Abstract
This article details the development and characterization of binary palladium alloys synthesized via a hydrothermal process. Palladium alloys, being good redox catalysts, could potentially replace platinum in many applications such as in dye sensitized solar cells, capacitors and vehicular catalytic converters where platinum is vital for maximum productivity. A good replacement should be cheap, readily available and be able to offer comparable catalytic activity to that of platinum. As such we hereby attempt to hydrothermally fabricate and characterize binary palladium alloys PdNi and PdCo that could be ideal replacements for platinum. XRD analysis of the as-synthesized binary alloys revealed the existence of only palladium peaks at 2θ values of 40.1°, 46.7°, 68.1°, 82.1° and 86.6°, indicative of the successful formation of the binary alloys. SEM micrographs revealed that both alloys consisted of spherical particles with PdCo agglomerating to an extent, whereas PdNi was widely distributed, thus it could enhance electrolyte adsorption during catalytic reduction reactions. Cyclic voltammetry analysis at 50 mV∙s−1 revealed that PdNi is more electrocatalytically active with a reduction current density of 41 mA∙cm−2 compared to 18 mA∙cm−2 for PdCo. Lower charge transfer resistance from electrochemical impedance spectroscopy confirmed the superior catalytic ability of PdNi. The two palladium alloys also produced maximum specific capacitances of 68 and 27 F∙g−1 for PdNi and PdCo respectively. Analysis of the sample stability yielded coulombic efficiency retention of 98.7 and 97% for PdNi and PdCo respectively after 1000 cycles. Results obtained have shown that the palladium alloys with their low charge transfer resistance could be ideal replacements for platinum in dye sensitized solar cells. Modest specific capacitance for PdNi illustrates its potential as an electrode catalyst in capacitors.
1. Introduction
There has been an increase in the global energy demand as a result of the increase in the world population, the depletion of fossil fuel reserves and the rapid spread of urbanization. Thus, efforts to deal with the energy crisis have led to more usage of renewable energy, with solar energy being one such energy [1]. The dye sensitized solar cell (DSSC) has been known to be one of the most promising thin film solar technology which has sparked major research interest in both scientific and industrial communities since its introduction in 1991 [2,3]. This has notably been due to its low fabrication cost, simple fabrication method, relatively modest efficiency and environmental compatibility [4,5]. The components of a DSSC include a wide band gap n-type semiconductor coated photo anode, a counter electrode (CE), a dye-sensitizer and a redox electrolyte [6,7]. The CE is one of the most crucial components of the DSSC and plays a role in collection of photogenerated electrons from the external load to the CE/electrolyte interface and catalyzing the reduction of triiodide to iodide ions (I3−/I−).
Platinum was the traditional CE of choice in DSSCs due to its high electrocatalytic ability and conductivity [8]. However, platinum is an expensive precious metal which is less abundant and its use in DSSCs limits their large-scale production. Chemical dissolution of platinum in the I3−/I− electrolyte as well as degradation of electrocatalytic activity are some of the unfavorable characteristics of platinum CEs [9,10]. Hence, research efforts have been focused on developing cost effective CEs from abundant materials with high conductivity and electrocatalytic properties whilst also seeking nonvolatile electrolytes to replace the iodine electrolyte.
Several materials have been investigated as substitutes for platinum in CE; these include carbon-based materials, metal carbides, metal nitrides, metal sulfides, conducting polymers and metal alloys [11,12].
Metal alloys, in particular binary metal alloys, have shown great promise for producing CEs of higher electrocatalytic activity, higher conductivity and better stability as compared to Pt CEs [13]. He et al. [14] reported a facile chemical reduction method for synthesis of PdCo alloy. The DSSC comprised of a TiO2 photoanode, PdCo cathode and I3−/I− redox electrolyte sandwiched between the cathode and photoanode. The PdCo based DSSC had an efficiency 6.44% greater than the compared Pt based DSSC [14]. This goes to show that metal alloying CEs is a viable method that can be explored in achieving better catalytic function. Various methods have been used in fabricating binary metal alloys for use in DSSCs including solvothermal, galvanic displacement and hydrothermal synthesis. Since the morphology of nanoparticles has an effect on their electrocatalytic activity [15], synthesis of binary metal alloys using a hydrothermal method might be a promising avenue. This is because hydrothermal fabrication offers an easier way to control morphology by manipulating reaction time, pressure, reaction ratio and packing ratio. Hence, PdCo and PdNi nanoparticles were synthesized by a hydrothermal method and their structure, morphology and electrochemical activity discussed so as to establish their suitability as counter electrode catalysts in dye sensitized solar cells. Despite the price of palladium occasionally fluctuating to higher prices than that of platinum, its incorporation with cheaper d-block metals nickel and cobalt serves to enhance the binary alloy. The binary alloy is required to be exceptionally conductive as well as a good reduction catalyst. Thus, each element chosen should provide a specific advantage to the function of the binary alloy. Palladium, being extremely effective as a redox catalyst, will be tasked to enhance the reduction reaction at the counter electrode/electrolyte interface whilst cobalt and nickel are tasked with enhancing the conductivity of the alloy as well as corrosion resistance in volatile electrolyte environments. Since the iodine electrolyte constitutes one of the most significant challenges limiting the commercial success of the DSSC this work endeavors to establish the functionality of the binary palladium alloys using a potassium hydroxide electrolyte. Nickel and cobalt also help to combat corrosion in aggressive electrolytes such as the iodine electrolyte [16]. As palladium is susceptible to microcracking, the addition of nickel and cobalt suppresses the formation of its less stable beta phase, thereby reducing the risk of microcracking and ultimately enhancing corrosion resistance [16].
Furthermore, binary metallic alloys could be ideal for use as electrodes in capacitors, particularly hybrid electrochemical capacitors (HEC). Capacitor electrodes must possess excellent electrical conductivity, good chemical stability, sufficient corrosion resistance and high surface area. Although most electrochemical capacitors consist of carbon-based electrodes, recent advances to develop hybrid electrochemical capacitors with an asymmetrical configuration of electrodes have gained more attention [17]. Hybrid electrochemical capacitors consist of a pseudocapacitance material as the cathode. Pseudocapacitance materials have the ability to increase specific capacitance of a capacitor as well as increase its working voltage through charge accumulation from faradic electrochemical processes Since platinum group metals partake in redox reactions with more vigor than most elements it is essential that they be incorporated in capacitors to improve their efficiency. The Ru//Ru and Carbon//Ru electrode configurations are already in existence, producing efficient results [17]. Platinum group metals are well known to be expensive, thus in order to limit costs binary alloys in which a minimal amount of the noble metal is used are a more plausible option. Especially attractive are core–shell alloys in which palladium forms the shell whilst the core consists of cheaper base materials like Nickel and Cobalt. However due to high cost of production as well as a greater degree of difficulty in synthesis, this work endeavors to produce an explorative hydrothermally fabricated binary palladium alloy which will be characterized to determine whether its properties could influence its capability as an electrode in both DSSCs and HEC. According to Zhang et al. [16] the highest reduction activity using a palladium–gold catalyst was observed when palladium coverage was extremely low. In that work the amount of palladium used for synthesis was 8 mM.
