Abstract
The 1.9 billion metric tons of steel globally manufactured in 2023 justify the steel industry’s pivotal role in modern society’s growth. Considering the rapid development of countries that have not fully taken part in the global market, such as Africa, steel production is expected to increase in the next decade. However, the environmental burden associated with steel manufacturing must be mitigated to achieve sustainable production, which would align with the European Green Deal pathway. Such a burden is associated both with the GHG emissions and with the solid residues arising from steel manufacturing, considering both the integrated and electrical routes. The valorisation of the main steel residues from the electrical steelmaking is the central theme of this work, referring to the steel electric manufacturing in the Dalmine case study. The investigation was carried out from two different points of view, comprising the action of a plasma electric reactor and a RecoDust unit to optimize the recovery of iron and zinc, respectively, being the two main technologies envisioned in the EU-funded research project ReMFra. This work focuses on those preliminary steps required to detect the optimal recipes to consider for such industrial units, such as thermodynamic modelling, testing the mechanical properties of the briquettes produced, and the smelting trials carried out at pilot scale. However, tests for the usability of the dusty feedstock for RecoDust are carried out, and, with the results, some recommendations for pretreatment can be made. The outcomes show the high potential of these streams for metal and mineral recovery.
1. Introduction
Steel production, with a global output of nearly two Gigatons (Gt) per year, is a cornerstone of the global industrial landscape. In Europe, over 0.17 Gt of steel was produced in 2023, with 53.8% utilizing the Blast Furnace–Basic Oxygen Furnace (BF-BOF) route—commonly referred to as Iron and Steel Making (ISM)—and 46.2% using Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) technology [1]. The production process generates a range of by-products, including slags, sludge, mill scale, flue dust, and tailings. These by-products mostly contain valuable materials such as iron, carbon, and metals, presenting opportunities for reuse [2].
Addressing global warming has become a pressing challenge for the steel industry, due to the increase in atmospheric CO2 concentration from approximately 315 ppm in 1958 to ~425 ppm by December 2024 [3]. A key pathway to reducing CO2 emissions in steelmaking involves replacing traditional blast furnace technology with alternative processes. These include natural gas-based direct reduction methods and emerging hydrogen-based technologies. Such transitions could lead to energy savings of approximately 57% and CO2 reductions of up to 95% [4]. Moreover, sustainable solutions for managing steel production by-products are urgently needed. Some traditional recycling processes, such as the sinter plant, may no longer be feasible following technological transformations [5,6]. Certain by-products, such as zinc-containing dusts, cannot be recycled internally due to zinc limitations in the blast furnace [7]. Although external recycling solutions exist, they are costly and constrained by zinc content restrictions [8,9,10]. For example, German companies cite annual figures between 2030 and 2050 as the time horizon for the transformation to virtually CO2-free steel production, depending on the depth of the transformation [5].
The ReMFra technology is a promising new approach for treating existing and future by-products. In contrast to extant processes such as the Waelz process, rotary hearth furnace, Oxycup, or DK process, RecoDust does not rely on coke [11]. This technology aligns with future demands for by-product recycling, like sustainable resource management, integration of current and alternative production routes, categorization of by-products and residual materials [12], while offering enhanced capabilities, such as recovering iron and zinc from basic oxygen furnace (=BOF) and electric arc furnace (=EAF) dusts. This study outlines the preliminary steps necessary for the successful pilot-scale implementation of ReMFra technologies, including modelling and defining mass and energy balances for the plasma reactor and RecoDust units. Historical industrial stream data provided by Bergamo, Italy, Dalmine S.p.A (Dalmine, Italy). served as the basis for this modelling, with the same data informing subsequent pilot operations. A scheme of the ReMFra process is shown in Figure 1. In addition to state-of-the-art wet granulation, the more efficient dry granulation method with optimal waste heat utilization is suitable for recycling RecoDust slag [13,14].
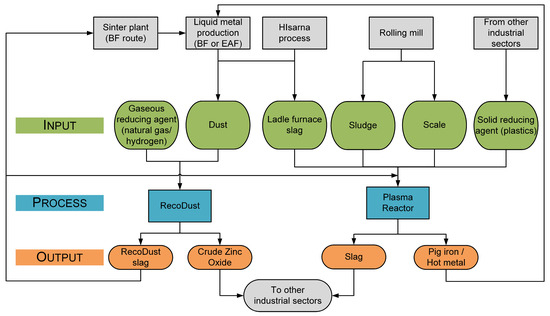
Figure 1.
Scheme of the ReMFra process, modified from [15].
For the plasma reactor, these outcomes served as a basis for the briquetting trials and the following smelting in laboratory-scale facilities; that is, to ensure sufficient mechanical stability of the briquettes and the efficiency of Fe and Zn recovery, once fed to the pilot-scale plasma reactor unit. The carbon source for this investigation was not conventional fossil-coke, but an extrudate made of I.BLU plastic® and iron scale from Dalmine facilities. These trials aim to demonstrate that smelting the selected recipes from Dalmine streams alongside the plastic/scale extrudate should lead to high metal recovery and carburization.
For the RecoDust unit, these results form the foundation for utilizing various types of dusty feedstocks in the RecoDust pilot plant. Even though the RecoDust process can process dry dust without pre-treatment, certain requirements for the use in the RecoDust pilot plant must be met for dust from the iron and steel industry: dust must be dry and free-floating, with a maximum grain size of about 400 µm [16]. To achieve these goals, pre-processing steps must be defined. Three different kinds of dust, two from BOF and one from EAF, were used to test the moisture and the smelting range.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preliminary Modelling and Historical Data Analysis
Historical data of the industrial streams have been analysed using the thermodynamics model of mass and energy. (Internal data provided by Tenaris Dalmine (Bergamo, Italy, ReMFra project).
