Atomic Interaction Mechanism of Heterogeneous Nucleation in Mg-Al Alloys Achieved by Carbon Inoculation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Calculation Method
2.1. Calculations of Valence Electron Structure (VES) of Al2C2Mg and Al4C3
2.2. Calculation of Bond Energy and Cohesive Energy of Al2C2Mg
3. Results and Discussion
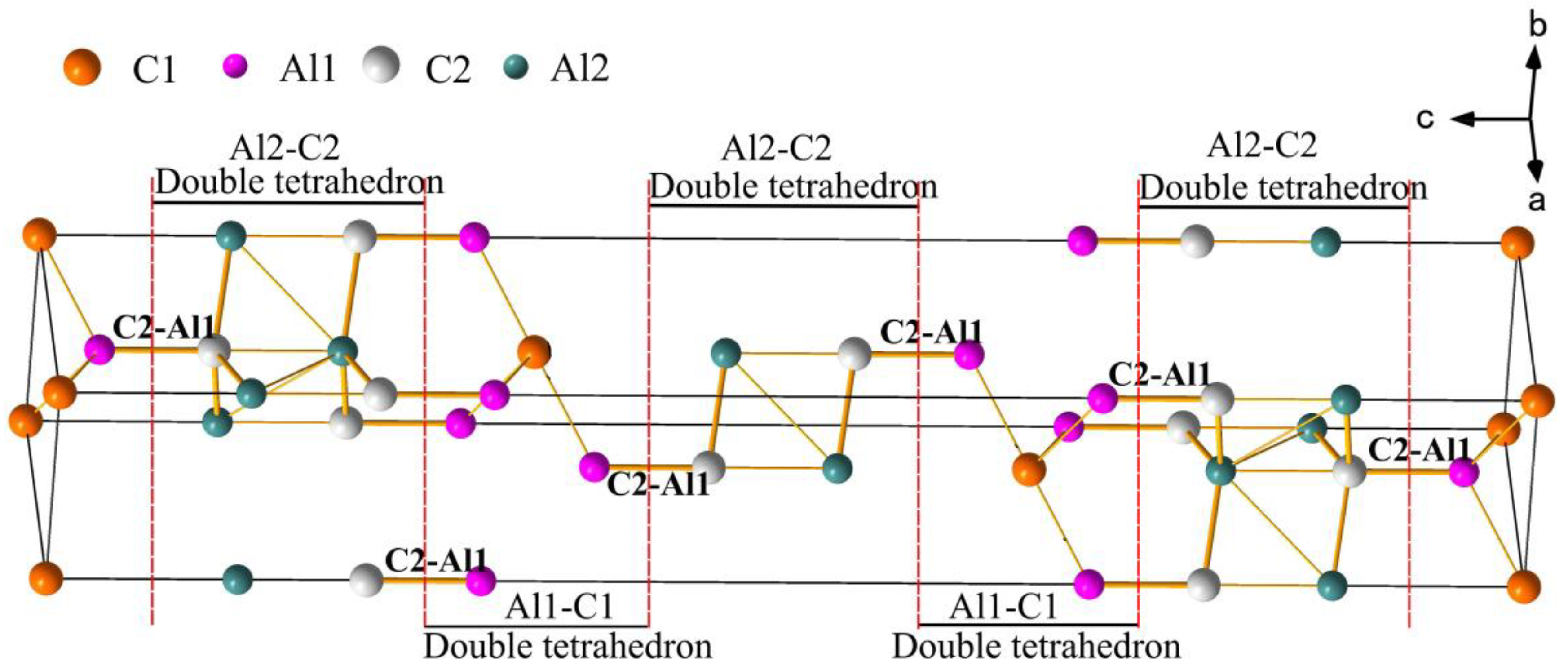
3.1. Elaborate Analysis of Al4C3 and Al2C2Mg Based on VES and Bond Energy
