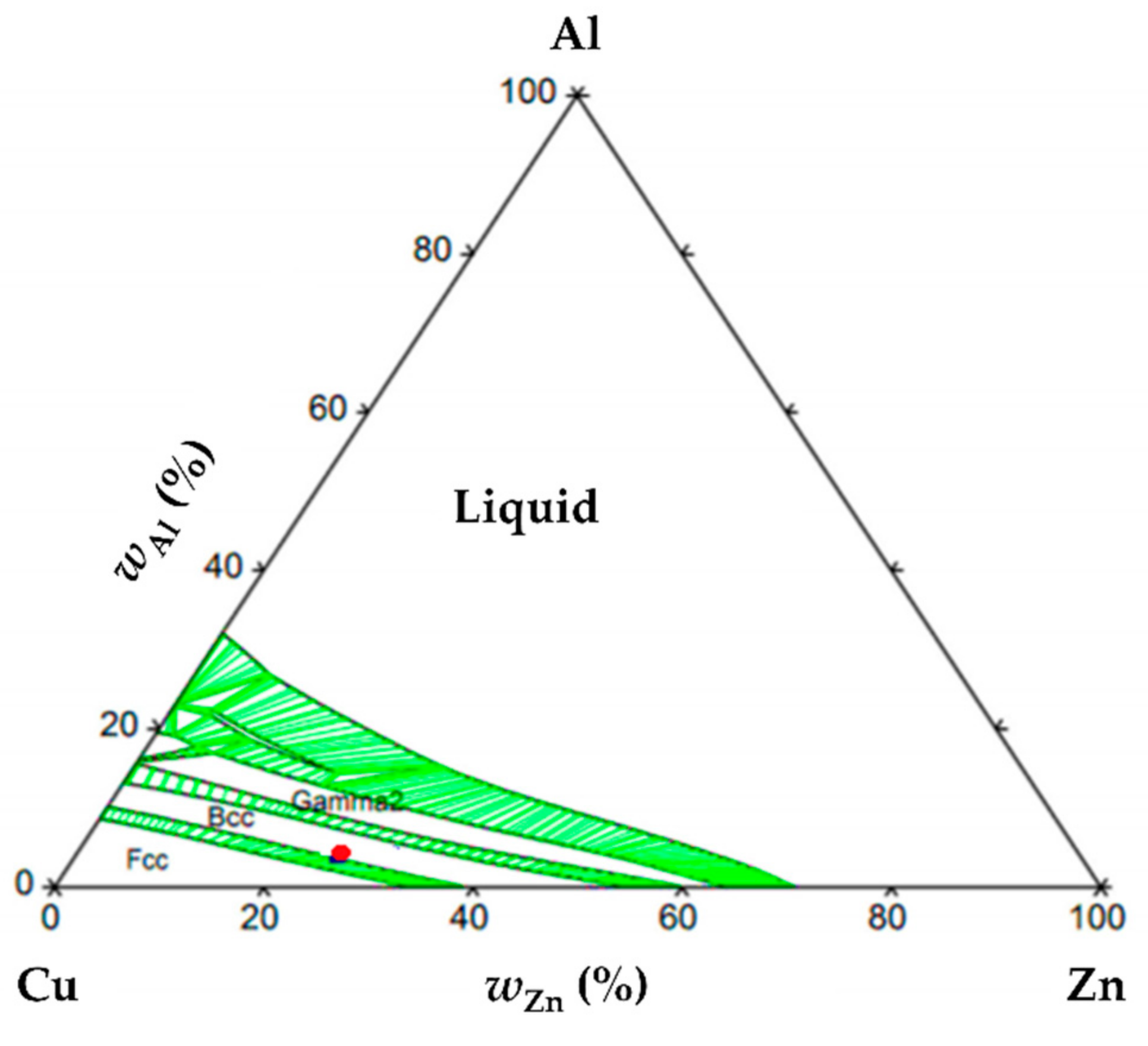
The β-phase in Cu-Zn-Al alloys is disordered at high temperatures and has a body-centered cubic (BCC) lattice [
38]. According to
Figure 3, it can be seen that the composition of the investigated alloy is situated in the monophase region, with only the BCC lattice (β-phase) being present at 800 °C, as indicated by the red dot. It may be noticed as well that the studied composition is also quite proximate to the dual phase, i.e., α
Cu + β area, where α
Cu (or simply α) is the solid solution of copper with zinc and aluminum, hence having the face-centered cubic lattice (FCC).
After the homogenization, the Cu-26Zn-4Al alloy was plastically deformed at 800 °C with various values of true plastic strain or true plastic deformation (
φg):
where
h0 is the plate thickness before hot rolling and
h1 represents the thickness after the rolling,
Figure 2. True strain (
φg) is sometimes called logarithmic strain, Equation (1). Strain is a dimensionless quantity and is often expressed as a percentage, which will be used in this paper. Sometimes the derived unit mm/mm may be used as well. Out of four prepared samples, one was not deformed, while the other three samples were hot rolled to true plastic strain of 20%, 98% and 151%. After hot rolling, the samples were quenched in water in order to retain the β-phase and to remove segregations [
39,
40,
41]. Moreover, the recrystallization and the recovery of structure were disabled by quenching. Quenching therefore restrained the removal of the lattice defects induced by hot deformation.
Samples used for optical microscopy were prepared using the standard metallographic procedures of grinding and polishing. After polishing, the samples were also electrochemically etched for 30 s in a solution containing 125 mL distilled water, 70 mL phosphoric acid, 70 mL ethanol, 12 mL propanol, 1.2 g urea and 0.5 mL dye. The applied voltage was 6 V and the current was 80 mA. Microstructure investigation of the prepared samples was carried out on the inverted metallurgical microscope type GX51F-5 (Olympus Corporation, Tokyo, Japan) with the integrated digital camera DP25.
The transformation temperatures were recorded by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) using the DSC823e measuring module (Mettler Toledo International Inc., Greifensee, Switzerland). The DSC was performed five days after the ausforming process using the samples of approximately 60 mg, in the temperature range from 100 °C to −120 °C and using 5 °C/min cooling and heating rates. The typical martensitic and austenitic transformation temperatures were recorded: martensite start (Ms), martensite finish (Mf), austenite start (As) and austenite finish (Af). The highest rate of martensitic and austenitic reaction can be detected in the DSC thermogram as they are marked by highest thermal flow peaks during cooling (Mm) and heating (Am). The values of typical transformation temperatures (i.e., Ms, Mf, As and Af) were detected from the DSC thermogram using the baseline tangents and the peak curve tangents.
