Abstract
To address the critical challenges in pyrometallurgical recycling processes—such as poor feedstock adaptability, high energy consumption during roasting conversion, and the low added value of rare earth products—this study systematically investigated the mechanism and process optimization of ammonium bifluoride (NH4HF2) roasting for the recovery of neodymium–iron–boron (NdFeB) waste. Thermodynamic analysis confirmed the feasibility of the conversion reaction between NH4HF2 and the rare earth components in NdFeB waste. Single-factor experiments were conducted to examine the effects of roasting temperature, reaction time, and NH4HF2 dosage on rare earth recovery. The optimal conditions were a roasting temperature of 600 °C, a reaction time of 120 min, and a NH4HF2 dosage of 75 wt%, achieving a rare earth recovery rate of 98.81%. Furthermore, the response surface methodology (RSM) was employed to establish a quantitative model correlating process parameters with recovery efficiency. Variance analysis demonstrated that the model was highly significant (F = 136.94, p < 0.0001), with excellent agreement between actual and predicted values (R2 = 0.9944). Factor contribution analysis revealed that NH4HF2 dosage had the most pronounced impact on rare earth fluorination, followed by roasting temperature and reaction time. Under optimized conditions, the purified rare earth fluoride obtained after acid leaching reached a purity of 99.43%, providing high-quality raw material for producing high-value-added rare earth products.
1. Introduction
Neodymium iron boron (NdFeB) permanent magnets, as third-generation rare earth permanent magnetic materials, have become indispensable key functional materials in modern industry due to their excellent magnetic properties (high magnetic energy product, high coercivity), favorable cost–performance ratio, and outstanding machinability [1]. These materials are widely used in high-tech fields such as new energy vehicle drive motors, wind turbine generators, medical magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) equipment, precision sensors, and consumer electronics, demonstrating broad market prospects [2].
During the production of NdFeB magnets, approximately 25% of scrap materials are generated through mechanical processing steps such as cutting and grinding. These scraps contain up to 30% rare earth elements (primarily Nd, Pr, Dy, etc.), exhibiting significant resource recovery value [3]. It is noteworthy that traditional rare earth mining and smelting processes face severe environmental challenges: for every ton of rare earth oxide (REO) produced, 60,000 cubic meters of waste gas, 200 cubic meters of acidic wastewater, and 1.4 tons of radioactive waste residue are generated (due to the presence of radioactive elements in most rare earth ores) [4]. Against the backdrop of global low-carbon development strategies, advancing rare earth scrap recycling technologies holds dual significance: on one hand, it can reduce the environmental burden caused by primary mineral resource extraction; on the other hand, it can effectively alleviate pressure on rare earth supply chain security [5,6,7,8,9]. Statistics indicate that the annual production of NdFeB magnets is growing at a rate of 8–10%, with corresponding scrap generation increasing exponentially. This trend has prompted academia and industry to accelerate the establishment of a new rare earth circular economy system [10,11,12].
Current NdFeB scrap recycling technologies are primarily divided into two routes: hydrometallurgy and pyrometallurgy. While hydrometallurgical processes (acid leaching-solvent extraction) can achieve single rare earth oxides with purity > 99%, their inherent limitations hinder sustainable development. First, the multi-stage extraction process results in a lengthy procedure lasting 5–7 days; second, processing one ton of scrap consumes 4–6 tons of concentrated hydrochloric acid and generates 10–15 tons of heavy metal-containing wastewater; furthermore, approximately 10–15% of rare earths are lost in iron slag due to mechanical entrainment, making it difficult to achieve an overall recovery rate exceeding 90% [13,14]. These technical and economic bottlenecks urgently require breakthroughs through process innovation.
The pyrometallurgical recovery process for NdFeB waste utilizes the favorable reaction kinetics under high-temperature conditions. Its principle is based on the differential binding affinity of rare earth elements (REEs) and other elements with sulfur, chlorine, or fluorine. By employing sulfidation, chlorination, or fluorination methods, the occurrence states of the elements are altered, enabling the efficient recovery of REEs [15,16,17,18].
The sulfation roasting–water leaching process consists of two steps [15]: (1) The first is the sulfation roasting of pre-oxidized NdFeB waste using a sulfating agent to convert rare earth oxides into rare earth sulfates, while iron and other impurities remain in oxide form. (2) The second is the water leaching of the sulfation-roasted material. Since rare earth sulfates are water-soluble whereas iron oxides are insoluble, REEs can be separated from other oxide impurities. Liu et al. [16] employed a two-step ammonium sulfate roasting–water leaching method to selectively extract REEs from waste NdFeB magnets. First, the waste NdFeB magnets were oxidized at 800 °C, and then mixed with (NH4)2SO4. The first roasting step was conducted at 400 °C for 1 h, converting 78% of REEs into rare earth sulfates and 22% into insoluble rare earth ammonium sulfates, while iron was transformed into insoluble ferric ammonium sulfate. The second step involved calcination at 750 °C for 2 h to convert the insoluble rare earth ammonium sulfates into soluble rare earth sulfates. The sulfation roasting–water leaching method significantly reduces acid and alkali consumption, offering notable environmental benefits. However, it requires both oxidation roasting and high-temperature roasting, leading to high energy consumption. Additionally, further steps such as precipitating REEs from the leachate with sodium carbonate and subsequent high-temperature calcination are needed, resulting in high production costs and a cumbersome process flow.
The selective chlorination method for recycling waste magnets exploits the strong reactivity between REEs and chloride ions, which readily form chlorides. Under conditions where other ions do not participate in the reaction, REEs in the waste react to form rare earth chlorides, thereby separating them from impurity ions. Currently, chlorinating agents such as FeCl2, NH4Cl, and MgCl2-KCl are commonly used. Shirayama et al. [17] employed magnesium chloride as a reaction medium to extract Nd and Dy from NdFeB waste. The waste was thoroughly mixed with MgCl2 and reacted at 1000 °C for 12 h. Although the extraction rate of REEs exceeded 80%, excess MgCl2 and byproduct magnesium had to be removed via vacuum distillation. The chlorination separation method is effective for minimally oxidized waste but performs poorly for heavily oxidized waste. Additionally, the resulting chlorides are hygroscopic and difficult to store. The excessive use of chlorinating agents not only worsens the working environment but also corrodes equipment. Further processing is also required to obtain individual rare earth elements.
Extensive research has also been conducted on molten salt extraction to recover REEs from both oxidized and non-oxidized NdFeB magnets. In this method, mixtures of fluoride or chloride salts are used to dissolve oxidized or non-oxidized magnets, producing rare earth metals or alloys. Abbasalizadeh et al. [18] also employed molten salt extraction to selectively dissolve REEs from NdFeB magnets in a molten fluoride electrolyte. They investigated the effects of different fluxing agents (AlF3, ZnF2, FeF3, Na3AlF6) on the selective dissolution of REEs in the LiF-NdFeB system. The results showed that these fluxing agents were suitable as fluorinating agents to form rare earth fluorides (REF3), which could then be used for the cathodic deposition of rare earth metals. This method is suitable for large-scale industrial production, but the high reaction temperature imposes stringent requirements on the reactor.
