On the Effect of Multi-Pass Friction Stir Processing on Microstructure-Tensile Deformation Behavior Relationships in Cast Al-7%Si-0.4%Mg Specimens
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Details
3. Results and Discussion
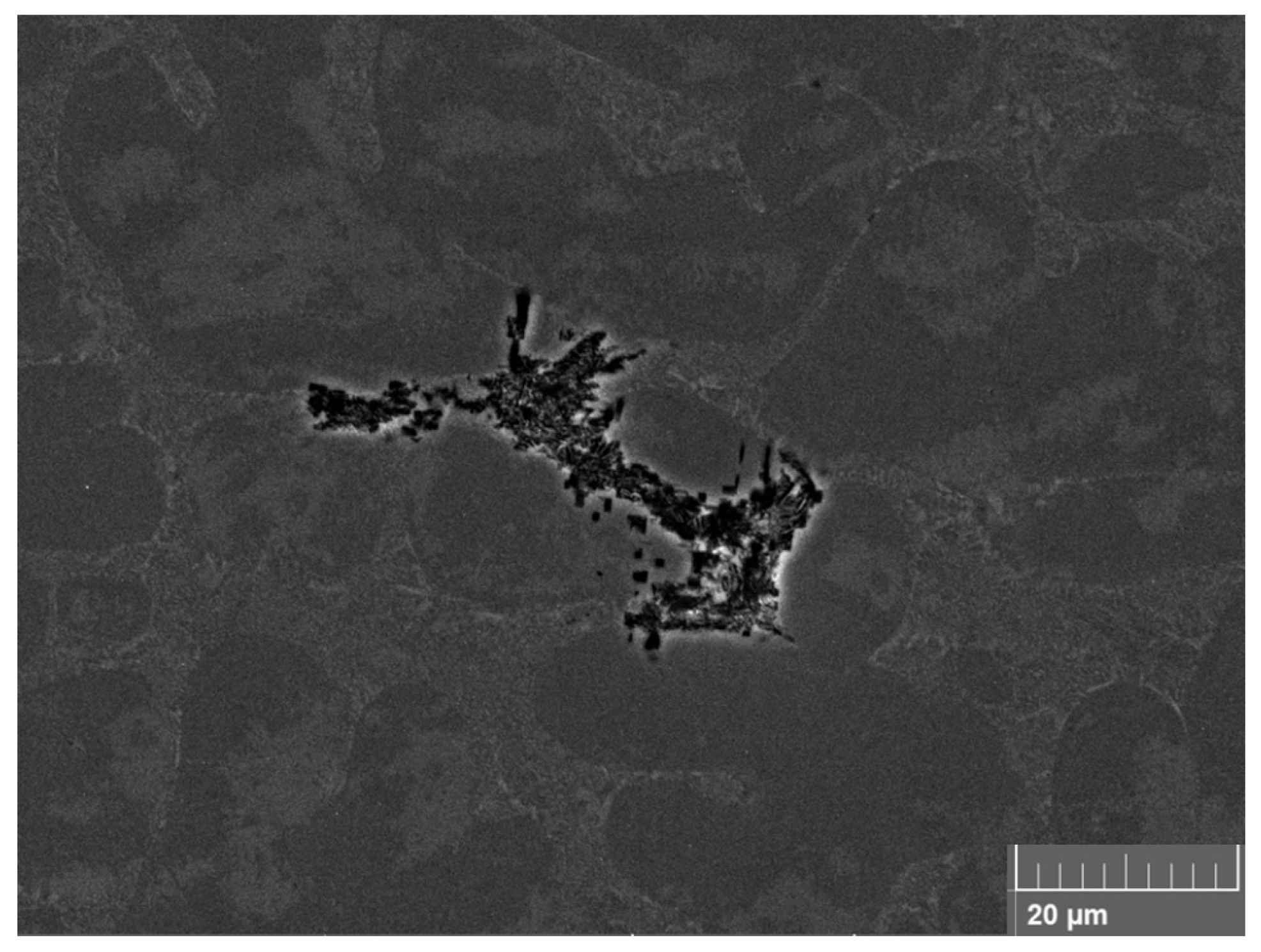
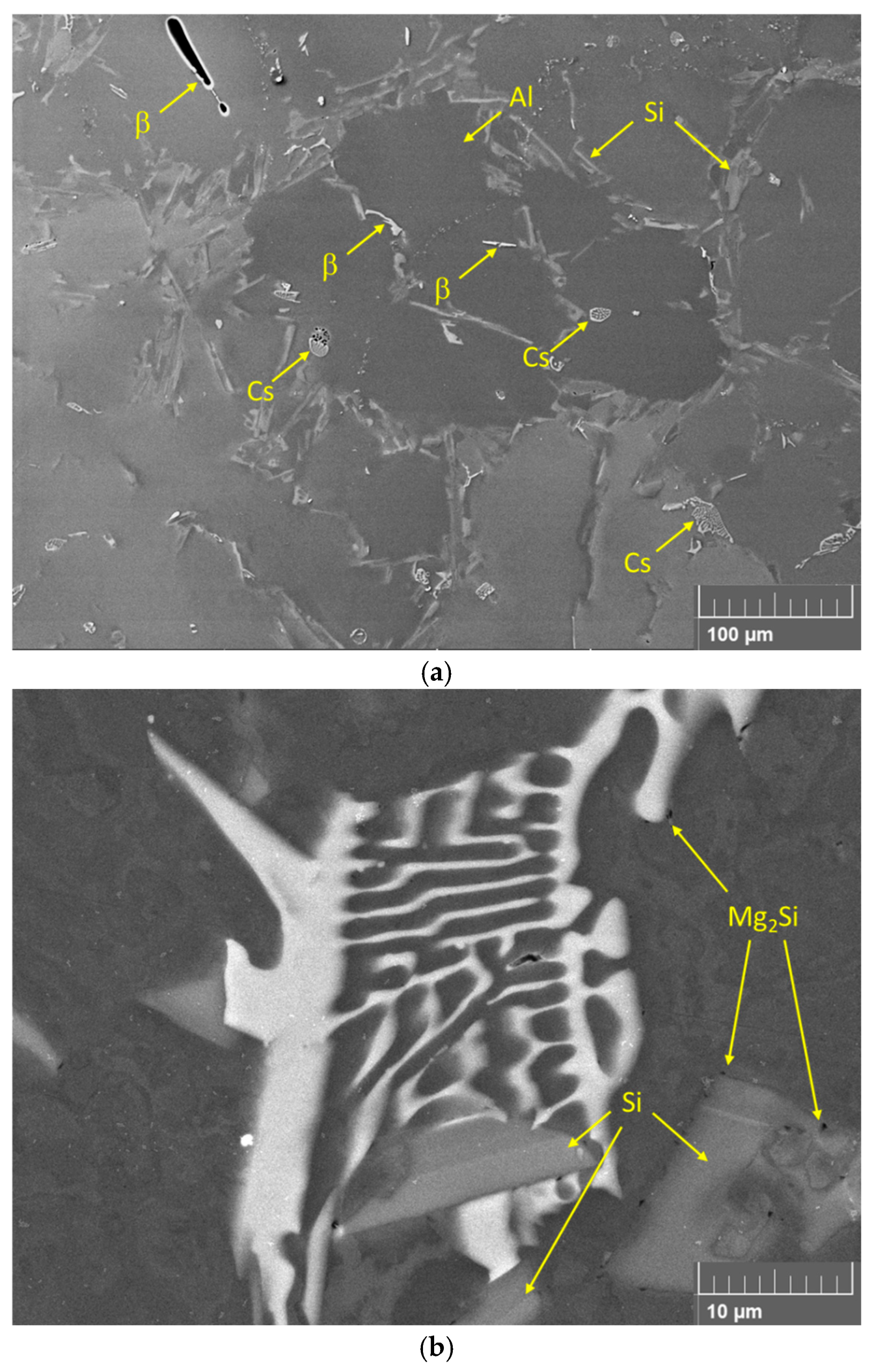
3.1. Microstructural Characterization of As-Cast Specimens
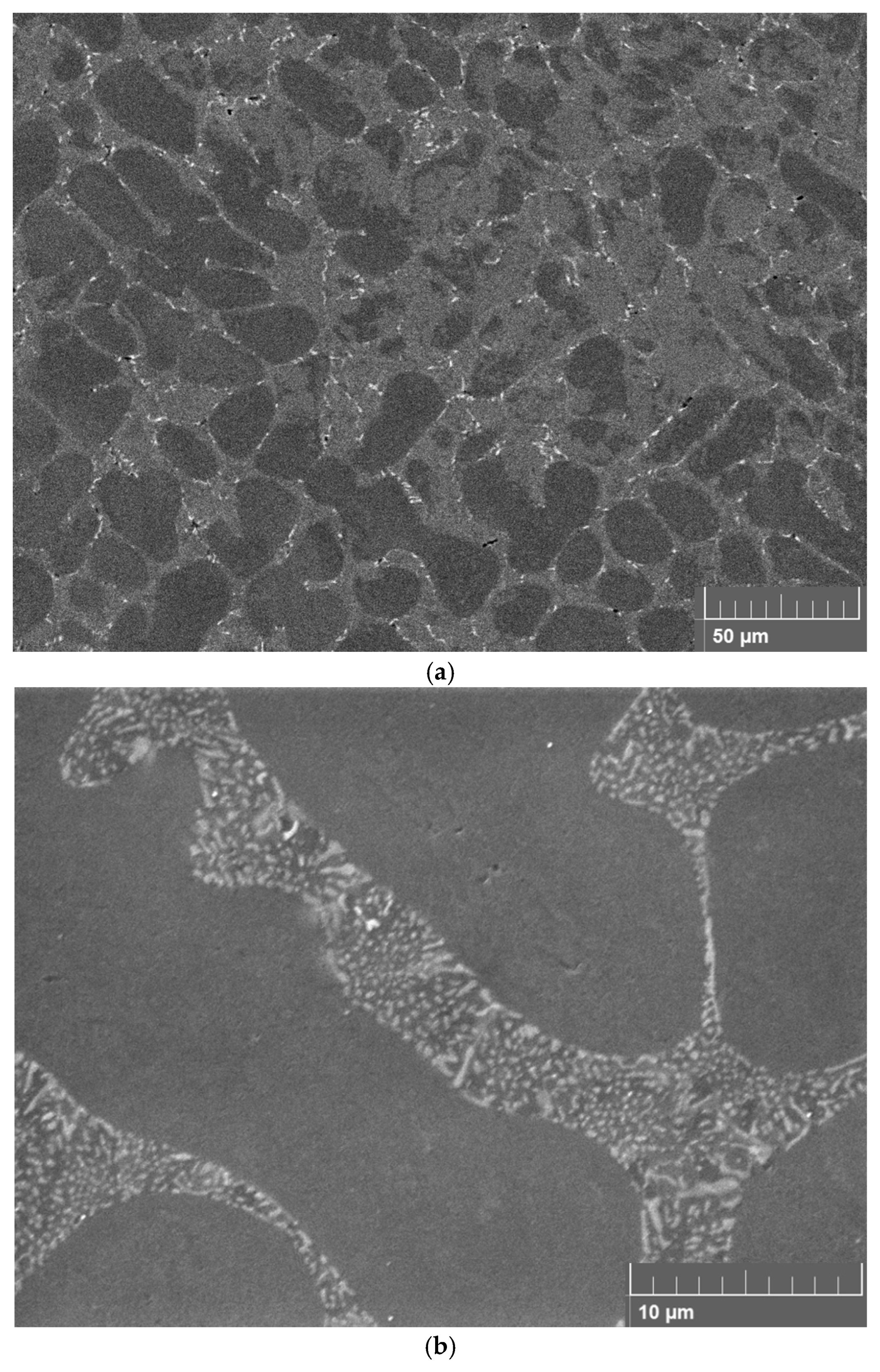
