A Novel Selective Oxygen Pressure Leaching for Zinc Extraction from Hemimorphite in Acid-Free Solutions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
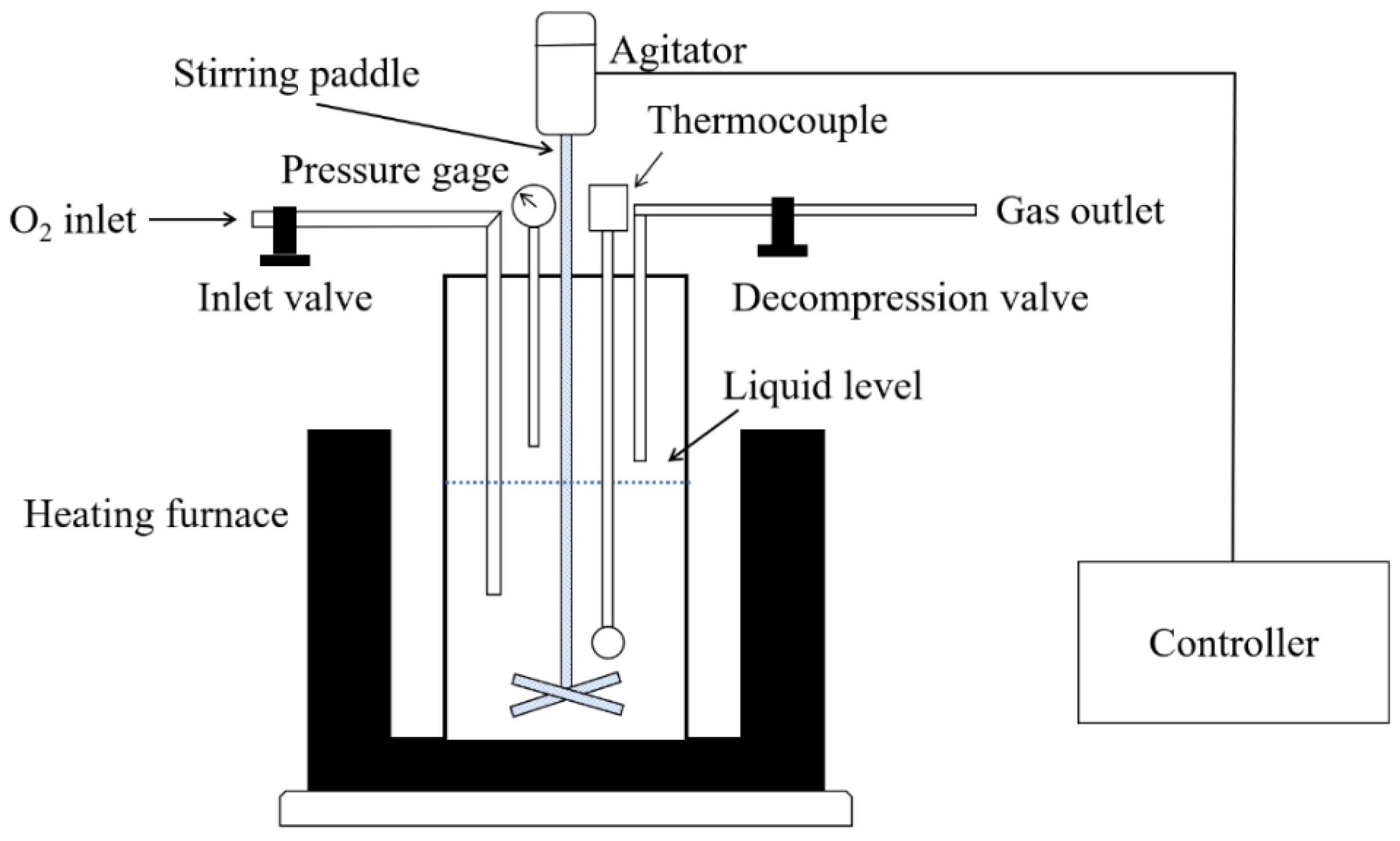
2.1. Materials and Procedure
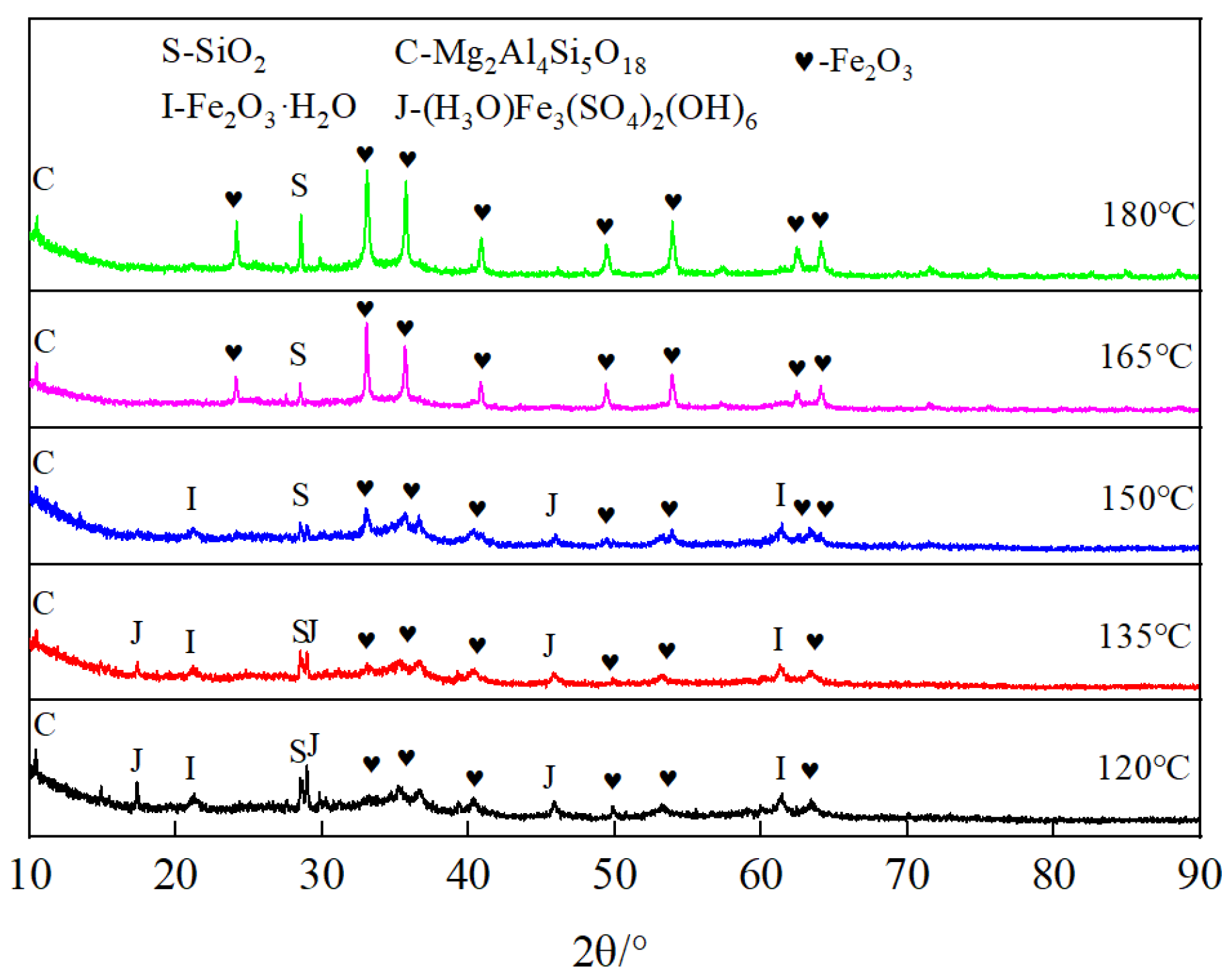
2.2. Analysis and Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
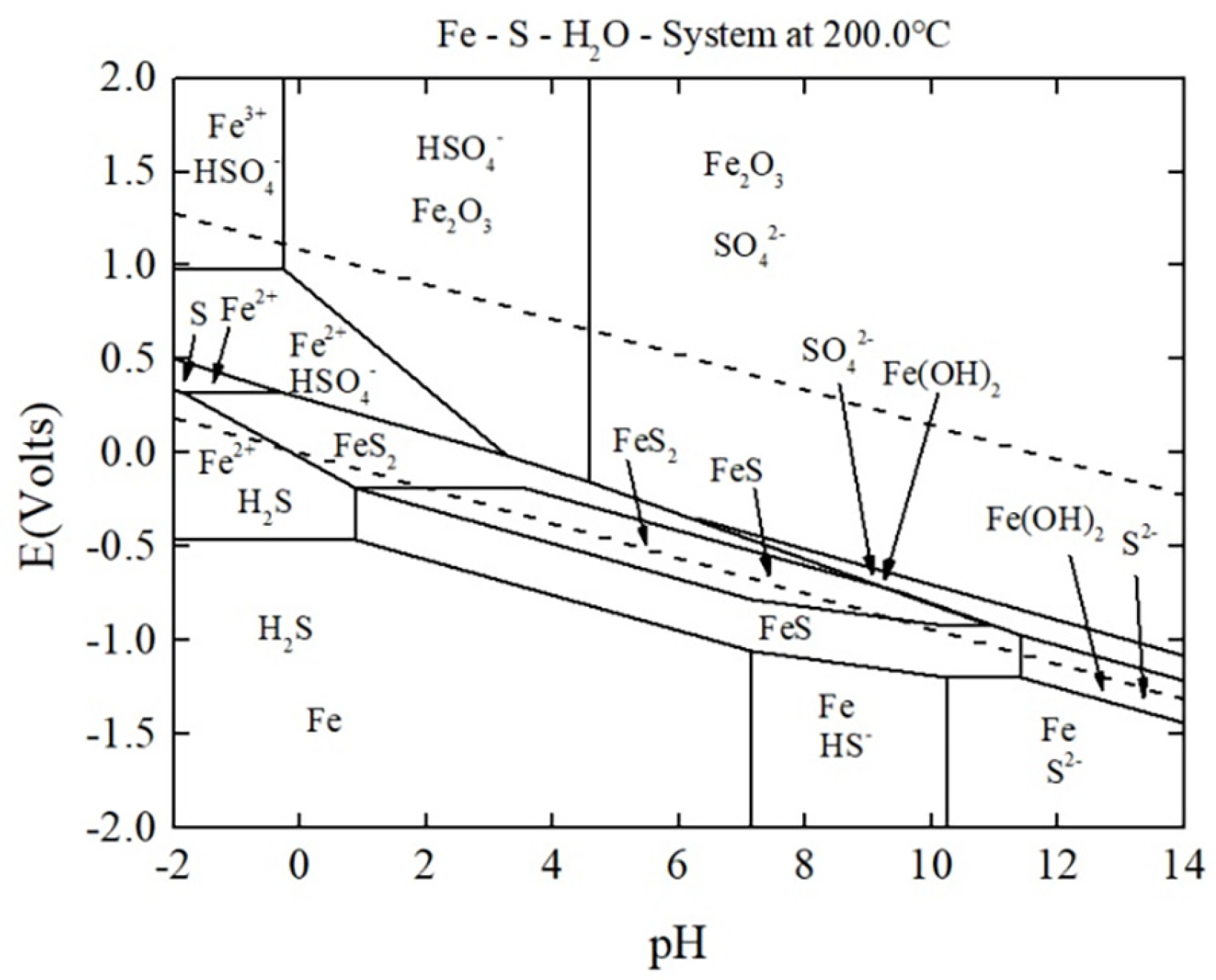
3.1. Feasibility Assessment
| O2(g) = O2(aq) | (3) | |
| FeSO4·7H2O = Fe2+ + SO42− + 7H2O | (4) | |
| 4Fe2+ + O2(g) + 4H+ = 4Fe3+ + 2H2O | ΔrGmθ = 0.25944T − 401.301 kJ/mol | (5) |
| 2Fe3+ + 3H2O = Fe2O3 + 6H+ | ΔrGmθ = −0.0514T − 180.617 kJ/mol | (6) |
| 4Fe2+ + 4H2O + O2(g) = 2Fe2O3 + 8H+ | ΔrGmθ = 0.15664T − 762.534 kJ/mol | (7) |
| Zn4(Si2O7)(OH)2 + 8H+ = 4Zn2+ + 2H4SiO4 + H2O | ΔrGmθ = 0.044T − 363.78 kJ/mol | (8) |
| 4Fe2+ + O2(g) + Zn4(Si2O7)(OH)2 = 4Zn2+ + 2SiO2 + H2O + 2Fe2O3 | ΔrGmθ = 0.158T − 1116.70 kJ/mol | (9) |
| H4SiO4 = 2H2O + SiO2 | ΔrGmθ = 4.811 − 0.0232T kJ/mol | (10) |
| M2SO4 + 3Fe2(SO4)3 + 12H2O = 2MFe3(SO4)2(OH)6 + 6H2SO4 (M = K,Na) | (11) |
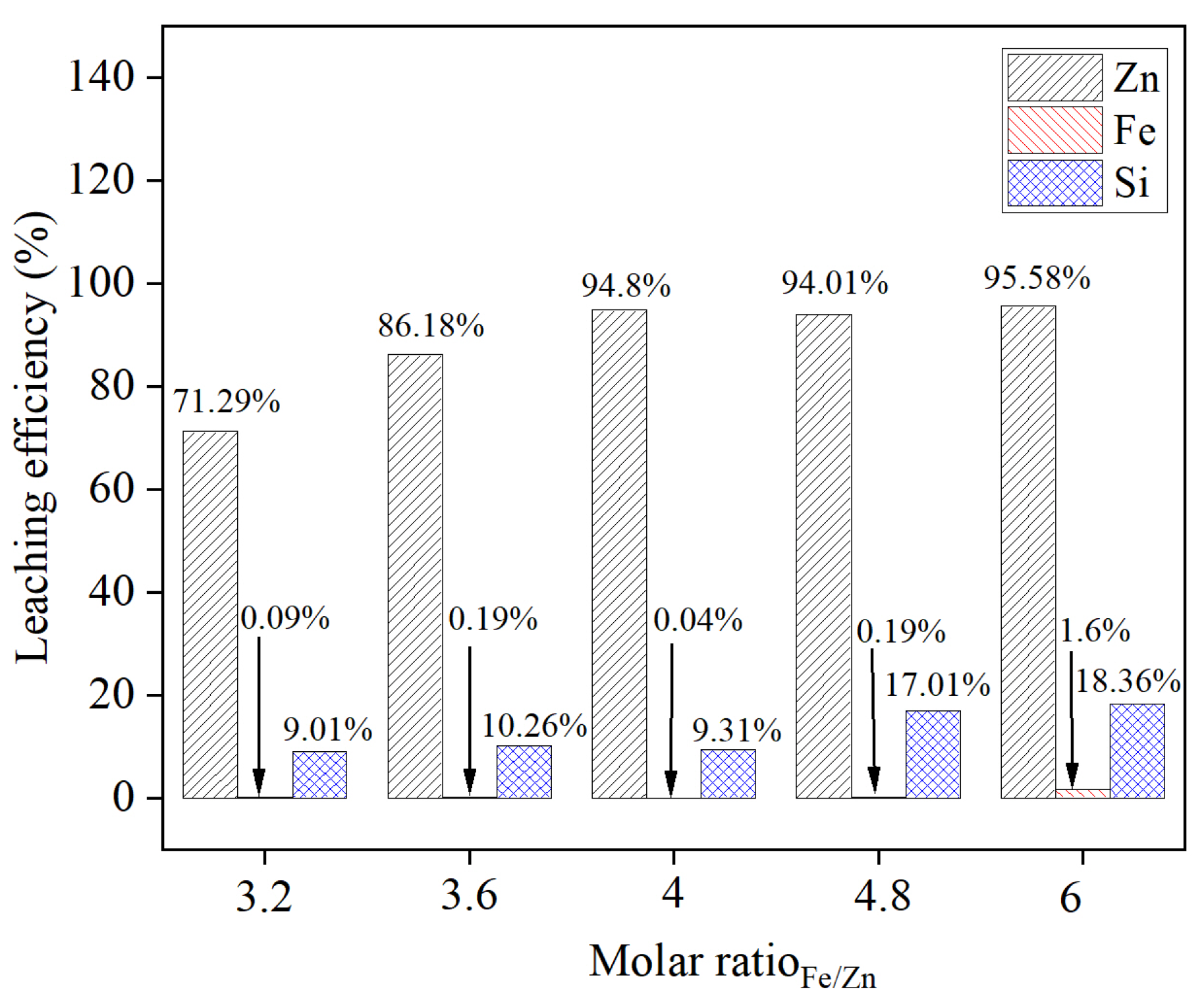
3.2. Effect of the Fe/Zn Molar Ratio
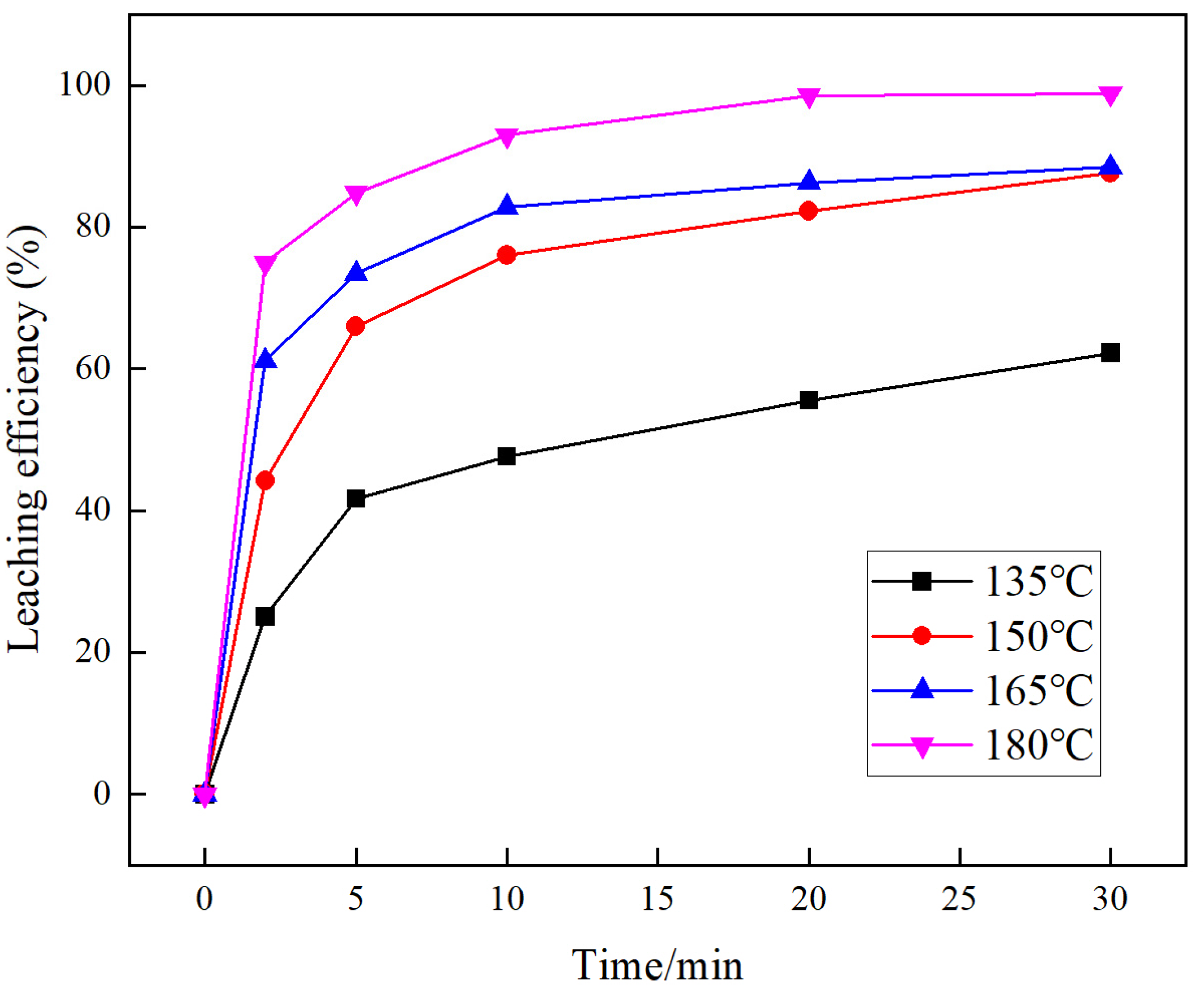
3.3. Effect of the Leaching Temperature
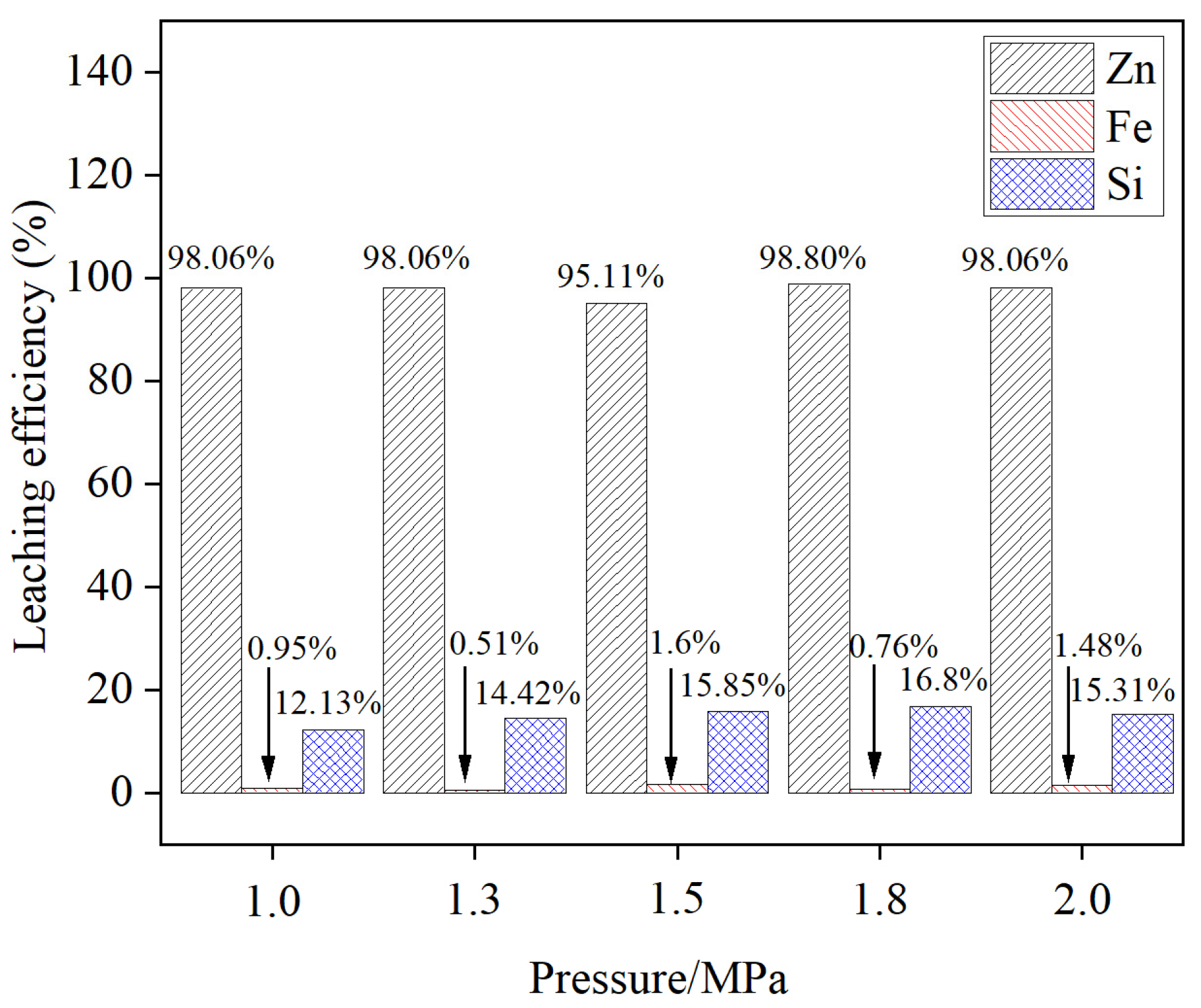
3.4. Effect of the Reaction Pressure
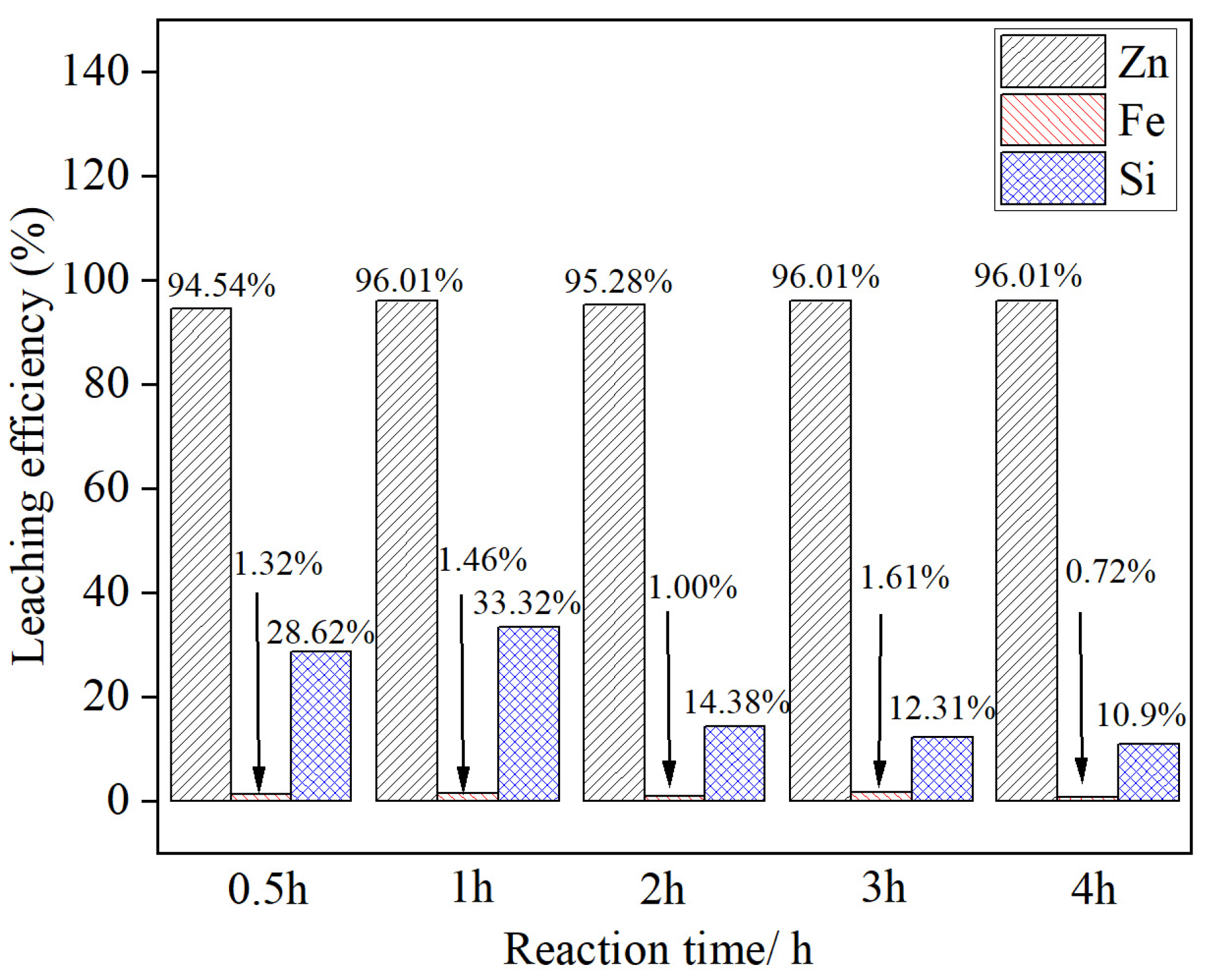