Compared to hydrometallurgical processes, pyrometallurgical recovery offers advantages such as a shorter process flow and environmental friendliness. However, it suffers from poor raw material adaptability, high energy consumption, low REE recovery rates, insufficient product purity, and long reaction times, hindering its industrial application [19]. Current pyrometallurgical processes urgently require improvements in the following areas. (1) Poor raw material adaptability: The waste typically must have low impurity content, requiring inspection and classification to ensure the main components meet recovery standards [20,21]. (2) Low product purity: Pyrometallurgically recovered REE products often contain impurities, yielding only rare earth–transition metal alloys with limited applications [22]. Among these, the fluorination roasting–acid leaching process is considered one of the pyrometallurgical methods capable of overcoming these technical challenges.
A comparative study on fluoride calcination technology in the recycling of neodymium–iron–boron scrap materials indicates that while both the ZnF2 and NaBF4 calcination systems can achieve rare earth recovery rates exceeding 95%, there are significant differences between them [23,24]. The ZnF2 system requires the addition of 100% ZnF2 and roasting at 850 °C for 90 min, with its high energy consumption and large dosage addition being obvious drawbacks, whereas the NaBF4 system only requires a 65% addition rate and roasting at 600 °C for 30 min to achieve similar results. It is noteworthy that both systems introduce impurity ions into the leachate, increasing the difficulty of subsequent purification of ferric chloride hexahydrate (FeCl3·6H2O).
In comparison, the NH4HF2 calcination system demonstrates unique advantages: the fluoride residues primarily consist of metal fluorides, significantly reducing the pressure on acid leaching solution treatment; the generated NH3 can be recycled, effectively reducing exhaust gas treatment costs; more importantly, NH4HF2 decomposes into HF and NH3 at low temperatures between 200 and 400 °C, releasing active fluorine that rapidly reacts with rare earth oxides to form rare earth fluorides, thereby avoiding energy consumption issues associated with high temperatures.
Currently, significant gaps remain in the research on the recovery of rare earth elements from NdFeB waste via fluoride roasting, particularly in the optimization of process parameters and the elucidation of reaction mechanisms, which urgently require breakthroughs. This study innovatively applies NH4HF2 roasting technology to the field of NdFeB waste recycling for the first time, developing a novel process route of “NH4HF2 roasting–acid leaching purification.” Through the systematic investigation of the roasting reaction process between NdFeB waste and NH4HF2, combined with thermodynamic analysis and response surface methodology (RSM), the thermodynamic mechanisms of rare earth fluorination roasting in this system were elucidated for the first time, revealing the synergistic interactions among key process parameters and successfully determining the optimal process conditions. This research not only provides a solid theoretical and experimental foundation for the application of pyrometallurgical processes in NdFeB waste recycling but also pioneers the use of NH4HF2 in this field.
2. Experimental Materials and Equipment
2.1. Materials
The NdFeB scrap used in the experiment was taken from a NdFeB scrap recycling enterprise in Jiangxi. The content of oxides in the scrap is shown in Table 1, and the X-ray diffraction (XRD) spectrum of the scrap is shown in Figure 1. The content of rare earth oxides in the scrap is 26.98%, and the content of iron trioxide and other small amount of metal elements is 68.94%. Additionally, as shown in Table 2, the rare earth composition of the neodymium–iron–boron scrap can be seen, with neodymium trioxide (Nd2O3), cerium oxide (CeO2), praseodymium oxide (Pr6O11), and gadolinium oxide (Gd2O3) accounting for 94.82% of the total rare earth elements. The results of the XRD analysis indicate that the iron and rare earths in the NdFeB waste mainly consist of ferric oxide and rare earth oxides.

Table 1.
Oxide content contained in NdFeB wastes.
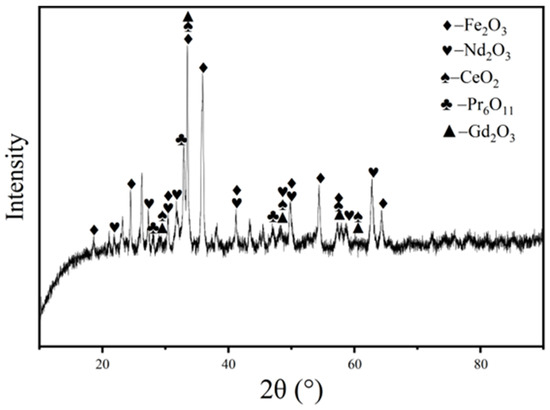
Figure 1.
XRD pattern of NdFeB wastes.

Table 2.
Rare earth compositions of NdFeB wastes.
2.2. Analytical Characterization
In this study, the feedstock was roasted in a KSL-1200X muffle furnace manufactured by Hefei Kejing Materials Technology Co. (Hefei, China). The rare earth content in the feedstock, the concentration of rare earths in the leach solution, and the fluorinated rare earth content in the leach slag were measured using an ICAP-PRO instrument manufactured by Thermo Fisher Scientific (Waltham, MA, USA). The calibration and verification of ICP Spectrometer: Certified Reference Materials (CRM) standard solutions are used, covering the concentration range of the target elements. Calibration Curve: This includes 5 concentration points (blank, 5 ppm, 10 ppm, 20 ppm, 40 ppm) with a linear correlation coefficient (R2) > 0.999. Accuracy and Error Range: This is verified through spike recovery (90–110%) and repeated measurements (RSD < 5%). The total iron content in neodymium–iron–boron scrap samples is tested using the titration method after reduction with titanium trichloride. The micromorphology of the leach slag was analyzed using a field emission scanning electron microscope model MLA650F manufactured by FEI (Hillsboro, OR, USA). The physical compositions of the raw material, roasted sand, and acid leaching slag were analyzed using an Empyrean type X-ray diffractometer manufactured by Panalytical (Almelo, The Netherlands). The main test specifications and parameters of the instrument were as follows: the target material was Cu-Kα (λ = 0.15406 nm), which was tested in a continuous scanning mode (2θ = 10–90° in steps of 0.013°). The calibration and verification of the XRD analyzer ensured the 2θ error < 0.01°. The consistency of detector response is validated using standard samples with a detection limit of 1–2 wt%. Peak position reproducibility is confirmed through triplicate scans of the same sample (RSD < 1%). The Gibbs free energies of the chemical reactions were calculated using the HSC6.0 software developed by Outotec (Espoo, Finland) and the temperature was set to 0–1000 °C. We fixed all input parameters (temperature, pressure, component concentration, thermodynamic database version) and performed two independent calculations using HSC Chemistry (restarting the software each time to eliminate cache effects). The data from each calculation are completely identical.