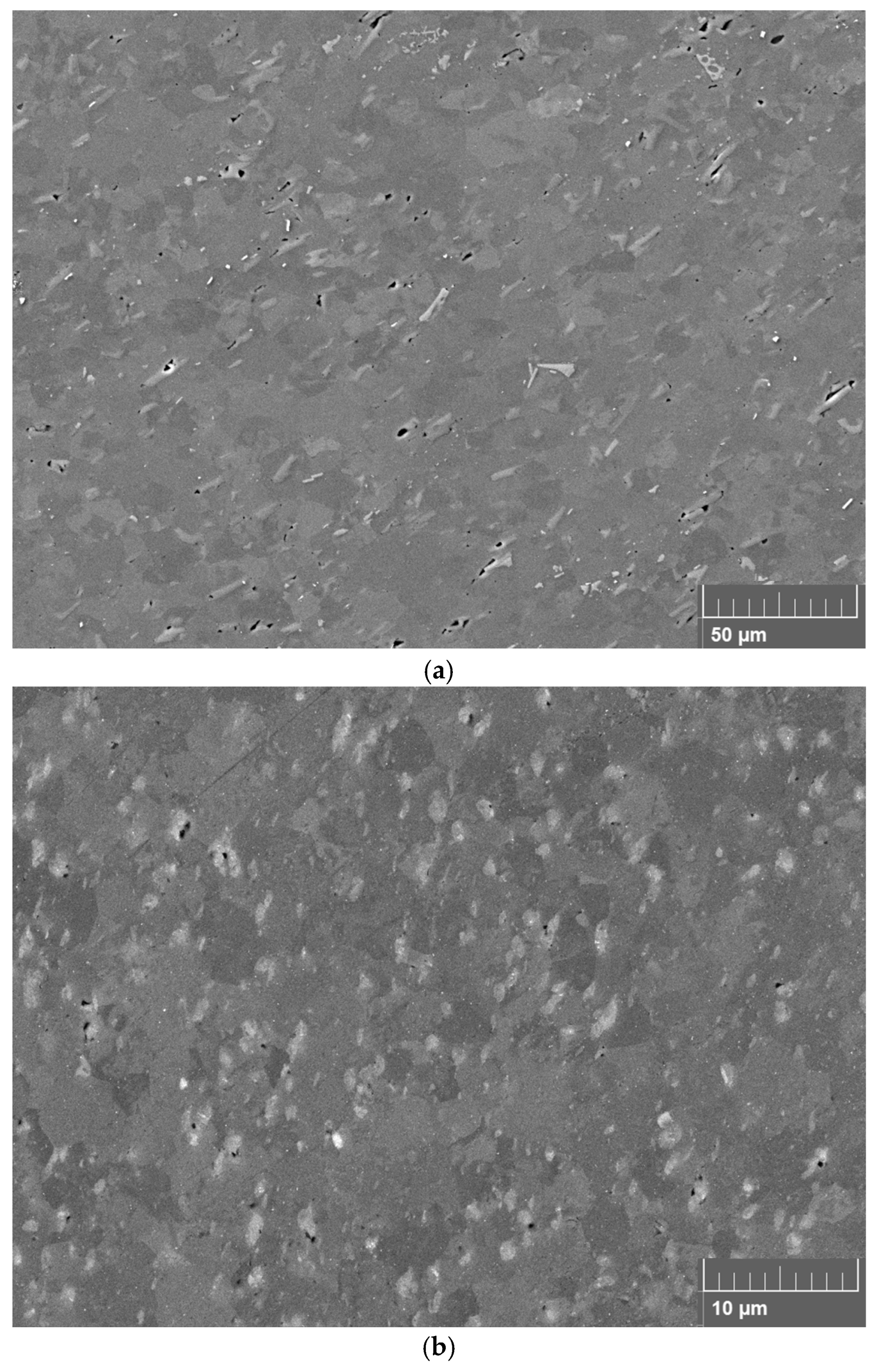
3.2. Microstructural Characterization of FSPed Specimens
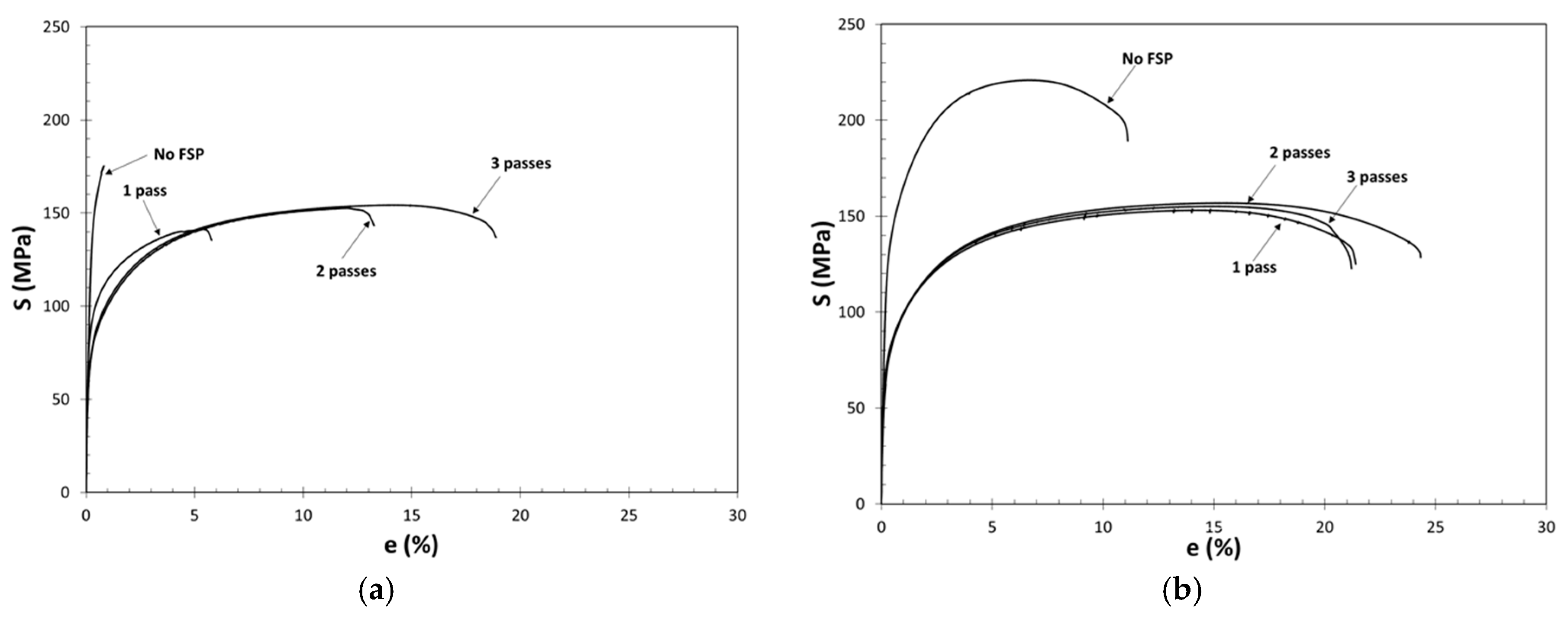
3.3. Characterization of Tensile Deformation
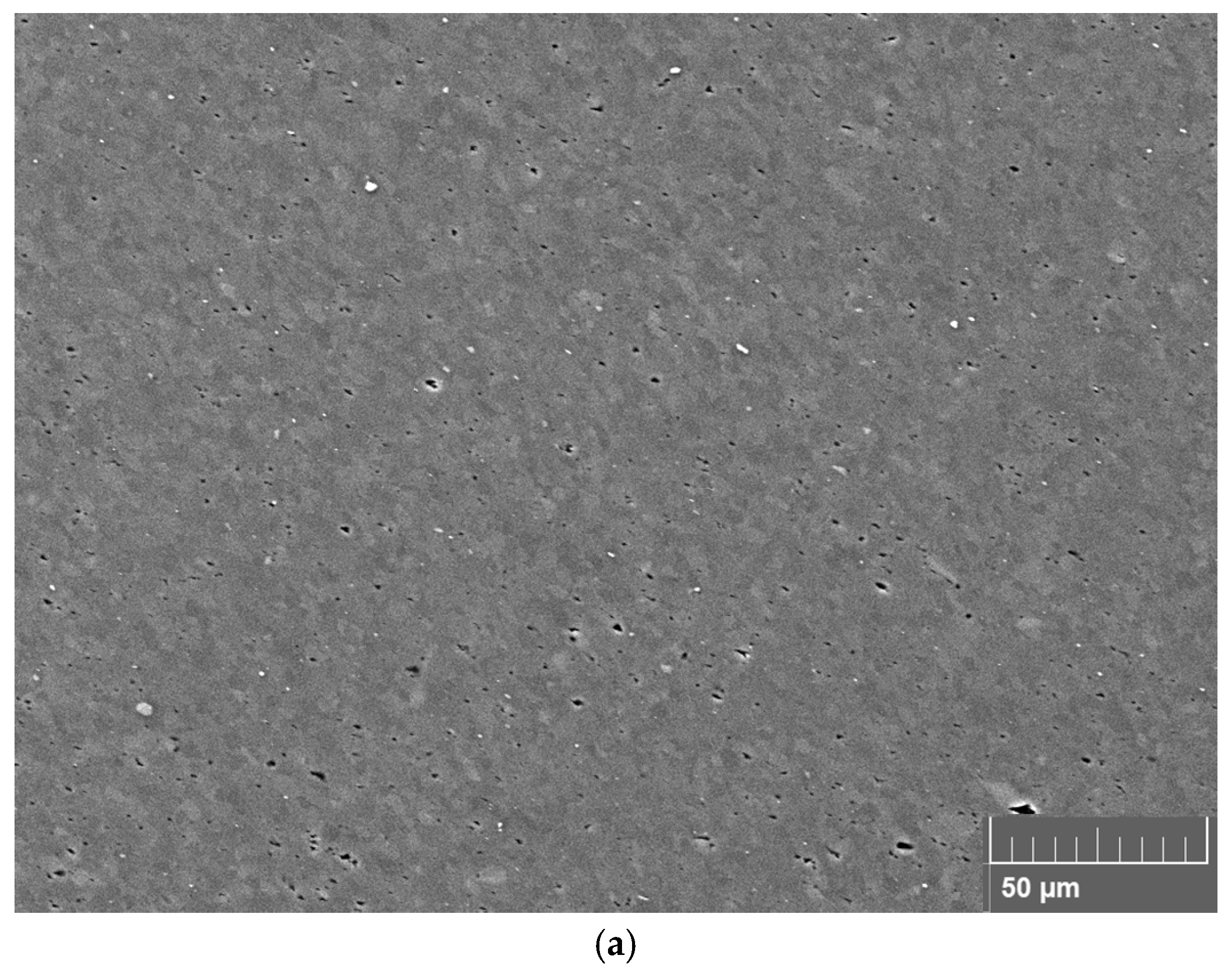
