Quantitative Analysis of Microstructure Evolution in Hot-Rolled Multiphase Steel Subjected to Interrupted Tensile Test
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Material
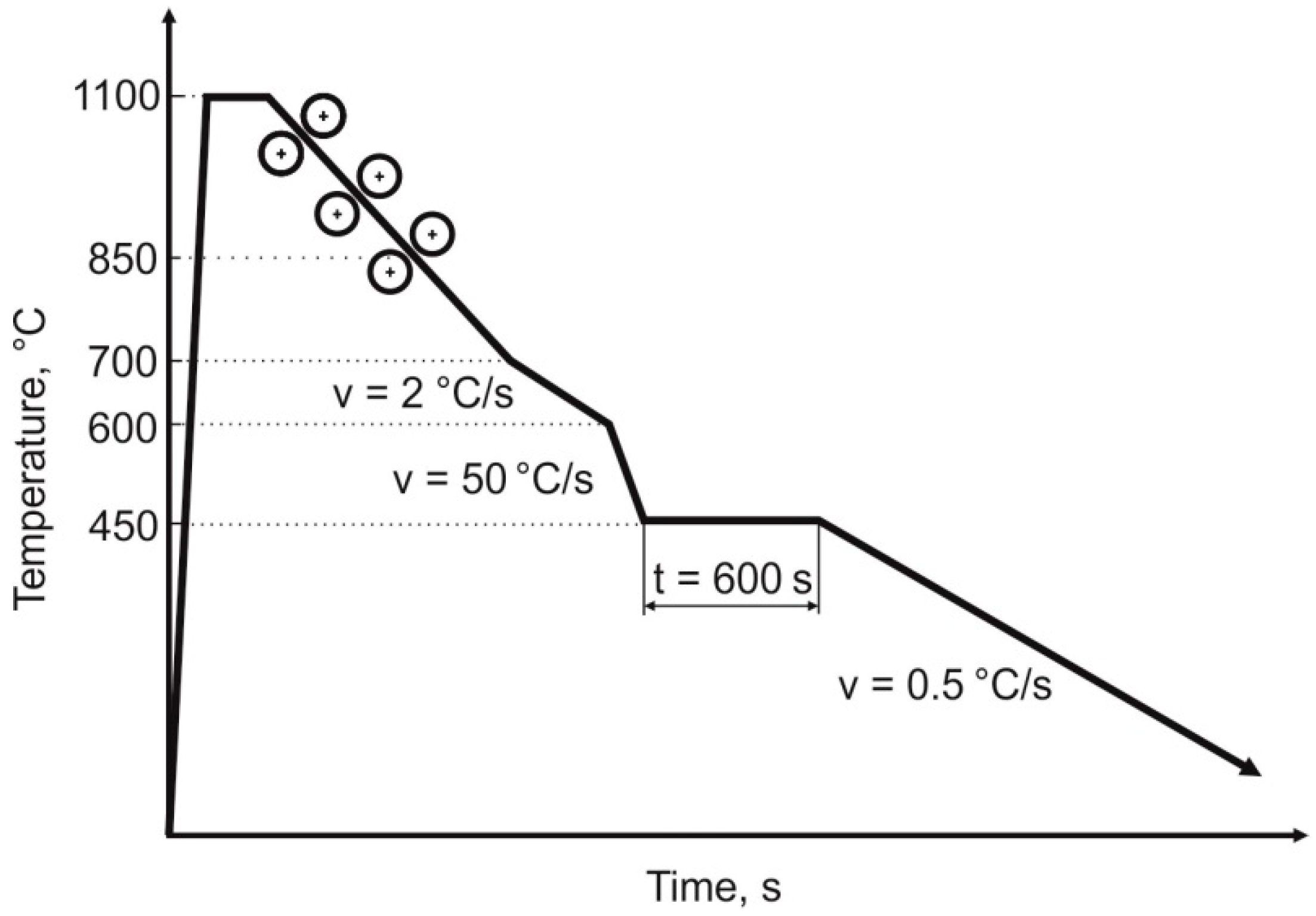
2.2. Description of Experimental Methods
3. Results
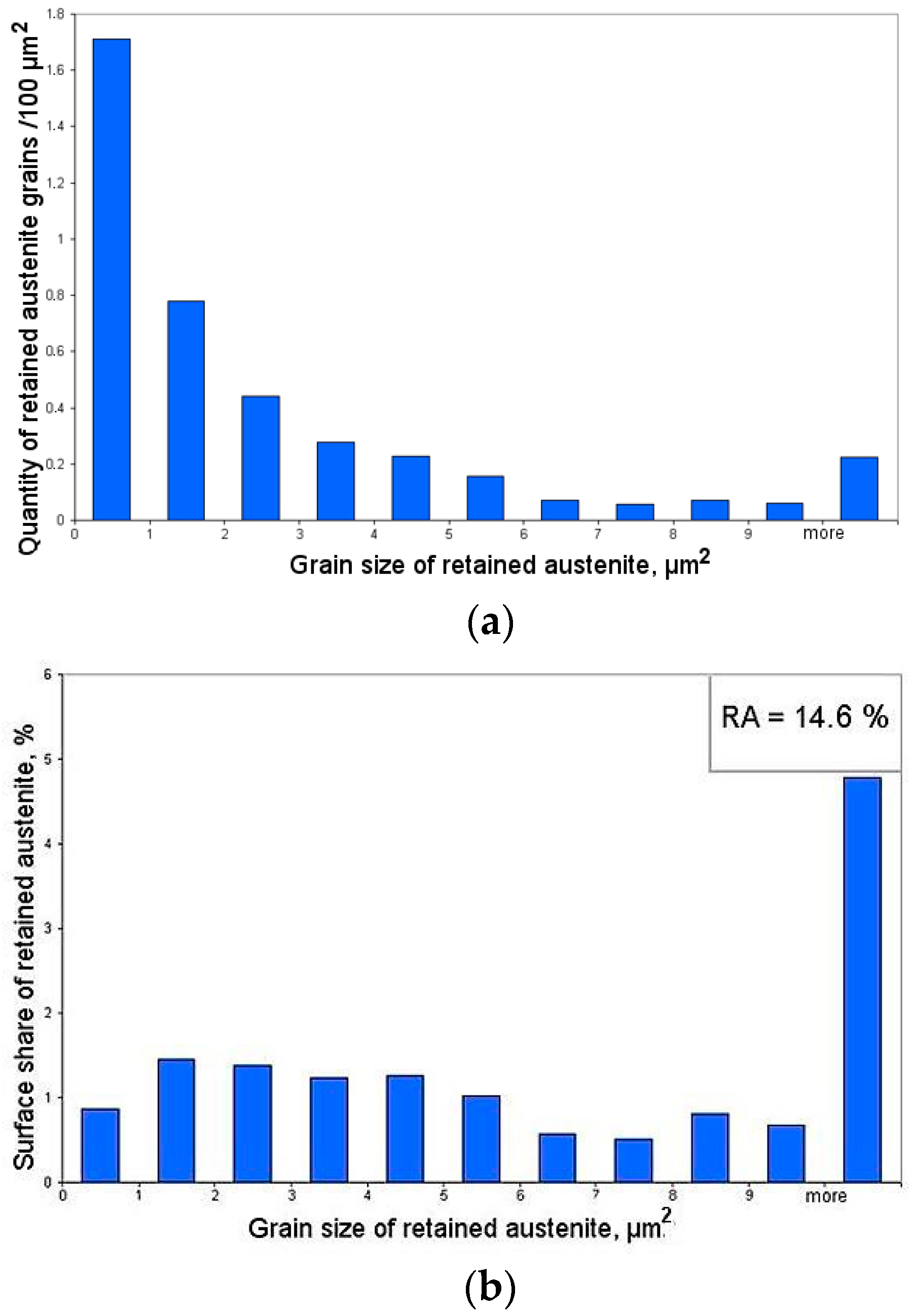
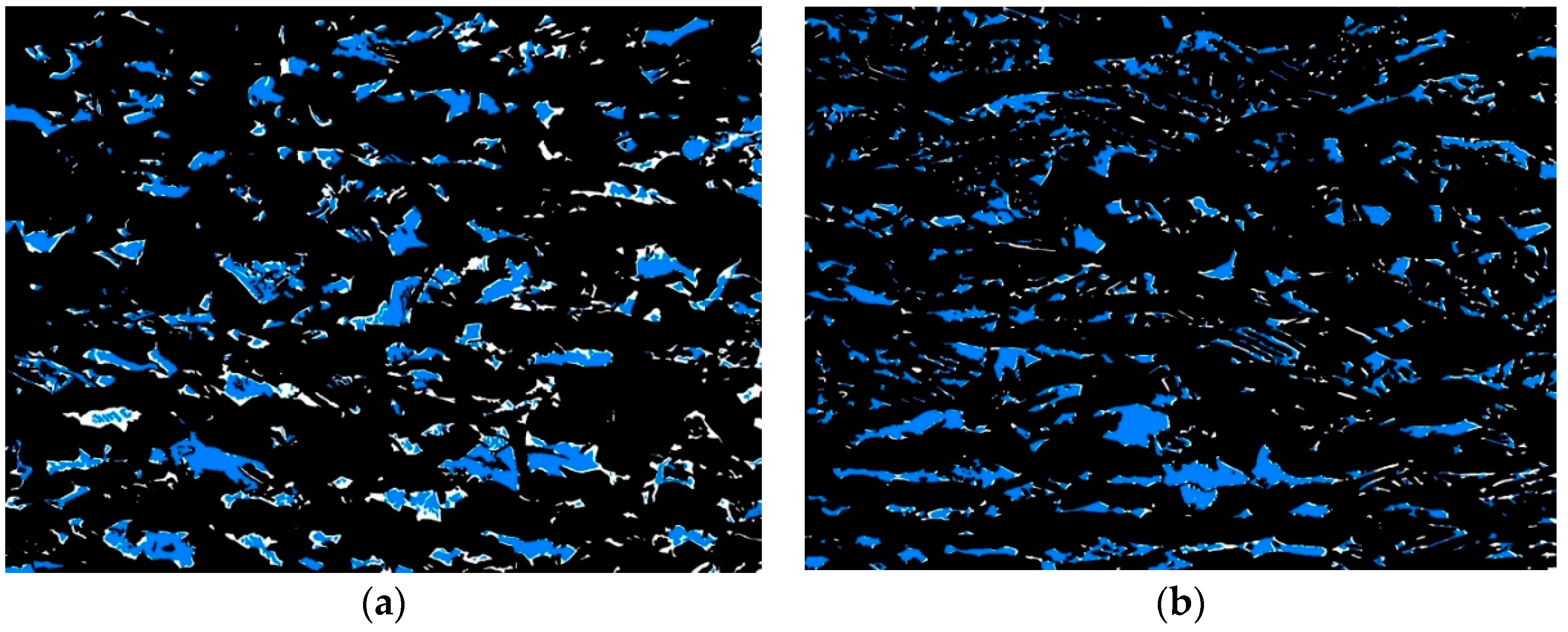
3.1. Initial Microstructure