2. Materials and Methods
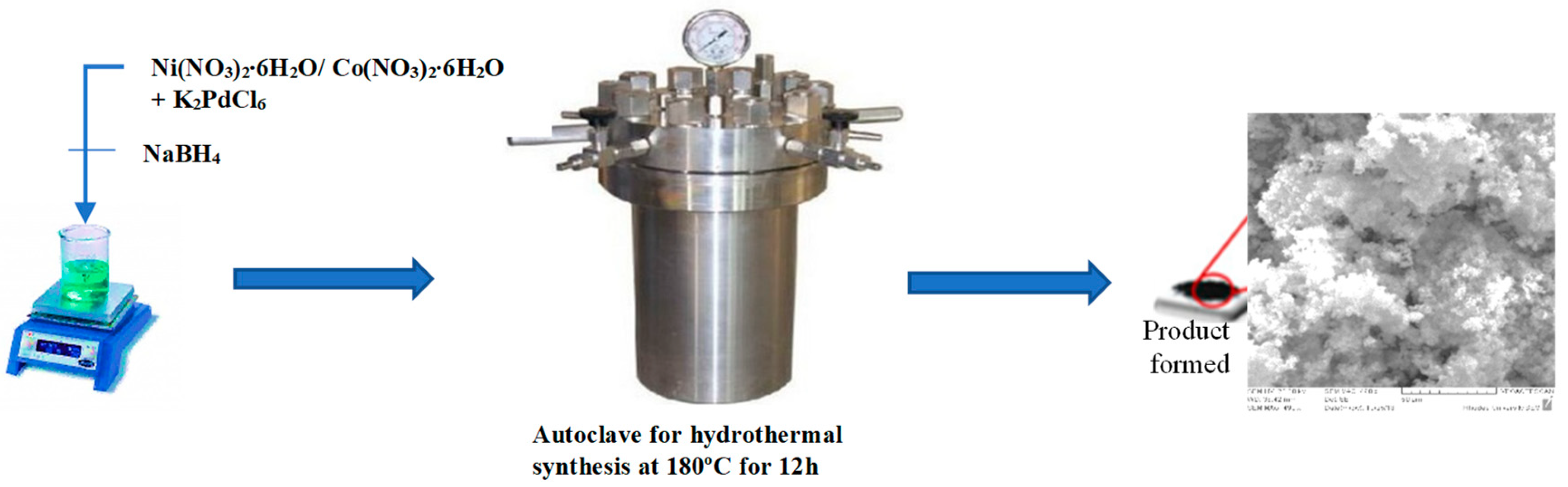
All materials used in the synthesis procedure were purchased from (Sigma Aldrich, Germany). In this experimental procedure, nickel and cobalt precursor solutions were obtained by dissolving 0.5 g of Ni(NO3)2∙6H2O and Co(NO3)2∙6H2O in two separate beakers containing 40 mL of deionized water. Subsequent addition of 0.3 g of K2PdCl6 to each precursor solution was preceded by rigorous ultrasonication so as to attain homogeneity. Under intensive ultrasonication 5 mL of 1 M NaBH4 was added to the precursor solutions resulting in a black mixture. The as-synthesized mixtures were then transferred into 50 mL Teflon lined stainless steel autoclaves for hydrothermal synthesis. The hydrothermal synthesis was undertaken at 180 °C for 12 h which resulted in black palladium alloy precipitates. The as-synthesized black palladium precipitates underwent filtration followed by thorough washing with deionized water and ethanol. Subsequent drying of the synthesized alloys at 100 °C for 2 h was conducted prior to characterization. Figure 1 shows the sequential procedure for hydrothermal fabrication of palladium alloys.

Figure 1.
Fabrication procedure for PdNi and PdCo alloys. The product formed depicted in Figure 1 is PdNi, more clearly illustrated in Figure 4a.
Phase composition of the as-synthesized binary alloys was evaluated using XRD spectra obtained from a Bruker D8 Advanced X-Ray Diffractometer (XRD) (Bruker, Madison, WI, USA) with a Cu anode, generating Kα radiation of wavelength 1.544 Â and operating at 40 kV and 40 mA. The XRD spectra were obtained at room temperature for a 2θ range from 15° to 90°. Morphological properties of the as-synthesized palladium alloys were evaluated using a Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscope (FE-SEM) Zeiss Auriga SEM (Carl Zeiss AGr, Oberkochen, Germany) equipped with EDS Smart SEM software. The microscope functioning with an accelerating voltage of 30 kV obtained images at different magnifications. Electrochemical analysis was conducted using an electrochemical workstation (CHI660, CH Instruments, Inc., Austin, TX, USA). A standard three electrode system with scanning rates from 5–100 mV∙s−1 was used to obtain the cyclic voltammetry (CV) profiles. The as-synthesized palladium alloys, Ag/AgCl electrode, and carbon black served as the working, reference and counter electrode respectively. A 6 M KOH electrolyte solution was used for electrochemical measurements. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) was conducted in a frequency range from 0.01–100 kHz at 0 V bias with an amplitude of 10 mV.
