The Zinc-Rich Corner of the Fe-Si-Sn-Zn Quaternary System at 450 °C
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Experimental Methods
4. Results and Discussion
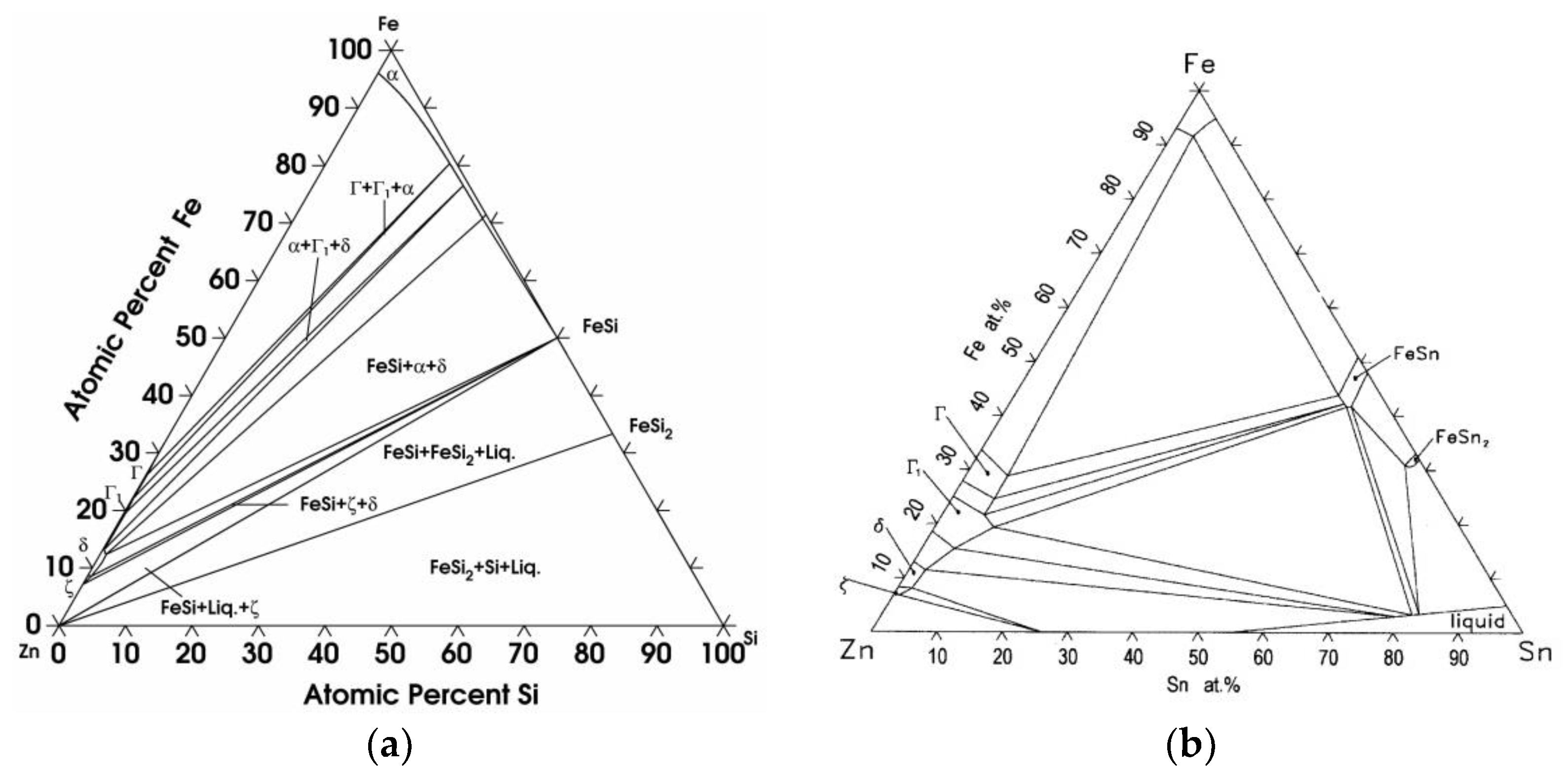
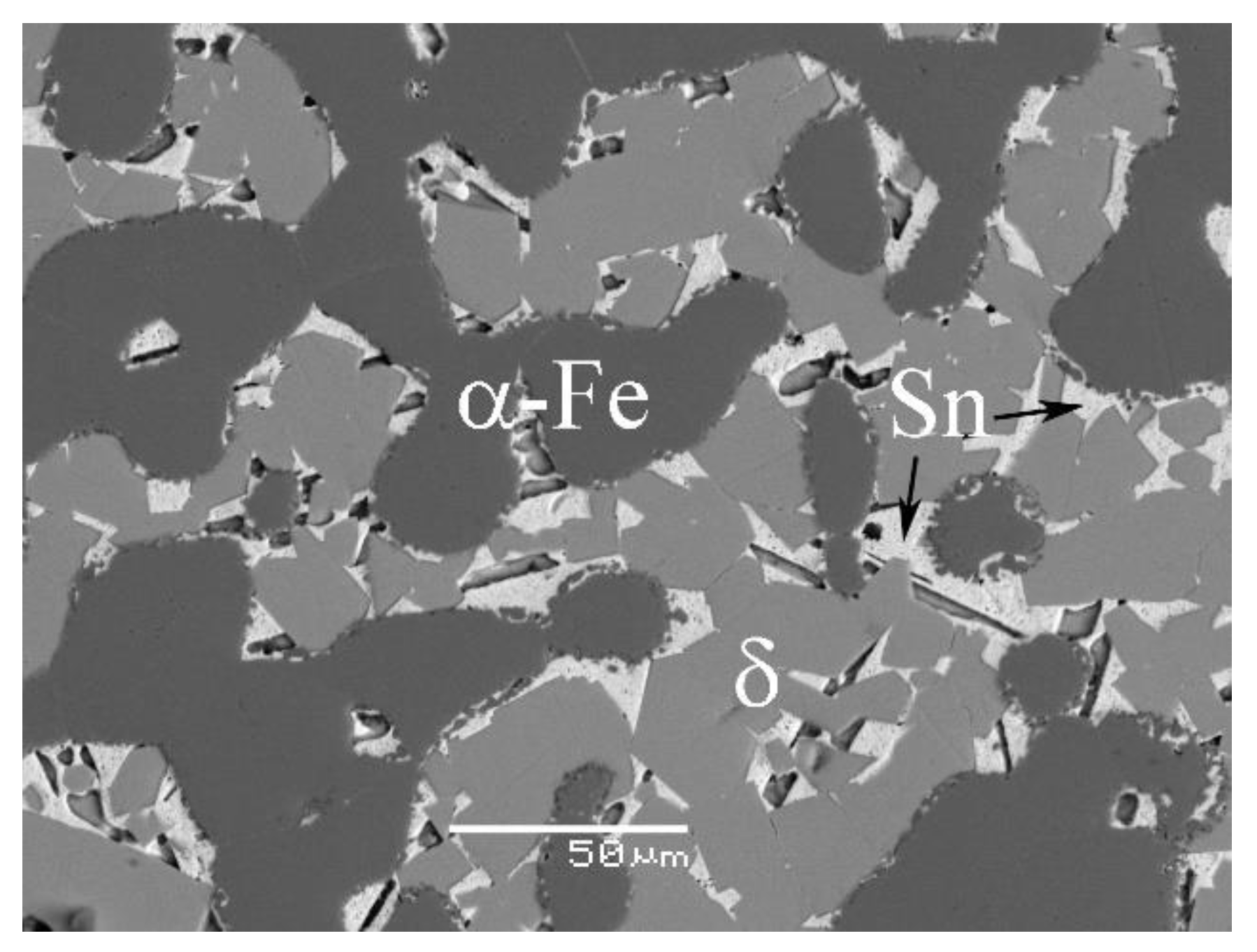
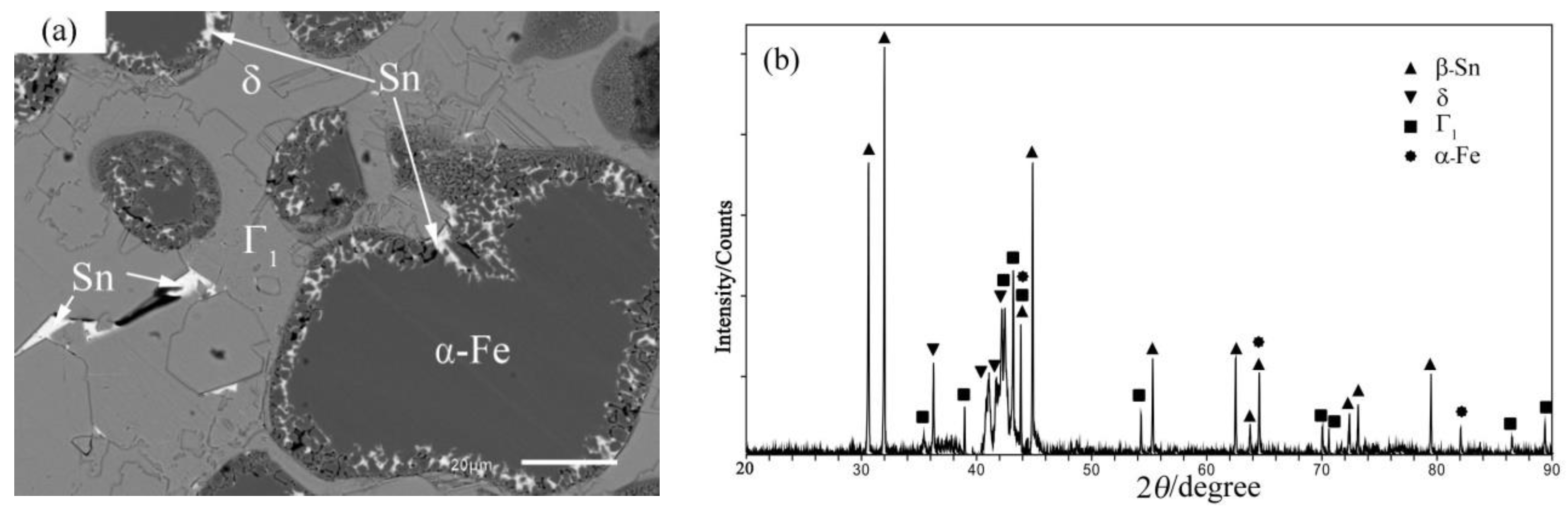
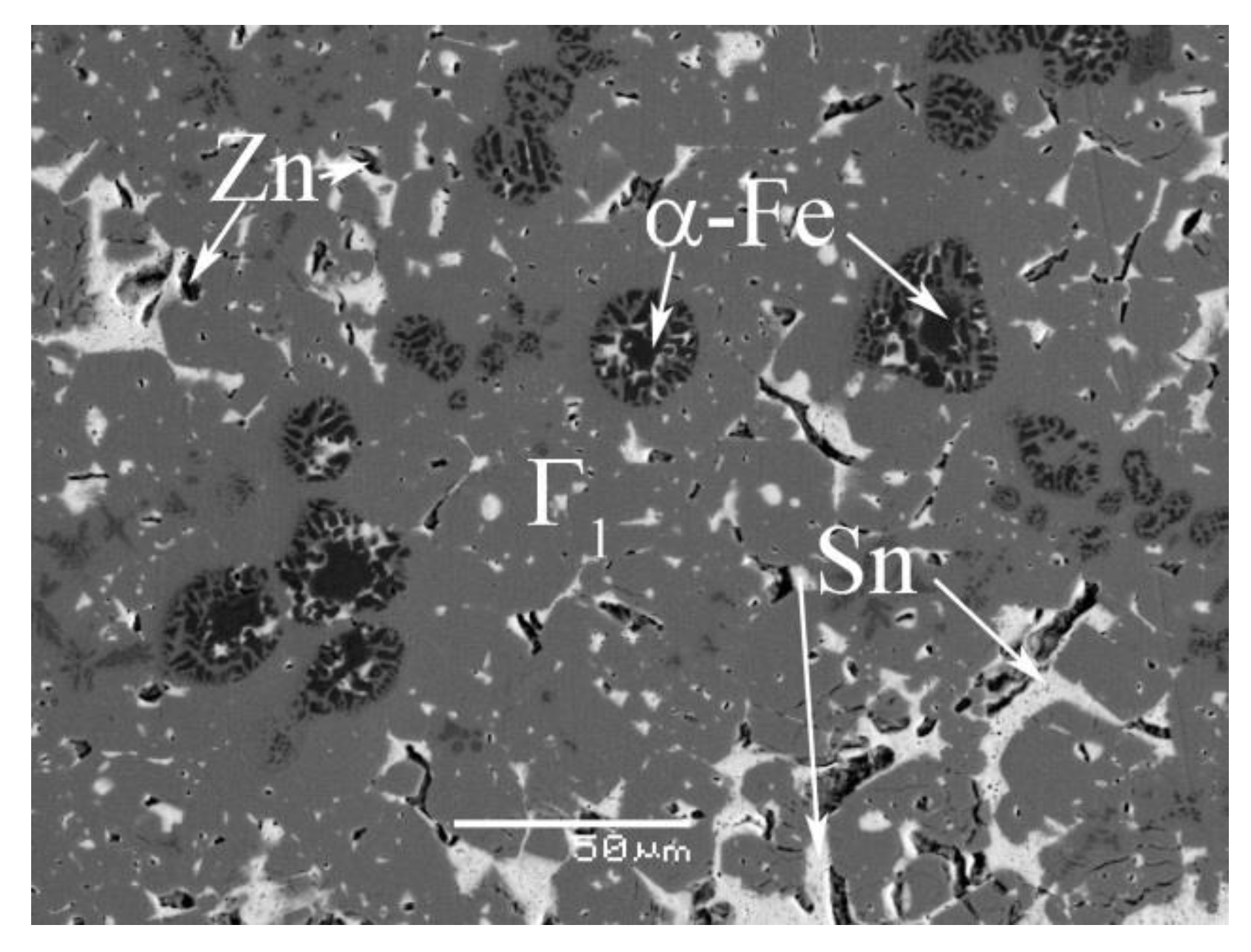
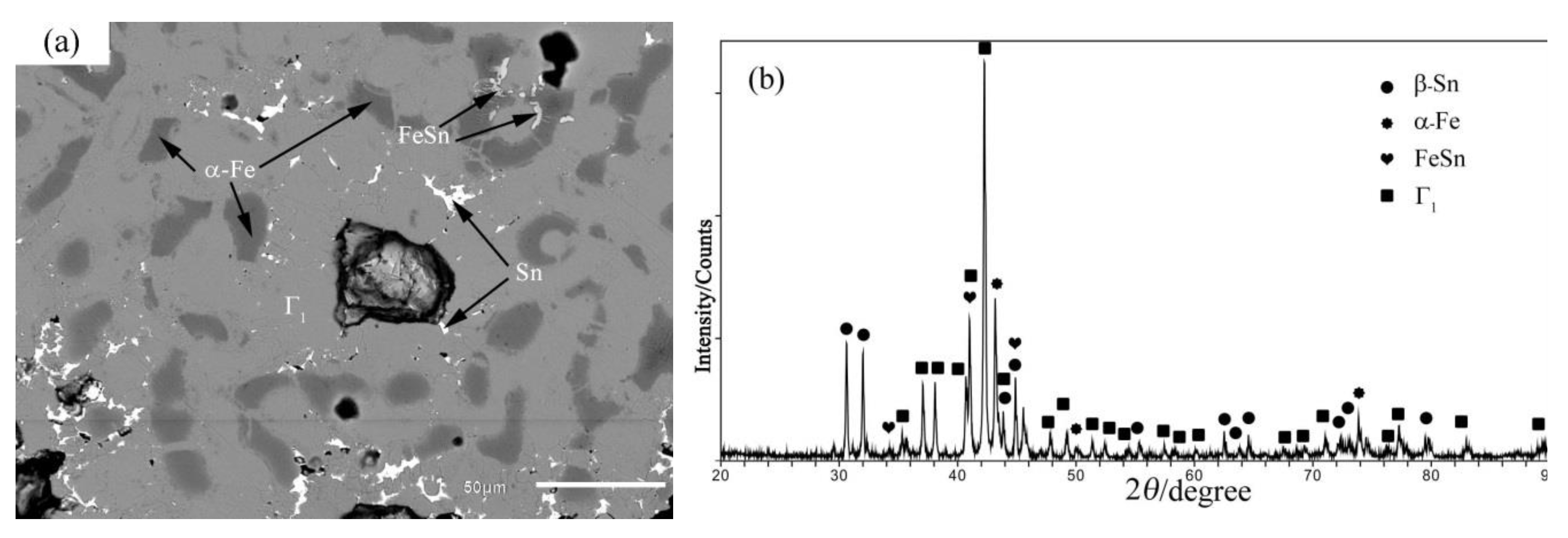
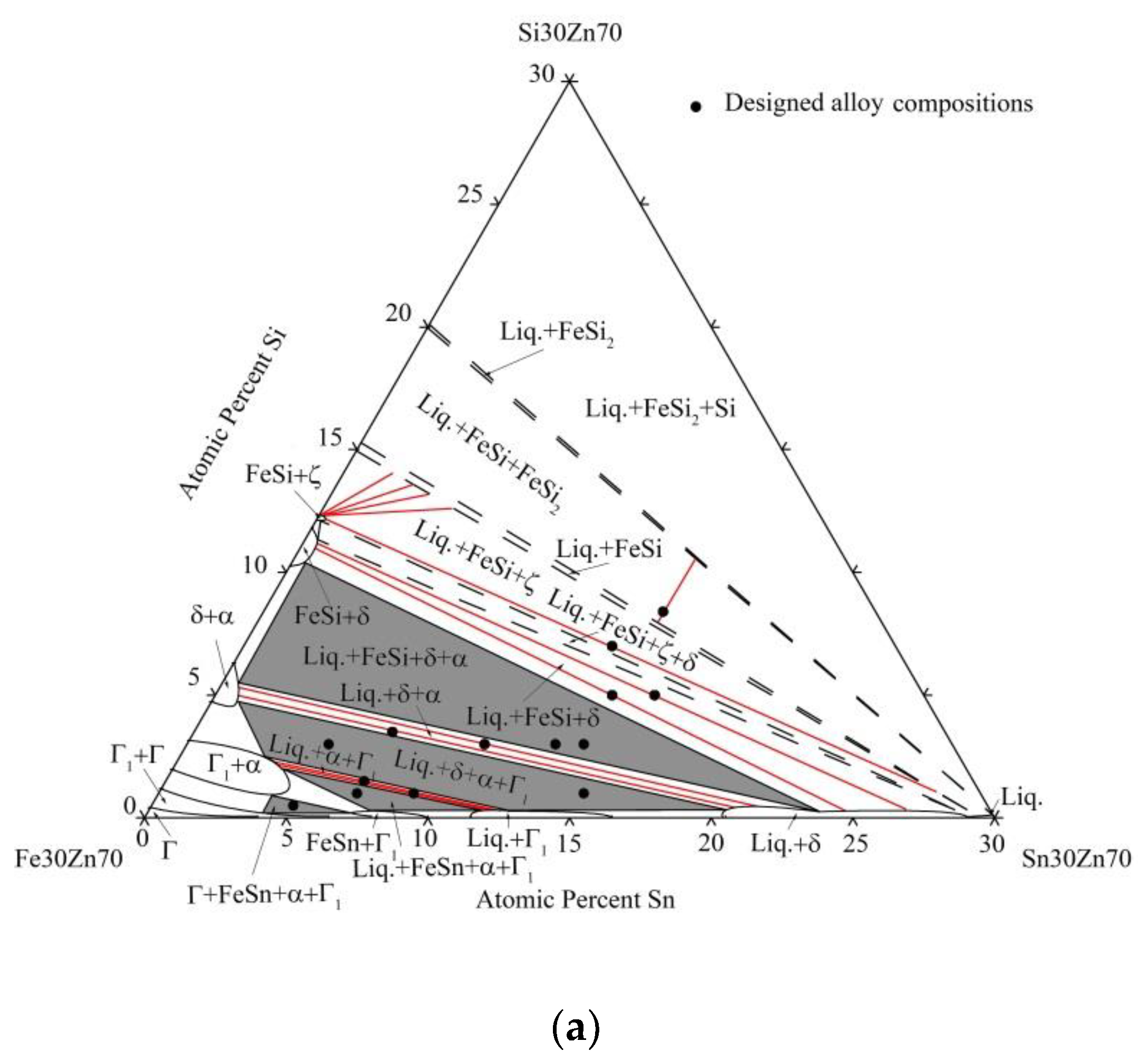
4.1. Phase Equilibrium of the Fe-Si-Sn-Zn Quaternary System at 450 °C with Zn Fixed at 70 at.%
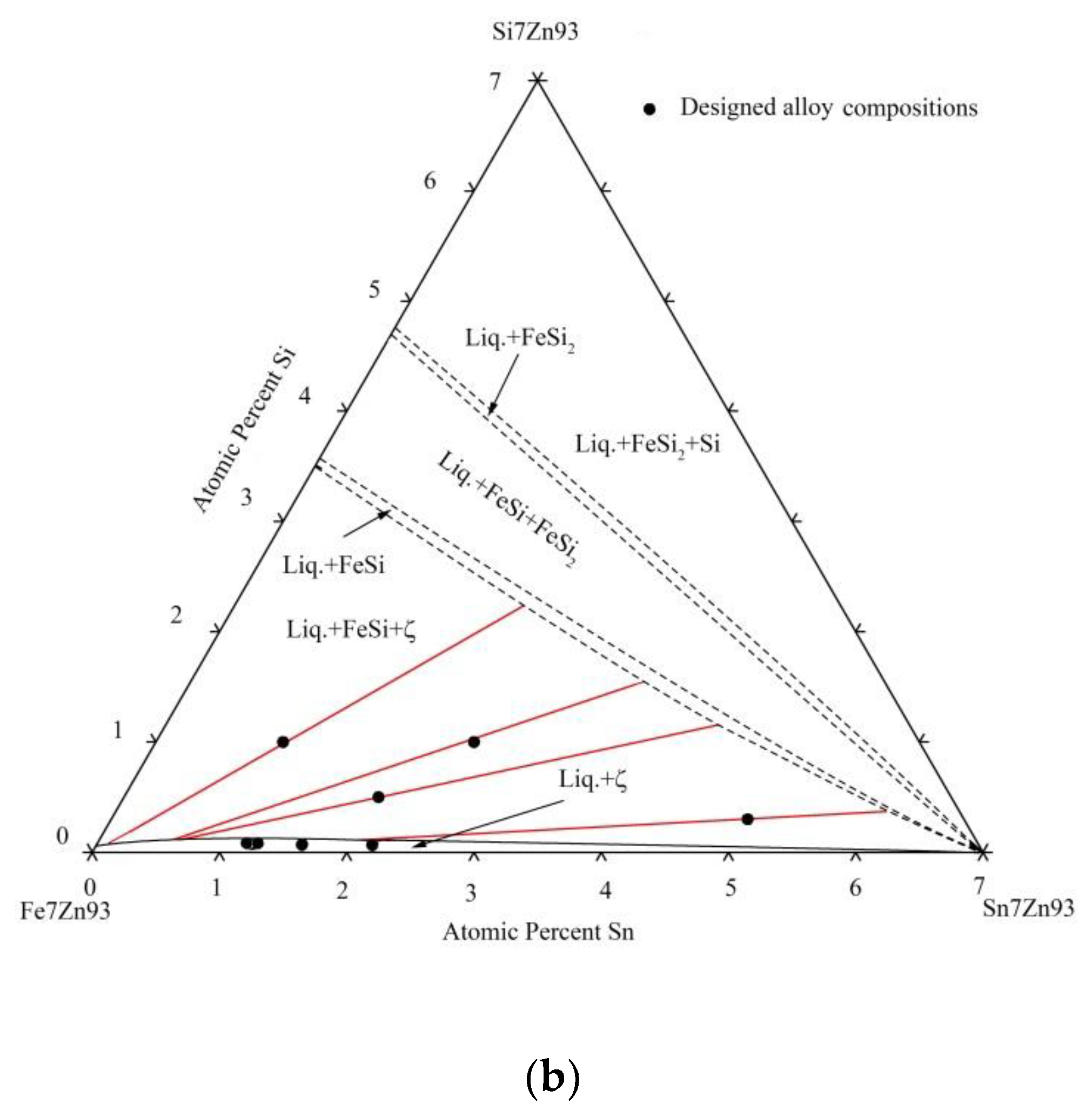
4.2. Phase Equilibrium of the Fe-Si-Sn-Zn Quaternary System at 450 °C with Zn Fixed at 93 At.%
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- Five four-phase regions exist in the isothermal section of the Fe-Si-Sn-Zn quaternary system at 450 °C with 70 at.% Zn. By contrast, no four-phase region is experimentally identified in the isothermal section with 93 at.% Zn.
- (2)
- The δ phase can coexist with the Liq. and FeSi phases.
- (3)
- The maximum solubility values of Sn and Zn in the FeSi phase are 0.4 and 1.2 at.%, respectively. The Sn percentages in the ζ, δ, Γ1, and Γ phases are 0.3, 1.1, 4.3, and 3.9 at.%, respectively. The Si percentages in the δ, Γ1, Γ, and FeSn phases are limited to 0.6, 0.3, 0.2, and 0.3 at.%, respectively.
- (4)
- No quaternary compound was found in the two sections.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, S.; Tu, H.; Wei, D.; Wu, C.; Wang, J.; Su, X. Experimental Determination of the Phase Equilibria of the La-Zn-Si System at 600 °C. J. Phase Equilib. Diffus. 2017, 38, 568–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellini, C.; Carlino, F. Intermetallic phase kinetic formation and thermal crack development in galvanized DCI. Frattura ed Integrita Strutturale 2019, 13, 740–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Su, X.; Liu, Y.; Ding, Y. 450 °C and 600 °C Isothermal Sections of the Zn-Cr-Si Ternary Phase Diagram. J. Phase Equilib. Diffus. 