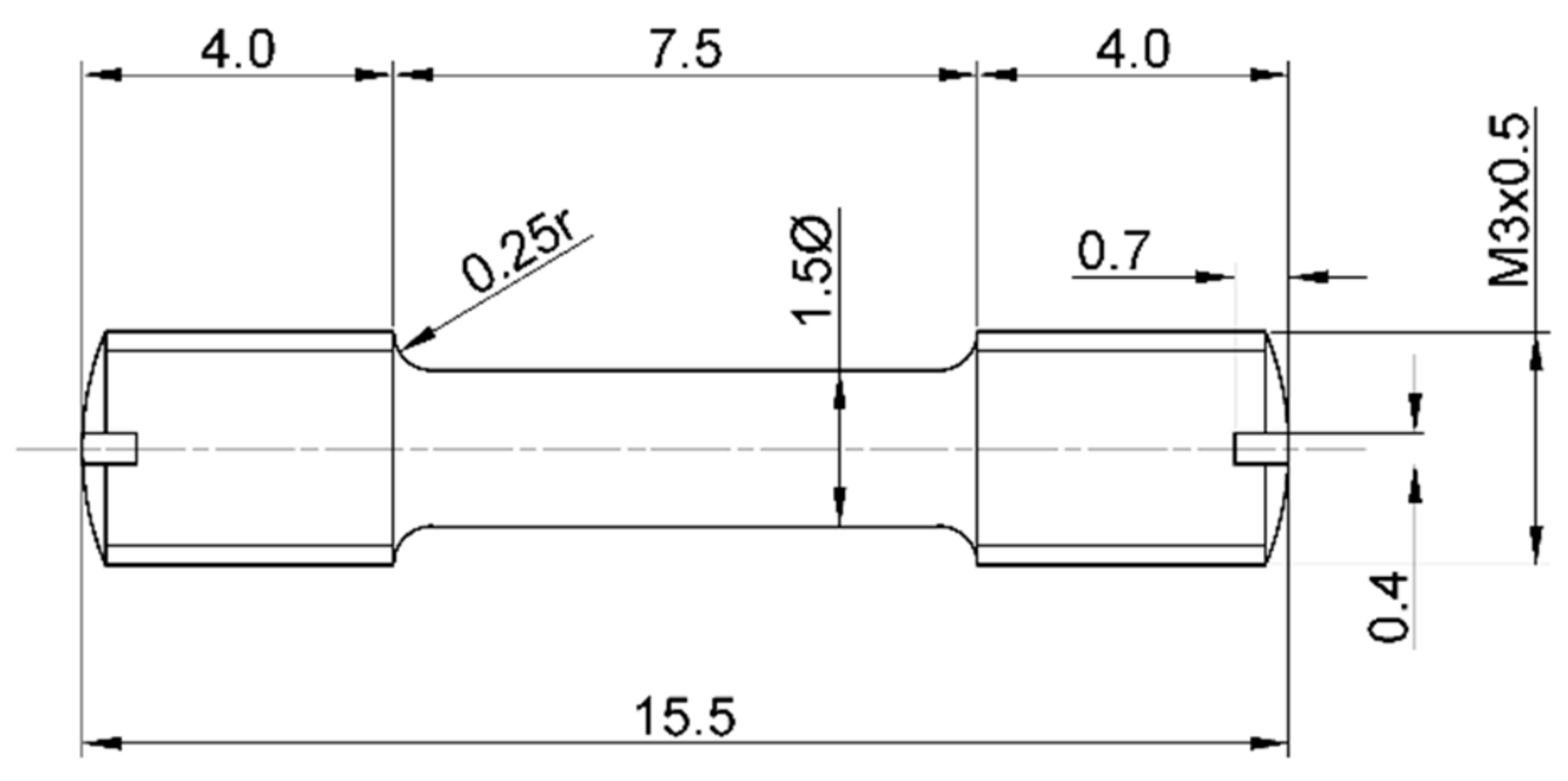
Tensile tests and super elasticity measurements were carried out using the Mi 34 microtesting machine (Alfred J. Amsler & Co., Schaffhausen, Switzerland) at room temperature. The crosshead separation rate was set to 0.005 mm/s, i.e., 0.3 mm/min. All tensile test samples were oriented in the rolling direction. The shape and the dimensions of the microtesting sample are presented in
Figure 4. Tensile tests and super elasticity measurements were performed on five samples for each thermomechanically treated state.
Recorded mechanical properties of the studied Cu-26Zn-4Al SMA in conditions of tensile load were as follows: Transformation stress (
Rtr), true yield strength (
Rp) and tensile strength (
Rm),
Figure 5. Mechanically induced austenite to martensite transformation occurred at the transformation stress (
Rtr) and at the corresponding super-elastic strain (
εSE.).
After the austenite was transformed into martensite, the martensite was deformed elastically in the beginning and then plastically only after the stress reached the value marked as
Rp,
Figure 5. When testing the super elasticity, the specimen began to unload before fracture, at the end of the strain range characteristic for the β → α
M transformation [
42].