3. Results
3.1. XRD Analysis
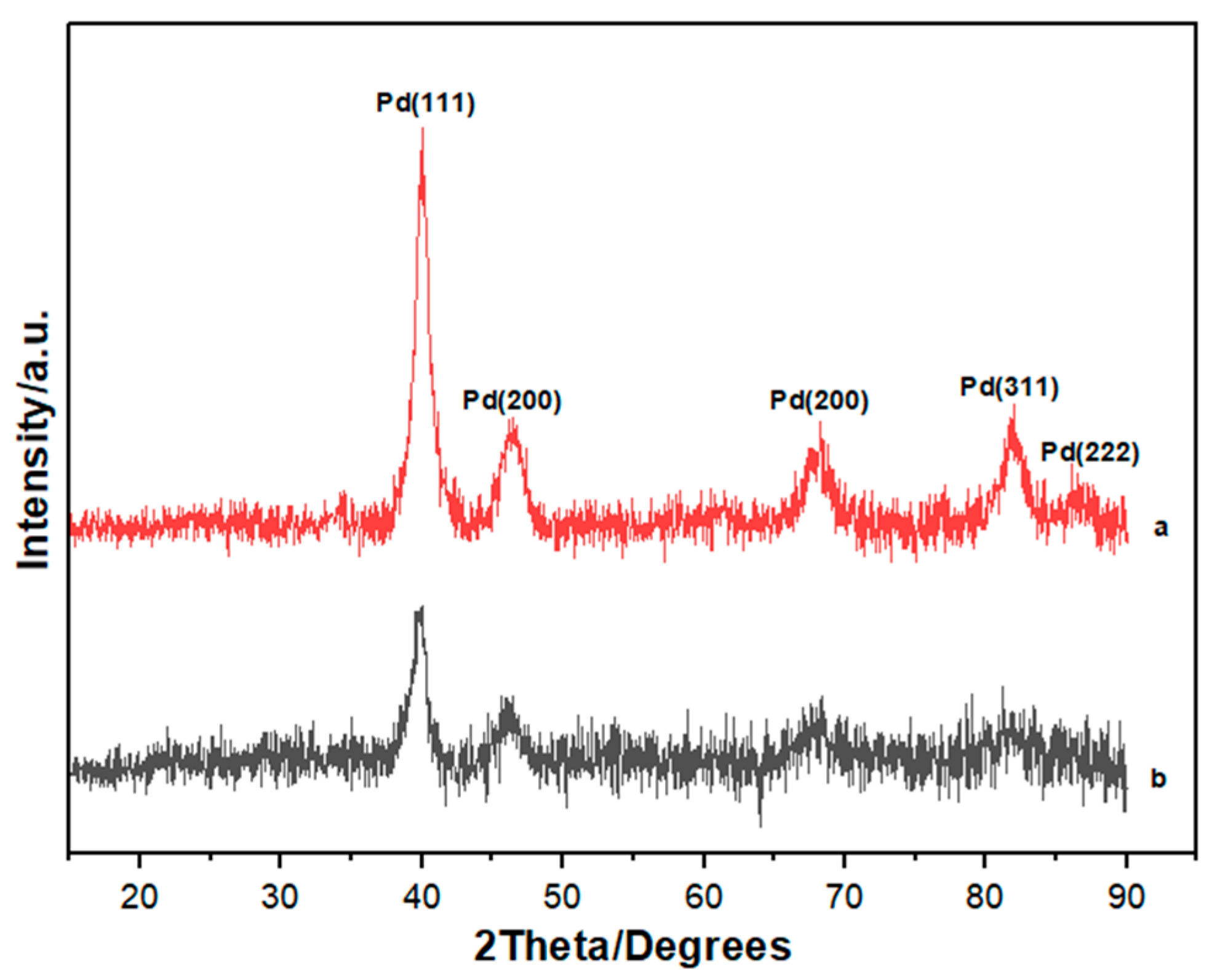
In order to determine the phase composition and crystal structures of the synthesized binary PdNi and PdCo alloys, X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) was conducted. Figure 2 depicts the result of the XRD analysis.
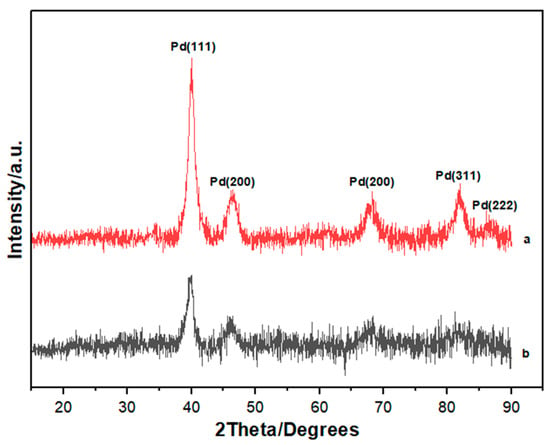
Figure 2.
X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns for (a) PdNi (b) PdCo alloys.
XRD profiles used to determine the structural features of the as-synthesized palladium alloys are shown in Figure 2. The diffraction pattern for PdNi revealed peaks at 2θ values of 40.1°, 46.7°, 68.1°, 82.1° and 86.6° which corresponded to the (111), (200), (220), (311) and (222) lattice planes of face centered cubic palladium (JCPDS No. 46-1043) with space group class (SG) of Fm3m 225. The highest intensity amongst the palladium peaks was observed inclined in the (111) plane, therefore the palladium alloy growth was orientated in this plane. A slight shift towards lower 2θ values was observed for PdCo diffraction peaks compared to the corresponding diffractograms for PdNi Diffraction peaks at 39.7°, 46.2°, 68°, 81.8° and 86.4° were observed for PdCo. Using the Scherrer equation, average particle sizes were estimated at 5.39 nm and 5.21 nm for PdCo and PdNi respectively. No diffraction peaks for cobalt and nickel were observed in the XRD profiles, indicating successful formation of the binary alloys. Sharp and strong peaks for PdNi indicated that the as-synthesized particles have a higher degree of crystallinity. Crystallite size, lattice constants and d-spacing for the most dominant (111) peak are detailed in Table 1.

Table 1.
Lattice parameters for the binary palladium alloys.
3.2. FTIR Analysis
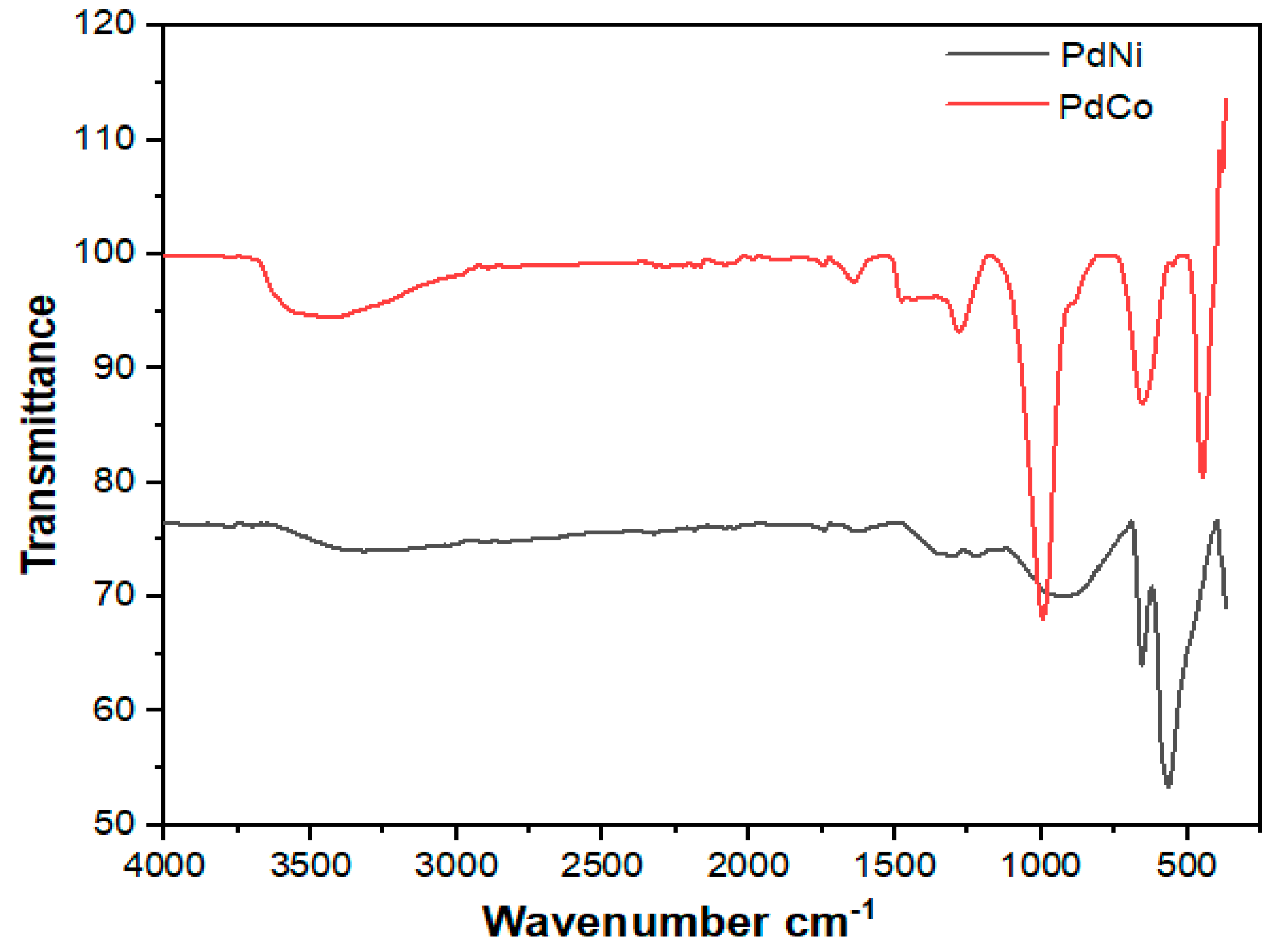
In order to determine the purity of the synthesized binary alloys, thereby identifying whether impurities were present, FTIR analysis was conducted. FTIR produces infrared absorption spectra through which identification of chemical bonds is made. These spectra with distinctive molecular fingerprints can be used to screen and differentiate the existing components. Figure 3 shows the results of the FTIR analysis of the two palladium alloys.
