Effect of Hybrid Reinforcements on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Ti-5Al-5Mo-5V-Fe-Cr Titanium Alloy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedure
3. Results and Discussion
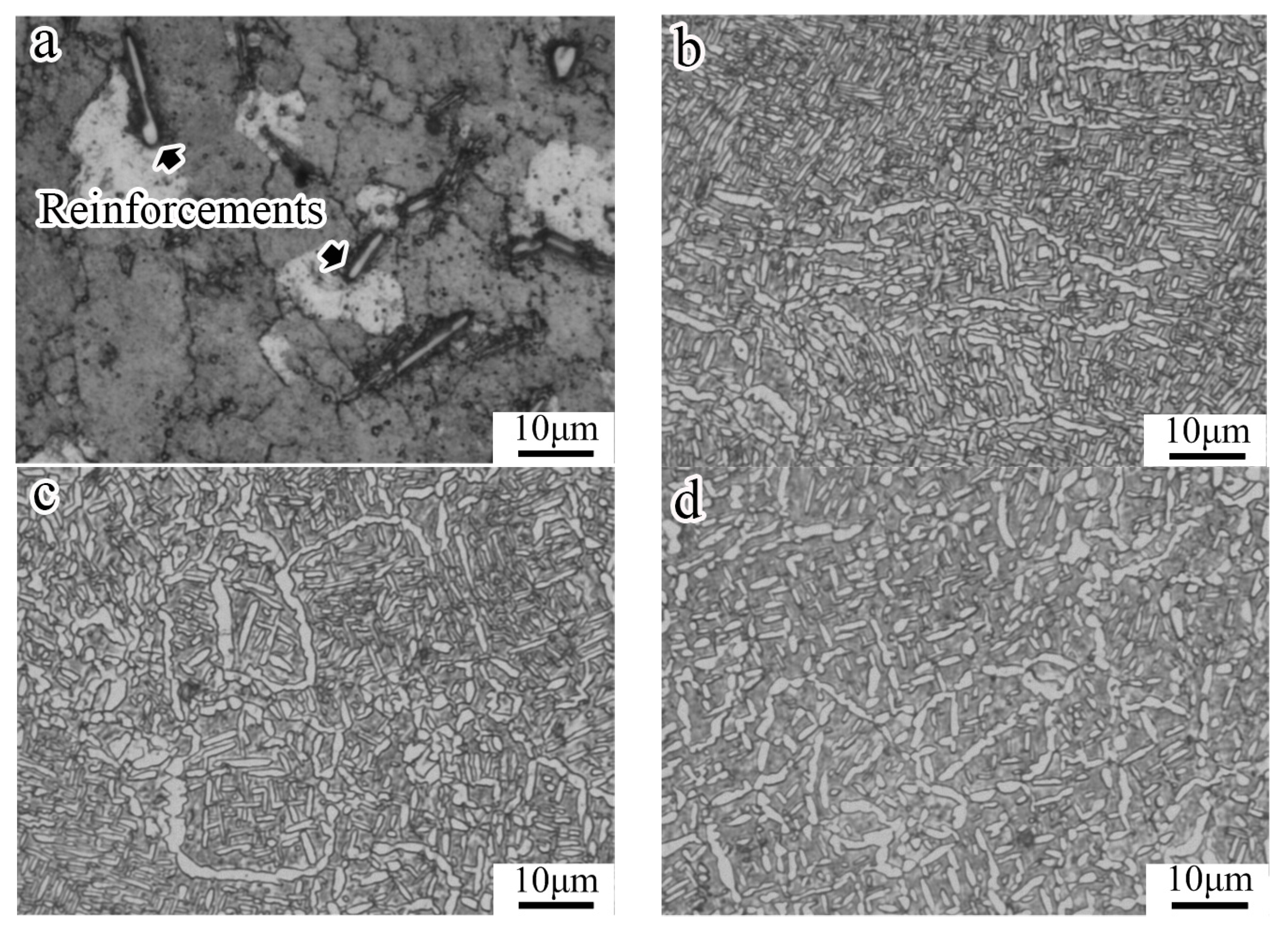
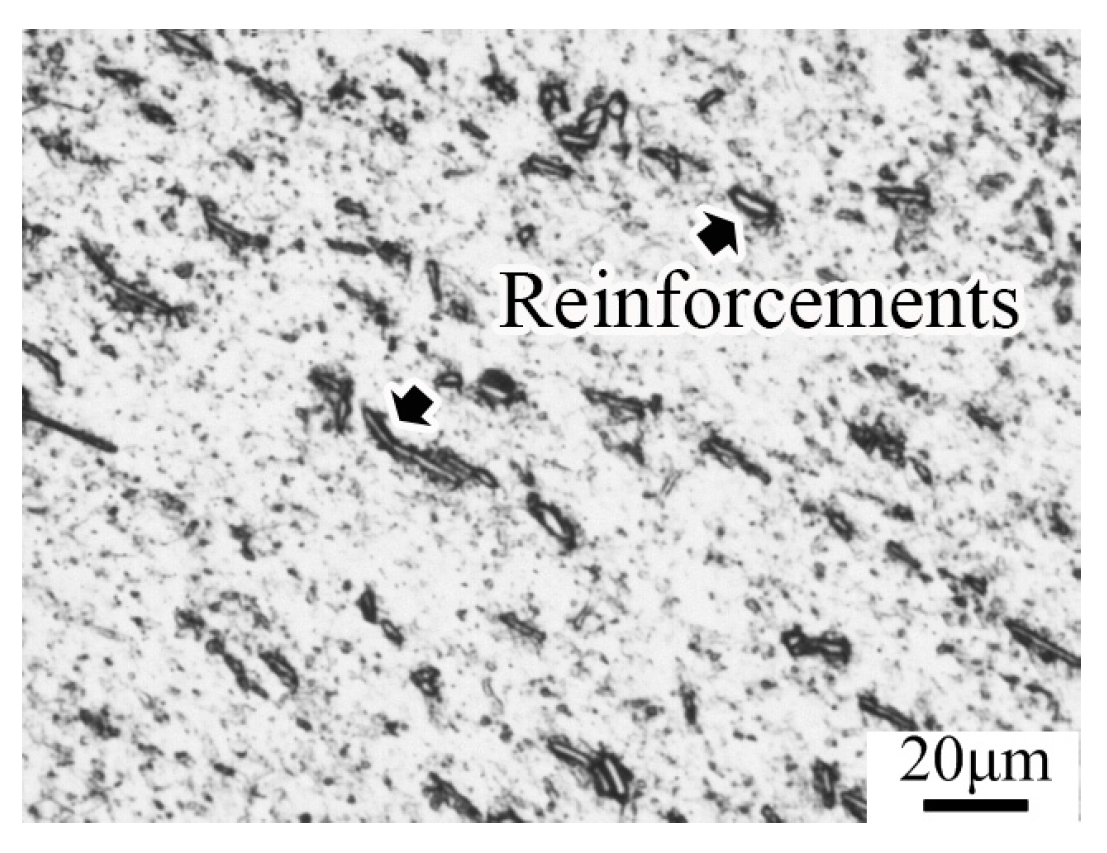
3.1. Microstructure of the Materials after Heat Treatment
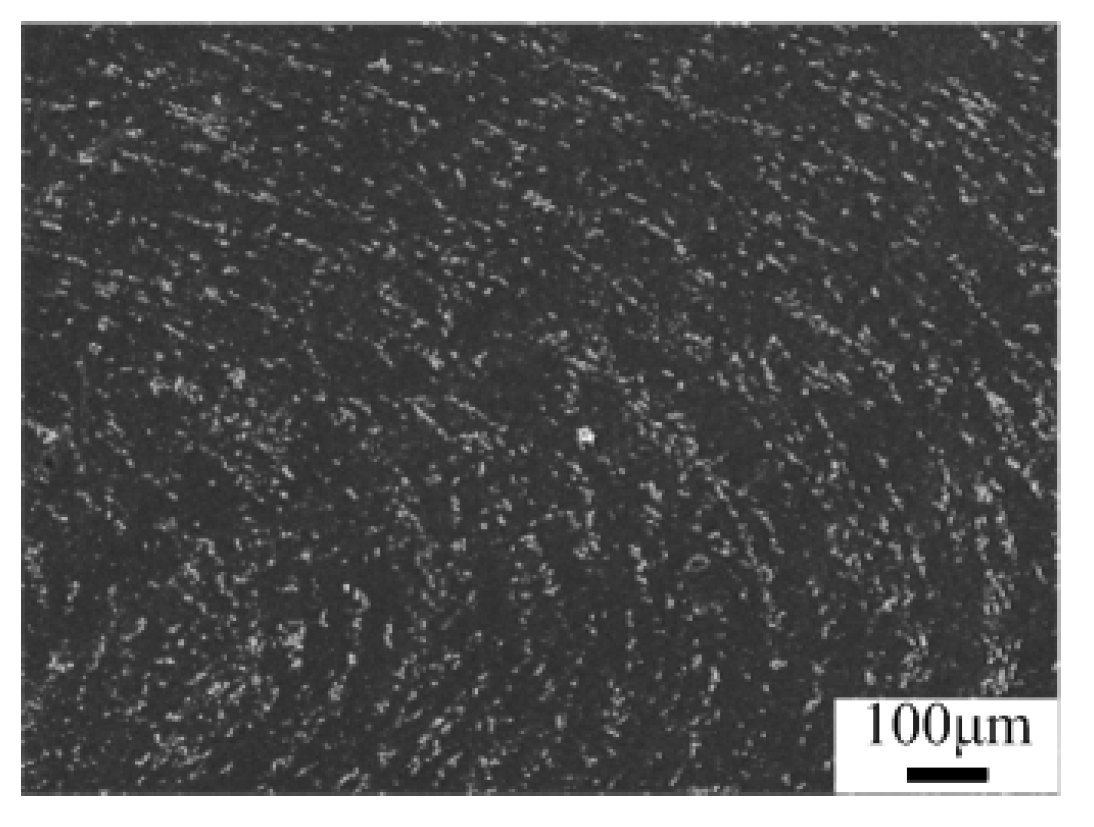
3.2. Effect of Reinforcements on the Toughness of the Alloy
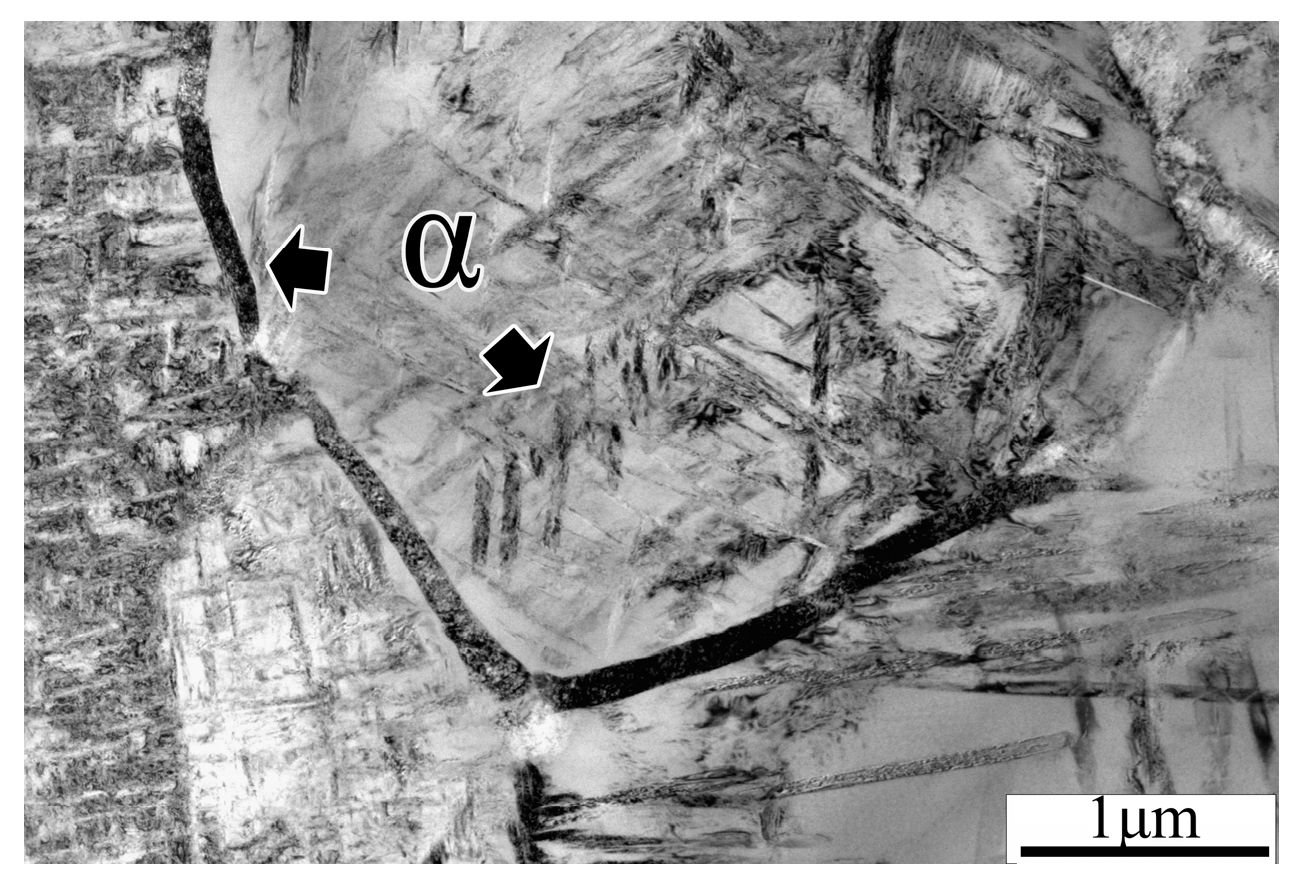
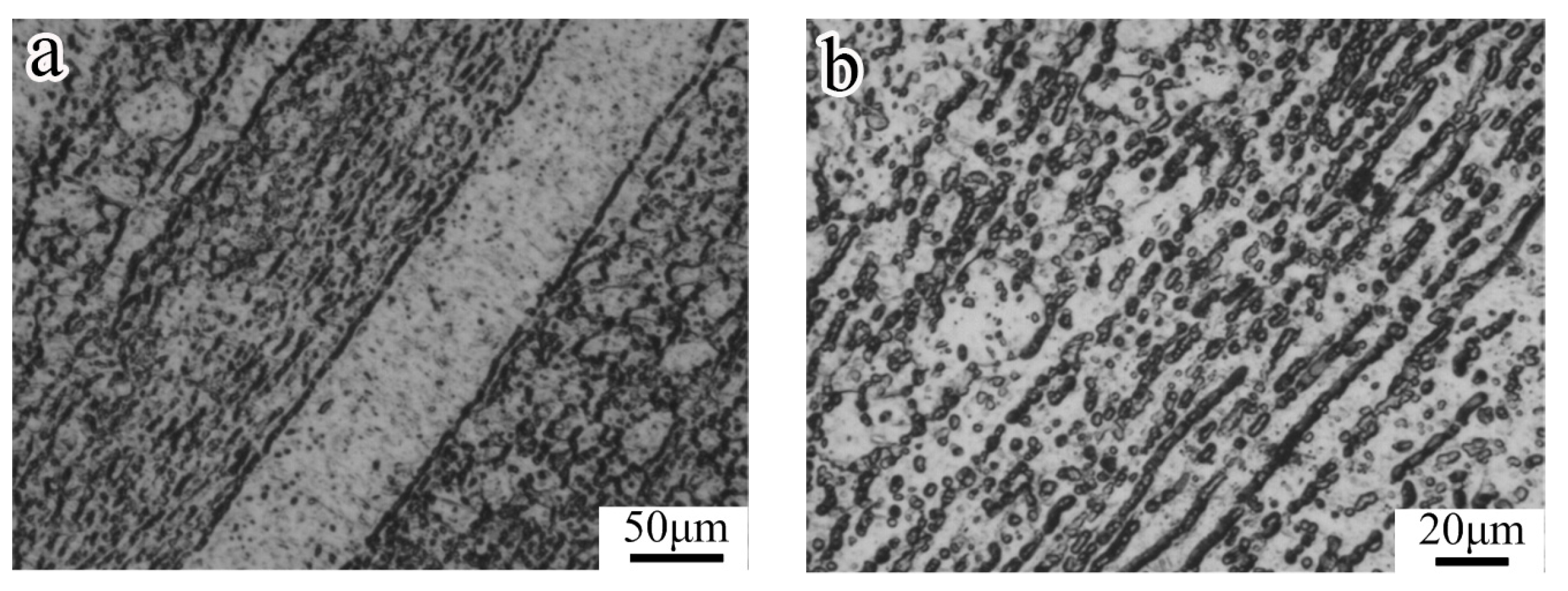
3.3. Microstructure of the Modified Alloy after Isothermal Compression
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The load bearing of TiB extends the strengthening process of the modified alloys. Moreover, the load bearing of TiB and the increase of the number of β grains can improve deformation homogeneity of the modified alloys, which decreases the crack nucleation. Therefore, the reinforcements increase the plasticity of the modified alloys. The toughening effect of the load bearing of TiB is mainly reflected in the strengthening process. The improvement of the toughness of the modified alloys is mainly attributed to the microstructural refinement during the necking process.
- (2)