2.3. Experimental Procedures and Methods
Figure 2 shows the experimental flowchart for investigating the roasting process of NdFeB scrap with NH4HF2. After crushing and grinding, the NdFeB scrap was thoroughly mixed with 15–95% NH4HF2 and continuously roasted in a muffle furnace at a constant temperature of 500–700 °C for 30–150 min. Since fluorine atoms tended to combine with hydrogen atoms under strongly acidic conditions to form hydrofluoric acid, the roasted clinker was finely ground and then added to deionized water in a three-neck flask at a liquid-to-solid ratio of 50 mL/g. The mixture was stirred at 25 °C in a constant-temperature water bath at 150 rpm for 60 min; this was followed by filtration to remove the generated FeF3. This step prevents the subsequent acid leaching process from producing hydrofluoric acid, which could react with rare earth oxides and interfere with the exploration of fluorination roasting conditions. The water-washed residue was dried at 80 °C for 12 h, after which 9 M hydrochloric acid solution was added at a liquid-to-solid ratio of 4 mL/g. The mixture was then placed in an 80 °C constant-temperature water bath and stirred continuously at 150 rpm for 2.5 h. Upon completion of the leaching process, the acid leachate was filtered while hot, and the filter residue finally dried at 80 °C for 12 h.
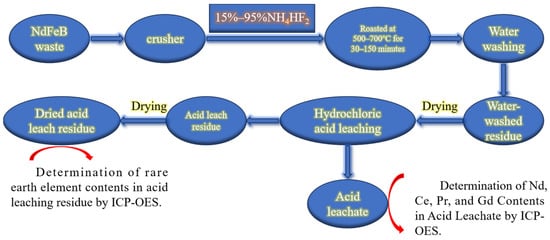
Figure 2.
Flowchart of roasting experiment for NdFeB scrap with NH4HF2.
The acid leachate of the roasted products was diluted with 5% nitric acid, and the concentration of rare earth elements was determined using a full-spectrum direct-reading inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometer (ICAP-PRO). The leaching rate was calculated as the ratio of the element content in the leachate to that in the raw NdFeB scrap material, with the rare earth leaching rate was calculated using Equation (1) and the total rare earth leaching rate was calculated using Equation (2). Since rare earth oxides and oxyfluorides are soluble in hydrochloric acid while fluorinated rare earth compounds remain insoluble and are retained in the leaching residue, the yield of fluorinated rare earths was calculated using Equation (3).
Equation (1):
- Xi—leaching rate of rare earth “i” (%);
- V—volume of leachate (L);
- Ci—concentration of rare earth “i” in the leach solution (g/L);
- m—weigh the mass of NdFeB scrap (g);
- ωi—content of rare earth “i” in NdFeB waste (%).
- X—total rare earth leaching rate (%);
- C—total concentration of rare earths in the leach solution (g/L);
- ω—total content of rare earths in the roasting product (%).
η = 1 – X
- η—rare earth recovery rate (%);
- X—total rare earth leaching rate (%).
Box–Behnken experimental design (BBD) is a response surface analysis method based on spherical spatial design, which is widely used in the optimization of various process parameters [25,26]. BBD is suitable for optimization experiments with fewer factors, and each factor can be taken at three levels, which are expressed by the corresponding codes as (−1, 0, 1) [27]. The BBD response surface methodology was used to further analyze the effects of factors and their interactions on the significance of rare earth recovery rates, and to optimize the process conditions for roasting to recover rare earths. Based on the results of 17 groups of designed experiments, analysis of variance (ANOVA) was performed using the RSM method and the quadratic polynomial shown in Equation (4) was obtained by fitting [28].
where y is the response value of RSM (rare earth recovery rate), a0 is the intercept term obtained by least squares regression ANOVA, ai is the first-order linear coefficient, aii is the squared effect between the factors, aij is the quadratic effect between the factors, and xi and xj are the uncorrelated factors, which are the random error terms caused by the inconsistency between the model predicted values and the actual measured values.
In this experiment, the response surface methodology was used to explore the effects of the roasting factors and their interactions on the significance of the rare earth recovery rates, and the process parameters obtained from the one-factor roasting experiments were optimized to obtain the best roasting process parameters.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Thermodynamic Analysis of Roasting Reactions
The main chemical reactions in the roasting process of the NdFeB waste–NH4HF2 system are shown in Table 3, and the calculated results are shown in Figure 2.

Table 3.
Chemical reactions in the roasting process of NdFeB waste–ammonium hydrogen fluoride system.
Figure 3a demonstrates that as the reaction temperature increases, the Gibbs free energy () of reactions 1–7 shows a monotonically decreasing trend while remaining negative throughout, indicating that the direct reaction between rare earth elements in NdFeB waste and NH4HF2 to form rare earth fluorides is thermodynamically spontaneous, and elevated temperatures significantly promote the reaction progress. Notably, the of reaction 8 undergoes a transition from positive to negative at 225 °C, marking this characteristic temperature point as the threshold for the significant decomposition of NH4HF2. Although the values of reactions 9–15 remain negative across the entire temperature range, their absolute values gradually decrease with increasing temperature, suggesting that while the reaction between rare earth elements in NdFeB waste and HF gas (generated from NH4HF2 decomposition) to form rare earth fluorides is thermodynamically feasible, the driving force weakens at higher temperatures. Particularly, reaction 16 maintains consistently negative values at 600 °C, whereas reaction 17 remains positive, demonstrating that the reaction between Fe2O3 in the waste and NH4HF2 is thermodynamically favorable at 600 °C, while the reaction with HF gas is non-spontaneous. The enlarged view in Figure 3b reveals more detailed patterns: below 225 °C, the values for fluorination reactions between rare earth elements and HF gas are generally lower than those for direct reactions with NH4HF2; however, above this critical temperature of 225 °C, the situation reverses, with values for reactions with HF gas becoming higher than those with NH4HF2. This phenomenon uncovers an important principle: HF gas generated from NH4HF2 decomposition above 225 °C actually diminishes the driving force for rare earth fluorination.
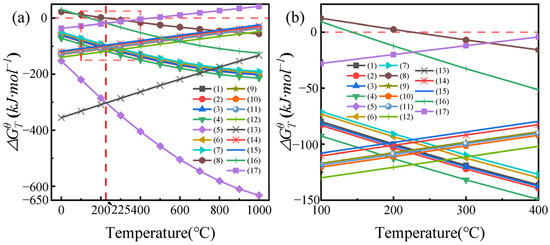
Figure 3.
(a) Relationship between and T during the roasting process of the NdFeB waste-NH4HF2 system; (b) partial enlargement of Figure (a).
Figure 4 illustrates the schematic diagram of NH4HF2 transformation and its mechanistic role in rare earth fluorination reactions. The diagram clearly demonstrates the dynamic evolution of the reaction system: during the low-temperature phase (<225 °C), NH4HF2 directly reacts with RE2O3 via solid–solid reactions to form REF3. It is particularly noteworthy that although thermodynamic analysis indicates temperatures above 225 °C reduce the spontaneity of fluorination reactions, when the temperature exceeds 225 °C, NH4HF2 undergoes thermal decomposition to generate reactive HF gas, establishing a triphase synergistic reaction system (NH4HF2-HF-RE2O3). This system significantly enhances rare earth fluorination efficiency through dual reaction pathways: solid–solid and gas–solid interactions. Based on this theoretical understanding and aiming to achieve higher rare earth recovery yields, this study specifically selected 500 °C as the starting temperature in the single-factor experiments, investigating roasting temperature, to systematically examine the influence of roasting temperature on rare earth fluoride conversion rates.
