Abstract
The effects of HfC content on the ablation resistance of W-HfC composites were systematically studied. The oxy-acetylene flame ablation test was conducted at 2800 °C. Post-ablation samples were characterized via XRD, section morphology, and EDS. W-10HfC showed the best ablation resistance, with a linear ablation rate of just 0.0175 mm/s. This enhanced performance is attributed to the formation of a dense HfW2O8 oxide layer with negative thermal expansion properties, reinforced by uniformly dispersed blocky HfO2 particles. However, excessive HfC content induces a stratified oxide structure. The thermal expansion coefficient mismatch between HfW2O8 and HfO2 causes microcrack formation, ultimately degrading ablation resistance. These findings establish critical guidelines for HfC content optimization in W-HfC composite design.
1. Introduction
Tungsten (W), as a typical refractory metal, exhibits outstanding properties, including a high melting point (3410 °C), high elastic modulus, thermal shock resistance, superior high-temperature strength, and excellent corrosion resistance [1,2,3,4,5]. Owing to these characteristics, W and its alloys have been extensively utilized in aerospace and nuclear industries as a critical material for high-temperature structural components, such as engine parts, rocket nozzles, and nuclear fusion reactors [6,7,8]. However, tungsten exhibits intrinsic limitations, including a high ductile-to-brittle transition temperature that induces low-temperature embrittlement [9,10,11]. The strength of pure tungsten significantly degrades with increasing temperature, with its tensile strength at 1000 °C reduced by 60–80% compared to room temperature [12]. Additionally, the severe oxidation of pure tungsten at high temperatures constitutes a critical restriction for engineering applications [13].
To effectively overcome these limitations, researchers have significantly enhanced the performance of W matrix composites through strategies such as alloying element doping, grain boundary engineering, and hierarchical structural design [14,15,16]. The incorporation of secondary-phase particles, such as rare-earth oxides, refractory metal nitrides, and carbide ceramic particles within the tungsten matrix, inhibits grain boundary migration. Thereby refining grain size and elevating the recrystallization temperature. This approach improves both the strength and ductility of tungsten-based alloys while enhancing their high-temperature performance and stability [17,18,19,20,21].
Compared to oxide particles, carbide reinforcements with higher melting points are ideal strengthening phases for tungsten-based composites [22]. The currently developed W-MeC composites possess an attractive combination of mechanical, physical, and chemical characteristics in the temperature region of 20–1600 °C compared with monolithic W and, especially, show unusual high-temperature strength and super ablation resistance at ultra-high temperatures [23,24]. Hafnium carbide (HfC), characterized by its ultrahigh melting point (3900 °C) and low thermal conductivity (20 W/m·K), is recognized as a superior candidate for enhancing the high-temperature performance of tungsten matrix composites. HfC dispersion-strengthened tungsten demonstrates significant enhancements in yield strength, compressive strength, and hardness [25]. Studies further reveal that HfC particles react with oxygen impurities to form HfO2 [26]. Moreover, the comparable coefficients of thermal expansion between HfC ceramics and the tungsten matrix enable improved high-temperature stability without compromising room-temperature ductility. These attributes establish W-HfC composites as a highly promising refractory material [27].
Ablation resistance is critical for materials serving in ultra-high-temperature environments. Studies have shown that W-HfC composites exhibit superior ablation resistance compared to pure W, with enhanced performance at 2200 °C as HfC content increases [25]. This improvement arises from the formation of a dense HfO2 oxide layer during ablation, which inhibits oxygen and heat flux penetration into the W matrix. However, inadequate interfacial bonding between HfC and the tungsten matrix, coupled with the formation of complex oxides exhibiting negative thermal expansion coefficients during ablation, introduces significant challenges. Thermal expansion mismatch among oxidation products promotes microcrack initiation, accelerating oxidative degradation and ultimately compromising ablation resistance. Current research lacks systematic investigations on the ablation behavior of W-HfC composites at elevated temperatures and the formation mechanisms of composite oxides during ablation, as well as the influence of HfC content on ablation resistance and associated mechanisms, which remain unclear.
In this study, tungsten matrix composites reinforced with different mass fractions of HfC were fabricated via powder metallurgy and the spark plasma sintering (SPS) process. The mass fraction-dependent ablation resistance evolution and oxidation–ablation mechanisms of W-HfC composites under extreme thermal loading were systematically studied and clarified. This work provides a valuable experimental and theoretical basis for the development of tungsten-based composites for high-temperature aerospace components.