3.2. Effect Mechanism of Overheating on the Refinement Efficiency of Carbon Inoculation
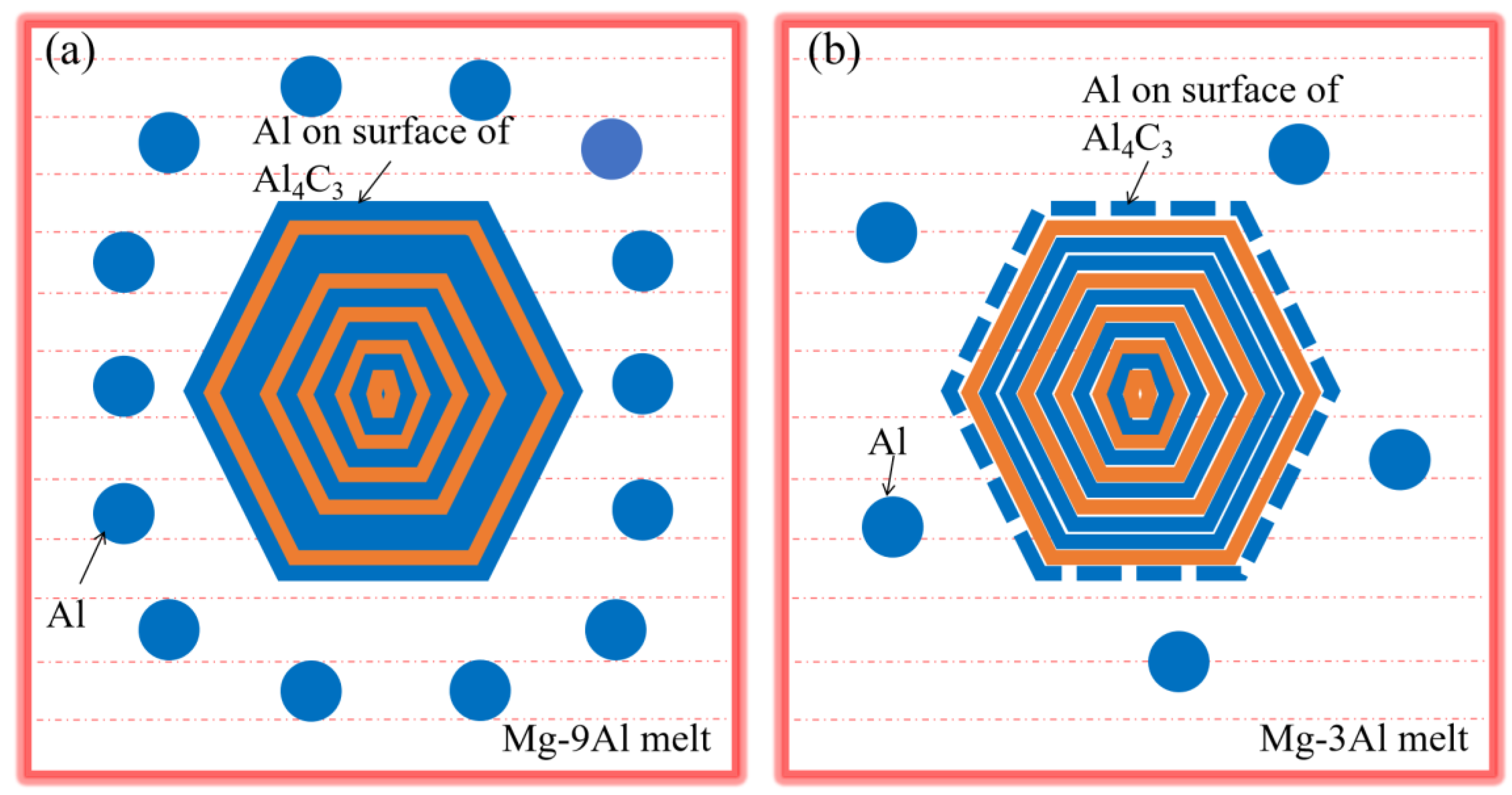
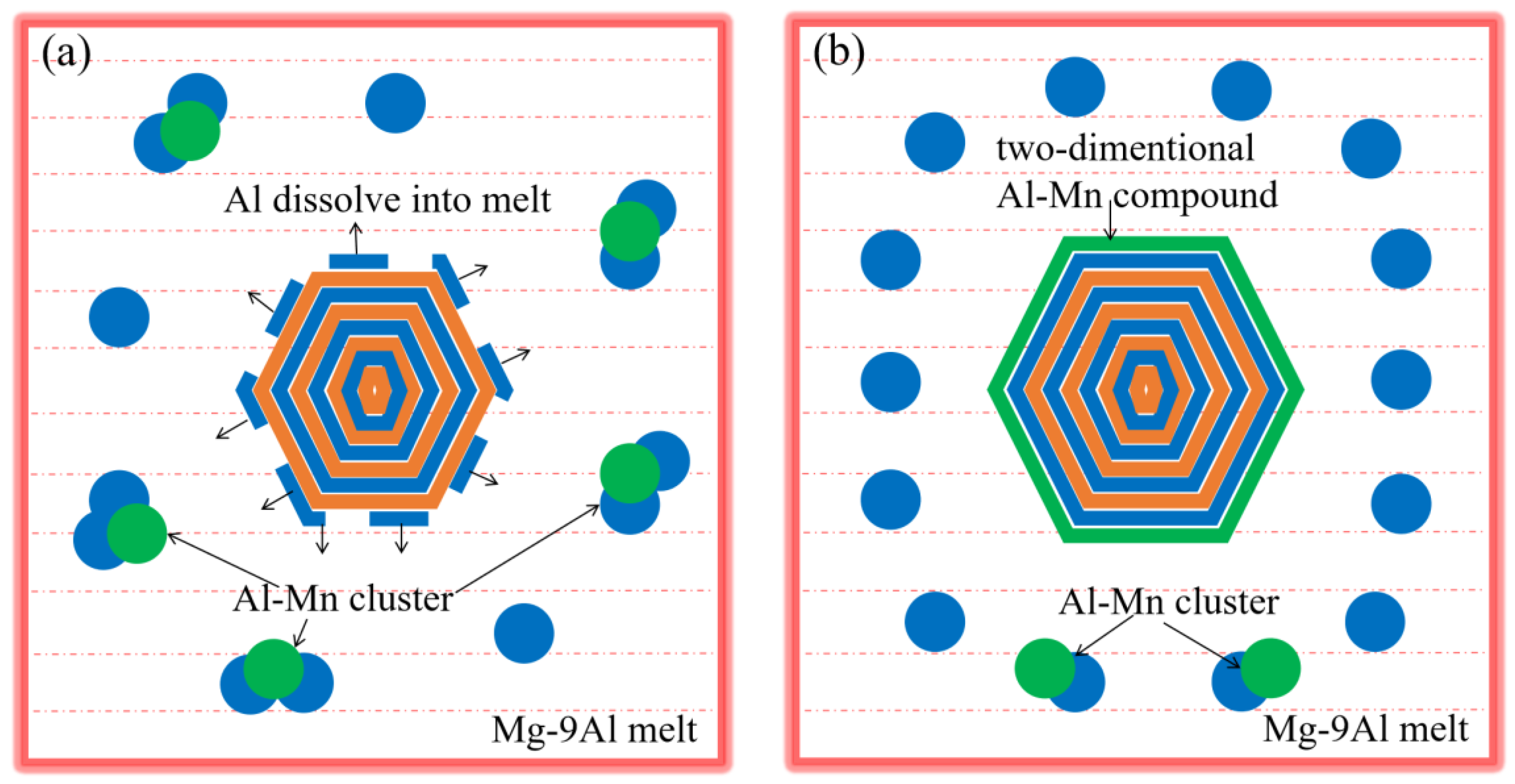
3.3. Effects Mechanism of Al and Mn Element on Nucleating Efficiency of Carbide
4. Conclusions
- 1.
- Under certain conditions, the broken Al1-C2 bonds in Al4C3 lead Al4C3 to decompose into an atomic cluster level with an Al-C tetrahedral skeleton in the Mg-Al melt, which has a strong force on Mg atoms in the liquid phase and finally forms Al2C2Mg as the heterogeneous core of α-Mg;
- 2.
- A higher melt temperature is beneficial for the fracture of Al1-C2 bonds and produces more nano-Al2C2Mg under the following rapid cooling process, which is responsible for the refinement mechanism of overheating treatment in Mg-Al alloy;
- 3.
