Influence of B2O3 on the Viscosity and Melt Structure of CaO-SiO2-M2O (M = Li, Na)-Based Slags
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Design of Experimental Slag System
3. Experimental Process
3.1. Preparation of Experimental Slag
3.2. Melting Temperature Measurement
3.3. Viscosity Measurement
3.4. Melt Structure Test
4. Results and Discussion
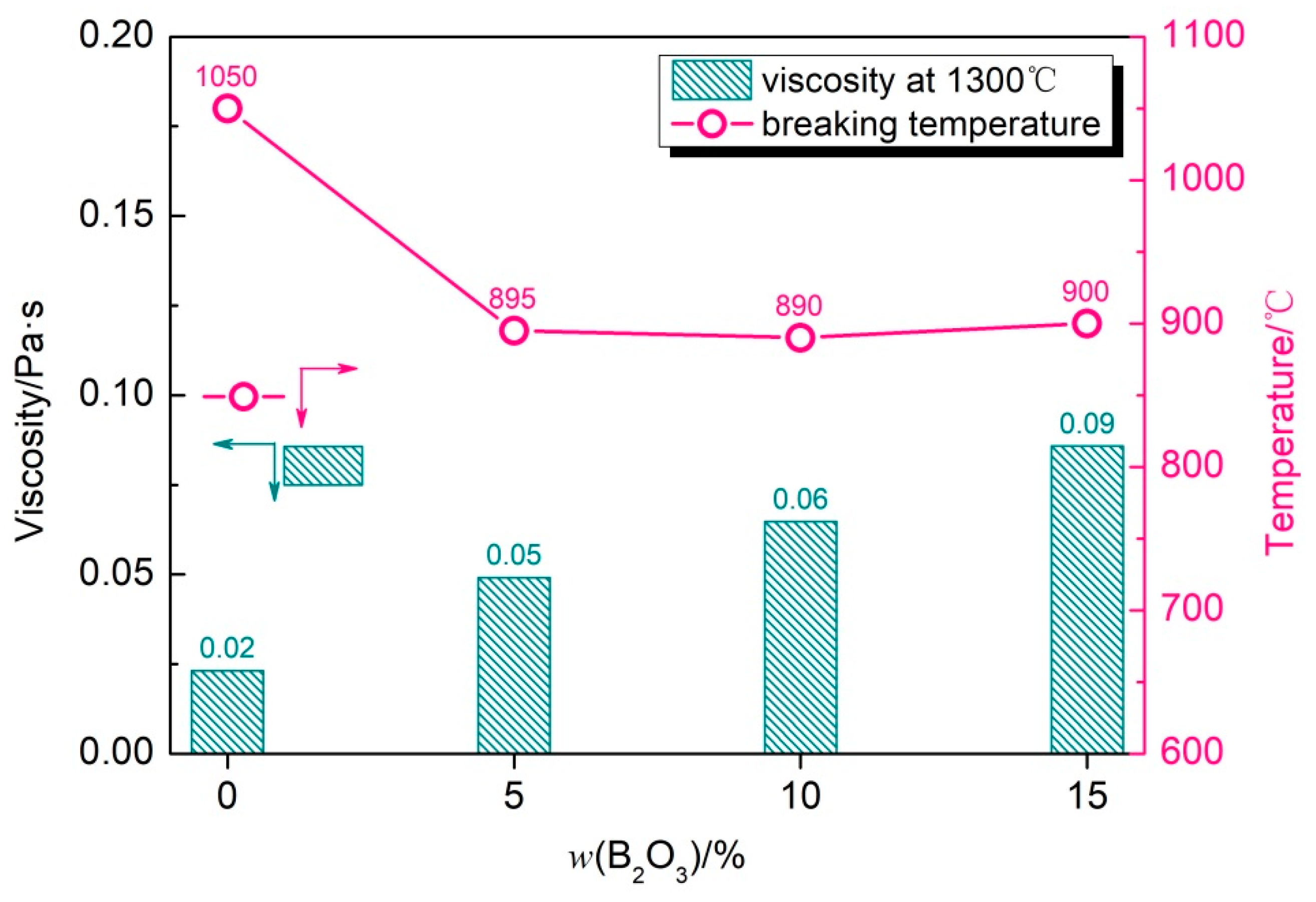
4.1. Change in Viscous Characteristics
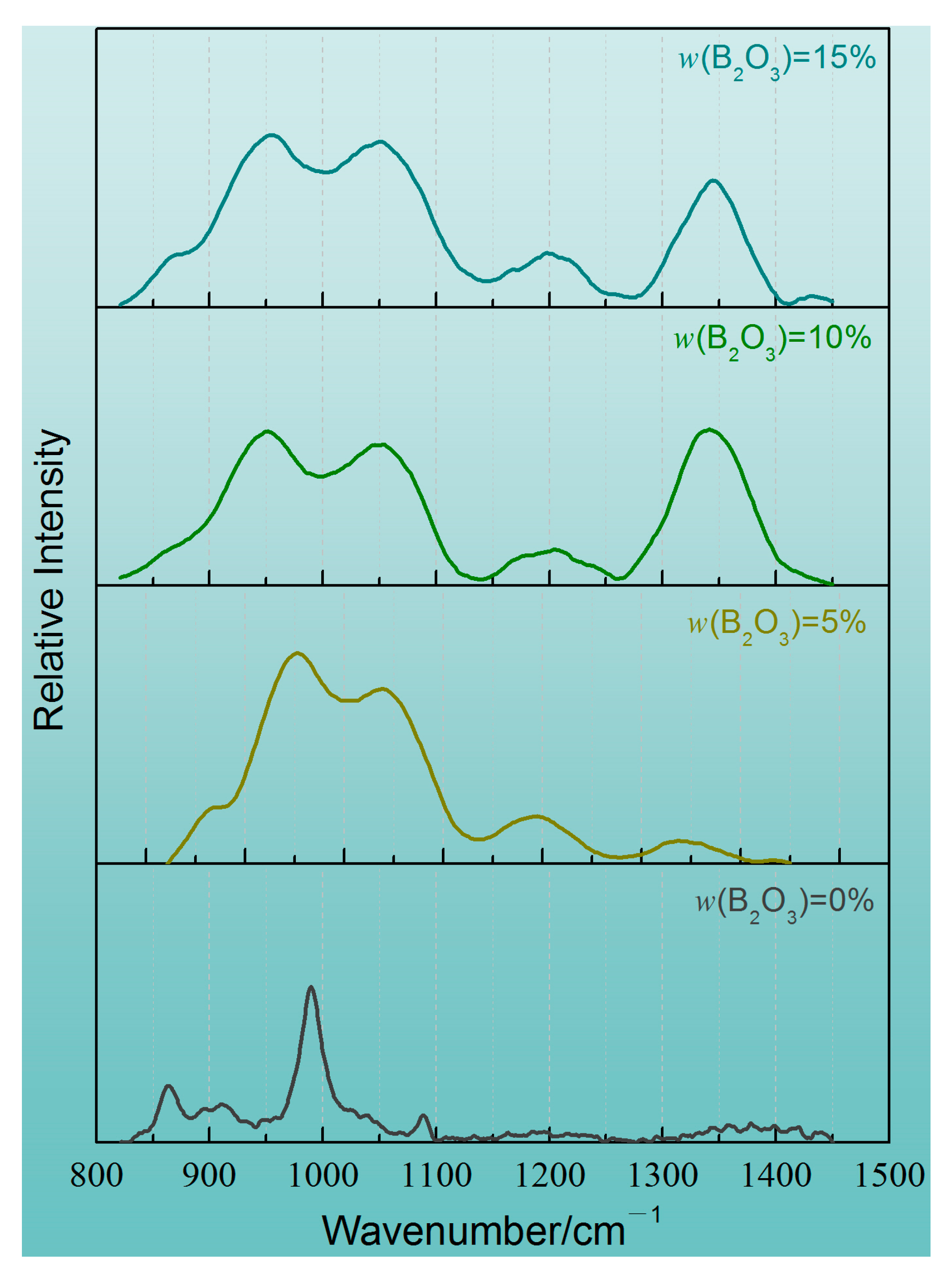
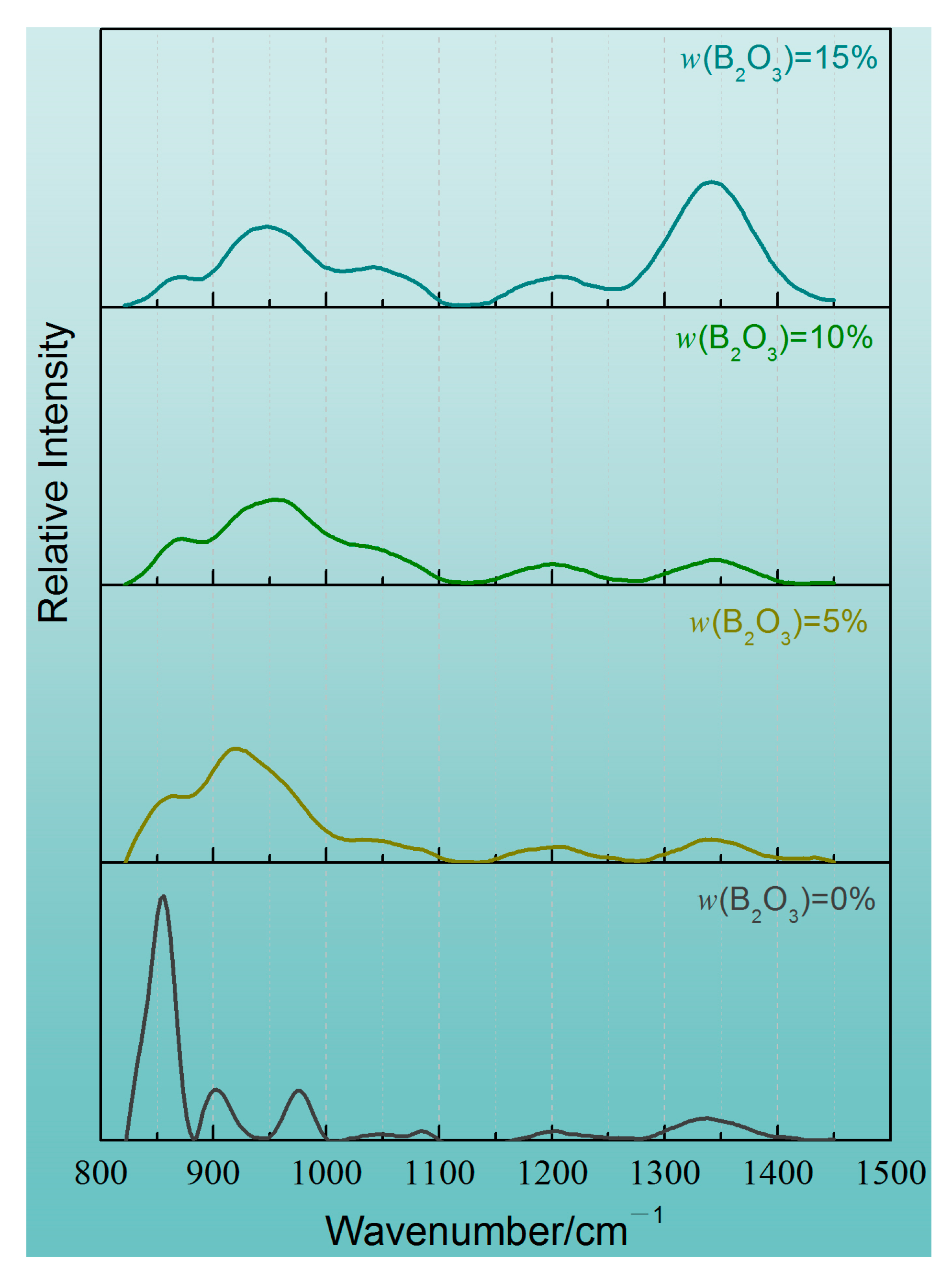
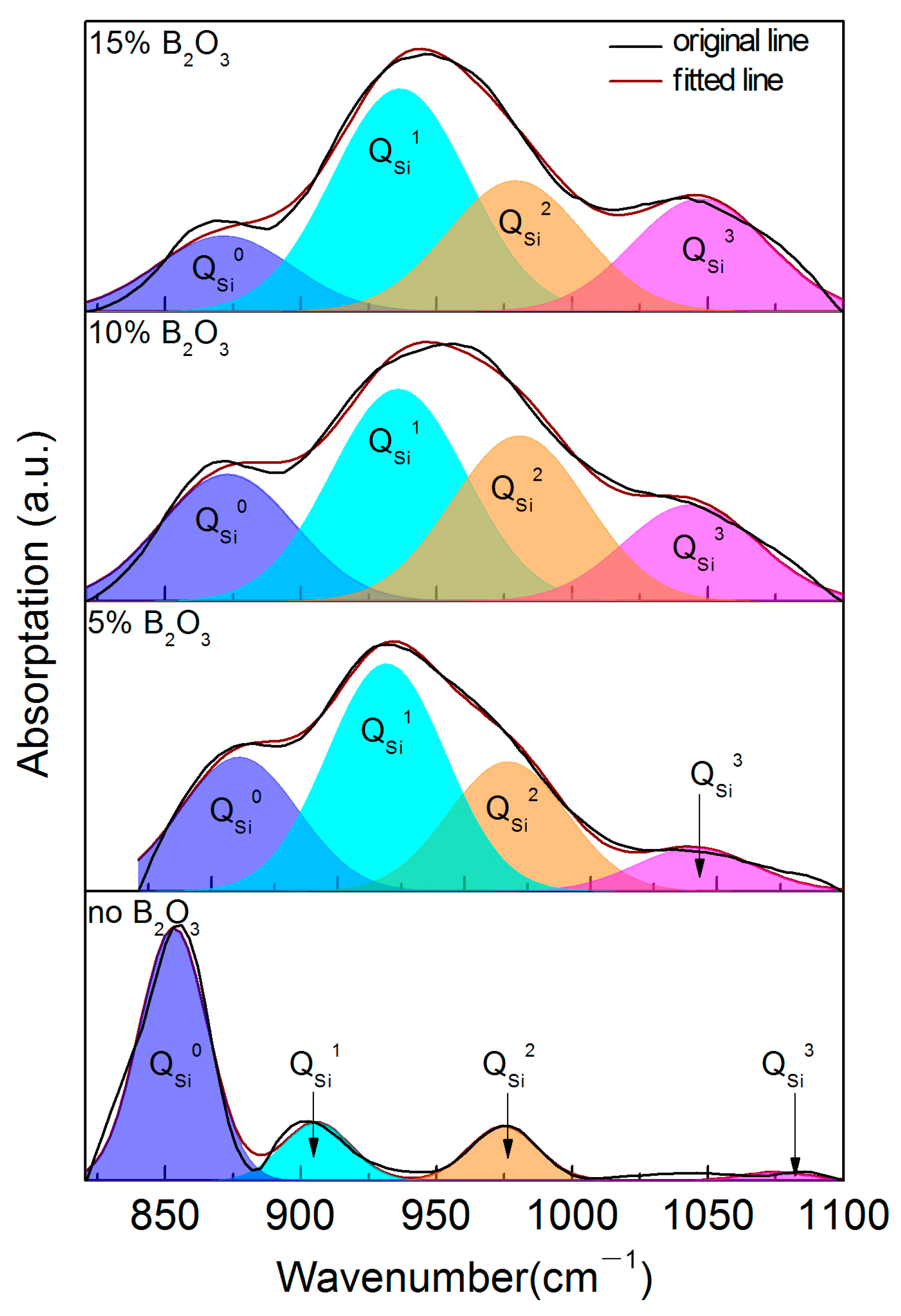
4.2. Microscopic Analysis of Slag Structure
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- In the CaO-SiO2-Na2O slag system, with the increase in the B2O3 addition, the viscosity and breaking temperature of the slag show a gradually decreasing trend. When the B2O3 addition is 15%, the viscosity reaches the lowest value at 1300 °C, which is 0.14 Pa·s. The breaking temperature drops to the lowest value, 1024 °C;
- (2)
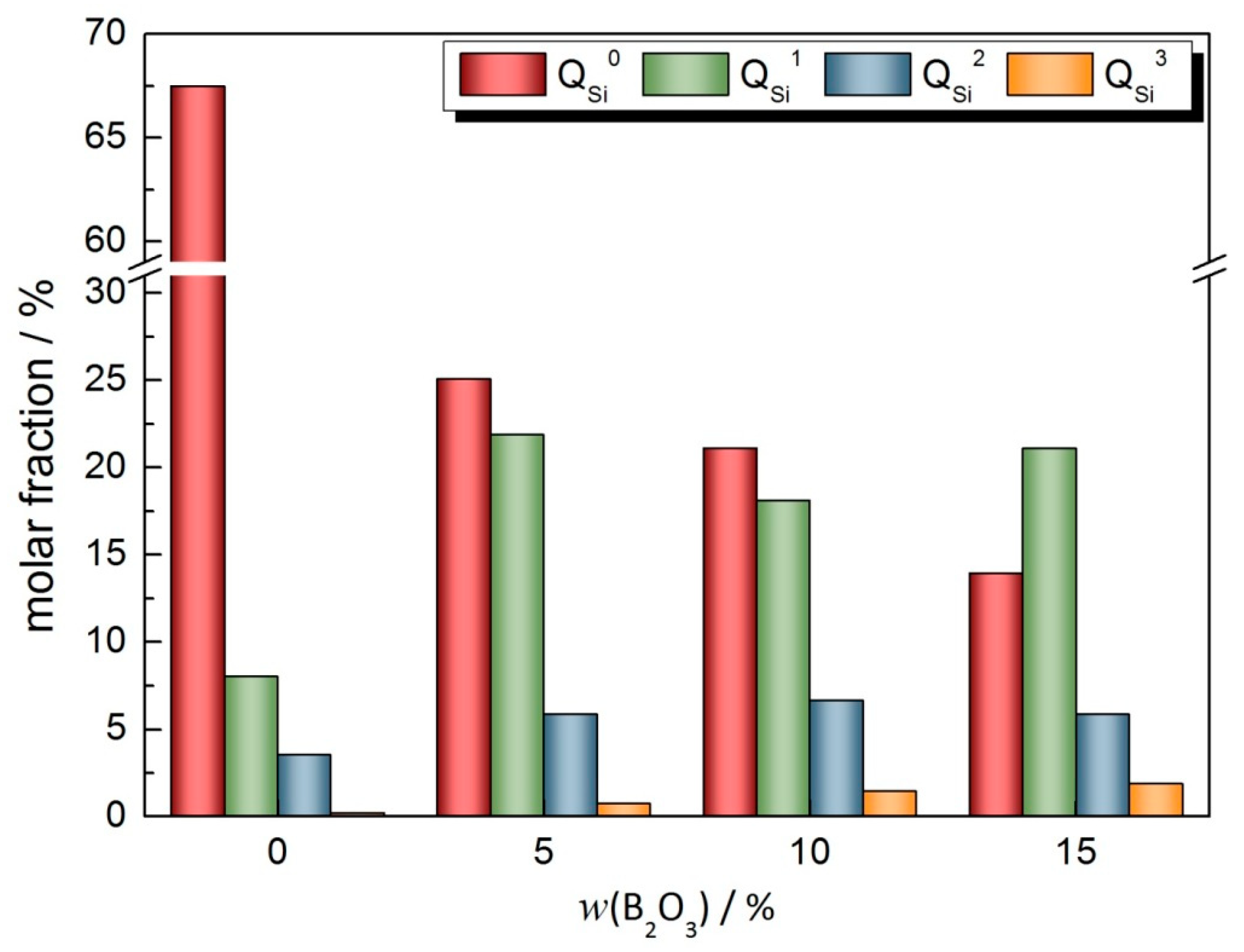
- In the CaO-SiO2-Na2O slag system, the polymerization degree of the mold flux decreases gradually with the increase in the addition of B2O3. When the addition of B2O3 increases from 0 to 10%, the increase in two-dimensional BO3 structural units plays a dominant role. When the addition of B2O3 is increased to 15%, the network depolymerization is influenced by the increase in BO3 structure units and the low degree of polymerization units of different polymers of SiO4 tetrahedron;
- (3)
- In the CaO-SiO2-Li2O slag system, the inflection point temperature of the slag after adding B2O3 is significantly reduced, and the inflection point temperature is reduced by 155 °C when 5% B2O3 is added. However, with the further increase in the B2O3 content, the breaking temperature of the slag can remain relatively stable, without any significant fluctuation. The CaO-SiO2-Li2O slag system has a lower breaking temperature, due to the formation of phases such as low-melting-point Li2O·2B2O3;
