Abstract
High-entropy alloys have garnered significant attention due to their unique composition and exceptional properties. Additive manufacturing technology, with its distinctive processing methods, offers new options for the fabrication of high-entropy alloys. However, due to the diversity of high-entropy alloys and additive manufacturing technologies, it is imperative to provide a comprehensive overview of the high-entropy alloys produced using various additive manufacturing methods. This paper presents a summary of the microstructure, mechanical properties, and corrosion resistance of high-entropy alloys fabricated using different additive manufacturing techniques. This paper initially reviews the impact of various additive manufacturing process parameters and the influence of different elements on the microstructure of additively manufactured high-entropy alloys. Subsequently, it discusses the effects of different additive manufacturing techniques on mechanical properties and summarizes four strengthening mechanisms in additively manufactured high-entropy alloys. Additionally, the corrosion resistance of various additively manufactured high-entropy alloys is summarized. Finally, based on the review of additively manufactured high entropy alloys presented in this paper, the current challenges and future research directions are proposed.
1. Introduction
High-entropy alloys (HEAs) are a novel class of alloys composed of five or more principal elements, with each element constituting an atomic fraction ranging from 5% to 35% [1,2]. Since HEAs were first proposed in 2004, the attention to HEAs has increased rapidly [3]. HEAs exhibit superior properties, including exceptional strength and ductility, superior physical and chemical properties, as well as outstanding wear resistance and corrosion resistance, which provide benefits to their unique core effects, including a high-entropy effect, lattice distortion, slower diffusion, and cocktail effect. Engineering materials have strict requirements for mechanical properties. HEAs show possible application potential in the fields of aerospace, automotive, chemical, and energy. Currently, the mechanical properties of HEAs mainly are regulated by two patterns, including adjusting the chemical composition of HEAs and controlling the manufacturing method. HEAs contain multiple major elements, offering a broad space for regulation. Adjusting the chemical compositions of HEAs affects the phase composition and microstructure, resulting in improvement in the mechanical property. Additionally, the different fabricated methods provide heterogeneous solidification strategies, also affecting the microstructure of HEAs. Vacuum arc melting and casting techniques are currently primary methods for the fabrication of HEAs. However, traditional casting methods are limited in their ability to produce large-sized and complex-structured HEA components. Additive manufacturing techniques create new options to produce HEAs. Additive manufacturing technology directly fabricates parts from digital models using a layer-by-layer material deposition process [4,5,6]. This method has great advantages over the traditional method, especially in the production of complex parts and enabling rapid prototyping. This makes additive manufacturing technology have potential applications in various fields.
This paper aims to provide a comprehensive analysis on additively manufactured HEAs, including production methods, microstructures, mechanical properties, and corrosion resistance. On this basis, we provide a perspective on the future development and direction of additively manufactured HEAs based on the existing research foundation.
2. Additive Manufacturing Methods for HEAs
Figure 1 shows the additive manufacturing methods and their history of development. The main additive manufacturing technologies for HEAs are laser powder bed fusion (PBF), laser-directed energy deposition (DED), and binder jet printing (BJP) [3]. Laser powder bed fusion (PBF) can be divided into laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) and electron beam powder bed fusion (EPBF). Laser-directed energy deposition (DED) is divided into directed energy deposition laser beam (DED-LB), directed energy deposition electron beam (DED-EB). and directed energy deposition arc melting (DED-Arc).
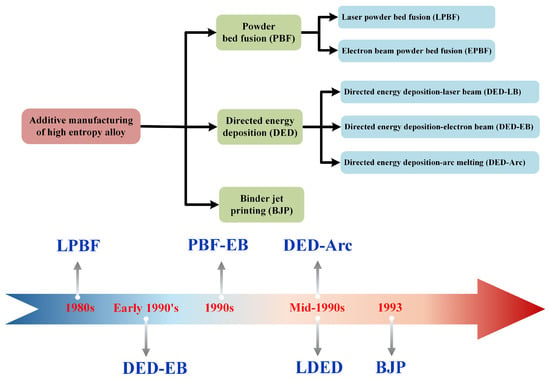
Figure 1.
History of the development of additively manufactured technology.
PBF technology fabricates HEAs by melting its feedstock [7]. This technology is capable of processing parts with complex shapes and forming the final part directly from the 3D model without subsequent machining. The grain size of the HEA parts prepared with LPBF is finer than those with EPBF due to its higher solidification rate [8]. DED technology produces HEAs by depositing layer upon layer of directly melted powders or wires. This method can be utilized for surface strengthening of components and tools, modification and repair of damaged parts and tools, as well as the processing and manufacturing of multi-material composite workpieces [9,10,11]. HEAs manufactured using DED technology have high forming accuracy and good surface quality. Unfortunately, the forming efficiency is low, and the forming size is limited. Owing to the appropriate binder properties and good processability of AlCoCrFeNi and CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloys (HEAs), binder jet printing (BJP) technology is currently mainly used for the fabrication of these two materials [3,12,13]. Despite its advantages of high production efficiency and simple process, the selection of binders remains challenging. Moreover, the shrinkage rate of the materials during the manufacturing process is also difficult to control and predict.
3. Microstructure of Additively Manufactured HEAs
3.1. Effect of Additive Manufacturing Methods on Microstructure
The microstructure of HEAs has an important effect on strength, hardness, and corrosion resistance. The microstructure of additively manufactured HEAs is often determined by a combination of factors, such as additive manufacturing methods, processing parameters, and heat treatment parameters. Therefore, it is necessary to study the microstructure of additively manufactured HEAs. The LPBF and DED-LB techniques are capable of preparing HEAs with single-phase and multiphase structures. Lin et al. [14] found that FeCoCrNiMo0.5 HEA prepared using the LPBF technique had a smaller grain size than that prepared using the DED-LB technique. Additionally, grain sizes of HEAs can be controlled through the manipulation of scanning strategies [15]. Using the methods of DED and EPBF, it is hard to accurately control the grain morphology of HEAs [3]. The grain sizes of HEAs constructed using the EPBF method have been reported to be in between those of parts prepared with casting and using the LPBF method [16]. For BJP technology, the HEAs produced by BJP technology generally exhibit porous structures, which can adversely affect the application of the material performance [12,13]. In addition to this, the classic CrMnFeCoNi HEA has been demonstrated to achieve well-formed grain sizes using a variety of additively manufactured technologies. Table 1 summarizes the microstructure of HEAs fabricated using different additive manufacturing methods.

Table 1.
Microstructure of HEA fabricated using different additive manufacturing methods.
3.2. Effect of Composition of HEAs on Microstructure
CrFeCoNi HEAs have become the basis for fabricating different HEAs. Various microstructures of HEAs are achieved by adding other elements into CrFeCoNi. Numerous researchers have incorporated Al into CrFeCoNi HEAs and investigated the formation process of the BCC phase [28,42,43]. Columnar, honeycomb-like mixtures were observed in this HEA system with different Al contents fabricated using both PBF and DED methods [3,44,45]. The addition of Al elements in the HEA system can reduce the generation of intermetallic compounds and refine the grains [46]. In addition, Al elements can promote the formation of the BCC phase. As a result, AlxCrFeCoNi HEAs have become the most studied single-phase or multiphase HEAs. As shown in Figure 2a,b, AlxCrFeCoNi HEAs were prepared using laser additive manufacturing. They found that AlxCrFeCoNi HEAs exhibited FCC single-phase, FCC + BCC, and completely BCC single-phase structures with varying Al content [46,47,48,49]. Due to the differences in solidification rates and thermal gradients between the melting preparation and additively manufactured preparation, dual-phase FCC + BCC structures of HEAs were generated. Wei et al. [50] prepared AlxCrFeCoNi (x = 0.07 − 0.88) HEA using the LPBF method and found that grain morphology and phase composition are closely related to the x value. As shown in Figure 2c, when x is in the range from 0.07 to 0.5, a single-phase FCC structure is observed. When x is between 0.67 and 0.78, the microstructure is in the BCC stage; when x is 0.88, the BCC stage transitions to the B2 stage. This change is attributed to Al-induced lattice distortion and valence electron concentration. Interestingly, AlxCrFeCoNi HEAs prepared using the DED-LB technique (Figure 2d) were also found to give different phase structures for different x [51]. When x is 0.3, the single-phase FCC phase was observed (Figure 2e,f). As shown in Figure 2g,h, when x is 0.7, the HEAs exhibits a two-phase structure. The reason why the element Al can introduce the formation of the BCC structure is that the electronic configuration of Al allows it to exhibit both metallic and non-metallic characteristics [52]. This phase change can be interpreted as an increase in the lattice constant of the alloy due to an increase in the Al element, thus destroying the original FCC structure. Therefore, in HEA systems fabricated using PBF and DED, Al content affects grain morphology and phase composition. Al reduces intermetallic compound generation, refines grains, suppresses the FCC phase, and promotes the formation of the BCC phase. Different preparation methods lead to differences in the structure of the FCC + BCC duplex phase, and the phase transition caused by the change in Al content is attributed to the increase in the lattice constant due to the addition of Al, which destroys the FCC structure and introduces the BCC phase.
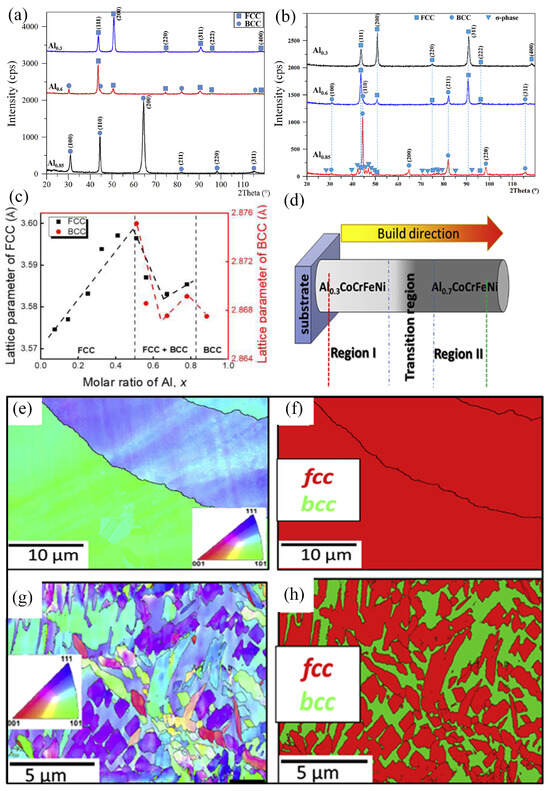
Figure 2.
(a,b) AlxCrFeCoNi HEA phase composition for different x values. (c) The number of lattice constants of FCC and BCC phases as a function of Al content. (d) Schematic demonstration of as-deposited graded AlXCoCrFeNi build, (e) Al0.3CoCrFeNi microstructural characterization: EBSD inverse pole figure (IPF) and (f) corresponding phase map. (g) Al0.7CoCrFeNi microstructural characterization: EBSD inverse pole figure (IPF) and (h) corresponding phase map (Reprinted with permission from Refs. [47,48,49,50,51]; 2024, Elsevier).
Numerous reports have indicated that Mn elements can influence the microstructure of HEAs. Zhang et al. [52] found that the microstructure of AlCoCrFeNiMnx (x = 0, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 1) transitions from coarse dendritic structures to finer dendritic structures and subsequently to columnar dendritic structures (Figure 3a–c) with changing Mn contents. Relatively similar elemental segregation exists between the dendritic (DR) and inter-dendritic (ID) regions of the alloy. Tong et al. [53] prepared CrMnFeCoNi HEAs using LPBF, and it can be seen in Figure 3d that columnar dendrites and equiaxed grains are the main microstructures of CrMnFeCoNi HEAs. Wang et al. [35] prepared CrMnFeCoNi HEAs using LPBF, and the results revealed the microstructure exhibits a layered structure including nanograin formation, elemental segregation and precipitation, a cellular dislocation structure, deformation twinning, and deformation-induced phase transitions. The additively manufactured CrMnFeCoNi HEA possesses a single-phase FCC structure, and its microstructure predominantly consists of columnar dendrites and equiaxed grains. The CrMnFeCoNi HEA fabricated using DED-LB exhibits a dendritic structure. Moreover, Mn tends to segregate at the grain boundaries due to the lower scanning speed [54,55]. However, employing appropriate process parameters can reduce or even eliminate the segregation of Mn elements [56].