2018, 39, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ma, K.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Su, X. Phase Equilibria of 450 °C Isothermal Section of Zn-Al-Mg-Si Quaternary System. J. Phase Equilib. Diffus. 2017, 38, 906–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallinder, I.O.; Leygraf, C.; Karle′n, C.; Heijerick, D.; Janssen, C.R. Atmospheric Corrosion of Zinc-Based Materials: Runoff Rates. Chemical Speciation and Ecotoxicity Effects. Corros. Sci. 2001, 43, 809–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondareva, O.S.; Melnikov, A.A. Effect of the Silicon Content in Steel on the Hot-Dip Zinc Coating Microstructure Formation. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 156, 012015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Zhu, Z.; Ma, W.; Dai, Z.; Yin, F. The Zn-rich Corner of the Zn-Fe-V-Sb Quaternary Systems at 450 and 600 °C. J. Phase Equilib. Diffus. 2018, 39, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marder, A.R. The metallurgy of Zinc coated steel. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2000, 45, 191–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilles, M.; Sokolowski, R. The Zinc-Tin Galvanizing Alloy: A Unique Zinc Alloy for Galvanizing any Reactive Steel Grade. Proc. Intergalva 1997, 97, 8–11. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, H.; Wu, C.; Liu, Y.; Su, X.; Peng, H. Experimental Investigation of the 450 and 600 °C Sections of the Ti-V-Zn System. J. Phase Equilib. Diffus. 2016, 37, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.T.; Che, C.S.; Gang, K.; Xu, Q.Y.; Chen, J.H. Influence of silicon on the α-Fe/Γ interface of hot-dip galvanized steels. Surf. Coat. Tech. 2006, 200, 5277–5281. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, N.Y. Control of Silicon Reactivity in General Galvanizing. J. Phase Equilib. 2008, 29, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reumont, G.; Perrot, P.; Foct, J. Thermodynamic Study of the Galvanizing Process in a Zn-0.1%Ni Bath. J. Mater. Sci. 1998, 33, 4759–4768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reumont, G.; Gloriant, T.; Perrot, P. Experimental Influence of Kinetics on Galvanized Coatings when Saturating a Zinc Bath with Alloying Elements. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 1996, 15, 445–449. [Google Scholar]
- Su, X.; Wu, C.; Liu, D.; Yin, F.; Zhu, Z.; Yang, S. Effect of Vanadium on Galvanizing Si-Containing Steels. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2010, 205, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zervoudis, J.; Anderson, G. A Review of Bath Alloy Additives and Their Impact on the Quality of the Galvanized Coating. In Proceedings of the 6th Asia Pacific General Galvanizing Conference, Mississauga, Canada, 29 May–2 June 2005; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Pistofidis, N.; Vourlias, G.; Pavlidou, E.; Chrissafis, K.; Stergioudis, G.; K olychroniadis, E.; Tsipa, D. A Combined Characterization of Zinc Hot-Dip Galvanized Wires with DSC, XRD and SEM. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2006, 86, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Tang, N.Y.; Toguri, J.M. Thermodynamic Evaluation of the Fe-Zn System. J. Alloys Compd. 2001, 325, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavan, V. Fe-Zn (Iron-Zinc). J. Phase Equilib. 