- (4)
- In the CaO-SiO2-Li2O slag system, the initial degree of depolymerization of the network is high. In order to maintain the stability of the network structure, when the addition of B2O3 increases from 0 to 15%, the relative proportion of the network modifier structural units in the protection slag will significantly increase, resulting in the enhanced instability of the network structure. The effect of SiO4 tetrahedral structure polymerization is stronger than that of two-dimensional BO3 unit depolymerization.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- 2024 World Steel in Figures. Available online: https://worldsteel.org/wp-content/uploads/World-Steel-in-Figures-2024.pdf (accessed on 1 February 2025).
- Mills, K.C.; Däcker, C.-Å. The Casting Powders Book; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.; Qi, J.; Zheng, X.; Liu, C.; Jiang, M. Dissolution behavior of CeAlO3 in mold fluxes with different w(CaO)/w(Al2O3). J. Iron Steel Res. 2023, 35, 1092–1099. [Google Scholar]
- Mills, K.C. A short history of mould powders. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2017, 44, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandaleze, E.; Di Gresia, G.; Santini, L.; Martín, A.; Benavidez, E. Mould Fluxes in the Steel Continuous Casting Process; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.N.; Bai, Y.; Shen, Y.; Wang, P.; Chen, B.; Wang, P. Mechanism and control measures of tail surface cracks near corners of peritectic steel slab castings. J. Iron Steel Res. 2024, 36, 736–742. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.J.; Shen, Y.Y.; Yan, W.; Wang, Y.; Li, D. Prediction of viscosity and melting temperature for mold fluxes based on machine learing algorithms. Contin. Cast. 2024, 43, 63–72. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.R.; Wang, M.; Wang, L.H.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Z. Research progress on mechanism and prediction model of continuous casting sticker breakout of automotive steel. Contin. Cast. 2024, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.; Yu, L.; Wen, G.; Tang, P.; Wang, Z.; Gao, Z. Qualitative, Quantitative and Mechanism Research of Volatiles in the Most Commonly Used CaO–SiO2–CaF2–Na2O Slag During Casting Process. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2021, 74, 775–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, X.; Long, S.; Luo, W.; Li, X.; Tu, C.; Na, Y.; Xu, J. Crystallization of Slag Films of CaO-Al2O3-BaO-CaF2-Li2O- Based Mold Fluxes for High-Aluminum Steels’ Continuous Casting. Materials 2023, 16, 1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Yu, L.; Wen, G.; Guo, J.; Ran, C.; Gu, S. Effect of Na2O on the Sintering and Melting Behavior of CaO-SiO2-CaF2 Slag. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 19, 866–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, R.; He, W.; Li, Z.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, L. Influence of BaO and MgO on viscosity, crystalline phase, and structure of CaO–Al2O3–10%SiO2–20%CaF2-based system. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 27311–27326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, C.; Jiang, M. Effect of Fluorine on Melt Structure for CaO-SiO2-CaF2 and CaO-Al2O3-CaF2 by Molecular Dynamics Simulations. ISIJ Int. 2020, 60, 2176–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, X.; Luo, W.; Li, X.; Long, S.; Ma, H.; Luo, D.; Zheng, C. Structure and