3. Results
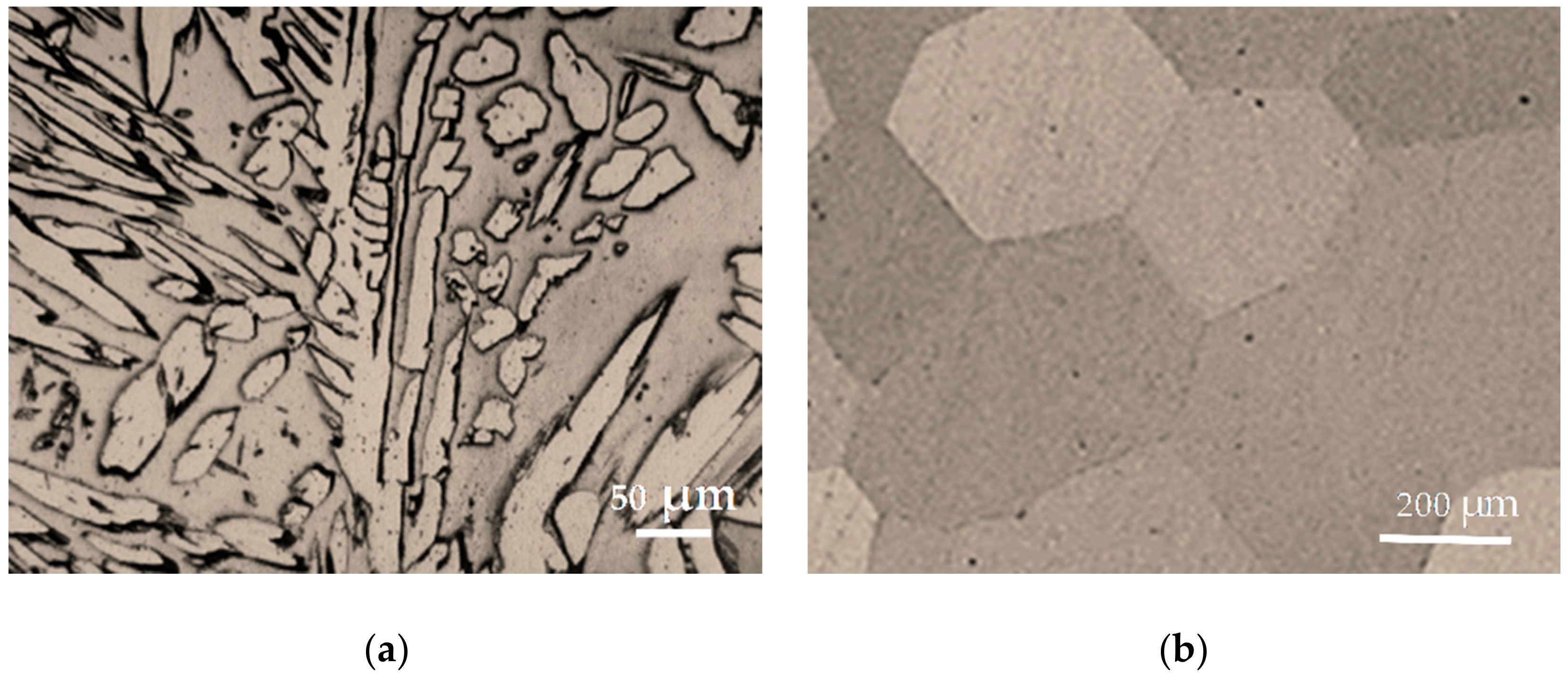
Based on the results of the optical microscopy testing, it was determined that the as-cast Cu-26Zn-4Al shape memory alloy has a dual phase microstructure, i.e., α + β,
Figure 6a. The microstructure of the as-cast state includes dendritic α-particles with FCC lattice, which are irregularly distributed in the β-phase matrix.
Sample that was homogenized and quenched with room temperature water and that had not been hot rolled had a single phase austenite microstructure, as shown in
Figure 6b. Based on the microscopic observations, it may be deduced that for the Cu-26Zn-4Al alloy, the martensite start temperature lies below room temperature.
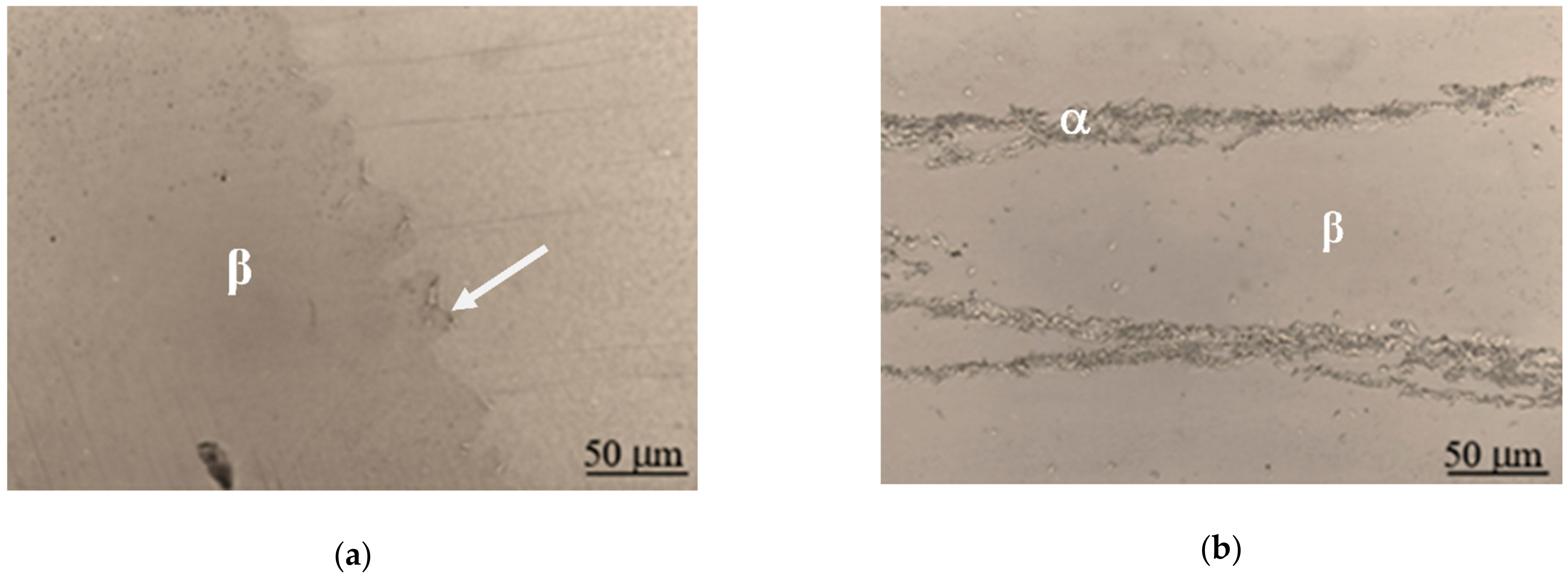
A low level of true plastic strain introduced by the hot rolling process has produced the curling of the austenite grain boundaries, which is marked by a white arrow in
Figure 7a. The microstructure of the plastically deformed sample (
φg = 20%), besides the austenite phase, also presents very fine precipitates of the α-phase, which are located at the austenite grain boundaries. Larger plastic strain (
φg = 98%) has resulted with changes in the crystal shape,
Figure 7b,c. Effects of the recrystallization and the grain growth ware not observed. A greater amount of strain (
φg = 151%) originates even more nucleation of the α-phase at the grain boundaries of the β-phase, as well as within the austenite (β-phase) grains,
Figure 7b,c.