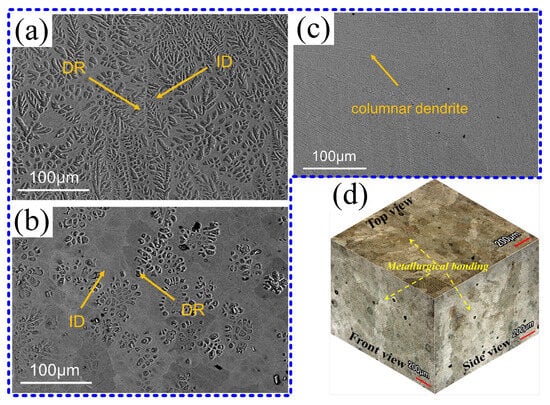
Figure 3.
Microstructure of AlCoCrFeNiMnx HEA: (a) x = 0, (b) x = 0.5, and (c) x = 1. (d) Three-dimensional microstructure of HEA (Reprinted with permission from Refs. [52,53]; 2024, Elsevier).
The effects of other elements and HEA systems on microstructure have also been widely studied. Gwalani et al. [57] utilized the DED method to fabricate AlCrFeMoVx HEA systems. The results demonstrated that V has a good solubility in AlCrFeMo HEAs. An increase in V content leads to an increase in grain size. Wu et al. [58] added the element V to CrFeCoNiNb hydroxides and showed that the microstructure of the V-free alloys consisted mainly of columnar dendritic crystals and fine C14 Laves phases. When V atoms replace some Nb atoms, the volume fraction of the C14 Laves phase decreases from 12.32% to 6.62%, which leads to a decrease in the size and amount of the C14 Laves phase, but the size of the dendrites becomes slightly coarser. Similar to elemental Al, elemental Zr is also capable of promoting the formation of the BCC phase. Sarswat et al. reported that the addition of Zr to AlCoFeNiSmTiVZr HEA promoted the formation of the BCC phase in the FCC matrix [32]. Dobbelstein et al. [59] used the DED-LB technique to prepare NbTaTiZr HEAs to investigate the effect of the ratio of Zr to Nb on the microstructure; the experimental setup is shown in Figure 4a. The results indicate that a high concentration of Zr is conducive to the formation of a dual BCC phase. In the Zr-enriched BCC regions, Ta elements segregate at the grain boundaries, forming a Ta-enriched secondary BCC phase. Furthermore, increasing the ratio of Zr to Nb yields a finer microstructure (Figure 4b). In brief, the impact of Zr elements on the microstructure is primarily manifested in its ability to form intermetallic compounds [59]. Similar to Zr and Al, the addition of Mo and Ta elements also favors the formation and stabilization of the BCC phase in the alloy [60].
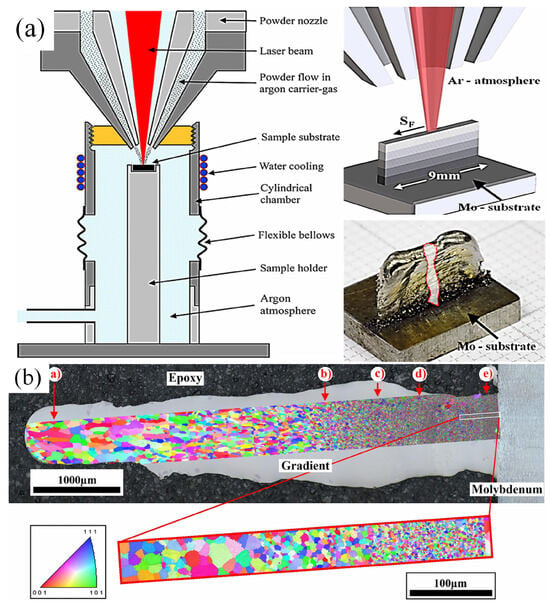
Figure 4.
(a) Experimental setup for laser energy deposition. (b) BSE image of the grain orientation of the entire wall structure (Adapted from Ref. [59]).
With the increasing demand for material performance, the doping of particulate compounds such as WC, TiN, and NbC in additively manufactured HEAs has been studied. Li et al. [61] prepared CrMnFeCoNi-WC composites using the DED method. With the addition of WC particles, the grain size became smaller and smaller (Figure 5a–c). Moreover, Cr23C6 precipitation-reinforced phases were formed. Zhang et al. [62] prepared CrMnFeCoNi + WCx (x = 0 − 8 wt %) using LPBF. As can be seen in Figure 5d–g, the grain refinement is obvious with the increase in WC addition, especially for the HEAs with the addition of 8 wt % WC. It has been demonstrated that a high concentration of WC particles inhibits grain growth at the grain boundaries during the LPBF process. In addition to doping WC particles to alter grain size, researchers have also introduced NbC particles into the HEA system. Li et al. [63] investigated the effect of doping NbC on the microstructure of AlCoCrFeNi HEAs. They found that AlCoCrFeNi HEA exhibits a mixture of BCC and FCC phases. Moreover, the microstructure has many elongated massive grains and a few equiaxed grains. The addition of NbC particles leads to a reduction in the FCC phase distributed at the grain boundaries. The grain growth of HEAs is inhibited due to the strong pinning effect of NbC particles. Furthermore, the addition of TiN particles to HEAs has been studied [20,64,65]. The results indicate that the microstructure is isotropic, and the grain size is very fine. The incorporation of these compound particles can effectively reduce grain size. Doping compounds such as WC, TiN, and NbC into additively manufactured HEAs can make the materials exhibit isotropic microstructures and fine grain sizes. The addition of these compounds can effectively reduce the grain size and improve the material properties.
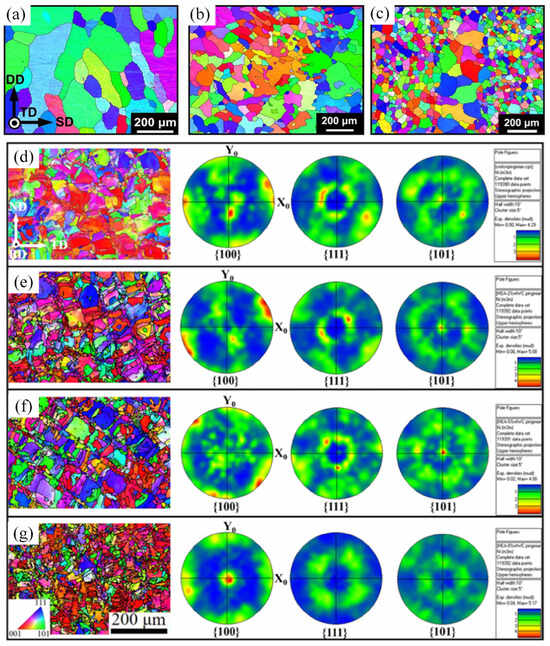
Figure 5.
EBSD map of WC addition: (a) 0 wt %, (b) 5 wt %, and (c) 10 wt %. (d–g) EBSD images and pole figures: (d) as-fabricated HEA, (e) HEA-2 wt %, (f) HEA-5 wt %, (g) HEA-8 wt % (Reprinted with permission from Ref. [61]. 2024, Elsevier; Adapted from Ref. [62]).
3.3. Effect of Additively Manufactured Process on Microstructure
The preparation process parameters of additively manufactured HEAs play an important role in microstructure [34,66,67,68]. Table 2 shows the effect of process parameters on the microstructure of HEAs. Currently, a variety of additively manufactured processes are being explored. Parameters for preparing HEAs by DED technology have covered the laser power range of 300–3700 W and scanning speeds of 100–6000 mm/min. The process parameters for the preparation of HEA using the DED-Arc methods correspond to the wire feed rates in the range of 5–10 m/min, arc voltages in the range of 22–25 V, and scanning speeds in the range of 8–100 mm/min [3]. Among these parameters, the laser power determines the energy radiated by the laser per unit area, while the scanning speed determines the time that the laser stays on the sample [69]. Park et al. [70] investigated the effect of laser scanning speed on the microstructure of CrMnFeCoNi HEAs. The results indicated that higher scanning speeds led to finer grain sizes (Figure 6a,b), suggesting that energy input is dependent on the scanning speed. Zhou et al. [71] fabricated FeCoCrNiC0.05 HEAs using laser powers ranging from 200 to 400 W and scanning speeds between 800 and 2000 mm/s. The results revealed that the grain size decreased with higher laser power or lower scanning speeds. As shown in Figure 6c–e, the grains in the three distinct regions exhibit random orientations. Equiaxed grains are observed in the middle and lower sections, while columnar grains are present in the upper section. This is attributed to differences in the temperature gradient and cooling rate. Zhu et al. [72] utilized the PBF technique to prepare Fe49.5Mn30Co10Cr10C0.5 HEAs with process parameters of P = 180 W and v = 1000 mm/s. Fe49.5Mn30Co10Cr10C0.5 HEAs exhibits a hierarchical microstructure consisting of equiaxed grains and columnar structures (Figure 7). Akinwande et al. [73] fabricated CrMnFeCoNi HEA by varying laser power. They found that the microstructure of HEAs depends on the solidification velocity (V) and the temperature gradient (G). A high G/V ratio promotes the formation of columnar grains, while a low G/V ratio favors the formation of equiaxed grains [69]. For example, Guan et al. [74] observed that a decrease in the G/V ratio makes the grain structure transition from columnar to equiaxed grains (Figure 6f).

Table 2.
Summary of fabrication process and microstructural characteristics.
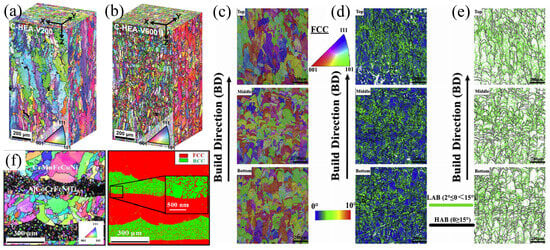
Figure 6.
(a) IPF plot for v = 200 mm/s and (b) IPF plot for v = 600 mm/s from EBSD analyses of FeCoCrNiC0.05 HEA (400 W, 800 mm/s). (c) Inverse pole figure (IPF), (d) local misorientation (LM) maps, and (e) grain boundaries (GB) maps of FeCoCrNiC0.05. (f) EBSD IPF map depicting the columnar structure of CrMnNiFeCo lamellae and equiaxed-grain structure for AlCoCrNiFeTi0.5 lamellae (Adapted from Ref. [70]; reprinted with permission from Refs. [71,74]. 2024, Elsevier).
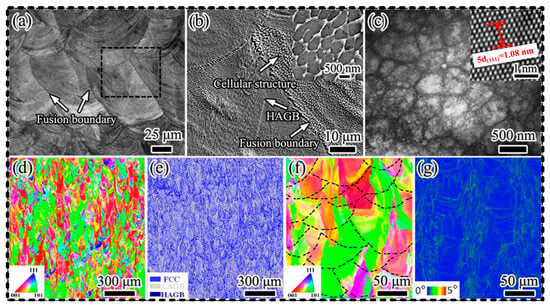
Figure 7.