Heat Transfer Characteristic Evolution of CaO-SiO2 -CaF2 -Based Solid Mold Flux Film upon Solidification. Metals 2024, 14, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lao, Y.; Gao, Y.; Wang, Q.; Li, G. Investigation on surface tension of CaF2–CaO–SiO2 (–MgO–Al2O3) melts. Metall. Res. Technol. 2024, 121, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, M.S.; Sohn, I. Volatilization of fluorine in a CaO–SiO2–CaF2-based system with the substitution of Na2O with K2O. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2022, 105, 6320–6334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.Y.; Zhang, D.; Feng, W.H.; Liu, L.; Han, X.; Liu, Z. Research progress on crystallization properties of protectine slag for fluorin free continuous casting mold. Gansu Metall. 2023, 45, 56–61. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, X.P.; Liu, L.; Han, X.L.; Wang, W.; Zhang, D. Effect of boron on microstructure of fluorine-free mold fluxes. Iron Steel 2022, 57, 72–80. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, K. Effect of Borax on Properties of Fluorine-Free Mold Flux and Mineralogical Constitution of Slag Film. Master’s Thesis, North China University of Science and Technology, Qinhuangdao, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, C.B.; Li, X.Y.; Xu, J.Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, D. Development and Application of Fluorine—Free Mould Fluxes for Peritectic Steel Billet Continuous Casting. Wide Heavy Plate 2020, 26, 15–20. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.Y.; Li, X.Y.; Xu, J.Y.; Zhao, C.; Qin, J. Development and Application of Fluorine Free Mould Powder for Low Carbon Steel Slab Continuous Casting. Wide Heavy Plate 2019, 25, 26–29. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.J.; Wu, B.B.; Zhu, L.G.; Fan, Y.; Tian, K. Study on Rheological Properties of Fluorine-free Continuous Casting Mould Powder. Iron Steel Vanadium Titan. 2017, 38, 135–139. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, M.T. Development of fluoride-free mold powder. Steelmaking 2013, 29, 57–59. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, J.; Li, Y.; Lin, W.; Che, J.; Zhou, F.; Tan, Y.; Li, D.; Dang, J.; Chen, C. Assessment of Inclusion Removal Ability in Refining Slags Containing Ce2O3. Crystals 2023, 13, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, Q.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, X.; He, S. Viscosity and structure of CaO–BaO–SiO2–Al2O3-based mold slags for continuous casting of high titanium steel with different TiO2 absorption. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2024, 31, 1936–1946. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, R.; Wu, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, W.; Liu, C.; Gu, S.; Xing, W.; Yu, L. Reaction mechanism between carbon and CaO–SiO2–Al2O3–Na2O slag system during continuous casting process. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 30, 8882–8893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hruška, B.; Svoboda, R.; Nowicka, A.; Michálková, J.; Pecušová, B.; Michalík, J.; Chromčíková, M. Systematic assessment of the compositional dominance over physico-chemical properties in the SiO2-Al2O3-B2O3 based glassy networks. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2025, 652, 123414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Z.; Li, K.; Jiang, C.; Zhang, J.; Ma, S.; Sun, M.; Wang, Z.; Li, H. Performance and Transition Mechanism from Acidity to Basicity of Amphoteric Oxides (Al2O3 and B2O3) in SiO2-CaO-Al2O3-B2O3 system: A Molecular Dynamics Study. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 12252–12260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.X.; Xi, Z.H.; He, S.P.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, X. Exploration of Li2O reduction by mold flux for high quality low carbon steel slab continuous casting. Iron Steel 2023, 58, 110–119. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.C.; Zeng, J.; Dou, K.; Wang, W.; Lin, H.; Liu, X. Analysis of comprehensive physical and chemical properties of medium and high carbon steel mold flux in thin slab. Contin. Cast. 2023, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zeng, K.; Chen, B.; Qian, J.; Wang, X.; Zhu, L. Prediction of viscosity of mold fluid-free protective slag based on improved whale optimization algorithm-extreme learning machine. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2024, 24, 14614–14622. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, J.; Liu, C.J.; Yang, D.P.; Zhang, C.; Jiang, M.F. Study of a new mold flux for heat-resistant steel containing cerium continuous casting. Steel Res. Int. 2016, 87, 890–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, Q.I.; Chengjun, L.I.U.; Chunlong, L.I.; Jiang, M. Viscous properties of new mould flux based on aluminate system with CeO2 for continuous casting of RE alloyed heat resistant steel. J. Rare Earths 2016, 34, 328–335. [Google Scholar]
- Mysen, B.O.; Finger, L.W.; Seifert, F.A.; Virgo, D. Curve-fitting of Raman spectra of amorphous materials. Am. Miner. 1982, 67, 686. [Google Scholar]
- McMillan, P.F.; Wolf, G.H.; Poe, B.T. Vibrational spectroscopy of silicate liquids and glasses. Chem. Geol. 1992, 96, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mysen, B.O. Structure and properties of magmatic liquids: From haplobasalt to haploandesite. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1999, 63, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mysen, B.O.; Frantz, J.D. Silicate melts at magmatic temperatures: In-situ structure determination to 1651 C and effect of temperature and bulk composition on the mixing behavior of structural units. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1994, 117, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.Q.; Jiang, G.C.; You, J.L.; Hou, H.Y.; Chen, H. Raman scattering coefficients of symmetrical stretching modes of microstructural units in sodium silicate melts. Acta Phys. Sin. 2005, 54, 961. [Google Scholar]
- Min, Y.; Zhong, M.; Huang, J.; Liu, C.; Jiang, M. Structural behavior of Al3+ in mould flux glasses of CaO–SiO2–Al2O3–Na2O–CaF2 system. Steel Res. Int. 2014, 85, 1194–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
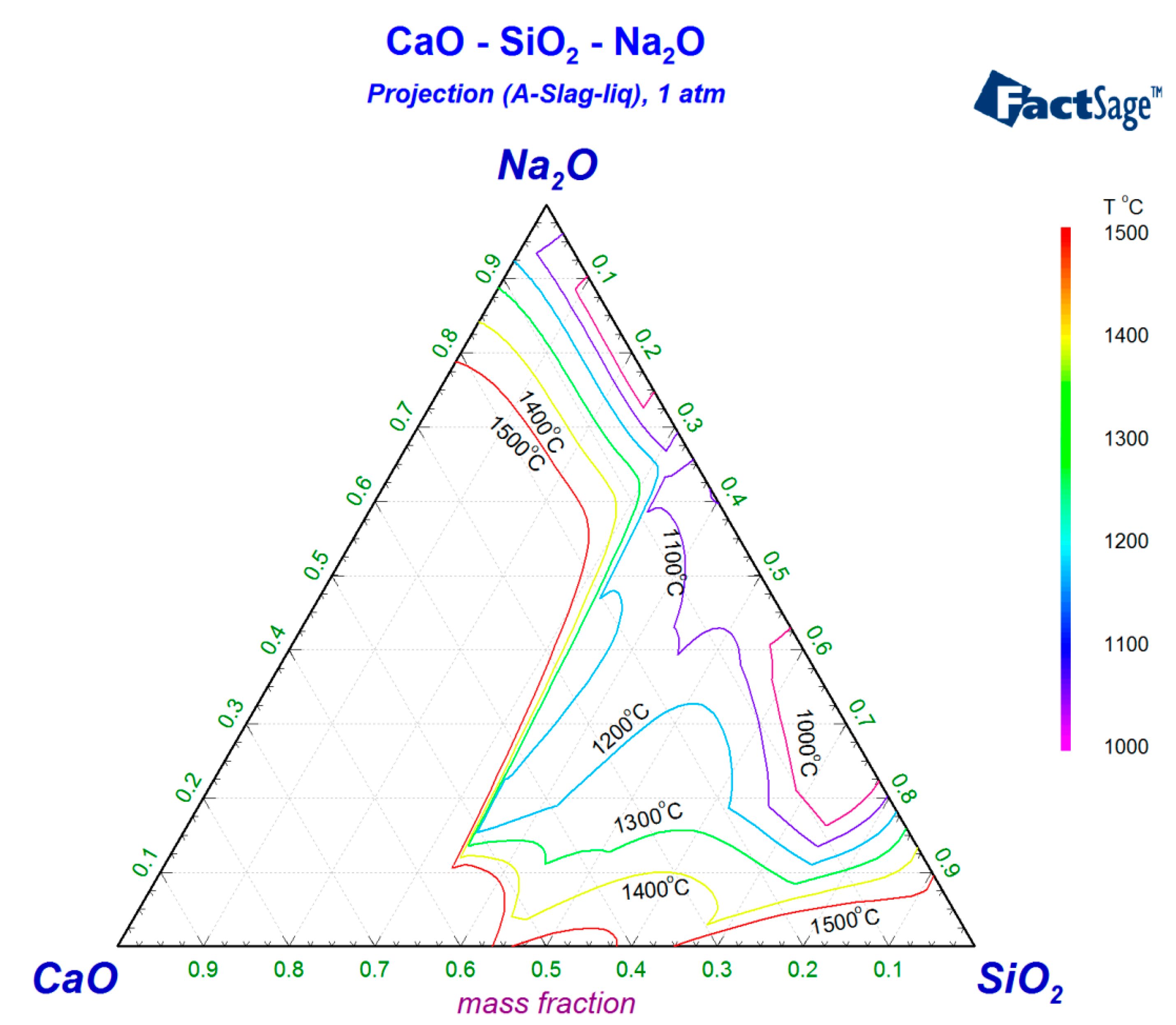

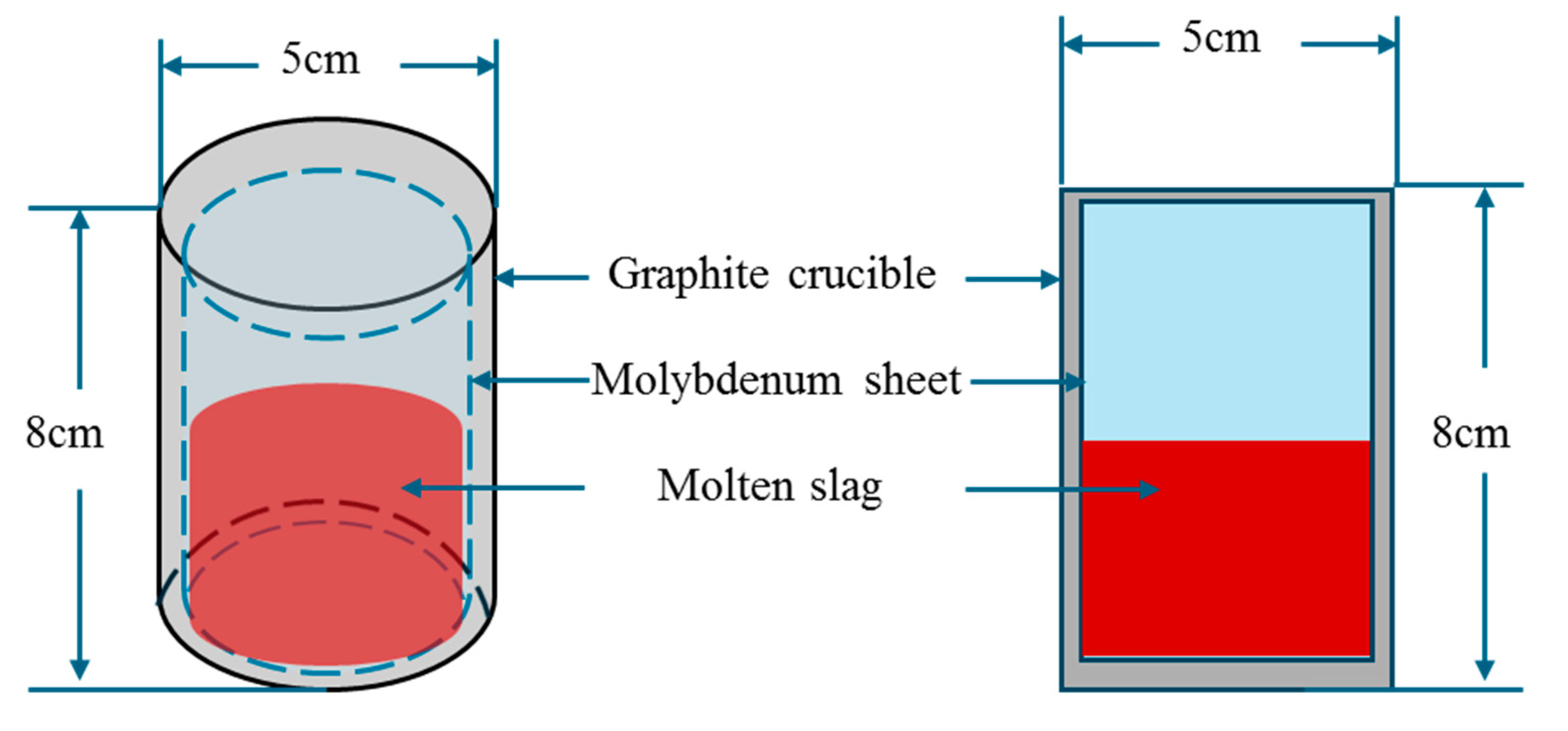
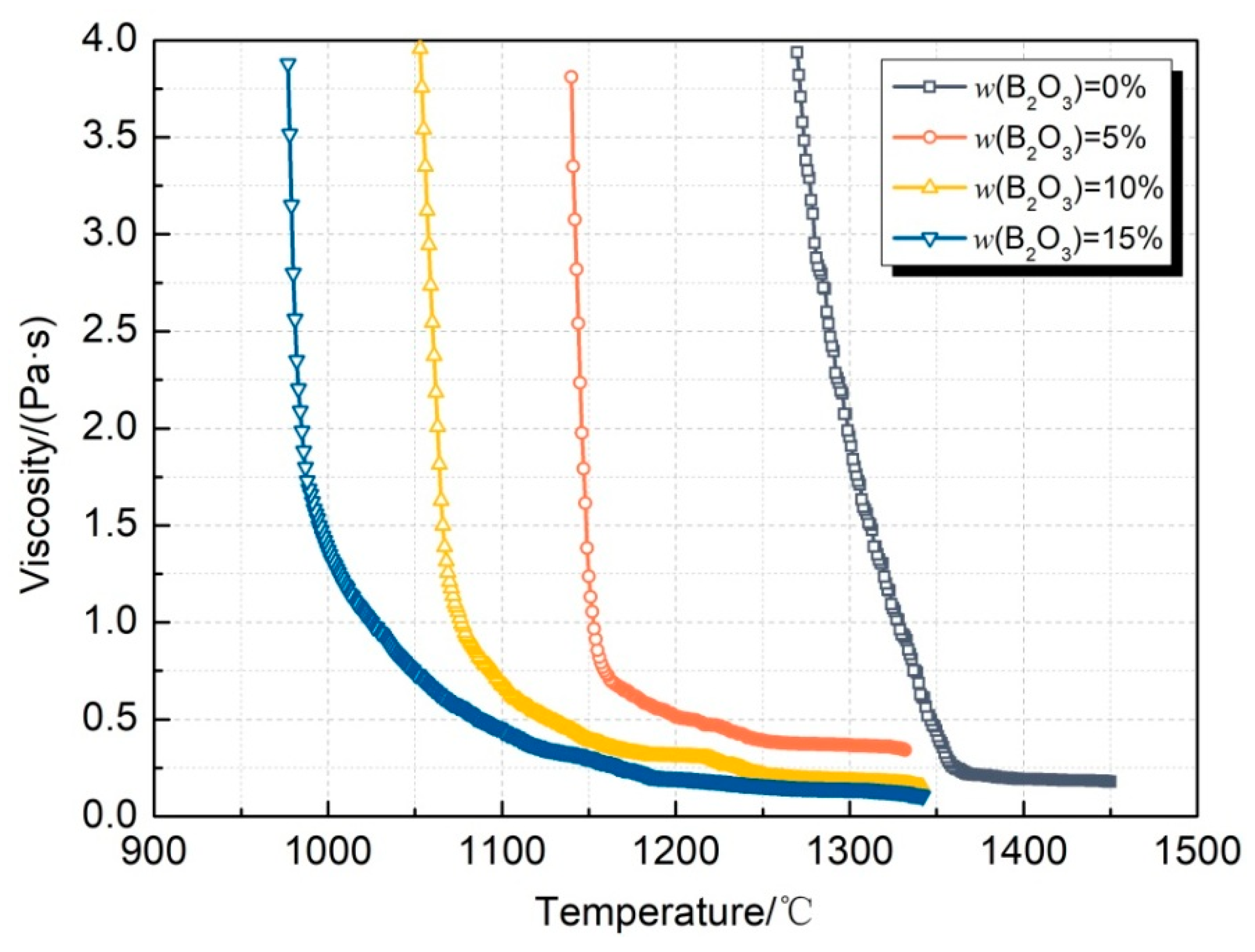

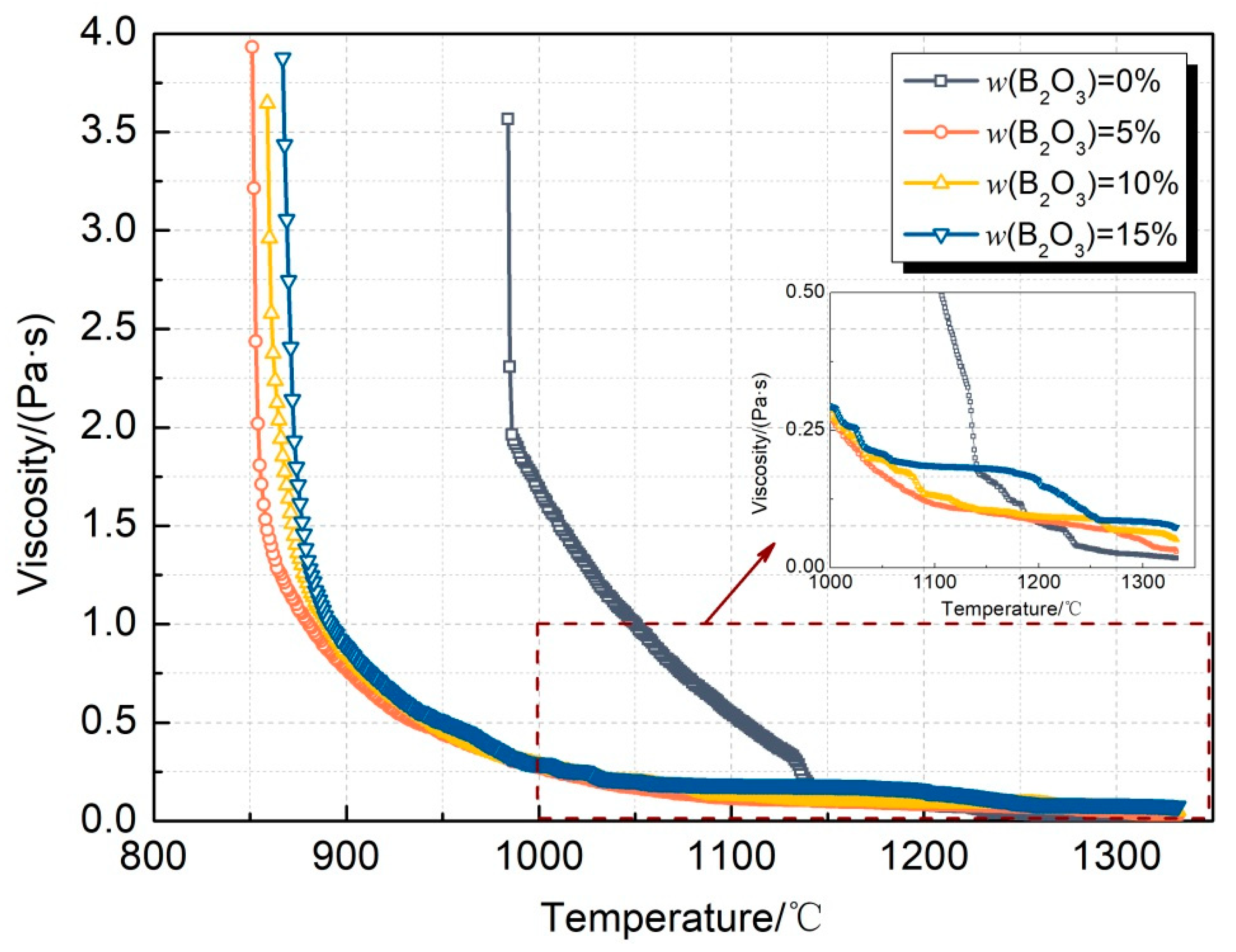


| No. | CaO | SiO2 | Na2O | B2O3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1 | 42.50 | 42.50 | 15.00 | 0 |
| N2 | 40.38 | 40.38 | 14.25 | 5.00 |
| N3 | 38.25 | 38.25 | 13.50 | 10.00 |
| N4 | 36.13 | 36.13 | 12.75 | 15.00 |
| No. | CaO | SiO2 | Li2O | B2O3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| L1 | 42.50 | 42.50 | 15.00 | 0 |
| L2 | 40.38 | 40.38 | 14.25 | 5.00 |
| L3 | 38.25 | 38.25 | 13.50 | 10.00 |
| L4 | 36.13 | 36.13 | 12.75 | 15.00 |
| Component | CaO | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Li2CO3 | B2O3 | Na2CO3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature/°C | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 500 | 300 | 600 |
| 1 | 0.514 | 0.242 | 0.09 | 0.009 |
| w(B2O3) /% | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Center | Area Fraction | Center | Area Fraction | Center | Area Fraction | Center | Area Fraction | |