For the plasma reactor, these outcomes served as a basis for the definition of mixtures for briquette production to be used in pilot trials after characterization at laboratory-scale facilities; that is, to ensure sufficient mechanical stability of the briquettes, and the efficiency of metal recovery once fed into the plasma reactor unit. The carbon source for this investigation was conventional anthracite, a patented recycled raw material IBLU (known also as BLUAIR) developed by Iren, made from post-consumer plastic packaging waste, and iron scale from Dalmine facilities. The characterization of the raw residues was performed through routine internal laboratory analysis. These included X-ray fluorescence (XRF) for main oxides, LECO combustion analysis for carbon and sulphur, gravimetric drying at 105 °C for moisture, bulk density tests, and particle size measurements by laser diffraction. The data were shared with the ReMFra consortium and used by RINA-CSM to define suitable briquette compositions. These trials will aim to demonstrate that smelting the selected recipes from Dalmine streams alongside the polymer/scale extrudate should lead to high metal recovery and metal bath carburization.
The plasma reactor is based on plasma technology. It utilizes an electrical arc generated by graphite electrodes and operates in a reducing atmosphere [17]. This pyrometallurgical process was selected for its ability to treat various waste streams. In the ReMFra project, the plasma reactor was applied to residues with high iron content, such as scale from rolling mills, sludge from cooling water circuits, EAF/BOF dusts, and slags. The scheme of the plasma reactor is shown in Figure 2.
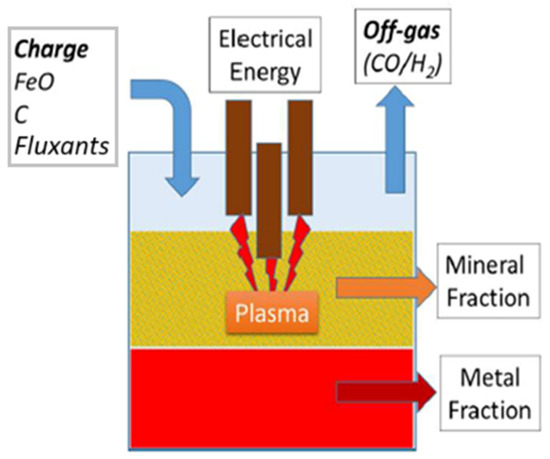
Figure 2.
Scheme of the plasma reactor, reprint from [18].
During the process, several key phenomena occur: the heating of briquettes or pellets to the process temperature of 1600 °C, the reduction of FexOy to metallic Fe, the melting of inert materials, FeO, and Fe, and the dissolution of FeO into the slag. Mass and energy balances, performed through thermodynamic calculations, were used to define operational ranges, evaluate the quality of the resulting metal and slag, and calculate the required amounts of reducing agents and energy demand. The input materials were briquetted to enhance the efficiency of the reduction reactions. The scheme of the plasma reactor reporting the input and output is shown in Figure 3.
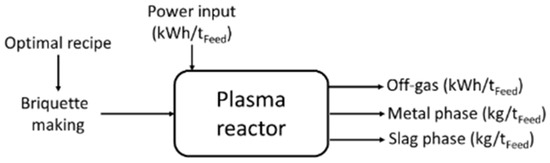
Figure 3.
Scheme reporting the input and output regarding the plasma reactor.
The briquette, with densities higher than the slag, were charged from the top of the reactor and passed through the slag layer to the metal/slag interface, where the reduction reactions occurred. Thermodynamic modelling provided initial insights into the optimal composition for the briquettes.
The briquettes were composed of a mix of industrial residues, including significant proportions of scale, LF slag, and rolling mill sludge, combined with smaller amounts of EAF dust and binders such as molasses and CaO [19].
Some assumptions were made for the mass balance, including the distribution of chemical species between metal, slag, and dust, which was based on literature data, prior experiments, and industrial tests. The metal bath was assumed to contain 3 wt.% carbon, and the coal used for reduction was considered to have 10% ash content.
For the energy balance, parameters were calculated at a process temperature of 1600 °C, assuming that only CO was generated during the reduction reaction and that the process gases reached the same temperature as the reactor. The metal-to-slag ratio was targeted to exceed 1.5, and the slag composition was optimized to achieve a basicity ((CaO + MgO)/(Al2O3 + SiO2)) between 1.2 and 1.8. Slag behaviour during the process, particularly foaming, was also considered. Foaming slag improves heat transfer, protects furnace components, and stabilizes the process by submerging the arc. However, foam height depends on the slag properties and gas velocity, and is challenging to control. Reactor design accounted for these phenomena, ensuring sufficient slag mass for productivity while maintaining optimal FeO concentration through strategic feeding and tapping.
Regarding RecoDust, the moisture and smelting range were tested with three different kinds of dust: two from a basic oxygen furnace and one from an electric arc furnace.
2.2. Material Plasma Reactor
The historical data provided by Tenaris Dalmine were considered as input for the first calculation; the industrial streams considered were EAF slag, LF slag, Scale, Rolling Mill Sludge, and EAF dust. These materials were characterized by chemical composition, moisture content, and density, to establish their suitability for briquetting and subsequent smelting in the plasma reactor. Specifically, the following analyses were carried out: chemical composition (main oxides) via X-ray fluorescence (XRF); carbon and sulfur contents using LECO combustion analysis; moisture content via oven-drying at 105 °C until constant weight; and bulk density via volume displacement methods.
To assess the potential of ReMFra technologies for the Dalmine case study, it is essential to determine the annual production of each stream. This will be the primary boundary condition considered for modelling, enabling a preliminary dimensioning of the processing unit. While Table 1 shows the chemical composition declared for the streams, Table 2 below shows their annual production, average density, and moisture degree.

Table 1.
Chemical composition (wt.%) of the industrial streams provided by Tenaris Dalmine is used for the formulation of ReMFra briquettes. Elemental values were determined by X-ray fluorescence (XRF) for oxides and by combustion analysis (LECO) for carbon and sulfur.

Table 2.
Annual production, average density and moisture content of the industrial streams provided by Tenaris Dalmine, a partner of the project. All values are based on internal reports and routine laboratory characterizations performed at the Dalmine plant.
