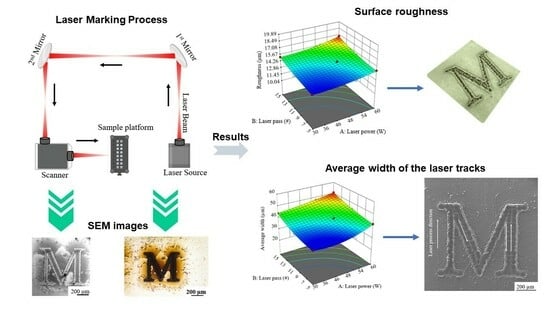
Statistical Modeling and Characterization of Laser Marking on AISI 301LN Stainless Steel Using Short-Pulsed Fiber Laser
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methodology
2.1. Methodology
2.2. Material and Laser
3. Results and Discussion
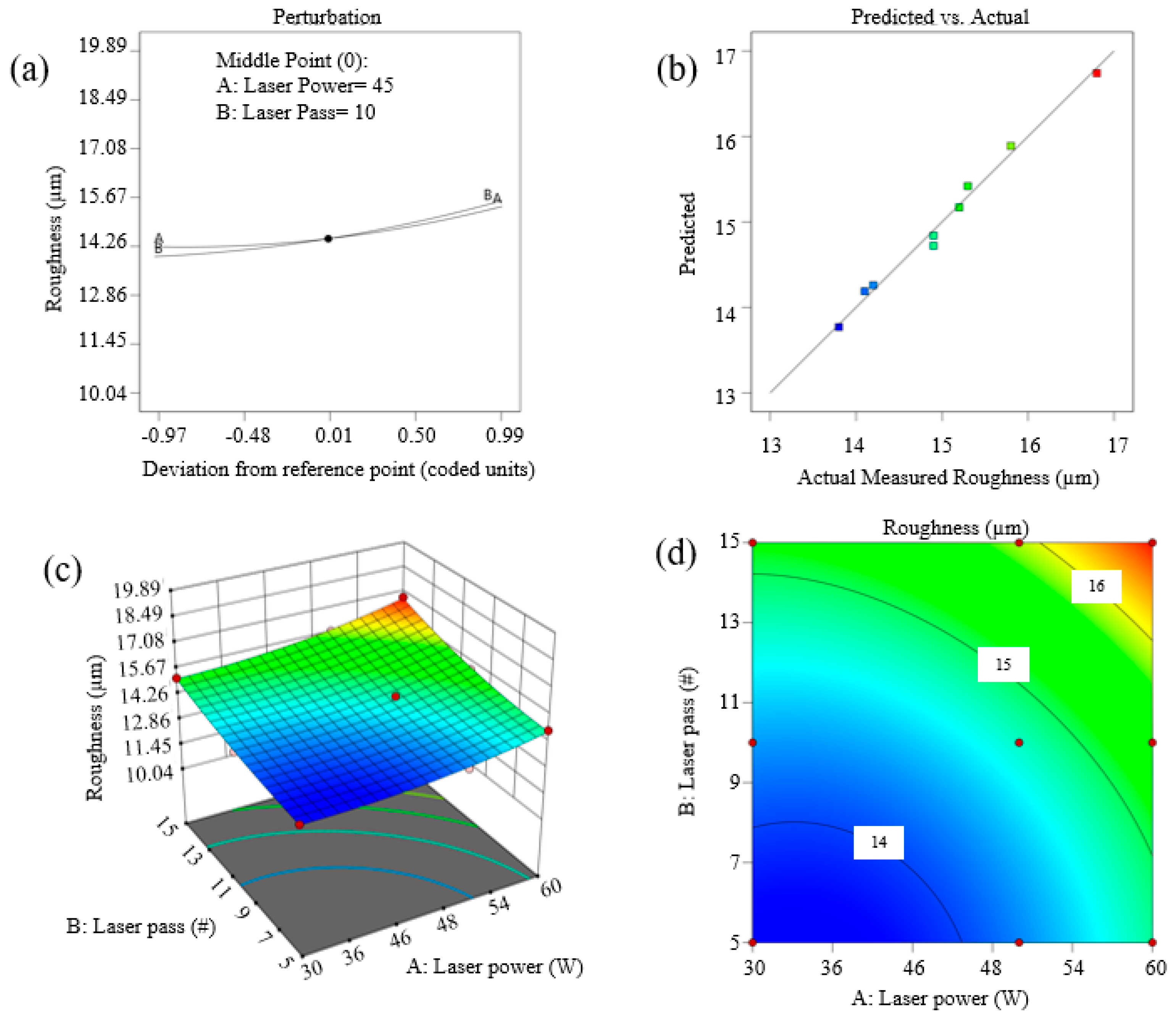
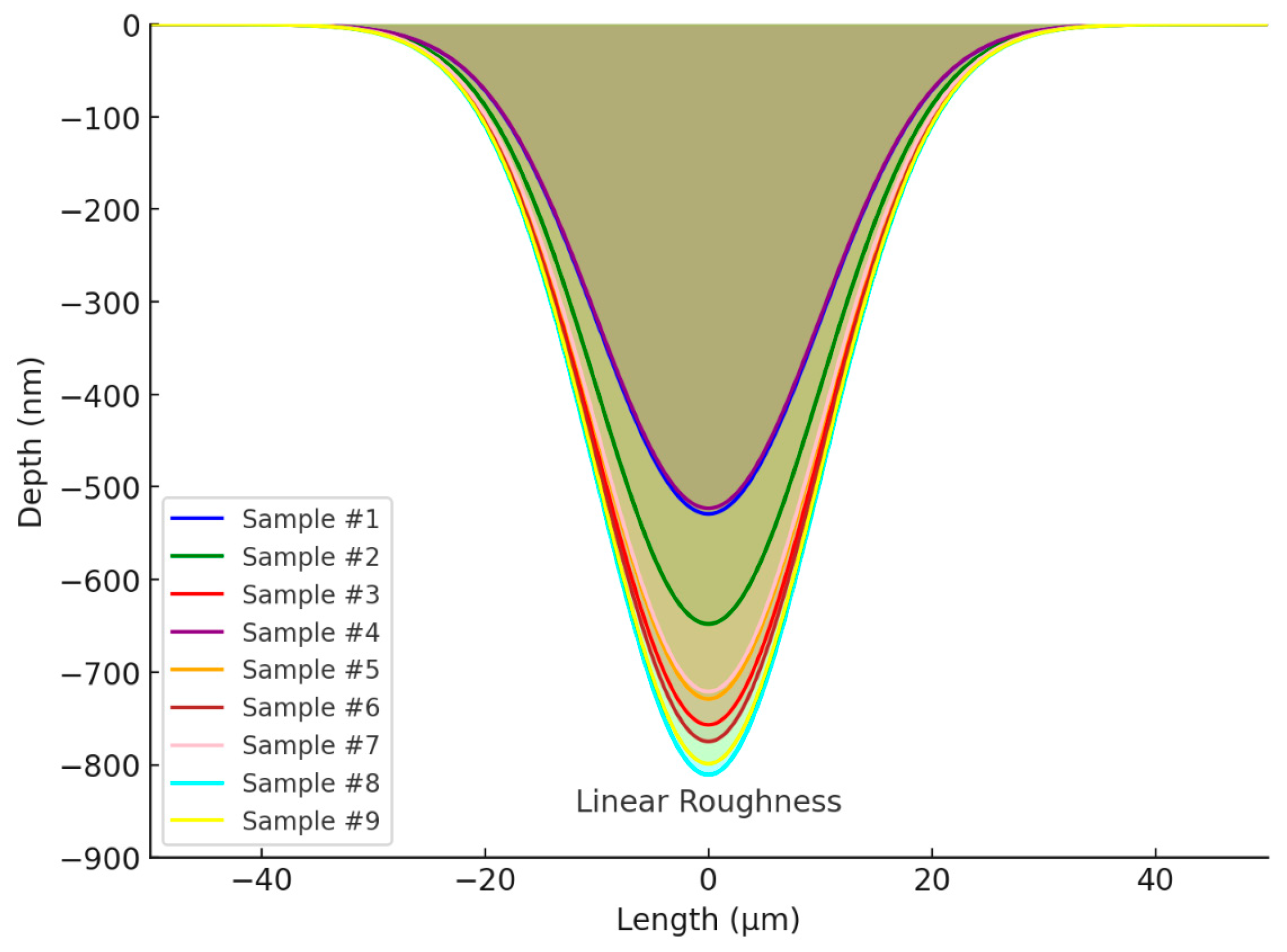