3.5. Effect of the Leaching Time
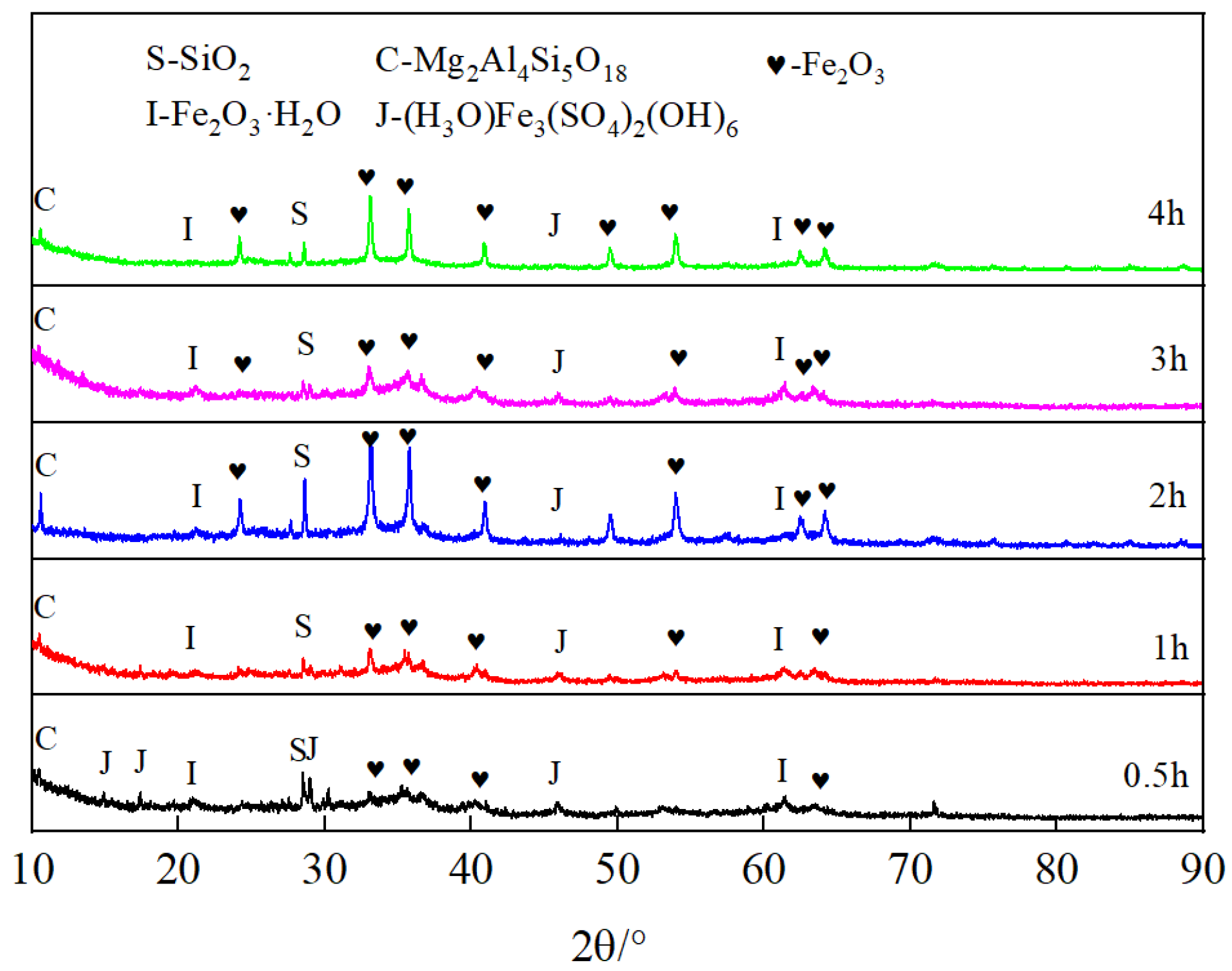
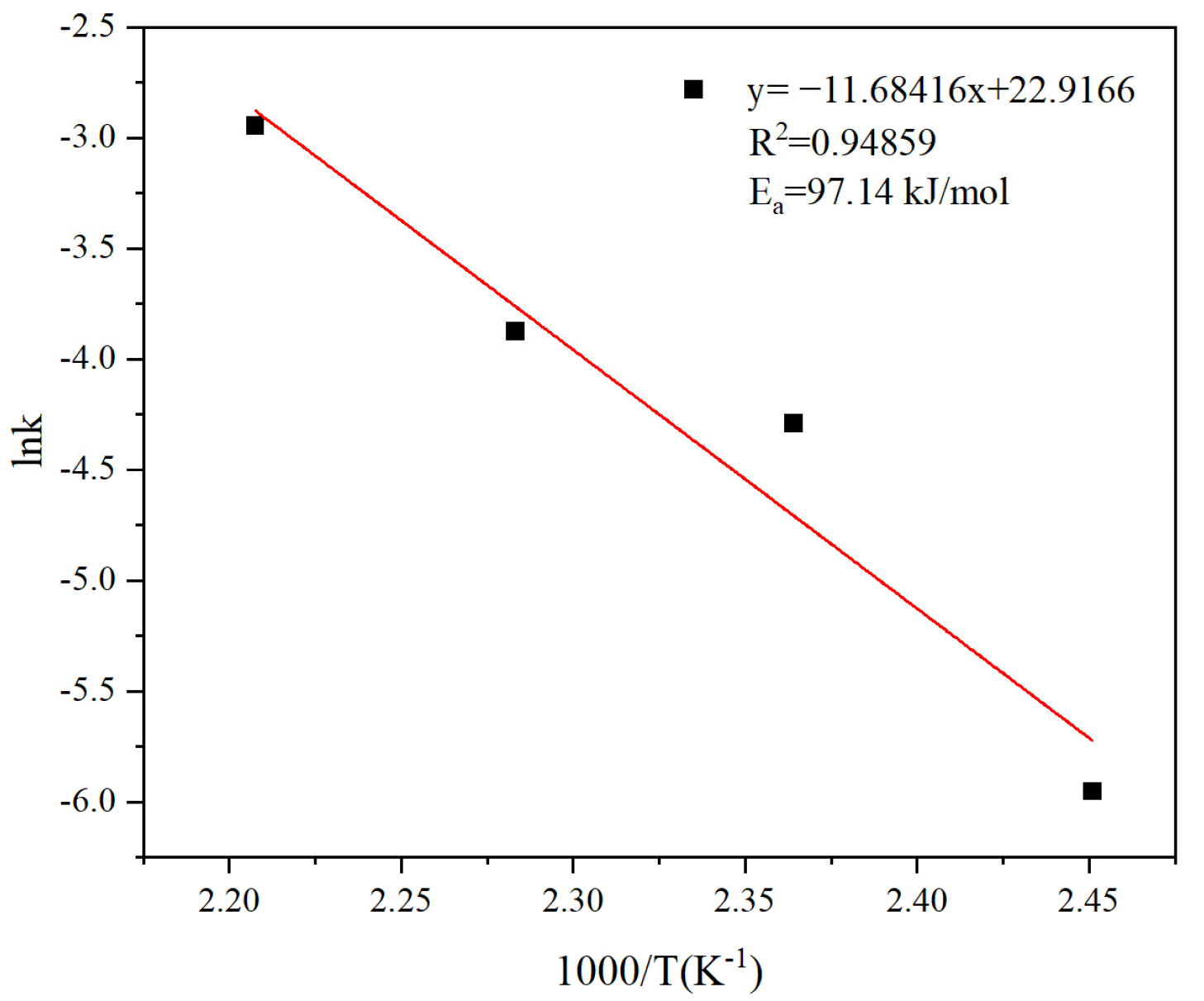
3.6. Analysis of Leaching Kinetics
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xing, Y.; Liu, H.; Deng, Z.; Wei, C.; Li, X.; Li, M.; Yang, Y. Dissolution behavior of ferrous sulfate in the hematite process. Hydrometallurgy 2021, 200, 105561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terry, B.; Monhemius, A.J. Acid dissolution of willemite (Zn, Mn)2 SiO4) and hemimorphite (Zn4Si2O7(OH)2 H2O). Metall. Trans. B 1983, 14, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Li, Q.; Yang, T.; Zhang, X. Leaching of hemimorphite in NH3–(NH4)2SO4–H2O system and its mechanism. Hydrometallurgy 2012, 125–126, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.Z.; Xiang, Y.; Wu, X.; He, Z.; Yin, Z. Preparation of high purity zinc from zinc oxide ore by vacuum carbothermic reduction. Vacuum 2017, 146, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Li, M.; Qian, Z.; Ma, Y.; Che, J.; Ma, Y. Hemimorphite Ores: A Review of Processing Technologies for Zinc Extraction. JOM 2016, 68, 2688–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, M.; Hussaini, S.; Kursunoglu, S. Critical review on secondary zinc resources and their recycling technologies. Hydrometallurgy 2020, 195, 105362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atia, T.A.; Spooren, J. Microwave assisted chloride leaching of zinc plant residues. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 398, 122814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussaini, S.; Kursunoglu, S.; Top, S.; Ichlas, Z.T.; Kaya, M. Testing of 17-different leaching agents for the recovery of zinc from a carbonate-type Pb-Zn ore flotation tailing. Miner. Eng. 2021, 168, 106935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kursunoglu, S.; Kursunoglu, N.; Hussaini, S.; Kaya, M. Selection of an appropriate acid type for the recovery of zinc from a flotation tailing by the analytic hierarchy process. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 283, 124659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehsani, I.; Üçyıldız, A.; Obut, A. Leaching behaviour of zinc from a smithsonite ore in sodium hydroxide solutions. Physicochem. Probl. Miner. Process. 2018, 55, 407–416. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Zhang, Q.; He, X.; Hu, H.; Liu, Y. Efficient separation of smithsonite and cerussite via mechanical ball milling-triggered selective leaching in the aqueous solution containing Pb chloride or Pb nitrate. Hydrometallurgy 2021, 202, 105589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wu, D.; Wang, Z. Investigation of the Leaching Kinetics of Zinc from Smithsonite in Ammonium Citrate Solution. Metals 2024, 14, 105589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Ding, Z.; Hu, H.; Liu, K.; Chen, Q. Dissolution of zinc silicate (hemimorphite) with ammonia–ammonium chloride solution. Hydrometallurgy 2010, 103, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, A.-C.; Yang, T.-Z.; Yang, J.-X.; Wu, J.-H.; Wang, A. Leaching of low grade zinc oxide ores in Ida2−-H2O system. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2011, 21, 2548–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.; Yang, T.; Zhang, D.; Liu, W.; Chen, L.; Hao, Z.; Xiao, Q.; Wen, J. Leaching of low grade zinc oxide ores in NH4Cl–NH3 solutions with nitrilotriacetic acid as complexing agents. Hydrometallurgy 2015, 158, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Rao, S.; Zhang, D.; Wen, J.; Liu, W.; Chen, L.; Zhang, X. Leaching of low grade zinc oxide ores in nitrilotriacetic acid solutions. Hydrometallurgy 2016, 161, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.; Zhang, D.; Yang, T.; Ling, H.; Liu, W.; Chen, L. Recovery of zinc and the regeneration of the complexation agent from the NH4Cl-NH3-NTA system. Hydrometallurgy 2017, 169, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wen, S.; Wu, D.; Feng, Q.; Li, S. Dissolution kinetics of hemimorphite in trichloroacetic acid solutions. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 1645–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, M.N.; Sahu, K.K.; Pandey, B.D. Zinc recovery from sphalerite concentrate by direct oxidative leaching with ammonium, sodium and potassium persulphates. Hydrometallurgy 2002, 64, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, A.; Pina, P.; Leão, V.; Silva, C.; Siqueira, P. The leaching kinetics of a zinc sulphide concentrate in acid ferric sulphate. Hydrometallurgy 2007, 89, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutrizac, J.E. The dissolution of sphalerite in ferric sulfate media. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2006, 37, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muravyov, M.; Panyushkina, A. Comparison of sphalerite concentrate leaching by chemical and microbially produced ferric sulfate. Miner. Eng. 2022, 187, 107792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Harahsheh, M.; Kingman, S. The influence of microwaves on the leaching of sphalerite in ferric chloride. Chem. Eng. Process.—Process Intensif. 2007, 46, 883–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wei, C.; Xu, H.-S.; Li, M.; Li, X.; Deng, Z.; Fan, G. Oxidative pressure leaching of sphalerite concentrate with high indium and iron content in sulfuric acid medium. Hydrometallurgy 2010, 102, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muravyov, M.; Panyushkina, A. Comparison of sphalerite, djurleite, and chalcopyrite leaching by chemically and biologically generated ferric sulfate solutions. Hydrometallurgy 2023, 219, 106067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Yu, X.Q.; Gong, A.; Wu, X.G.; Zhang, T.A.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Z.F. Kinetic models of zinc dissolution from artificial sphalerite with different iron contents in oxygen pressure leaching. Can. Metall. Q. 2020, 59, 343–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crundwell, F.K. The impact of light on the rate and mechanism of dissolution and leaching of natural iron-containing sphalerite, (Zn,Fe)S. Miner. Eng. 2021, 160, 106702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raba, J.; Fontan, C.A.; Cortinez, V.A. 4-(3,5-Dichloro-2-pyridylazo)-1-3-diaminobenzene-graphite paste electrode for end-point detection in the automatic potentiometric titration of zinc(II) with EDTA. Talanta 1994, 41, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, H.E. Potential-pH diagrams at elevatedtemperature for the system Fe-H2O. Corros. Sci. 1970, 10, 