(a) OM images of the as-built HEA. (b) SE image obtained from the area in (a). The inset shows the equiaxed cellular structures. (c) STEM image of the equiaxed cellular structures and the inset HRTEM image showing the distance across 5 (111) planes. (d) IPF map and (e) phase map superimposed with the GB map. (f,g) IPF (the dashed lines show the fusion boundaries) and KAM maps (Reprinted from Ref. [72]).
In addition to scanning speed and power, factors such as volumetric energy density (VED), cooling rate, and scanning strategy also significantly influence the microstructure. For the PBF technique, the microstructure (grain morphology) of alloys can be modified by adjusting the VED [3]. Niu et al. [77] observed that the relative density of AlCoCrFeNi-based HEAs increased with increasing VED. As shown in Figure 8, the growth direction, size, and grain boundary characteristics of the HEAs vary with changes in VED. It has been reported that an increase in cooling rate transforms dendritic microstructures into equiaxed and columnar structures [78]. The microstructure of the HEAs fabricated using DED-LB at a higher cooling rate exhibits a layered dendritic structure, while the HEAs produced using PBF exhibits columnar grains with a specific growth direction. The laser scanning strategy is an important parameter used to control and mitigate microstructural defects. An appropriate scanning scheme is crucial for HEAs, as it not only enables the sample to achieve a uniform and ultra-fine microstructure but also improves its mechanical properties [69]. Guo et al. [68] revealed the effect of scanning strategy on the microstructure of CoCrFeMnNi- (N, Si) HEAs constructed using LPBF. It was shown that the HEAs exhibited different microstructural features using 45° and 67° scanning rotations. Xiang et al. [79] employed unidirectional and bidirectional scanning schemes and observed a transition from columnar grains to equiaxed grains in the subsequent layers. Jin et al. [80] utilized three different scanning strategies to fabricate CrMnFeCoNi HEAs, and the results indicated that the scanning strategy influences the grain structure.
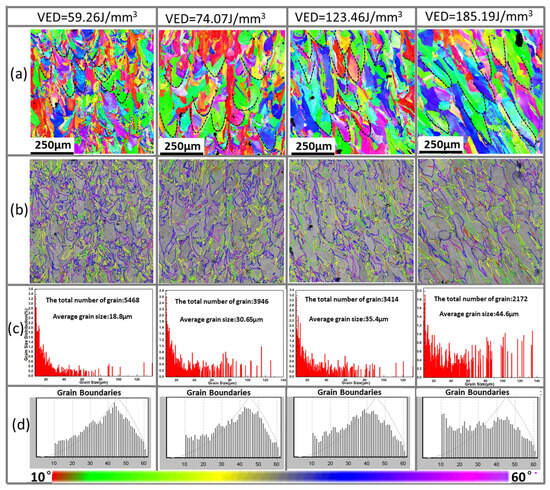
Figure 8.
The PBF samples with different VEDs: (a) IPF images, (b,d) images of grain boundary angle distribution, and (c) images of grain size distribution (Reprinted with permission from Ref. [77]. 2024, Elsevier).
4. Mechanical Property
4.1. Hardness
The microhardness of materials is an important parameter for evaluating the mechanical properties of additively manufactured HEAs. Table 3 lists the hardness of various HEAs fabricated using different additively manufactured techniques. It can be concluded that the hardness of HEAs varies significantly depending on the additively manufactured method. Due to the slower cooling rate of PBF, the hardness of the AlCoCrFeNi HEAs produced using PBF is relatively lower compared to that produced using DED. This higher hardness is attributed to the finer microstructure generated by the latter. Additionally, the hardness of HEAs with a BCC phase structure is higher than that of HEAs with an FCC phase structure [49]. For AlxCrCuFeNi HEAs obtained using DED, the hardness increases with the increase in Al elements [1]. The hardness of AlCoCrFeNi HEAs gradually decreases from the top of sample to the bottom due to an increasing FCC phase [18]. This agrees with the results of Gwalani et al. [51]. Dobbelstein et al. [59] fabricated TiZrNbTa HEAs using DED technology and found that the hardness increased from approximately 220 HV to around 400 HV, with increasing Zr content. Gwalani et al. [57] fabricated compositionally graded AlCrFeMoVx HEAs. As the V content increased, the hardness of the alloy rose from 485 HV to 581 HV. This strengthening effect is attributed to solid solution strengthening. Li et al. [81] found that the hardness of the WNbMoTa HEAs increases from 459.2 ± 9.7 HV to 497.6 ± 5.6 HV with increasing W content. This increase in hardness is attributed to the refinement of the grain size. Li et al. [75] used DED-LB to fabricate a finer microstructure of FeCoCrAlCu HEAs without microcracks, resulting in a significant increase in hardness, which is attributed to the addition of yttria partially stabilized ZrO2. Additionally, the incorporation of NbC and TiN particles into HEAs would also enhance the hardness [62,82]. In summary, the enhancement of material hardness can be achieved by accelerating the cooling rate of the additive manufacturing process. In addition, the introduction of Al or V elements to the original material can also be considered to improve the hardness of the material.

Table 3.
Hardness of additively manufactured HEAs.
4.2. Mechanical Properties
Different additively manufactured methods, process parameters, and elements have varying effects on the tensile strength of HEA materials. Table 4 summarizes the mechanical properties of HEAs obtained using different fabrication methods. Among them, YS refers to the yield strength, UST indicates the ultimate tensile strength, and EI signifies the elongation. Previous studies have shown that the CrMnFeCoNi HEAs produced by additively manufacturing exhibits superior yield strength compared to its cast counterpart, due to its finer microstructure [3]. Furthermore, the HEAs fabricated using DED technology experience rapid solidification, which introduces more dislocations, resulting in a higher yield strength compared to the HEAs produced using PBF-LB technology. In addition, HEAs fabricated using PBF-EB technology exhibit higher ductility. Shuo et al. [102] adjusted the ratio of columnar to equiaxed grains by varying the laser power, ultimately achieving improved mechanical properties. The importance of scanning speed and laser power process parameters in fabricating materials with better mechanical properties has been demonstrated [71]. In addition, some researchers have attempted to add other elements to HEAs to enhance their mechanical performance. Wang et al. [103] employed nitrogen doping in CoCrFeNi HEAs, and the results showed that the addition of nitrogen led to the formation of twinning and dislocations, as well as intersecting slip bands, as shown in Figure 9a, thereby improving the mechanical properties. Zhou et al. [71] added carbon to the FeCoCrNi HEAs, which increased the tensile strength to 797 MPa. This improvement is attributed to grain refinement and solid solution strengthening induced by the addition of carbon. Subsequently, the effect of Si addition on the mechanical properties was investigated. Hou et al. [104] found that the strength of the HEAs increased with the addition of Si. The Si element stabilized the FCC phase and promoted phase transformation-induced plasticity by adjusting twinning strain during deformation. This allowed total elongation to exceed 30%. The combined effects of multiple strengthening mechanisms, including dislocations, deformation twinning, and phase transformation, significantly enhanced the strength of the HEAs (Figure 9b). Additionally, WC was added to the DED-fabricated CrMnFeCoNi HEAs, resulting in a high tensile strength of 800 MPa and an elongation of 37%. The improvement in mechanical properties is likely attributed to the formation of Cr23C6 strengthening phases [61]. Amar et al. [105] added TiC to CrMnFeCoNi HEAs, and the CrMnFeCoNi HEAs with 5 wt% TiC exhibited a tensile strength of 723 MPa and a tensile strain of 32% (Figure 9c). The improvement in mechanical properties is attributed to the introduction of micro-sized TiC reinforcing phases. Therefore, different additive manufacturing methods, process parameters, and elemental additions have significant effects on the tensile properties of HEAs. Additive manufacturing technology significantly enhanced the yield strength of HEAs compared to conventional casting due to finer grain size microstructure. Among them, DED technology has higher yield strength than the PBF-LB technology due to the introduction of more dislocations by rapid solidification, while the PBF-EB technology exhibits higher ductility. By adjusting process parameters such as laser power and scanning speed, the grain morphology can be optimized to further enhance the material properties. In addition, elemental doping such as N, Si, and WC is also an important means to enhance the performance of HEAs. These studies show that a combination of strengthening mechanisms can significantly enhance the strength and ductility of HEAs.

Table 4.
Tensile properties of HEAs obtained using different preparation processes.
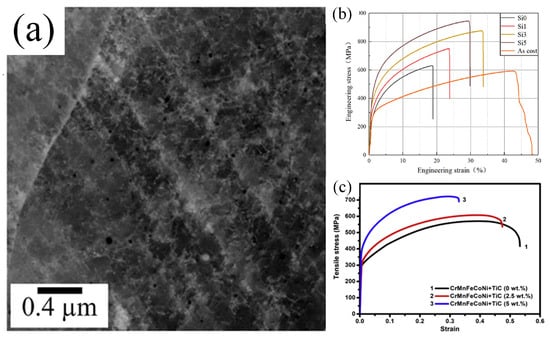
Figure 9.
(a) ECC images showing the dislocation substructures at a tensile strain of 15% for the N-doped FeCoNiCr HEA. (b) The stress–strain curve of the as-cast metastable Fe50Mn30Co10Cr10 and PBF technology forming the Si-containing metastable high-entropy alloy. (c) The tensile curves of DED CrMnFeCoNi HEA with different TiC additions under room temperature (Reprinted with permission from Refs. [103,104,105]. 2024, Elsevier).
5. Strengthening Mechanism
The strengthening mechanisms of additively manufactured HEAs primarily include refined crystalline strengthening [61,114,115,116], dislocation strengthening [15,16,28,45,72,116], solid solution strengthening [71,116,117], and precipitation strengthening [30,32,61,111,118].
Zhou et al. [88] found that Cr23C6 mainly accumulates at the grain boundaries (Figure 10a,b). These carbides restrict grain growth, resulting in fine grains. As a result, the mechanical properties of the HEAs are enhanced. Li et al. [34] fabricated CoCrFeMnNi HEAs using PBF technology, and the results showed that the mechanical properties of HEAs are enhanced due to grain refinement (Figure 10c). In addition, Yang et al. [110] developed novel Ni6Cr4WFe9Ti HEAs with a fine-grained structure. The high grain boundary density (Figure 10d–i) enables the HEAs to exhibit a fracture strength exceeding 970 MPa and a tensile elongation of up to ~12.2% at room temperature. Subsequently, Gao et al. [111] found fine BCC phases at the grain boundaries of the FCC matrix, and the printed HEAs demonstrated an excellent combination of high strength and outstanding ductility. This was attributed to the synergistic effect of high cooling rates and the precipitation strengthening of BCC phases at the grain boundaries.
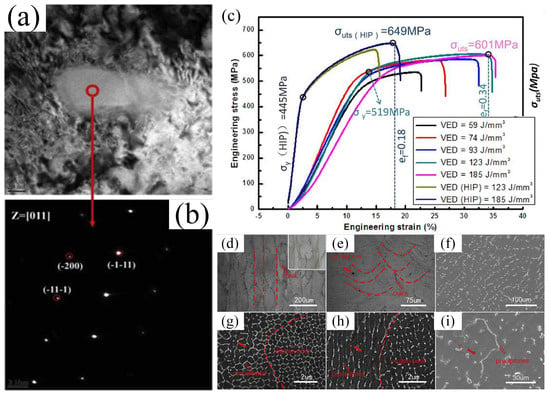
Figure 10.
(a) Bright-field TEM image of FeCoCrNiC0.05 HEA. (b) Selected area diffraction pattern. (c) Mechanical properties of CoCrFeMnNi HEA. The microstructures of the SLM alloy and VAM alloy: (d,g) horizontal image of SLM alloy, (e,h) vertical image of SLM alloy, and (f,i) the microstructures of VAM alloy (Reprinted with permission from Refs. [34,88,110]. 2024, Elsevier).