2003, 24, 544–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, J.; Malakhov, D.V.; Purdy, G.R. A Crystallographic Consistent Optimization of the Zn-Fe System. Calphad 2005, 29, 276–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.; Kong, Y.; Du, Y.; Liu, Z.K.; Selleby, M.; Sun, W.H. Thermodynamic Investigation of the Galvanizing Systems, I: Refinement of the Thermodynamic Description for the Fe-Zn System. Calphad 2009, 33, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weitzer, F.; Schuster, J.C.; Naka, M.; Stein, F.; Palm, M. On the Reaction Scheme and Liquidus Surface in the Ternary System Fe-Si-Ti. J. Intermetallics 2008, 16, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giefers, H.; Nicol, M. High Pressure X-Ray Diffraction Study of All Fe-Sn Intermetallic Compounds and One Fe-Sn Solid Solution. J. Alloys Compd. 2006, 422, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koster, W. The Iron-Silicon-ZincTernary System. Metallurgia 1969, 80, 219–229. [Google Scholar]
- Bretez, M.; Dauphin, J.Y.; Foct, J.; Perro, P. Phase Relations and Diffusion Paths in the System Zinc Vapor-Iron Silicon Alloys at 773 and 973 K. Z. Metallkd. 1987, 78, 137–140. [Google Scholar]
- Perrot, P.; Dauphin, J.Y. Calculation of the Fe-Zn-Si Phase Diagram between 773 and 1173 K. Calphad 1988, 12, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foct, J.; Perrot, P.; Reumont, G. Interpretation of the Role of Silicon on the Galvanizing Reaction Based on Kinetics, Morphology and Thermodynamics. Script. Metall. Mater. 1993, 98, 1195–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Tang, N.Y.; Toguri, J.M. 450 °C Isothermal Section of the Fe-Zn-Si Ternary Phase Diagram. Can. Metall. Q. 2001, 40, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Su, X.; Yin, F.; Li, Z.; Zhao, M. The 480 °C and 405 °C Isothermal Sections of the Phase Diagram of the Fe-Zn-Si Ternary System. J. Alloys Compd. 2005, 399, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, C.; Liu, S.; Du, Y.; Xu, H.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y. Experimental Investigation and Thermodynamic Reassessment of the Fe-Si-Zn System. Calphad 2010, 34, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, N.Y.; Su, X.; Yu, X. A Study of the Zn-Rich Corner of the Zn-Fe-Sn System. J. Phase Equilib. 2003, 24, 528–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