2. Materials and Methods
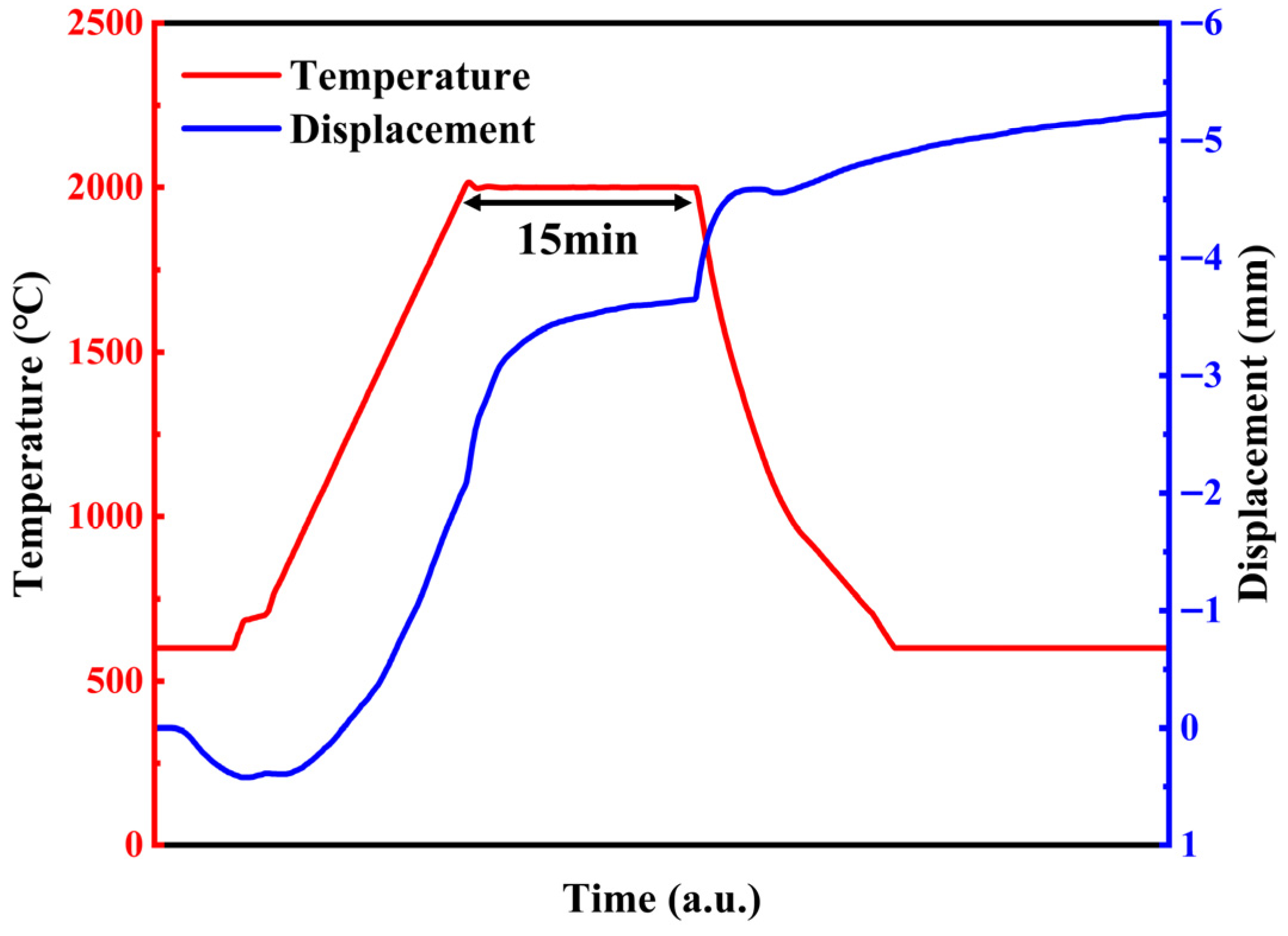
Tungsten powders (99.95%, 1–3 μm) and HfC powder (99.9%, 1–3 μm) were used to fabricate the composites. Four W-HfC composites with different HfC contents (5, 10, 15, and 20 wt%) were prepared and labeled as W-5HfC, W-10HfC, W-15HfC, and W-20HfC, respectively. Both powders were dry ball-milled by a ball milling machine using a ball-to-powder mass ratio of 4:1. The mixture was processed at a rotation speed of 300 rpm for 8 h under Ar, with intermittent pauses of 10 min after every 30 min of milling to prevent overheating. The ball-milling process used tungsten carbide balls. The microstructures of W powder, HfC powder, and the mixed powder are shown in Figure 1. The composite powders were consolidated by SPS (20T-6-IV, Shanghai Chenhua Technology Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China) in a graphite mold at 2000 °C for 15 min in vacuum under a pressure of 40 MPa. The heating rate was maintained at 100 °C min−1 up to the sintering temperature. Figure 2 shows the ram displacement and temperature curves during the ablation process. The sample size is 40 mm in diameter and 5 mm in thickness, and the relative densities of the composites were measured using Archimedes’ method.
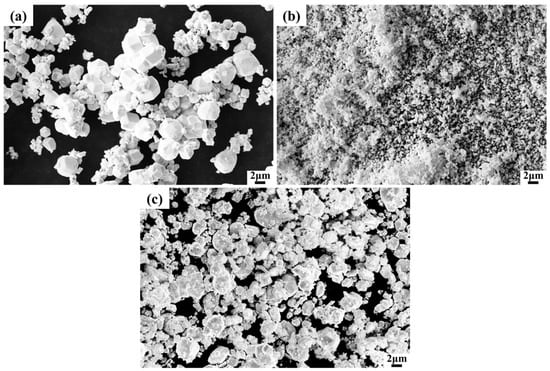
Figure 1.
SEM images of the powders: (a) W powder; (b) HfC powder; (c) mixed powder.
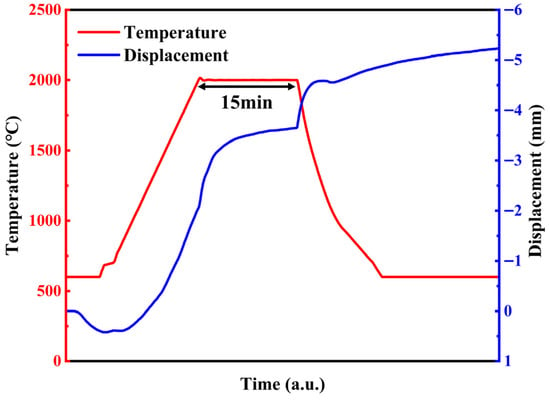
Figure 2.