The abovementioned materials were used to create briquettes. The briquetting process involved blending these streams with additives such as molasses and CaO [20,21] to improve cohesion and mechanical properties through the formation of calcium saccharate bonds. The specific weight proportions for each component are reported in Table 3.

Table 3.
Weight percentages (wt.%) of each component in the three ReMFra briquette formulations.
Adjustments to water content were made to optimize the workability of the mixtures, ensuring consistent briquette quality. Briquettes were formed using a 20-ton hydraulic press and dried under controlled conditions (100 °C for 24 h) before being subjected to mechanical testing, including drop tests from 1 m height (10 repetitions), to evaluate their resistance during handling and feeding into the reactor.
Thermodynamic modelling was conducted to define the optimal compositions of the briquettes, considering factors such as slag basicity, energy balance, and metal recovery efficiency. Recipes were iteratively refined to balance the proportion of materials, with the goal of achieving high-density briquettes suitable for the operational conditions of the plasma reactor.
2.3. Materials and Description of RecoDust
The RecoDust process consists of four steps, as shown in Figure 4. The first step, the slagging and melting, takes place in the so-called Flash-Reactor at temperatures of 1500 °C to 1800 °C and a reducing atmosphere. The heat and the reducing atmosphere are provided by a natural gas/oxygen burner using an air excess ratio of below one. The fuel, natural gas, can be mixed with up to 10% hydrogen, which is the first step towards decarbonization. The second step involves post-combustion through the injection of oxygen. In addition to the combustion of CO and H2, the gaseous zinc is also oxidized to solid zinc oxide. After the quenching by the ignition of water and air, the flue gas cleaning takes place in a bag house filter. The non-volatile components form a slag phase, the so-called RecoDust slag (RDS = Product #1), and are tapped discontinuously out of the Flash-Reactor. The second product in the filter house is the so-called Crude Zinc Oxide (CZO = Product #2) and consists of volatile components like zinc, lead, and halogens.
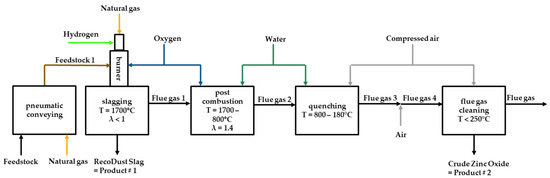
Figure 4.
Steps of the RecoDust process, reproduced from [16], with permission from Springer Nature, 2025.
The experimental work for the samples comprised testing of the moisture content and the smelting range. The samples used were taken from two different basic oxygen furnace dusts (=samples BOF 1 and BOF 2) and one EAF dust (=sample EAF 1). Sample BOF 1 contained 19.2% zinc oxide and 38.7% total iron, while sample BOF 2 contained 2.6% zinc oxide and 58.4% total iron. The last sample, EAF 1, had a zinc oxide content of 5.0% and a total iron content of 32.4%.
The moisture testing was performed using a vacuum drying oven in an air atmosphere, and the heating microscope was utilized to determine the smelting range in a normal air atmosphere. The oven used for the determination of the moisture (shown in Figure 5) is set at at 105 °C, with a pressure of 0.5 bar, until the weight consistency is reached.
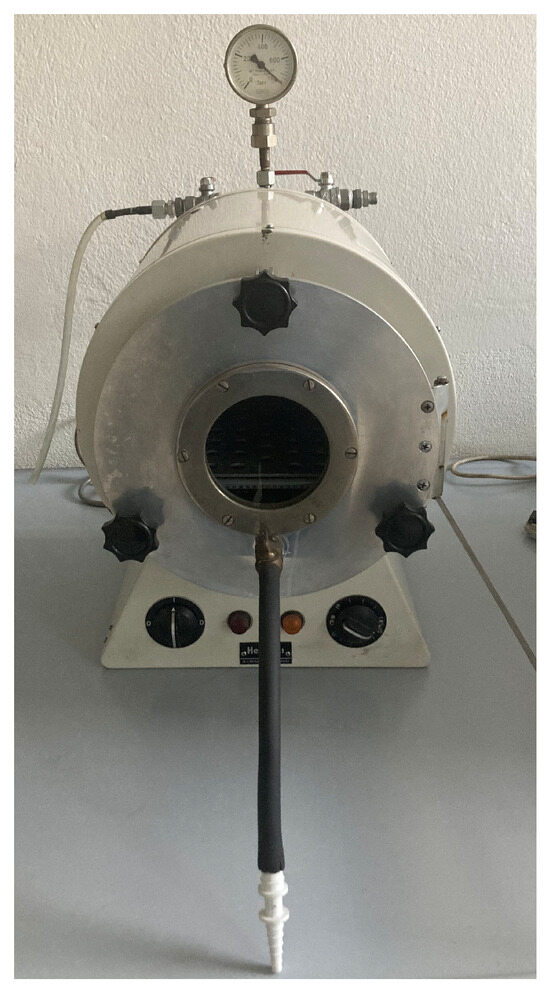

Figure 5.
Drying oven for the determination of the moisture.
3. Results
3.1. Plasma Reactor
The first compositions of the briquettes will be defined starting from the annual tons and the chemical composition of the residues of Tenaris Dalmine to be treated.
To lower the CO2 footprint of the process and to minimize the consumption of non-renewable resources, a testing campaign replacing anthracite with a waste polymer produced by IBLU as a reducing agent was performed. IBLU is a Recycled Raw Material, compliant with UNI 10667-17 used in metallurgical and steel processes as a substitute for coal. It intervenes in the production cycle with the functions provided by the technical standard (e.g., reducing agent), improving economic and environmental performance. The IBLU polymer is characterized by a low density (0.35 g cm−3), measured according to the Archimedean principle by determining the volume displaced by the solid sample in a liquid medium, a low moisture content of 0.37%, and an ash content of 4.15%. It consists almost entirely of volatile matter of 95.9%, with a total carbon content of 73.99%, of which less than 1% is fixed carbon, and a hydrogen content of 11.87%. A fraction of scale was used to produce, by IBLU, a product with 75% scale and 25% of polymer, obtained by extrusion and then charged in the plasma reactor. The composition of IBLU (75% scale and 25% polymer) was defined to obtain an appropriate density value permitting the passage through the slag phase during the charging in EAF. The value obtained was 2.55 g cm−3.