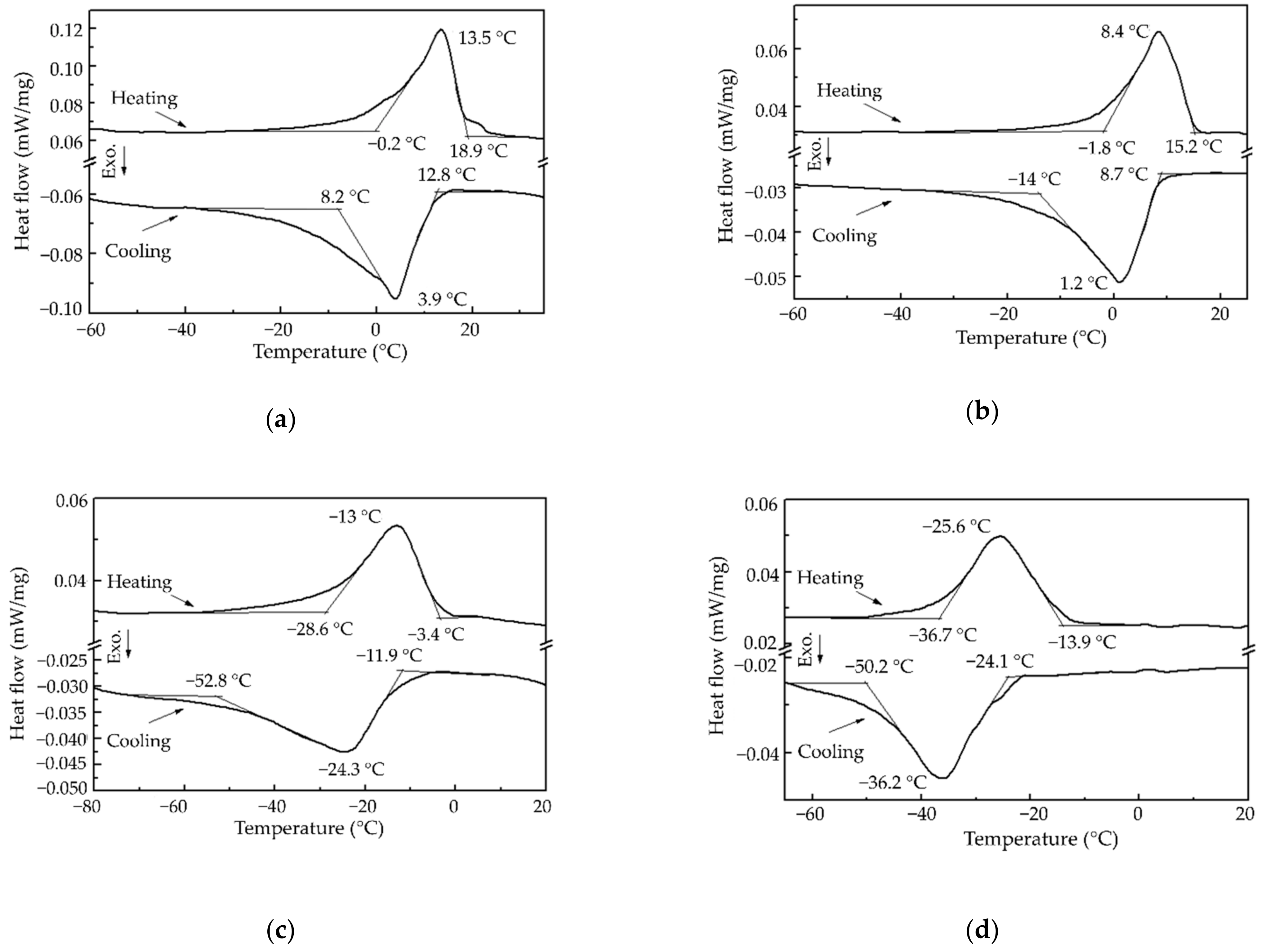
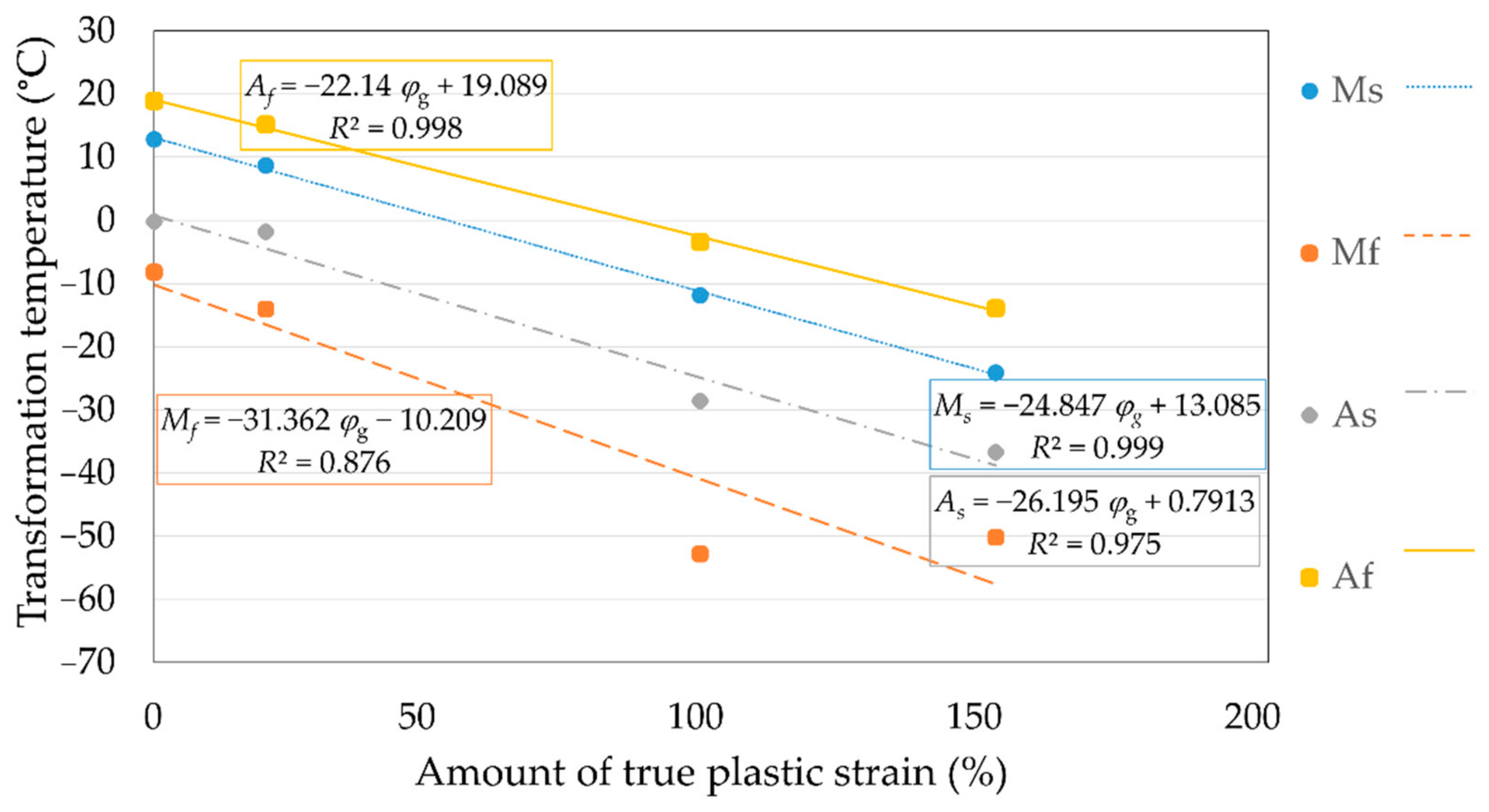
Figure 8 shows the differential scanning calorimetry curves of heat flow for the Cu-26Zn-4Al alloy treated by the ausforming process to different plastic strains.
Peaks of the heat flow of the martensitic and austenitic transformation can be clearly detected in
Figure 8, both for cooling and heating. Based on the position of transformation peaks, the values of characteristic temperatures were determined and are presented in
Table 1.
When there is enough driving force for the diffusionless formation of αM-crystals, the martensitic transformation starts and the set temperature is Ms. The martensitic transformation is an exothermic process. Therefore, in order not to interrupt the transformation process, the material must be cooled continuously through the martensitic transformation process. To achieve the complete transformation of martensite, the material must be cooled below the martensite finish temperature, Mf.