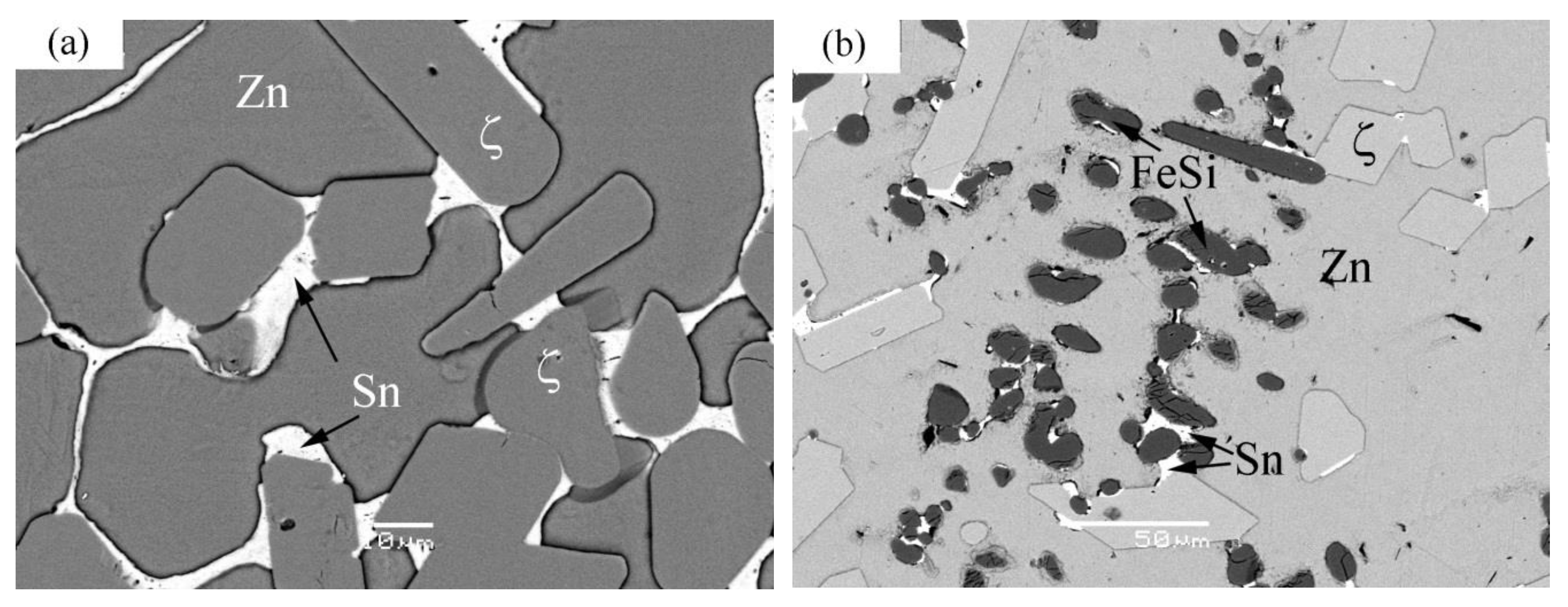
| Phase | Compositions, at.% | Lattice Parameter, nm | Space Group | Prototype | Reference | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zn | Fe | Si | Sn | a | b | c | ||||
| Γ-Fe3Zn10 | 68.5-82.5 | 17.5-32.5 | - | - | 0.8932 | - | - | I43m | Cu5Zn8 | [20] |
| Γ1-Fe11Zn40 | 75-81 | 19-25 | - | - | 1.7963 | - | - | F43m | - | [20] |
| δ-FeZn10 | 86.5-91.8 | 8.2-13.5 | - | - | 1.282 | - | 5.704 | P63mc | FeZn10 | [20] |
| ζ-FeZn13 | 92.8-94 | 6-7.2 | - | - | 1.3424 | 0.7608 | 0.5061 | C2/m | CoZn13 | [20] |
| FeSi | - | 50 | 50 | - | 0.44891 | - | - | P213 | FeSi | [22] |
| FeSi2 | - | 66.7 | 33.3 | - | 0.98792 | 0.77991 | 0.78388 | Cmca | FeSi2 | [22] |
| FeSn | - | 50 | - | 50 | 0.5298 | - | 0.4448 | P6/mmm | CoSn | [23] |
| Sample | Design Composition | Phase | Composition (at.%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zn | Fe | Si | Sn | |||
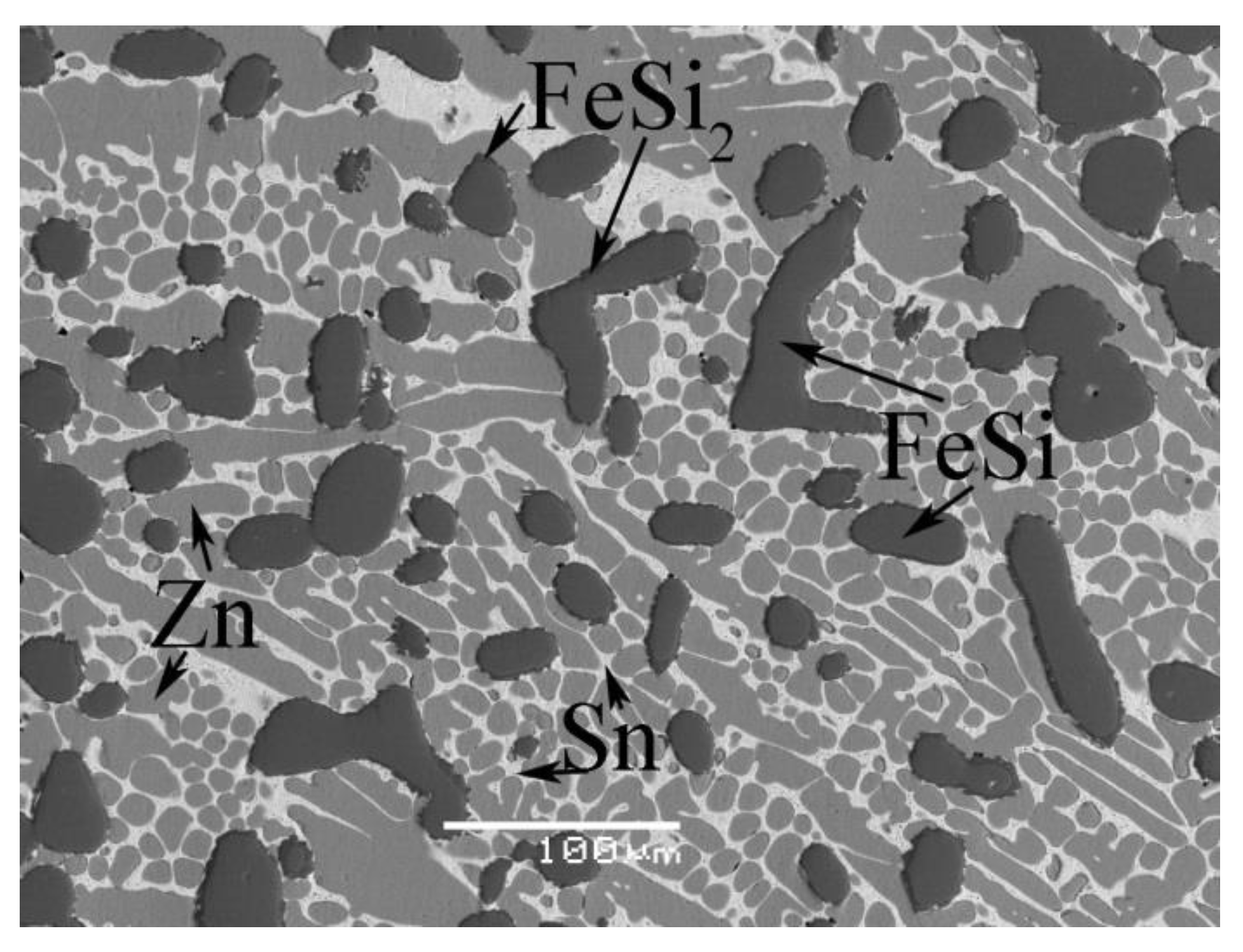
| A1 | 7.5Fe-8.5Si-14Sn-70Zn | Liq. | 83.2 ± 0.3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 16.8 ± 0.2 |
| FeSi | 0.8 ± 0.1 | 49.3 ± 0.8 | 49.7 ± 0.4 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | ||
| FeSi2 | 1.7 ± 0.3 | 32.6 ± 0.6 | 65.2 ± 0.2 | 0.5 ± 0.1 | ||
| A2 | 10Fe-7Si-13Sn-70Zn | Liq. | 71.5 ± 0.4 | 0.5 ± 0.2 | 0.0 | 28.0 ± 0.4 |
| FeSi | 1.1 ± 0.1 | 48.9 ± 0.9 | 49.6 ± 0.6 | 0.4 ± 0.1 | ||
| ζ | 92.4 ± 0.4 | 7.3 ± 0.4 | 0.0 | 0.3 ± 0.1 | ||
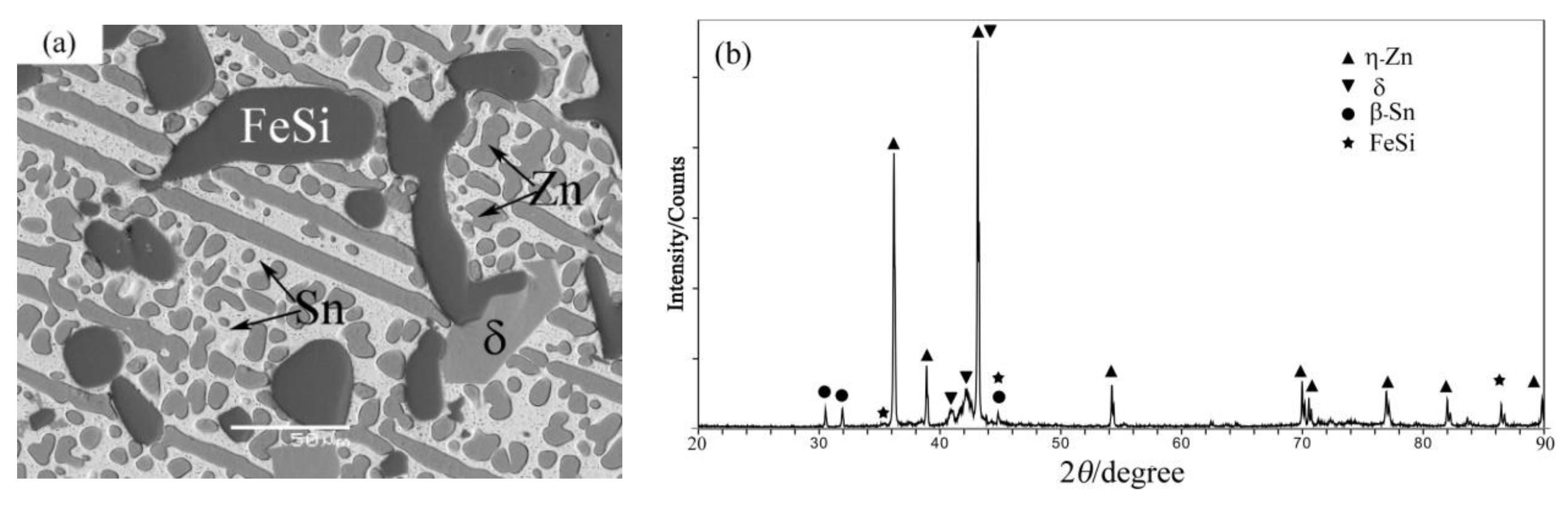
| A3 | 11Fe-5Si-14Sn-70Zn | Liq. | 60.5 ± 0.2 | 0.0 | 0.5 ± 0.2 | 39.0 ± 0.4 |
