Production of ZnO Nanofibers from Zinc Galvanizing Flue Dust
Abstract
1. Introduction
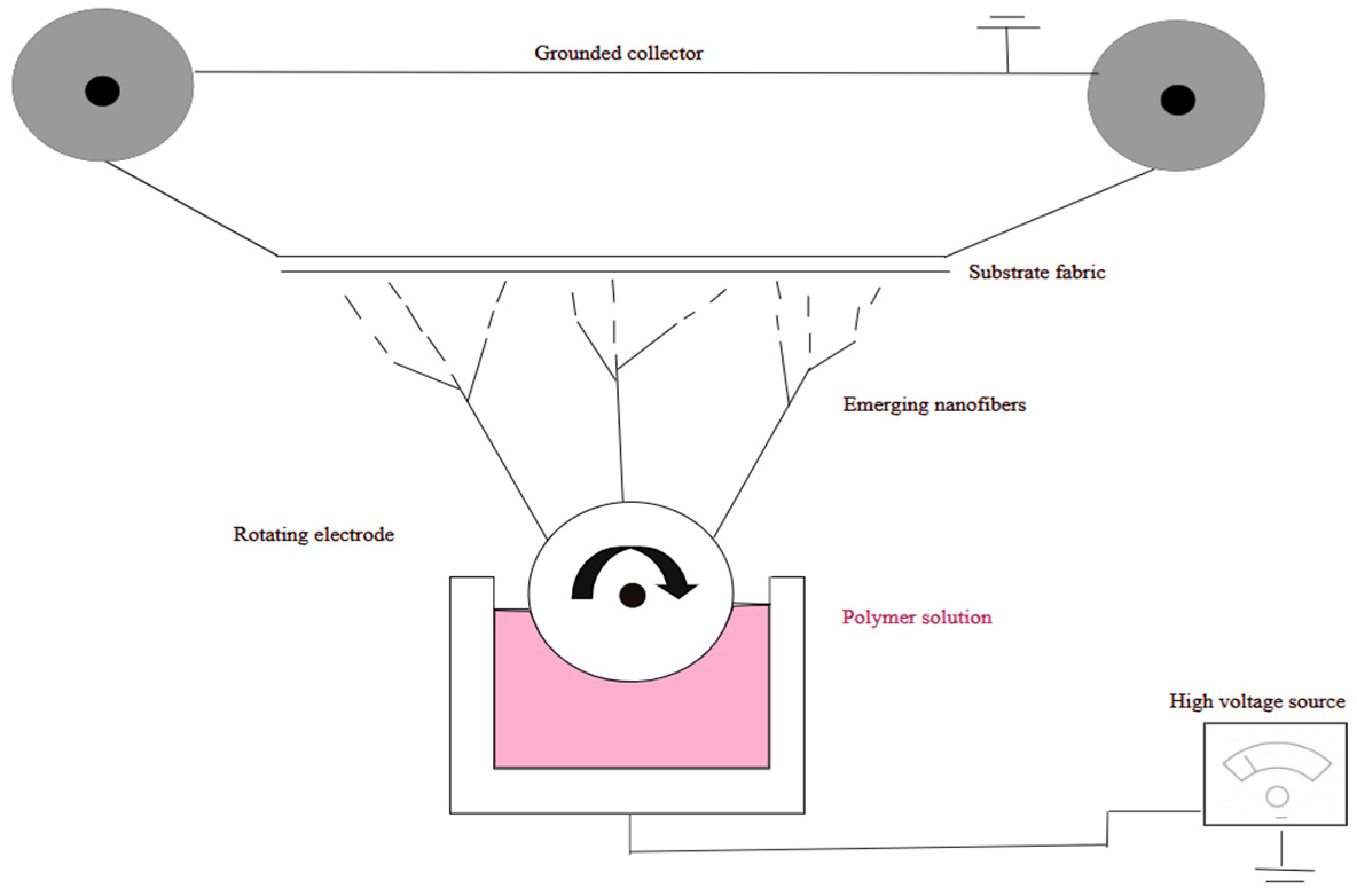
- Electrostatic spinning includes several types:
- The process of manufacturing nanofibers consists of several steps:
- Preparation of electrostatic spinning solution;
- Electrostatic spinning of polymer-inorganic composite fibers;
- Calcination of composite fibers to remove the organic components (polymer and solvent) and obtain a pure ceramic phase;