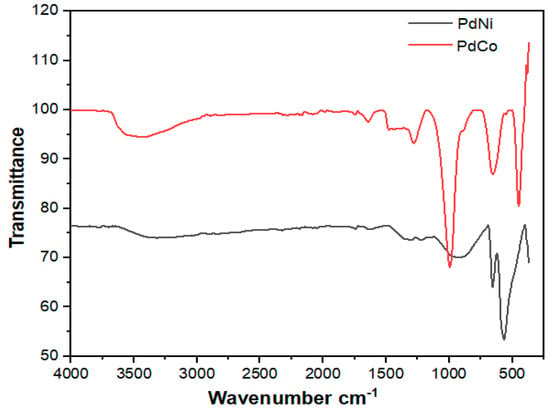
Figure 3.
FTIR spectra for PdNi and PdCo alloys.
The FTIR spectra revealed weak bands of absorption for PdCo with a peak at 3500–3650 cm−1 which are characteristic of stretching vibration of O–H bonds in water adsorbed on the particles. For both alloys PdNi and PdCo the peak at 1500–1550 cm−1 indicated the bending O–H vibrations of water molecules from alcohols. The strong peaks at 1000 cm−1 are characteristic of C–OH stretching in alcohols. Peaks observed at approximately 680 cm−1, 570 cm−1 for PdNi and 682 cm−1 for PdCo are attributed to stretching vibrations of PdO.
3.3. SEM Analysis
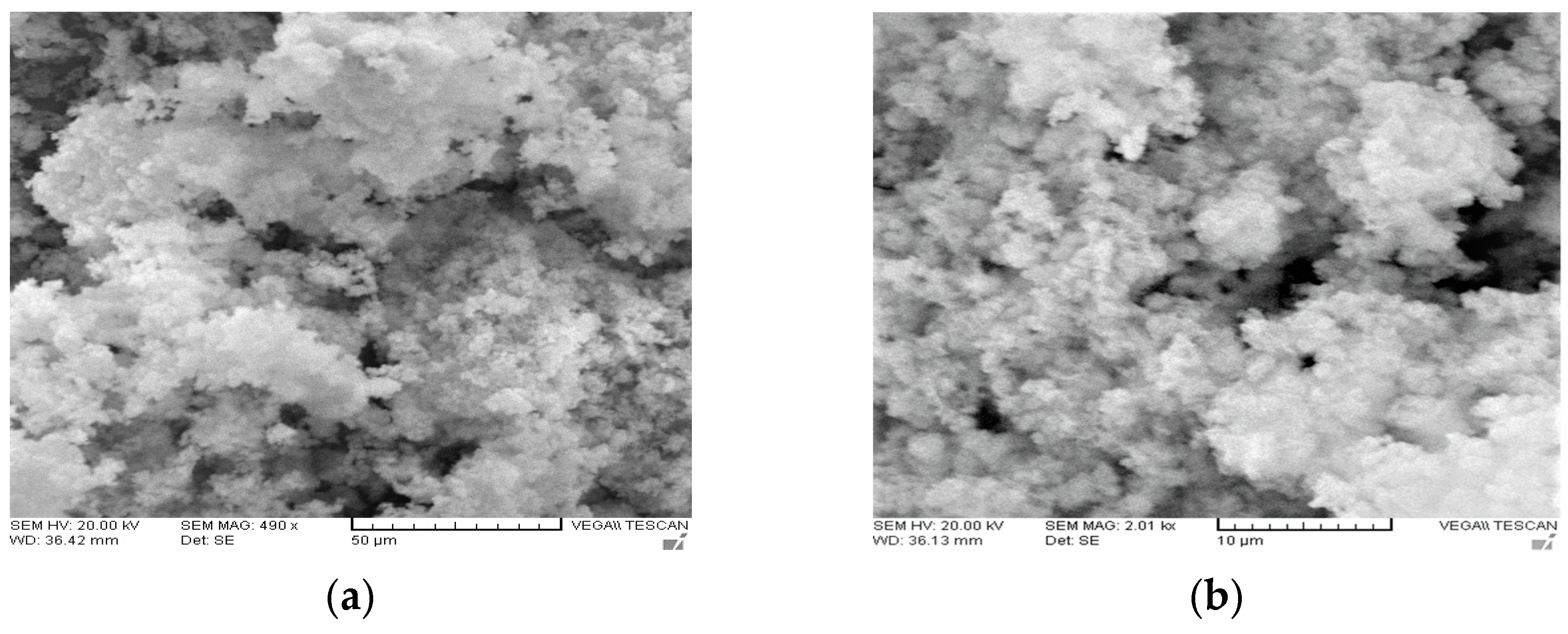
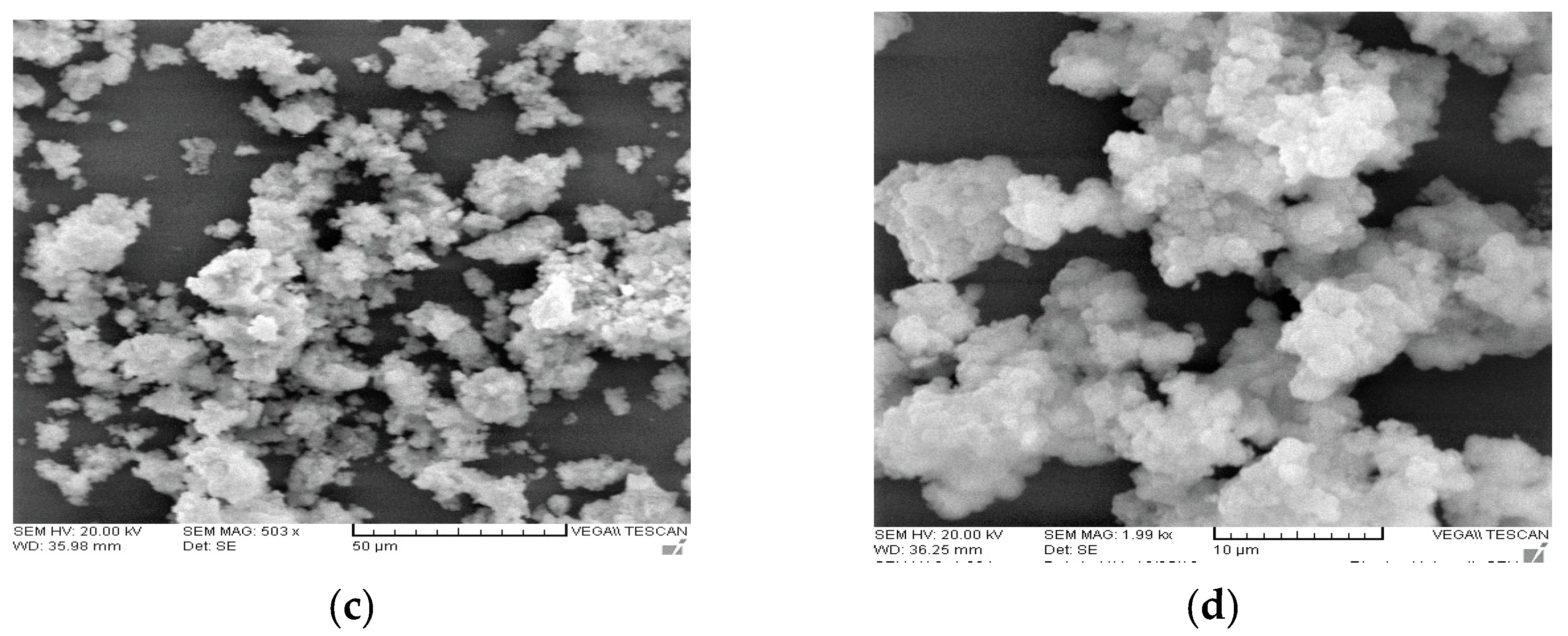
SEM micrographs obtained to establish the morphology of the as-synthesized palladium alloys are depicted in Figure 4a–d. At lower magnifications both samples consisted of irregular spherical aggregates. It is clearly visible that PdCo in Figure 4c,d underwent agglomeration which resulted in its narrow distribution as compared to PdNi which exhibited a wider particle distribution. The irregularity of the alloy particles as well as their wider distribution could be vital for electrolyte adsorption thereby leading to increased catalytic activity in the reduction of the triiodide ion. At higher magnifications the irregularity of the palladium alloy particles is more prominent. Aggregation of palladium alloys could be due to magnetism which results in attraction of aggregates leading to formation of larger particles [18].
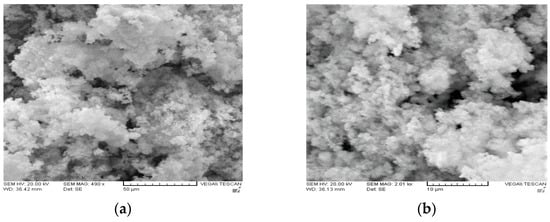

Figure 4.
SEM images of (a,b) PdNi, (c,d) PdCo alloys. Images (a) and (c) were obtained at 50 µm magnification whilst (b) and (d) were obtained at 10 µm.
3.4. Electrochemical Analysis
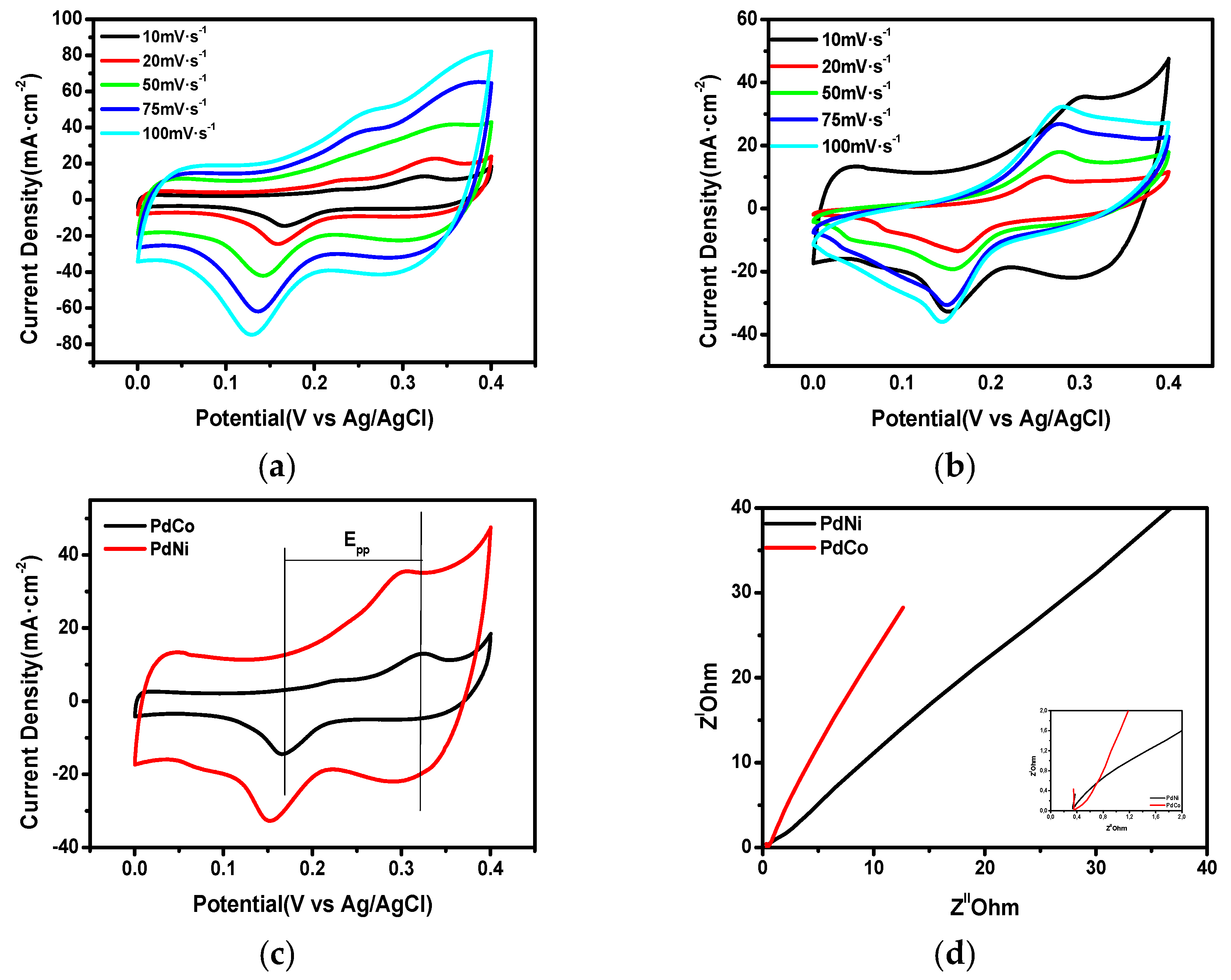