| FeSi | 1.2 ± 0.3 | 49.3 ± 0.2 | 49.3 ± 0.2 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | ||
| δ | 90.2 ± 0.8 | 9.2 ± 0.8 | 0.0 | 0.6 ± 0.2 | ||
| A4 | 9.5Fe-15Si-15.5Sn-70Zn | Liq. | 49.6 ± 0.4 | 0.5 ± 0.1 | 0.6 ± 0.3 | 49.3 ± 0.8 |
| FeSi | 1.2 ± 0.4 | 49.4 ± 0.4 | 49.2 ± 0.5 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | ||
| δ | 89.8 ± 1.0 | 9.6 ± 0.4 | 0.0 | 0.6 ± 0.1 | ||
| A5 | 13Fe-3Si-14Sn-70Zn | Liq. | 51.4 ± 0.2 | 0.6 ± 0.1 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 47.8 ± 0.6 |
| FeSi | 0.8 ± 0.1 | 49.4 ± 0.5 | 49.4 ± 0.4 | 0.4 ± 0.1 | ||
| δ | 87.9 ± 0.4 | 11.3 ± 0.2 | 0.3 ± 0.1 | 0.5 ± 0.1 | ||
| α | 0.9 ± 0.1 | 72.6 ± 0.4 | 25.6 ± 0.6 | 0.9 ± 0.2 | ||
| A6 | 14Fe-3Si-13Sn-70Zn | Liq. | 51.3 ± 0.2 | 0.5 ± 0.2 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 48.0 ± 0.5 |
| FeSi | 0.7 ± 0.1 | 49.5 ± 0.6 | 49.5 ± 0.6 | 0.3 ± 0.1 | ||
| δ | 87.9 ± 0.5 | 11.3 ± 0.2 | 0.4 ± 0.1 | 0.4 ± 0.1 | ||
| α | 0.9 ± 0.1 | 72.7 ± 0.7 | 25.5 ± 0.6 | 0.9 ± 0.2 | ||
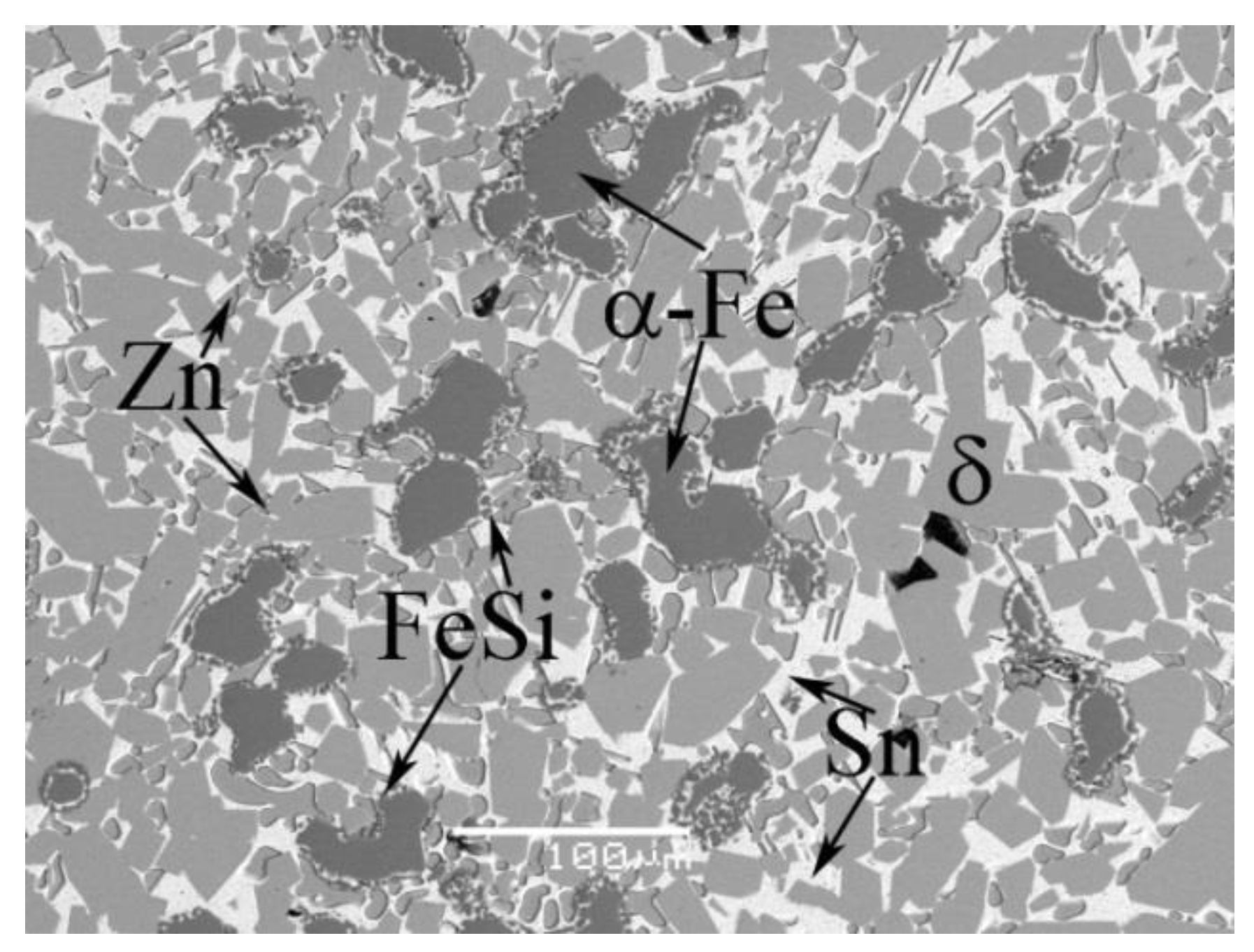
| A7 | 16.5Fe-3Si-10.5Sn-70Zn | Liq. | 36.0 ± 0.6 | 0.4 ± 0.1 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 63.4 ± 0.1 |
| δ | 86.7 ± 0.5 | 11.9 ± 0.2 | 0.6 ± 0.1 | 0.8 ± 0.1 | ||
| α | 4.2 ± 0.1 | 71.7 ± 0.1 | 23.9 ± 0.5 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | ||
| A8 | 19.5Fe-3.5Si-7Sn-70Zn | Liq. | 35.5 ± 0.5 | 0.6 ± 0.1 | 0.5 ± 0.1 | 63.4 ± 0.6 |
| δ | 85.9 ± 0.6 | 12.8 ± 0.2 | 0.4 ± 0.1 | 0.9 ± 0.1 | ||
| α | 4.9 ± 0.4 | 70.8 ± 0.7 | 23.8 ± 0.5 | 0.5 ± 0.1 | ||
| A9 | 22Fe-3Si-5Sn-70Zn | Liq. | 10.9 ± 0.1 | 0.1 ± 0.1 | 0.4 ± 0.1 | 88.6 ± 0.1 |
| δ | 86.7 ± 0.3 | 11.9 ± 0.5 | 0.3 ± 0.1 | 1.1 ± 0.1 | ||
| α | 7.2 ± 0.6 | 71.0 ± 0.6 | 21.4 ± 0.5 | 0.4 ± 0.1 | ||
| Γ1 | 77.3 ± 0.5 | 19.1 ± 0.6 | 0.3 ± 0.1 | 3.3 ± 0.6 | ||
| A10 | 14Fe-1Si-15Sn-70Zn | Liq. | 10.8 ± 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.3 ± 0.1 | 88.9 ± 0.6 |