The ram displacement (blue line) and temperature (red line) curves during the ablation process.
Ablation tests were carried out using a plasma flame at 2800 °C. The temperature at the ablation center of the samples was measured by using a non-contact infrared thermometer. The temperature fluctuation during the ablation process is within ±25 °C. The ablation temperature was maintained and controlled through the automatic adjustment of the ablation distance, and the ablation distance was about 30 mm. The plasma jet was generated by ionizing argon and hydrogen in a direct current plasma torch, with gas flow rates of 45 L/min and 5 L/min, respectively. The inner diameter of the nozzle was 6 mm. The specimen was firmly held in its position in a graphite holder. The linear ablative rate was calculated based on the thickness and burn-through time. The microstructure and elemental distribution of the ablated samples were analyzed using a scanning electron microscope (SEM, TESCAN MIRA3) equipped with energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) and operated in backscattered electron (BSE) mode. Phase identification of the specimens was performed using X-ray diffraction (XRD, 10°/min, 20–70° range). The partial oxidation products on the surface of the ablated samples were removed, ground into powder using an alumina mortar, and then subjected to XRD testing. The ablated samples were radially cut by diamond wire cutting to facilitate the observation of the cross-sectional morphology. The cross-section of the samples was polished by mechanical and vibration polishing.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Ablation Properties
The high-temperature ablation behavior of W-HfC composites was investigated. Figure 3 reveals the post-ablation surface morphologies of four W-HfC variants subjected to 2800 °C oxy-acetylene flame testing. The ablation process involves synergistic thermomechanical loading from both extreme temperatures and high-pressure conditions induced by high-velocity gas flow scouring, resulting in coupled oxidative and erosive degradation [28]. Gas flow dynamics from the central impingement zone toward peripheral regions caused mechanical perforation at the sample core. Surface analysis identified a continuous oxide layer with localized yellowish oxidation products near the central region. While W-5HfC and W-10HfC specimens maintained structural integrity without discernible cracking, W-15HfC and W-20HfC exhibited radial crack propagation from the core to periphery, leading to catastrophic fracture.
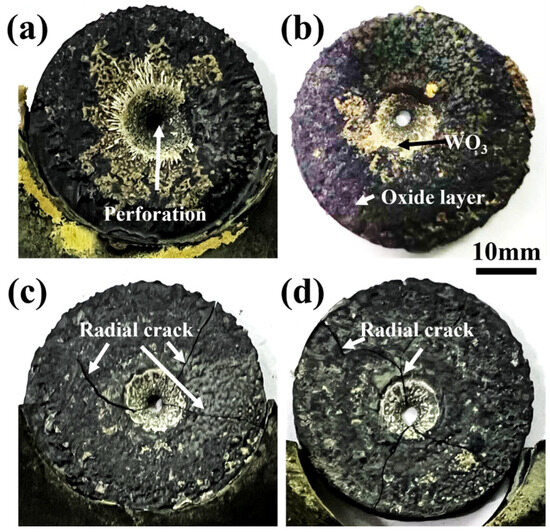
Figure 3.
Macroscopic topography of the ablated surface of composites with different HfC mass fractions: (a) W-5HfC; (b) W-10HfC; (c) W-15HfC; (d) W-20HfC.
Table 1 presents the relative density, thickness, burn-through time, and linear ablative rates of fabricated W-HfC composites. Among the four samples, W-10HfC and W-15HfC exhibited superior densification. Notably, W-10HfC demonstrated the minimum linear ablation rate (0.0175 mm/s), indicating optimal ablation resistance under 2800 °C oxy-acetylene flame exposure. The linear ablative rate of W-HfC composites exhibits a non-monotonic dependence on the increase in HfC content, initially decreasing and then increasing. This trend reveals a critical optimization threshold, where ablation resistance is best at intermediate HfC concentrations.

Table 1.
Relative density, thickness, burn-through time, and linear ablative rate of W-HfC composites.