The choice of Tenaris for plasma reactor charge materials, was IBLU (Figure 6) made with a fraction of the scale and the remaining scale in briquettes, with the other materials (named ReMFra briquettes).

Figure 6.
I.BLU extrudate, reprint from [18].
IBLU is used as alternative reducing agents in the plasma reactor trials. These compact “biscuit-like” elements were produced by extruding a homogeneous mixture of 75 wt.% iron-rich scale and 25 wt.% IBLU polymer. Their cylindrical geometry, mechanical cohesion, and bulk density of 2.55 g/cm3 were specifically designed to allow them to sink through the slag layer and promote contact with the molten bath. Their low moisture content (<0.4%) and high volatile matter (>95%) make them particularly reactive in high-temperature reducing environments.
The compositions considered were as follows:
- Ratio 70:30, ReMFra 1: IBLU.
- Ratio 30:70, ReMFra 2: IBLU.
- Ratio 50:50, ReMFra 3: IBLU.
The definition of the three ReMFra briquette compositions, reported in Table 4, was guided by detailed mass and energy balance calculations, aiming to ensure optimal performance regarding metal recovery, slag behaviour, and energy input in the plasma reactor. These recipes were designed to valorise the total annual quantity of iron scale produced at the Dalmine steel shop (24,000 t/y). The proportion of each stream was adjusted to meet several targets: maintain a metal-to-slag ratio above 1.5, achieve a slag basicity in the range 1.2–1.8, ensure an overall Fe/C weight ratio compatible with the desired level of carburization in the molten metal, and optimize the density of the input materials to guarantee their proper sinking through the slag layer during charging. Recipe 1 includes the highest proportion of rolling mill sludge and EAF dust among the three, while maintaining moderate levels of LF slag and coal as reducing agents. Recipe 2 further increases the fraction of sludge and EAF dust while reducing the coal content, resulting in a higher Fe/C ratio and, consequently, a lower expected carburization of the molten metal. Recipe 3 maximizes the use of iron-rich scale and balances the remaining components to ensure both mechanical stability and metallurgical performance.

Table 4.
Weight percentages (wt.%) of each component in the three ReMFra briquette formulations.
Table 4 shows the composition of the ReMFra briquettes for the three cases. Considering the treatment in the plasma reactor of all the scale produced in one year in the Dalmine steel shop, with IBLU and the rest in ReMFra briquettes, these three compositions have been defined.
The behaviour of briquettes has been studied through melting tests.
To ensure efficient heat transfer and uniform melting of the materials, the smelting trials were conducted using a molten metal bath composed of iron with an addition of 10 wt.% nickel. The nickel was intentionally added as a tracer element to enable accurate tracking of the metal phase during post-process chemical analysis and calculation of the metallic yield.
Adding nickel, which acts as a tracer, was necessary to allow for considerations and subsequent calculations downstream of the chemical analyses and the metal yield. The briquettes, ReMFra and IBLU, were weighed each time to obtain the compositions of the three cases.
Both ReMFra and IBLU briquette are loaded into an external cup addition system of the Balzer induction furnace: as soon as the metal bath is completely melted, they are gradually inserted through a lever. Figure 7 shows the moment immediately after the briquettes have been inserted into the metal bath.
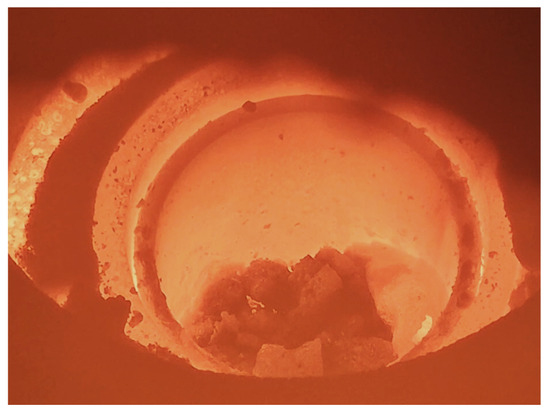
Figure 7.
Loading of both ReMFra/IBLU briquettes into the metal bath.
Once everything is melted, the furnace is turned off, and the sample is allowed to cool, first inside the furnace itself and then in air.
The extracted metal ingot is then processed to obtain chips and thin sheets, which will undergo chemical analysis to determine the content of carbon, sulfur, and nickel. The slag will also be set aside for XRF analysis of oxides. Specifically chemical composition was determined by X-ray fluorescence (XRF) using a benchtop spectrometer. The samples were prepared as pressed powder pellets, and the results were calibrated using certified reference materials. Data processing was carried out with the standard software provided by the instrument manufacturer. Table 5 below shows the slag analysis.

Table 5.
Chemical composition of the slag (wt.%).
Knowing the metal’s carbon content, for metal ingots 1, 2, and 3, it was possible to calculate the carbon content only on the reduced metal: this is defined as the sum of the metal loaded initially and the recovered fraction of metal multiplied by the percentage of total carbon and divided by the recovered fraction of metal. These results are shown in Table 6.

Table 6.
Recovered fraction of metal, metallic yield, and carbon content on the reduced metal.
Melting tests of IBLU and ReMFra briquettes showed high recovery of the metal fraction but low carburization of the metal bath. The different compositions of anthracite and IBLU polymer could explain this. The latter has no fixed carbon, but only carbon from volatiles, with low efficiency for bath carburization compared to the fixed carbon of anthracite. While the experimental trials focused on the IBLU extrudate as an alternative reductant, the modelling phase also considered a conventional scenario based on anthracite coal, assuming 10% ash content and a significant proportion of fixed carbon. This comparison helped define baseline values for carbon efficiency, energy demand, and Fe/C ratios. As expected, anthracite showed superior carburization potential compared to IBLU, which consists mainly of volatile carbon and lacks fixed carbon. From a technical standpoint, the lower carbon yield from IBLU indicates that additional carbon input or complementary reductants may be required to reach the target of 3 wt.% C in the molten bath. Moreover, an economic comparison is currently ongoing to evaluate the cost-performance trade-offs between using recycled polymer-based materials and conventional reductants. While IBLU offers potential cost and environmental advantages, due to its waste-based origin, its lower metallurgical efficiency in carburization must be carefully considered in industrial applications. It is possible to calculate the amount of carbon required to obtain a metal bath with 3% carbon (obtaining hot metal). In order to decide which ReMFra briquettes to use for industrial testing, an economic and environmental impact assessment will be made to understand the impact on the plasma reactor process of producing steel (low carbon) versus cast iron (high carbon).