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Synthetic Solutions Containing Zn
2.2. Preparation of Real Solutions Containing Zn
2.3. Methodology of Experimental Work on Electrostatic Spinning
3. Results and Discussion
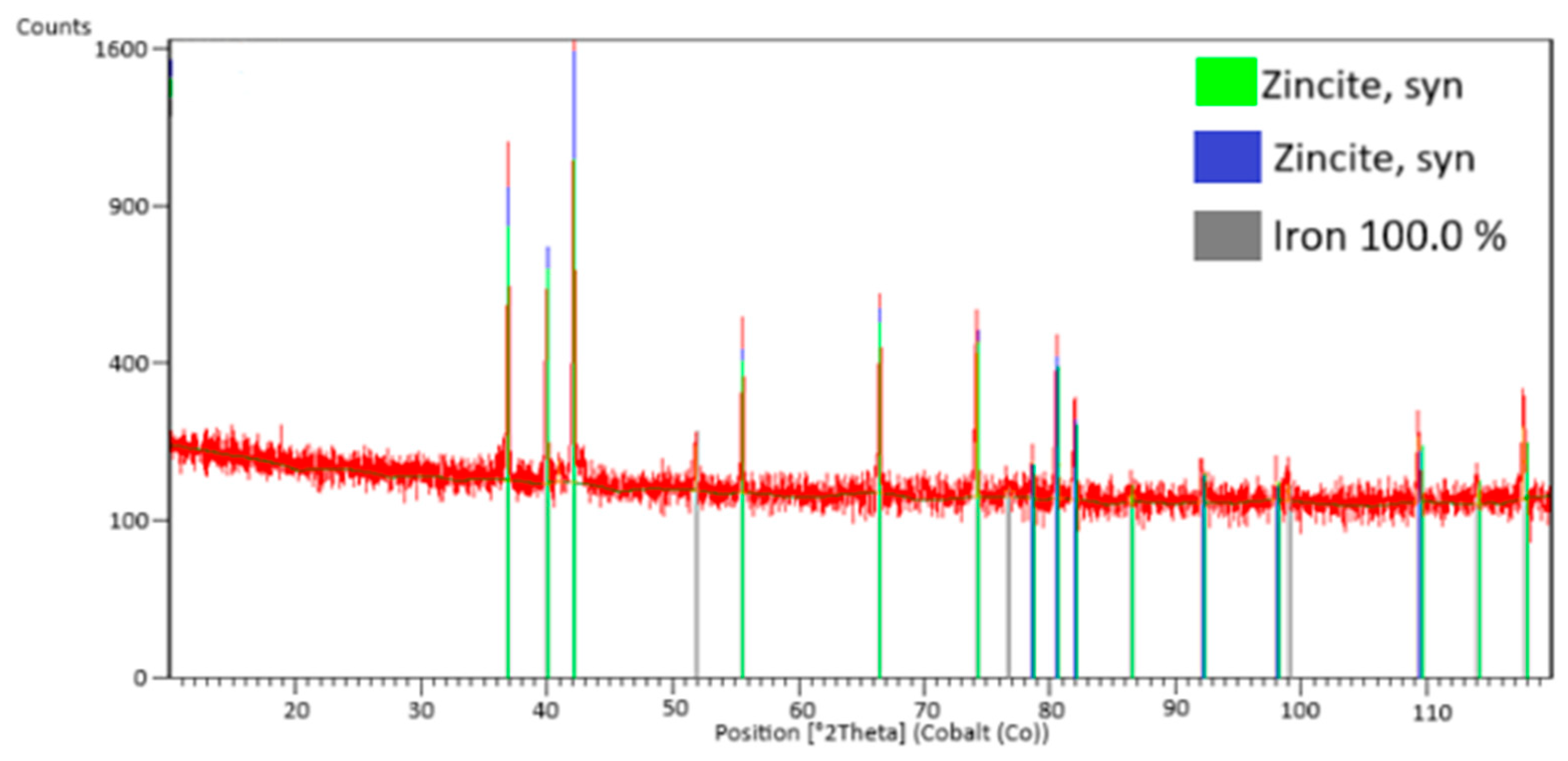
3.1. Composition of Zinc Galvanizing Flue Dust
3.2. Thermodynamic Study
3.3. Leaching—Synthetic and Real Solutions
3.4. Electrospinning of Synthetic Solutions—Production of ZnO Ceramic Nanofibers
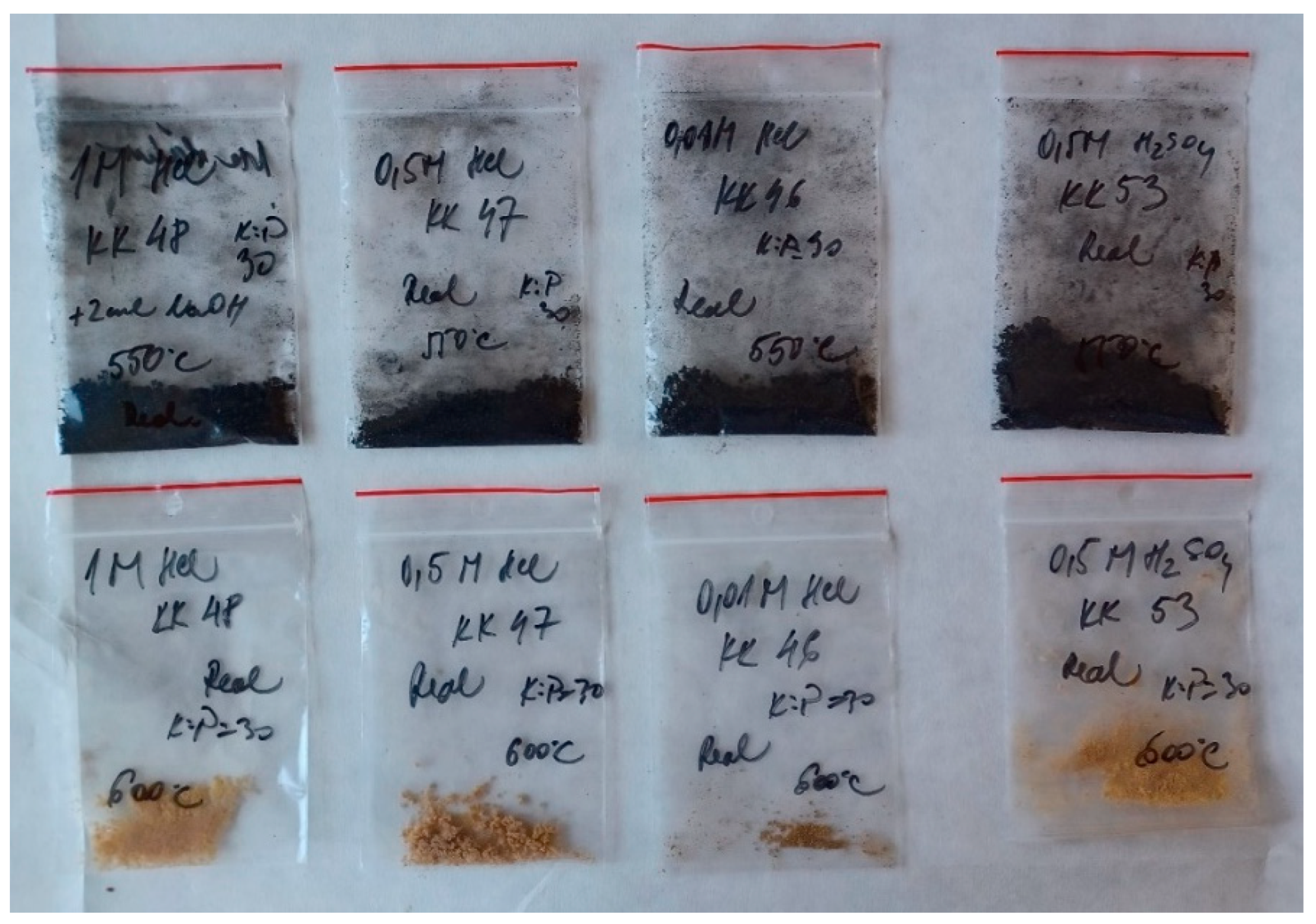
3.5. Electrospinning of Real Solutions—Production of ZnO Ceramic Nanofibers