3.4. Structural Quality Assessment
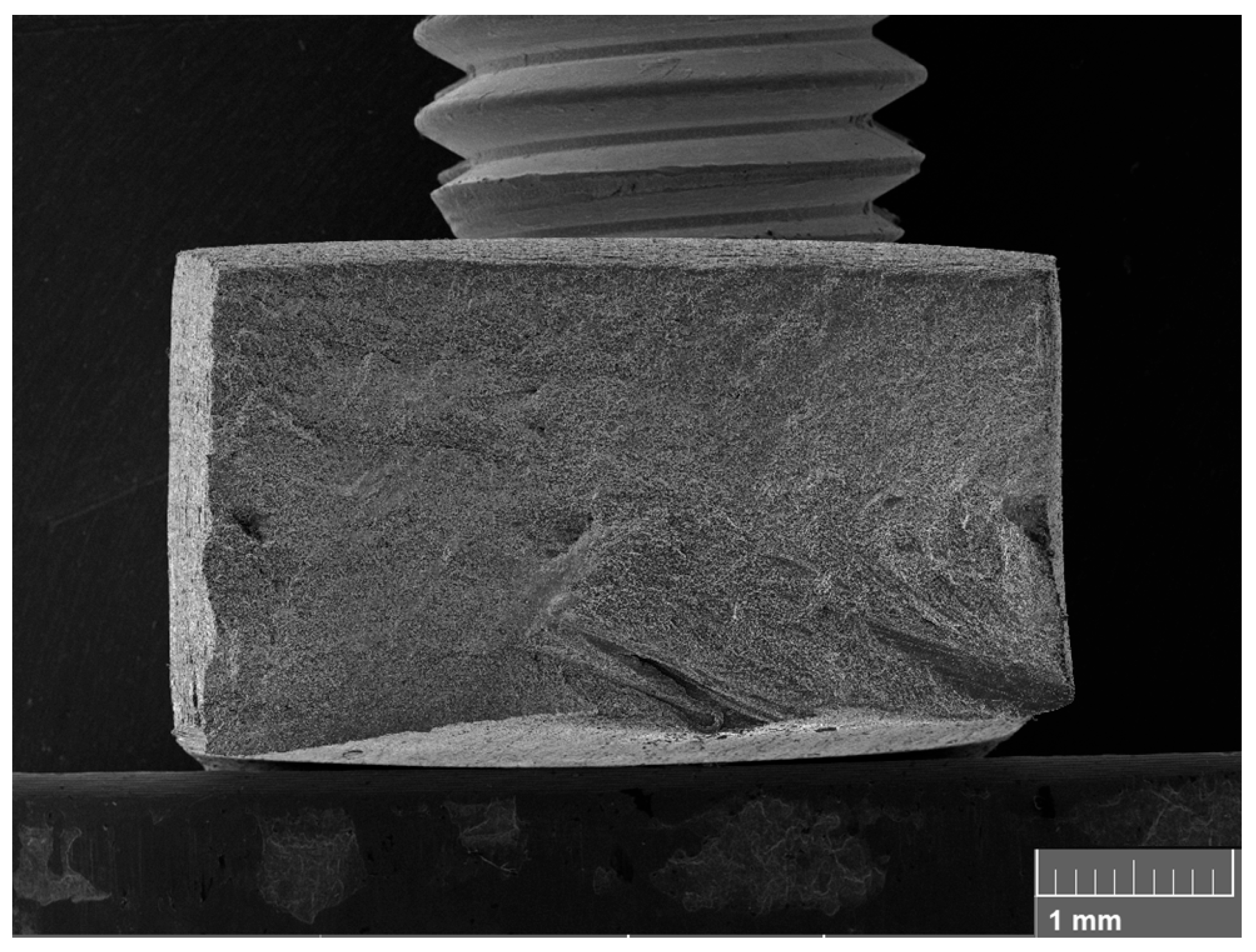
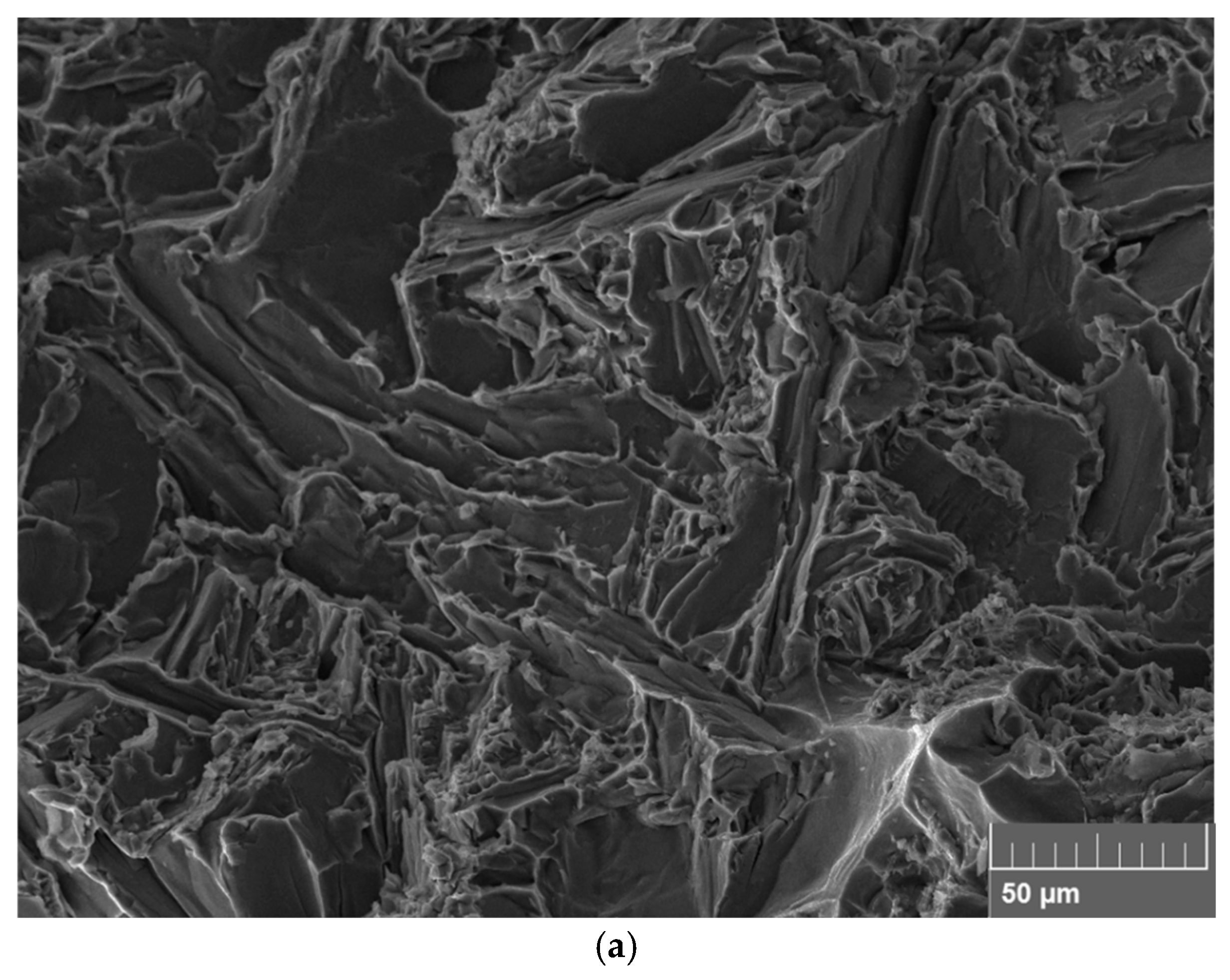
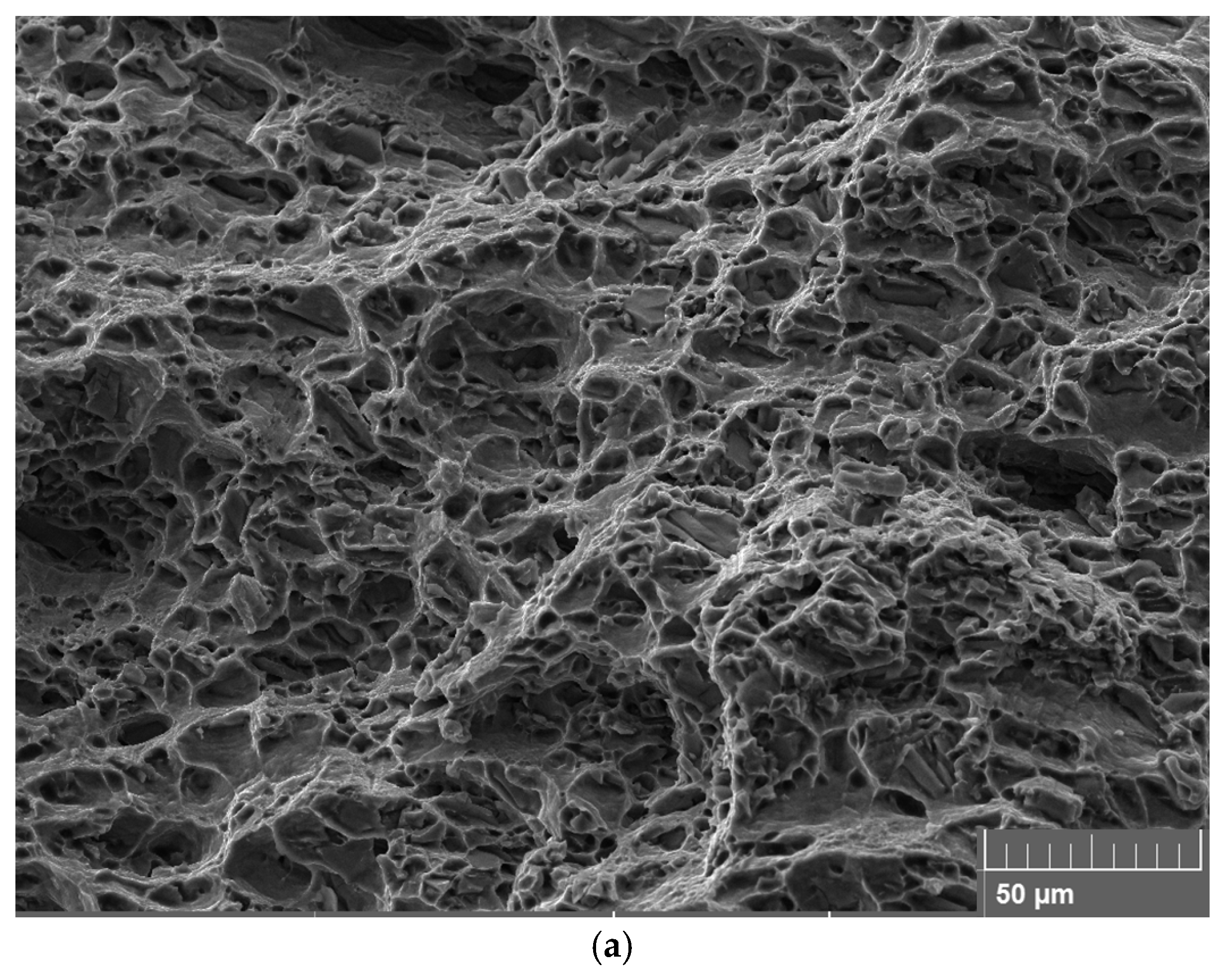
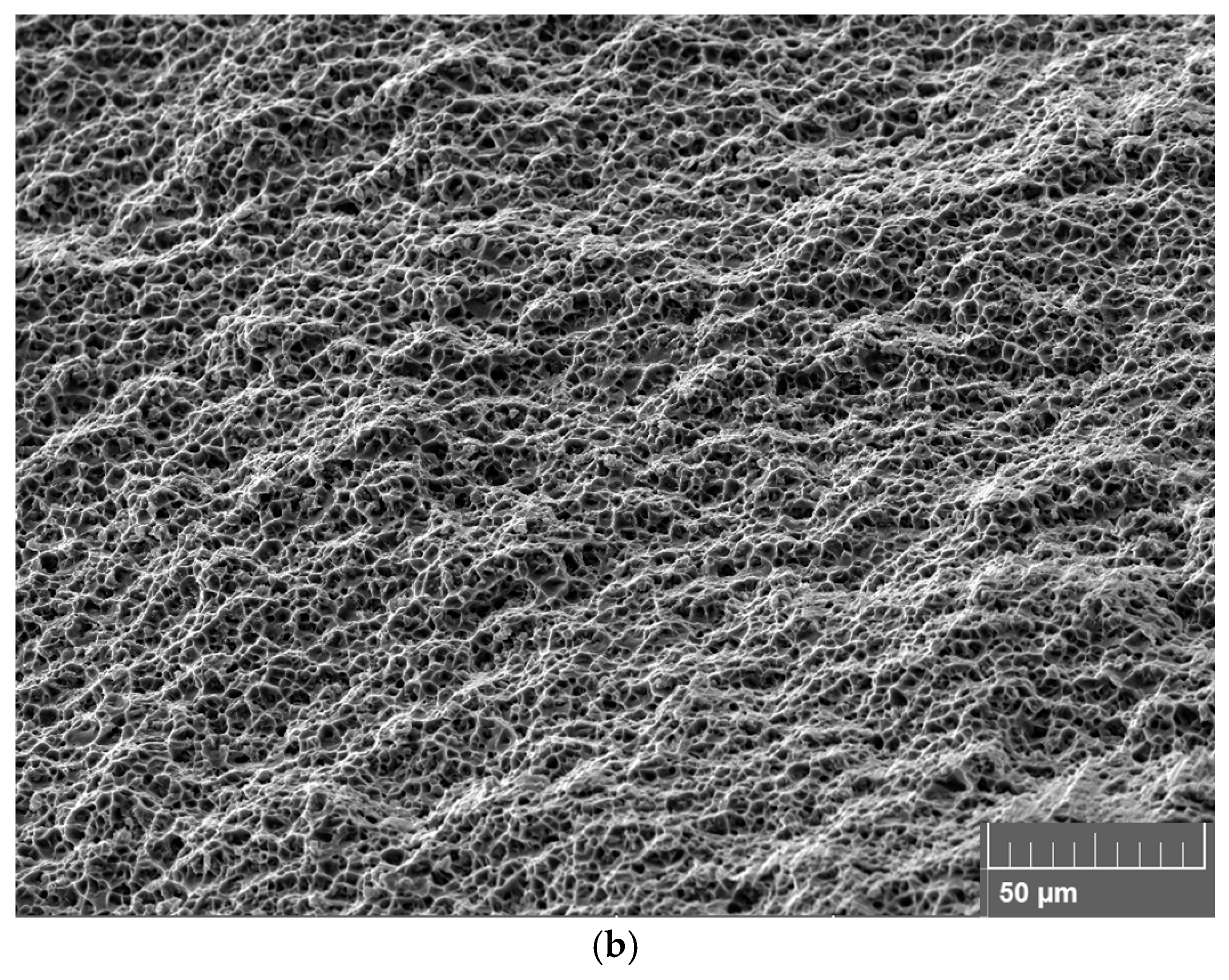
3.5. Fracture Surfaces