- The changes in Al and Mn content both affect the fracture of Al1-C2 bonds and the formation of Al2C2Mg, which in turn affects whether a carbon agent can become an effective heterogeneous core for α-Mg.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Akhmadieva, A.A.; Khrustalev, A.P.; Grigoriev, M.V.; Zhukov, I.A.; Vorozhtsov, A.B. Structure, Phase Composition, and Mechanical Properties of ZK51A Alloy with AlN Nanoparticles after Heat Treatment. Metals 2024, 14, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanabal, N.; Silambarasan, R.; Seenuvasaperumal, P.; Althaf Basha, D.; Elayaperumal, A. Microstructure and mechanical behavior of AXM Mg alloy systems—A review. J. Magn. Alloys 2024, 12, 2624–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hösele, T.; Neunteufl, E.; Li, J. Investigation on the Duration of Action of Mg3N2 as a Grain Refiner for AZ80 Alloy. Metals 2024, 14, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q. The role of solutes in grain refinement of hypoeutectic magnesium and aluminum alloys. J. Magn. Alloys 2022, 10, 1846–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easton, M.A.; Qian, M.; Prasad, A.; St. John, D.H. Recent advances in grain refinement of light metals and alloys. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2016, 20, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, Y.; Qiu, D.; Jiang, B.; Pan, F.; Zhang, M.X. Current research progress in grain refinement of cast magnesium alloys: A reviewarticle. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 619, 639–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.C.; Dahle, A.K.; StJohn, D.H. The role of solute in grain refinement of magnesium. Metall. Mater. Trans. 2000, 31, 2895–2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Q.; Eom, J.P.; Lim, S.G.; Park, W.W.; You, B.S. Grain refining mechanism of a carbon addition method in a Mg–Al magnesium alloy. Scr. Mater. 2003, 49, 1129–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Liu, X.F.; Ding, H.M. Grain refinement of Mg-Al based alloys by a new Al–C master alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 467, 202–207. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, L.; Dahle, A.K.; StJohn, D.H. Heterogeneous nucleation of Mg-Al alloys. Scr. Mater. 2006, 54, 2197–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Chen, Y.; Han, H. Grain refinement of AZ91D magnesium alloy by a new Mg–50%Al4C3 master alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 624, 266–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.X.; Kelly, P.; Qian, M.; Taylor, J. Crystallography of grain refinement in Mg–Al based alloys. Acta Mater. 