Abstract
To expand the fundamental understanding of eutectic high-entropy alloys (EHEAs), three novel alloy systems—Cr1.3Ni2TiAl, CoCr1.5NiTi1.5Al0.2, and V0.3CoCr1.2NiTi1.1Al0.2—were rationally designed through synergistic phase diagram analysis and thermodynamic parameter calculations. Comprehensive microstructural characterization coupled with mechanical property evaluation revealed that these alloys possess FCC+BCC dual-phase architectures with atypical irregular eutectic morphologies. Notably, progressive microstructural evolution was observed, including amplified grain boundary density and the emergence of brittle nanoscale precipitates. Mechanical testing demonstrated superior compressive yield strengths in these alloys compared to conventional FCC+BCC EHEAs with ordered eutectic structures, albeit accompanied by reduced fracture strain. The Cr1.3Ni2TiAl alloy exhibited optimal ductility, with a maximum fracture strain of 15.6%, while V0.3CoCr1.2NiTi1.1Al0.2 achieved peak strength, with a compressive yield strength of 1389.5 MPa. Multiscale analysis suggests that the enhanced mechanical performance arises from the synergistic interplay between irregular eutectic configurations, expanded grain boundary area, and precipitation strengthening mechanisms.
1. Introduction
Eutectic high-entropy alloys (EHEAs) are produced by mixing four or more elements in specific ratios, enabling coupled growth and solidification of two (or more) phases in the liquid state, ultimately forming a eutectic microstructure [1]. EHEAs possess not only the high-entropy, lattice distortion, cocktail, and sluggish diffusion effects characteristic of high-entropy alloys [2,3] but also exhibit excellent casting properties and enhanced mechanical properties derived from their eutectic nature [4,5]. This dual-phase structure addresses the traditional challenge of achieving a balance between strength and ductility in single-phase high-entropy alloys, and their potential for manufacturing large components presents promising applications in engineering.
EHEAs can be classified into structural EHEAs and functional EHEAs based on their applications [5]. From the perspective of phase structure types, they can be divided into six categories: FCC+BCC [1,6,7], FCC+Laves [8,9], FCC+IMC [10,11], FCC+NMC [12], BCC+B2 [13,14], and BCC+Laves [15,16]. Among these, FCC+BCC EHEAs offer the best combination of mechanical properties, which is more conducive to promoting the application of EHEAs in the field of engineering structures [1,6,7]. Currently, FCC+BCC-type EHEAs primarily include systems such as Co-Cr-Fe-Ni-Al [1,4] and Co-Cr-Fe-Ni-Al-M (M: W [17], Mo [18], Ti [19]). The Co-Cr-Fe-Ni-Al system of EHEAs exhibits a microscopic morphology characterized by a regular eutectic structure, with mechanical properties primarily determined by the coordination relationship at the interface between the two phases [20]. The addition of trace amounts of large atomic radius elements (W, Mo, Ti) can effectively enhance the mechanical properties of EHEAs by increasing the degree of phase structure distortion [17,18,19,21,22]. Among these, the incorporation of W and Mo elements does not alter the regular eutectic morphology [17,18], whereas the addition of the Ti element induces a transformation from a regular eutectic to an irregular eutectic morphology [19,23,24]. The Ti element also tends to segregate at grain boundaries, contributing to the refinement of grain size [25]. Furthermore, the low density of Ti (4.507 g·cm−3) can facilitate the expansion and application of such EHEAs in the field of lightweight structures. Consequently, research on EHEAs containing the Ti element has garnered attention from some scholars in recent years.
C.-F. Lee et al. [19] investigated the influence of the Fe element on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Al0.5CoCrFexNiTi0.5 high-entropy alloys (HEAs). The study revealed that the Al0.5CoCrFe2.0NiTi0.5 alloy system exhibits a three-phase eutectic structure consisting of FCC+BCC+B2. The synergistic effect of the eutectic structure endowed the sample with a compressive yield strength of 866 MPa and a true strain of 0.45. J. Wang et al. [24] investigated the inhibitory effect of the Ti element on crack propagation in CoCrFeNiMnTix HEAs during laser remelting. The segregation of the Ti element in the CoCrFeNiMnTi0.6 alloy promoted the formation of a eutectic structure. The generation of the eutectic phase facilitated the transformation of large tensile residual stresses into compressive stresses, which is beneficial for preventing crack propagation. X. Chen et al. [22] introduced the Ti element into the AlCoCrFeNi2.1 EHEA, resulting in a gradual transformation of the regular lamellar eutectic structure into an irregular petal-like eutectic structure. The lamellar L12 and B2 phases form a strict Kurdjumov–Sachs (K-S) orientation relationship (OR): {111}FCC//{011}B2, <011>FCC//<111>B2. In contrast, such an OR was not observed in the petal-like microstructure. The Ti0.15 alloy demonstrated the most excellent combination of high ultimate tensile strength (UTS) (1253 MPa) and ductility (12.9%). J.-Q. Zheng et al. [26] observed similar phenomena in their study on the influence of the Ti element on Al18Co13Cr10Fe14Ni45 EHEAs. S. Li et al. [27] investigated the effect of the Ti element on the microstructure and mechanical properties of AlCrFeNiTix EHEAs. Variations in Ti content resulted in four distinct morphologies of net-like eutectic microstructures, with the eutectic structure size gradually increasing. The AlCrFeNiTi0.2 EHEA exhibited the lowest density (<7 g·cm−3), and its specific yield strength reached up to 237 MPa·cm−3·g−1.
To summarize, current research primarily focuses on the influence of the Ti element on the microstructure and mechanical properties of EHEAs within fixed systems (such as Al, Co, Cr, Fe, Ni, Mn), yielding numerous valuable and significant findings. However, selecting alloy elements based on practical requirements, combined with rational theoretical design and calculations, to develop lightweight EHEAs containing the Ti element will enhance the tunability of these alloy systems. Our team has previously employed similar methods to develop six types of lightweight EHEAs (V-Co-Cr-Ni-Ti-Al system), demonstrating diversity in microstructure and mechanical properties [28]. Therefore, based on prior research, this study will further expand the database of V-Co-Cr-Ni-Ti-Al system EHEAs and investigate the coupling relationship between microstructure and mechanical properties under the synergistic effects of Ti and other elements.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Theoretical Calculations and Phase Diagram Simulations
In this study, V-Co-Cr-Ni-Ti-Al alloy systems were selected based on previous design concepts [28]. Combining the basic physical parameters of the alloying elements (Table 1 [29]), the thermodynamic empirical parameters of the alloy system were calculated using Equations (1)–(6) [28,30]. By compiling research data on HEAs, the range of physical parameters satisfying the FCC+BCC dual-phase structure is summarized in Table 2 [31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38]. Based on the reported research findings on EHEAs since the concept was introduced by the scholar Y.-P. Lu in 2014 [1], and incorporating the theoretical studies on eutectic formation by Chanda et al., it was found that the thermophysical parameters required to form EHEAs satisfy the following: −18 kJ·mol−1 < ΔHmix < −6 kJ.mol−1, Δδ > 3% and 6 < VEC < 8.5 [30,39,40].
where, R is the gas constant; ci is the atomic fraction of the ith element; is the mixing enthalpy between the ith and jth elements; Tm is the average melting point temperature; Δδ, ri and are the atomic size difference, atomic size of the ith element, and the average atomic radius, respectively; χi and are the valence electron concentrations of the ith element and the average valence electron concentration; and VECi is the electron concentration of the ith element [28].

Table 1.
The basic physical parameters for the elements [29].

Table 2.
Criteria for phase structure evaluation of HEAs.
Thermo-Calc software 2024b [41], combined with the TCHEA4 database, was used to perform thermodynamic calculations on the evolution of equilibrium phases and potential precipitates. Solidification calculations were conducted under the Scheil model assumption and the classic Scheil–Gulliver conditions (assuming infinite diffusion in the liquid, no diffusion in the solid, and thermodynamic equilibrium at the interface). Solidification simulations for solute trapping were carried out under Scheil–Gulliver conditions.