- The distribution of TiB constantly changes in order to seek the equilibrium of forces until the length direction tends to parallel to the direction of maximum shear stress during isothermal compression. Moreover, the lattice distortion is nearly the largest when the length direction of TiB approximately parallels to the direction of maximum shear stress. This plays a pinning effect on the distribution variation of TiB. Therefore, the length direction of TiB tends to parallel the direction of maximum shear stress during the compression, which can promote the effective aspect ratio of TiB.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, S.-Y.; Lv, W.-J. Microtructure and mechanical properties of TC18 Titanium alloy. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2016, 45, 1138–1141. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, S.-Y.; Lv, W.-J. Effects of trace reinforcements on microstructure and tensile properties of in-situ synthesized TC18 Ti matrix composite. J. Comp. Mater. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamirisakandala, S.; Bhat, R.-B.; Miracle, D.-B.; Boddapati, S.; Bordia, R.; Vanover, R.; Vasudevan, V.-K. Effect of boron on the beta transus of Ti-6Al-4V alloy. Scr. Mater. 2005, 53, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Kagawa, Y.; Liu, Y.-F.; Masuda, C. Interface damage mechanism during high temperature fatigue test in sic fiber-reinforced Ti alloy matrix composite. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2001, 314, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, D.-R.; Geng, L.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, Z.-Z. Effect of B4C particle size on microstructure of in situ titanium matrix composites prepared by reactive processing of Ti-B4C system. Scr. Mater. 2006, 55, 429–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Huang, L.-J.; Geng, L.; Rong, X.-D. Compressive behaviors and mechanisms of TiB whiskers reinforced high temperature Ti60 alloy matrix composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 648, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.-Q.; Chang, Y.; He, Y.-Z.; Sui, Y.-W.; Wei, F.-X.; Meng, Q.-K.; Wei, Z.-J. Effect of Zr, Mo and TiC on microstructure and high-temperature tensile strength of cast titanium matrix composites. Mater. Des. 2016, 99, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, X.; Zhang, S.; Chai, L.; Chen, Z.; Kong, F.; Chen, Y. Effects of direct rolling deformation on the microstructure and tensile properties of the 2.5 vol% (TiBw + TiCp)/Ti composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 684, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shufeng, L.-I.; Kondoh, K.; Imai, H.; Chen, B.; Jia, L.; Umeda, J. Microstructure and mechanical properties of P/M titanium matrix composites reinforced by in-situ synthesized TiC–TiB. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 628, 75–83. [Google Scholar]