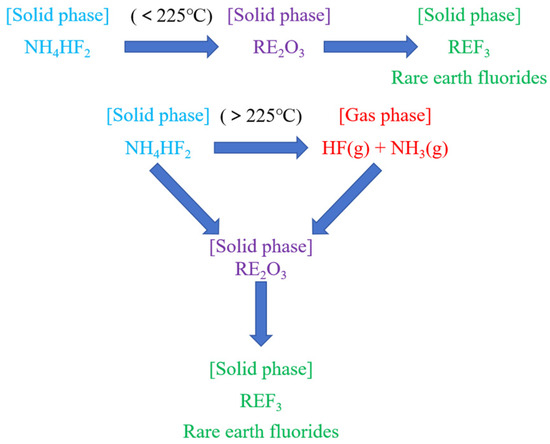
Figure 4.
Mechanism of NH4HF2 conversion to HF and fluorination process.
3.2. Effect of Roasting Conditions on Rare Earth Recovery Rates
3.2.1. Effect of Roasting Temperature on Rare Earth Recovery Rates
The experiments were conducted with a fixed roasting time of 120 min and an NH4HF2 addition ratio of 75%, systematically investigating the effect of roasting temperature (500–700 °C) on rare earth recovery efficiency. As shown in Figure 5a, when the roasting temperature increased from 500 °C to 600 °C, the leaching rates of all rare earth elements decreased significantly. Notably, at 600 °C, the leaching rates of cerium (Ce), gadolinium (Gd), neodymium (Nd), and praseodymium (Pr) converged to similar levels, indicating the synchronous fluorination conversion of all rare earth components in the NdFeB waste. When the temperature was further increased to 650 °C and 700 °C, the rare earth recovery rates reached 99.15% and 99.21%, respectively, showing only minimal variation compared to the recovery rate at 600 °C and stabilizing at a high level. As illustrated in Figure 5b, distinct diffraction peaks corresponding to NdF3, CeF3, PrF3, and GdF3 phases were detected at 500 °C, confirming the onset of fluorination reactions between NdFeB waste and NH4HF2 at this temperature, albeit with limited rare earth conversion efficiency. When the temperature was elevated to 600 °C, a remarkable intensification of these characteristic peaks was observed, indicating enhanced fluorination kinetics and consequently higher rare earth recovery yields. Notably, further increasing the temperature to 650 °C did not significantly alter the peak intensities of the fluorinated rare earth phases, suggesting reaction equilibrium had been achieved. This observation correlates well with the plateau in rare earth recovery rates at 650 °C. Through the holistic evaluation of process economics, 600 °C was identified as the optimal roasting temperature, balancing reaction efficiency with operational costs.
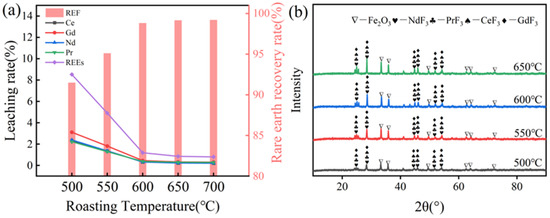
Figure 5.
(a) Effect of roasting temperature on rare earth recovery rate; (b) XRD spectra of clinker at different roasting temperatures.
3.2.2. Effect of Roasting Time on Rare Earth Recovery Rate
The experiment was conducted with 75% NH4HF2 addition at a roasting temperature of 600 °C to systematically investigate the effect of roasting duration (30–150 min) on rare earth recovery efficiency. As shown in Figure 6a, extending the roasting time from 30 to 120 min resulted in significant reductions in the leaching rates of all rare earth elements. Correspondingly, the total rare earth leaching rate decreased substantially while the recovery rate showed remarkable improvement. When the roasting time was further extended to 150 min, the recovery rate reached 98.50%, demonstrating negligible difference compared to the result at 120 min. These findings indicate that while prolonged roasting time facilitates the fluorination reaction, the process reaches saturation at 120 min, making the further extension of time practically ineffective for additional recovery rate enhancement. XRD analysis of the roasted products (Figure 6b) demonstrated the progressive intensification of fluorinated rare earth phase diffraction peaks with increasing roasting time from 60 to 120 min, indicating enhanced fluorination conversion efficiency. However, extending the duration to 150 min did not yield further peak enhancement, suggesting reaction equilibrium was attained by 120 min. This behavior correlates well with the plateau in rare earth recovery yields observed beyond 120 min. Through comprehensive techno-economic evaluation accounting for both processing efficiency and operational costs, 120 min was determined to represent the optimal roasting duration for this process.
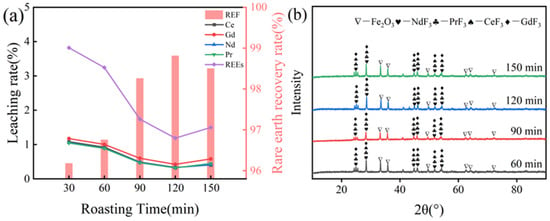
Figure 6.
(a) Effect of roasting time on rare earth recovery rate; (b) XRD spectra of clinker at different roasting times.
3.2.3. Effect of NH4HF2 Addition on Rare Earth Recovery Rate
The study investigated the effect of NH4HF2 dosage (15–95%) on rare earth element (REE) recovery during the roasting process (600 °C, 120 min), with results presented in Figure 7. As shown in Figure 7a, increasing the NH4HF2 dosage from 15% to 35% significantly enhanced the total REE recovery rate from 57.55% to 93.39%. Further increasing the dosage to 75% resulted in gradually decreasing leaching rates for individual elements (Ce: 0.32%, Gd: 0.45%, Nd: 0.32%, Pr: 0.37%), with the total leaching rate stabilizing at 1.19% and the recovery rate reaching 98.81%. However, at 95% dosage, the recovery rate slightly decreased to 98.62%, suggesting that excessive additive amounts may marginally impair fluorination efficiency. The optimal NH4HF2 dosage was determined to be 75%, at which point the fluorination reaction reached equilibrium. Figure 7b reveals that the diffraction peaks of fluorinated rare earth compounds intensified progressively with NH4HF2 additions up to 75%, but plateaued thereafter, further confirming the 75% dosage as the threshold for maximizing REEs conversion.
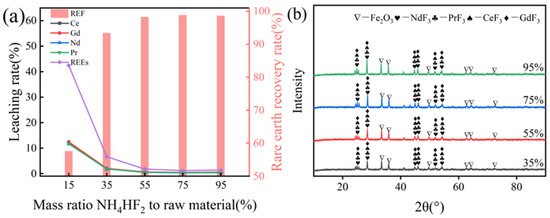
Figure 7.
(a) Effect of NH4HF2 to raw material mass ratio on rare earth recovery rate; (b) XRD spectra of clinker at different NH4HF2 dosages.
3.3. Optimization of NH4HF2 Roasting Process Conditions by Response Surface Methodology (RSM)
3.3.1. Box–Behnken Experimental Design
While response surface methodology (RSM) cannot elucidate chemical reaction mechanisms, it serves as an efficient tool for experimental parameter optimization with minimal experimental runs. As an integration of mathematical and statistical approaches, RSM identifies optimal parameter ranges through modeling analysis and establishes corresponding predictive models to determine optimal conditions [29,30]. Compared with full factorial and single-factor experiments, RSM demonstrates superior performance in optimization precision. Among various RSM designs (Box–Behnken Design (BBD), Central Composite Design, and Plackett–Burman Design), the BBD method is particularly advantageous for characterizing the individual and interactive effects of experimental factors on response variables, while effectively mapping the relationship between factors and responses—making it ideal for optimization studies with limited factors [31].