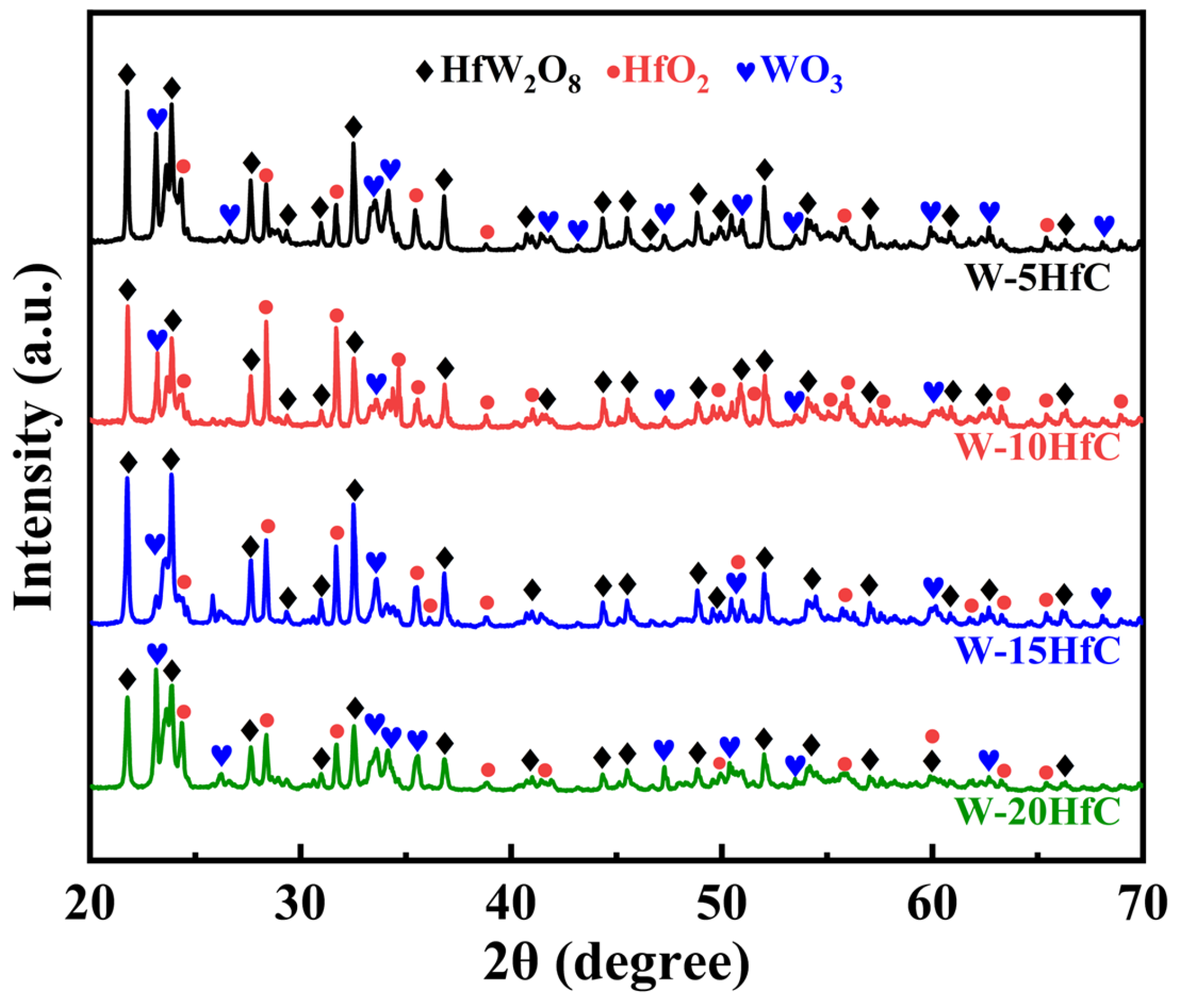
The XRD diffraction pattern presented in Figure 4 indicates that the oxidation products generated by W-HfC composites during the ablation process primarily consist of WO3, HfO2, and the composite oxide HfW2O8. This suggests that W and HfC phases within the composite are both oxidized to form an oxide layer throughout the ablation process.
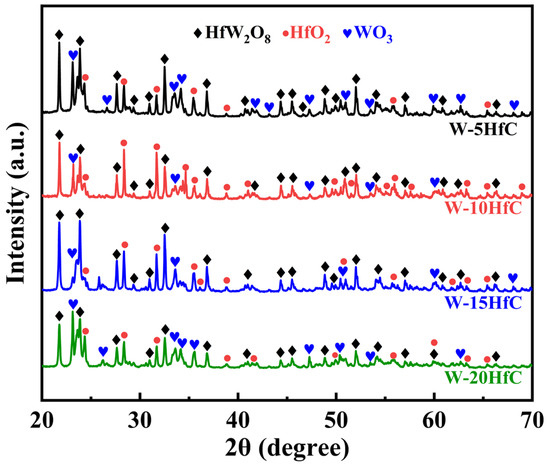
Figure 4.
XRD patterns of the ablated specimen surfaces.
During ablation, tungsten undergoes oxidation to form WO3, exhibiting a bright yellow coloration as observed in the central region of specimens in Figure 3. This porous oxide phase (melting point ≈ 1470 °C) melts and migrates toward the outer area of the surface [25]. HfC additions promote the formation of beneficial HfO2 and HfW2O8 phases, constituting the protective surface oxide layer shown in Figure 3. Notably, the progressive increase in HfC content correlates with a marked reduction in surface WO3 concentration, indicating that the oxidation product of W changes from WO3 to HfW2O8 with the increase in HfC content. The enhanced ablation resistance of W-HfC composites is attributed to the formation of a dense HfO2-HfW2O8 composite oxide scale, which seals surface pores and suppresses both inward oxygen permeation and outward metallic species migration during ablation. Ideally, sufficient HfC additions enable complete oxide scale coverage to maximize oxidation–ablation resistance. However, exceeding the 10 wt% HfC threshold induces a marked decline in ablation resistance concurrent with the emergence of ablation-induced crack propagation in post-test specimens. This performance degradation likely stems from HfC-induced embrittlement, where excessive HfC additions reduce fracture toughness, rendering the composite susceptible to thermomechanical stress cracking under coupled high temperature and high-velocity gas flow, which eventually led to a decline in ablation resistance [29].