Study of the electrocatalytic capability of the as-synthesized palladium binary alloys was undertaken using cyclic voltammetry analysis (CV), electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) and charge discharge analysis (CD). Electrochemical analysis was conducted using a three electrode system in which the synthesized palladium alloy was the counter electrode, glassy carbon was the reference electrode, and Ag/AgCl was the working electrode. Figure 5a,b show the CV profiles for the two palladium alloys at different scan rates. A pair of redox peaks was observed in the CV curves for both alloys. Two significant parameters obtainable from the CV profiles that are used in evaluating the electrocatalytic capability of the as-synthesized alloys are the peak reduction current density as well as the potential difference between the cathodic and anodic peaks (∆Epp). Since ∆Epp is inversely proportional to the rate of progression of a reaction, its value should be low in order for desirable catalytic activity to be experienced, whereas a high peak reduction current density is required for any meaningful catalytic activity to be observed. Figure 5c shows CV profiles obtained at 50 mV∙s−1 for both alloys, in which PdNi had a higher reduction current density (41 mA∙cm−2) than PdCo (18 mA∙cm−2). Hence, the reduction rate should be expected to proceed at a faster rate when PdNi is used as the catalyst on the counter electrode compared to PdCo. ∆Epp for both palladium alloys confirmed the superiority of PdNi over PdCo. Electrochemical impedance measurements to determine how electron transfer from the outer surface to the electrolyte is hindered or emboldened by the palladium alloys were conducted. Nyquist plots in Figure 5d show the charge transfer resistance (Rct) for the two palladium alloys. Rct for PdNi (0.345 Ω∙cm−2) was smaller than for PdCo (0.372 Ω∙cm−2) indicating that a greater degree of electron conductivity from the outer circuit to the electrolyte would be expected when PdNi is used as the counter electrode. Thus, from the results obtained, the lower charge transfer resistance for PdNi verified its higher catalytic capability. Furthermore, evaluation of the catalytic activity of the as-synthesized alloys through calculation of the standard exchange current density for electrochemical reactions showed that PdNi has greater catalytic qualities.