In this study, the BBD-based RSM was employed to systematically evaluate factor effects and their interactions on rare earth recovery rates, ultimately optimizing the NH4HF2 roasting process. The experimental design center points were set as follows: roasting temperature 600 °C, duration 90 min, and NH4HF2 dosage 65%. The complete factor levels and corresponding coding scheme for the RSM design are presented in Table 4.

Table 4.
Experimental design levels and factors based on RSM principles.
3.3.2. BBD Experimental Results
Response surface experiments were conducted based on the BBD principle and the results are shown in Table 5.

Table 5.
Box–Behnken design matrix and rare earth recovery rates.
3.3.3. Statistical Analysis and Analysis of Variance
The ANOVA results for the regression model of rare earth recovery rate from NdFeB waste are presented in Table 6. The model demonstrates a highly significant performance (F-value = 136.94, p < 0.0001), indicating only a 0.01% probability of noise interference, which confirms the model’s exceptional reliability [32,33]. The model exhibits outstanding goodness of fit with R2 = 0.9944 and adjusted R2 = 0.9871, explaining 99.44% of the variance in rare earth recovery rates. The close agreement between predicted R2 (0.9457) and adjusted R2 further validates the model’s predictive capability [34]. The signal-to-noise ratio (Adeq Precision) of 41.94, significantly exceeding the threshold value of 4, confirms the excellent model resolution, suitable for process optimization. Experimental precision evaluation shows a coefficient of variation (C.V.) of merely 0.81%, demonstrating the high reproducibility and reliability of the experimental data.

Table 6.
ANOVA table for response surface quadratic modeling.
Single-factor analysis reveals that roasting temperature (A, F = 204.65, p < 0.0001) and NH4HF2 addition amount (C, F = 6351, p < 0.0001) are the dominant factors influencing rare earth recovery, with the additive amount showing particularly significant effects. Although roasting time (B, F = 13.58, p = 0.0078) demonstrates statistical significance, its actual contribution is relatively minor. Interaction analysis indicates significant synergistic effects between temperature and additive amount (AC, F = 56.23, p = 0.0001), as well as between temperature and time (AB, F = 20.70, p = 0.0026), while the interaction between time and additive amount (BC) is insignificant (p = 0.7634). Quadratic term analysis shows that both temperature (A2) and additive amount (C2) quadratic terms are highly significant (p < 0.0001), suggesting nonlinear optimization windows for process parameters where excessively high temperatures may reduce recovery rates.
Model validation results show a lack-of-fit p-value of 0.3072 (> 0.05), confirming no significant factors were omitted and the model fits well. The low pure error (0.4411) further verifies excellent experimental repeatability. Based on these findings, this study recommends prioritizing the optimization of the NH4HF2 addition amount and roasting temperature as key process parameters, while fully leveraging their significant synergistic effect (AC). By establishing a coordinated control mechanism between roasting temperature and additive amount, the rare earth recovery rate can be effectively enhanced. This model not only elucidates the quantitative relationship between process parameters and recovery rate, but also provides a scientific optimization framework and reliable theoretical guidance for the resource recovery of NdFeB waste materials.
The experimental dataset comprising 17 trials was initially subjected to multiple regression analysis. Subsequently, the coefficients of the approximating polynomial were determined through least squares fitting, yielding the second-order polynomial Equation (5) that describes the rare earth recovery rate from NdFeB waste.
Rare earth recovery rate (%) = 97.33 + 3.82A + 0.9834B + 6.72C − 1.72AB − 2.83AC + 0.1181BC − 3.31A2 − 0.2173B2 − 5.26C2
Figure 8 shows a normal probability plot comparing the predicted and actual values of the dependent variable over the selected range of the independent variable. The plot shows a straight line with negligible residual values, indicating a good model fit. The plot also shows that all data points fall within a narrow range, indicating that the data are normally distributed.
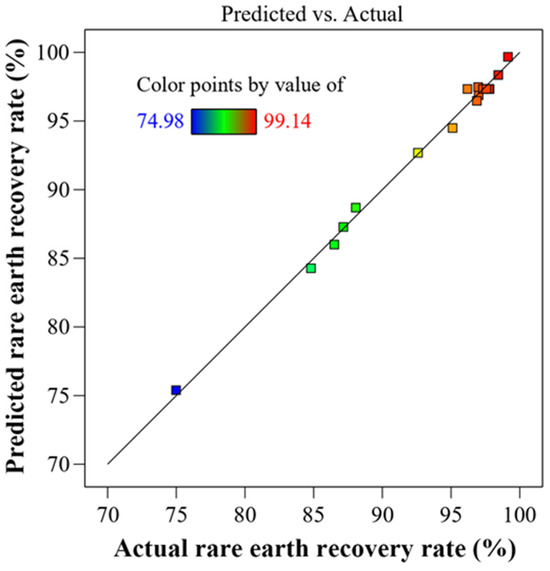
Figure 8.
Comparison of predicted versus actual rare earth element (REEs) recovery rates.
3.3.4. Response Surface Analysis
The corresponding two-dimensional contour plots and three-dimensional response surface plots (Figure 9, Figure 10 and Figure 11) were generated based on the regression equations to investigate the interaction effects between different factors. The slope characteristics of the response surfaces provide intuitive indications of each factor’s influence degree: a steeper slope suggests greater impact on rare earth recovery rate, while a gentler slope indicates relatively minor influence [31].
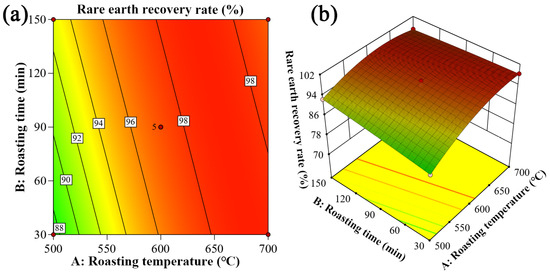
Figure 9.
Two-factor interaction between roasting temperature and roasting time: (a) two-dimensional contour plot; (b) three-dimensional response surface plot.
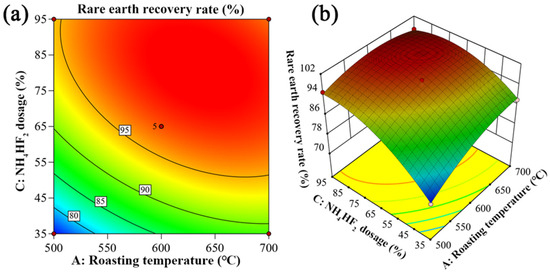
Figure 10.
Two-factor interaction between roasting temperature and NH4HF2 dosage: (a) two-dimensional contour plot; (b) three-dimensional response surface plot.