Additively manufactured HEAs have a high dislocation density, and this dislocation network can impede the movement of internal dislocations during deformation, thereby enhancing the mechanical properties of material. As shown in Figure 11a,b, CrMnFeCoNi HEAs fabricated using laser additively manufacturing generates a high density of dislocations, which enhances the mechanical properties [55]. In Ma et al.’s study [119], dislocation strengthening was primarily attributed to the addition of Fe-based amorphous alloys (Figure 11c–h). As shown in Figure 11i–m, the HEAs exhibit a large number of low-angle grain boundaries. The dislocation strengthening mechanism is related to the subgrain. These subgrains and dislocation networks form during the non-equilibrium solidification process and have a significant impact on the strength and plasticity of the material [23].
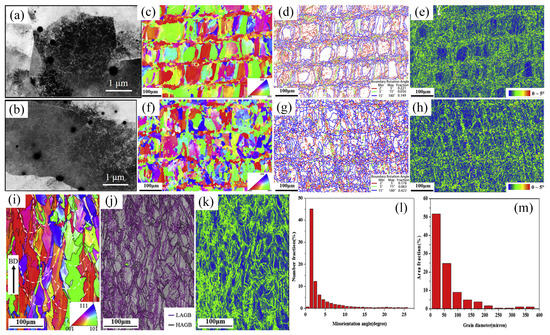
Figure 11.
(a,b) Images of CrMnFeCoNi HEA. EBSD analysis of the FeCoNiCrMn and FeCoNiCrMn-5MG (on the top view): (c) color inverse pole figure (IPF), (d) grain boundary map, (e) kernel average misorientation (KAM) map, (f) IPF, (g) grain boundary map, and (h) KAM map. EBSD analysis of AlCrFeNiV HEA: (i) IPF map, (j) image quality (IQ) map with LAGBs and HAGBs superimposed, (k) kernel average misorientation (KAM) map, (l) misorientation angle plot corresponding to (j), and (m) grain size distribution (Reprinted with permission from Refs. [23,55]. 2024, Elsevier; reprinted from Ref. [119]).
Solid solution strengthening occurs due to lattice distortions. These distortions increase the resistance to dislocation movement, making slip more difficult, thereby increasing the strength and hardness. For laser additively manufacturing methods, the incorporation of interstitial atoms such as C, N, and O into HEAs leads to lattice distortions. HEAs containing small amounts of interstitial atoms will exhibit interstitial solid solution strengthening [69]. The addition of carbon to HEAs can achieve solid solution strengthening and dislocation strengthening, leading to improved mechanical properties. Wu et al. [44] used carbon as a solute and CoCrFeNi as a solvent, causing solid solution strengthening in the HEAs. Zhu et al. [72] introduced carbon to achieve solid solution strengthening, which enabled the alloy to activate both twinning-induced plasticity and phase transformation-induced plasticity mechanisms, resulting in a better strength and plasticity combination. The effect of various V elements on solid solution strengthening was subsequently studied [57], and the results showed that the addition of V Influenced the lattice parameters, thereby increasing solid solution strengthening. Solid solution strengthening was achieved with increasing V concentration (Figure 12a), and the hardness of the alloy increased from 0.3 Hv to 18.5 Hv. Yang et al. [120] found that the addition of Si significantly improved the hardness of HEAs. In AlCrCuFeCoNi HEAs, the hardness increased from 200.5 HV to 751.8 HV with the addition of Si, due to the solid solution strengthening effect (Figure 12b). Additionally, the addition of TiC and TiN has also been used to improve mechanical performance. Amar et al. [105] indicated that the effect of TiC mainly improved the mechanical properties of CrMnFeCoNi-based HEAs, especially the yield strength and tensile strength, but sacrificed some ductility. This strengthening effect was primarily due to the introduction of micro-sized TiC phases, which hindered the propagation of slip bands and thus enhanced the strength of material. Furthermore, the addition of TiN also improved mechanical performance [20]. Subsequently, Pegues et al. [121] added refractory metals Ta and Nb to CrMnFeCoNi HEAs, which have very different melting points from the HEAs matrix. This caused partial melting and differences in powder flowability, which in turn affected the microstructure and mechanical properties of alloy. As shown in Figure 12c, as the Ta content increased, the hardness also gradually increased, especially near the equiatomic composition, where the hardness significantly increased, indicating the enhanced solid solution strengthening effect. Lin et al. also observed the presence of solid solution strengthening mechanisms in the additively manufactured FeCoSiCrNi [109].
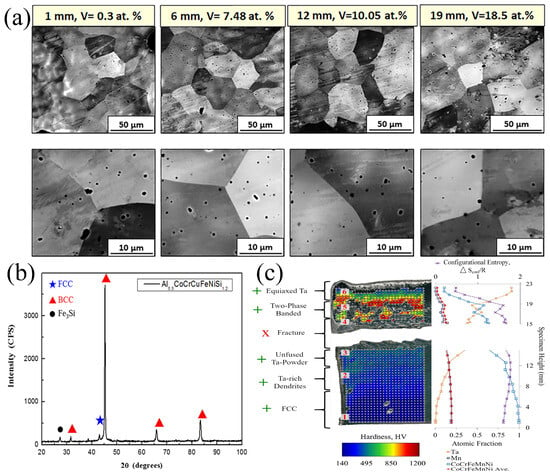
Figure 12.
(a) Microstructure of AlCrFeMoVx at various distances (from the substrate) or with various vanadium contents along the length. (b) Phase structure after addition of Si (c) Ta x CoCrFeMnNi hardness overlay map with associated EDS compositions and hardness (Reprinted with permission from Refs. [57,109,120]. 2024, Elsevier).
The precipitates formed by additively manufactured HEAs can enhance hardness and plasticity. Nano-sized precipitates in additively manufactured HEA materials mainly include carbide phases, γ′ phase, B2 phases, and D022 phases [γ′′ phase] [69]. He et al. [122] observed that in CoCrNiFeNb0.25 HEA, the unstable γ′′ phase eventually transformed into the stable ε phase. These precipitates can enhance the mechanical properties of the material. Yuan et al. [123] found that L12 precipitates were dispersed in the matrix and enriched at subgrain boundaries. After annealing, the microhardness and yield strength of the HEA billet were significantly improved. Zhang et al. [124] studied the effect of Al content on the mechanical properties of CoCrFeNi3 HEAs prepared using DED. As the Al content increased, the structure transformed from an FCC phase and L12 precipitates to a dual-phase FCC coexisting with a BCC phase (Figure 13). The increase in hardness was attributed to solid solution strengthening and precipitation strengthening. Additionally, after adding Nb and Ti/Al elements to HEAs, γ′′ [125] and γ′ [126], nano-precipitates were formed, and the presence of these precipitates enhanced the mechanical properties. Furthermore, Joseph et al. also found that adding different amounts of Al to CoCrFeNi HEAs resulted in the formation of B2 precipitates, which reinforced the material [47,48]. Therefore, the introduction of appropriate precipitates to form precipitate strengthening phases is an effective strategy to improve the mechanical properties of materials.
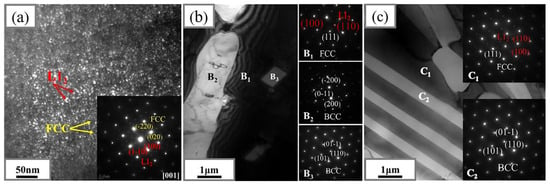
Figure 13.
TEM results of HEA0.5-HEA1.5: (a) DFTEM image and SAED patterns from [001] of HEA0.5, (b) TEM image and corresponding SAED patterns of the inter-dendritic of HEA1, and (c) TEM image and corresponding SAED patterns of HEA1.5 (Reprinted with permission from Ref. [124]. 2024, Elsevier).
Figure 14 illustrates the strengthening mechanisms of additively manufactured HEAs and their relationship. HEAs with fine grains are formed by increasing the solidification rate, resulting in the enhancement of mechanical properties. Furthermore, the high-temperature gradient in additively manufactured methods offers a high density of initial dislocations, which also plays a positive role in enhancing the mechanical performance of material. Another factor that enhances dislocation density is the precipitate phase. The precipitates are formed by adding other elements that suppress grain growth and form fine grains. Then the dislocation movement is hindered, positively affecting the dislocation strengthening mechanism. The improvement in the mechanical properties of HEAs are the result of the synergistic effects of grain boundary strengthening, solid solution strengthening, dislocation strengthening, and precipitation strengthening.
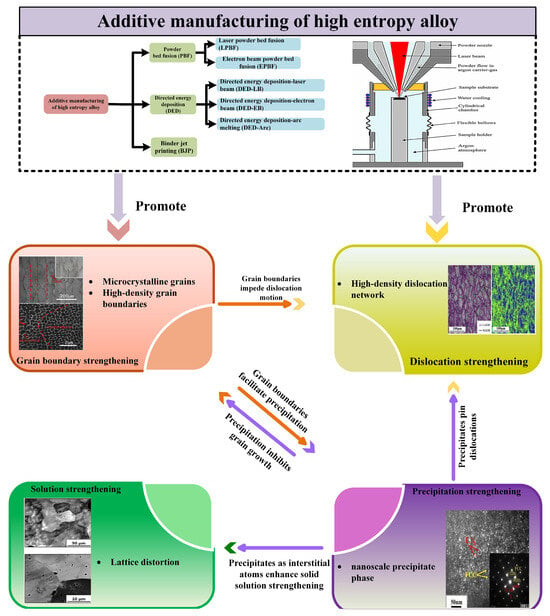
Figure 14.
Reinforcement mechanism for additively manufactured HEAs.
Appropriate additive manufacturing methods and process parameters can achieve superior mechanical properties compared to conventional casting. Liu et al. [127] conducted a comparative study on the microstructure and mechanical properties of CrMnFeCoNi HEAs fabricated using DED and conventional casting. The results indicated that the DED-fabricated samples exhibited higher hardness and yield strength due to their higher dislocation density and more pronounced grain boundary strengthening effects compared to the cast materials. Qiu et al. [128] found that CrMnFeCoNi HEAs manufactured using LPBF demonstrated exceptional mechanical properties. Compared to the cast materials, the dislocation density of LPBF-fabricated HEAs increased by over 100%, resulting in superior mechanical properties. Additively manufactured CrMnFeCoNi HEAs, characterized by a higher density of grain boundaries and enhanced resistance to dislocation cation movement, exhibited better tensile properties and yield strength than cast HEAs [3]. Joseph et al. [47] fabricated AlxCoCrFeNi HEAs using both DED and casting methods. The results showed that the DED-fabricated AlxCoCrFeNi HEAs had higher hardness, primarily attributed to their finer grain size. Dobbelstein et al. [59] manufactured TiZrNbHfTa HEAs using DLD. Compared to cast alloys, the DLD-fabricated alloys exhibited higher strength and better microstructural homogeneity.
6. Corrosion Resistance
The characteristics related to the microstructure of HEAs are summarized above. The microstructure of HEAs affects not only the mechanical properties, but also the corrosion resistance. HEAs with a high content of corrosion-resistant elements are expected to be a promising material for corrosion protection. The additively manufactured methods, heat treatment parameters, addition of different elements, and process parameters all influence corrosion resistance. Table 5 summarizes the corrosion current densities of various additively manufactured HEAs.

Table 5.
Summary of corrosion current density for various additively manufactured methods and different materials.