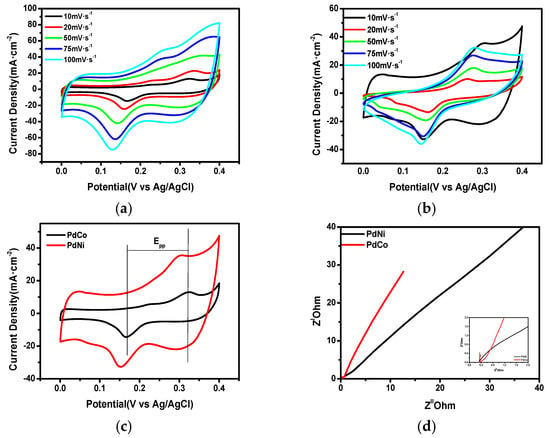
Figure 5.
Cyclic voltammetry analysis (CV) curves of (a) PdNi, (b) PdCo, (c) comparison of CVs of PdNi and PdCo obtained at a scan rate of 10 mV∙s−1, (d) Nyquist plots recorded at 0 V potential for the PdNi and PdCo binary alloys.
Thus, from the low charge transfer resistance for PdNi, superior catalytic capability to PdCo is expected. Furthermore, evaluation of the catalytic activity of the as-synthesized alloys through calculation of the standard exchange current density I0 for electrochemical reactions using Equation (1) shows that PdNi (5.66 × 10−2 mA) had greater catalytic ability and overall was marginally better than PdCo (5.25 × 10−2 mA). A summary of the relevant electrochemical properties for the fabricated binary alloys is detailed in Table 2.
where:
I0 = RT/nFRct,

Table 2.
Electrochemical parameters for the as-synthesized binary palladium alloys.
- R—gas constant in J∙mol−1∙K−1;
- T—Temperature in Kelvins;
- n—number of electrons participating in the reduction reaction;
- F—Faradays constant;
- Rct—Charge transfer resistance.
The results depicted in Table 2 show the electrochemical capability of the binary palladium alloys. Since the main function of the counter electrode catalyst is to facilitate a greater rate of reduction at the counter electrode/electrolyte interface, a well-functioning CE should exhibit a greater reduction current density. PdNi, with a density of 41 mA∙cm2, partook in the requisite reduction reaction with more vigor than PdCo (18 mA∙cm2). Furthermore, since the reduction process at the counter electrode ensures electron availability for dye regeneration, it is vital that the counter electrode catalyst not impede electron transfer in the cell. Table 2 clearly shows that PdNi, with a 0.345 Ω∙cm−2 charge transfer resistance ensured greater electron mobility than PdCo (0.372 Ω∙cm−2).