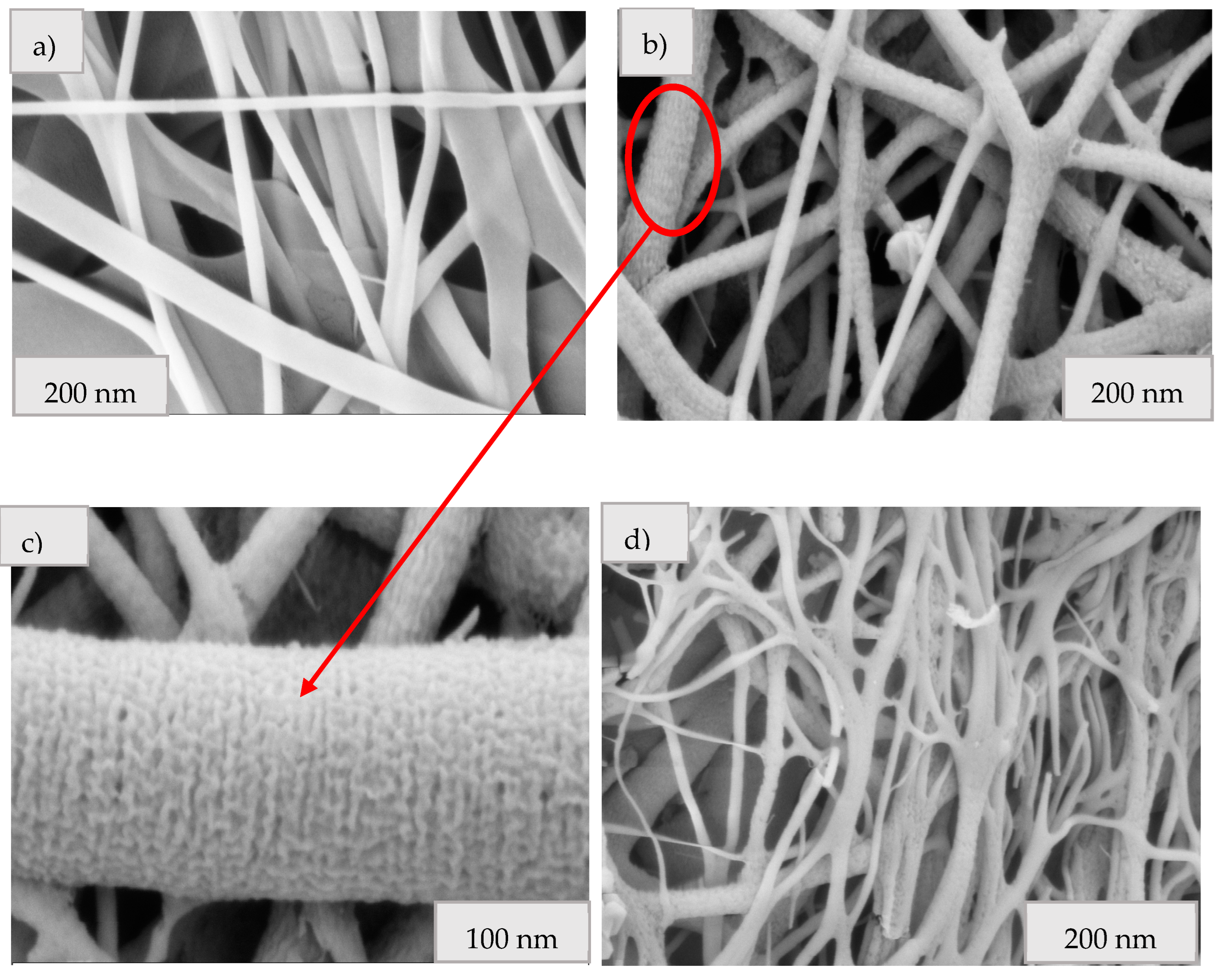
3.6. Comparison of ZnO Fibers from Synthetic and Real Solutions in Terms of Their Structure and Morphology
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Trpčevská, J.; Laubertová, M. Kovový Odpad a Jeho Spracovanie; Technical University of Kosice: Košice, Slovakia, 2015; ISBN 9788055323657. [Google Scholar]
- Maaß, P.; Peißker, P. Handbook of Hot-Dip Galvanization; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Lemke, E.E.; Hammond, W.F.; Thomas, G. Air Pollution Control Measures for Hot Dip Galvanizing Kettles. J. Air Pollut. Control Assoc. 1960, 10, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Piroskova, J.; Trpcevska, J.; Orac, D.; Laubertova, M.; Horvathova, H.; Holkova, B. Production of Zinc Oxide from Hazardous Waste-Sal Ammoniac Skimming. J. Min. Metall. Sect. B Metall. 2018, 54, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. Hazardous Waste Listings a User-Friendly Reference Document; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2012.