3.2. Interrupted Tensile Test
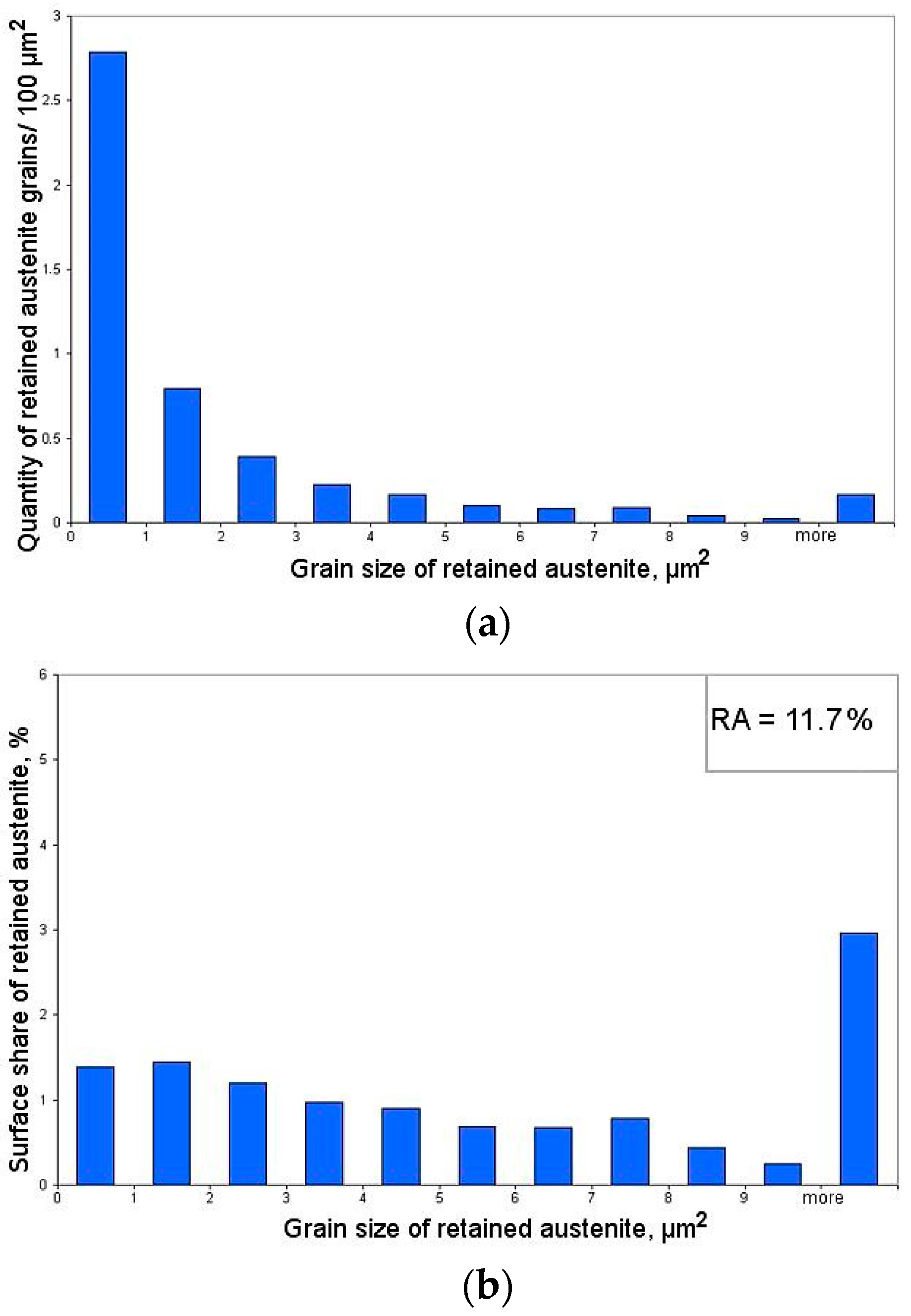
3.2.1. Sample Deformed to 5% Strain
3.2.2. Sample Deformed to 10% Strain
3.2.3. Sample Deformed to 15% Strain and to the Rupture