- Rahoma, H.-K.-S.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Wang, X.-P.; Xiao, S.-L. Influence of (TiC + TiB) on the microstructure and tensile properties of Ti-B20 matrix alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 627, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, I.; Tamirisakandala, S.; Miracle, D.-B.; Ramamurty, U. Microstructural effects on the mechanical behavior of B-modified Ti-6Al-4V alloys. Acta Mater. 2007, 55, 4983–4993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, X.; Wu, R.; Sakata, T.; Mori, H. HREM study of TiB/Ti interfaces in a TiB-TiC in situ, composite. Scr. Mater. 2001, 44, 1069–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozerov, M.; Klimova, M.; Vyazmin, A.; Stepanov, N.; Zherebtsov, S. Orientation relationship in a Ti/TiB metal-matrix composite. Mater. Lett. 2016, 186, 168–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lütjering, G. Influence of processing on microstructure and mechanical processing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1998, 243, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.-C.; Yang, H.; Han, G.-J.; Fan, X.-G. A numerical model based on internal-state-variable method for the microstructure evolution during hot-working process of TA15 titanium alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 3464–3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.-Y.; Lv, W.-J. Microstructure heterogeneity of TC18 Ti alloy during hot deformation. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2016, 45, 1545–1548. [Google Scholar]
- Eivani, A.-R.; Valipour, S.; Ahmed, H.; Zhou, J.; Duszczyk, J. Effect of the size distribution of nanoscale dispersed particles on the zener drag Pressure. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2011, 42, 1109–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.-Y.; Wang, L.-Q.; Qin, J.-N.; Chen, Y.-F.; Lv, W.-J.; Zhang, D. Microstructural characteristics and mechanical properties of in situ synthesized (TiB + TiC)/TC18 composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 530, 602–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxter, W.-J. The strength of metal matrix composites. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 1992, 23, 3045–3053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehlert, C.-J.; Tamirisakandala, S.; Curtin, W.-A.; Miracle, D.-B. Assessment of in situ TiB whisker tensile strength and optimization of TiB-reinforced titanium alloy design. Scr. Mater. 2009, 61, 245–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjong, S.-C.; Ma, Z.-Y. Microstructural and mechanical characteristics of in situ metal matrix composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. R 2000, 29, 49–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soboyejo, W.