2005, 53, 3261–3270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinotha, D.; Raghukandan, K.; Pillai, U.T.S.; Pai, B.C. Grain refining mechanisms in magnesium alloys—An overview. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2009, 62, 521–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Kainer, K.U.; Hort, N. Mechanism of grain refinement of Mg–Al alloys by SiC inoculation. Scr. Mater. 2011, 64, 793–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimityongskul, S.; Jones, M.; Choi, H. Grain refining mechanisms in Mg-Al alloys with Al4C3 microparticles. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 2104–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, Y.; Haitani, T.; Yano, E.; Motegi, T.; Kono, N.; Sato, E. Grain Refinement of High-Purity Mg-Al Alloy Ingots and Influences of Minor Amounts of Iron and Manganese on Cast Grain Size. Mater. Trans. 2002, 43, 2784–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zeng, G.; Xian, J.W.; Gourlay, C.M. Nucleation and growth crystallography of Al8Mn5 on B2-Al (Mn,Fe) in AZ91 magnesium alloys. Acta Mater. 2018, 153, 364–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.M.; Yim, C.D.; You, B.S. Grain refining mechanism in Mg-Al base alloys with carbon addition. Scr. Mater. 2007, 57, 691–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.F.; Li, K.; Zhou, N.G. First–principles study of Mn adsorption on Al4C3(0001) surface. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 363, 168–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Zhu, X.; Gao, T.; Liu, X. Revealing the roles of Al4C3 and Al8Mn5 during α–Mg nucleation in Mg-Al based alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 705, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Gao, F. Grain Initiation and Grain Refinement: An Overview. Metals 2022, 12, 1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, T.; Zhou, X.R.; Thompsonm, G.E.; Pennycook, T. Grain refining mechanism in the Al/Al-Ti-B system. Acta Mater. 2015, 84, 292–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.F.; Dai, Y.B.; Shu, D.; Wang, J.; Sun, B.D. First-Principles Calculations on the Stability of Al/TiB2 Interface. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 89, 144107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, T.; Ruan, Z.; Zhong, F.; Xie, C.; Li, X.; Chen, D.; Tang, P.; Wu, Y. Nucleation and growth of L12-Al3RE particles in aluminum alloys: A first-principles study. J. Rare Earth 2023, 41, 1116–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Yin, G.L. Calculation of the lattice constant of solids with the use of valence electron structure parameters. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2015, 97, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Yin, G.L.; Zhao, Y.Q. Calculation of the cohesive energy of solids with the use of valence electron structure parameters. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2015, 101, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Huang, S.; Yin, G.; Zhang, A.M.; Zhao, Z.; Zhao, Y. A simple models to ascertain the initial formation concentration of athermal ω phase in titanium alloys. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2016, 123, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Yin, G.L.; Zhang, A.M.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Q. Simple models to account for the formation and decomposition of athermal ω phase in titanium alloys. Scr. Mater. 2016, 117, 28–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.M.; Li, J.; Li, F.; Su, G. Investigation on the Atomic Mechanism for Grain Refinement of magnesium alloy by Mg-Zr master alloy. Materials 2022, 15, 7063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deffrennes, G.; Gardiola, B.; Lomello, M.; Andrieux, J.; Dezellus, O.; Schmid-Fetzer, R. Thermo-dynamics of Phase Formation in Mg–Al–C Alloys Applied to Grain Refinement. In Magnesium Technology 2018; The Minerals, Metals & Materials Series; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 323–327. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, P.; Qian, M.; StJohn, D.H. Mechanism for grain refinement of magnesium alloys by superheating. Scr. Mater. 2007, 56, 633–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.S.; Son, Y.G.; Park, Y.H.; Lee, Y.C. A Study on the Grain Refining Mechanisms and Melt Superheat Treatment of Aluminum-Bearing Mg Alloys. Metals 2022, 12, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Liu, X. Phase control and formation mechanism of Al–Mn(–Fe) intermetallic particles in Mg–Al–based alloys with FeCl3 addition or melt superheating. Acta Mater. 2016, 114, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
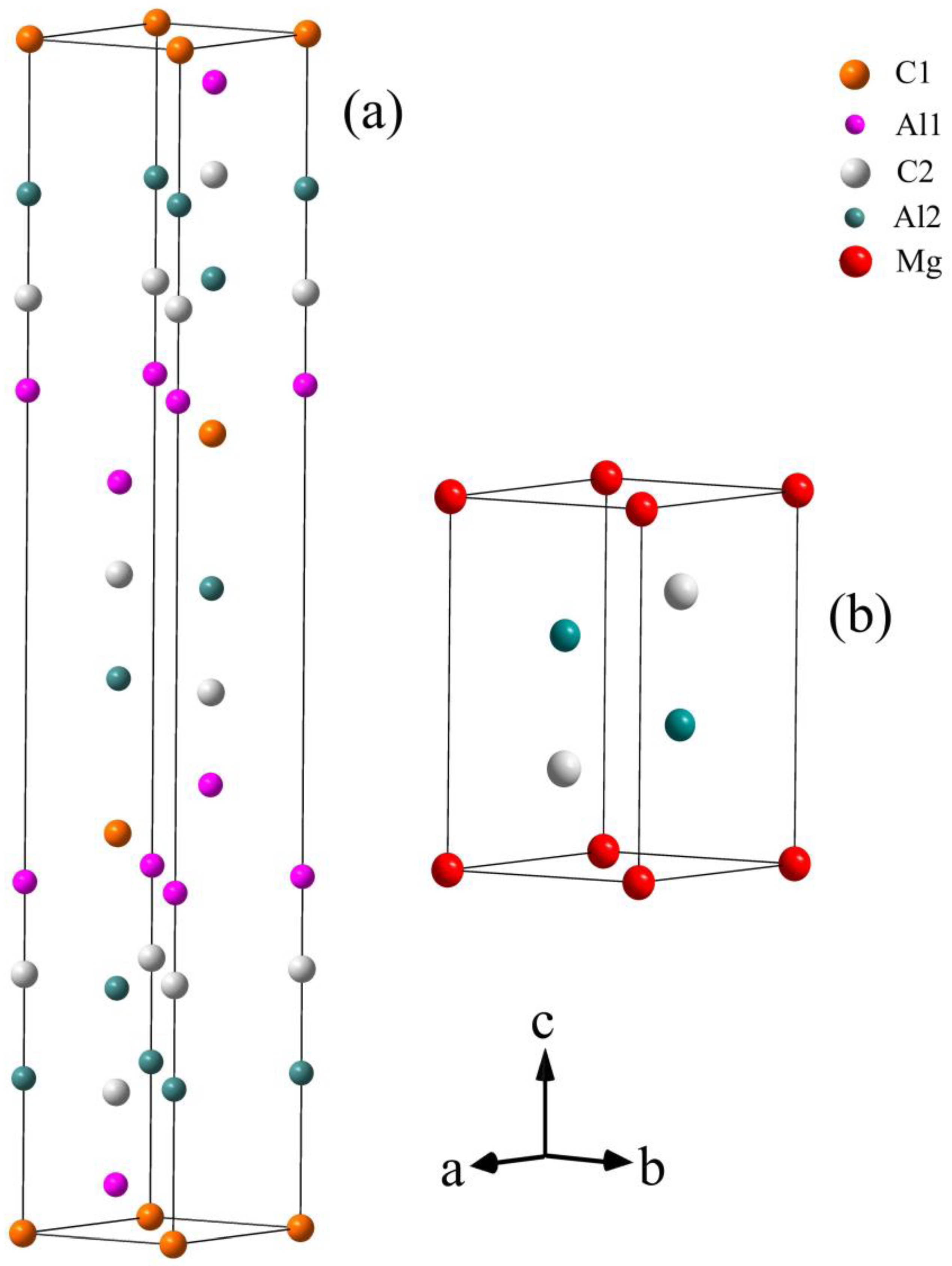
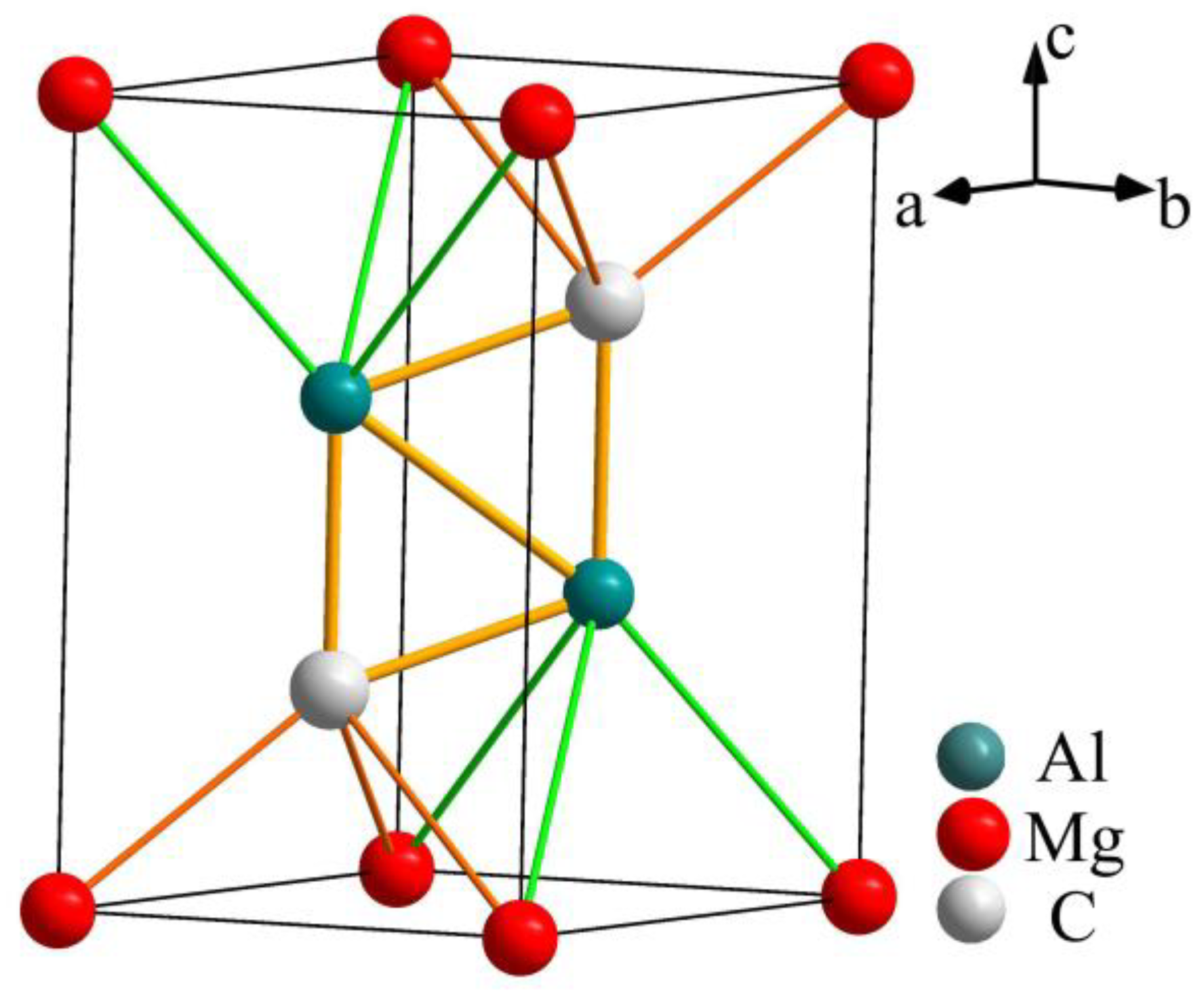

| Chemical Formula | Space Group | Lattice Constants /nm | Atomic Parameters | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atoms | Wyckoff Sites | x/a | y/b | z/c | |||
| Al2C2Mg | (164) | a = 0.3377 c = 0.5817 | Mg | 1a | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Al | 2d | 1/3 | 2/3 | 0.3773 | |||
| C | 2d | 1/3 | 2/3 | 0.7346 | |||