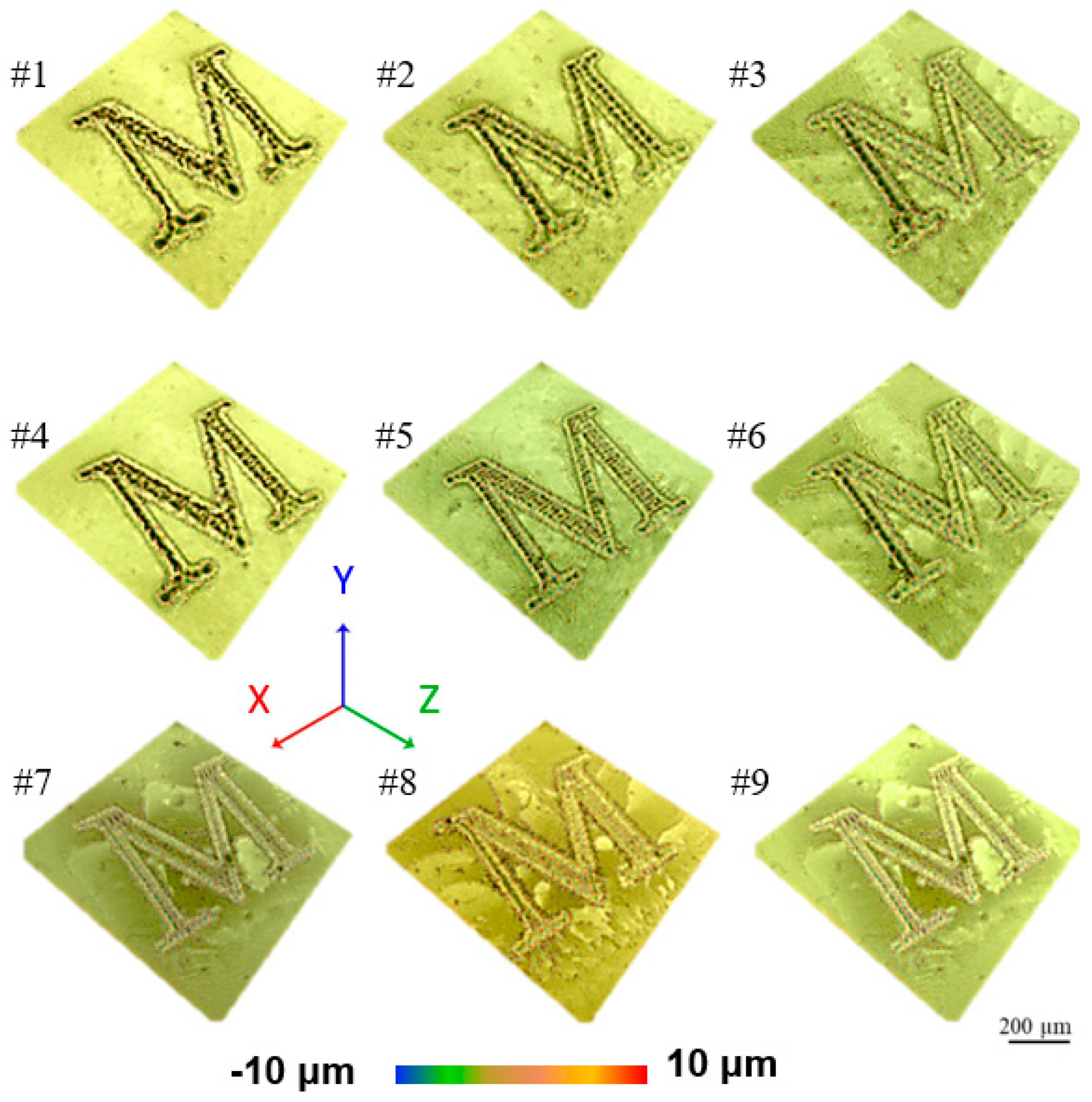
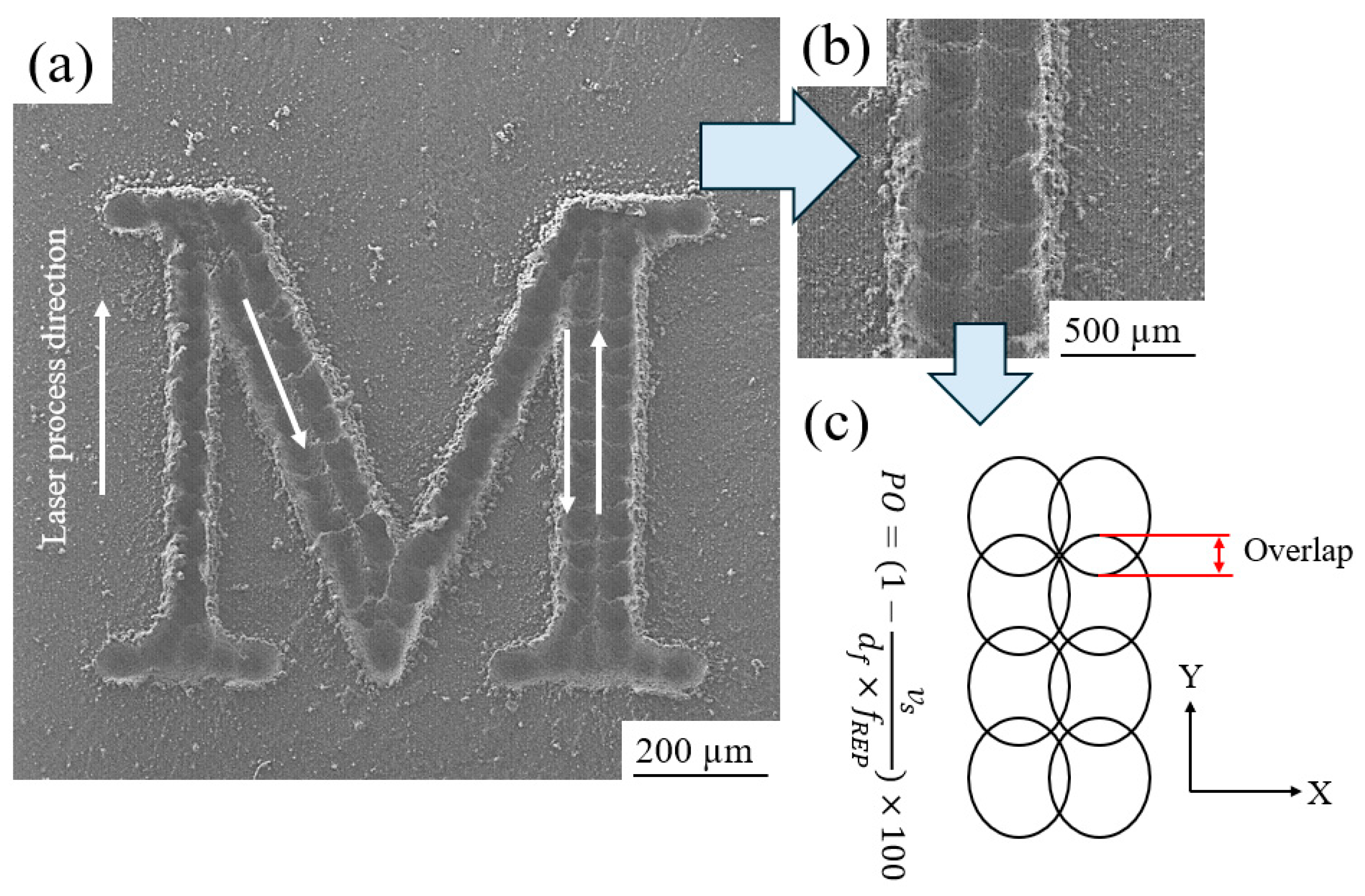
3.1. Roughness
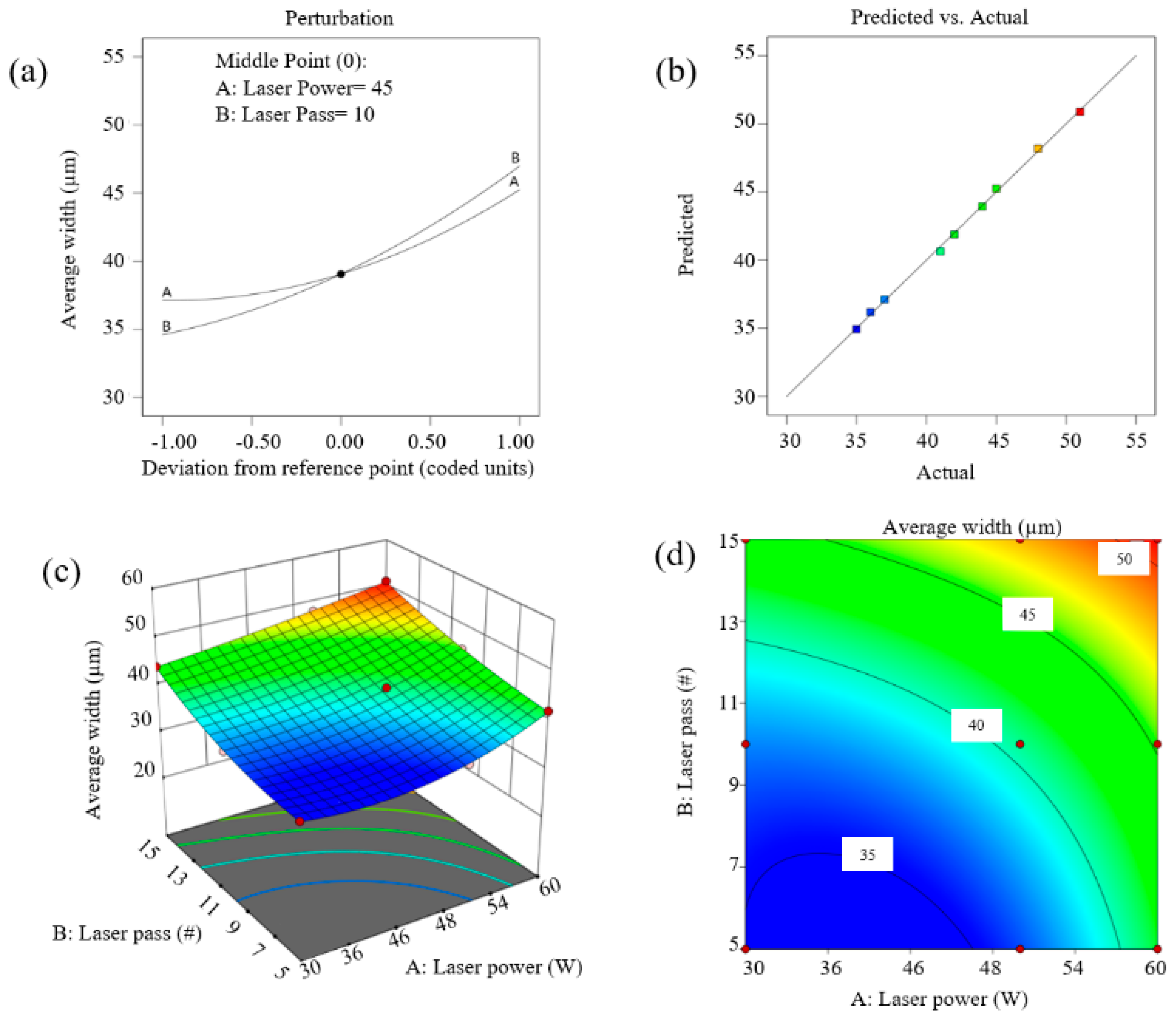
3.2. Average Width (AW)
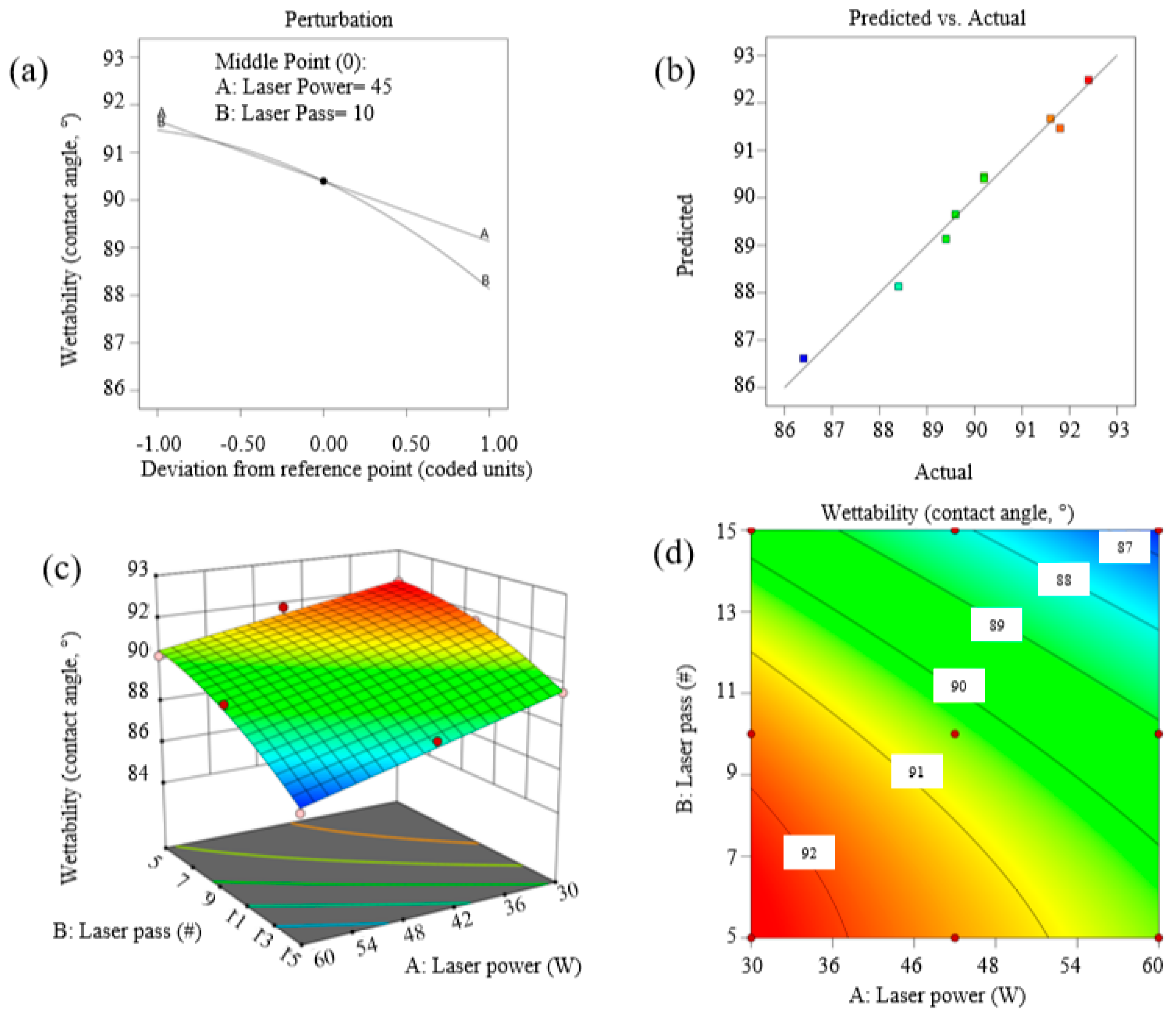
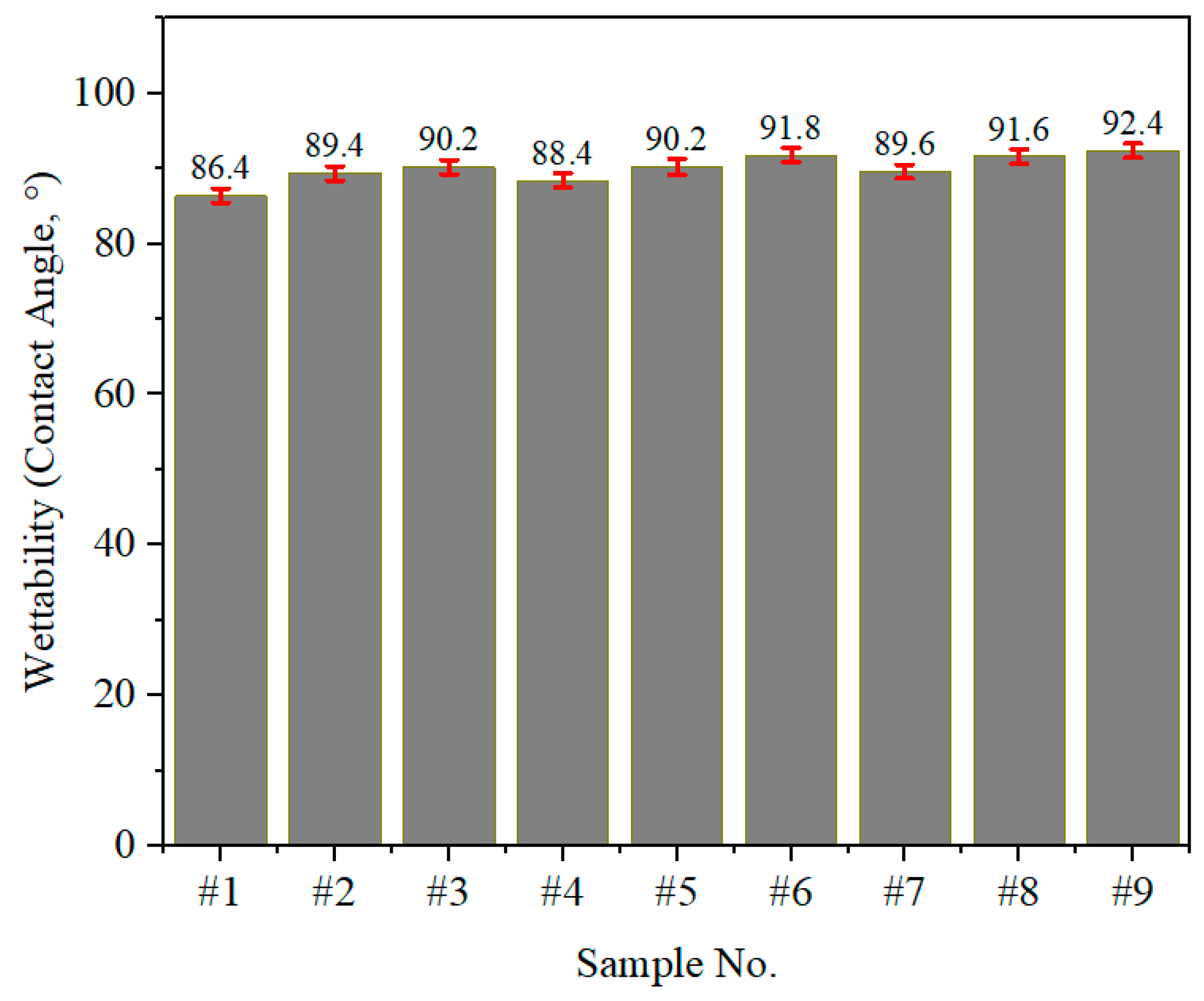
3.3. Wettability
4. Conclusions
- This study demonstrated effective control over surface roughness and engraving width through the optimization of short-pulsed fiber laser parameters, specifically laser power and the number of passes. The highest roughness (16.8 µm) and widest engraving width (51 µm) were achieved at 60 W laser power with 15 passes, while the lowest roughness (13.8 µm) and narrowest width (35 µm) were observed at 30 W power with 5 passes.
- An inverse relationship between surface roughness and wettability was clearly observed. Rougher surfaces (e.g., Sample #1 with a roughness of 16.8 µm) exhibited a contact angle of 86.4°, indicating increased wettability. Conversely, smoother surfaces (e.g., Sample #9 with a roughness of 13.8 µm) displayed a higher contact angle of 92.4°, reflecting reduced wettability.
- The results emphasize the critical importance of optimizing laser power and the number of passes to achieve targeted surface characteristics. Higher laser power and increased passes led to greater material ablation and enhanced surface texturing, while lower parameters produced smoother textures, which are beneficial for applications requiring lower wettability.