6.1. Comparison of Corrosion Resistance of Cast and Additively Manufactured HEAs
The main additively manufactured technologies used for the fabrication of HEAs are LPBF and EPBF technologies. Fujieda et al. [108] studied the CoCrFeNiTi HEAs produced using LPBF and EPBF technologies and found that the CoCrFeNiTi HEAs produced using LPBF exhibited better corrosion resistance compared to that produced using EPBF. This improvement was attributed to the more uniform microstructure, more homogeneous chemical composition, and the finer grain size. Xia et al. [132] compared the corrosion resistance of FeCrCuTiV HEAs produced using DED-LB and cast HEAs. The results showed that the HEAs produced using DED-LB had a higher corrosion potential (Ecorr) and lower corrosion current (Icorr), indicating better corrosion resistance for the HEAs prepared using DED technology. This was attributed to the lower volume fraction (31.5%) of Cu-enriched phases in the DED-produced HEAs compared to the cast sample (44.7%). Additionally, the more uniform structure and finer grain size of the DED-produced HEAs (Figure 15a,b) contributed to its enhanced corrosion resistance. Xu et al. [135] studied the corrosion resistance of CoCrFeMnNi HEAs produced using PBF technology compared to cast CoCrFeMnNi HEAs in NaCl solution. The results showed that the PBF-produced HEAs exhibited more uniform composition and finer grain size, while the cast HEAs primarily consisted of coarse dendritic crystals with an average grain size greater than 34 μm. The Icorr of the PBF-produced HEAs was 58% lower than that of the cast HEAs, indicating superior corrosion resistance. This improvement was mainly attributed to the rapid solidification and complex thermal cycles during PBF, which resulted in fine grains and multi-scale microstructures in the PBF-HEAs, as well as a high Cr content in the passive film that enhanced the stability of the passive film. However, Thapliyal et al. [136] investigated the corrosion resistance of the LPBF-produced Fe38.5Mn20Co20Cr15Si5Cu1.5 HEA system. They found that the corrosion resistance of Fe38.5Mn20Co20Cr15Si5Cu1.5 HEA produced using LPBF is worse than the cast HEAs studied by Nene et al. [137]. The LPBF-produced Cu-HEAs were prone to microcracks and voids (Figure 15c). Furthermore, the accumulation of Cu near corrosion pits led to the formation of localized pitting corrosion (Figure 15d–f). The corrosion resistance of Cu-HEAs could be improved by adjusting the LPBF process parameters, including grain size, phase distribution, and porosity. Due to the numerous advantages of HEAs and the clear disadvantages of conventional cast stainless steels, the corrosion resistance of traditional cast stainless steels and additively manufactured HEAs has been studied. Zhang et al. [40] investigated the corrosion resistance of NbMoTaW HEAs produced by PBF and 316 L stainless steel. The results showed that the NbMoTaW HEAs had a lower Icorr. This better corrosion performance was primarily attributed to the contribution of easily passivating elements such as Nb, Mo, and Ta in the alloy. In conclusion, due to the advantages of additively manufactured technology, HEAs produced using appropriate process parameters can achieve better corrosion resistance than traditional cast HEAs.
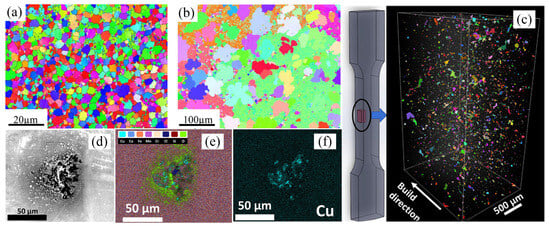
Figure 15.
EBSD results in the specimens prepared using different processes. (a) Inverse pole figure of the DED-LB specimen. (b) Inverse pole figure of the as-cast specimen. (c) Three-dimensional reconstruction representing distribution of microcracks and pores within as-built Cu-HEA. (d) SEM micrograph of corroded as-built Cu-HEA. (e–f) EDS maps corresponding to (d) from corroded as-built specimen of Cu-HEA (Reprinted with permission from Refs. [132,136]. 2024, Elsevier).
6.2. Effect of Heat Treatment on Corrosion Performance
Heat treatment is an effective method for improving the corrosion resistance of additively manufactured HEAs. Fujieda et al. [108] found that heat treatment significantly affects the corrosion resistance of CoCrFeNiTi HEAs. Heat treatment alters the microstructure of CoCrFeNiTi HEAs, particularly the size and distribution of ordered particles, which in turn influences the corrosion resistance of material. In another study [138], the authors used a combination of EPBF and solution treatment to fabricate Co1.5CrFeNi1.5Ti0.5Mo0.1 HEAs. The results showed that solution treatment enhanced the pitting potential by promoting the homogenization of finely ordered phase particles. Pang et al. [130] studied the effect of different heat treatment temperatures on the corrosion resistance of AlCoCrFeNi HEAs produced using DED technology. The results indicated that the best corrosion resistance was achieved at a heat treatment temperature of 500 °C, which was attributed to the increased segregation of Cr, Al, Fe, and Ni elements in the alloy and the formation of a single BCC phase structure. This may contribute to the development of a more uniform passive film. Wang et al. [134] found that AlCoCrFeNi HEAs treated at 1200 °C exhibited better corrosion resistance than those treated at 800 °C and 1000 °C. This was due to the precipitation of FCC phases in the B2 matrix during heat treatment. Melia et al. [112] found that heat treatment promotes the homogenization of the microstructure in CoCrFeMnNi HEAs produced using DED at high temperatures, reducing chemical segregation and consequently minimizing the formation of micro-electrochemical couples.
6.3. Effect of Elements and Preparation Process Parameters on Corrosion Performance
The effect of adding different elements and using various process parameters during additively manufacturing on the corrosion resistance of HEAs has also been studied. For example, Sarswat et al. [32] used DED technology to fabricate AlCoFeNiTiV0.9Smx HEAs with varying amounts of Sm. The study showed that the HEAs doped with Sm exhibited good corrosion resistance. After high-temperature corrosion tests, the material showed a single-phase FCC structure without significant surface cracking. The addition of Sm may help form a more compact and uniform microstructure, thereby enhancing the corrosion resistance of the system. In another study [139], researchers found that the addition of Ti to AlCoFeNiV0.9Sm0.1 HEAs increased the corrosion potential. Unfortunately, the addition of Ti led to the formation of Laves phases, which are more susceptible to localized corrosion. Ma et al. [119] added Fe-based amorphous alloy to FeCoNiCrMn HEAs, and the results showed an 18.9% reduction in corrosion current density. This can be attributed to the addition of Cr from the Fe-based amorphous alloy, improving the stability of the passive film. The influence of additively manufactured process parameters on corrosion performance was also studied. Xie et al. [129] investigated the effect of different laser powers on the corrosion performance of FeCrCoNiMoB1.1Si1.2 HEAs. The results showed that the corrosion resistance first increased and then decreased with increasing laser power, with the best corrosion resistance observed at 2600 W. This could be due to the enrichment of Mo at dendrite and cell boundaries, which may help form a more effective passive film. Wang et al. [131] prepared CoCrFeNiMo0.2 HEAs with varying laser powers and compared the resulting corrosion resistance. The results indicated that the grain size of HEA increased with increasing laser power. Larger grains might lead to fewer grain boundaries, potentially reducing the path for corrosion media to penetrate, thus improving corrosion resistance.
7. Summary and Outlook
In this paper, a systematic review of the current research status of additively manufactured HEAs is carried out, focusing on summarizing the effects of elemental composition and process parameters on the microstructure. On this basis, the mechanical properties and corrosion properties of additively fabricated HEAs are discussed. It is shown that the material properties can be improved by selecting appropriate process parameters, doping elements, and post-treatment methods. A useful reference for researchers working with HEAs is provided to help one rationalize the selection of additively manufactured technologies and to facilitate the development of novel HEA compositions. However, the complexity of the additively manufactured HEA process poses new challenges to material properties. The microstructure, uniformity of chemical composition, cracks, porosity, and other defects of additively manufactured HEAs are difficult to precisely control. This review provides a good reference for the usefulness of additively manufactured HEAs. From this review, the future recommendations and challenges for additively manufactured HEAs are as follows:
- (1)
- Selection of elements
The additively manufactured HEAs primarily utilized CrFeCoNi and CrMnFeCoNi systems. For the exploration of novel HEAs, new alloying elements can be introduced to develop new HEAs systems. For instance, the addition of non-metal elements such as C or Si can enhance the mechanical properties of HEAs. The design of new HEAs systems may consider incorporating rare earth elements, as well as low-density metals such as Si, Li, Mg, and transition metals. These materials are considered to be challenging for additive manufacturing.
- (2)
- Other additively manufactured processes
Currently, the binder jetting additively manufacturing methods are mainly applied to the AlCoCrFeNi and CoCrFeMnNi HEA systems. HEAs fabricated using DED and PBF technologies experience thermal stresses, making it essential to develop new binders and employ binder jetting techniques to address this issue. Although HEAs produced using additive manufacturing methods were reported in 2015, the development has been slow. Therefore, it is crucial to explore other additively manufactured technologies for the fabrication of HEAs.
- (3)
- Optimization of process parameters
HEAs prepared using DED and PBF generally have defects such as porosity and cracks. The impact of these defects on material properties is enormous. Therefore, it is essential to eliminate these defects to ensure the excellent mechanical properties of HEA-based laser-printed components. During the DED and PBF additively manufacturing processes of HEAs, increasing the energy input or adding other alloying elements can help prevent the formation of excessive defects. In addition, based on the summary in this paper, it can be seen that the subsequent use of different scanning strategies can also help to improve the microstructure of additively manufactured HEAs.
- (4)
- For other performance studies
For additively manufactured HEAs, most studies have focused on the mechanical properties. However, research on characteristics such as fatigue life, fractured toughness, and corrosion resistance remain limited, and these functional properties are yet to be fully explored. Regarding corrosion, some researchers have primarily compared the corrosion resistance of HEAs produced using traditional casting methods with those produced using additive manufacturing. However, there is limited research on the effects of different elements, manufacturing parameters, and additively manufactured techniques on corrosion resistance and fatigue life. Additively manufactured HEAs, designed with a functional focus, offer new possibilities for the use and design of HEAs. Therefore, it is crucial to explore other performance aspects of additively manufactured HEAs.