2.2. Raw Material Alloying Process
V-Co-Cr-Ni-Ti-Al EHEAs were prepared and screened using a GDHL-500A vacuum arc melter (Chengdu Jituo Instruments & Equipment Co., Ltd., Chengdu, China), which also verified the design scheme’s accuracy. High-purity elemental constituents (V, Co, Cr, Ni, Ti, Al ≥ 99.9 wt.%) were arc-melted in a water-cooled copper crucible under precisely controlled parameters: a current intensity of 250–400 A; an applied voltage of 30–45 V; a power input of 7.5–18 kW; and a chamber vacuum of <5 × 10−3 Pa. Ingots were remelted five times to ensure the chemical homogeneity of the alloys. To compensate for elemental burning loss during melting, the alloy formulation strategically incorporated compensation ratios: chromium was overcharged by 0.2 wt.% and aluminum by 0.1 wt.% relative to their theoretical stoichiometric ratios, while other alloying elements were maintained at nominal compositions. This protocol ensures precise alignment between the final alloy composition and the original design specifications.
2.3. Microstructural Characterization
Wire cutting was used to prepare samples with dimensions of 10 mm × 10 mm × 5 mm for phase structure and microstructure characterization, followed by grinding and polishing of the samples. The phases were identified using a D8 advanced X-ray diffractometer (XRD, BRUKER AXS GMBH, Billerica, MA, USA, 40 kV, 40 mA, Cu Kα radiation, 4°.min−1 scanning speed). The metallographic specimens were etched with Kroll’s reagent—a precisely formulated solution comprising 2 vol% HF, 6 vol% HNO3, and 92 vol% deionized H2O—employing latex-free rubber droppers for controlled etchant application to ensure uniform surface reaction kinetics while preventing metallic contamination. After 40 s, it was rinsed thoroughly with pure water and then alcohol. The microstructures were characterized using a HITACHI-S4700 scanning electron microscope (SEM, HITACHI, Tokyo, Japan). Energy dispersed X-ray spectrometry (EDS) was used to measure the content and distribution of alloying elements in the EHEAs. A 10 mm × 10 mm × 0.5 mm thin sheet was polished with sandpaper to a thickness of 50–100 μm, and then ion thinning technology was used to obtain a sample with a thickness of 20 μm. An FEI TECNAI F30 transmission electron microscope (TEM, Royal Philips, Amsterdam, The Netherlands) was used to obtain magnified electron images, the distributions of elements and selected area diffraction patterns.
2.4. Mechanical Property Testing
A cylindrical sample with a diameter of 4 mm and a height of 6 mm was used for compression testing. The compression test was conducted at room temperature using an Instron 5969 universal testing machine, with a strain rate of 1 × 10−3 s−1. The compressive properties were measured twice to calculate the average value. After compression, the fracture morphology was observed using SEM.
3. Result and Discussion
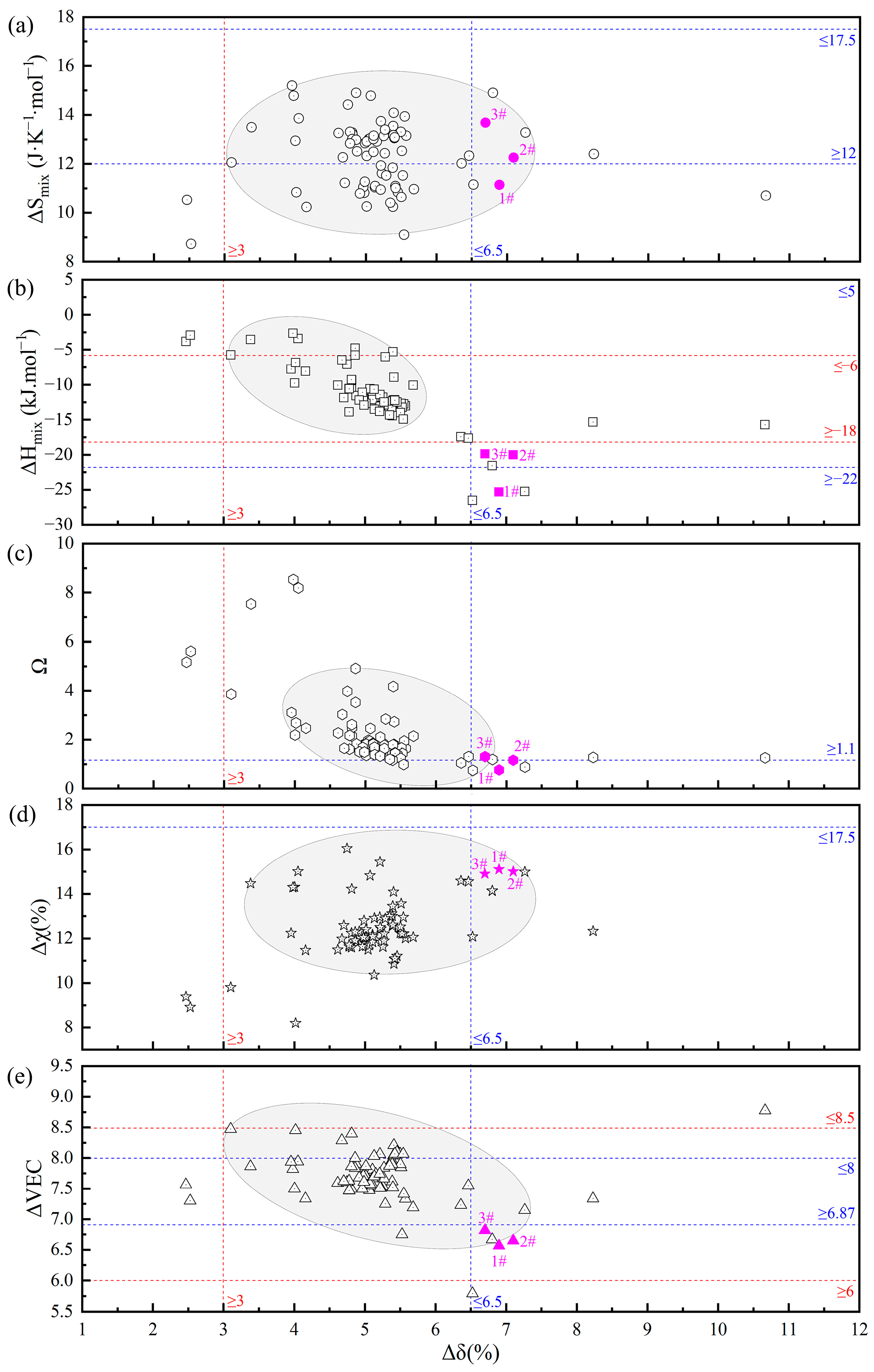
In the preliminary stage, the team first employed thermodynamic parameter calculations for initial screening to narrow down the range of alloy systems, followed by phase diagram calculations to determine the eutectic composition range, thereby achieving precise design and screening of EHEAs [28]. However, significant discrepancies exist among the criteria for solid solution HEAs (blue dashed line), the theoretical criteria for FCC+BCC EHEAs (red dashed line), and the literature data on FCC+BCC EHEAs (hollow points), as illustrated in Figure 1. Therefore, this study focused on the V-Co-Cr-Ni-Ti-Al alloy system and, after preliminary thermodynamic parameter calculations, appropriately expanded the screening range to avoid omissions.