3.2. Ablated Microstructure
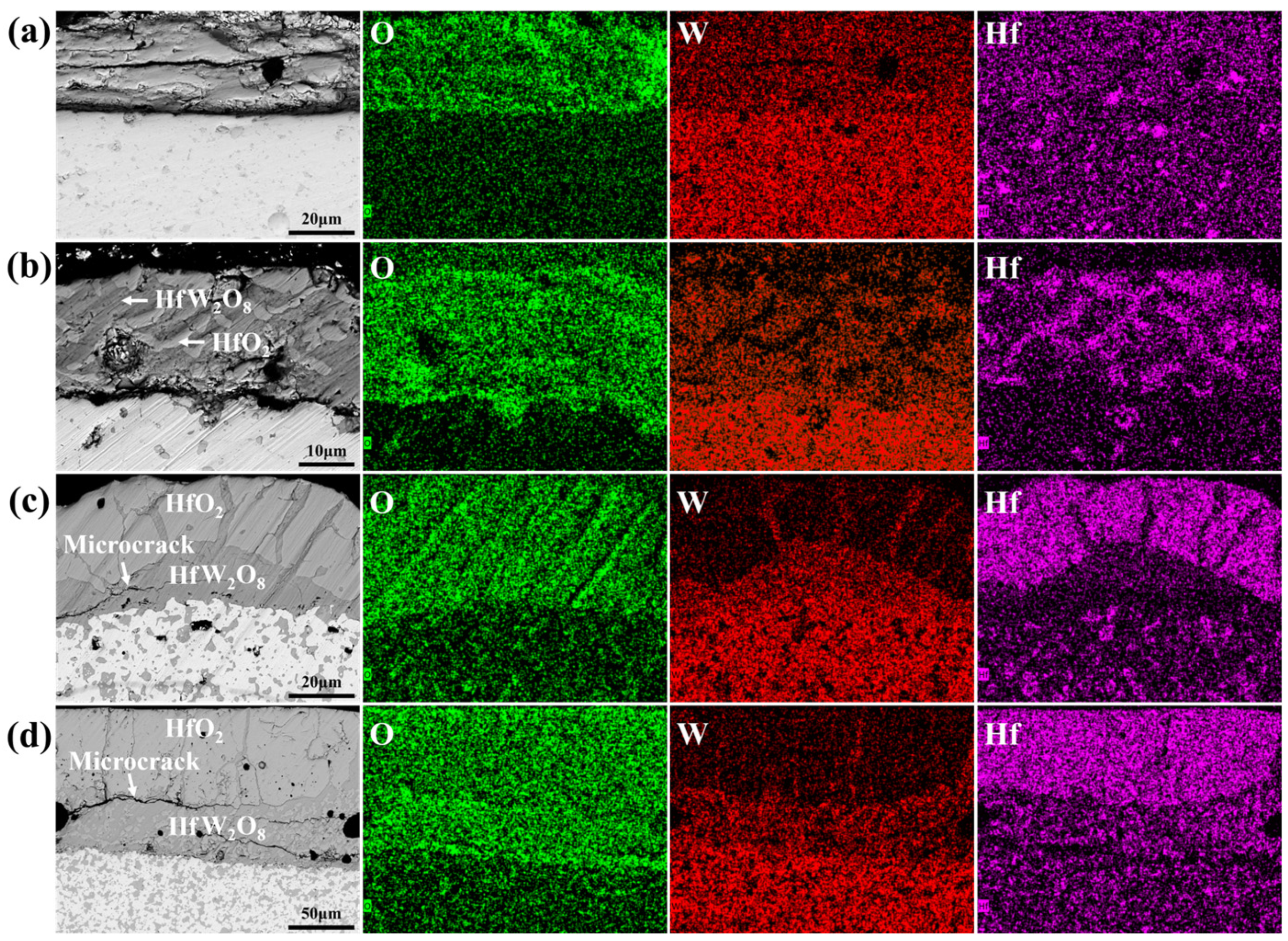
Figure 5 presents section BSE micrographs and EDS elemental mapping of the ablated interface in W-HfC composites. The BSE images reveal a bilayered structure: the lower region corresponds to the bulk W-HfC material, while the upper region constitutes the oxide layer. Within the bulk material, the light-gray matrix is identified as W, and dark-gray particulates represent HfC reinforcements. EDS analysis confirms compositional segregation in the oxide layer, with W-rich phases (primarily HfW2O8 and minor WO3) and Hf-rich phases (HfO2) coexisting. The oxide scale across all W-HfC composites comprises a mixture of WO3, HfW2O8, and HfO2.
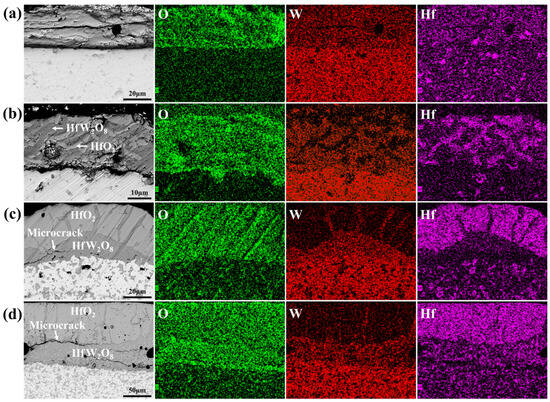
Figure 5.
Section BSE and EDS mapping images of ablated specimens: (a) W-5HfC; (b) W-10HfC; (c) W-15HfC; (d) W-20HfC.
