Sonication-Assisted Surface Erosion and Its Impact on the Flotation of Ultrafine Smithsonite
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Morphological Characterizations of Ultrafine Smithsonite Particles
2.3. ICP Analysis
2.4. Flotation of Ultrafine Smithsonite
2.5. Nanoparticle Tracking in Smithsonite Suspensions
2.6. Zeta Potential Measurements
2.7. XPS Tests
3. Results and Discussion
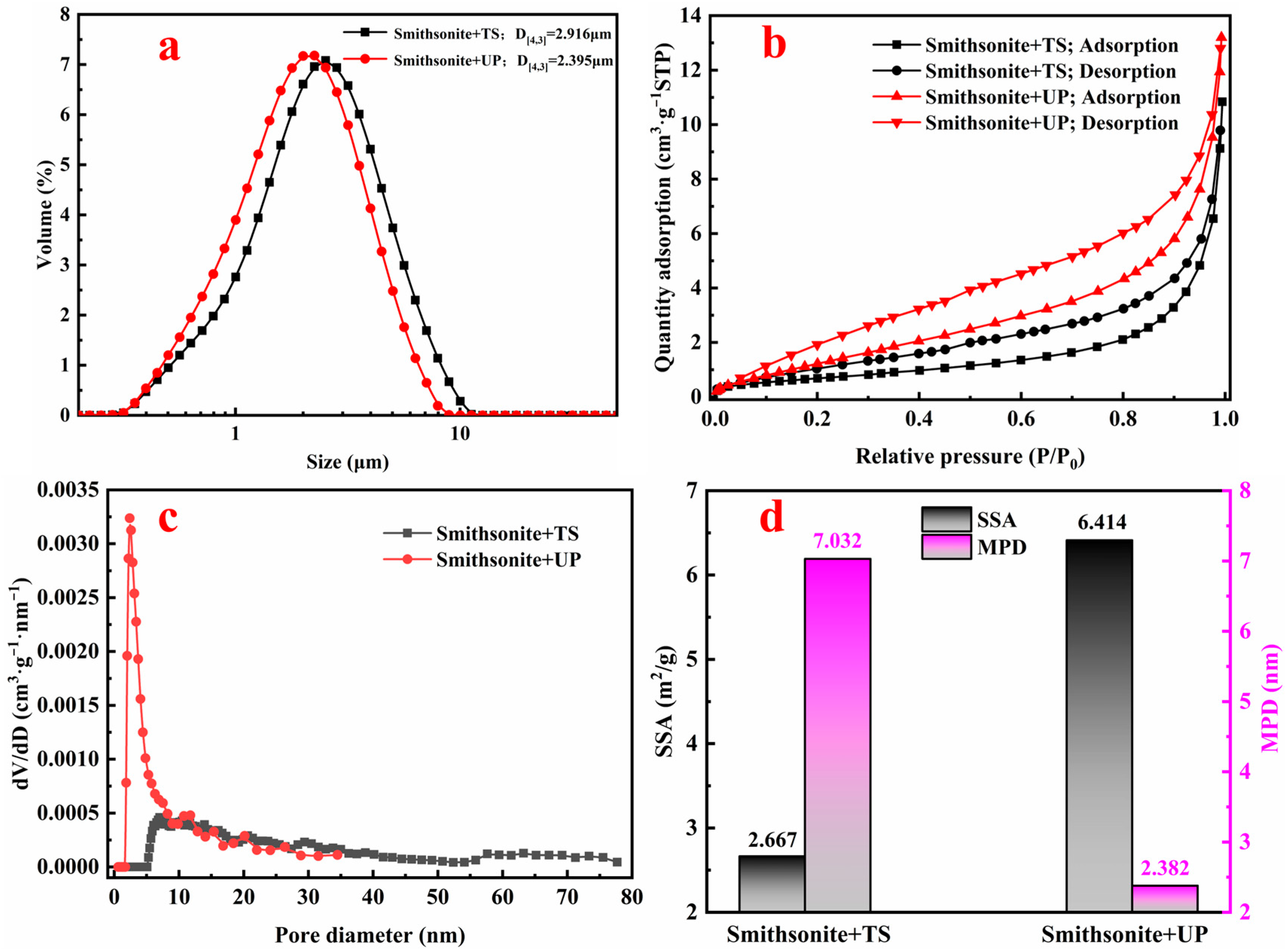
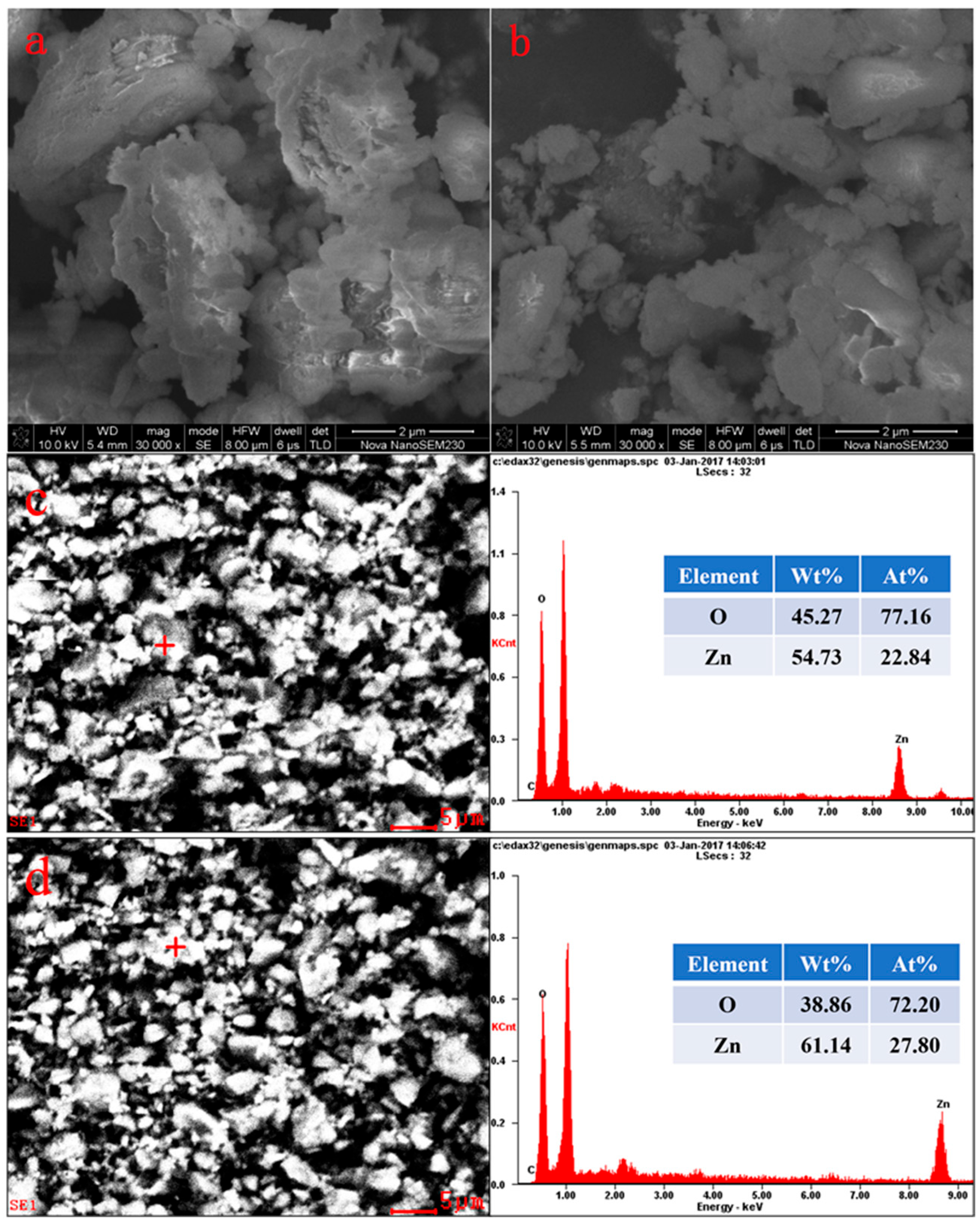
3.1. Morphological Characterization Results
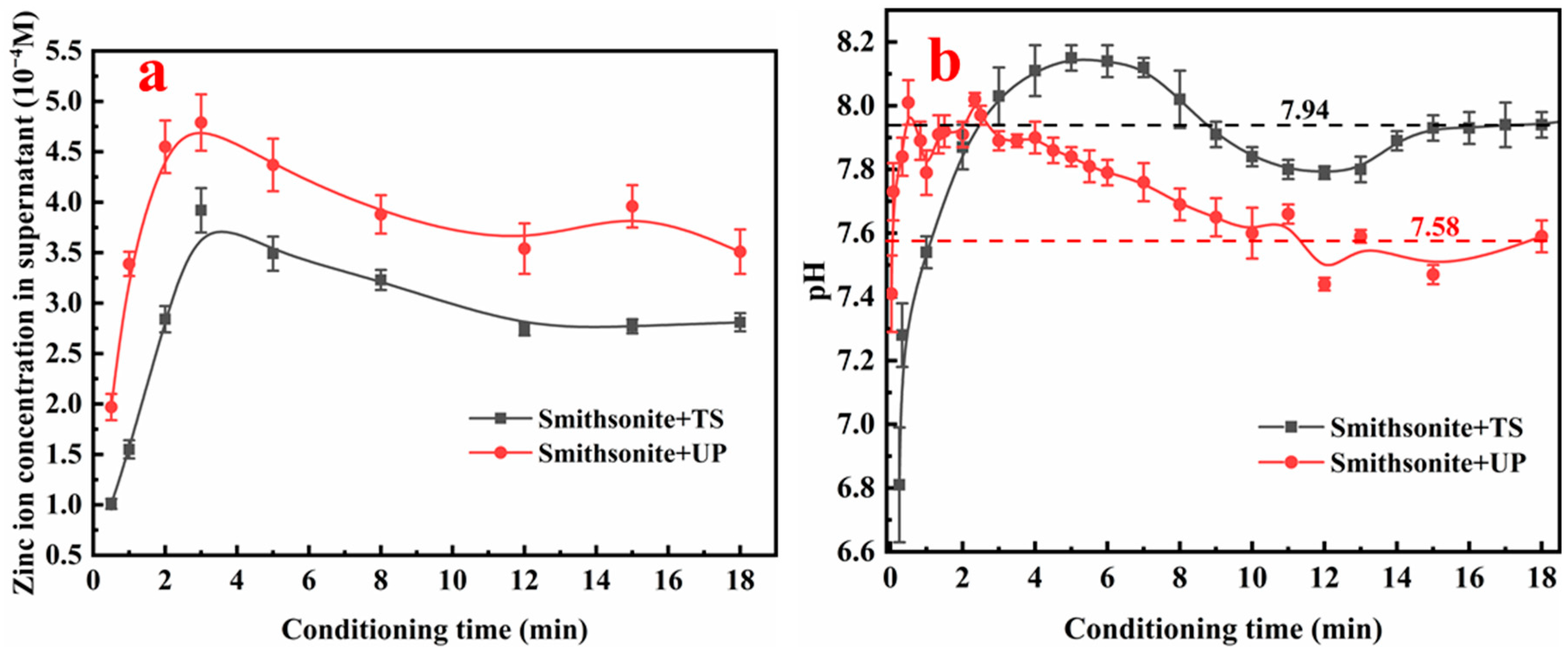
3.2. Mineral Dissolution and Solution Chemical Analysis
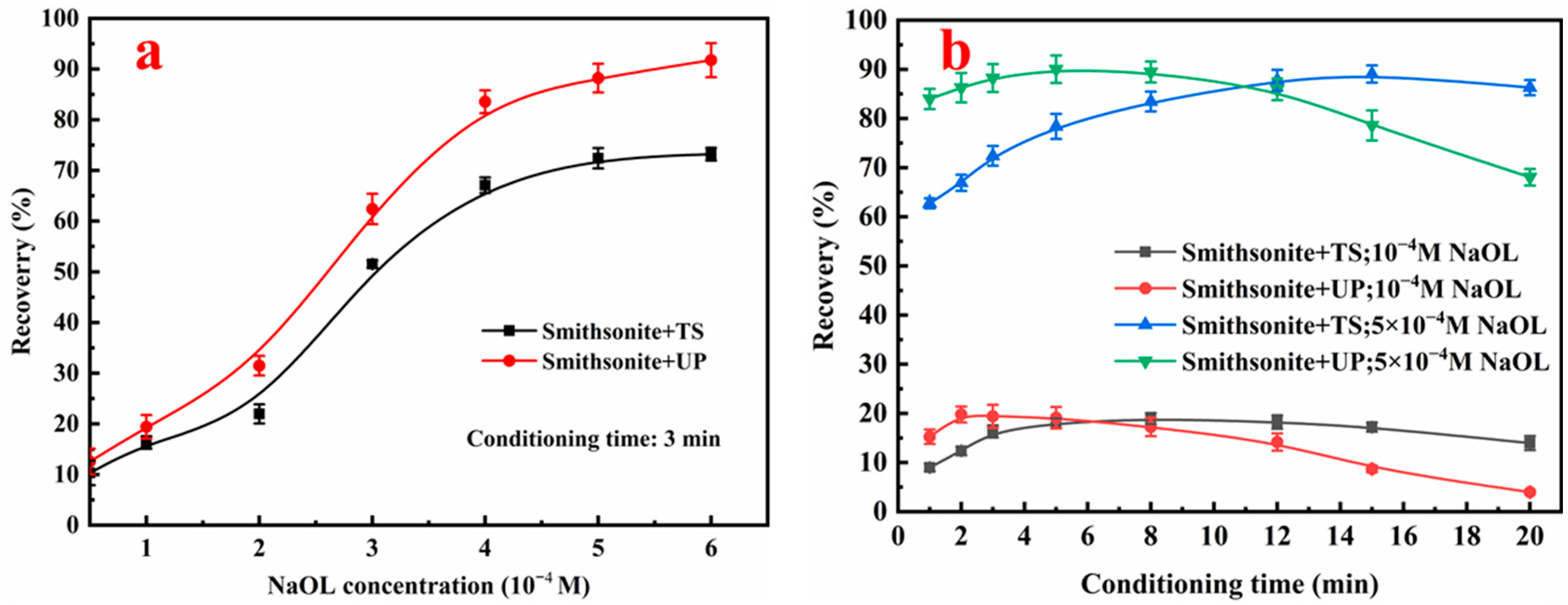
3.3. Flotation Results
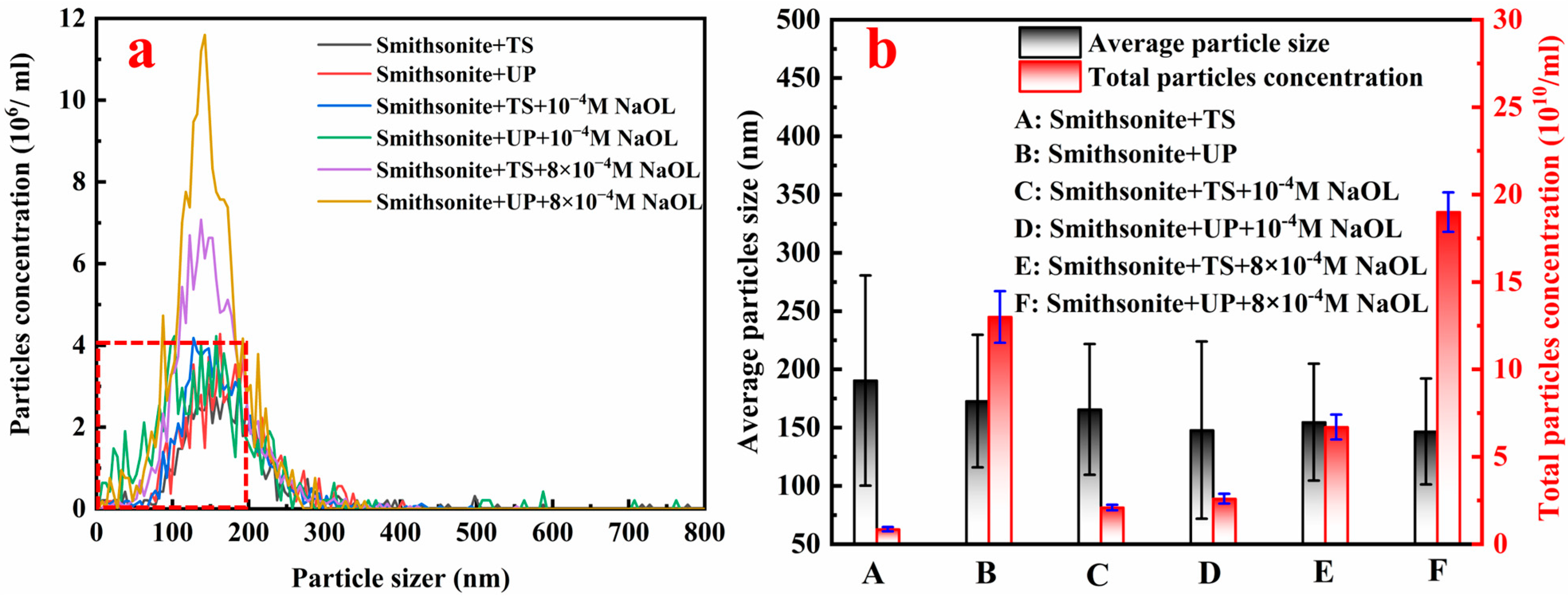
3.4. Nanoparticle Tracking and Analysis
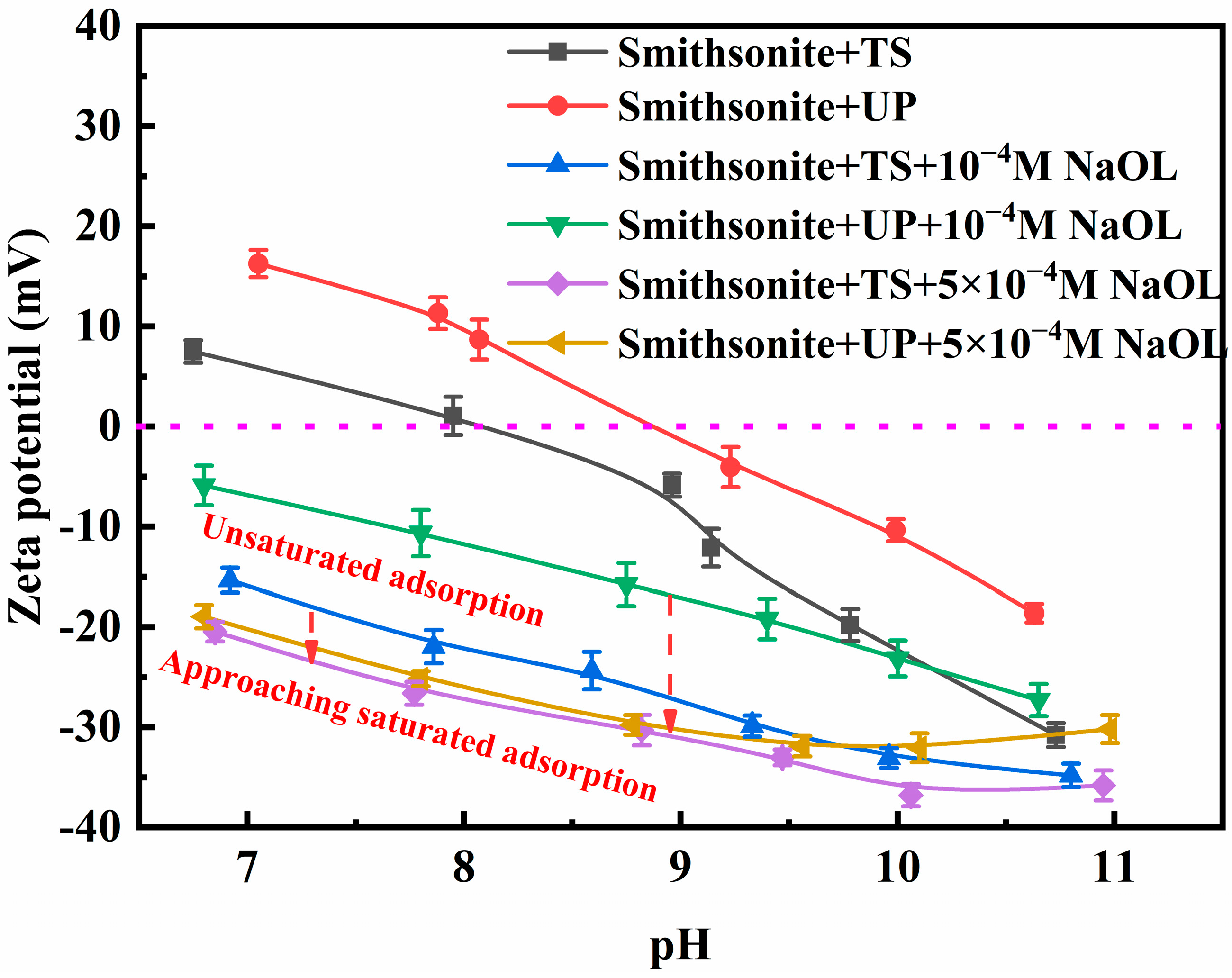
3.5. Zeta Potential Results
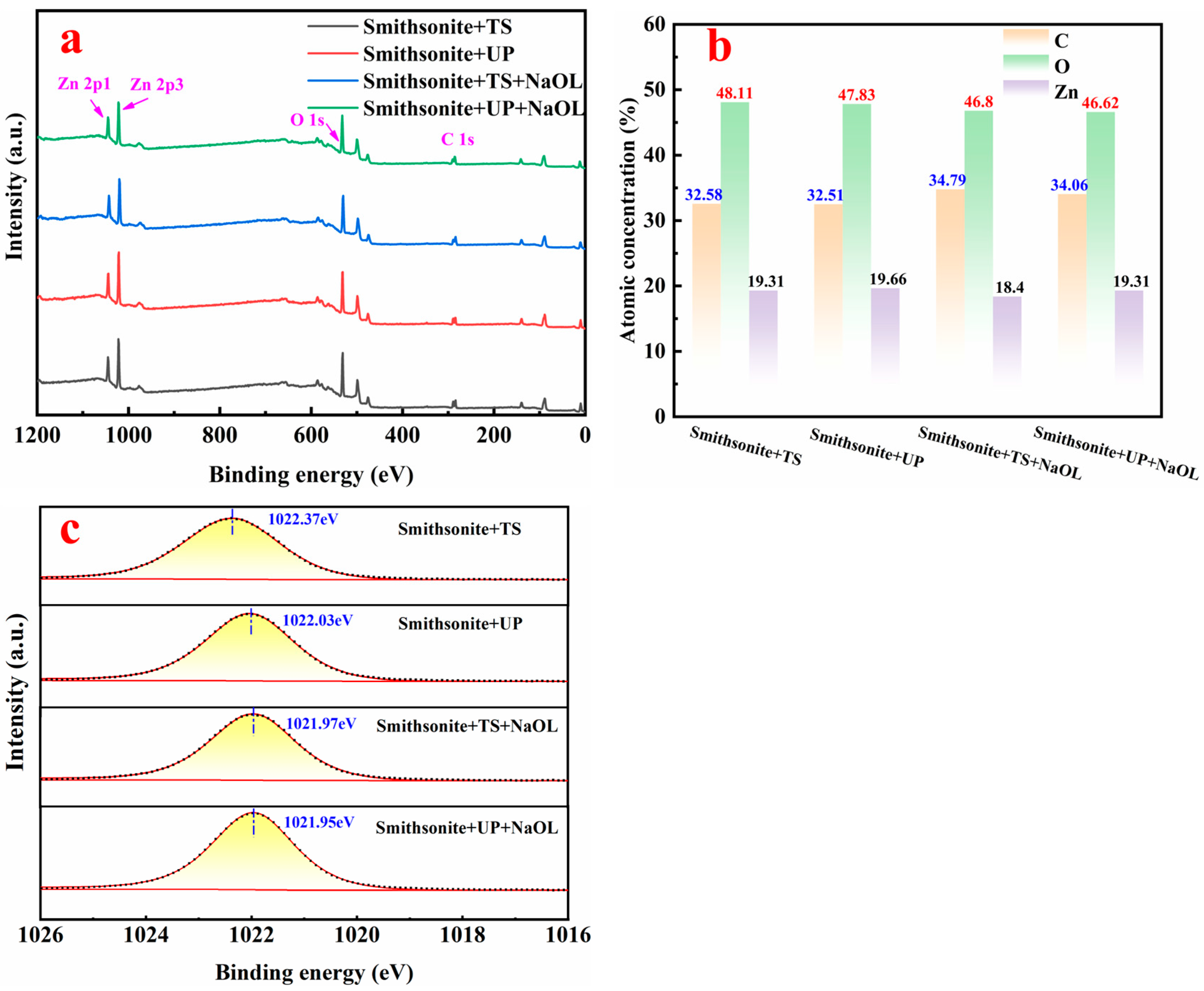
3.6. XPS Analysis
4. Conclusions
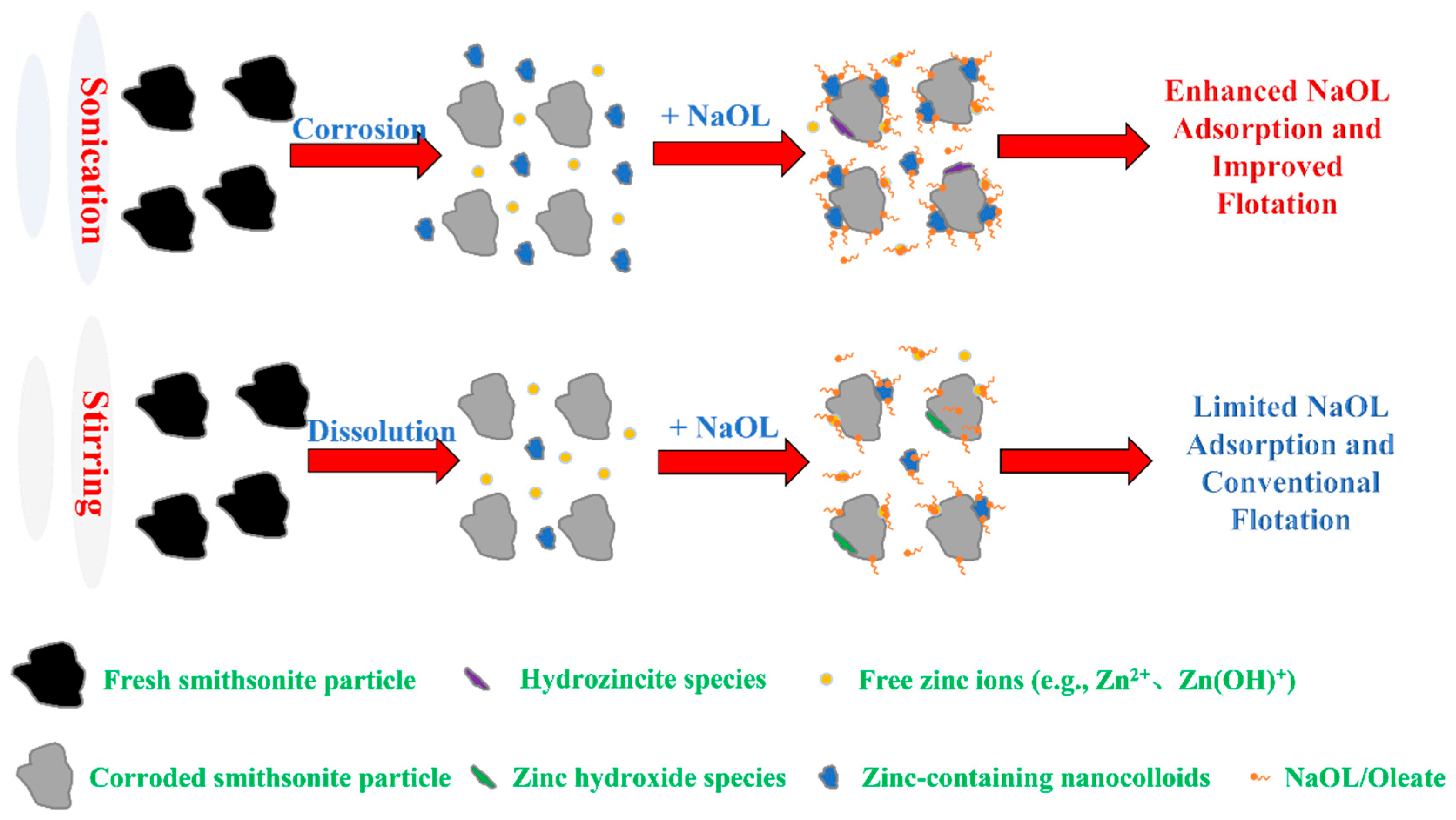
- UP significantly modifies the physicochemical properties of smithsonite suspensions, including particle geometry and morphology, ionic composition, electrokinetic properties, and pulp pH. Among these changes, ultrasonic-assisted selective surface dissolution is the key factor in enhancing NaOL adsorption and improving the flotation of ultrafine smithsonite.
- Compared with TS, UP significantly enhances the release of Zn ions (mainly as Zn2+, Zn(OH)+, or zinc-containing colloids) from the smithsonite lattice under neutral-to-weakly alkaline conditions, creating more active sites for NaOL adsorption. Additionally, within the tested short-term conditioning time, a metastable dissolution–hydrolysis–precipitation equilibrium is established in UP cases rather than the TS cases, which is conducive to the stable NaOL adsorption on ultrafine smithsonite particles.
- TS conditioning creates more free zinc ions during the dissolution, while UP conditioning leads to a significantly higher concentration of smaller nanoparticles in the smithsonite suspension. These nanoparticles can facilitate NaOL adsorption on the smithsonite surface via surface precipitation, thereby increasing the surface hydrophobicity and floatability.