Since the goal is to reach around 3% carbon in the molten metal, the assessments indicated that an increased carbon input is required in the original blends.
Table 7, below, reports some output from the model necessary for the technical engineering of the plasma reactor (made by Tenova, Milano, Italy) and the process, including the volume of the reactor (depending on the height achieved by the metal bath and the foam of the slag), the volume and heat of the off-gas before and after Zn recovery (off-gas and post-combustion, respectively), the energy demand for the process, and the coal to be added for oxide reduction.

Table 7.
Calculated parameters related to using three recipes with the materials from Dalmine, necessary for the engineering of the plasma reactor.
The process required 1795 kWh to 1868 kWh per ton of feed, including the energy to heat the reactor and sustain the reduction reactions, converting FeO and ZnO into metallic Fe and Zn. The off-gases generated offered a heat recovery potential of 163–193 kWh per ton of feed, which could be harnessed using technologies such as Organic Rankine Cycles (ORC) or heat exchangers. The briquettes were tailored to optimize iron and zinc recovery from residues generated in EAF processes, balancing chemical reactivity, mechanical strength, and slag compatibility.
Some first calculations for reactor volume were made, starting from the ladle diameter. This is to control the formation of foam during the reduction reaction. The foaming can be difficult to control properly, since the evolution of the chemical and physical conditions in the slag/steel system that affect foam height is generally unknown. Foam is generated by the gas (CO) passing through the liquid slag; the foam height depends on slag properties and the gas velocity. The following is a classical formulation to calculate slag height.
Where is a foaming index, depending on slag characteristics: viscosity (μ), density (ρ) and surface tension ():
where k is a coefficient specific to slag type. For the slag composition calculated with this first briquette composition, k~214 [22].
Knowing the reactor diameter, it is possible to calculate the hight (Hfoam) of the foaming slag, as follows:
3.1.1. Engineering Solution
Tenova performed both the basic and detailed engineering for modifying Ladle Furnace #3 (LF3) at the Tenaris Dalmine steel shop to accommodate the ReMFra smelting and reduction process. The main objective was to enable the treatment of steelmaking residues, including slags, scales, sludges, and filter dusts, while keeping LF3 fully functional under normal operations. By strategically limiting design changes to the ladle, material handling system, and automation layer, Tenova minimized the impact on routine production and streamlined the overall implementation.
A new ladle was devised specifically for the ReMFra project, addressing two major constraints: (i) the limited electrode travel length that sets the minimum molten bath level and (ii) the maximum foaming slag volume that can be safely contained to prevent overflow. As illustrated in Figure 8, the basic ladle design accounts for these dimensional limits in order to maintain both adequate arc operation and slag-freeboard distance, and the 3D model of the ladle, where the refractory lining concept is detailed; load-stability checks are verified for various configurations of steel bath height and slag layers.
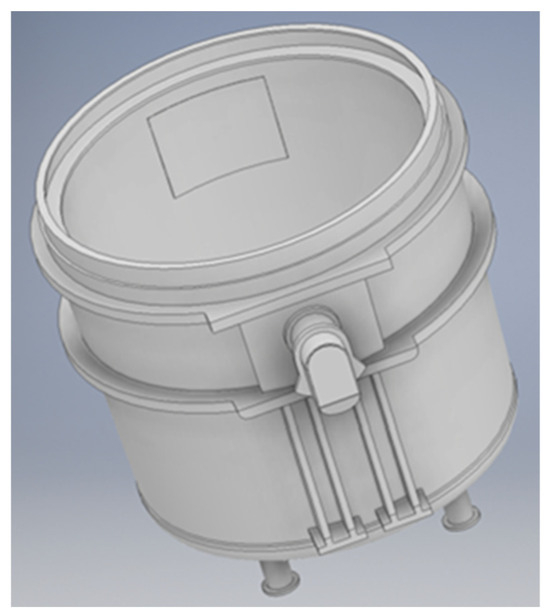

Figure 8.
Basic 3D design of the new ladle.
Based on thermodynamic data from earlier project phases, Tenova set a nominal briquette feed rate of around 7.5 t h−1 to balance high throughput with safe foaming behaviour. This rate is expected to produce roughly 9 t/h of molten metal and 4.5 t/h of slag, under the specified metallurgical conditions. The materials, thickness, and metallic structures of the ladle’s lining were chosen to withstand repeated thermal cycles between normal LF treatments and the higher-reduction environment typical of ReMFra.
Ensuring stable and continuous briquette feeding to the ladle is crucial to the ReMFra process. Batch feeding would lead to significant CO surges and exacerbate slag foaming. Therefore, Tenova expanded the existing Material Handling System by adding two new silos, each with a capacity of around 10 m3, along with vibratory feeders that can operate between 5 and 10 t/h.
This continuous feeding setup enables operators to regulate briquette supply in real time, preventing sudden peaks in CO evolution and promoting uniform melting conditions. Furthermore, it enables LF3 to quickly transition from standard steel-refining tasks to ReMFra operations without significant equipment reconfiguration.
3.1.2. CFD Simulation of Off-Gases
A key step in validating these modifications was verifying that the LF3 roof and off-gas system could manage the increased CO production and partial combustion inside the ladle. Tenova therefore conducted comprehensive CFD simulations of the hood and duct network, modelling scenarios at briquette feed rates of 5, 7.5, and 10 t/h. Figure 9 illustrates a simplified model used for CFD inputs.