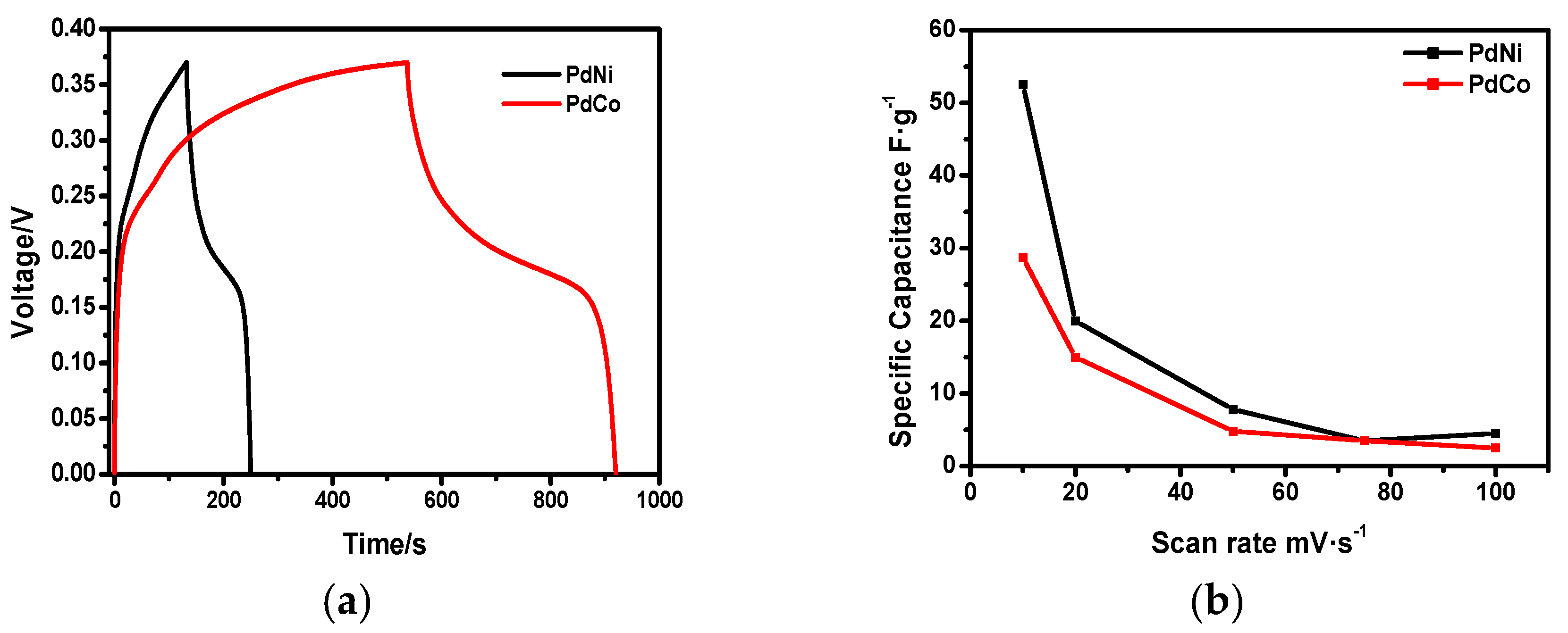
To further understand the electrochemical properties of the developed binary palladium alloys, charge discharge behavior was investigated using amperometry. Results were obtained in a potential range between 0 and 0.4 V in a 6 M KOH solution at a current density of 1 mA∙cm−2. Figure 6a shows the comparison of the CD curves for PdNi and PdCo clearly showing higher electrochemical storage capacity for PdNi highlighted by the larger discharge time over a fixed current density. Figure 6b shows the specific capacity curves for the two binary alloys. Equation (2) was used to calculate the specific capacitance.
where i is the current in the cyclic voltammetry analysis, v is the scan rate and m is the mass of the sample used for electrochemical analysis. Current values at 0.2 V were used for the calculation of specific capacitance. From Figure 6b, specific capacitance decreased as scan rate increased due to slow diffusion of ions from the electrolyte to available sites by absorption. Furthermore, specific capacitance tended to decrease at higher scan rates due to the reduced interaction between the electrolyte and the ions. Figure 6b shows that the specific capacitance of PdNi was higher than that of PdCo, however it decreased at a faster rate than PdCo, which can only be attributed to weaker absorption caused by minimized interaction between electrolyte and ions. Consequently, the stability of the PdNi based capacitor could be of greater concern.
Csp = i/vm,
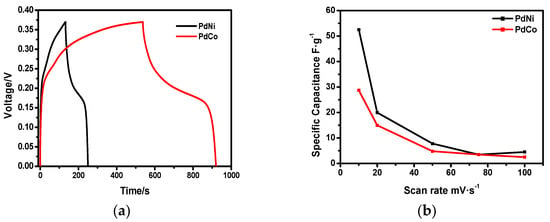
Figure 6.
(a) Galvanostatic charge discharge curves for the binary palladium alloys at 1 Ag−1. (b) Specific capacity as a function of scan rate.
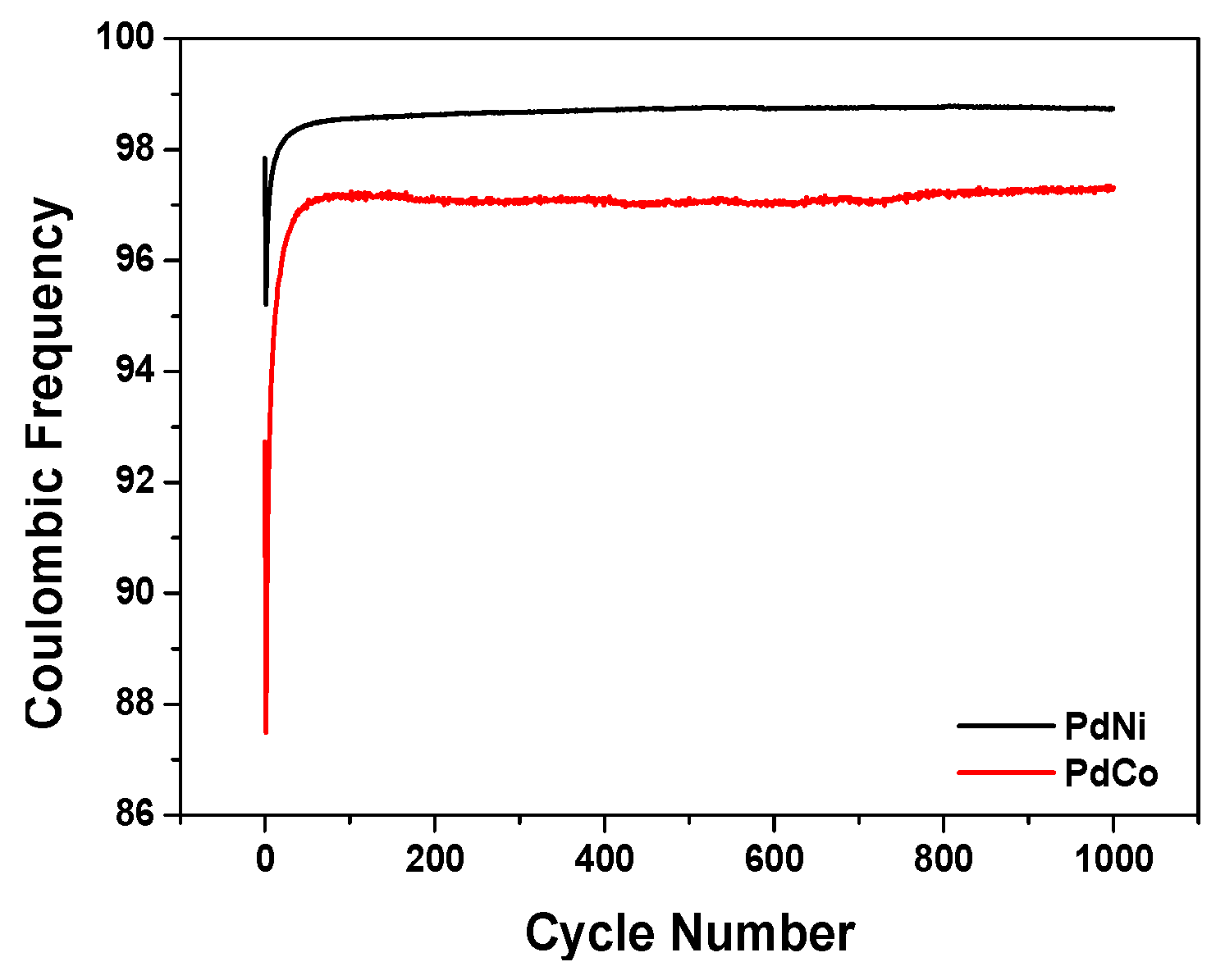
Another valuable parameter used for evaluating the electrochemical capability of the binary palladium alloys for capacitor efficiency is their cycling ability. Figure 7 depicts the coulombic efficiency of the palladium alloys as a function of the cycle number at constant current density. Coulombic efficiency retention after 1000 cycles was 98.7% for PdNi as compared to 97% for PdCo. Both binary palladium alloys exhibited high retention capacity although PdNi performed better than PdCo. Resultantly, this research has shown that binary palladium alloys could function very well in electrochemical capacitors.