- Rahman, L.; Quddus, S.; Khanam, J.; Bilkis, K.; Rahman, M. Fabrication of Zinc Oxide from Zinc Dust and Its Characterization. IOSR J. Appl. Chem. 2017, 10, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorsen, G.; Grislingas, A.; Steintveit, G. Recovery of Zinc from Zinc Ash and Flue Dusts by Hydrometallurgical Processing. J. Met. 1981, 33, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirošková, J.; Klimko, J.; Trpčevská, J.; Laubertová, M.; Plešingerová, B.; Liptai, P.; Vindt, T.; Oráč, D. Characterization of Galvanizing Flue Dust and Recycling Possibilities. Metals 2022, 12, 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirošková, J.; Klimko, J.; Ružičková, S.; Laubertová, M.; Marcinov, V.; Múdra, E.; Vojtko, M.; Oráč, D. Utilization of Galvanizing Flue Dust Residue: A Sustainable Approach towards Complete Material Recycling. Metals 2024, 14, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, M.A. Recovery of Zinc from Zinc Ash and Flue Dust by Pyrometallurgical Processing. In Proceedings of the TMS Fall Extraction and Processing Conference; Minerals, Metals and Materials Society, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 22–25 October 2000; pp. 211–223. [Google Scholar]
- Lukáš, D.; Sarkar, A.; Martinová, L.; Vodsed’álková, K.; Lubasová, D.; Chaloupek, J.; Pokorný, P.; Mikeš, P.; Chvojka, J.; Komárek, M. Physical Principles of Electrospinning (Electrospinning as a Nano-Scale Technology of the Twenty-First Century). Text. Prog. 2009, 41, 59–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi Bonakdar, M.; Rodrigue, D. Electrospinning: Processes, Structures, and Materials. Macromol 2024, 4, 58–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CeCe, R.; Jining, L.; Islam, M.; Korvink, J.G.; Sharma, B. An Overview of the Electrospinning of Polymeric Nanofibers for Biomedical Applications Related to Drug Delivery. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2024, 26, 2301297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Song, W.; Tang, Y.; Xu, X.; Huang, Y.; Yu, D. Polymer-Based Nanofiber-Nanoparticle Hybrids and Their Medical Applications. Polymers 2022, 14, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigmund, W.; Yuh, J.; Park, H.; Maneeratana, V.; Pyrgiotakis, G.; Daga, A.; Taylor, J.; Nino, J.C. Processing and Structure Relationships in Electrospinning of Ceramic Fiber Systems. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2006, 89, 395–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepa, I.; Mudra, E.; Dusza, J. Electrospinning through the Prism of Time. Mater. Today Chem. 2021, 21, 100543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotus, A.F.; Kang, Y.C.; Walker, J.I.; Ramsier, R.D.; Chase, G.G. Effect of Aluminum Oxide Doping on the Structural, Electrical, and Optical Properties of Zinc Oxide (AOZO) Nanofibers Synthesized by Electrospinning. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2010, 166, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baylan, E.; Altintas Yildirim, O. Highly Efficient Photocatalytic Activity of Stable Manganese-Doped Zinc Oxide (Mn:ZnO) Nanofibers via Electrospinning Method. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2019, 103, 104621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangavel, K.; Roshini, T.; Balaprakash, V.; Gowrisankar, P.; Sudha, S.; Mohan, M. Structural, Morphological and Antibacterial Properties of ZnO Nanofibers Fabricated by Electrospinning Technique. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 33, 2160–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khankhuean, A.; Kuratsameethong, W.; Santibenchakul, S.; Laobuthee, A.; Sugimoto, M.; Srisawat, N.; Jamnongkan, T. Oriented ZnO Nanoflowers Obtained after Calcination of Electrospinning Poly(Vinyl Alcohol)/Zinc Oxide/Zinc Acetate Composite Mats. S. Afr. J. Chem. Eng. 2021, 37, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercante, L.A.; Andre, R.S.; Facure, M.H.M.; Fugikawa-Santos, L.; Correa, D.S. Design of a Bioelectronic Tongue for Glucose Monitoring Using Zinc Oxide Nanofibers and Graphene Derivatives. Sens. Actuators Rep. 2021, 3, 100050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kale, S.M.; Kirange, P.M.; Kale, T.V.; Jee Kanu, N.; Gupta, E.; Chavan, S.S.; Kumar Vates, U.; Kumar Singh, G. Synthesis of Ultrathin ZnO, Nylon-6,6 and Carbon Nanofibers Using Electrospinning Method for Novel Applications. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 47, 3186–3189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, H.S.; Elkady, M.F.; Farghali, A.A.; Salem, A.M.; AbdEl-Hamid, A.I. Fabrication of Novel Magnetic Zinc Oxide Cellulose Acetate Hybrid Nano-Fiber to Be Utilized for Phenol Decontamination. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2017, 78, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Sample | Zn [wt%] | Fe [wt%] | Al [wt%] | Cu [wt%] | Pb [wt%] | Cl− [wt%] | Residual [wt%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average | 25.33 | 0.38 | 0.91 | 0.006 | 0.09 | 24.87 | 48.41 |
| % | % | % | % | % | % | - | |
| Standard deviation | 0.46 | 0.01 | 0.14 | 0.0008 | 0.06 | 2.07 | - |
| Relative standard deviation | 1.81 | 2.63 | 650 | 750 | 150 | 8.32 | - |
| Conditions | 0.01 M HCl | 0.5 M HCl | 1 M HCl | 0.5 M H2SO4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synthetic solutions | - | - | - | -+ |
| Zn content [g/L] | 7.10 | 12.64 | 27.33 | 21.55 |
| Conditions | Acid Concentration | Zn [g/L] | Fe [g/L] | Pb [g/L] | Cu [g/L] | Al [g/L] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L:S 30 | 0.01 M HCl | 6.514 | 0.001 | 0.0002 | 0.012 | 0.009 |
| 0.5 M HCl | 9.307 | 0.063 | 0.0024 | 0.015 | 0.388 | |
| 1 M HCl | 9.089 | 0.080 | 0.0022 | 0.025 | 0.344 | |
| 0.5 M H2SO4 | 10.130 | 0.038 | 0.0028 | 0.0017 | 0.412 | |
| L:S 5 | 0.01 M HCl | 28.83 | 0.001 | 0.0012 | 0.038 | 0.010 |
| 0.5 M HCl | 49.76 | 0.002 | 0.0014 | 0.052 | 0.123 | |
| 1 M HCl | 51.43 | 0.342 | 0.0080 | 0.114 | 1.951 | |
| 0.5 M H2SO4 | 68.20 | 0.132 | 0.0968 | 0.041 | 0.216 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kundráková, K.; Pirošková, J.; Trpčevská, J.; Múdra, E. Production of ZnO Nanofibers from Zinc Galvanizing Flue Dust. Metals 2025, 15, 522. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15050522
Kundráková K, Pirošková J, Trpčevská J, Múdra E. Production of ZnO Nanofibers from Zinc Galvanizing Flue Dust. Metals. 2025; 15(5):522. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15050522
Chicago/Turabian StyleKundráková, Klaudia, Jana Pirošková, Jarmila Trpčevská, and Erika Múdra. 2025. "Production of ZnO Nanofibers from Zinc Galvanizing Flue Dust" Metals 15, no. 5: 522. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15050522
APA StyleKundráková, K., Pirošková, J., Trpčevská, J., & Múdra, E. (2025). Production of ZnO Nanofibers from Zinc Galvanizing Flue Dust. Metals, 15(5), 522. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15050522