- (5)
- Computer predictive modelling
The current development of additively manufactured HEAs is dominated by iterative experiments to obtain optimal solutions. Such an approach is both time-consuming and labor-intensive. Deep learning can be utilized to develop new additively manufactured HEAs [140], accelerating the development of novel HEAs. Machine learning can be applied to predict various properties of additively manufactured HEAs, such as surface roughness, density, fatigue performance, and tensile strength. This approach allows for the extraction of hidden relationships between process parameters and alloy properties from large experimental datasets, effectively shortening the development cycle for specific alloy process parameters and reducing research and development costs.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.H. and C.L.; methodology, J.H.; validation, F.H. and J.W.; investigation, L.X. and Y.Z.; resources, L.X. and C.W.; data curation, C.W. and J.W.; writing—original draft preparation, F.H. and C.L.; writing—review and editing, C.W. and Y.Z.; visualization, F.H.; supervision, L.X.; project administration, C.W. and Y.Z.; funding acquisition, C.W. and J.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2022YFB4601800), the National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2022YFB4701105), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 52405338), and the Yong Elite Scientists Sponsorship Program by BAST (No BYESS2023040).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Cantor, B.; Chang, I.T.H.; Knight, P.; Vincent, A.J.B. Microstructural development in equiatomic multicomponent alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 375–377, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.W.; Chen, S.K.; Lin, S.J.; Gan, J.Y.; Chin, T.S.; Shun, T.T.; Tsau, C.H.; Chang, S.Y. Nanostructured high-entropy alloys with multiple principal elements: Novel alloy design concepts and outcomes. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2004, 6, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cagirici, M.; Guo, S.; Ding, J.; Ramanurty, U.; Wang, P. Additive manufacturing of high-entropy alloys: Current status and challenges. Smart Mater. Manuf. 2024, 2, 1000058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, M.A.; Alabtah, F.G.; Al-Hamidi, Y.; Khraisheh, M. On the laser additive manufacturing of high-entropy alloys: A critical assessment of in-situ monitoring techniques and their suitability. Mater. Des. 2023, 226, 111658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogrebnjak, A.D.; Bagdasaryan, A.A.; Yakushchenko, I.V.; Beresnev, V.M. The structure and properties of high-entropy alloys and nitride coatings based on them. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2014, 83, 1027–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; He, J.; Tian, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, A.; Lian, Q.; Jin, Z.; Lu, B. Additive manufacturing: Integrated fabrication of macro/microstructures. J. Mech. Eng. 2013, 49, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Nai, M.L.S.; Sin, W.J.; Lu, S.; Zhang, B.; Bai, J.; Song, J.; Wei, J. Realizing a full volume component by in-situ welding during electron beam melting process. Addit. Manuf. 2018, 22, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amano, H.; Ishimoto, T.; Hagihara, K.; Suganuma, R.; Aiba, K.; Sun, S.-H.; Wang, P.; Nakano, T. Impact of gas flow direction on the crystallographic texture evolution in laser beam powder bed fusion. Virtual Phys. Prototyp. 2023, 18, e2169172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobbelstein, H.; Gurevich, E.L.; George, E.P.; Ostendorf, A.; Laplanche, G. Laser metal deposition of a refractory TiZrNbHfTa high-entropy alloy. Addit. Manuf. 2018, 24, 386–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, M.R.U.; Seo, G.-J.; Fan, X.; Liaw, P.K.; Motaman, S.; Haase, C.; Kim, D.B. Effects of process parameters on bead shape, microstructure, and mechanical properties in wire + arc additive manufacturing of Al0.1CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy. J. Manuf. Process. 2021, 68, 1314–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.; Kong, X.; Chen, X. Fabrication of bulk Al-Co-Cr-Fe-Ni high-entropy alloy using combined cable wire arc additive manufacturing (CCW-AAM): Microstructure and mechanical properties. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 74, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, D.; Lindwall, G.; Lundbäck, A.; Amnebrink, M.; Boström, M.; Riekehr, L.; Schuisky, M.; Sahlberg, M.; Jansson, U. Binder jetting of the AlCoCrFeNi alloy. Addit. Manuf. 2019, 27, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, P.; Meenashisundaram, G.K.; Nai, S.M.L.; Wei, J. Fabrication of porous CoCrFeMnNi high entropy alloy using binder jetting additive manufacturing. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 35, 101441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.Y.; Hu, J.X.; Liu, M.Q.; Li, Z.H.; Xi, X.; Dai, J.H.; Ma, R.; Shi, Z.F.; Tan, C.W.; Li, R.S.; et al. Enhancing plasticity in laser additive manufactured high-entropy alloys: The combined effect of thermal cycle induced dissolution and twinning. Addit. Manuf. 2024, 39, 104427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Tan, X.P.; Descoins, M.; Mangelinck, D.; Tor, S.B.; Lim, C.S. Revealing hot tearing mechanism for an additively manufactured high-entropy alloy via selective laser melting. Scr. Mater. 2019, 168, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Huang, P.; Ng, F.L.; Sin, W.J.; Lu, S.; Nai, M.L.S.; Dong, Z.; Wei, J. Additively manufactured CoCrFeNiMn high-entropy alloy via pre-alloyed powder. Mater. Des. 2019, 168, 107576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haase, C.; Tang, F.; Wilms, M.B.; Weisheit, A.; Hallstedt, B. Combining thermodynamic modeling and 3D printing of elemental powder blends for high-throughput investigation of high-entropy alloys-Towards rapid alloy screening and design. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 688, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiratori, H.; Fujieda, T.; Yamanaka, K.; Koizumi, Y.; Kuwabara, K.; Kato, T.; Chiba, A. Relationship between the microstructure and mechanical properties of an equiatomic AlCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy fabricated by selective electron beam melting. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 656, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.C.; Gao, P.; Yu, H.C.; Yang, J.J.; Wang, Z.M.; Zeng, X.Y. Selective laser melting of an equiatomic AlCrCuFeNi high-entropy alloy: Processability, non-equilibrium microstructure and mechanical behavior. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 771, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Y.; Liu, Z.Y.; Qian, B.; Xuan, F.Z. Selective laser melting of CoCrFeNiMn high entropy alloy powder modified with nano-TiN particles for additive manufacturing and strength enhancement: Process, particle behavior and effects. Powder Technol. 2020, 360, 509–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunce, I.; Polanski, M.; Bystzycki, J. Microstructure and hydrogen storage properties of a TiZrNbMoV high entropy alloy synthesized using Laser Engineered Net Shaping (LENS). Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 9904–9910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapliyal, S.; Agrawal, P.; Agrawal, P.; Nene, S.S.; Mishra, R.S.; Mcwilliams, B.A.; Cho, K.C. Segregation engineering of grain boundaries of a metastable Fe-Mn-Co-Cr-Si high entropy alloy with laser-powder bed fusion additive manufacturing. Acta Mater. 2021, 219, 117271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Tan, Z.; He, D.Y.; Zhou, Z.L.; Zhou, Z.; Xue, Y.F.; Cui, L.; Wang, G.H.; Yang, Y. High strength and ductility AlCrFeNiV high entropy alloy with hierarchically heterogeneous microstructure prepared by selective laser melting. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 813, 152196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.W.; Chang, K.C.; Yeh, A.C. On the microstructure and properties of an advanced cemented carbide system processed by selective laser melting. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 782, 440–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarswat, P.; Smith, T.; Sarkar, S.; Murali, A.; Free, M. Design and Fabrication of New High Entropy Alloys for Evaluating Titanium Replacements in Additive Manufacturing. Materials 2020, 13, 3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Yu, Z.; Hu, W.; Lu, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Ji, Y.; Lu, Y.; Qin, Z.; Lu, X. In situ strengthening of CrMnFeCoNi high-entropy alloy with Al realized by laser additive manufacturing. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 847, 156563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.F.; Xiao, D.H.; Wu, Z.; Ou, X.Q. Al0.5FeCoCrNi high entropy alloy prepared by selective laser melting with gas-atomized pre-alloy powders. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 739, 86–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyrouzet, F.; Hachet, D.; Soulas, R.; Navone, C.; Godet, S.; Gorsse, S. Selective laser melting of Al0.3CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy: Printability, microstructure, and mechanical properties. J. Miner. Met. Mater. Soc. 2019, 71, 3443–3451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Peng, W.; Yang, L.; Fang, L. Effect of SLM processing parameters on microstructures and mechanical properties of Al0.5CoCrFeNi high entropy alloys. Metals 2020, 10, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.-C.; Chang, Y.-J.; Hsu, T.-H.; Gorsse, S.; Sun, F.; Furuhara, T.; Yeh, A.-C. Microstructure and tensile property of a precipitation strengthened high entropy alloy processed by selective laser melting and post heat treatment. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 36, 101601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewald, S.; Kies, F.; Hermsen, S.; Voshage, M.; Haase, C.; Schleifenbaum, J.H. Rapid alloy development of extremely high-alloyed metals using powder blends in laser powder bed fusion. Materials 2019, 12, 1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarswat, P.K.; Sarkar, S.; Murali, A.; Huang, W.; Tan, W.; Free, M.L. Additive manufactured new hybrid high entropy alloys derived from the AlCoFeNiSmTiVZr system. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 476, 242–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malatji, N.; Popoola, A.P.I.; Lengopeng, T.; Pityana, S. Effect of Nb addition on the microstructural, mechanical and electrochemical characteristics of AlCrFeNiCu high-entropy alloy. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2020, 27, 1332–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Niu, P.; Yuan, T.; Cao, P.; Chen, C.; Zhou, K. Selective laser melting of an equiatomic CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy: Processability, non-equilibrium microstructure and mechanical property. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 746, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhu, Z.G.; Chen, H.; Wang, A.G.; Liu, J.Q.; Liu, H.W.; Zhang, R.K.; Nai, S.L.M.; Primig, S.; Babu, S.S.; et al. Effect of cyclic rapid thermal loadings on the microstructural evolution of a CrMnFeCoNi high-entropy alloy manufactured by selective laser melting. Acta Mater. 2020, 196, 609–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, Y.; Bi, G.; Zhu, Z.; Ng, F.; Weng, F.; Liu, S.; Nai, S.; Lee, B. Microstructure and enhanced strength of laser aided additive manufactured CoCrFeNiMn high entropy alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 744, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cagirici, M.; Wang, P.; Ng, F.L.; Nai, M.L.S.; Ding, J.; Wei, J. Additive manufacturing of high-entropy alloys by thermophysical calculations and in situ alloying. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 94, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huser, G.; Demirci, I.; Aubry, P.; Guillot, I.; Perrière, L.; Rigal, E.; Maskrot, H. Study of the elaboration of high entropy material from powder by laser additive manufacturing. Procedia CIRP 2020, 94, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishimoto, T.; Ozasa, R.; Nakano, K.; Weinmann, M.; Schnitter, C.; Stenzel, M.; Matsugaki, A.; Nagase, T.; Matsuzaka, T.; Todai, M.; et al. Development of TiNbTaZrMo bio-high entropy alloy (BioHEA) super-solid solution by selective laser melting, and its improved mechanical property and biocompatibility. Scr. Mater. 2021, 194, 113658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhao, Y.Z.; Huang, S.; Zhu, S.; Wang, F.; Li, D.C. Manufacturing and Analysis of High-Performance Refractory High-Entropy Alloy via Selective Laser Melting (SLM). Materials 2019, 12, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.W.; Luo, P.; Zhang, L.J.; Lu, B.H. Selective laser melting of multi principal NiCrWFeTi alloy: Processing, microstructure and performance. Mater. Sci. Forum 2019, 944, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhou, X.; Wang, D.; Zhu, W.; Li, J.; Zhao, Y.F. AlCoCuFeNi high-entropy alloy with tailored microstructure and outstanding compressive properties fabricated via selective laser melting with heat treatment. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 743, 773–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwabara, K.; Shiratori, H.; Fujieda, T.; Yamanaka, K.; Koizumi, Y.; Chiba, A. Mechanical and corrosion properties of AlCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy fabricated with selective electron beam melting. Addit. Manuf. 