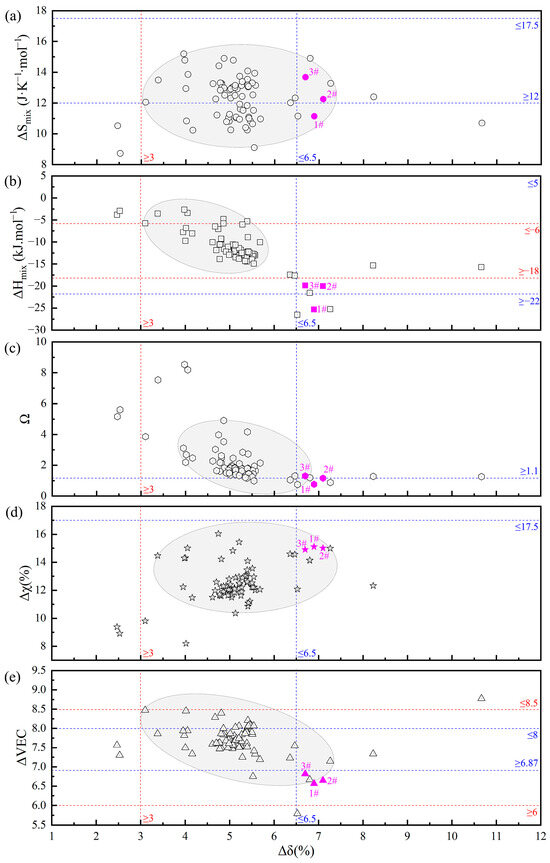
Figure 1.
Confidence diagram of thermodynamic empirical parameters for FCC+BCC-type EHEAs: (a) ΔSmix; (b) ΔHmix; (c) Ω; (d) Δχ; and (e) ΔVEC.
Thermo-Calc software was utilized to calculate the solidification path diagrams for the alloy systems screened in the first step. Combined with the “lever rule” [42] in EHEAs, the EHEA systems were more precisely identified. Through preliminary screening, three groups of EHEAs were obtained: Cr1.3Ni2TiAl (1#), CoCr1.5NiTi1.5Al0.2 (2#), and V0.3CoCr1.2NiTi1.1Al0.2 (3#), with the specific compositions of alloying elements listed in Table 3. The alloy element contents in the samples, as detected by SEM-EDS, were in good agreement with the theoretical calculations. The thermodynamic parameter calculation results for the three groups of EHEAs are summarized in Figure 1 (pink points), further illustrating the limitations of traditional HEA phase structure criteria and EHEA criteria.

Table 3.
Element compositions of the three new EHEAs (wt.%).
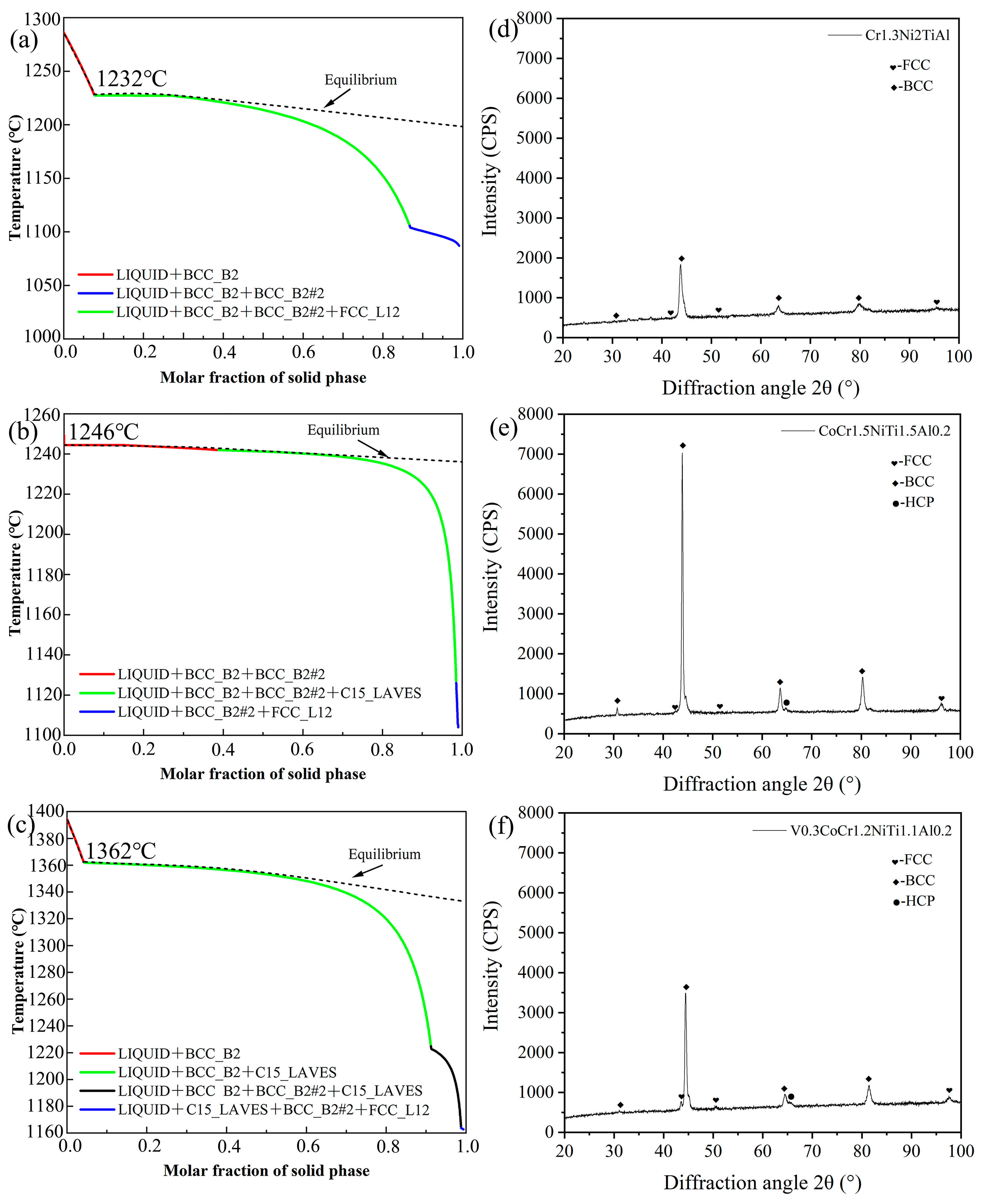
Figure 2a–c shows the solidification path diagrams for the three new EHEAs based on the Scheil model. The initial solidification temperatures for the alloys Cr1.3Ni2TiAl, CoCr1.5NiTi1.5Al0.2, and V0.3CoCr1.2NiTi1.1Al0.2 were all above 1200 °C, and the final solidification temperatures were all above 1000 °C. The actual final solidification temperature was lower than the equilibrium solidification temperature due to the potential occurrence of undercooling during the actual solidification process, which led to the formation of the non-equilibrium phases in the alloy, reducing the final solidification temperature. The alloys Cr1.3Ni2TiAl, CoCr1.5NiTi1.5Al0.2, and V0.3CoCr1.2NiTi1.1Al0.2 exhibit solidification temperatures of 1232 °C, 1246 °C, and 1362 °C, respectively. The phase structure of the alloy Cr1.3Ni2TiAl consisted of FCC+BCC phase structures, while the alloys CoCr1.5NiTi1.5Al0.2 and V0.3CoCr1.2NiTi1.1Al0.2 consisted of FCC+BCC+HCP phase structures. The XRD results of the three groups of EHEAs are shown in Figure 2d–f, and are largely consistent with the phase diagram calculations.