Figure 5 indicates that W-HfC composites with different HfC contents formed different oxide layer structures during the ablation process. EDS mapping reveals distinct phase distributions: W-5HfC primarily forms the composite oxide HfW2O8 with limited HfO2 particles. The oxide layer exhibits internal cracking, while the outer surface transforms into a granular structure under high-temperature and high-velocity gas flow scouring, indicating insufficient HfO2 formation to protect the matrix at low HfC additions. In contrast, W-10HfC develops a dense oxide layer comprising an HfW2O8 matrix uniformly reinforced with monolithic HfO2 particles. The synergistic combination of HfW2O8 (exhibiting negative thermal expansion) and HfO2 (exhibiting exceptional high-temperature stability and oxidation resistance) ensures tight interfacial bonding, resulting in optimal ablation resistance at 2800 °C. With increasing HfC content, W-15HfC and W-20HfC develop a stratified oxide structure where HfO2 aggregates into an outer protective layer, while HfW2O8 predominantly resides in the inner oxide region, with a small part diffusing outward into the HfO2 layer. The thermal expansion coefficient mismatch between HfO2 and HfW2O8 induces deleterious microcracks within the oxide layer, accelerating oxygen inward diffusion, thereby increasing the linear ablation rate and reducing the ablation resistance.
3.3. Ablation Mechanisms
There are various reactions in the ablation process of W-HfC composites, written as follows [25,30]:
2W + 3O2 → 2WO3
W + 3H2O → 2WO3 + 3H2
W + 3CO2 → WO3 + 3CO
2HfC + 3O2 → 2HfO2 + 2CO
HfC + 3CO2 → HfO2 + 4CO
2WO3 + HfO2 → HfW2O8
The primary oxidation product of W at high temperatures is WO3, while HfC predominantly forms HfO2 under similar conditions. WO3 and HfO2 can react via solid-state interactions to generate composite oxide HfW2O8 at elevated temperatures.
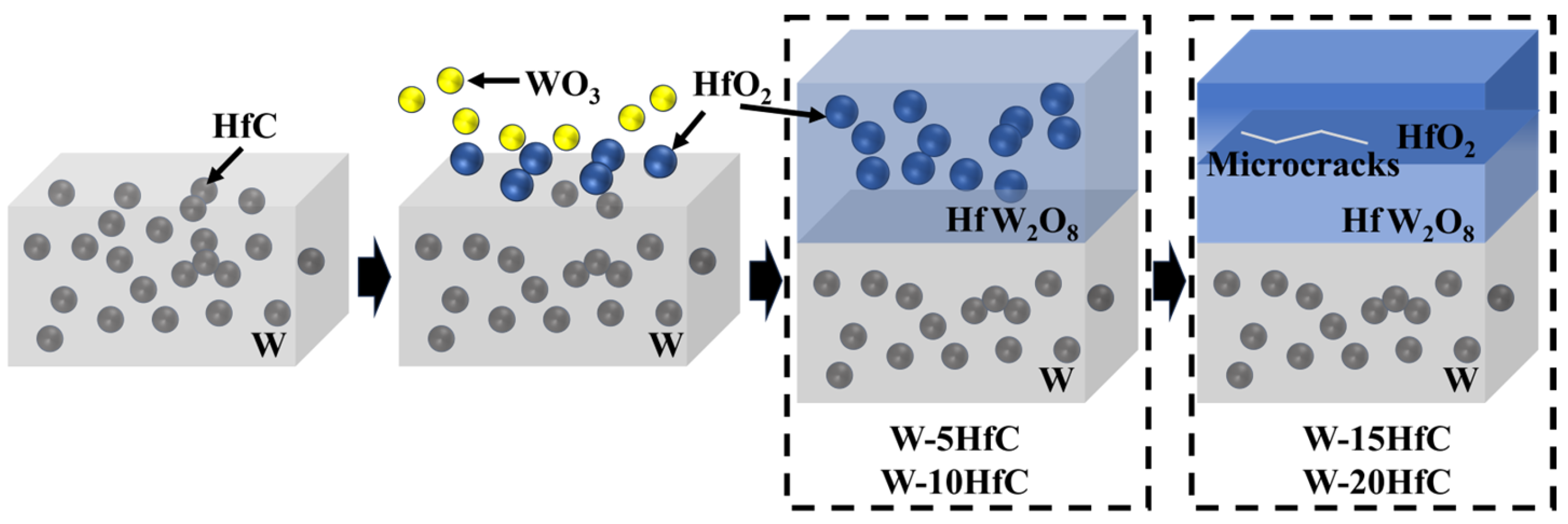
The proposed ablation mechanism of the composite material is illustrated in Figure 6. Tungsten initiates oxidation at approximately 400 °C, forming porous and loosely structured yellow WO3, which partially sublimates or melts during subsequent ablation. Subsequently, HfC particles oxidize under ablation temperatures to primarily generate blocky HfO2. For W-5HfC and W-10HfC composites, the resultant HfO2 reacts with WO3 at elevated temperatures to form HfW2O8, a composite oxide exhibiting negative thermal expansion behavior [31]. HfW2O8 demonstrates low thermal conductivity and enhanced thermodynamic stability under high-temperature oxygen-rich environments, effectively converting detrimental WO3 into a protective phase. HfW2O8 forms a dense barrier layer that encapsulates residual blocky HfO2 particles. The HfO2 phase contributes superior thermophysical properties, including a high melting point (2900 °C) and low thermal conductivity (1.5 W/m·K) [32]. The synergistic combination of this dense oxide structure and uniformly distributed HfO2 effectively impedes inward heat transfer and oxygen diffusion, thereby shielding the bulk W-HfC from further ablation damage. Consequently, moderate HfC additions (~10 wt%) optimize the ablation resistance of W-HfC composites.
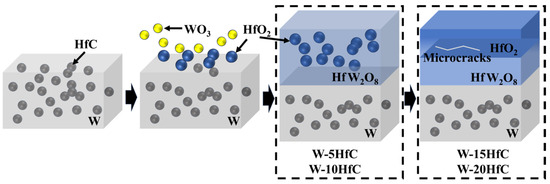
Figure 6.