| Al4C3 | (166) | a = 0.3335 c = 2.4967 | Al1 | 6c | 0 | 0 | 0.29422 |
| Al2 | 6c | 0 | 0 | 0.12967 | |||
| C1 | 3a | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| C2 | 6c | 0 | 0 | 0.2168 | |||
| Crystals | CBN | EBN | EBL (nm) | n′α | E′α (kJ/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al2C2Mg | 2.4 | 0.24862 | 0.164619 | 17.37550 | |
| 2.4 | 0.29357 | 0.150971 | 14.58221 | ||
| 1.2 | 0.3377 | 0.036500 | 2.729387 | ||
| 2.4 | 0.20555 | 0.654524 | 89.18834 | ||
| 0.8 | 0.20784 | 0.599381 | 80.77451 | ||
| 1.2 | 0.24164 | 0.843422 | 106.5203 | ||
| 2.4 | 0.3377 | 0.021138 | 1.910899 | ||
| 1.2 | 0.33542 | 8.705 × 10−4 | 0.065904 | ||
| 2.4 | 0.3377 | 7.975 × 10−5 | 0.599728 | ||
| Crystals | CBN | EBN | EBL (nm) | n ′α | E ′α (kJ/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al4C3 | 0.57143 | 0.19329 | 0.901025 | 140.6895 | |
| 1.71429 | 0.21589 | 0.404659 | 56.7197 | ||
| 0.85714 | 0.35307 | 0.014245 | 1.3669 | ||
| 1.71429 | 0.29698 | 0.103878 | 11.8197 | ||
| 1.71429 | 0.33350 | 0.028487 | 2.8916 | ||
| 3.42857 | 0.38547 | 9.969 × 10−4 | 0.07896 | ||
| 1.71429 | 0.19532 | 0.838577 | 129.6129 | ||
| 0.57143 | 0.21754 | 0.381740 | 53.1114 | ||
| 0.85714 | 0.26683 | 0.302200 | 38.1997 | ||
| 0.57143 | 0.32375 | 8.867 × 10−3 | 0.8350 | ||
| 1.71429 | 0.33350 | 0.028487 | 2.8916 | ||
| 1.71429 | 0.38649 | 9.605 × 10−4 | 0.07596 | ||
| 0.85714 | 0.33350 | 1.383 × 10−3 | 0.11253 | ||
| 1.71429 | 0.34889 | 8.019 × 10−4 | 0.06241 | ||
| 0.85714 | 0.31583 | 2.586 × 10−3 | 0.22205 | ||
| 1.71429 | 0.33350 | 1.383 × 10−3 | 0.11253 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, A.; Zhu, Y.; Tao, K.; Zhang, Z. Atomic Interaction Mechanism of Heterogeneous Nucleation in Mg-Al Alloys Achieved by Carbon Inoculation. Metals 2025, 15, 594. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15060594
Zhang A, Zhu Y, Tao K, Zhang Z. Atomic Interaction Mechanism of Heterogeneous Nucleation in Mg-Al Alloys Achieved by Carbon Inoculation. Metals. 2025; 15(6):594. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15060594
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Aimin, Ying Zhu, Kai Tao, and Zhiyuan Zhang. 2025. "Atomic Interaction Mechanism of Heterogeneous Nucleation in Mg-Al Alloys Achieved by Carbon Inoculation" Metals 15, no. 6: 594. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15060594
APA StyleZhang, A., Zhu, Y., Tao, K., & Zhang, Z. (2025). Atomic Interaction Mechanism of Heterogeneous Nucleation in Mg-Al Alloys Achieved by Carbon Inoculation. Metals, 15(6), 594. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15060594