| δ | 86.8 ± 0.7 | 11.9 ± 0.2 | 0.3 ± 0.1 | 1.0 ± 0.2 | ||
| α | 7.1 ± 0.2 | 71.1 ± 0.7 | 21.4 ± 0.5 | 0.4 ± 0.2 | ||
| Γ1 | 77.3 ± 0.3 | 19.2 ± 0.5 | 0.3 ± 0.1 | 3.2 ± 0.2 | ||
| A11 | 20Fe-1Si-9Sn-70Zn | Liq. | 12.6 ± 0.5 | 0.1 ± 0.1 | 0.1 ± 0.1 | 87.2 ± 0.7 |
| α | 7.2 ± 0.7 | 71.1 ± 0.3 | 21.1 ± 0.5 | 0.6 ± 0.1 | ||
| Γ1 | 76.6 ± 0.7 | 19.3 ± 0.4 | 0.3 ± 0.1 | 3.8 ± 0.1 | ||
| A12 | 21.5Fe-1.5Si-7Sn-70Zn | Liq. | 14.7 ± 0.3 | 0.0 | 0.3 ± 0.1 | 85.0 ± 0.5 |
| α | 6.5 ± 0.4 | 72.1 ± 0.3 | 21.4 ± 0.2 | 0.0 | ||
| Γ1 | 76.1 ± 0.7 | 19.6 ± 0.5 | 0.3 ± 0.5 | 4.0 ± 0.1 | ||
| A13 | 22Fe-1Si-7Sn-70Zn | Liq. | 10.4 ± 0.2 | 0.0 | 0.4 ± 0.1 | 89.2 ± 0.8 |
| FeSn | 1.9 ± 0.4 | 47.7 ± 0.5 | 0.3 ± 0.1 | 50.1 ± 0.5 | ||
| α | 6.9 ± 0.1 | 72.2 ± 0.4 | 20.5 ± 0.8 | 0.4 ± 0.1 | ||
| Γ1 | 75.8 ± 0.5 | 19.7 ± 0.1 | 0.3 ± 0.1 | 4.2 ± 0.1 | ||
| A14 | 24.5Fe-0.5Si-5Sn-70Zn | Γ | 66.8 ± 0.7 | 29.1 ± 0.2 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 3.9 ± 0.1 |
| FeSn | 4.3 ± 0.4 | 46.1 ± 0.5 | 0.1 ± 0.1 | 49.5 ± 0.3 | ||
| α | 2.5 ± 0.2 | 85.8 ± 0.6 | 11.4 ± 0.2 | 0.3 ± 0.1 | ||
| Γ1 | 74.5 ± 0.5 | 21.0 ± 0.2 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 4.3 ± 0.4 | ||
| B1 | 4.9Fe-0.1Si-2Sn-93Zn | Liq. | 94.3 ± 1.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 5.7 ± 0.3 |
| ζ | 92.2 ± 0.5 | 7.7 ± 0.2 | 0.1 ± 0.1 | 0.0 | ||
| B2 | 5.3Fe-0.1Si-1.6Sn-93Zn | Liq. | 94.5 ± 1.0 | 0.1 ± 0.1 | 0.0 | 5.4 ± 0.1 |
| ζ | 92.4 ± 0.5 | 7.4 ± 0.2 | 0.1 ± 0.1 | 0.1 ± 0.1 | ||
| B3 | 5.7Fe-0.1Si-1.2Sn-93Zn | Liq. | 95.1 ± 0.4 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 4.9 ± 0.2 |
| ζ | 92.3 ± 0.3 | 7.6 ± 0.4 | 0.1 ± 0.1 | 0.0 | ||
| B4 | 5.5Fe-0.1Si-1.4Sn-93Zn | Liq. | 94.7 ± 1.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 5.3 ± 0.4 |
| ζ | 92.4 ± 0.8 | 7.5 ± 0.1 | 0.1 ± 0.1 | 0.0 | ||