Proposed ablation mechanism of W-HfC composites.
For W-15HfC and W-20HfC composites, elevated HfC content drives excessive HfO2 generation during ablation. Beyond reacting with WO3 to form HfW2O8, residual HfO2 progressively aggregates and migrates toward the surface, culminating in a bilayered oxide structure: an outer HfO2-rich layer and an inner HfW2O8-dominated zone. Owing to the negative thermal expansion coefficient of HfW2O8, interfacial thermal expansion mismatch arises between the HfO2 and HfW2O8 layers. This mismatch induces microcrack nucleation within the oxide scale during ablation, which accelerates inward heat transfer and oxygen diffusion. Consequently, intensified oxidative penetration degrades the ablation resistance of W-HfC composites.
4. Conclusions
In this study, W-HfC composites with varying HfC contents were fabricated via spark plasma sintering (SPS). Their high-temperature ablation behaviors under an oxyacetylene flame at 2800 °C were systematically investigated, and the ablation mechanisms were analyzed, leading to the following conclusions:
- (1)
- For insufficient HfC content (5 wt%), the dominant ablation product of W-HfC composites is HfW2O8, with limited HfO2 formation during high-temperature ablation. The sparse HfO2 distribution fails to effectively block heat flux and oxygen ingress. The W-5HfC composite exhibits a linear ablation rate of 0.0208 mm/s.
- (2)
- Optimal ablation resistance is achieved at 10 wt% HfC content with a minimized linear ablation rate of 0.0175 mm/s. The W-10HfC composite forms HfW2O8 with negative thermal expansion coefficients and uniformly dispersed HfO2 blocks during ablation. The dense oxide layer, featuring strong interfacial bonding between HfW2O8 and HfO2, effectively impedes heat and oxygen penetration, thereby enhancing ablation resistance.
- (3)
- Excessive HfC additions (15, 20 wt%) promote excessive HfO2 formation, which aggregates and migrates outward, forming a layered structure with HfW2O8. The thermal expansion mismatch between these oxides induces microcracks, accelerating heat flux and oxygen infiltration, and degrading ablation performance.
These findings demonstrate that moderate HfC incorporation (~10 wt%) significantly enhances the ablation resistance of W-HfC composites, establishing them as promising candidate materials for rudders and nozzles of rocket motors.
Author Contributions
Methodology, Y.W. and Z.D.; validation, L.D. and B.Z. (Baohong Zhang); investigation, B.Z. (Boyuan Zheng) and Y.W.; resources, Z.D. and X.H.; data curation, B.Z. (Boyuan Zheng) and C.S.; writing—original draft preparation, B.Z. (Boyuan Zheng); writing—review and editing, Y.W. and X.H.; project administration, Y.W., X.H. and Z.D.; funding acquisition, Y.W. and X.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed at the corresponding authors.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors Zhong Du, Liye Du, and Baohong Zhang were employed by the company Advanced Technology & Materials Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Federici, G.; Zhitlukhin, A.; Arkhipov, N.; Giniyatulin, R.; Klimov, N.; Landman, I.; Podkovyrov, V.; Safronov, V.; Loarte, A.; Merola, M. Effects of ELMs and disruptions on ITER divertor armour materials. J. Nucl. Mater. 2005, 337–339, 684–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.F.; Xie, Z.M.; Liu, R.; Fang, Q.F.; Liu, C.S.; Han, W.Z.; Wu, X.B. Hierarchical microstructures enabled excellent low-temperature strength-ductility synergy in bulk pure tungsten. Acta Mater. 2022, 228, 117765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.; Fang, Z.Z.; Xu, L.; Ligda, J.P.; Paramore, J.D.; Butler, B.G. An investigation of the microstructure and ductility of annealed cold-rolled tungsten. Acta Mater. 2019, 162, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Ma, Z.; Yu, L.; Liu, Y. Achieving high strength and ductility in ODS-W alloy by employing oxide@W core-shell nanopowder as precursor. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Dong, D.; Zhang, M.; Gao, Y.; Wu, Z.; Wang, D. Enhanced ultra-high temperature creep resistance originating from preferred microstructures of W-Re-HfC alloys. Mater. Charact. 2024, 218, 14585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.W.; Li, Z.R.; Wu, Z.P.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Liu, S.C.; Zhao, W.L.; Mao, C.R.; Li, L.Y.; Liu, J.M.; Jie, J.C. Novel insight into relationship between microstructure and ablation behavior of Cu-W alloys prepared by melt infiltration: Experiments and molecular dynamics. Compos. Struct. 2025, 363, 119126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.X.; Zhu, J.P.; Jin, W.; Jiang, C.L.; Zhang, X.D.; Wang, J.W.; Ye, X.Q.; Chen, C.G. The transport, retention, and distribution behavior of deuterium in W-Ni-Fe alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2025, 931, 148223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Lu, Z.L.; Li, Y.L.; Ding, Y.H.; Chen, Q.Y.; Li, H.; Xu, H.X.; Cui, X.Y.; Sun, T.T. Effect of different composition ratio on mechanical properties of W-Fe-B alloy. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2025, 130, 107181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesemann, I.; Spielmann, W.; Heel, P.; Hoffmann, A. Fracture strength and microstructure of ODS tungsten alloys. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2010, 28, 687–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.J.; Zhang, L.M.; Luo, G.Q.; Zhang, J.; Tu, R.; Wu, C.D.; Shen, Q. Microstructural evolution and mechanical behavior of W-Si-C multi-phase composite prepared by arc-melting. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 712, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.N.; Miao, Q.; Wei, S.Z.; Li, Z.; Sun, T.L.; Xu, L.J. Microstructure and mechanical properties of W-ZrO2 alloys by different preparation techniques. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 774, 210–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.K.; Miao, S.; Xie, Z.M.; Liu, R.; Zhang, T.; Fang, Q.F.; Hao, T.; Wang, X.P.; Liu, C.S.; Liu, X.; et al. Thermal stability and mechanical properties of HfC dispersion strengthened W alloys as plasma-facing components in fusion devices. J. Nucl. Mater. 2017, 492, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattern, A.; Huchler, B.; Staudenecker, D.; Oberacker, R.; Nagel, A.; Hoffmann, M.J. Preparation of interpenetrating ceramic–metal composites. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2004, 24, 3399–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.T.; Li, X.W.; Zha, Y.F.; Zhou, X.L.; Peng, D.L.; Hua, N.B.; Chen, W.Z. Fabrication and high temperature tribological properties of WC reinforced W-Cu composites. Mater. Today Commun. 2021, 28, 102550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, J.R.; Zhang, G.H. Preparation and properties of W-30 wt% Cu alloy with the additions of Ni and Fe elements. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 928, 167040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.L.; Fu, Y.Q.; Liu, Y.; Lu, J.W.; Zhang, W.; Huo, W.T.; Jin, L.H.; Zhang, Y.S. Interface engineering of graphene/copper matrix composites decorated with tungsten carbide for enhanced physico-mechanical properties. Carbon 2021, 173, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.F.; Cheng, J.G.; Wei, B.Z.; Zhang, M.L.; Luo, L.M.; Wu, Y.C. Microstructure and properties of La2O3 doped W composites prepared by a wet chemical process. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2017, 66, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.J.; Tu, R.; Luo, G.Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, J.W.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, L.M. Synergetic effect of Re alloying and SiC addition on strength and toughness of tungsten. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 767, 1064–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, S.; Xie, Z.M.; Yang, X.D.; Liu, R.; Gao, R.; Zhang, T.; Wang, X.P.; Fang, Q.F.; Liu, C.S.; Luo, G.N.; et al. Effect of hot rolling and annealing on the mechanical properties and thermal conductivity of W-0.5wt.% TaC alloys. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2016, 56, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.W.; Xie, Z.M.; Wang, Y.K.; Liu, R.; Zhang, T.; Hao, T.; Wang, X.P.; Fang, Q.F.; Liu, C.S. Mechanical properties and thermal stability of pure W and W-0.5wt%ZrC alloy manufactured with the same technology. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 715, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, X.J.; He, P.F.; Zhang, P.; Sun, C.; Liang, X.B.; Xing, Y.; Duan, X.M.; Wang, Y.J.; Hu, Z.F. In-situ formation and ablation mechanism of dense and multilayered ZrB2-ZrSi2-MoSi2 ultra-high temperature ceramic composite coating on Ta-W alloy under plasma blame beyond 2000 °C. Corros. Sci. 2024, 237, 112316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xie, Z.; Cheng, X.; Jing, K.; Zhang, L.; Yang, J. Microstructural evolution and thermal fatigue damage mechanism of second-phase dispersion strengthened tungsten composites under repetitive thermal loads. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2023, 140, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhang, T.; Song, G.M.; Chen, L.; Wei, B.X.; Zhao, Y.W.; Zhou, Y. Refractory carbide reinforced tungsten matrix composites. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 925, 166342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.N.; Chen, Y.; Ma, M.F.; Zhu, L.H.; Li, Y.R.; Guo, B.B. Investigation on microstructure and reinforcement mechanism of the TiC-reinforced W-matrix composite prepared by high-energy ball milling and spark plasma sintering. Vacuum 2024, 220, 112841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.J.; Umer, M.A.; Ryu, H.J.; Hong, S.H. Elevated temperature ablation resistance of HfC particle-reinforced tungsten composites. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2014, 43, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ma, S.; Zhu, J.; Kang, K.; Luo, G.; Wu, C.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, L. Microstructure and Compression Strength of W/HfC Composites Synthesized by Plasma Activated Sintering. Met. Mater. Int. 2019, 25, 416–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.Z.; Gao, L.; Lou, L.H.; Li, R.; Song, J.P.; Liu, Y.L.; Qi, Y. Microstructure and mechanical properties of W-HfC alloy synthesized by in-situ fabrication via pressureless sintering. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2025, 127, 106978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.M.; Tang, Z.X.; Liu, R.Z.; Zhou, Z.; Yi, M.Z.; Peng, K. Preparation and ablation behavior of solid solution ceramic Ta0.2Zr0.8C-SiC matrix-modified C/C composites under high heat flux. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2025, 35, 1875–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, P.; Wang, S.; Yu, Y.P.; Fang, B.; Li, H. Improved toughness of HfC with tantalum fibre net and tantalum foil. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 19260–19266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamura, Y.; Nakajima, N.; Tsuji, T.; Iwasa, Y.; Saito, K.; Sorai, M. Heat capacity and Grüneisen function of negative thermal expansion compound HfW2O8. Solid State Commun. 2002, 121, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.F.; Wang, G.; Zhang, Z.P.; Pan, K.M.; Zeng, X.H. Synthesis of negative thermal expansion HfW2O8 thin film using pulsed laser deposition. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 13855–13859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, H.P.; Stevens, R. Hafnia and hafnia-toughened ceramics. J. Mater. Sci. 1992, 27, 5397–5430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).