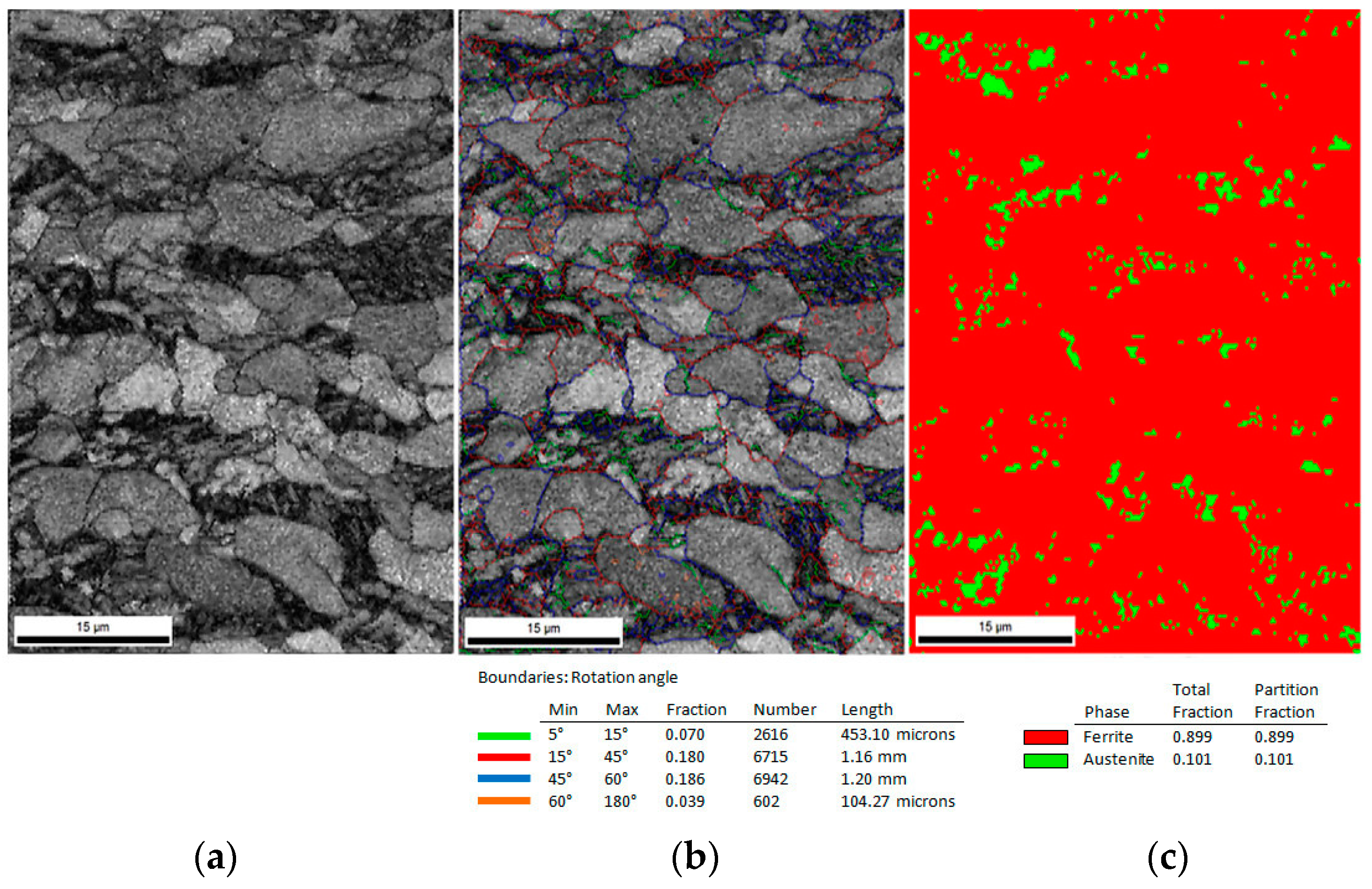
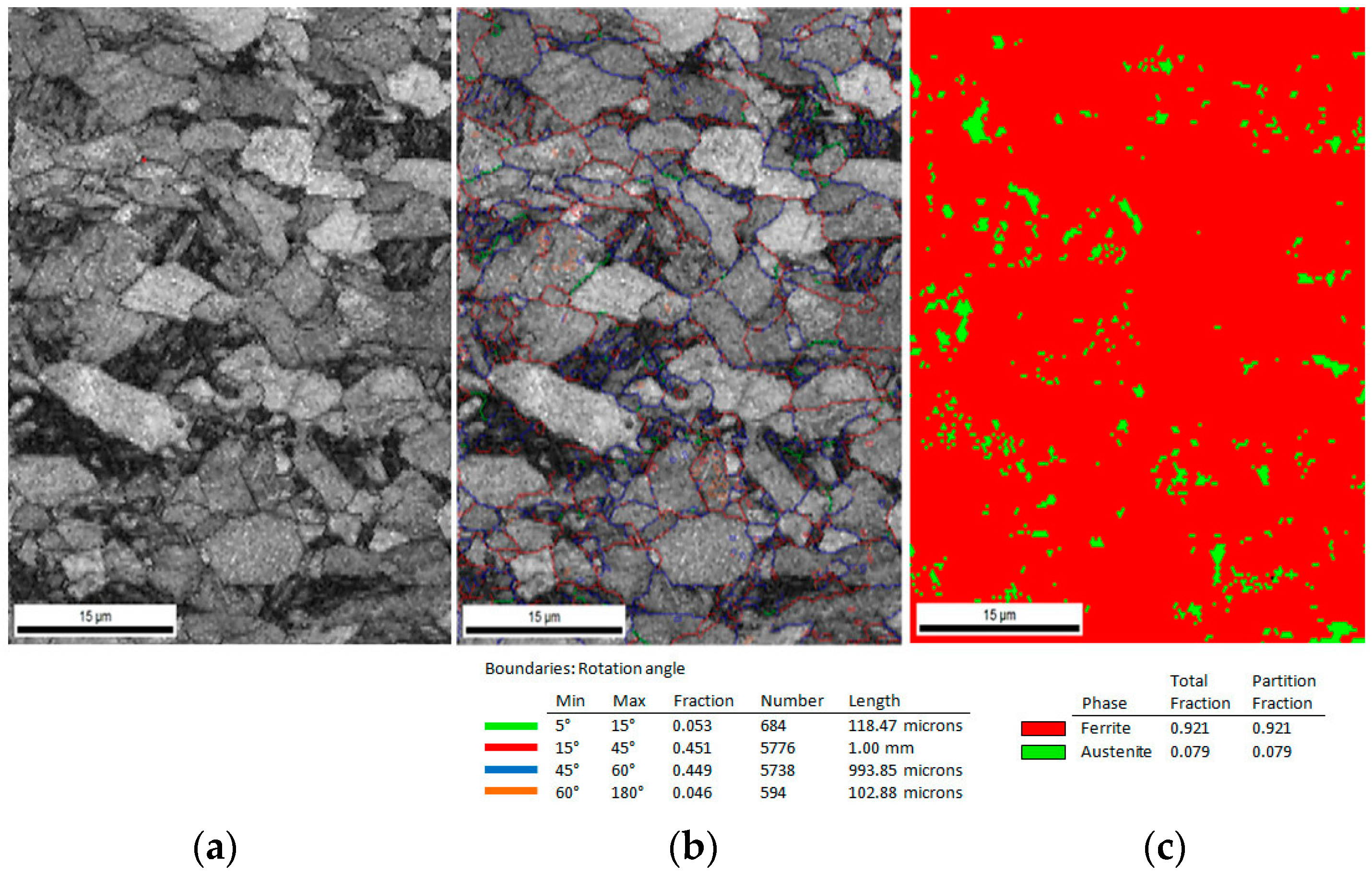
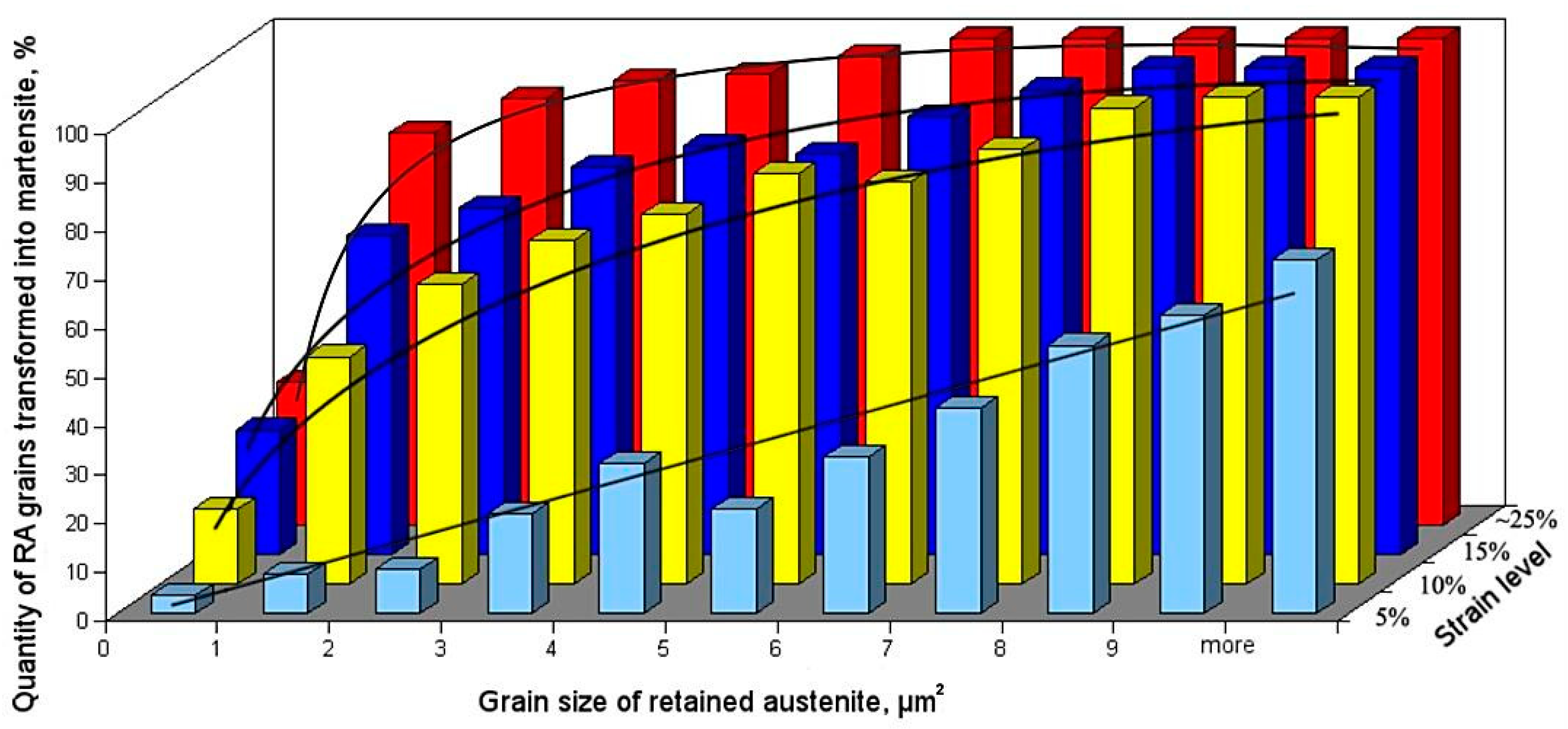
3.3. Electron Backscatter Diffraction (EBSD) Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
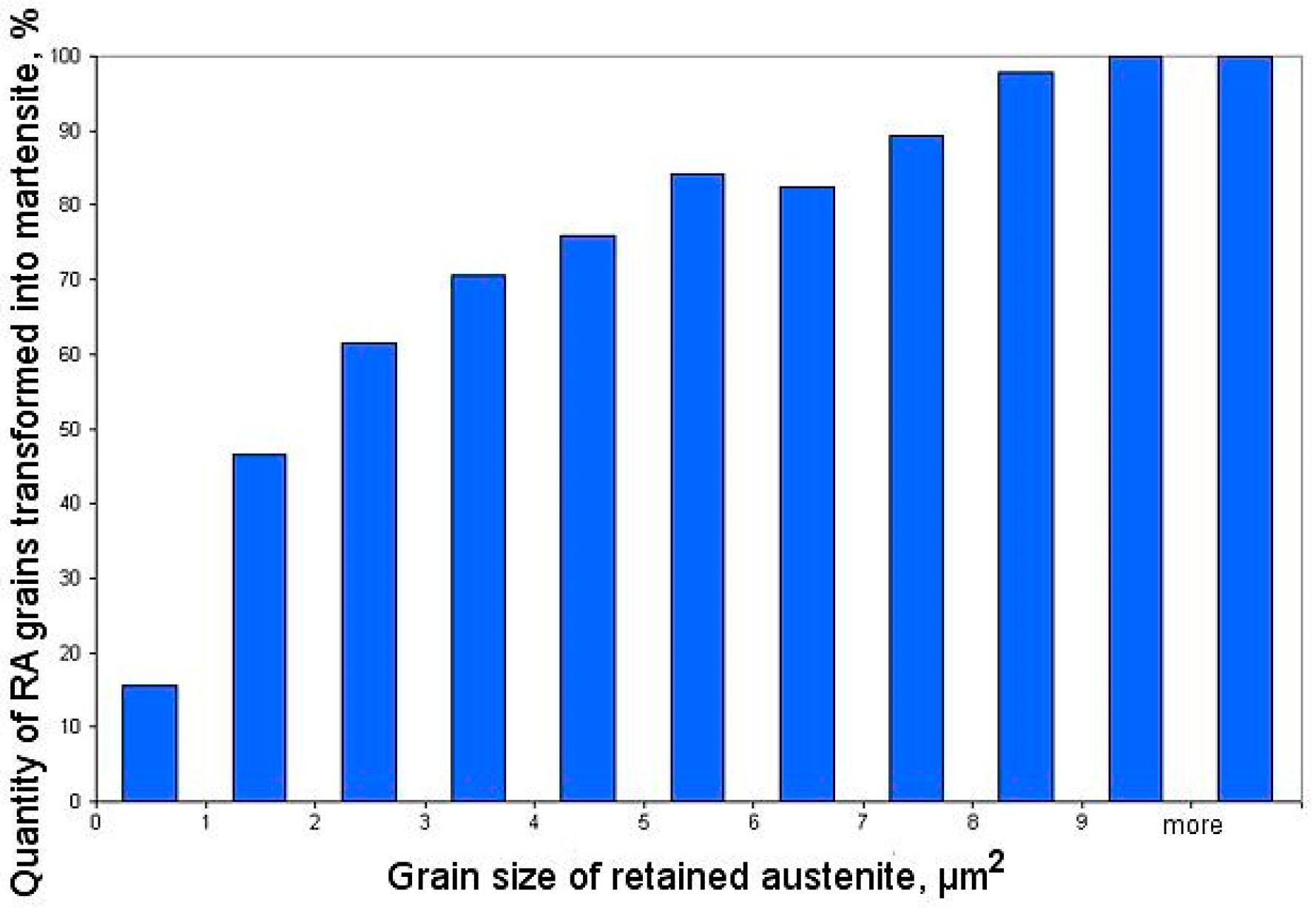
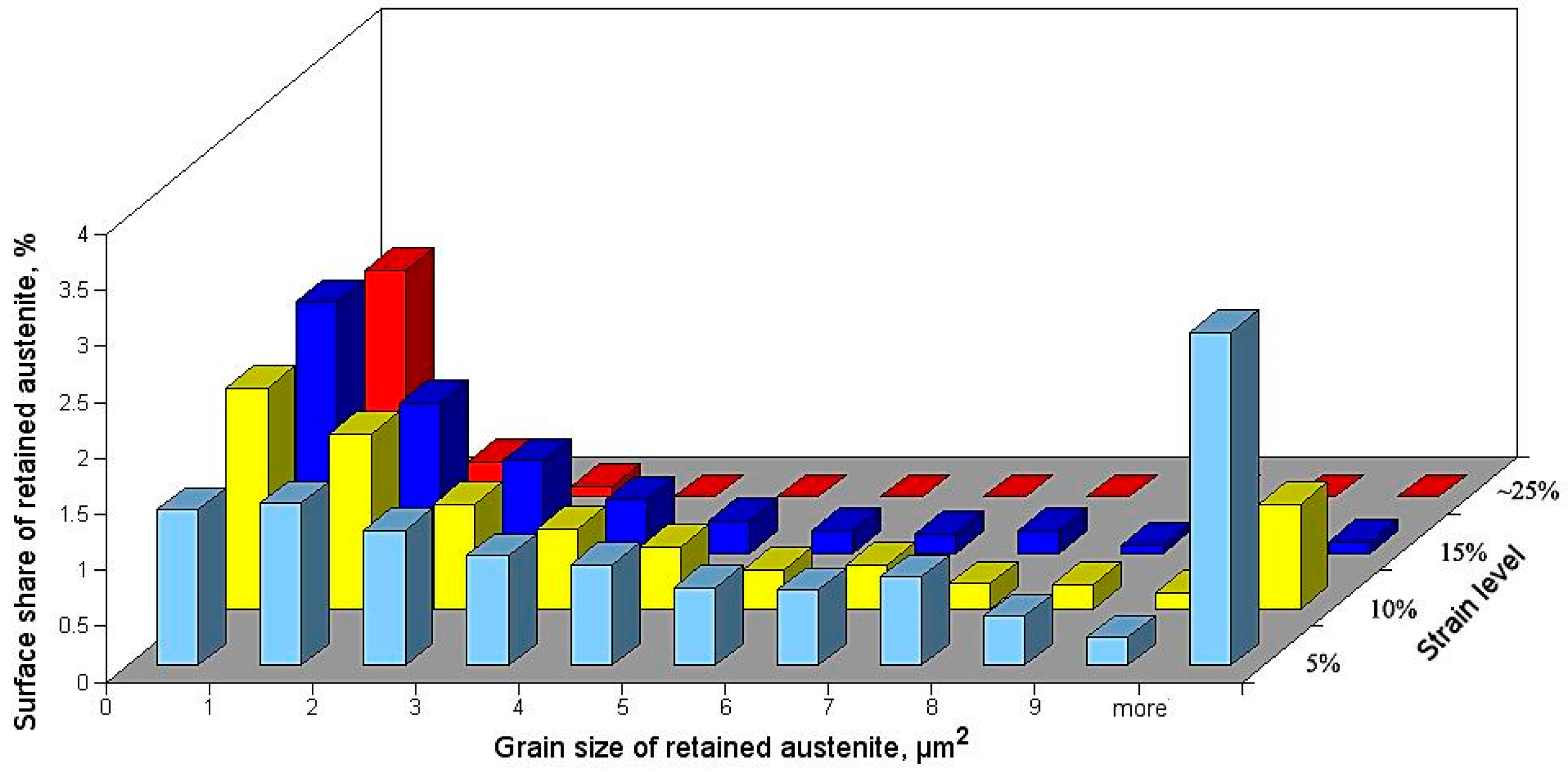
- Martensitic transformation began in the central area of large blocky-type austenitic grains located in the ferritic matrix. As the deformation level increased the intensity of martensitic transformation decreased due to the lower amount of large austenite grains.