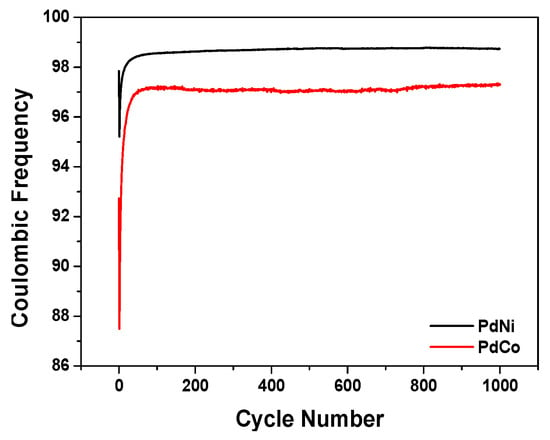
Figure 7.
Coulombic efficiency over 1000 cycles for PdNi and PdCo respectively.
4. Conclusions
In conclusion, binary palladium alloys PdNi and PdCo were successfully synthesized using a hydrothermal process. Particle size of the as-synthesized palladium alloys were determined to be 5.39 and 5.21 nm for PdNi and PdCo respectively. XRD analysis revealed the existence of only palladium peaks at 40.1°, 46°, 63°, and 82°. FTIR analysis revealed the presence of water molecules in PdNi and PdCo as well as traces of PdO which could potentially impact its catalytic ability. SEM analysis showed that both palladium alloys were composed of spherical particles with PdCo undergoing agglomeration whereas PdNi particles exhibit greater distribution and coverage. Reduction current density from CV analysis showed that PdNi has greater catalytic activity than PdCo. Resultantly, PdNi offers lower impedance to electron transfer as illustrated by a lower charge transfer resistance of 0.345 Ω∙cm−2 compared to 0.372 Ω∙cm−2 for PdCo. The high reduction current density and low charge transfer resistance for PdNi compared to PdCo indicate that it is a better catalyst for use in counter electrodes. The existence of impurities in PdCo could potentially have impacted its catalytic capability. Electrochemical analysis of the two samples also revealed high specific capacitances of 68 and 27 F∙g−1 for PdNi and PdCo respectively. Coulombic efficiency retention rates after 1000 cycles were 98.7% and 97% for PdNi and PdCo respectively. The capacitance values show that at the present moment the two alloys would not be ideal for use in capacitors although they exhibit good stability. Although the capacitance values are low PdNi and PdCo could potentially be attractive for hybrid electrochemical capacitors where higher specific capacitances and working voltages could be realized due to charge accumulation from the faradic redox process.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.Z. and D.M.; writing—review and editing, N.Z. and D.M.; visualization, R.T.; supervision, R.T.; funding acquisition, E.M.
Funding
This research was funded by South African National Research Foundation (NRF) and the South African Department of Science and Technology (DST). We also extend our sincere gratitude to the Govan Mbeki Research and Development Centre (GMRDC) at the University of Fort Hare for their support.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful for financial support from our sponsors South African National Research Foundation (NRF), Department of Science & Technology (DST), Eskom tertiary education support (TESP), and Govan Mbeki Research & Development Centre (GMRDC) of the University of Fort Hare.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Islam, M.T.; Shahir, S.A.; Uddin, T.M.I.; Saifullah, A.Z.A. Current energy scenario and future prospect of renewable energy in Bangladesh. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 39, 1074–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Tang, Q. Robust counter electrodes from nanoporous NiM(M = Pt, Pd) alloys for dye-sensitized solar cells. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 182, 827–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, C.C.; Prasanth, R. A critical review of recent developments in nanomaterials for photoelectrodes in dye sensitized solar cells. J. Power Sources 2016, 317, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Wei, A.; Liu, J.; Liu, Z.; Xiao, Z.; Zhao, Y. NiCo2S4 nanosheet thin film counter electrodes prepared by a two-step approach for dye-sensitized solar cells. Mater. Lett. 2018, 217, 185–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Duan, J.; Duan, Y.; Yuan, H.; Tang, Q. 9.07%-Efficiency dye-sensitized solar cell from Pt-free RuCoSe ternary alloy counter electrode. Mater. Lett. 2018, 218, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutraleeswaran, M.; Venkatachalam, M.; Saroja, M.; Gowthaman, P.; Shankar, S. Dye sensitized solar cells-A Review. J. Adv. Res. Appl. Sci. 2017, 4, 26–38. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, S.; Deepak, T.G.; Anjusree, G.S.; Arun, T.A.; Nair, S.V.; Nair, A.S. A review on counter electrode materials in dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 4474–4490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Deng, K.; Li, L. Pt-free and efficient counter electrode with nanostructured CoNi2S4 for dye-sensitized solar cells. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mozaffari, S.; Nateghi, M.R.; Zarandi, M.B. An overview of the Challenges in the commercialization of dye sensitized solar cells. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 71, 675–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Qi, T.; Zhang, Y.C.; Shi, H.Y.; Tian, J.Q. Fabrication and characterization of a multi-walled carbon nanotube-based counter electrode for dye-sensitized solar cells. New Carbon Mater. 2015, 30, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Shao, L.L. Review on the recent progress of carbon counter electrodes for dye-sensitized solar cells. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 304, 629–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Han, Q.; Wu, M. Review on transition metal compounds based counter electrode for dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Energy Chem. 2018, 27, 703–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Gao, Y.; Ge, S. Alloyed PtNi counter electrodes for high-performance dye-sensitized solar cell applications. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 725, 1272–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Tang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Yu, L. Counter electrode electrocatalysts from binary Pd–Co alloy nanoparticles for dye-sensitized solar cells. Sol. Energy 2016, 124, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalsamy, K.; Balamurugan, J.; Thanh, T.D.; Kim, N.H.; Hui, D.; Lee, J.H. Surfactant-free synthesis of NiPd nanoalloy/graphene bifunctional nanocomposite for fuel cell. Compos. Part B Eng. 2017, 114, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Chang, Q.; Chen, H.; Shaw, M. Recent advances in palladium based electrocatalysts for fuel cell rections and hydrogen evolution reaction. Nano Energy 2016, 29, 198–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Feng, H.; Wu, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, A.; Xia, T.; Li, X.; Zhang, L. Progress of electrochemical capacitor electrode materials: A review. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2009, 34, 4889–4899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, K.; Kosseva, M. Nanoparticle aggregation influenced by magnetic fields. Colloids Surf. A 2006, 286, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).