343–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Zhao, Z.W.; Jia, X.; Long, S.; Huo, G.; Chen, X. Alkaline leaching Zn and its concomitant metals from refractory hemimorphite zinc oxide ore. Hydrometallurgy 2009, 97, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Wei, C.; Li, C.X.; Deng, Z.G.; Li, M.T.; Li, X.B. Kinetic Study and Mathematical Model of Hemimorphite Dissolution in Low Sulfuric Acid Solution at High Temperature. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2014, 45, 1622–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Yin, Z.; Hu, H.; Chen, Q. Dissolution kinetics of zinc silicate (hemimorphite) in ammoniacal solution. Hydrometallurgy 2010, 104, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




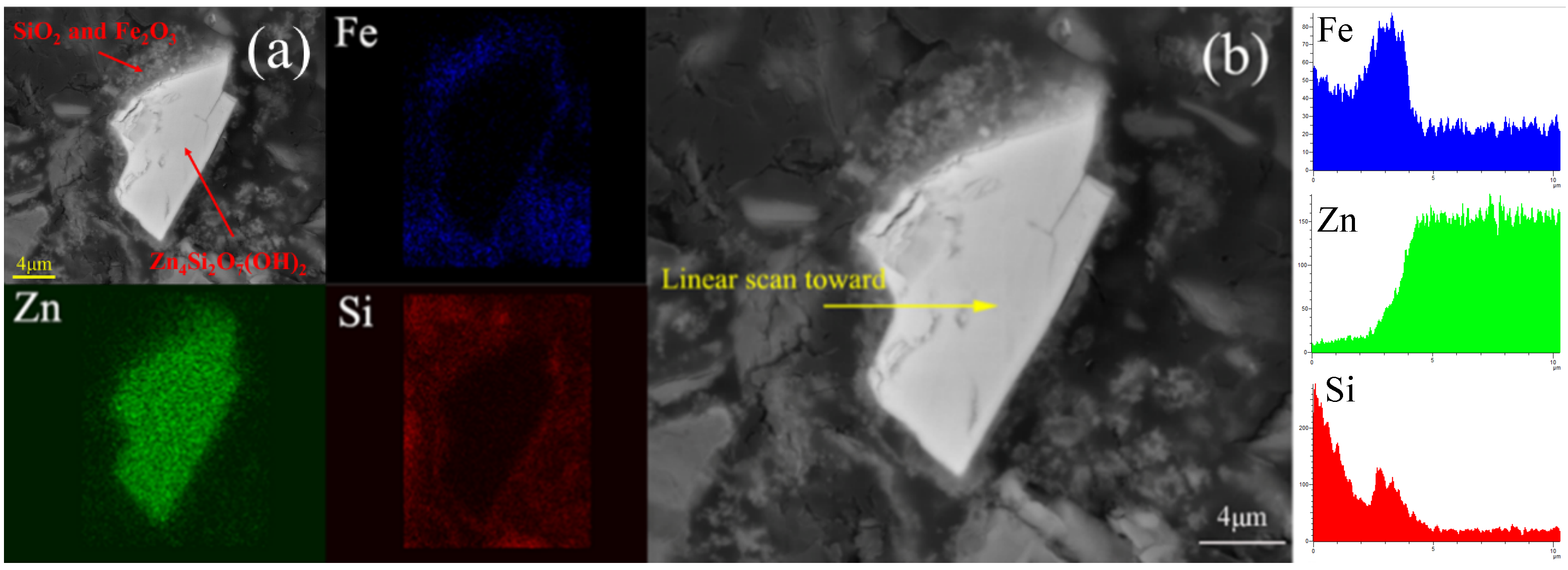

| Compositions | Zn | O | Si | Mg | Fe | Al | Ca | K | LOI * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| contents | 38.24 | 37.37 | 8.77 | 3.85 | 3.77 | 3.28 | 1.46 | 1.05 | 2.21 |
| Controlling Step | 1 − (1 − α)2/3 | 1 − 2/3α − (1 − α)2/3 | 1 − (1 − α)1/3 | 1/3ln(1 − α) − [1 − (1 − α)−1/3] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Correlation Coefficient/Rate Constant | R2 | k1 | R2 | k2 | R2 | k3 | R2 | k4 |
| 135 °C | 0.819 | 0.0325 | 0.939 | 0.00332 | 0.837 | 0.0182 | 0.957 | 0.0026 |
| 150 °C | 0.820 | 0.0562 | 0.964 | 0.0107 | 0.865 | 0.0354 | 0.993 | 0.0137 |