- A size of austenite grains which transformed into martensite decreased when deformation level was increasing.
- An amount of small austenitic grains increased along with the deformation level due to the fragmentation of large austenitic grains by newly-formed martensite. The corresponding fractions of low-angle and high-angle boundaries were a synergistic effect of the dislocation increase due to straining and new boundaries formed by strain-induced martensite formation.
- Austenitic grains smaller than 1 μm2 and thin layers showed the highest mechanical stability. It was due to their high mechanical stability related to the relatively high carbon content.
- An amount of retained austenite detected in the specimen at the initial state was ca. 14%. Specimens deformed up to rupture possessed ca. 2.5% of RA (i.e., ~17% of untransformed retained austenite).
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Streicher-Clarke, A.M.; Speer, J.G.; Matlock, D.K.; De Cooman, B.C.; Williamson, D.L. Analysis of lattice parameter changes following deformation of a 0.19C-1.63Si-1.59Mn Transformation-Induced Plasticity sheet steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2005, 36, 907–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suliga, M.; Muskalski, Z.; Wiewiorowska, S. The influence of drawing speed on fatigue strength TRIP steel wires. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2009, 9, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, J.; Tonegawa, H.; Sugimoto, K. Cold formability of 22SiMnCrB TRIP-aided martensitic sheet steel. Proc. Eng. 2014, 81, 1336–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Krizan, D.; De Cooman, B.C. Analysis of the strain-induced martensitic transformation of retained austenite in cold rolled micro-alloyed TRIP steel. Steel Res. Int. 2008, 79, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samek, L.; De Moor, E.; Penning, J.; De Cooman, B.C. Influence of alloying elements on the kinetics of strain-induced martensitic nucleation in low-alloy, multiphase high-strength steels. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2006, 37, 109–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haidemenopoulos, G.N.; Aravas, N.; Bellas, I. Kinetics of strain-induced transformation of dispersed austenite in low-alloy TRIP steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 615, 416–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaar, S.; Krizan, D.; Schwabe, J.; Hofmann, H.; Hebesberger, T.; Commenda, C.; Samek, L. Influence of the Al and Mn content on the structure-property relationship in density reduced TRIP-assisted sheet steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 735, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucerova, L.; Bystriansky, M. Comparison of thermo-mechanical treatment of C-Mn-Si-Nb and C-Mn-Si-Al-Nb TRIP steels. Proc. Eng. 2017, 207, 1856–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.S.; Han, J.C.; Lim, N.S.; Seol, J.B.; Park, C.G. Nano-scale observation on the transformation behavior and mechanical stability of individual retained austenite in CMnSiAl TRIP steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 627, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabłońska, M.B.; Śmiglewicz, A.; Niewielski, G. The effect of strain rate on the mechanical properties and microstructure of the high-Mn steel after dynamic deformation tests. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2015, 60, 577–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, K.; Usui, N.; Kobayashi, M.; Hashimoto, S. Effects of volume fraction and stability of retained austenite on ductility of TRIP-aided dual-phase steels. ISIJ Int. 1992, 32, 1311–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Cooman, B.C. Structure—Properties relationship in TRIP steels containing carbide-free bainite. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2004, 8, 285–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacques, P.J.; Girault, E.; Catlin, T.; Geerlofs, N.; Kop, T.; Van der Zwaag, S.; Delannay, F. Bainite transformation of low carbon Mn-Si TRIP-assisted multiphase steels: Influence of silicon content on cementite precipitation and austenite retention. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1999, 273, 475–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girault, E.; Mertens, A.; Jacques, P.; Hubaert, Y.; Verlinden, B.; Van Humbeeck, J. Comparison of the effect of silicon and aluminium on the tensile behavior of multiphase TRIP-assisted steels. Scr. Mater. 2001, 44, 885–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grajcar, A.; Radwanski, K. Microstructural comparison of the thermomechanically treated and cold deformed Nb-microalloyed TRIP steel. Mater. Tehnol. 2014, 48, 679–683. [Google Scholar]
- Javaheria, V.; Khodaie, N.; Kaijalainen, A.; Porter, D. Effect of niobium and phase transformation temperature on the microstructure and texture of a novel 0.40% C thermomechanically processed steel. Mater. Charact. 2018, 124, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opiela, M.; Grajcar, A. Hot deformation behavior and softening kinetics of Ti-V-B microalloyed steels. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2012, 12, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Ding, H.; Tang, Z.Y.; Zhang, J. Effect of isothermal bainitic processing on microstructures and mechanical properties of novel Mo and Nb microalloyed TRIP steel. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2015, 42, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hausmann, K.; Krizan, D.; Spiradek-Hahn, K.; Pichler, A.; Werner, E. The influence of Nb on transformation behavior and mechanical properties of TRIP-assisted bainitic–ferritic sheet steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 588, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereloma, E.V.; Timokhina, I.B.; Hodgson, P.D. Transformation behaviour in thermomechanically processed C-Mn-Si TRIP steels with and without Nb. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1999, 273–275, 448–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kammouni, A.; Saikaly, W.; Dumont, M.; Marteaud, C.; Banod, X.; Charai, A. Effect of the bainitic transformation temperature on retained austenite fraction and stability in Ti microalloyed TRIP steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2009, 518, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sozańska-Jędrasik, L.; Mazurkiewicz, J.; Borek, W.; Matus, K. Carbides analysis of the high strength and low density Fe-Mn-Al-Si steels. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2018, 63, 265–276. [Google Scholar]