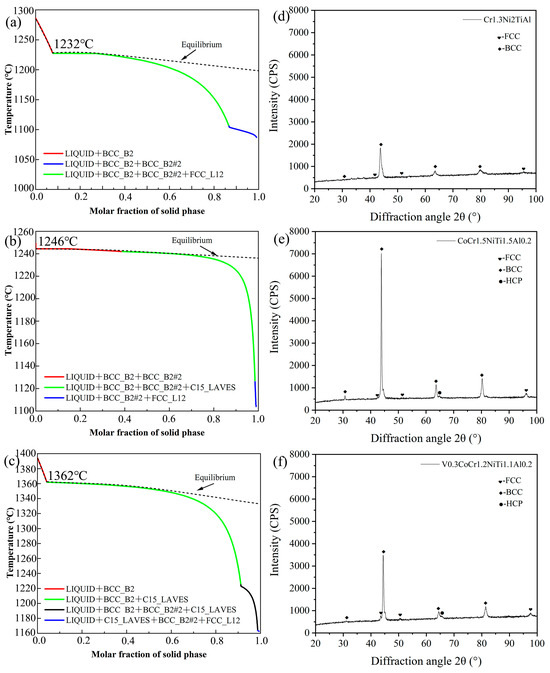
Figure 2.
Solidification path diagrams and XRD results of the three new EHEAs: (a,d) Cr1.3Ni2TiAl; (b,e) CoCr1.5NiTi1.5Al0.2; (c,f) V0.3CoCr1.2NiTi1.1Al0.2.
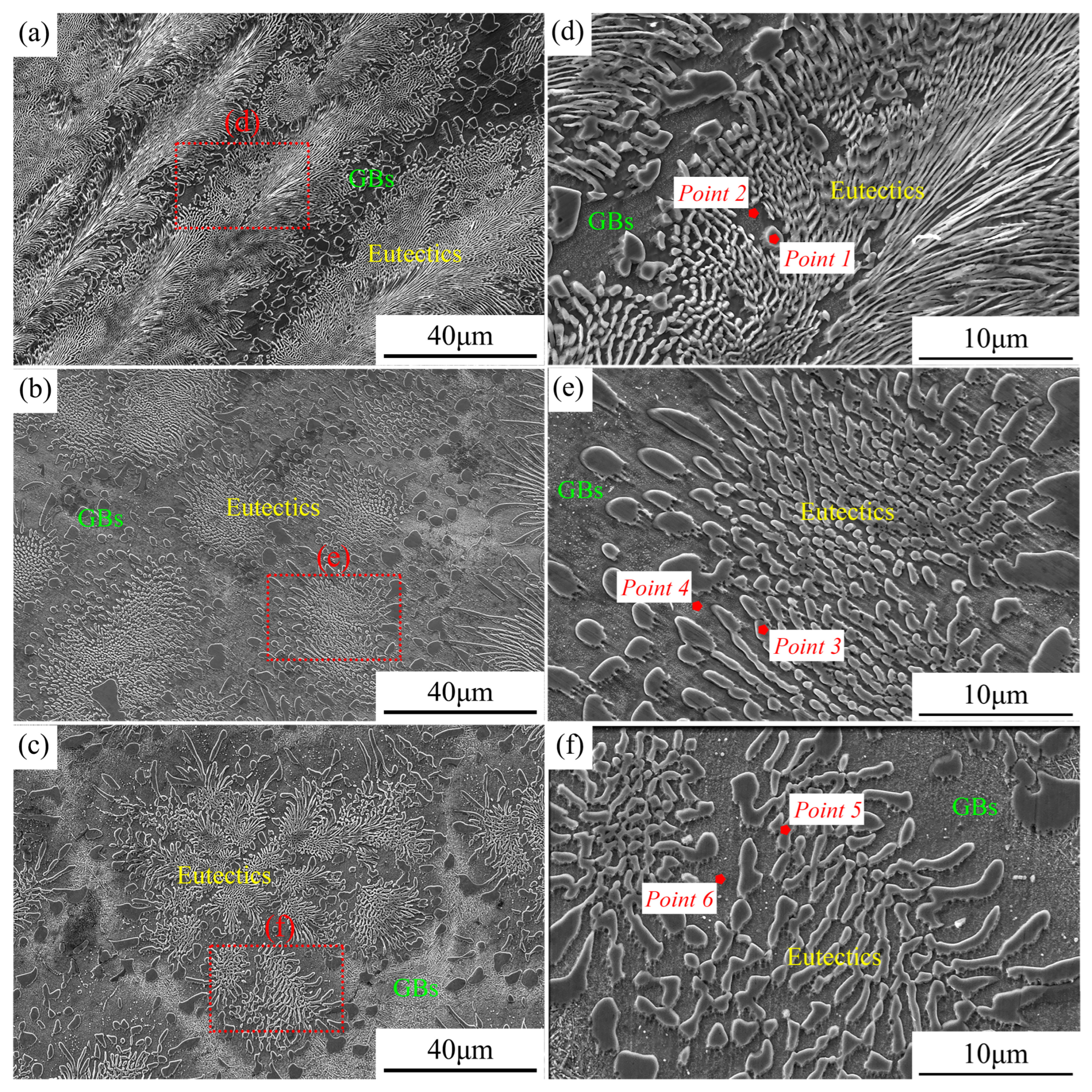
The microstructures of the three new EHEAs were shown in Figure 3. The eutectic structure of the alloy Cr1.3Ni2TiAl exhibited a feather-like appearance, while the eutectic structures of the alloys CoCr1.5NiTi1.5Al0.2 and V0.3CoCr1.2NiTi1.1Al0.2 appeared petal-like, with the grain boundary regions gradually increasing in size. The microstructures of the three novel EHEAs were fully eutectic, validating the accuracy of the design in this study. The three alloy groups exhibited irregular eutectic microstructures, rendering the quantitative characterization of the eutectic structure dimensions challenging. However, qualitative observations revealed that the eutectic structures systematically underwent progressive coarsening with increasing multiplicity of the principal alloying elements. The elemental composition of the eutectic structures in the three groups of samples was examined using SEM-EDS, and the results are presented in Table 4. In the microstructural morphology of the three EHEAs, the phase with higher potential in the eutectic structure was predominantly composed of the Cr element (Point 1, 3, and 5). In the Cr1.3Ni2TiAl sample, the low-potential phase was mainly composed of the Ni, Ti, and Al elements (Point 2). In both the CoCr1.5NiTi1.5Al0.2 and V0.3CoCr1.2NiTi1.1Al0.2 samples, the low-potential phases were primarily composed of the Co, Ni, and Ti elements (Point 4 and Point 6).
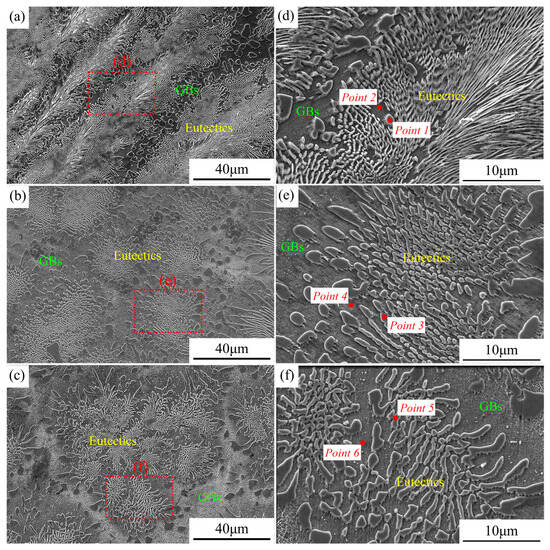
Figure 3.
SEM results of the three new EHEAs: (a,d) Cr1.3Ni2TiAl; (b,e) CoCr1.5NiTi1.5Al0.2; and (c,f) V0.3CoCr1.2NiTi1.1Al0.2.

Table 4.
Element compositions of the eutectic structures in the new EHEAs (wt.%).