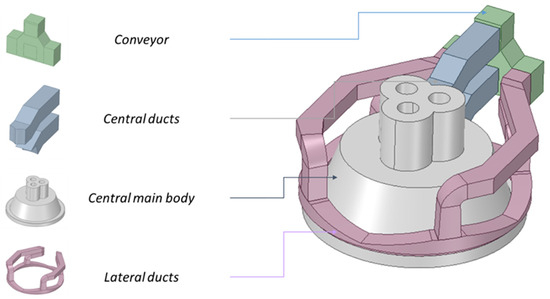
Figure 9.
Design of the LF roof for the CFD analysis.
The detailed boundary conditions, summarized in Figure 10, were established to capture reactive flow, heat transfer, and the entrainment of ambient air through the gap around the ladle.
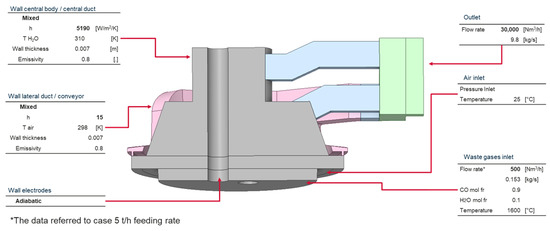
Figure 10.
CFD boundary condition.
The results, illustrated by the temperature maps in Figure 11 and wall temperature distributions in Figure 12, confirmed that the existing hood design stays within acceptable thermal limits if the nominal feed rate is around 7.5 t/h.
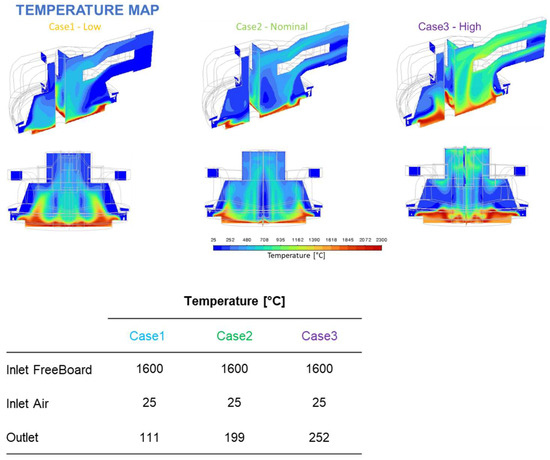
Figure 11.
Off-gas temperature map for the three cases, and numerical results, reprint from [18].
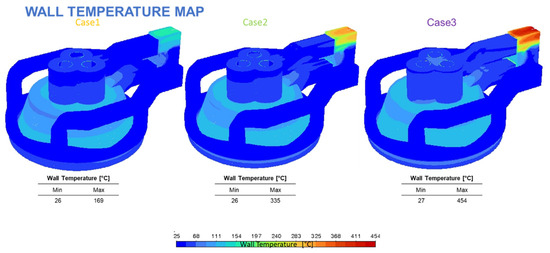
Figure 12.
Wall temperature map for the three scenarios, and numerical results.
Even in the higher 10 t h−1 scenario, local temperature hotspots were identified but did not exceed critical thresholds for brief operation. Figure 13 shows how the velocity fields in the off-gas converge smoothly toward the extraction ducts. Overall, these findings indicate that no significant hardware alterations (e.g., to the off-gas duct or roof structure) are necessary under normal ReMFra operating conditions.
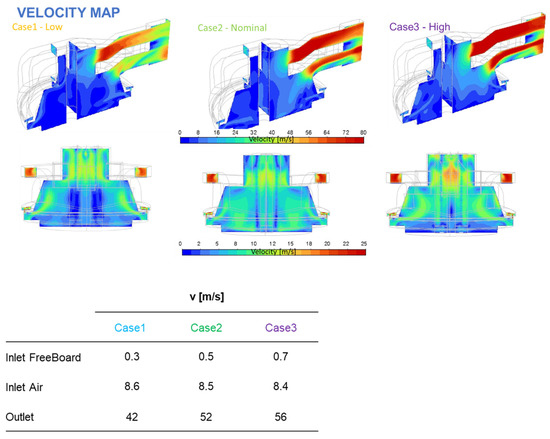
Figure 13.
Off-gas velocity map and numerical results.
Moreover, an integrated control platform enables a safe transition from typical production cycles to ReMFra campaigns, providing both the necessary flexibility and the robust constraints to avoid undesired fluctuations in slag foaming or off-gas composition.
3.2. RecoDust
Figure 14 shows the results of the moisture content determination. Sample BOF 1 has a very low moisture content of less than 1%, sample BOF 2 has a moisture content of approximately 3.1%, and sample EAF 1 has the highest moisture content, at over 4.1%.
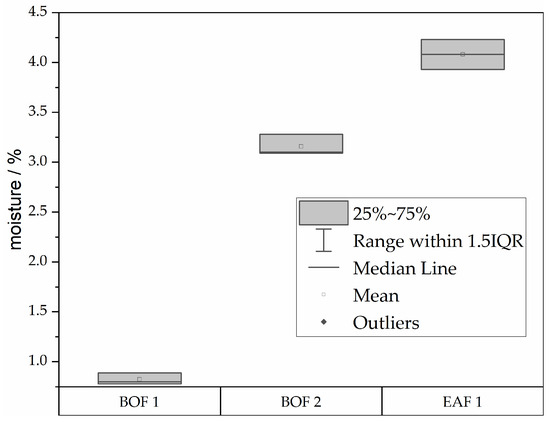
Figure 14.
Moisture of both BOF dust samples and the EAF dust.
The smelting behaviour is shown in Figure 15. The comparison of the initial sample height and the sample height in relation to the temperature indicates that the flow temperature of the EAF dust sample could not be determined until a temperature of 1600 °C. The samples of BOF dust, BOF Dust 1, and BOF Dust 2 show a very similar smelting behaviour. For sample BOF Dust 1, a flow temperature of 1269 °C, and for BOF Dust 2, a flow temperature of 1309 °C, could be determined. The lines for the determination of the flow temperature are dashed.