Conversely, the austenite transformation, which starts at the austenite start temperature (As), is an endothermic process. This means that it is needed to constantly heat up the material during the austenite transformation, in order not to interrupt this transformation process. When the material reaches a temperature higher than austenite finish (Af), the whole of austenite transformation is completed.
It was observed that the austenitic transformation occurs within a narrower temperature interval in comparison to the martensitic transformation at all amounts of true plastic strain.
Both martensitic and austenitic transformation processes moved to lower temperature ranges when the true plastic strain of the alloy was increased. As shown in
Table 1, all transformation temperatures were below room temperature, which satisfies the conditions for the super-elastic effect. The effect of the amount of true plastic strain on the Cu-26Zn-4Al shape memory alloy’s transformation temperatures,
Ms and
Mf, as well as
As and
Af, is shown in
Figure 9. Equations in rectangles in
Figure 9 represent linear regression equations between each transformation temperature and true plastic strain (
φg).
The data presented in
Figure 9 confirm that the Cu-26Zn-4Al shape memory alloy is completely transformable for every studied amount of true plastic strain by the ausforming process. It may be deduced that both phase transformations, austenitic and martensitic reactions, start and finish at ever lower temperatures; the higher the strain, the lower the transformation temperatures. The highest influence of the amount of plastic strain on the change in phase transformation temperatures was observed for the
Mf temperature (Δ 42 °C). The other phase transformation temperature changes were as follows: Δ
Ms = 36.9 °C, Δ
Af = 32.8 °C and Δ
As = 36.5 °C.
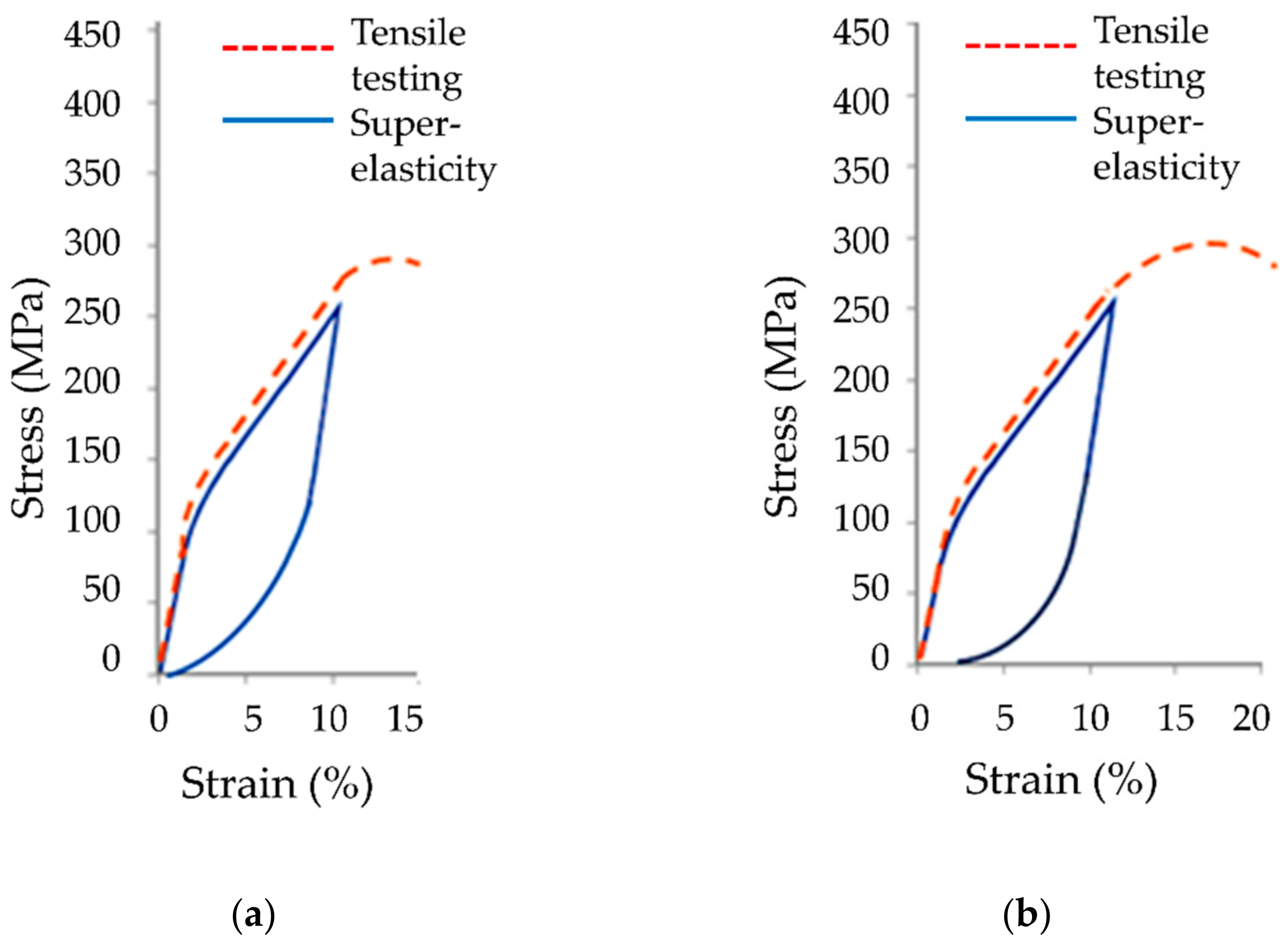
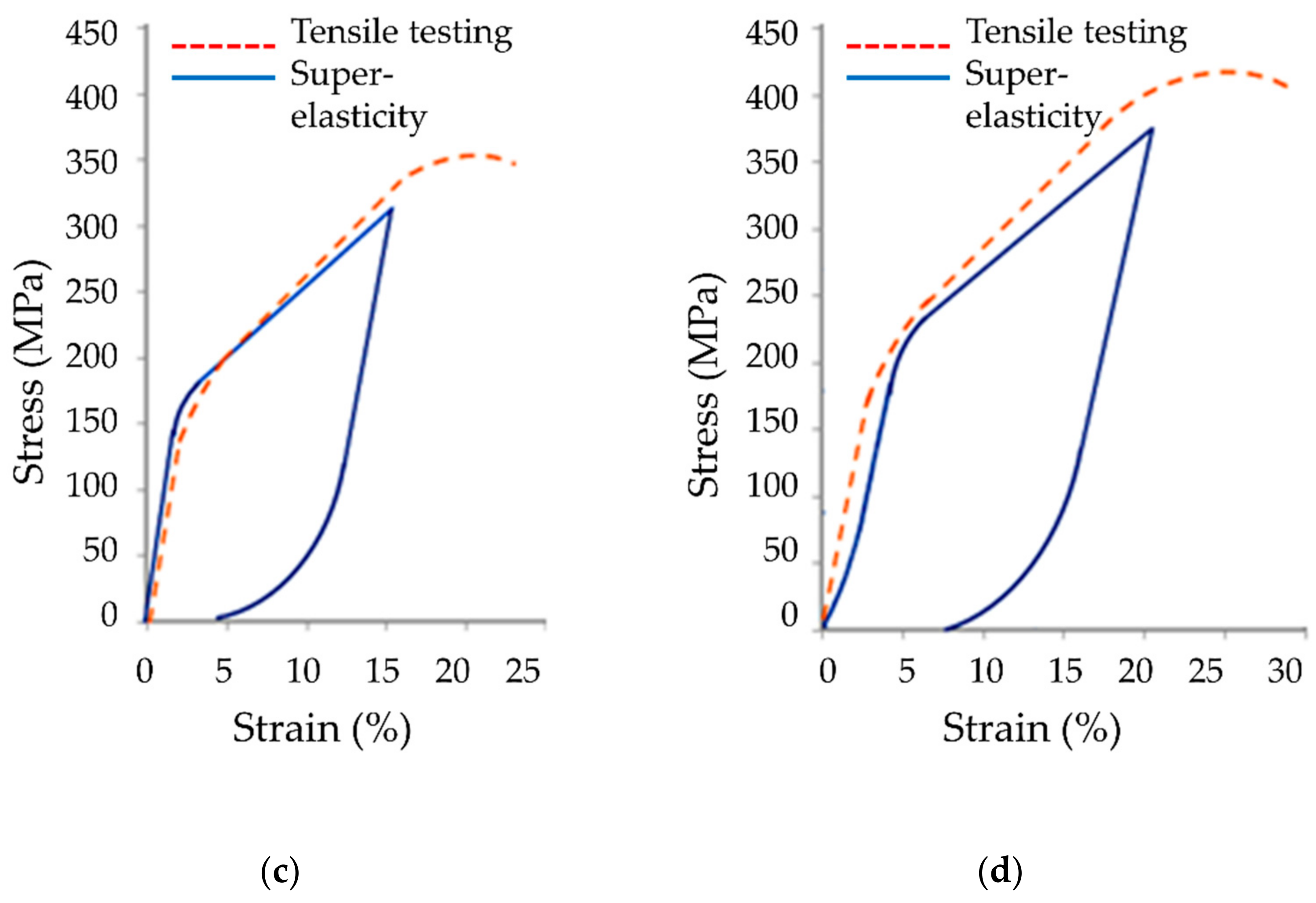
The typical tensile stress–strain curves of the Cu-26Zn-4Al shape memory alloy treated by ausforming are presented with the red dashed line in
Figure 10. Super-elastic behavior is clearly visible on all charts, presented with the blue line. All presented diagrams showing the super-elastic behavior were recorded during the first mechanical loading cycle.