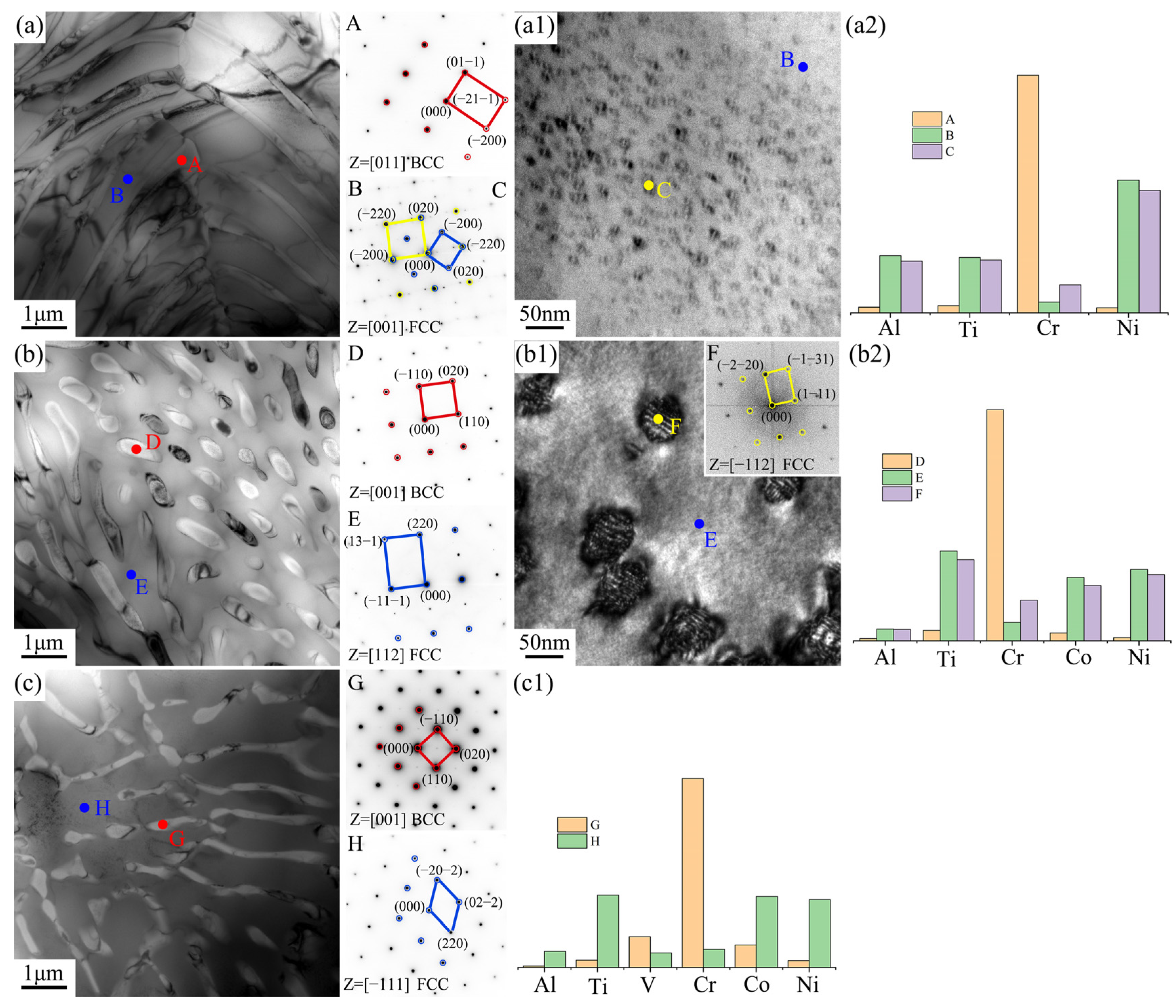
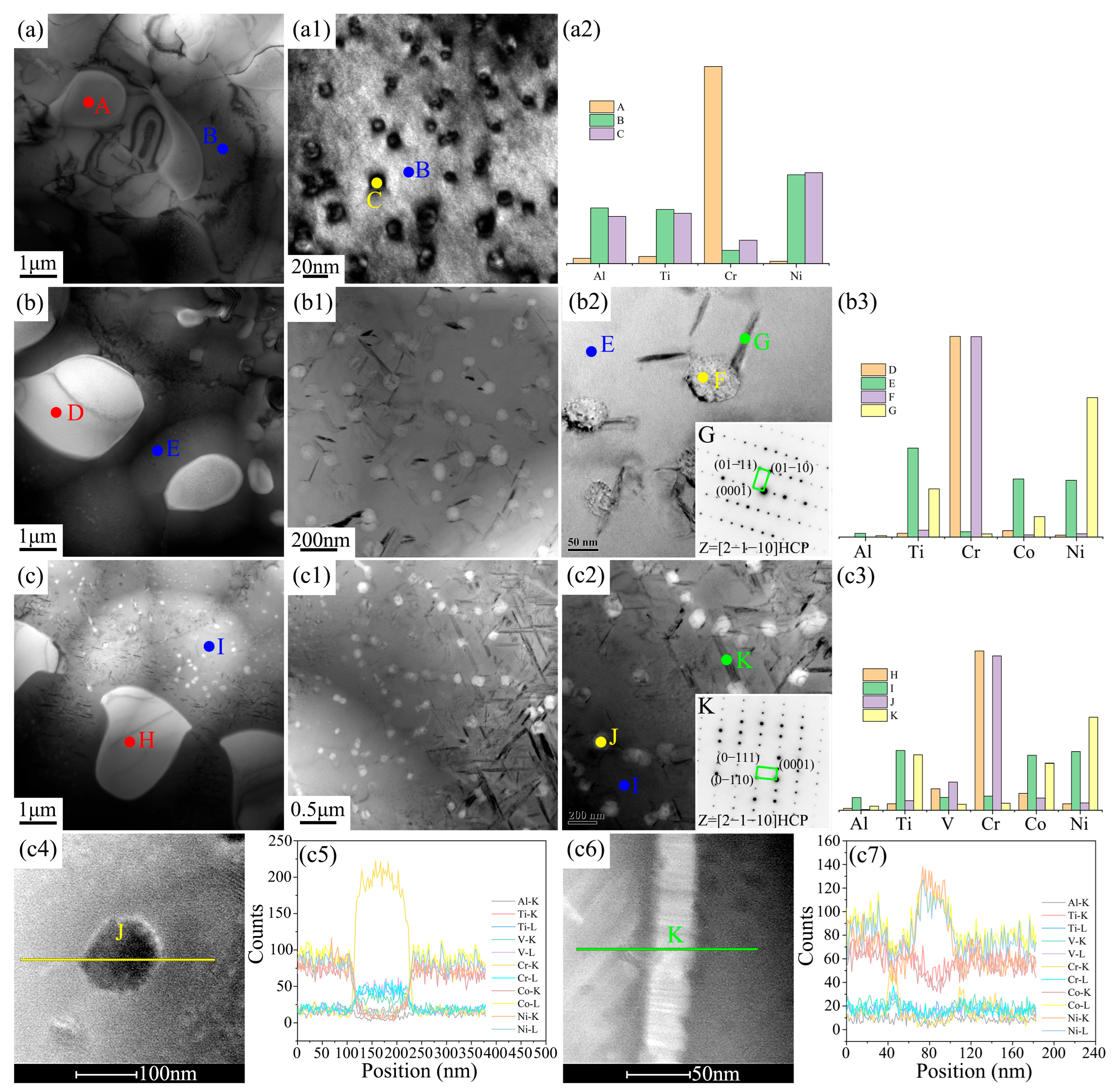
Figure 3 effectively validated that the three new EHEAs were successfully designed and fabricated, with the main differences in their microstructures reflected in the eutectic structure and grain boundary size. Therefore, TEM characterization was used in this study to conduct an in-depth analysis of these two regions, as shown in Figure 4 and Figure 5. The eutectic structures of the three EHEAs primarily consisted of the FCC and BCC phases, with the BCC phase (Points A, D, G) enriched in the Cr element. The FCC phase (Point B) in the Cr1.3Ni2TiAl alloy exhibited significant enrichment with Ni, Ti, and Al, accompanied by the formation of nanoscale precipitates (10–20 nm in diameter) with lattice parameters and elemental partitionning behavior identical to those of the ordered FCC matrix phase. The FCC phase (Point E) of CoCr1.5NiTi1.5Al0.2 was enriched in the Ni, Ti, and Co elements. Although the lattice structure and elemental distribution of the nanoscale precipitates were also similar to the matrix phase, their size (50–60 nm in diameter) was larger compared to those in Cr1.3Ni2TiAl. The FCC phase (Point H) of V0.3CoCr1.2NiTi1.1Al0.2 was also rich in the Ni, Ti, and Co elements, but no nanoscale precipitates were observed.