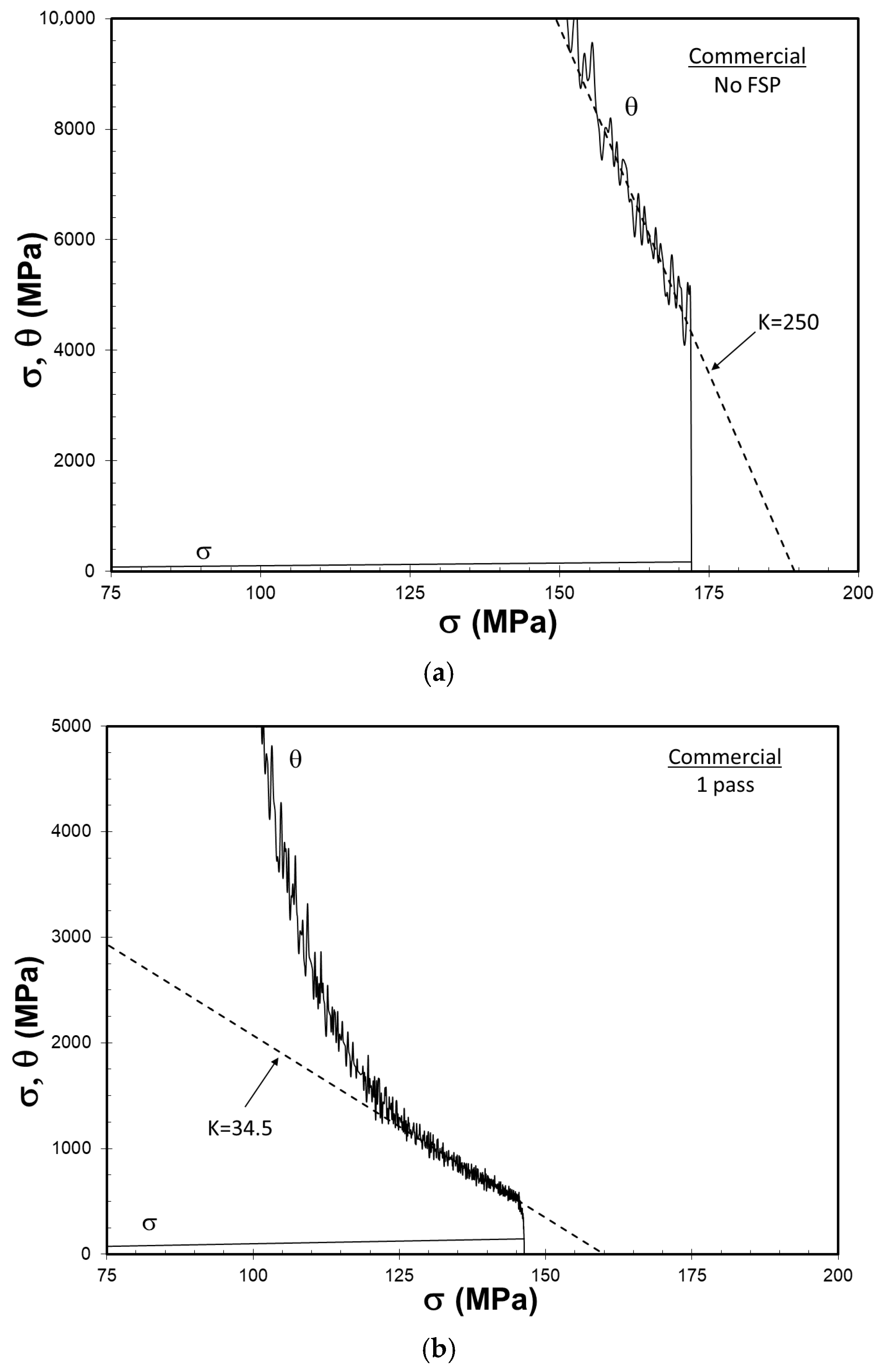
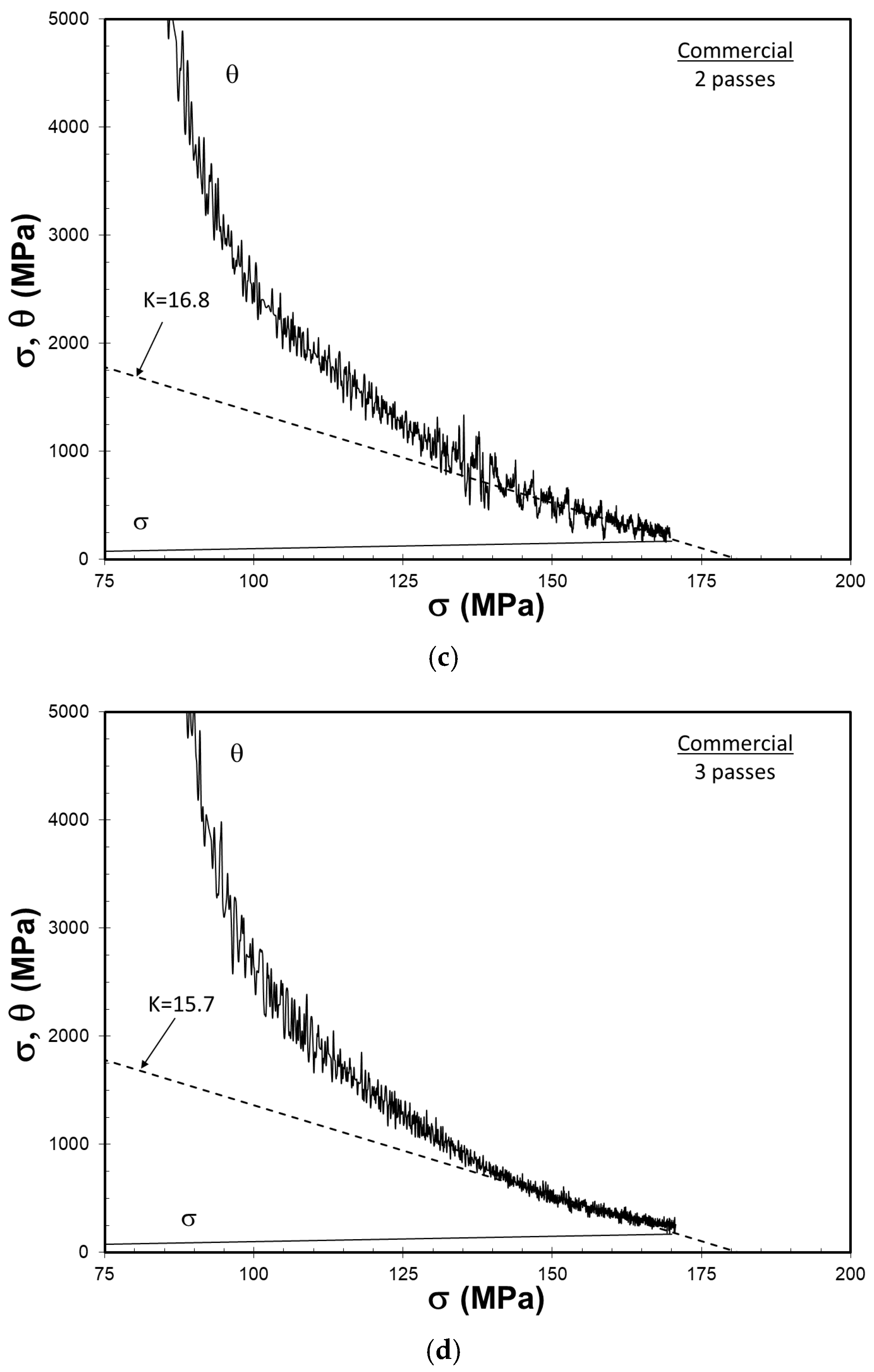
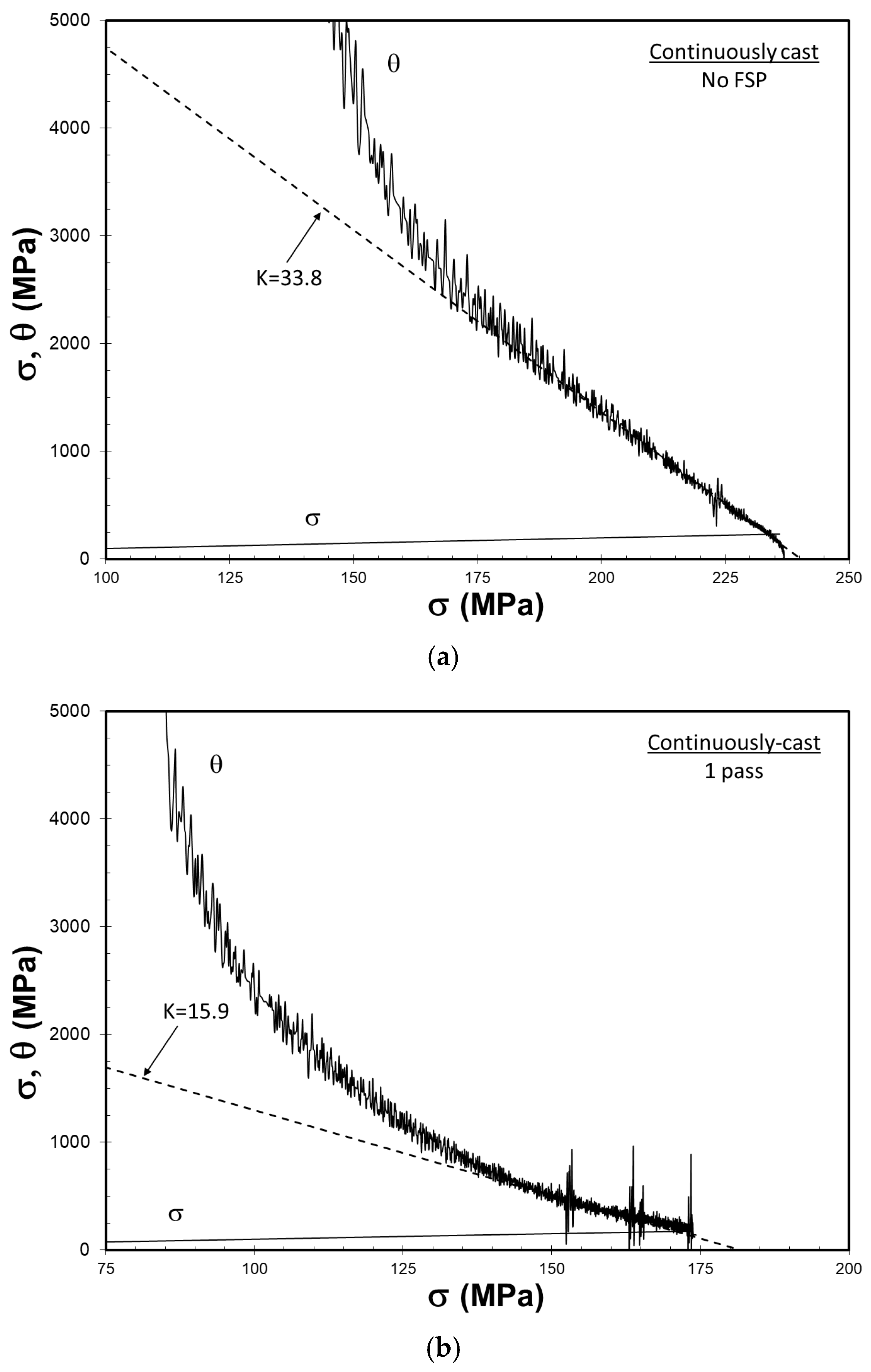
3.6. Characterization of Work Hardening Behavior
3.7. Correlation Between Si Particle Size and Tensile Deformation
4. Conclusions
- The effect of FSP on microstructure is determined by the as-cast microstructure. When the as-cast microstructure contains acicular Si particles, each FSP pass reduces the size of these particles and their nearest neighbor distance. When the as-cast material has fine Si particles, Si particles coalesce more after each FSP pass, and their nearest neighbor distance increases.