The strain recovery of Cu-26Zn-4Al shape memory alloy by the super-elastic effect is evident from
Figure 10. Nevertheless, a low plastic strain was also recorded, i.e., residual strain (
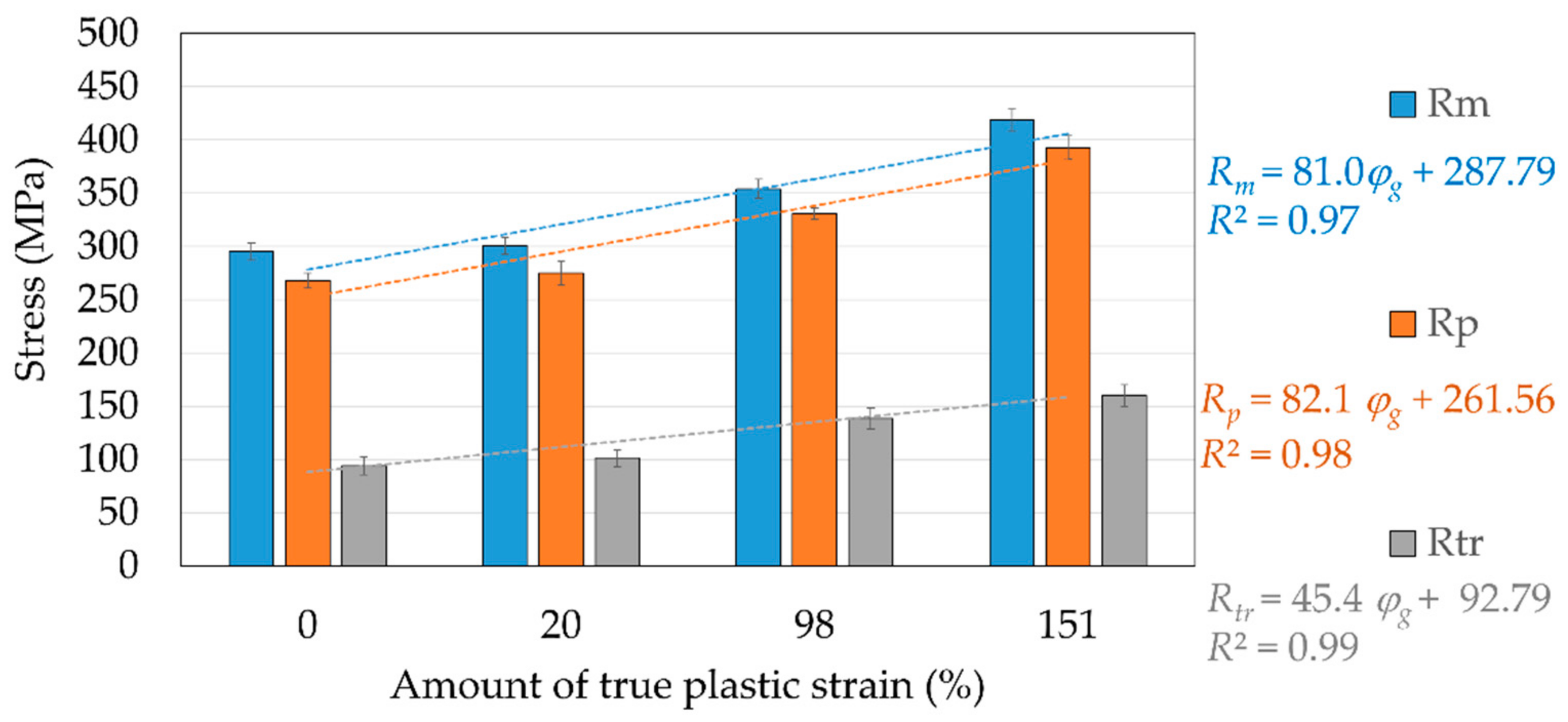
εRS.), showing the presence of the stress-induced martensite, which is stable after removing the load. Mean values of the tensile testing results in terms of characteristic values: transformation stress (
Rtr), true yield strength (
Rp) and tensile strength (
Rm), percentage elongation after fracture (
ε), strain recovery (
εSE.) and residual strain (
εRS.) are presented in
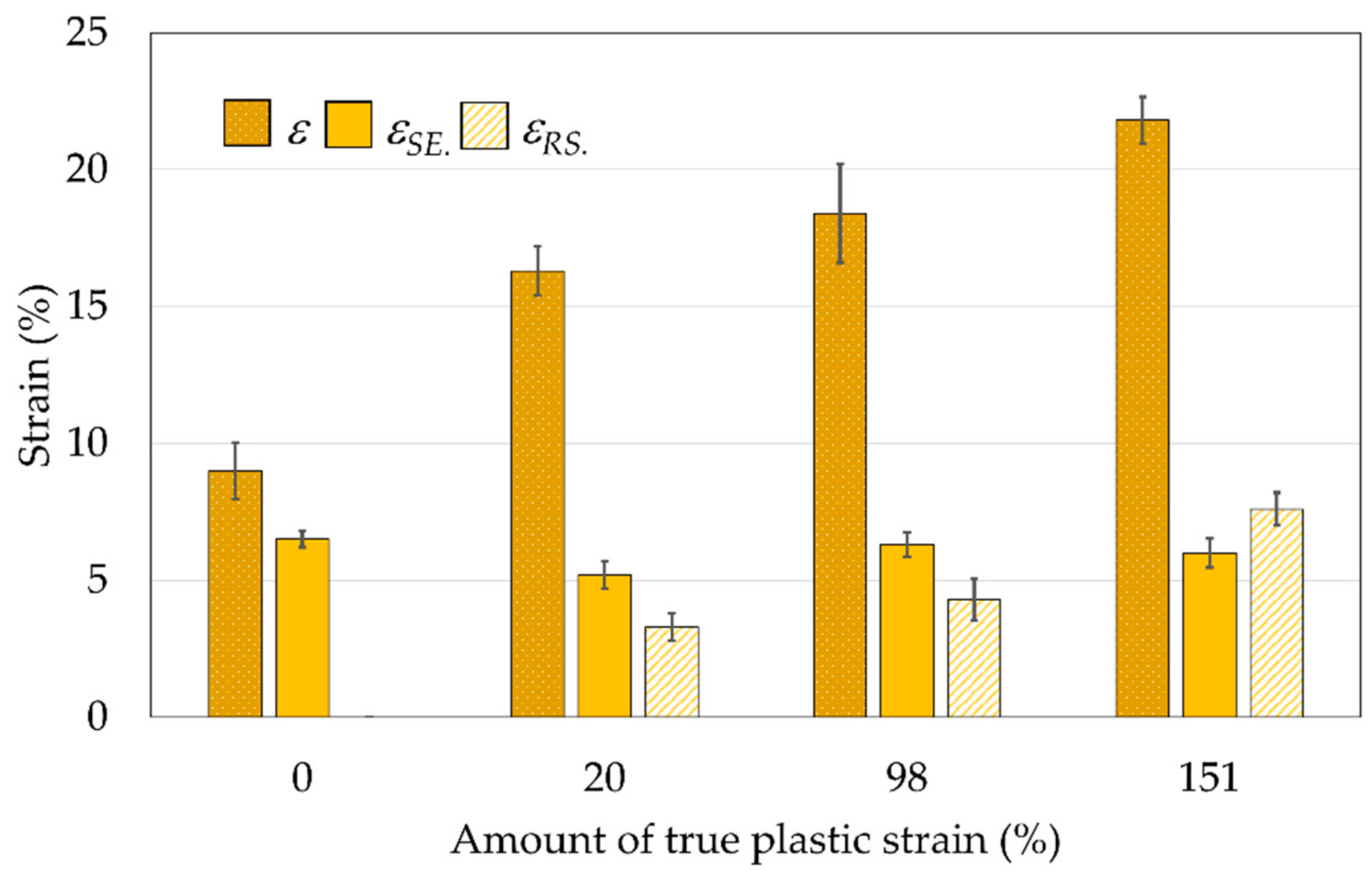
Figure 11 and
Figure 12, along with the appropriate standard deviation bars (error bars).