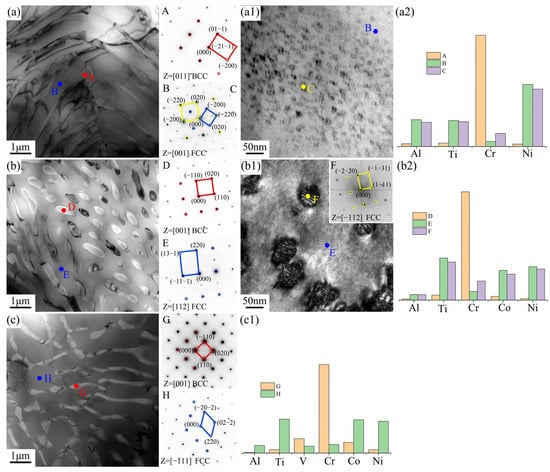
Figure 4.
TEM results of the eutectic structures and elemental distribution for the three new EHEAs: (a–a2) Cr1.3Ni2TiAl; (b–b2) CoCr1.5NiTi1.5Al0.2; and (c,c1) V0.3CoCr1.2NiTi1.1Al0.2.
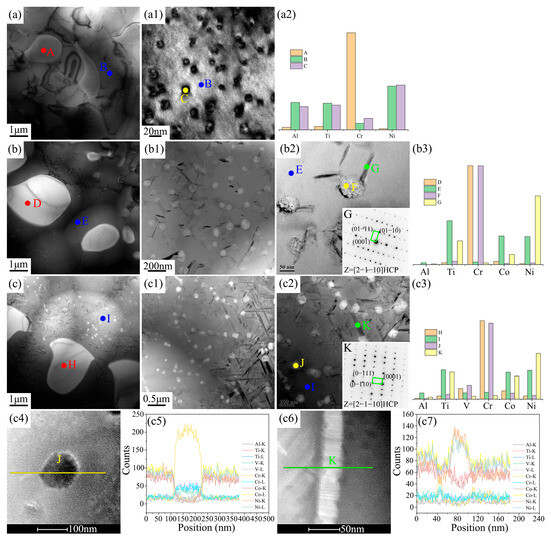
Figure 5.
TEM results of the grain boundary microstructure and element distribution of the three new EHEAs: (a–a2) Cr1.3Ni2TiAl; (b–b3) CoCr1.5NiTi1.5Al0.2; and (c–c7) V0.3CoCr1.2NiTi1.1Al0.2.
The grain boundaries of the three new EHEAs were primarily composed of the FCC and BCC phases, with the FCC phase being significantly more abundant than the BCC phase, as shown in Figure 5. The FCC matrix phase of Cr1.3Ni2TiAl contained nanoscale precipitates (Point C), which, based on elemental distribution, could be identified as an ordered FCC phase, similar to the nanoscale precipitates in the FCC phase of the eutectic structure. In the FCC matrix phases of both CoCr1.5NiTi1.5Al0.2 and V0.3CoCr1.2NiTi1.1Al0.2, two types of nanoscale phases precipitated: a spherical nanoscale phase (Points F, J) and a needle-like nanoscale phase (Points G, K). The spherical nanoscale phase was mainly composed of Cr, similar to the BCC matrix phase. The needle-like nanoscale phase was rich in Ni, Ti, and Co, and based on the elemental content of these three elements, this precipitate was identified as Ti(Ni,Co)3 (a hexagonal close-packed structure), which aligns with the phase diagram calculations. The Cr1.3Ni2TiAl, CoCr1.5NiTi1.5Al0.2, and V0.3CoCr1.2NiTi1.1Al0.2 systems exhibited spherical nanoscale precipitates with distinct size distributions of 10–20 nm, 50–70 nm, and 100–150 nm, respectively. Needle-like phases in the CoCr1.5NiTi1.5Al0.2 and V0.3CoCr1.2NiTi1.1Al0.2 systems displayed lengths of 100–200 nm and 200–1000 nm, respectively, with aspect ratios exceeding 10:1.
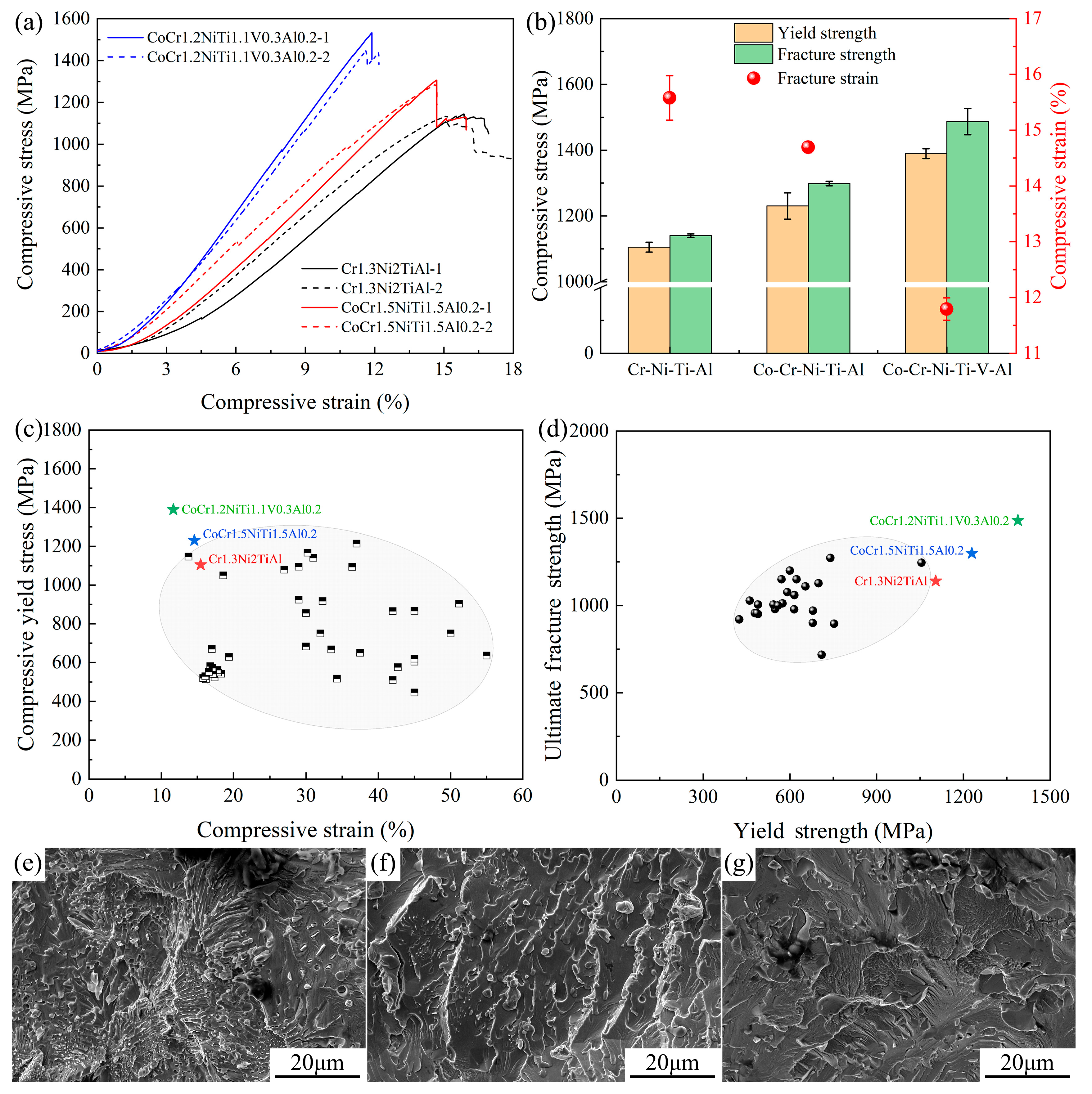
The compression performance test results for the three new EHEAs are shown in Figure 6a,b. The compressive yield strength of Cr1.3Ni2TiAl exceeded 1100 MPa, with a compressive strain close to 16%. As the number of principal elements increased (CoCr1.5NiTi1.5Al0.2 and V0.3CoCr1.2NiTi1.1Al0.2), the yield strength of the samples gradually increased, but the compressive strain gradually decreased. The compressive yield strength and fracture strength of the three EHEAs (especially V0.3CoCr1.2NiTi1.1Al0.2) were superior to existing FCC+BCC EHEAs (Figure 6d), although their compressive strain was lower (Figure 6c). The fracture surfaces of the three EHEAs displayed cleavage patterns characteristic of brittle fractures. However, a eutectic fracture morphology was visible in the fracture surface of the sample of Cr1.3Ni2TiAl (Figure 6e), with this morphology reduced in the sample of CoCr1.5NiTi1.5Al0.2 (Figure 6f), and entirely consisting of cleavage patterns in the sample of V0.3CoCr1.2NiTi1.1Al0.2 (Figure 6g).