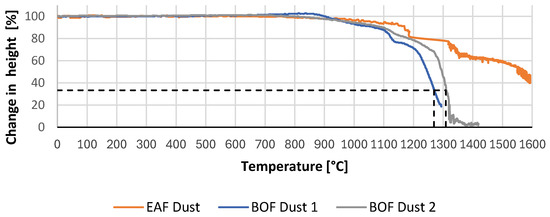
Figure 15.
Sample height compared to its initial height, of the samples BOF 1, BOF 2 and EAF 1 over the temperature.
4. Discussion
The plasma-based smelting trials demonstrated the feasibility of recovering iron-rich metal from various steelmaking residues—including scale, rolling mill sludge, and EAF dust—using briquettes formulated through thermodynamic modelling. The results confirm that industrial by-products can be transformed into high-value outputs (metal, slag, and ZnO dust-enriched) when operating at around 1600 °C in a reducing atmosphere, with the key advantage of the plasma technology being its adaptability to various residue streams. A critical factor emerging from the trials concerns bath carburization. The metal yield proved high, exceeding 75% in most formulations. The final choice of reductant—or reductant blend—will need to balance the environmental benefits of using secondary raw materials with the operational demands for generating a sufficiently carburized liquid metal.
Process economics and environmental impact also arise from the interplay between slag basicity, energy input, and reductant addition. Thermodynamic calculations indicate that slag foaming is likely with these briquette recipes, offering both advantages and challenges. Although foaming can enhance heat transfer and thermal efficiency, it also demands careful furnace dimensioning and control of the gas evolution rate (CO) to prevent excessive foam formation and potential slag overflow. From a design perspective, the optimal ratio of metal to slag, as well as the control of basicity ((CaO + MgO)/(Al2O3 + SiO2)), must be maintained to ensure appropriate slag viscosity and to keep foaming within manageable limits. Energy requirements, ranging from approximately 1795 kWh to 1868 kWh per ton of feed, were broadly consistent with pilot-scale plasma processes targeting similar temperature ranges. Notably, the off-gas carried a substantial portion of recoverable heat (163–193 kWh per ton of feed), suggesting potential for energy recovery via heat exchangers or ORC systems. This aligns with the overall circularity goals of the ReMFRa project, where secondary raw materials and heat recovery strategies can collectively reduce the environmental footprint of steelmaking. Overall, these results underpin the technical viability of employing plasma reactors for valorising iron-rich residues and substituting part of the conventional reductant with polymer-based alternatives.
The results from the three feedstock samples for RecoDust indicate that pre-treatment steps are required for certain types of dust. For the BOF 1 dust sample, both test results fall within the acceptable limits for use in the RecoDust process, meaning that pre-treatment, such as drying or reducing the smelting range, is unnecessary. In contrast, the moisture content of the BOF 2 dust sample revealed that drying is essential, as wet feedstocks cannot be pneumatically introduced into the Flash Reactor. Besides conventional drying, utilizing microwave treatment to dry the dust may be a viable solution [23]. However, the smelting range for BOF 2 dust is suitable for use without further adjustments.
The single EAF sample, on the other hand, shows excessively high moisture content that exceeds acceptable limits, and therefore needs to be dried. Additionally, unlike the BOF samples, its smelting range needs to be lowered. This can be accomplished by mixing the dust with a flux or combining it with another potential feedstock [24]. While the required drying process is technically straightforward, the energy for evaporation would otherwise be consumed within the Flash Reactor if wet feedstocks were utilized. However, drying before trials is more energy-efficient because it avoids heating the water to the reactor’s operating temperature of about 1700 °C.
The humidity test has proven to be highly effective in achieving the desired results. When determining the smelting range, it is important to note that the test atmosphere does not replicate the conditions within the Flash-Reactor. In the Flash-Reactor, the chemical composition of the injected dust undergoes significant changes due to the reduction of zinc, the evaporation of volatile components, and changes in the valence state of iron. As a result, the smelting range test provides only an approximate guide. Nevertheless, it remains a useful and practical measure, particularly when the results indicate a sufficient margin from the application limits.
A key next step is to test whether different types of dusts can achieve high de-zincing rates of more than 98% in the RecoDust process [25]. This involves evaluating the composition and behaviour of various dust samples under standard process conditions. The results will determine the process’s adaptability and efficiency across a broader range of input materials.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, V.P., L.D.S. and W.R.; writing—original draft preparation, V.P., W.R. and M.G.; writing—review and editing, L.D.S., K.D.-H. and W.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This project receives funding by the European Commission within the framework of the Clean Steel Partnership (Grant Agreement no. 101058362).
Data Availability Statement
The original data presented in the study are openly available in Zenodo ReMFra at [Search ReMFra].
Acknowledgments
Grammarly (v1.2.167.1681) was used to revise the article’s language, including orthographic, grammatical, and stylistic improvements.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Wolfgang Reiter was employed by the company K1-MET GmbH, Loredana Di Sante, Vincenzo Pepe were employed by company RINA-CSM, Marta Guzzon was employed by the company TENOVA. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| EU | European Union |
| BF-BOF | Blast Furnace–Basic Oxygen Furnace |
| ISM | Iron and Steel Makin |
| EAF | Electrical Arc Furnace |
| EAFD | Electric Arc Furnace Dust |
| CO2 | Carbon Dioxide |
| ZnO | Zinc Oxide |
| Fe | Iron |
| Zn | Zinc |
| LF | Ladle Furnace |
| CaO | Calcium Oxide |
| MgO | Magnesium Oxide |
| Al | Aluminium |
| Si | Silicon |
| Mg | Magnesium |
| Mn | Manganese |
| Ni | Nickel |
| Cr | Chrome |
| V | Vanadium |
| CFD | Computational Fluid Dynamics |
| GHG | Greenhouse gas |
References
- World Steel Association. 2024 World Steel in Figures. Available online: https://worldsteel.org/data/world-steel-in-figures/world-steel-in-figures-2024/ (accessed on 12 June 2025).