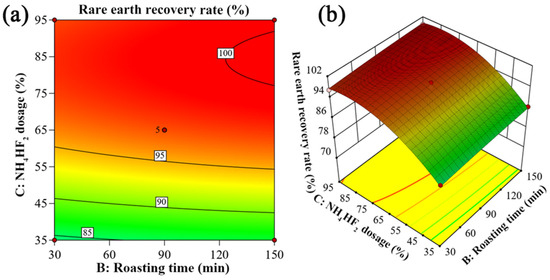
Figure 11.
Two-factor interaction between roasting time and NH4HF2 dosage: (a) two-dimensional contour plot; (b) three-dimensional response surface plot.
Figure 9 illustrates the interaction between roasting temperature and time. The results demonstrate that (1) at a fixed roasting duration, the rare earth recovery rate increases rapidly with rising temperature before stabilizing, and that (2) at a constant temperature, prolonged roasting time only leads to a gradual increase in recovery rate followed by stabilization. Particularly noteworthy is that when the roasting temperature reaches 650 °C, the recovery rate becomes essentially unaffected by variations in roasting time. Comparative analysis clearly shows that roasting temperature exerts significantly greater influence on rare earth recovery than duration.
As shown in Figure 10, the interaction between roasting temperature and NH4HF2 dosage significantly affects rare earth recovery rate, which is primarily reflected in the steepness of the response surface slope. Experimental results demonstrate that within the temperature range of 500–700 °C, as NH4HF2 dosage increases, the rare earth recovery rate first rises rapidly and then stabilizes. A higher NH4HF2 dosage is more favorable for promoting the fluorination reaction of rare earth elements. Similarly, when NH4HF2 dosage is held constant, increasing roasting temperature also causes the rare earth recovery rate to rise rapidly before reaching a stable state. However, comparative analysis reveals that NH4HF2 dosage has a more pronounced effect on rare earth recovery rate.
Figure 11 presents the two-dimensional contour plots and three-dimensional response surface analysis results of the interaction between roasting time and NH4HF2 dosage. The study demonstrates that when maintaining a constant NH4HF2 dosage, extending the roasting time has a minimal impact on the rare earth recovery rate, which remains essentially stable; with a fixed roasting duration, increasing NH4HF2 dosage leads to an initial rapid rise followed by gradual stabilization in rare earth recovery. These findings indicate that NH4HF2 dosage serves as the predominant factor influencing rare earth recovery, while roasting time exhibits relatively minor effects, with no significant interaction effect observed between the two parameters.
Systematic analysis of Figure 9, Figure 10 and Figure 11 reveals that among the three process parameters (roasting temperature, duration, and NH4HF2 dosage), the NH4HF2 addition amount demonstrates the most decisive influence on rare earth recovery rate. Experimental data show that with increasing NH4HF2 dosage, the recovery rate exhibits a characteristic pattern of rapid initial ascent followed by gradual stabilization, showing excellent consistency with previous single-factor experiment results. Mechanistic analysis indicates that under high-temperature roasting conditions, when NH4HF2 exceeds the optimal dosage, the fluorination reaction with rare earth materials reaches chemical equilibrium. The excess NH4HF2 undergoes thermal decomposition at elevated temperatures, releasing gaseous byproducts, and thereby causing the recovery rate to plateau. The study confirms that although synergistic effects exist between roasting temperature and NH4HF2 dosage, the ultimate maximum recovery rate is predominantly determined by the optimal NH4HF2 addition.
Through response surface methodology optimization, the ideal parameters for rare earth fluorination roasting were established as a 631 °C roasting temperature with an 85 min duration and an 82% NH4HF2 dosage, achieving a 99.77% rare earth recovery rate. From a green chemistry perspective, these optimized conditions not only ensure high extraction efficiency but also minimize reagent consumption. Repeated verification experiments confirmed that under these conditions, the relative deviation of recovery rates remains below 3%, demonstrating excellent reproducibility and fully meeting industrial production requirements for process stability.
3.4. Acid Leach Analysis
Under optimal process conditions (roasting temperature 631 °C, reaction time 85 min, NH4HF2 dosage 82%), the obtained fluorinated roasted clinker was crushed and ground; it was then leached with 9 mol/L hydrochloric acid solution (liquid-to-solid ratio 4 mL/g) at 80 °C for 2.5 h, followed by drying at 80 °C for 12 h. The final rare earth fluoride product achieved a purity of 99.43% (Table 7). This product demonstrates outstanding industrial application value: it can be directly used to prepare ultra-high-purity rare earth oxides and metals to meet high-end application requirements; the process flow is significantly simplified, with a product recovery rate reaching 99.77%, far surpassing the level of comparable processes.

Table 7.
Rare earth fluoride content.
The physical phase and morphology of the acid leaching products under optimal roasting conditions were characterized by XRD and SEM, as shown in Figure 12 and Figure 13. From the XRD patterns, we determined that the characteristic peaks of the fluorinated rare earths in the acid leaching residue were consistent with the standard peaks of NdF3, CeF4, PrF3 and GdF3, and there were no impurity peaks, which indicated that the fluorinated rare earths were products with homogeneous structures. The SEM patterns showed that the fluorinated rare earths had granular agglomerated structures.
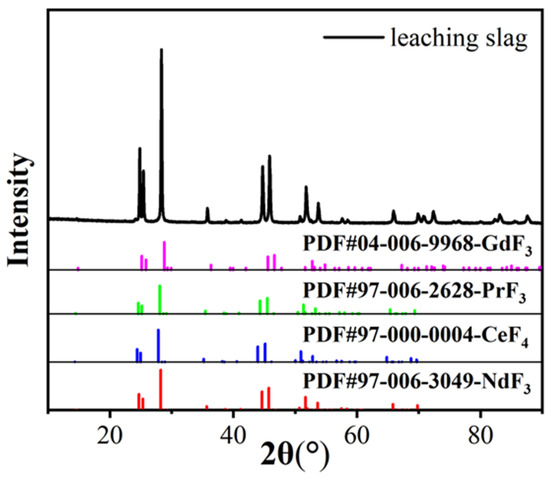
Figure 12.
XRD graph of leaching slag.

Figure 13.
Scanning electron microscope images of leaching slag at different scales: (a) 1 µm; (b) 500 nm; (c) 200 nm; (d) 100 nm.
3.5. Recommendations for the Process
In this study, NdFeB waste was crushed and mixed with 82% NH4HF2 and roasted for 85 min at 631 °C. Subsequently, the clinker was washed and roasted for 2.5 h at 80 °C with a liquid–solid ratio of 4 mL/g and 9 M hydrochloric acid to obtain fluorinated rare earths. Hydrochloric acid could be added continuously to adjust the pH of the leaching solution during the operation. After drying, the fluorinated rare earth slag can be used for oxidized roasting or molten salt electrolysis to obtain high-purity oxidized rare earths or rare earth metals. At the same time, the leachate can be concentrated and crystallized to obtain FeCl3-6H2O crystal products using reduced-pressure distillation. This process, outlined in Figure 14, can realize the synergistic extraction and comprehensive utilization of NdFeB wastes. It is suitable for industrial applications and has good economic benefits. Process optimization recommendations and challenge analysis for scrap materials from different sources (oxidized scrap/non-oxidized magnets) can be systematically improved in the following aspects. First, in the raw material pretreatment stage, establish classification standards based on scrap characteristics to achieve differentiated processing. In the leaching step, focus on developing a temperature-time synergistic control model to optimize reaction efficiency, while adopting a stepwise acid addition method and a dynamic pH regulation system (maintaining the optimal pH range) to reduce hydrochloric acid consumption and stabilize reaction conditions. For exhaust gas treatment, it is recommended to configure a two-stage series scrubber (NaOH + H2O2 combination) to achieve the efficient removal of HF and NH3. To enhance overall economic efficiency, it is advisable to construct a waste heat recovery system to reduce energy costs and establish a hydrochloric acid regeneration system for resource recycling. In the product treatment stage, the process can be shortened by establishing a direct electrolysis process for rare earth slag, while developing deep-processed FeCl3 products to increase their added value. These improvement measures need to be implemented synergistically to achieve overall process optimization.