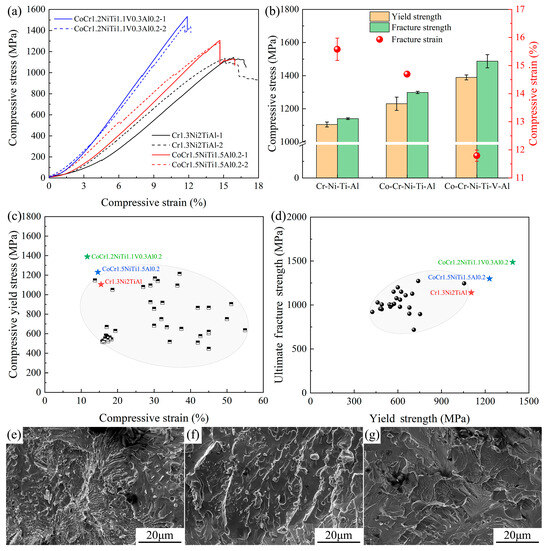
Figure 6.
Compression test results of the three new EHEAs: (a) Engineering stress–strain curves; (b) distribution chart of fracture strength, yield strength, and fracture strain; (c) compressive yield stress–strain distribution for FCC+BCC-type EHEAs; (d) fracture strength–yield strength distribution for FCC+BCC-type EHEAs; and (e–g) the microstructures of the compression fracture surface of the EHEAs #1, #2 and #3, respectively.
In summary, the addition of Ti elements increases the sensitivity of the FCC phase-to-temperature gradient during the growth of EHEAs, resulting in an irregular growth morphology [43,44]. The BCC phase structure grows along with the FCC in a coupling growth mode, and finally forms the irregular FCC+BCC-type EHEAs. The irregular eutectic morphology will cause the atomic coordination relationship at the interface of the FCC and BCC phase to be disordered, which is different from most FCC+BCC-type EHEAs at present. The disordered atomic coordination relationship at the interface will increase the resistance of dislocation passing through the interface during the mechanical property testing process, thus improving the strength but decreasing the plasticity. With the increase in the number of principal alloying elements, the grain boundary area of the EHEAs increased significantly, accompanied by the precipitation of spherical nanoscale FCC phases and needle-like nanoscale Laves phases within the FCC matrix. Notably, the size of these nanoscale precipitates progressively enlarged. The combined effects of enhanced grain boundary density, coarsening of nanoscale precipitates, and increased content of brittle nanoscale precipitates deteriorated the ability of dislocations to pass through these barriers during plastic deformation. Consequently, this microstructural evolution led to a gradual enhancement in strength-related properties of EHEAs, while simultaneously causing a progressive reduction in ductility indicators.
4. Conclusions
(1) A phase-diagram-aided thermodynamic parameter calculation method successfully designed three FCC+BCC-type EHEAs: Cr1.3Ni2TiAl, CoCr1.5NiTi1.5Al0.2, and V0.3CoCr1.2NiTi1.1Al0.2.
(2) In the eutectic microstructure of the Cr1.3Ni2TiAl and CoCr1.5NiTi1.5Al0.2 EHEAs, ordered FCC nano-precipitates were formed within the FCC phase, whereas no such nano-precipitates were observed in a similar region of the V0.3CoCr1.2NiTi1.1Al0.2 EHEA. Additionally, ordered FCC nano-precipitates were also formed in the grain boundary regions of the FCC phase in the Cr1.3Ni2TiAl EHEA, while BCC- and HCP-structured nano-precipitates were observed in the corresponding regions of the CoCr1.5NiTi1.5Al0.2 and V0.3CoCr1.2NiTi1.1Al0.2 EHEAs. Furthermore, both the grain boundary regions and the size of the nano-precipitates increased with the number of principal elements in the EHEAs.
(3) The compressive strength of the three EHEAs gradually increased, while the compressive strain decreased. The eutectic structure with an irregular morphology, the gradually increasing grain boundary size, and the increasing content of the brittle nano-precipitated phase in the FCC base phase at the grain boundary were the main reasons for the mechanical properties.
Author Contributions
Methodology, H.Y.; Investigation, X.Z.; Data curation, Y.X. and W.F.; Writing—review & editing, Y.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by [National Natural Science Foundation of China] grant number [52205409] and [Suzhou Frontier Technology Research—Advanced Materials Program] grant number [SYG202353].