2018, 23, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Zhou, R.; Wei, B.; Ni, S.; Liu, Y.; Song, M. Nanosized precipitates and dislocation networks reinforced C-containing CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy fabricated by selective laser melting. Mater. Charact. 2018, 144, 605–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.G.; Nguyen, Q.B.; Ng, F.L.; An, X.H.; Liao, X.Z.; Liaw, P.K.; Nai, S.M.L.; Wei, J. Hierarchical microstructure and strengthening mechanisms of a CoCrFeNiMn high entropy alloy additively manufactured by selective laser melting. Scr. Mater. 2018, 154, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Chabok, A.; Kooi, B.J.; Pei, Y. Additive manufactured high entropy alloys: A review of the microstructure and properties. Mater. Des. 2022, 220, 110875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, J.; Jarvis, T.; Wu, X.; Stanford, N.; Hodgson, P.; Fabijanic, D.M. Comparative study of the microstructures and mechanical properties of direct laser fabricated and arc-melted AlxCoCrFeNi high entropy alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 633, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, J.; Hodgson, P.; Jarvis, T.; Wu, X.; Stanford, N.; Fabijanic, D.M. Effect of hot isostatic pressing on the microstructure and mechanical properties of additive manufactured AlxCoCrFeNi high entropy alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 733, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, J.; Stanford, N.; Hodgson, P.; Fabijanic, D.M. Understanding the mechanical behaviour and the large strength/ductility differences between FCC and BCC AlxCoCrFeNi high entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 726, 885–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.; Wei, S.; Lau, K.B.; Teh, W.H.; Lee, J.J.; Seng, H.L.; Tan, C.C.; Wang, P.; Ramamurty, U. Compositionally graded AlxCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy manufactured by laser powder bed fusion. Materialia 2022, 21, 101308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwalani, B.; Gangireddy, S.; Shukla, S.; Yannetta, C.J.; Valentin, S.G.; Mishra, R.S.; Banerjee, R. Compositionally graded high entropy alloy with a strong front and ductile back. Mater. Today Commun. 2019, 20, 100602. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Li, Q.; Sun, R.; Chang, C.; Liu, B.; Ma, X. Effect of Mn addition on microstructure and corrosion behavior of AlCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy. Intermetallics 2024, 167, 108236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Z.P.; Liu, H.L.; Jiao, J.F.; Zhou, W.F.; Yang, Y.; Ren, X.D. Laser additive manufacturing of CrMnFeCoNi high entropy alloy: Microstructural evolution, high-temperature oxidation behavior and mechanism. Opt. Laser Technol. 2020, 130, 106326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Z.P.; Ren, X.D.; Jiao, J.F.; Zhou, W.F.; Ren, Y.P.; Ye, Y.X.; Larson, E.A.; Gu, J.Y. Laser additive manufacturing of FeCrCoMnNi high-entropy alloy: Effect of heat treatment on microstructure, residual stress and mechanical property. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 785, 1144–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, S.; Wan, D.; Solberg, K.; Berto, F.; Welo, T.; Yue, T.M.; Chan, K.C. Additive manufacturing of fine-grained and dislocation-populated CrMnFeCoNi high entropy alloy by laser engineered net shaping. J. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 761, 138056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.L.; Zhang, H.; Li, W.H.; Mao, A.Q.; Wang, L.; Song, G.S.; He, Y.Z. Microstructure and nanoindentation creep behavior of CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy fabricated by selective laser melting. Addit. Maanuf. 2019, 28, 766–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwalani, B.; Soni, V.; Waseem, O.A.; Mantri, S.A.; Banerjee, R. Laser additive manufacturing of compositionally graded AlCrFeMoVx (x = 0 to 1) high-entropy alloy system. Opt. Laser. Technol. 2019, 113, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.W.; Guo, Y.X.; Wang, F.P.; Shang, X.J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Q.B. A D019 precipitate strengthened laser additively manufactured V and Nb bearing CoCrFeNi based high entropy alloys. Mater. Des. 2023, 235, 112464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobbelstein, H.; Gurevich, E.L.; George, E.P.; Ostendorf, A.; Laplanche, G. Laser metal deposition of compositionally graded TiZrNbTa refractory high-entropy alloys using elemental powder blends. Addit. Manuf. 2019, 25, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, K.K.; Juan, C.C.; Tso, S.; Chen, H.C.; Tsai, C.W.; Yeh, J.W. Effects of Mo, Nb, Ta, Ti, and Zr on Mechanical Properties of Equiatomic Hf-Mo-Nb-Ta-Ti-Zr Alloys. Entropy 2019, 21, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.F.; Xiang, S.; Luan, H.W.; Amar, A.; Liu, X.; Lu, S.Y.; Zeng, Y.Y.; Le, G.M.; Wang, X.Y.; Qu, F.S.; et al. Additive manufacturing of high-strength CrMnFeCoNi high-entropy alloys-based composites with WC addition. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2019, 35, 2430–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.F.; Gao, M.D.; Shan, X.Y.; Shen, Q.Q.; Li, H.Z.; Li, Q.; Guan, B.Y.; Gao, R. synchronously enhancing the strength and ductility of CrMnFeCoNi high-entropy alloy with WC addition fabricated by laser additive manufacturing. Addit. Manuf. 2024, 31, 3212–3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Feng, Y.; Liu, B.; Yi, D.; Yang, X.; Zhang, W.; Chen, G.; Liu, Y.; Bai, P. Influence of NbC particles on microstructure and mechanical properties of AlCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy coatings prepared by laser cladding. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 788, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Qian, B.; Xu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xuan, F. Fine-structured CoCrFeNiMn high-entropy alloy matrix composite with 12 wt% TiN particle reinforcements via selective laser melting assisted additive manufacturing. Mater. Lett. 2019, 252, 88–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhang, L.; Yang, B. Grain refinement and localized amorphization of additively manufactured high-entropy alloy matrix composites reinforced by nano ceramic particles via selective-laser-melting/remelting. Compos. Commun. 2020, 19, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svetlizky, D.; Das, M.; Zheng, B.; Vyatskikh, A.L.; Bose, S.; Bandyopadhyay, A.; Schoenung, J.M.; Lavernia, E.J.; Eliaz, N. Directed energy deposition (DED) additive manufacturing: Physical characteristics, defects, challenges and applications. Mater. Today 2021, 49, 271–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, P.; Haridas, R.S.; Thapliyal, S.; Yadav, S.; Mishra, R.S.; McWilliams, B.A.; Cho, K.C. Metastable high entropy alloys: An excellent defect tolerant material for additive manufacturing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 826, 142005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Gu, J.; Gan, B.; Ni, S.; Bi, Z.; Wang, Z.; Song, M. Effects of elemental segregation and scanning strategy on the mechanical properties and hot cracking of a selective laser melted FeCoCrNiMn-(N,Si) high entropy alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 865, 158892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, Z.U.; Khalid, M.Y.; Rehman, E.U. Laser-aided additive manufacturing of high entropy alloys: Processes, properties, and emerging applications. Addit. Manuf. 2022, 78, 131–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.M.; Choe, J.; Kim, J.G.; Bae, J.W.; Moon, J.; Yang, S.; Kim, K.T.; Yu, J.H.; Kim, H.S. Superior tensile properties of 1%C-CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy additively manufactured by selective laser melting. Mater. Res. Lett. 2019, 8, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, C.; Li, S.; Wu, W.; Song, M.; Liu, B.; Liang, X.; Liaw, P.K. Microstructures and mechanical properties of C-containing FeCoCrNi high entropy alloy fabricated by selective laser melting. Intermetallics 2018, 94, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.G.; An, X.H.; Lu, W.J.; Li, Z.M.; Ng, F.L.; Liao, X.Z.; Ramamurty, U.; Nai, S.M.L.; Wei, J. Selective laser melting enabling the hierarchically heterogeneous microstructure and excellent mechanical properties in an interstitial solute strengthened high entropy alloy. Mater. Res. Lett. 2019, 7, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinwande, A.A.; Balogun, O.A.; Adediran, A.A.; Adesina, O.S.; Romanovski, V.; Jen, T.C. Experimental analysis, statistical modeling, and parametric optimization of quinary-(CoCrFeMnNi) 100-x/TiCx high-entropy-alloy (HEA) manufacturing by laser additive manufacturing. Results Eng. 2023, 17, 100802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, S.; Wan, D.; Solberg, K.; Berto, F.; Welo, T.; Yue, T.; Chan, K. Additively manufactured CrMnFeCoNi/AlCoCrFeNiTi0.5 laminated high-entropy alloy with enhanced strength-plasticity synergy. Scr. Mater. 2020, 183, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Craeghs, W.; Jing, C.; Gong, S.; Shan, F. Microstructure and physical performance of laser-induction nanocrystals modified high-entropy alloy composites on titanium alloy. Mater. Des. 2017, 117, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ye, Z.; Fu, J.; Qi, W.; Tian, Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, X. Microstructure evolution, texture and laser surface HEACs of Al-Mg-Si alloy for light automobile parts. Mater. Charact. 2020, 160, 110093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, P.; Li, R.; Zhu, S.; Wang, M.; Chen, C.; Yuan, T. Hot cracking, crystal orientation and compressive strength of an equimolar CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy printed by selective laser melting. Opt. Laser Technol. 2020, 127, 106147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabban, R.; Dash, K.; Suwas, S.; Murty, B.S. Strength-ductility synergy in high entropy alloys by tuning the thermo-mechanical process parameters: A comprehensive review. J. Indian Inst. Sci. 2022, 102, 91–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, S.; Li, J.; Luan, H.; Amar, A.; Lu, S.; Li, K.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X.; Le, G.; Wang, X.; et al. Effects of process parameters on microstructures and tensile properties of laser melting deposited CrMnFeCoNi high entropy alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 743, 412–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Piglione, A.; Dovgyy, B.; Hosseini, E.; Hooper, P.A.; Holdsworth, S.R.; Pham, M.-S. Cyclic plasticity and fatigue damage of CrMnFeCoNi high entropy alloy fabricated by laser powder-bed fusion. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 36, 101584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, D.C.; Chen, Z.H.; Huang, S.; Lu, Z.L.; Yan, H.Q. WxNbMoTa Refractory High-Entropy Alloys Fabricated by Laser Cladding Deposition. Materials 2019, 12, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.X.; Shang, X.J.; Liu, Q.B. Microstructure and properties of in-situ TiN reinforced laser cladding CoCr2FeNiTix high-entropy alloy composite coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 344, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brif, Y.; Thomas, M.; Todd, I. The use of high-entropy alloys in additive manufacturing. Scr. Mater. 2015, 99, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzminova, Y.O.; Firsov, D.G.; Dagesyan, S.A.; Konev, S.D.; Sergeev, S.N.; Zhilyaev, A.P.; Kawasaki, M.; Akhatov, I.S.; Evlashin, S.A. Fatigue behavior of additive manufactured CrFeCoNi medium-entropy alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 863, 158609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, B.; Chen, B.; Xuan, F. High-cycle fatigue induced twinning in CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy processed by laser powder bed fusion additive manufacturing. Addit. Manuf. 2023, 61, 103319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocelík, V.; Janssen, N.; Smith, S.N.; De Hosson, J.T.M. Additive manufacturing of high-entropy alloys by laser processing. J. Miner. Met. Mater. Soc. 2016, 68, 1810–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, P.D.; Li, R.D.; Yuan, T.C.; Zhu, S.Y.; Chen, C.; Wang, M.B.; Huang, L. Microstructures and properties of an equimolar AlCoCrFeNi high entropy alloy printed by selective laser melting. Intermetallics 2019, 104, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Liu, Y.; Liu, B.; Li, J.; Fang, Q. Precipitation behavior of selective laser melted FeCoCrNiC0.05 high entropy alloy. Intermetallics 2019, 106, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Li, S.; Zhou, Y.; Yan, M.; Attallah, M.M. Fabricating CoCrFeMnNi high entropy alloy via selective laser melting in-situ alloying. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2020, 43, 40–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Goh, M.; Zhu, Z.; Lee, X.; Nai, M.L.S.; Wei, J. On the machining of selective laser melting CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy. Mater. Des. 2018, 153, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piglione, A.; Dovgyy, B.; Liu, C.; Gourlay, C.M.; Hooper, P.A.; Pham, M.S. Printability and microstructure of the CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy fabricated by laser powder bed fusion. Mater. Lett. 2018, 224, 22–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, P.F.; Qi, T.B.; Chen, L.; Ge, T.; Ren, X.D. Manufacturing and analysis of VNbMoTaW refractory high-entropy alloy fabricated by selective laser melting. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2022, 105, 834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhao, Y.Z.; Cai, J.L.; Zheng, S.S.; Liu, Q.B. evolution of refractory MoFeCrTiWAlNb3 eutectic high-entropy alloy coating by laser cladding. Mater. Des. 2021, 129, 107039. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Yuan, T.C.; Li, R.D.; Lin, S.Q.; Niu, P.D.; Cristino, V. Effect of Mo on the morphology, microstructure and mechanical properties of NbTa0.5TiMox refractory high entropy alloy fabricated by laser powder bed fusion using elemental mixed powders. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2023, 111, 106107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, M.; Wang, H.; Li, Z.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, B.; Li, J.; Ran, X. Mitigating hot-cracking of laser melted CoCrFeNiMnTix high-entropy alloys. Mater. Lett. 2022, 314, 131771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunce, I.; Polanski, M.; Karczewski, K.; Plocinski, T.; Kurzydlowski, K.J. Microstructural characterisation of high-entropy alloy AlCoCrFeNi fabricated by laser engineered net shaping. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 648, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sistla, H.R.; Newkirk, J.W.; Liou, F.F. Effect of Al/Ni ratio, heat treatment on phase transformations and microstructure of AlxFeCoCrNi2 x (x=0.3, 1) high entropy alloys. Mater. Des. 2015, 81, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, Q.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Xu, S.; Zhao, F.; Gong, L.; Liu, B.; Liu, J.; Liu, G. The microstructure and mechanical properties of the additive manufactured AlCoCrFeNi high entropy alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 833, 142507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Xie, S.; Niu, P.; Zhang, Z.; Yuan, T.; Ren, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Li, R. Additive manufacturing of Al0.3CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy by powder feeding laser melting deposition. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 862, 158286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Guo, Y.; Liu, Q.; Shang, X. A novel D022 precipitation-hardened Ni2.1CoCrFe0.5Nb0.2 high entropy alloy with outstanding tensile properties by additive manufacturing. Virtual Phys. Prototyp. 2023, 18, e2147553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B.; Li, J.; Yang, C.; Zhang, Y.S.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.H. Microstructure and mechanical properties of a refractory AlMo0.5NbTa0.5TiZr high-entropy alloy manufactured by laser-directed energy deposition. Mater. Lett. 2023, 335, 133748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, S.; Luan, H.; Wu, J.; Yao, K.F.; Li, J.; Liu, X.; Tian, Y.; Mao, W.; Bai, H.; Le, G.; et al. Microstructures and mechanical properties of CrMnFeCoNi high entropy alloys fabricated using laser metal deposition technique. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 773, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.W.; Gu, J.; An, D.Y.; Liu, Y.; Song, M. Characterization of the microstructure and deformation substructure evolution in a hierarchal high-entropy alloy by correlative EBSD and ECCI. Intermetallics 2020, 121, 106788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.X.; Liu, T.; He, D.D.; Li, Z.J.; Chen, L.; Su, H.H.; Fu, P.X.; Dai, P.Q.; Huang, W.D. Sustaining strength-ductility synergy of SLM Fe50Mn30Co10Cr10 metastable high-entropy alloy by Si addition. Intermetallics 2022, 145, 107565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amar, A.; Li, J.F.; Xiang, S.; Liu, X.; Zhou, Y.Z.; Le, G.M.; Wang, X.Y.; Qu, F.S.; Ma, S.Y.; Dong, W.M.; et al. Additive manufacturing of high-strength CrMnFeCoNi-based High Entropy Alloys with TiC addition. Intermetallics 2019, 109, 162–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.K.; Baek, M.S.; Yang, S.; Lee, K.A. In-situ formed oxide enables extraordinary high-cycle fatigue resistance in additively manufactured CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy. Addit. Manuf. 2021, 38, 101832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Yang, C.; Li, S.; Attallah, M.M.; Yan, M. In-situ alloyed, oxide-dispersion-strengthened CoCrFeMnNi high entropy alloy fabricated via laser powder bed fusion. Mater. Des. 2020, 194, 108966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujieda, T.; Chen, M.; Shiratori, H.; Kuwabara, K.; Yamanaka, K.; Koizumi, Y.; Chiba, A.; Watanabe, S. Mechanical and corrosion properties of CoCrFeNiTi-based high-entropy alloy additive manufactured using selective laser melting. Addit. Manuf. 2019, 25, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Xu, L.; Li, X.; Jing, H.; Qin, G.; Pang, H.; Minami, F. A si-containing FeCoCrNi high- entropy alloy with high strength and ductility synthesized in situ via selective laser melting. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 35, 101340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Xi, S.; Chen, Z.; Wei, P.; He, C.; Li, T.; Gao, Y.; Wu, H. Additively manufactured fine grained Ni6Cr4WFe9Ti high entropy alloys with high strength and ductility. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 767, 138394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Lu, Y. Laser 3D printing of CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy. Mater. Lett. 2019, 236, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melia, M.A.; Carroll, J.D.; Whetten, S.R.; Esmaeely, S.N.; Locke, J.; White, E.; Anderson, I.; Chandross, M.; Michael, J.R.; Argibay, N.; et al. Mechanical and corrosion properties of additively manufactured CoCrFeMnNi high entropy alloy. Addit. Manuf. 2019, 29, 100833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhou, S.; Xiong, Z.; Liang, Y.J.; Xue, Y.; Wang, L. Enabling stronger eutectic high-entropy alloys with larger ductility by 3D printed directional lamellae. Addit. Manuf. 2021, 39, 101901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujieda, T.; Shiratori, H.; Kuwabara, K.; Kato, T.; Yamanaka, K.; Koizumi, Y.; Chiba, A. First demonstration of promising selective electron beam melting method for utilizing high-entropy alloys as engineering materials. Mater. Lett. 2015, 159, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nartu, M.S.K.K.Y.; Alam, T.; Dasari, S.; Mantri, S.A.; Gorsse, S.; Siller, H.; Dahotre, N.; Banerjee, R. Enhanced tensile yield strength in laser additively manufactured Al0.3CoCrFeNi high entropy alloy. Materialia 2020, 9, 100522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Xu, L.; Han, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jing, H.; Zhao, L.; Minami, F. Structure and mechanical properties of a FeCoCrNi high-entropy alloy fabricated via selective laser melting. Intermetallics 2020, 127, 106963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Zhou, R.; Gu, J.; Wang, Z.; Ni, S.; Liu, Y. Nitrogen induced heterogeneous structures overcome strength-ductility trade-off in an additively manufactured high-entropy alloy. Appl. Mater. Today 2020, 18, 100498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Su, Y.; Wang, Z. Tailored microstructures and strengthening mechanisms in an additively manufactured dual-phase high-entropy alloy via selective laser melting. Sci. China Mater. 2020, 63, 1279–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.H.; Zhai, Q.; Wang, K.L.; Chen, G.X.; Yin, X.T.; Zhang, Q.X.; Meng, L.T.; Wang, S.H.; Wang, L. Fabrication of Fe-based metallic glass reinforced FeCoNiCrMn high-entropy alloy through additive manufacturing: Mechanical property enhancement and corrosion resistance improvement. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 16, 899–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.C.; Chau, J.L.H.; Weng, C.J.; Chen, C.S.; Chou, Y.H. Preparation of high-entropy AlCoCrCuFeNiSi alloy powders by gas atomization process. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2017, 202, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegues, J.W.; Melia, M.A.; Puckett, R.; Whetten, S.R.; Argibay, N.; Kustas, A.B. Exploring additive manufacturing as a high-throughput screening tool for multiphase high entropy alloys. Addit. Manuf. 2021, 37, 101598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Wu, Q.; Chen, D.; Han, B.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Kai, J.J. Abnormal γ′′-ε phase transformation in the CoCrFeNiNb0.25 high entropy alloy. Scr. Mater. 2018, 146, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Dong, Y.; Li, C.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, P. Excellent strengthening effect of L12 precipitates on the selective laser melting Al0.3CoCrFeNiCu high entropy alloy via annealing treatment. Mater. Lett. 2021, 304, 130628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Cheng, X. Effect of Al addition on the microstructure and hardness of the (AlxCoCrFe)50Ni high-entropy alloy prepared by directed energy deposition technique. Mater. Lett. 2021, 285, 128778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Chen, D.; Han, B.; Wu, Q.; Wang, Z.; Wei, S.; Wei, D.; Wang, J.; Liu, C.; Kai, J.-J. Design of D022 superlattice with superior strengthening effect in high entropy alloys. Acta Mater. 2019, 167, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.Y.; Wang, H.; Huang, H.L.; Xu, X.D.; Chen, M.W.; Wu, Y.; Liu, X.J.; Nieh, T.G.; An, K.; Lu, Z.P. A precipitation-hardened high-entropy alloy with outstanding tensile properties. Acta Mater. 2016, 102, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.Q.; Wan, D.; Guan, S.; Fu, Y.Q.; Zhang, Z.L.; He, J.Y. comparative study on nanoscale mechanical properties of CrMnFeCoNi high-entropy alloys fabricated by casting and additive manufacturing. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 22, 1211–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.; Yao, C.; Feng, K.; Li, Z.; Chu, P.K. Cryogenic deformation mechanism of CrMnFeCoNi high-entropy alloy fabricated by laser additive manufacturing process. Int. J. Lightweight Mater. Manuf. 2018, 1, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; Zhang, X.; Zhai, C.S.; Jiang, S.N.; Emre, A.; Zhang, X.; Hua, X.J. Microstructure evolution and electrochemical corrosion behavior of FeCrCoNiMoB1.1Si1.2 high-entropy alloy coating via laser cladding. Electrochim. Acta 2024, 507, 145153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.F.; An, L.B.; Shao, G.H.; Wang, K.; Mi, Y.Y.; Du, X.D. Effect of heat treatment temperature on microstructure and electrochemical behavior of additive-manufactured AlCoCrFeNi high entropy alloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 30, 1228–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Amar, A.; Jiang, C.; Luan, H.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, H.; Le, G.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Yang, X.; et al. CoCrFeNiMo0.2 high entropy alloy by laser melting deposition: Prospective material for low temperature and corrosion resistant applications. Intermetallics 2020, 119, 106727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Xia, Z.; Zhao, D.; Xie, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, L. Microstructure formation mechanism and corrosion behavior of FeCrCuTiV two-phase high entropy alloy prepared by different processes. Fusion Eng. Des. 2021, 172, 112792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.Y.; Sheikh, S.; Ou, P.; Chen, D.C.; Hu, Q.; Guo, S. Corrosion behavior of Hf0.5Nb0.5Ta0.5Ti1.5Zr refractory high entropy in aqueous chloride solutions. Electrochem. Commun. 2019, 98, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhang, K.; Davies, C.; Wu, X. Evolution of microstructure, mechanical and corrosion properties of AlCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy prepared by direct laser fabrication. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 694, 971–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.L.; Zhang, H.; Du, X.J.; He, Y.Z.; Luo, H.; Song, G.S.; Mao, L.; Zhou, T.W.; Wang, L.L. Corrosion resistance enhancement of CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy fabricated by additive manufacturing. Corros. Sci. 2021, 177, 108954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapliyal, S.; Nene, S.S.; Agrawal, P.; Wang, T.; Morphew, C.; Mishra, R.S.; McWilliams, B.A.; Cho, K.C. Damage-tolerant, corrosion-resistant high entropy alloy with high strength and ductility by laser powder bed fusion additive manufacturing. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 36, 101455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nene, S.S.; Frank, M.; Liu, K.; Sinha, S.; Mishra, R.S.; McWilliams, B.A.; Cho, K.C. Corrosion-resistant high entropy alloy with high strength and ductility. Scr. Mater. 2019, 166, 168–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujieda, T.; Shiratori, H.; Kuwabara, K.; Hirota, M.; Kato, T.; Yamanaka, K.; Koizumi, Y.; Chiba, A.; Watanabe, S. CoCrFeNiTi-based high-entropy alloy with superior tensile strength and corrosion resistance achieved by a combination of additive manufacturing using selective electron beam melting and solution treatment. Mater. Lett. 2016, 189, 148–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.; Sarswat, P.K.; Free, M.L. Elevated temperature corrosion resistance of additive manufactured single phase AlCoFeNiTiV0.9Sm0.1 and AlCoFeNiV0.9Sm0.1 HEAs in a simulated syngas atmosphere. Addit. Manuf. 2019, 30, 100902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Xin, H.Y.; Li, X.M.; Chen, X.Z. Complex multiphase predicting of additive manufactured high entropy alloys based on data augmentation deep learning. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 28, 2388–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).