- The findings of this study offer practical guidelines for the design and optimization of laser-textured surfaces in industrial applications, including manufacturing, biomedical devices, and anti-corrosion coatings. Future research should focus on evaluating the long-term performance of these textured surfaces under real-world operating conditions, particularly in environments requiring high corrosion resistance, enhanced adhesion, or tailored wettability.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ndeda, R.; Botes, A.; Olakanmi, E.O. Framework for Incorporating Machine Learning (ML) Driven Optimisation into Laser Materials Processing (LMP) Technologies for e-Mobility Applications towards Attaining Zero-Material Waste. Lasers Manuf. Mater. Process. 2024, 11, 77–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamimoghadam, M.; Rezayat, M.; Moradi, M.; Mateo, A.; Casalino, G. Laser Surface Transformation Hardening for Automotive Metals: Recent Progress. Metals 2024, 14, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pani, R.; Roy, S.; Behera, R.R.; Chakraborty, S.; Das, D.; Mahanta, K. Laser texturing for biomedical application: A state of art. In AIP Conference Proceedings, Proceedings of the14th International Conference on Materials Processing and Characterization 2023, Hyderabad, India, 24–26 March 2023; AIP Publishing: Melville, NY, USA, 2024; Volume 3007. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Xia, J.; Liu, Z.; Xu, L.; Liu, J.; Xiao, Y.; Gao, J.; Ru, H.; Jiao, J. A comprehensive review of metal laser hardening: Mechanism, process, and applications. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2024, 134, 5087–5115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, W.; Xiong, D. Direct laser texturing technique for metal surfaces to achieve super hydrophobicity. Mater. Today Phys. 2022, 23, 100651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Tan, Z.; Zhang, C.; Tang, J.; Yao, C.; You, X.; Hao, B. Research on metal corrosion resistant bioinspired special wetting surface based on laser texturing technology: A Review. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlãdescu, S.C.; Tadokoro, C.; Miyazaki, M.; Reddyhoff, T.; Nagamine, T.; Nakano, K.; Sasaki, S.; Tsujii, Y. Exploiting the synergy between concentrated polymer brushes and laser surface texturing to achieve durable superlubricity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 15818–15829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani-Kordshuli, F.; Miller, C.; Harris, N.; Zou, M. Laser surface texturing of both thin polytetrafluoroethylene coatings and stainless steel substrates for improving tribological properties. Polym. Test. 2023, 117, 107852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, P.; Zhang, P.; Song, S.; Liu, Z.; Yan, H.; Sun, T.; Lu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Gromov, V.; Shi, H. Research status of laser surface texturing on tribological and wetting properties of materials: A review. Optik 2023, 298, 171581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nsilani Kouediatouka, A.; Ma, Q.; Liu, Q.; Mawignon, F.J.; Rafique, F.; Dong, G. Design methodology and application of surface texture: A review. Coatings 2022, 12, 1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezayat, M.; Karamimoghadam, M.; Moradi, M.; Casalino, G.; Roa Rovira, J.J.; Mateo, A. Overview of Surface Modification Strategies for Improving the Properties of Metastable Austenitic Stainless Steels. Metals 2023, 13, 1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butkus, S.; Jukna, V.; Kažukauskas, E.; Svirksas, Ž.; Paipulas, D.; Sirutkaitis, V. High-Contrast Marking of Stainless-Steel Using Bursts of Femtosecond Laser Pulses. Micromachines 2023, 14, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schkutow, A.; Frick, T. Laser Color Marking of Stainless Steel—Investigation of the Fluence-Dependent and Thermal Mechanisms in Generating Laser Induced Surface Modifications. Procedia CIRP 2024, 124, 661–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, M.; Doloi, B. Analysis on Fiber Laser Marking Characteristics of Elliptical Shaped Geometry Marked on SS 304. Adv. Mater. Process. Technol. 2024, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Liu, Y.; Pacella, M. Surface Texturing and Wettability Modification by Nanosecond Pulse Laser Ablation of Stainless Steels. Coatings 2024, 14, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soria-Biurrun, T.; Dorronsoro-Larbide, A.; Navarrete-Cuadrado, J.; Lozada-Cabezas, L.; Pan-Cabo, A.; Castaño-Carmona, E.; Alkorta, J.; Sánchez-Moreno, J.M. Surface texturing, residual stresses and edge treatment of hardmetal tools by means of femtosecond pulsed laser. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2024, 118, 106442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, V.; Singh, R.; Marla, D. A 3D computational model of nanosecond pulsed laser texturing of metals for designing engineered surfaces. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2024, 146, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velayuthaperumal, S.; Radhakrishnan, R. A novel nanosecond pulsed laser textured moat configurations for enhancing surface wettability, corrosion and tribology behaviour of Ti6Al4V implant material. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 39, 108701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Duan, X.; Chen, Z.; Liu, B.; Fu, H.; Ji, J.; Zhang, Y. Precision fabrication of micro-textures array for surface functionalization using picosecond pulse laser. Opt. Laser Technol. 2024, 177, 111200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Fang, Z.; Fei, Y.; Wang, S.; Perrie, W.; Edwardson, S.; Dearden, G. Wettability Behaviour of Metal Surfaces after Sequential Nanosecond and Picosecond Laser Texturing. Micromachines 2024, 15, 1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezayat, M.; Morales, M.; Moradi, M.; Mateo, A. Laser wobbling surface texturing of AISI 301LN steel for enhancement of the corrosion resistance at high temperature. Opt. Laser Technol. 2024, 171, 110375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawadzki, P.; Dobrotvorskiy, S.; Aleksenko, B.A.; Basova, Y.; Trubin, D.; Prykhodko, V.; Kościński, M. Features of Modification of the Roughness and Hardness of the Surface of AISI 321 Stainless Steel with Short-Pulse Laser Radiation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Reliable Systems Engineering, Bucharest, Romania, 5–6 September 2024; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 51–60. [Google Scholar]
- Lubig, K.; Wonneberger, R.; Picker, J.; Undisz, A.; Turchanin, A.; Müller, F.A.; Gräf, S. Ageing of commercial austenitic, martensitic and duplex stainless steel surfaces after formation of laser-induced periodic surface structures by fs-laser irradiation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2025, 679, 161156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralls, A.M.; Menezes, P.L. Realizing the tribological feasibility of novel laser surface texturing techniques for cold spray kinetically metallized stainless steel. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2024, 133, 3529–3547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, F.; Peng, Y.; Yang, S.; Tang, F. Effect of pulsed laser energy on grain morphology and texture characteristics of stainless steel fabricated by laser-PTA additive manufacturing. Opt. Laser Technol. 2023, 158, 108799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Pan, J.; Chen, X. Texture morphologies and residual stresses due to laser surface texturing on the 304 stainless steel. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2024, 255, 123951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekube, B.M.; Badiola, J.H.; Larreategi, P.; Ares, F.; Chiminelli, A.; Valero, C.; Ozgur, T. Metal-composite hybrid joint adhesion and testing optimization for electric vehicle applications. J. Adhes. 2023, 101, 91–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigoriev, S.N.; Volosova, M.A.; Okunkova, A.A. Advances in Laser Materials Processing. Metals 2022, 12, 917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezayat, M.; Karamimoghadam, M.; Dezaki, M.L.; Zolfagharian, A.; Casalino, G.; Mateo, A.; Bodaghi, M. Enhancing Corrosion Resistance and Mechanical Strength of 3D-Printed Iron Polylactic Acid for Marine Applications via Laser Surface Texturing. Adv Eng Mater 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezayat, M.; Morales, M.; Zahrani, E.G.; Moradi, M.; Azarhoushang, B.; Mateo, A. Effect of Repetition Passes in the Laser Surface Texturing of AISI 301LN Steel on the Anticorrosion Properties in Molten Carbonate Salts. Materialia 2025, 39, 102365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralston, J. Solid–Liquid Interactions and Functional Surface Wettability. Aust. J. Chem. 2005, 58, 644–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, J.; Sha, J.; Li, D.; Li, Z.; Chen, Y. Fluid release pressure for nanochannels: The Young–Laplace equation using the effective contact angle. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 8408–8415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Lee, T.R. Contact angle and wetting properties. In Surface Science Techniques; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 3–34. [Google Scholar]