| 0 | 865.15 | 0.214 | 908.06 | 0.152 | 989.42 | 0.573 | 1025.6 | 0.062 |
| 5 | 876.06 | 0.102 | 942.72 | 0.397 | 992.55 | 0.191 | 1050 | 0.310 |
| 10 | 882.38 | 0.087 | 944.22 | 0.416 | 996.95 | 0.173 | 1051.7 | 0.325 |
| 15 | 870.09 | 0.098 | 941.44 | 0.399 | 989.92 | 0.218 | 1045.4 | 0.285 |
| w(B2O3) /% | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Center | Area Fraction | Center | Area Fraction | Center | Area Fraction | Center | Area Fraction | |
| 0 | 853.08 | 0.675 | 905.72 | 0.156 | 974.66 | 0.146 | 1075.1 | 0.023 |
| 5 | 860.87 | 0.251 | 919.09 | 0.426 | 967.17 | 0.242 | 1041 | 0.081 |
| 10 | 872.92 | 0.211 | 935.86 | 0.353 | 980.55 | 0.275 | 1043.8 | 0.161 |
| 15 | 871.62 | 0.139 | 936.51 | 0.411 | 979.08 | 0.242 | 1047.3 | 0.208 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Qi, J.; Shi, Y.; Dou, Y.; Liu, C. Influence of B2O3 on the Viscosity and Melt Structure of CaO-SiO2-M2O (M = Li, Na)-Based Slags. Metals 2025, 15, 286. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15030286
Wang J, Qi J, Shi Y, Dou Y, Liu C. Influence of B2O3 on the Viscosity and Melt Structure of CaO-SiO2-M2O (M = Li, Na)-Based Slags. Metals. 2025; 15(3):286. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15030286
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jinhui, Jie Qi, Yuanxin Shi, Yingying Dou, and Chengjun Liu. 2025. "Influence of B2O3 on the Viscosity and Melt Structure of CaO-SiO2-M2O (M = Li, Na)-Based Slags" Metals 15, no. 3: 286. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15030286
APA StyleWang, J., Qi, J., Shi, Y., Dou, Y., & Liu, C. (2025). Influence of B2O3 on the Viscosity and Melt Structure of CaO-SiO2-M2O (M = Li, Na)-Based Slags. Metals, 15(3), 286. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15030286