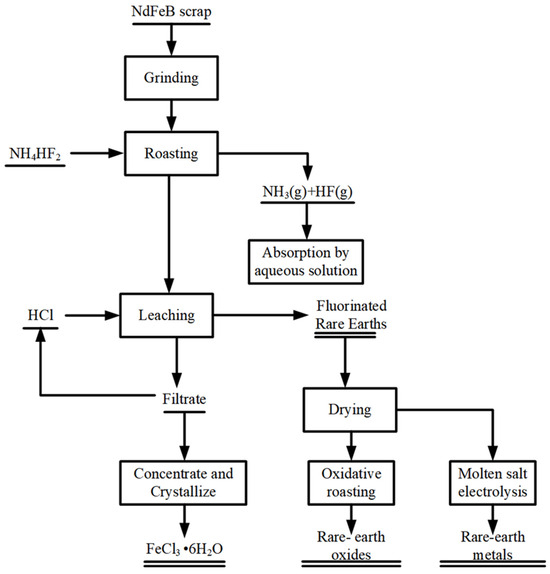
Figure 14.
Process flow for recovery of rare earths from NdFeB waste by fluorination reaction.
4. Conclusions
This study thoroughly investigated the reaction mechanism and process conditions for the recovery of rare earths in NdFeB wastes by a NH4HF2 fluoride roasting process, and the research results can provide experimental and theoretical bases for the promotion of pyrometallurgical technology in NdFeB wastes. The main research results are as follows: Thermodynamic analysis indicates that the fluorination reaction between NH4HF2 and rare earth oxides (REOs) in NdFeB waste proceeds spontaneously ( < 0) within the temperature range of 0–1000 °C. NH4HF2 decomposes at 225 °C to generate reactive HF gas, which further promotes the fluorination conversion of rare earth elements. Although the thermodynamic driving force slightly decreases when the temperature exceeds 225 °C, experimental results demonstrate that elevated temperatures significantly improve the reaction kinetics and facilitate the progression of the reaction. The optimal roasting process was obtained by a one-factor experiment, with the addition of NH4HF2 of 75%, and roasting conditions of 600 °C and 120 min, and the rare earth recovery rate could reach 98.81%. The influence of each process factor was confirmed using a response surface methodology and it was found that the NH4HF2 addition had the greatest influence on the fluorination rate of rare earths, followed by roasting temperature and roasting time. The optimum roasting conditions were determined as 82% NH4HF2 dosage, 631 °C, and 85 min. The validation experiments showed that the rare earth recovery could reach 99.77% under the optimum process conditions. The rare earth fluoride obtained after acid leaching achieved a purity of 99.43%, meaning it can be directly used as high-quality raw material for molten salt electrolysis or oxidative roasting processes. The solid-state NH4HF2 reagent demonstrates superior safety in storage and transportation, while the simplified process flow (roasting → acid leaching) renders it highly promising for industrial-scale applications. This innovative approach effectively addresses key challenges in conventional pyrometallurgical recycling, including poor feedstock adaptability, high energy consumption, and low product value added. By synergizing fluorination conversion with acid leaching, the process achieves efficient rare earth–iron separation while circumventing the massive wastewater generation characteristic of hydrometallurgical methods. Notably, the NH3 byproduct in off-gases can be recycled, and the crystallized FeCl3·6H2O byproduct is valorizable, aligning perfectly with green metallurgy principles. Future research should prioritize mechanistic studies of reaction kinetics to further optimize energy efficiency. Although this process shows promising prospects, its industrial application still requires us to address the following issues: Current research has only been completed on a laboratory scale, and pilot-scale verification is needed to assess equipment corrosion, process stability, and economic viability. NH4HF2 is highly corrosive, necessitating safety measures such as HF exhaust scrubbing and NH3 recovery. A comprehensive cost–benefit comparison with wet processes is required to clarify its commercial advantages. Follow-up research should focus on establishing kinetic models, conducting continuous reactor validation, exploring low-corrosivity reagents like NaF/CaF2 to reduce safety risks, and quantifying the carbon emission reduction benefits of this process compared to traditional methods.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.L. and X.L.; Methodology, X.L. and J.W.; Software, Y.L.; Validation, Y.L., D.L. and J.W.; Formal analysis, Y.L. and Y.X.; Investigation, Y.L.; Data curation, Y.L.; Writing—original draft, Y.L.; Writing—review and editing, Y.L., X.L. and J.W.; Visualization, Y.L.; Supervision, D.L. and X.L.; Project administration, J.W. and Y.X.; Funding acquisition, J.W. and Y.X. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by China Baowu Low Carbon Metallurgy Innovation Foudation (grant number BWLCF202121), Jiangxi Provincial Key Laboratory of Flash Green Development and Recycling (grant number 20193BCD40019), Academic and technical leaders of major disciplines in Jiangxi Province (grant number 20213BCJ22003), Jiangxi Province Science and Technology Innovation High end Talent Project (grant number jxsq2023201012), Jiangxi Provincial Natural Science Foundation Youth Fund (grant number 20242BAB20194), and Jiangxi Provincial Natural Science Foundation (grant number 20244BAB28056).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Dewei Li is currently employed by company Anhui Conch Environmental Protection Group Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Zhou, T.; Qu, P.; Pan, W.; Liu, R.; Li, M.; Rehman, S.U.; Zhong, Z.; Xie, G. Sintered NdFeB Magnets with Tb-Dy Double-Layer Core/Shell Structure Fabricated by Double Alloy Method and Grain Boundary Diffusion. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 856, 158191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, A.; Sahu, S.K. A Comprehensive Review on Recycling of Critical Raw Materials from Spent Neodymium Iron Boron (NdFeB) Magnet. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 317, 123527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, J.; Sarker, S.K.; Bruckard, W.; Jegatheesan, V.; Haque, N.; Singh, N.; Pramanik, B.K. Greening the Supply Chain: Sustainable Approaches for Rare Earth Element Recovery from Neodymium Iron Boron Magnet Waste. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 113169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alguacil, F.J. Utilizing Deep Eutectic Solvents in the Recycle, Recovery, Purification and Miscellaneous Uses of Rare Earth Elements. Molecules 2024, 29, 1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Shao, P.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, X.; Yang, L.; Shi, H.; Yu, K.; Luo, X.; Luo, X. A Critical Review of the Recovery of Rare Earth Elements from Wastewater by Algae for Resources Recycling Technologies. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 169, 105519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Chen, J. Extraction and Separation of Heavy Rare Earth Elements: A Review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 276, 119263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaustad, G.; Williams, E.; Leader, A. Rare Earth Metals from Secondary Sources: Review of Potential Supply from Waste and Byproducts. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 167, 105213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinnunen, P.H.-M.; Kaksonen, A.H. Towards Circular Economy in Mining: Opportunities and Bottlenecks for Tailings Valorization. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 228, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, L.H.; Giese, E.C.; Ribeiro-Duthie, A.C.; Lins, F.A.F. Sustainability and the Circular Economy: A Theoretical Approach Focused on E-Waste Urban Mining. Resour. Policy 2019, 74, 101467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandara, H.M.D.; Darcy, J.W.; Apelian, D.; Emmert, M.H. Value Analysis of Neodymium Content in Shredder Feed: Toward Enabling the Feasibility of Rare Earth Magnet Recycling. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 6553–6560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimer, M.V.; Schenk-Mathes, H.Y.; Hoffmann, M.F.; Elwert, T. Recycling Decisions in 2020, 2030, and 2040—When Can Substantial NdFeB Extraction be Expected in the EU? Metals 2018, 8, 867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestri, L.; Forcina, A.; Silvestri, C.; Traverso, M. Circularity Potential of Rare Earths for Sustainable Mobility: Recent Developments, Challenges and Future Prospects. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 292, 126089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choubey, P.K.; Singh, N.; Panda, R.; Jyothi, R.K.; Yoo, K.; Park, I.; Jha, M.K. Development of Hydrometallurgical Process for Recovery of Rare Earth Metals (Nd, Pr, and Dy) from Nd-Fe-B Magnets. Metals 2021, 11, 1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, G. Recovering REEs from NdFeB Wastes with High Purity and Efficiency by Leaching and Selective Precipitation Process with Modified Agents. J. Rare Earths 2019, 37, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Önal, M.A.R.; Borra, C.R.; Guo, M.; Blanpain, B.; Van Gerven, T. Recycling of NdFeB Magnets Using Sulfation, Selective Roasting, and Water Leaching. J. Sustain. Metall. 2015, 1, 199–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Chen, F.; Wang, L.; Ma, S.; Wan, X.; Wang, J. Selective Separation of Rare Earths from Spent Nd-Fe-B Magnets Using Two-Stage Ammonium Sulfate Roasting Followed by Water Leaching. Hydrometallurgy 2021, 203, 105626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirayama, S.; Okabe, T.H. Selective Extraction and Recovery of Nd and Dy from Nd-Fe-B Magnet Scrap by Utilizing Molten MgCl2. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2018, 49, 1067–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasalizadeh, A.; Malfliet, A.; Seetharaman, S.; Sietsma, J.; Yang, Y. Electrochemical Recovery of Rare Earth Elements from Magnets: Conversion of Rare Earth Based Metals into Rare Earth Fluorides in Molten Salts. Mater. Trans. 2017, 58, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zhu, N.; Li, Y.; Wu, P.; Dang, Z.; Ke, Y. Efficient Recovery of Rare Earth Elements from Discarded NdFeB Magnets. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2019, 124, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gergoric, M.; Ravaux, C.; Steenari, B.-M.; Espegren, F.; Retegan, T. Leaching and Recovery of Rare-Earth Elements from Neodymium Magnet Waste Using Organic Acids. Metals 2018, 8, 721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Walton, A.; Sheridan, R.; Güth, K.; Gauß, R.; Gutfleisch, O.; Buchert, M.; Steenari, B.-M.; Van Gerven, T.; Jones, P.T.; et al. REE Recovery from End-of-Life NdFeB Permanent Magnet Scrap: A Critical Review. J. Sustain. Metall. 2017, 3, 122–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Zhao, Z.; Li, X.; Xiao, Y.; Yang, Y. Selective Extraction of Rare Earth Elements from NdFeB Scrap by Molten Chlorides. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 2536–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Lei, X.; Lin, S.; Zhu, X.; Wang, J. Mechanism and Experimental Study on the Recovery of Rare Earth Elements from Neodymium Iron Boron Waste by NaBF4 Fluorination Method. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2025, 126, 106943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Lei, X.; Wang, J. Mechanism and Experimental Study on the Recovery of Rare Earth Elements from Neodymium Iron Boron Waste Using the ZnF2 Fluorination Method. Materials 2024, 17, 5807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botla, G.; Barmavatu, P.; Pohorely, M.; Jeremias, M.; Sikarwar, V.S. Optimization of Value-Added Products Using Response Surface Methodology from the HDPE Waste Plastic by Thermal Cracking. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2024, 50, 102514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anaklı, D.; Erşan, M. Optimization of Reduced Graphene Oxide Yield Using Response Surface Methodology. Diamond Relat. Mater. 2024, 148, 111524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battestini-Vives, M.; Xiao, X.; Lipnizki, F.; Rudolph-Schöpping, G. Response Surface Methodology to Optimize Membrane Cleaning in Nanofiltration of Kraft Black Liquor. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 354, 128626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, Q.; Xu, C.; Gao, Y.; Yu, X. Response Surface Optimization for Deep Eutectic Solvents Extraction of Bamboo Shoots Proteins. Adv. Bamboo Sci. 2024, 7, 100080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Liu, Y.; Ma, B.; Wang, C.; Chen, Y. Strengthening Extraction of Lithium and Rubidium from Activated α-Spodumene Concentrate via Sodium Carbonate Roasting. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2023, 123, 248–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwanat, H.-M.M.; Kasongo, K.B. Cobalt Dissolution from Concentrate in Sulfuric Acid-Ferrous Sulfate System: Process Parameters Optimization by Response Surface Methodology (RSM). J. Sustain. Metall. 2021, 7, 1838–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeng, D.; Sutaryo, S.; Purnomoadi, A.; Susanto, S.; Purbowati, E.; Adiwinarti, R.; Purwasih, R.; Widiharih, T. Optimization of Methane Production from Dairy Cow Manure and Germinated Papaya Seeds Using Response Surface Methodology. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2024, 10, 100927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, F.; Hu, Y.; Kang, K.; Lam, S.S.; Foong, S.Y.; Yong, C.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, S.; et al. Optimization of Photo-Fermentation Bio-Hydrogen Production from Corncob via Genetic Algorithm Optimized Neural Network and Response Surface Method Model. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2025, 138, 1293–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OuYang, J.; He, Q.; Liao, X.; Deng, Q.; Bai, J.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, F.; Shi, L.; Jiang, J. Optimizing High-Water-Resistance Cementitious Materials Using Modified Phosphogypsum Synergy Multiple Solid Wastes with Response Surface Methodology. J. Build. Eng. 2025, 111, 113443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putra, V.G.V.; Mohamad, J.N.; Abdullah, F.; Paramahasti, M. Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs) and Response Surface Methodology (RSM) for Optimizing Wetting and Anti-Bacterial Properties of Woven Fabric. J. Text. Inst. 2025, 116, 1078–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).