- Biswal, S.; Pahlevani, F.; Sahajwalla, V. Wastes as resources in steelmaking industry—Current trends. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2020, 26, 100377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeling, R. Keeling Curve Lessons. Available online: https://scrippsco2.ucsd.edu/graphics_gallery/mauna_loa_record/mauna_loa_record.html (accessed on 15 May 2025).
- Kienberger, T.; Mobarakeh, M.R.; Lachner, E.; EVT, P.N.; Pomberger, R.; Haslauer, P.; Nigl, T. Systematisches Zusammenwirken von Dekarbonisierung und Kreislaufwirtschaft am Beispiel der Österreichischen Industrie; Montanuniversität Leoben: Leoben, Austria, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Thiel, S.; Thomé-Kozmiensky, E.; Senk, D.G.; Wotruba, H.; Antrekowitsch, H. (Eds.) Mineralische Nebenprodukte und Abfälle 10: Aschen, Schlacken, Stäube und Baurestmassen: Aschen, Schlacken, Stäube und Baurestmassen; Thomé-Kozmiensky Verlag GmbH: Nietwerder, Germany, 2023; pp. 235–242. [Google Scholar]
- Rentz, O.; Geldermann, J. Stoffstrommanagement in der Eisen-und Stahlindustrie: Konkretisierung des § 5 Abs. 1 Nr. 3 BimSchG; Erich Schmidt: Berlin, Germany, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Esezobor, D.E.; Balogun, S.A. Zinc accumulation during recycling of iron oxide wastes in the blast furnace. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2006, 33, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suetens, T.; Klaasen, B.; van Acker, K.; Blanpain, B. Comparison of electric arc furnace dust treatment technologies using exergy efficiency. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 65, 152–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassen, K.-J.; Hillmann, C. The DK Process—A Solution for the By-Products of the European Steel Industry. In Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Metallurgy and Materials, Brno, Czech Republic, 23–25 May 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Rieger, J.; Schenk, J. Residual processing in the European steel industry: A technological overview. J. Sustain. Metall. 2019, 5, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoni, M.; Reiter, W.; Suer, J.; Di Sante, L.; Cirilli, F.; Praolini, F.; Mosconi, M.; Guzzon, M.; Malfa, E.; Algermissen, D.; et al. Towards the Circularity of the EU Steel Industry: Modern Technologies for the Recycling of the Dusts and Recovery of Resources. Metals 2024, 14, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colla, V.; Branca, T.A.; Pietruck, R.; Wölfelschneider, S.; Morillon, A.; Algermissen, D.; Rosendahl, S.; Granbom, H.; Martini, U.; Snaet, D. Future Research and Developments on Reuse and Recycling of Steelmaking By-Products. Metals 2023, 13, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krammer, A.C.; Doschek-Held, K.; Steindl, F.R.; Weisser, K.; Gatschlhofer, C.; Juhart, J.; Wohlmuth, D.; Sorger, C. Valorisation of metallurgical residues via carbothermal reduction: A circular economy approach in the cement and iron and steel industry. Waste Manag. Res. 2024, 42, 797–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raupenstrauch, H.; Doschek-Held, K.; Rieger, J.; Reiter, W. RecoDust—An Efficient Way of Processing Steel Mill Dusts. J. Sustain. Metall. 2019, 5, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doschek-Held, K.; Wolfgang, R. ReMFra—REcovering Metals and Mineral FRAction from steelmaking residues. In Proceedings of the Science4Technology Poster Exhibition, Leoben, Austria, 23–31 May 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Reiter, W.; Lasser, M.; Rieger, J.; Raupenstrauch, H.; Tappeiner, T. Der RecoDust-Prozess—Behandlung von zinkhaltigen Stahlwerksstäuben und weiteren Nebenprodukten aus integrierten Hüttenwerken. BHM Berg-Und Huttenmann. Monatshefte 2020, 165, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samal, S.; Blanco, I. An overview of thermal plasma arc systems for treatment of various wastes in recovery of metals. Materials 2022, 15, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Sante, L. Development of a Pyrometallurgical Approach for Iron and Zinc Recovery: Design and Modeling of a Plasma Reactor within the ReMFRa Projec. Available online: https://www.estep.eu/assets/Events/2024-ESTEP-Annual-event-Linz/Presentations-to-share/Session-4/2_RINA_ESTEP_Annual_Event_2024_Linz_Di-Sante-rev.pdf (accessed on 12 June 2025).
- Lohmeier, L.; Thaler, C.; Harris, C.; Wollenberg, R.; Schröder, H.-W. Briquetting of fine-grained residues from iron and steel production using organic and inorganic binders. Steel Res. Int. 2020, 91, 2000238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousa, E.; Ahmed, H.; Söderström, D. Potential of alternative organic binders in briquetting and enhancing residue recycling in the steel industry. Recycling 2022, 7, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryou, J.-H.; Cho, J.-E.; Park, S.-H.; Kang, C.-O.; Lee, H.-G. Coal Briquette Having Superior Strength and Briquetting Metho Thereof. Patent WO2002050219A1, 12 December 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.S.; Min, D.J.; Park, J.H. Foaming Behavior of CaO–SiO2–FeO–MgOsatd–X (X = Al2O3, MnO, P2O5, and CaF2) Slags at High Temperatures. ISIJ Int. 2001, 41, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ślęzak, M.; Migas, P.; Bernasowski, M. The Use of Microwave Treatment as a Sustainable Technology for the Drying of Metallurgical Sludge. Materials 2024, 17, 6207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fladischer, M. Beeinflussung des Schmelzintervalls von EAF-Stäuben. Bachelor-Thesis, Technical University of Leoben, Leoben, Austria, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Reiter, W.; Rieger, J.; Raupenstrauch, H.; Cattini, L.; Maystrenko, N.; Kovalev, D.; Alexey, A.; Mitrofanov, A. Recovery of valuable materials with the RecoDust process. Metals 2023, 13, 1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).