- Gorka, J.; Opiela, M. Structure and properties of high-strength low-alloy steel melted by the laser beam. Mater. Perform. Charact. 2019, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorka, J.; Janicki, D.; Fidali, M.; Jamrozik, W. Thermographic assessment of the HAZ properties and structure of thermomechanically treated steel. Int. J. Thermophys. 2017, 38, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grajcar, A.; Grzegorczyk, B.; Różański, M.; Stano, S. Microstructural aspects of bifocal laser welding of TRIP steels. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2017, 62, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.Y.; Huang, J.N.; Ding, H.; Cai, Z.H.; Misra, R.D.K. Austenite stability and mechanical properties of a low-alloyed ECAPed TRIP-aided steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 724, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.D.; Huang, B.X.; Rong, Y.H.; Wang, L. Microstructures and stability of retained austenite in TRIP steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 438–440, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Ding, H.; Ding, H.; Cal, M.; Du, L. Effect of prestrain on microstructures and properties of Si-AI-Mn TRIP steel sheet with niobium. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2010, 17, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Findley, K.O. Quantitative assessment of the effects of microstructure on the stability of retained austenite in TRIP steels. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 1895–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Ghosh, M.; Tarafder, S.; Sivaprasad, S.; Chakrabarti, D. Micromechanisms of deformation in dual phase steels at high strain rates. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 680, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Zhang, B.; Cheng, C.; Zhao, P.; Zhang, H.; Bai, B. Very high cycle fatigue behaviors of bainite/martensite multiphase steel treated by quenching-partitioning-tempering process. Int. J. Fatigue 2016, 92, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.F.; Qiu, L.N.; Sun, X.; Zuo, L.; Liaw, P.K.; Raabe, D. Effects of retained austenite volume fraction, morphology, and carbon content on strength and ductility of nanostructured TRIP-assisted steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 636, 551–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Qian, L.; Tan, J.; Meng, J.; Zhang, F. Inconsistent effects of mechanical stability of retained austenite on ductility and toughness of transformation-induced plasticity steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 578, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Hu, Z.; Zou, Y.; Tan, X.; Han, D.; Chen, S.; Ma, D.; Misra, R.D.K. Effect of two-step intercritical annealing on microstructure and mechanical properties of hot-rolled medium manganese TRIP steel containing δ-ferrite. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 688, 40–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, K.; Misu, M.; Kobayashi, M.; Shirasawa, H. Effects of second phase morphology on retained austenite morphology and tensile properties in a TRIP-aided dual phase steel sheet. ISIJ Int. 1993, 33, 775–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timokhina, I.; Hodgson, P.; Pereloma, E.V. Effect of microstructure on the stability of retained austenite in transformation-induced-plasticity steels. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2004, 35, 2331–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereloma, E.V.; Gazder, A.A.; Timokhina, I.B. Retained austenite: Transformation-Induced Plasticity. In Encyclopedia of Iron, Steel, and Their Alloys; Taylor and Francis: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 3088–3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grajcar, A.; Krztoń, H. Effect of isothermal bainitic transformation temperature on retained austenite fraction in C-Mn-Si-Al-Nb-Ti TRIP-type steel. J. Achiev. Mater. Manuf. Eng. 2009, 35, 169–176. [Google Scholar]
- Jimenez-Melero, E.; Van Dijk, N.; Zhao, L.; Sietsma, J.; Offerman, S. Characterization of individual retained austenite grains and their stability in low-alloyed TRIP steels. Scr. Mater. 2007, 55, 6713–6723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| C | Mn | Si | Al | Nb | Ti | P | S | N | O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.24 | 1.55 | 0.87 | 0.40 | 0.034 | 0.023 | 0.010 | 0.004 | 0.0028 | 0.0006 |
| Strain Level, % | Amount of RA (Image Analysis),% | Standard Deviation, % | Amount of RA (EBSD Method), % |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 14.6 | 1.3 | 13.8 |
| 5 | 11.7 | 1.2 | 10.9 |
| 10 | 8.0 | 1.2 | 7.9 |
| 15 | 6.0 | 1.0 | 5.8 |
| 25 | 2.4 | 0.8 | 3.9 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grajcar, A.; Kozłowska, A.; Radwański, K.; Skowronek, A. Quantitative Analysis of Microstructure Evolution in Hot-Rolled Multiphase Steel Subjected to Interrupted Tensile Test. Metals 2019, 9, 1304. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9121304
Grajcar A, Kozłowska A, Radwański K, Skowronek A. Quantitative Analysis of Microstructure Evolution in Hot-Rolled Multiphase Steel Subjected to Interrupted Tensile Test. Metals. 2019; 9(12):1304. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9121304
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrajcar, Adam, Aleksandra Kozłowska, Krzysztof Radwański, and Adam Skowronek. 2019. "Quantitative Analysis of Microstructure Evolution in Hot-Rolled Multiphase Steel Subjected to Interrupted Tensile Test" Metals 9, no. 12: 1304. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9121304
APA StyleGrajcar, A., Kozłowska, A., Radwański, K., & Skowronek, A. (2019). Quantitative Analysis of Microstructure Evolution in Hot-Rolled Multiphase Steel Subjected to Interrupted Tensile Test. Metals, 9(12), 1304. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9121304