4. Discussion
The transformation behavior of Cu-26Zn-4Al shape memory alloy is based on the reversible austenitic–martensitic transformation. After the austenitization process, i.e., homogenization in the austenite temperature range, the shape memory alloy is quenched in the aim of retaining the austenite (β-phase) at room temperature. Additionally, hot rolling may also be applied at the homogenization temperature to the austenitic microstructure. Hot rolling prolongs the β-crystals, and also promotes the deformation of grain boundaries. Furthermore, hot rolling intensifies the precipitation of α-phase at the β-phase grain boundaries as well as within the β-phase crystal grains. Moreover, hot rolling significantly increases the dislocation density in the β-phase.
DSC testing provided evidence of cooling-induced martensitic (αM) reaction and reverse austenitic transformation induced by heating. The reversible β ↔ αM phase transformation was detected in all ausforming-treated samples, despite the induced plastic deformation. As the amount of true plastic strain increased, all martensitic and austenitic transformation temperatures decreased to lower temperature ranges.
The observed relation between true plastic strain (φg) and Ms and other transformation temperatures is approximately linear. Martensite reaction temperature (Mm) without plastic deformation was 3.9 °C, while at a strain of φg = 151% it decreased to −36.2 °C; for the same true strains, austenite reaction temperature (Am) decreased from 13.5 °C to −25.6 °C. The lowering of the transformation temperatures is a consequence of the increased defect density in β-crystals and precipitated α-grains. The α-phase has an adverse influence on the motion of the β/αM transformation interface, thus making its mobility difficult. When all transformation temperatures were compared, it was observed that the Mf temperature decreases slightly more quickly, which can be ascribed to difficult forming of the final martensite portions in narrow corners of the deformed crystals.
Thermally induced reversible β ↔ αM transformation is characterized by the existence of the transformation hysteresis. Austenitic transformation during heating will not start immediately above the Mf temperature, but a certain driving force in the form of heating, i.e., supplied heat, is necessary in order to start the process. A similar phenomenon is also found in the martensitic transformation, which will not start immediately at Af temperature during cooling, but at some lower temperature Ms. The occurrence of hysteresis in the stress–strain chart is related to the friction between the crystal lattices on the β/αM transformation interface.
The analysis of mechanical properties for different ausforming-treated states of Cu-26Zn-4Al alloy is fully consistent with the results of metallographic analysis and conducted DSC tests. The results of the tensile test indicated the occurrence of the mechanically induced martensitic transformation. As the true plastic strain increased, so did the transformation stress as a consequence of the increasing share of non-transformable α-phase that occurs in the microstructure of hot rolled and quenched alloys, but also because of the consequent deformation of austenitic grains,
Figure 7b,c. These microstructural changes affect the mobility of the β/α
M transformation interface, i.e., the transition of austenite into stress-induced martensite that requires additional driving force in the form of an external applied load. Besides increasing the transformation stress, microstructural alterations are equally responsible for lowering the transformation temperatures. Thermally induced β ↔ α
M transformation at higher degrees of deformation also requires additional energy, which is no longer mechanical but thermal energy, introduced by heating or removed by cooling. The increase in the transformation stress was followed as well by an increase in true yield strength (
Rp) and tensile strength (
Rm). It may be concluded that a larger true plastic strain results in a more strengthened Cu-26Zn-4Al shape memory alloy.
Rp stresses vary within the range of 268 MPa (
φg = 0) to 393 MPa (
φg = 151%), and
Rm from 295 MPa (
φg = 0) to 419 MPa (
φg = 151%). The increase in these stresses is the result of the strengthening processes caused by an increase in the density of dislocations introduced by hot rolling and retained by quenching (in the absence of recrystallization and recovery) and the appearance of deformed boundaries of austenitic grains.
Preliminary results of hardness measurements at temperatures lower than
Md (maximum temperature at which stress-induced β → α
M reaction occurs) also support the hardening of the alloy, which indicate, for higher degrees of deformation, an increase in hardness of the stress-induced martensite. The higher slope outlining the trend of
Rp and
Rm changes in relation to the trend of
Rtr change,
Figure 11, is attributed to the β → α
M transformation, which additionally introduces defects in the crystal structure that lead to subsequent hardening of the alloy.
All measured elongations increase with the increase in plastic deformation,
Figure 12, due to the formation of finer grain structure, which is generally known for having higher strength, but also higher toughness and ductility. At the highest applied amount of true plastic strain (
φg = 151%), the percentage elongation after fracture (
ε) is almost three times higher than the percentage elongation in the undeformed state, while the super-elastic strain (
εSE.) is approximately constant (around 6%,
Figure 12) and independent of the degree of induced deformation. By increasing the true plastic strain, the residual strain after unloading residual strain (
εRS.) also significantly increases due to the formation of highly deformed non-transformable martensite, which does not have the ability to reverse the transformation back into austenite.