- TS conditioning typically forms some zinc hydroxide on the smithsonite surface, whereas UP conditioning forms some hydrozincite. Hydrozincite is more stable and inherently hydrophobic, enhancing the surface hydrophobization of smithsonite.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ejtemaei, M.; Gharabaghi, M.; Irannajad, M. A review of zinc oxide mineral beneficiation using flotation method. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 206, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ejtemaei, M.; Irannajad, M.; Gharabaghi, M. Influence of important factors on flotation of zinc oxide mineral using cationic, anionic and mixed (cationic/anionic) collectors. Miner. Eng. 2011, 24, 1402–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, C.A.; Peres, A.E.C. Reagents in calamine zinc ores flotation. Miner. Eng. 2005, 18, 275–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Dong, L.; Shen, P.; Liu, D. A novel activation scheme for fine cassiterite flotation by using a metal ion modified collector. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2025, 710, 136310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.; Forssberg, E. Studies on selective flotation of smithsonite from silicate minerals using mercaptans and one-stage desliming. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. 2011, 120, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Assis, T.A.; Reis, F.D.A.A. Dissolution of minerals with rough surfaces. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2018, 228, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irannajad, M.; Nuri, O.S.; Mehdilo, A. Surface dissolution-assisted mineral flotation: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Zhang, G.; Li, C.; Li, B.; Ye, G. The surface dissolution process of smithsonite and its effect on flotation behaviour. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 676, 132118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhang, G.; Shi, Q. Atomic insights into the interaction mechanism underpinning carbonate ion adsorption in smithsonite flotation. Process Saf. Environ. 2024, 190, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, N.; Chu, H.; Zheng, X.; Lu, D.; Zheng, H. Surface dissolution behavior and its influences on the flotation separation of spodumene from silicates. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2021, 56, 1407–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Miao, Y.; Li, C.; Ye, G.; Wu, W.; Li, B.; Zhang, G. Deep insight into the effect of smithsonite particle size on surface heterogeneity and adsorption behavior: A case of fatty acid system. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 414, 126214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Dong, L.; Shen, P.; Liu, D. A novel oxidation reagent scheme to realize efficient flotation separation of chalcopyrite and pyrrhotite. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2025, 693, 162794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhu, G.; Zhang, L.; Lu, D.; Wang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zheng, H. Surface dissolution of spodumene and its role in the flotation concentration of a spodumene ore. Miner. Eng. 2018, 125, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, K.; Jin, Y.; Liu, S.; Qin, W.; Zhang, C.; Li, G.; Cao, Y. The application and mechanism of degradable activator biologically small molecule organic acids in smithsonite flotation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2024, 660, 159907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Feng, Q.; Zhang, G.; Deng, H. Electrokinetic properties of smithsonite and its floatability with anionic collector. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2012, 410, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Zhang, G.; Feng, Q.; Deng, H. Effect of solution chemistry on the flotation system of smithsonite and calcite. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2013, 119, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.; Xu, L.; Wu, H.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Shu, K.; Hu, Y. Influence of surface dissolution on sodium oleate adsorption on ilmenite and its gangue minerals by ultrasonic treatment. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 500, 144038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, W.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Chen, K. Effects of ultrasonic treatment on the flotation behavior of magnesite and dolomite in a sodium oleate system. Green Smart Min. Eng. 2024, 1, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.; Chen, L.; Lu, D.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, X.; Zhu, G. Ultrasound application in alkaline pretreatment process of spodumene to improve particle floatability. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2023, 33, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Fang, S.; Shu, K.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Luo, L.; Yang, J.; Xu, L. Selective flotation and adsorption of ilmenite from titanaugite by a novel method: Ultrasonic treatment. Powder Technol. 2020, 363, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, A. Wang, L. A fundamental study of flotation separation of mineral particles using ultrasound-induced bubbles. Miner. Eng. 2024, 207, 108573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Fang, J.; Liu, M.; Li, Y.; Wang, D.; Xue, K.; Tian, J.; Shu, K.; Wang, Z.; Xie, L.; et al. Ultrasound-assisted alkali pretreatment enhances the flotation of spodumene. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2025, 716, 136685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Liu, X.; Jiang, B.; Huang, R.; Sun, L.; Luo, X.; Wang, Y. First application of a bench-scale ultrasonic flotation column: Investigating ultrasound effects on fine particle phosphate ore purification. Miner. Eng. 2025, 229, 109378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkan, S.G. Beneficiation of magnesite slimes with ultrasonic treatment. Miner. Eng. 2002, 15, 99–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, A.; Park, H.; Wang, L. Ultrasonic flotation of chalcopyrite in a piezoelectric tube: Particle size effects and energy dissipation. Miner. Eng. 2025, 230, 109412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kursun, H.; Ulusoy, U. Zinc recovery from a lead–zinc–copper ore by ultrasonically assisted column flotation. Particul. Sci. Technol. 2015, 33, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kursun, H. A study on the utilization of ultrasonic pretreatment in zinc flotation. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2014, 49, 2975–2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özkan, Ş.G.; Kuyumcu, H.Z. Design of a flotation cell equipped with ultrasound transducers to enhance coal flotation. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2007, 14, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasui, K.; Tuziuti, T.; Iida, Y. Dependence of the characteristics of bubbles on types of sonochemical reactors. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2005, 12, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, N.H.; Palaniandy, S. Comparative study of water-based and acid-based sonications on structural changes of talc. Appl. Clay Sci. 2011, 51, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Chen, Z.; Wei, Z.; Hu, J.; Guo, Y.; Deng, T. Titanium-based ion sieve with enhanced post-separation ability for high performance lithium recovery from geothermal water. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 410, 128320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trainor, T.P.; Brown, G.E.; Parks, G.A. Adsorption and precipitation of aqueous Zn (II) on alumina powders. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2000, 231, 359–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waychunas, G.A.; Fuller, C.C.; Davis, J.A. Surface complexation and precipitate geometry for aqueous Zn (II) sorption on ferrihydrite I: X-ray absorption extended fine structure spectroscopy analysis. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2002, 66, 1119–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, D.R.; Ford, R.G.; Sparks, D.L. Kinetics and mechanisms of Zn complexation on metal oxides using EXAFS spectroscopy. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2003, 263, 364–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preis, W.; Gamsjäger, H. (Solid + solute) phase equilibria in aqueous solution. XIII. Thermodynamic properties of hydrozincite and predominance diagrams for (Zn2++ H2O+ CO2). J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2001, 33, 803–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morse, J.W.; Arvidson, R.S. The dissolution kinetics of major sedimentary carbonate minerals. Earth Sci. Rev. 2002, 58, 51–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Tao, D. Effect of solution chemistry on flotability of magnesite and dolomite. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2004, 74, 343–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokrovsky, O.; Schott, J. Surface chemistry and dissolution kinetics of divalent metal carbonates. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Wen, S.; Deng, J.; Liu, J.; Mao, Y. Study on the sulfidation behavior of smithsonite. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 329, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Liu, W.; Duan, H.; Yang, T.; Li, Z.; Zhou, S. Sodium carbonate effects on the flotation separation of smithsonite from quartz using N,N′-dilauroyl ethylenediamine dipropionate as a collector. Miner. Eng. 2018, 126, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Nanda, A. Synthesis of highly dispersed zinc oxide nanoparticles through ultrasonication assisted by hydrothermal treatment: A novel approach. Synth. React. Inorg. Met.Org. Chem. 2015, 45, 1121–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, B.C.; Aldrich, C. Effect of ultrasonic treatment on zinc removal from hydroxide precipitates by dissolved air flotation. Miner. Eng. 2002, 15, 1105–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, A.F. Structural Inorganic Chemistry; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Luo, L.; Qiu, G.; Wang, D. Solution chemistry of electrokinetic behavior of carbonate minerals. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 1995, 5, 26–30. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Xu, J.; Luo, C.; Yuan, C. Solution chemistry studies on dodecylamine flotation of smithsonite/calcite. J. Cent. S. Univ. Technol. 1995, 26, 589–594. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Truong, V.N.T.; Bu, X.; Xie, G. A review of effects and applications of ultrasound in mineral flotation. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2020, 60, 104739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Z.; Fornasiero, D.; Ralston, J. Particle–bubble collision models—A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2000, 85, 231–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.A.; Xu, Z.; Finch, J.A.; Masliyah, J.H.; Chow, R.S. On the role of cavitation in particle collection in flotation—A critical review. II. Miner. Eng. 2009, 22, 419–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrokhpay, S.; Lev, F.; Fornasiero, D. Flotation of fine particles: A review. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 2021, 42, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horta, D.; de Mello Monte, M.B.; Filho, S.L. The effect of dissolution kinetics on flotation response of apatite with sodium oleate. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2016, 146, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Drelich, J.; Miller, J.D. Oleate adsorption at an apatite surface studied by ex-situ FTIR internal reflection spectroscopy. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1998, 202, 462–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Han, H.; Sun, W.; Wang, R.; Wei, Z. Novel insights into the role of colloidal calcium dioleate in the flotation of calcium minerals. Miner. Eng. 2022, 175, 107274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atrafi; Gomez, C.O.; Finch, J.A.; Pawlik, M. Frothing behavior of aqueous solutions of oleic acid. Miner. Eng. 2012, 36–38, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Zhou, W.; Dong, L.; Peng, Y.; Xie, G. Micellization transformations of sodium oleate induced by gas nucleation. Langmuir 2021, 37, 9701–9710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Jiao, F.; Qin, W.; Zhu, H.; Jia, W. Activation effect of lead ions on scheelite flotation: Adsorption mechanism, AFM imaging and adsorption model. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 209, 955–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Chen, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, Y. Interaction between smithsonite and carboxyl collectors with different molecular structure in the presence of water: A theoretical and experimental study. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 510, 145410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Pelton, R.; Montgomery, M.; Cui, Y. Nanoparticle flotation collectors III: The role of nanoparticle diameter. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 4882–4890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuerstenau, D.W. Zeta potentials in the flotation of oxide and silicate minerals. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 114–115, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwan, A.K.; Williams, P.A. Mineral formation from aqueous solution. Part I. The deposition of hydrozincite, Zn5(OH)6(CO3)2, from natural waters. Transit. Met. Chem. 1979, 4, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zachara, J.M.; Kittrick, J.A.; Dake, L.S.; Harsh, J.B. Solubility and surface spectroscopy of zinc precipitates on calcite. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1989, 53, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turianicová, E.; Kaňuchová, M.; Zorkovská, A.; Holub, M.; Bujňáková, Z.; Dutková, E.; Baláž, M.; Findoráková, L.; Balintová, M.; Obut, A. CO2 utilization for fast preparation of nanocrystalline hydrozincite. J. CO2 Util. 2016, 16, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deroubaix, G.; Marcus, P. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy analysis of copper and zinc oxides and sulphides. Surf. Interface Anal. 1992, 18, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretti, G.; Fierro, G.; Jacono, M.L.; Porta, P. Characterization of CuO–ZnO catalysts by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy: Precursors, calcined and reduced samples. Surf. Interface Anal. 1989, 14, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosking, N.C.; Ström, M.A.; Shipway, P.H.; Rudd, C.D. Corrosion resistance of zinc–magnesium coated steel. Corros. Sci. 2007, 49, 3669–3695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Lyu, W.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, H. The role of sodium phytate in the flotation separation of smithsonite from calcite. Miner. Eng. 2022, 187, 107775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| ZnO | Fe | Al2O3 | SiO2 | CaO | L.O.I |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 64.1 | 0.10 | 0.015 | 0.75 | 0.05 | 34.98 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, W.; Cao, W.; Wei, H.; Shi, S.; Li, C.; Dong, L. Sonication-Assisted Surface Erosion and Its Impact on the Flotation of Ultrafine Smithsonite. Metals 2025, 15, 731. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15070731
Zhou W, Cao W, Wei H, Shi S, Li C, Dong L. Sonication-Assisted Surface Erosion and Its Impact on the Flotation of Ultrafine Smithsonite. Metals. 2025; 15(7):731. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15070731
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Weiguang, Weiwei Cao, Haobin Wei, Shulan Shi, Chenwei Li, and Liuyang Dong. 2025. "Sonication-Assisted Surface Erosion and Its Impact on the Flotation of Ultrafine Smithsonite" Metals 15, no. 7: 731. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15070731
APA StyleZhou, W., Cao, W., Wei, H., Shi, S., Li, C., & Dong, L. (2025). Sonication-Assisted Surface Erosion and Its Impact on the Flotation of Ultrafine Smithsonite. Metals, 15(7), 731. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15070731