-O.; Shen, W.; Srivatsan, T.-S. An investigation of fatigue crack nucleation and growth in a Ti-6Al-4V/TiB in situ composite. Mech. Mater. 2004, 36, 141–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sample | B4C/wt % | C/wt % | TiB/wt % | TiC/wt % | TiB/TiC Molar Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alloy A | 0.1 | 0 | 0.4 | 0.1 | 4:1 |
| Alloy B | 0.06 | 0.04 | 0.27 | 0.27 | 1:1 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, S.; Lu, W. Effect of Hybrid Reinforcements on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Ti-5Al-5Mo-5V-Fe-Cr Titanium Alloy. Metals 2017, 7, 250. https://doi.org/10.3390/met7070250
Sun S, Lu W. Effect of Hybrid Reinforcements on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Ti-5Al-5Mo-5V-Fe-Cr Titanium Alloy. Metals. 2017; 7(7):250. https://doi.org/10.3390/met7070250
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Shuyu, and Weijie Lu. 2017. "Effect of Hybrid Reinforcements on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Ti-5Al-5Mo-5V-Fe-Cr Titanium Alloy" Metals 7, no. 7: 250. https://doi.org/10.3390/met7070250
APA StyleSun, S., & Lu, W. (2017). Effect of Hybrid Reinforcements on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Ti-5Al-5Mo-5V-Fe-Cr Titanium Alloy. Metals, 7(7), 250. https://doi.org/10.3390/met7070250