| B5 | 1.7Fe-0.3Si-5Sn-93Zn | Liq. | 93.7 ± 0.6 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 0.0 | 6.1 ± 0.2 |
| FeSi | 1.2 ± 0.2 | 49.5 ± 0.2 | 49.2 ± 0.8 | 0.1 ± 0.1 | ||
| ζ | 92.8 ± 0.7 | 6.9 ± 0.3 | 0.1 ± 0.1 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | ||
| B6 | 4.5Fe-0.5Si-2Sn-93Zn | Liq. | 95.3 ± 0.7 | 0.1 ± 0.1 | 0.0 | 4.6 ± 0.3 |
| FeSi | 1.1 ± 0.2 | 49.5 ± 0.2 | 49.1 ± 0.7 | 0.3 ± 0.2 | ||
| ζ | 92.8 ± 0.3 | 6.9 ± 0.2 | 0.1 ± 0.1 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | ||
| B7 | 5Fe-1Si-1Sn-93Zn | Liq. | 97.4 ± 0.6 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 0.0 | 2.4 ± 0.3 |
| FeSi | 1.4 ± 0.1 | 49.3 ± 0.7 | 49.2 ± 0.7 | 0.1 ± 0.1 | ||
| ζ | 92.6 ± 0.7 | 7.2 ± 0.2 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 0.0 | ||
| B8 | 3.5Fe-1Si-2.5Sn-93Zn | Liq. | 95.9 ± 0.7 | 0.5 ± 0.1 | 0.0 | 3.6 ± 0.2 |
| FeSi | 0.8 ± 0.2 | 49 ± 0.7 | 49.9 ± 0.2 | 0.3 ± 0.1 | ||
| ζ | 92.6 ± 0.7 | 7.2 ± 0.6 | 0.1 ± 0.1 | 0.1 ± 0.1 | ||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Chen, X.; Su, X.; Yin, F.; Li, Z. The Zinc-Rich Corner of the Fe-Si-Sn-Zn Quaternary System at 450 °C. Metals 2019, 9, 908. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9080908
Wang X, Chen X, Su X, Yin F, Li Z. The Zinc-Rich Corner of the Fe-Si-Sn-Zn Quaternary System at 450 °C. Metals. 2019; 9(8):908. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9080908
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xinming, Xiaqi Chen, Xuping Su, Fucheng Yin, and Zhi Li. 2019. "The Zinc-Rich Corner of the Fe-Si-Sn-Zn Quaternary System at 450 °C" Metals 9, no. 8: 908. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9080908
APA StyleWang, X., Chen, X., Su, X., Yin, F., & Li, Z. (2019). The Zinc-Rich Corner of the Fe-Si-Sn-Zn Quaternary System at 450 °C. Metals, 9(8), 908. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9080908