| 165 °C | 0.714 | 0.0592 | 0.917 | 0.0130 | 0.779 | 0.0390 | 0.995 | 0.0208 |
| 180 °C | 0.765 | 0.0808 | 0.968 | 0.0266 | 0.901 | 0.0681 | 0.995 | 0.0526 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, T.; Zeng, Y.; Zhang, S.; Chen, C.; Li, Y.; Ma, W.; Ni, H. A Novel Selective Oxygen Pressure Leaching for Zinc Extraction from Hemimorphite in Acid-Free Solutions. Metals 2025, 15, 858. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15080858
Wang T, Zeng Y, Zhang S, Chen C, Li Y, Ma W, Ni H. A Novel Selective Oxygen Pressure Leaching for Zinc Extraction from Hemimorphite in Acid-Free Solutions. Metals. 2025; 15(8):858. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15080858
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Tong, Yubo Zeng, Shuang Zhang, Chen Chen, Yang Li, Wenhui Ma, and Hongwei Ni. 2025. "A Novel Selective Oxygen Pressure Leaching for Zinc Extraction from Hemimorphite in Acid-Free Solutions" Metals 15, no. 8: 858. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15080858
APA StyleWang, T., Zeng, Y., Zhang, S., Chen, C., Li, Y., Ma, W., & Ni, H. (2025). A Novel Selective Oxygen Pressure Leaching for Zinc Extraction from Hemimorphite in Acid-Free Solutions. Metals, 15(8), 858. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15080858