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Haitao Yan was employed by the company Jiangsu Shengpo New Materials Technology Co., Ltd., author Yangchuan Cai was employed by the company Ningbo Qiyi Metal Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Lu, Y.P.; Dong, Y.; Guo, S.; Jiang, L.; Kang, H.J.; Wang, T.M.; Wen, B.; Wang, Z.J.; Jie, J.C.; Cao, Z.Q.; et al. A Promising New Class of High-temperature Alloys: Eutectic High-entropy Alloys. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miracle, D.B.; Senkov, O.N. A Critical Review of High Entropy Alloys and Related Concepts. Acta Mater. 2017, 122, 448–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.F.; Wang, Q.; Lu, J.; Liu, C.T.; Yang, Y. High-entropy Alloy: Challenges and Prospects. Mater. Today 2016, 19, 349–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Ren, W.; Zheng, T.; Ren, Z.; Hou, X.; Peng, J.; Hu, P.; Gao, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Liaw, P.K. Enhanced Strength-ductility Synergy in Ultrafine-grained Eutectic High-entropy Alloys by Inheriting Microstructural Lamellae. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, Z.; Lin, D.; Tang, Z.; Song, X.; He, P.; Zhang, S.; Bian, H.; Fu, W.; Song, Y. Eutectic High-entropy Alloys and Their Applications in Materials Processing Engineering: A Review. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2024, 189, 211–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Zhai, Y.; Lai, M.; Song, M.; Zou, S.; Huang, G.; Yaqoob, K.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, N. Corrosion of Eutectic High-entropy Alloys: A Review. Crystals 2023, 13, 1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wu, Q.; Wei, Y.; Bai, X.; Liu, L.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, L.; He, F.; et al. Boron Microalloying for High-temperature Eutectic High-entropy Alloys. Acta Mater. 2024, 262, 119427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Lei, H.; Liu, X.; Zhao, G.; Feng, J.; Chen, J.; Li, B.; Fang, D.; Gao, N. Design of Synergistic Alloying CoCrFeNi Eutectic High Entropy Alloy Based on Infinite Solid Solution. Mater. Lett. 2023, 343, 134395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Xiong, Z.; An, M.; Xu, Z.; Cheng, X. Large Strength and Decent Ductility at 600 °C Achieved in Bimodal Eutectic High-entropy Alloys. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 22, 3436–3441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.X.; Chang, J.; Wang, W.L.; Zhu, X.N.; Lin, M.J.; Wei, B. Eutectic Growth Kinetics and Microscopic Mechanical Properties of Rapidly Solidified CoCrFeNiMo0.8 High Entropy Alloy. Acta Mater. 2022, 237, 118149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, W.; Jiang, H.; Qiao, D.; He, J.; Zhao, H.; Lu, Y.; Li, T. Effects of Mo on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Fe2Ni2CrMox Eutectic High Entropy Alloys. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2021, 260, 124175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Lu, Y.; Amar, A.; Chen, X.; Ren, Z.; Wang, T.; Li, T. Eutectic High Entropy Alloys Containing B and Si with Excellent Mechanical Properties in Annealing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 856, 143994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, W.; Li, T.; Chang, X.; Lu, Y.; Yin, G.; Cao, Z.; Li, T. A Novel Co-free Al0.75CrFeNi Eutectic High Entropy Alloy with Superior Mechanical Properties. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 902, 163814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Ye, X.; Xu, D.; Liu, C.; Fang, D.; Li, B. Microstructures and Properties of CrxFeNi(3-x)Al High-entropy Alloys. Appl. Phys. A 2021, 128, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Wang, S.; Xiao, F.; Shen, G.; Tian, Y.; Yang, C.; Zhu, G.; Wang, D.; Shu, D.; Sun, B. Designing Lightweight Dual-phase Refractory VNbTiSi-based Eutectic High-entropy Alloys for Use at Elevated Temperatures. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 842, 143112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Jia, Y.; Yi, J.; Ma, X.; Pu, J.; Wang, D. Composition Design, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Novel Multiphase Ti-Cu-Ni-Nb Complex Concentrated Alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 844, 156175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; He, F.; Li, J.; Kim, H.S.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J. Phase-Selective Recrystallization Makes Eutectic High-entropy Alloys Ultra-ductile. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wu, Q.; He, F.; Li, J.; Wang, J. Enhancing the Yield Strength of Ni-Co-Cr-Fe-Al as-Cast Hypoeutectic High-entropy Alloys by Introducing γ′ Precipitation. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 858, 144190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.F.; Shun, T.T. Effect of Fe Content on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Al0.5CoCrFexNiTi0.5 High-entropy Alloys. Mater. Charact. 2016, 114, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, T.; Yang, W.; Zheng, S.; Liu, Z.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, R.; Zhou, Y.; Shao, X.; Zhang, B.; Wang, J.; et al. Faceted Kurdjumov-Sachs Interface-induced Slip Continuity in the Eutectic High-entropy Alloy, AlCoCrFeNi2.1. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 65, 216–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Dou, Y.K.; He, X.F.; Jin, K.; Wang, C.L.; Dong, Y.G.; Wang, C.Y.; Xue, Y.F.; Yang, W. Effects of Nb Addition on Charpy Impact Properties of TiVTa Refractory High-entropy Alloy. Acta Metall. Sin.-Engl. 2023, 36, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xie, W.; Zhu, J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Yang, M.; Jiang, W.; Yu, H.; Wu, Y.; et al. Influences of Ti Additions on the Microstructure and Tensile Properties of AlCoCrFeNi2.1 Eutectic High Entropy Alloy. Intermetallics 2021, 128, 107024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Wu, C.; Zeng, J.; Tu, H.; Wang, J.; Su, X. Phase Composition and Microhardness of the as-Cast and Long-time Annealed CoxNi2-xCrFeTi Multi-component Alloys. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 056527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, M.; Wang, H.; Li, Z.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, B.; Li, J.; Ran, X. Mitigating Hot-cracking of Laser Melted CoCrFeNiMnTix High-entropy Alloys. Mater. Lett. 2022, 314, 131771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Na, Y.S.; Lim, K.R.; Chang, H.J. Effect of Trace Additions of Ti on the Microstructure of AlCoCrFeNi-based High Entropy Alloy. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2016, 8, 1984–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, M.; Wen, N.; Long, J.; Yan, D. Effect of Ti Addition on Microstructure Evolution and Mechanical Properties of Al18Co13Cr10Fe14Ni45 Eutectic High-entropy Alloys. Acta Metall. Sin.-Engl. 2023, 36, 1493–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Chen, F.; Tang, X.; Ge, G.; Sun, Z.; Geng, Z.; Fan, M.; Huang, P. Effect of Ti on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of AlCrFeNiTix Eutectic High-entropy Alloys. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2022, 31, 8294–8303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Han, J.; Ge, F.; Zhang, X.; Cai, Y.; Cui, Y. Design of Eutectic High-entropy Alloys in the Co-Cr-Ni-V-Ti-Al System Using Scheil Solidification Path Optimization. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 1002, 175327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, A.; Inoue, A. Classification of Bulk Metallic Glasses by Atomic Size Difference, Heat of Mixing and Period of Constituent Elements and Its Application to Characterization of the Main Alloying Element. Mater. Trans. 2005, 46, 2817–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanda, B.; Jana, P.P.; Das, J. A Tool to Predict the Evolution of Phase and Young’s Modulus in High Entropy Alloys Using Artificial Neural Network. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2021, 197, 110619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.J.; Lin, J.P.; Chen, G.L.; Liaw, P.K. Solid-solution Phase Formation Rules for Multi-component Alloys. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2008, 10, 534–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, Y. Prediction of High-Entropy Stabilized Solid-solution in Multi-component Alloys. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2012, 132, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lu, Z.; Ma, S.; Liaw, P.K.; Tang, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Gao, M. Guidelines in Predicting Phase Formation of High-entropy Alloys. MRS Commun. 2014, 4, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.; Xiao, X.; Xia, L.; Li, W.; Dong, Y. Relationship between the Widths of Supercooled Liquid Regions and Bond Parameters of Mg-based Bulk Metallic Glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids. 2003, 321, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allred, A.L. Electronegativity Values from Thermochemical Data. J. Inorg. Nucl. Chem. 1961, 17, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.S.; Zhou, Z.Q.; Zhang, J.L.; Yao, M.Y.; Feng, F.; Northwood, D.D. Two Mathematical Models for the Hydrogen Storage Properties of AB2 Type Alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 1999, 293–295, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Chen, S.; Cotton, J.D.; Zhang, Y. Phase Stability of Low-density, Multiprincipal Component Alloys Containing Aluminum, Magnesium, and Lithium. JOM 2014, 66, 2009–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.; Tsai, K.; Tsai, C.; Lee, C.; Juan, C.; Yeh, J. Criterion for Sigma Phase Formation in Cr- and V-containing High-entropy Alloys. Mater. Res. Lett. 2013, 1, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Liu, C.T. Phase stability in high entropy alloys: Formation of Solid-solution Phase or Amorphous Phase. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 2011, 21, 433–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, W.; Zhou, H.; Fang, F.; Xie, Z.; Jiang, J. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of CoCrFeNiZrx Eutectic High-entropy Alloys. Mater. Des. 2017, 134, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, L. CALPHAD: Computer Coupling of Phase Diagrams and Thermochemistry—Foreword. Calphad 2002, 26, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Cai, Y.; Cui, Y.; Yan, Y.; Wang, K. Design of Novel Structural Eutectic High Entropy Alloys (EHEAs) Containing High-temperature Resistant Alloying Elements. Intermetallics 2024, 175, 108535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easton, M.; StJohn, D. Grain Refinement of Aluminum Alloys: Part I. the Nucleant and Solute Paradigms. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2001, 32, 1915–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thijs, L.; Kempen, K.; Kruth, J.-P.; Van Humbeeck, J. Fine-structured Aluminium Products with Controllable Texture by Selective Laser Melting of Pre-alloyed AlSi10Mg Powder. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 1809–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).