- Morales, M.; Rezayat, M.; Mateo, A. Enhancing the Corrosion Resistance of 2205 Duplex Stainless Steel in Molten Carbonate Salts by Laser-Surface Texturing. J. Energy Storage 2024, 78, 110053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezayat, M.; Morales, M.; Moradi, M.; Mateo, A. Influence of Laser Heat Input on the Corrosion Mitigation of Laser Textured AISI 301LN Steel in Molten Carbonate Salts. Opt. Laser Technol. 2025, 186, 112692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Variable | Unit | Level | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| −1 | 0 | 1 | ||
| Laser Power | W | 30 | 45 | 60 |
| Laser Pass | # | 5 | 10 | 15 |
| Sample No. | Input Parameters | Response | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Laser Power (W) | Laser Pass (#) | Roughness Sa (µm) | Average Width (µm) | Wettability Contact Angle, (°) | |
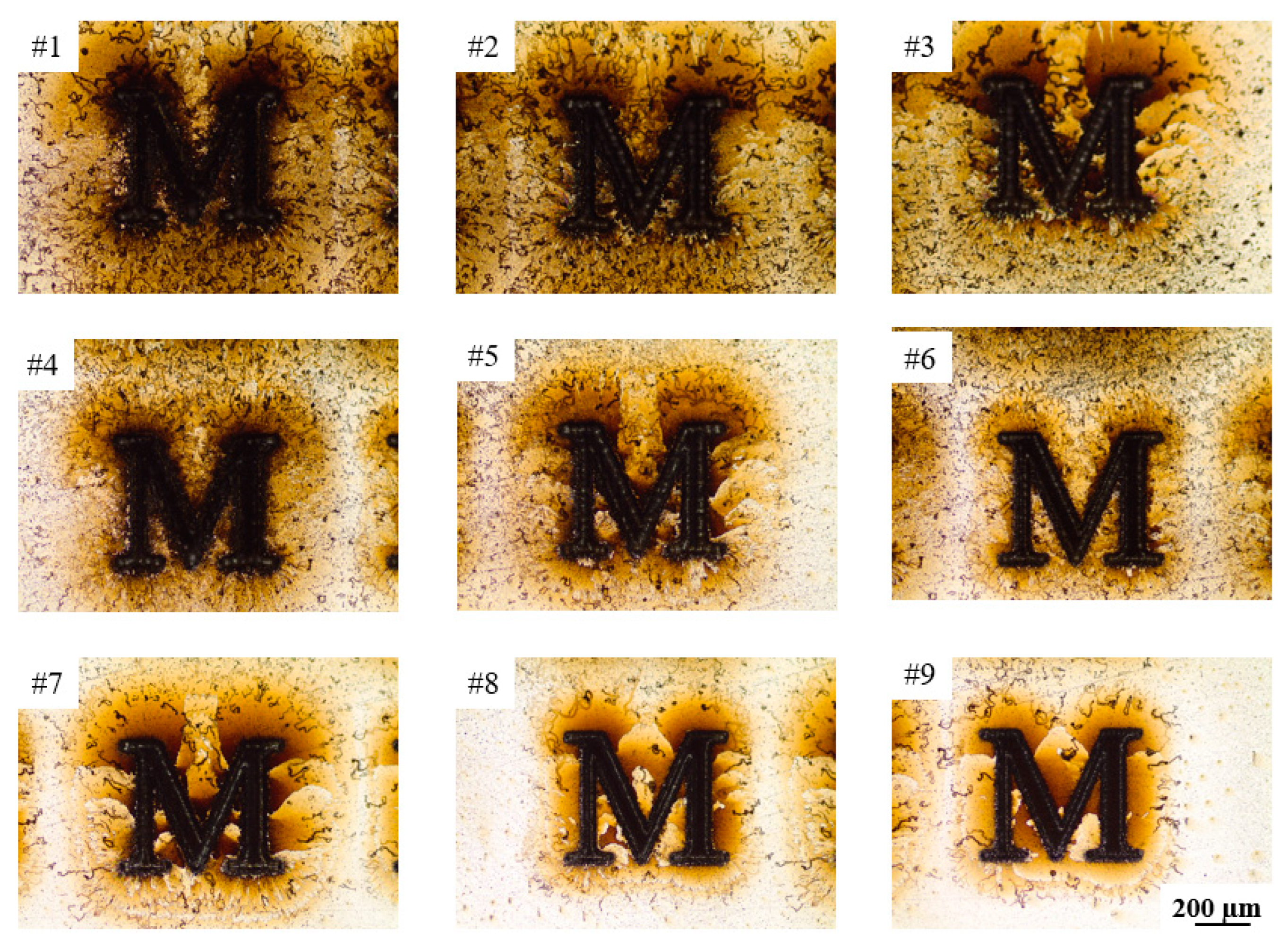
| #1 | 60 | 15 | 16.8 ± 1.8 | 51 | 86.4 ± 0.9 |
| #2 | 60 | 10 | 15.3 ± 1.7 | 45 | 89.4 ± 0.9 |
| #3 | 60 | 5 | 14.9 ± 1.6 | 42 | 90.2 ± 0.9 |
| #4 | 45 | 15 | 15.8 ± 1.7 | 48 | 88.4 ± 0.9 |
| #5 | 45 | 10 | 14.9 ± 1.6 | 41 | 90.2 ± 0.9 |
| #6 | 45 | 5 | 14.1 ± 1.5 | 36 | 91.8 ± 1.0 |
| #7 | 30 | 15 | 15.2 ± 1.7 | 44 | 89.6 ± 0.9 |
| #8 | 30 | 10 | 14.2 ± 1.6 | 37 | 91.6 ± 1.0 |
| #9 | 30 | 5 | 13.8 ± 1.5 | 35 | 92.4 ± 1.0 |
| Elements | Fe | Mo | Cr | Mn | N | C | Ni | Si |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % | Bal. | 0.04 | 17.6 | 1.13 | 0.17 | 0.02 | 6.50 | 0.42 |
| Source Model | Sum of Squares | Df | Mean Square | F-Value | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6.84 | 5 | 1.37 | 49.01 | 0.0045 | significant | |
| A-Laser Power | 2.41 | 1 | 2.41 | 86.27 | 0.0026 | |
| B-Laser Pass | 3.96 | 1 | 3.96 | 141.96 | 0.0013 | |
| AB | 0.0630 | 1 | 0.0630 | 2.26 | 0.2300 | |
| A2 | 0.1867 | 1 | 0.1867 | 6.69 | 0.0813 | |
| B2 | 0.1800 | 1 | 0.1800 | 6.45 | 0.0847 | |
| Residual | 0.0837 | 3 | 0.0279 | |||
| Cor Total | 6.92 | 8 | ||||
| Adjusted R2 = 96.77% | R2 = 98.79% | |||||
| Source | Sum of Squares | Df | Mean Square | F-Value | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 237.22 | 5 | 47.44 | 38.78 | 0.0063 | significant |
| A-Laser Power | 80.67 | 1 | 80.67 | 65.93 | 0.0039 | |
| B-Laser Pass | 146.32 | 1 | 146.32 | 119.59 | 0.0016 | |
| AB | 0.1071 | 1 | 0.1071 | 0.0876 | 0.7866 | |
| A2 | 6.88 | 1 | 6.88 | 5.62 | 0.0984 | |
| B2 | 5.56 | 1 | 5.56 | 4.54 | 0.1229 | |
| Residual | 3.67 | 3 | 1.22 | |||
| Cor Total | 240.89 | 8 | ||||
| Adjusted R2 = 95.94% | R2 = 98.48% | |||||
| Source | Sum of Squares | Df | Mean Square | F-Value | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 27.26 | 4 | 6.82 | 65.43 | 0.0007 | significant |
| A-Laser Power | 9.63 | 1 | 9.63 | 92.42 | 0.0007 | |
| B-Laser Pass | 16.67 | 1 | 16.67 | 160.00 | 0.0002 | |
| AB | 0.2500 | 1 | 0.2500 | 2.40 | 0.1963 | |
| B2 | 0.7200 | 1 | 0.7200 | 6.91 | 0.0582 | |
| Residual | 0.4167 | 4 | 0.1042 | |||
| Cor Total | 27.68 | 8 | ||||
| Adjusted R2 = 96.99% | R2 = 98.49% | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rezayat, M.; Karamimoghadam, M.; Contuzzi, N.; Casalino, G.; Mateo, A. Statistical Modeling and Characterization of Laser Marking on AISI 301LN Stainless Steel Using Short-Pulsed Fiber Laser. Metals 2025, 15, 519. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15050519
Rezayat M, Karamimoghadam M, Contuzzi N, Casalino G, Mateo A. Statistical Modeling and Characterization of Laser Marking on AISI 301LN Stainless Steel Using Short-Pulsed Fiber Laser. Metals. 2025; 15(5):519. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15050519
Chicago/Turabian StyleRezayat, Mohammad, Mojtaba Karamimoghadam, Nicola Contuzzi, Giuseppe Casalino, and Antonio Mateo. 2025. "Statistical Modeling and Characterization of Laser Marking on AISI 301LN Stainless Steel Using Short-Pulsed Fiber Laser" Metals 15, no. 5: 519. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15050519
APA StyleRezayat, M., Karamimoghadam, M., Contuzzi, N., Casalino, G., & Mateo, A. (2025). Statistical Modeling and Characterization of Laser Marking on AISI 301LN Stainless Steel Using Short-Pulsed Fiber Laser. Metals, 15(5), 519. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15050519