- There is evidence suggesting that there may be a limiting microstructure that can be reached from both as-cast conditions with more than three FSP passes. Once reached, additional FSP passes would not change the Si particle size or their spacing. More research is needed to test this hypothesis.
- A clear benefit of FSP is the breaking up of bifilms entrained into the metal in its liquid state, in addition to the refinement and homogenization of the microstructure. The number of passes necessary to eliminate all bifilms is determined by the extent of liquid metal damage in the specimens.
- With each FSP pass, structural quality has improved progressively in the commercial ingot, as evidenced by an increase in elongation from 1.0 to 18.8% after three FSP passes. In the continuously cast ingot, elongation has almost doubled after the first FSP pass, increasing from 10.9 to 21.1%. However, additional FSP passes have had essentially no effect on elongation.
- Work hardening characteristics of FSPed specimens have displayed a distinct Stage III work hardening, following the model developed by Kocks and Mecking.
- Elongation and quality index of all specimens have been correlated with the Kocks–Mecking parameter, K, for the first time, to the authors’ knowledge. The empirical relationship developed in this study is consistent with the data from two independent studies for Al–7 wt.%Si–Mg alloys processed differently.
- There is evidence that the improvement in elongation and structural quality in Al-Si alloys with FSP may not be due to the refinement of Si particles, but rather to the reduction and elimination of bifilms, i.e., liquid metal damage.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- John Baruch, L.; Raju, R.; Balasubramanian, V.; Rao, A.G.; Dinaharan, I. Influence of Multi-pass Friction Stir Processing on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Die Cast Al–7Si–3Cu Aluminum Alloy. Acta Metall. Sin. 2016, 29, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alidokht, S.A.; Abdollah-zadeh, A.; Soleymani, S.; Saeid, T.; Assadi, H. Evaluation of microstructure and wear behavior of friction stir processed cast aluminum alloy. Mater. Charact. 2012, 63, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangulee, A.; Gurland, J. On the Fracture of Silicon Particles in Aluminum-Silicon Alloys. Trans. TMS-AIME 1967, 239, 269–272. [Google Scholar]
- Mueller, M.G.; Fornabaio, M.; Žagar, G.; Mortensen, A. Microscopic strength of silicon particles in an aluminium–silicon alloy. Acta Mater. 2016, 105, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, M.G.; Žagar, G.; Mortensen, A. In-situ strength of individual silicon particles within an aluminium casting alloy. Acta Mater. 2018, 143, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiryakioğlu, M. Intrinsic and Extrinsic Effects of Microstructure on Properties in Cast Al Alloys. Materials 2020, 13, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umeno, Y.; Kushima, A.; Kitamura, T.; Gumbsch, P.; Li, J. Ab initiostudy of the surface properties and ideal strength of (100) silicon thin films. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 72, 165431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, S.M.M.; Rignanese, G.M.; Pardoen, T.; Charlier, J.C. Ideal strength of silicon: An ab initio study. Phys. Rev. B 2006, 74, 235203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finlayson, T.; Griffiths, J.; Viano, D.; Fitzpatrick, M.; Oliver, E.; Wang, Q. Stresses in the Eutectic Silicon Particles of Strontium-Modified A356 Castings Loaded in Tension. In Proceedings of the Shape Casting: 2nd International Symposium, Orlando, FL, USA, 25 February–1 March 2007; pp. 127–134. [Google Scholar]
- Joseph, S.; Kumar, S.; Bhadram, V.S.; Narayana, C. Stress states in individual Si particles of a cast Al–Si alloy: Micro-Raman analysis and microstructure based modeling. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 625, 296–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, S.J.; O’Neill, A.; Boileau, J.; Donlon, W.; Su, X.; Majumdar, B. Application of the Raman technique to measure stress states in individual Si particles in a cast Al–Si alloy. Acta Mater. 2007, 55, 1681–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, M.G.; Fornabaio, M.; Mortensen, A. Silicon particle pinhole defects in aluminium–silicon alloys. J. Mater. Sci. 2016, 52, 858–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, C.J.; Finlayson, T.R.; Fitzpatrick, M.E.; Griffiths, J.R.; Oliver, E.C.; Wang, Q. Observations of the stress developed in Si inclusions following plastic flow in the matrix of an Al–Si–Mg alloy. Philos. Mag. 2017, 97, 1398–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J. Entrainment defects. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2006, 22, 127–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dispinar, D.; Campbell, J. Supercooling of metal in fine filters. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 10296–10298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J. The Mechanisms of Metallurgical Failure: On the Origin of Fracture; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Fox, S.; Campbell, J. Visualisation of oxide film defects during solidification of aluminium alloys. Scr. Mater. 2000, 43, 881–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.; Tiryakioğlu, M. Fatigue Failure in Engineered Components and How It Can Be Eliminated: Case Studies on the Influence of Bifilms. Metals 2022, 12, 1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J. The Origin of Griffith Cracks. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2011, 42, 1091–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.G. Microstructural effects on the tensile and fracture behavior of aluminum casting alloys A356/357. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2003, 34, 2887–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiser, M.; Zok, F.; Wilkinson, D. Plastic flow and fracture of a particulate metal matrix composite. Acta Mater. 1996, 44, 3465–3476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiglionda, G.; Poole, W.J. The role of damage on the deformation and fracture of Al–Si eutectic alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2002, 336, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caceres, C.; Griffiths, J. Damage by the cracking of silicon particles in an Al-7Si-0.4 Mg casting alloy. Acta Mater. 1996, 44, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.L.; Zheng, L.H.; StJohn, D.H. Effect of solution treatment temperature on tensile properties of AI-7Si-O.3Mg (wt-%) alloy. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2013, 14, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruzleski, J.E.; Closset, B.M. The Treatment of Liquid Aluminum-Silicon Alloys; American Foundrymen’s Society: Des Plaines, IL, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Mazahery, A.; Shabani, M.O. Modification Mechanism and Microstructural Characteristics of Eutectic Si in Casting Al-Si Alloys: A Review on Experimental and Numerical Studies. JOM 2014, 66, 726–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, M.D.; Lu, S.-Z.; Hellawell, A. Modification in the aluminum silicon system. Metall. Trans. A 1984, 15, 459–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.-Z.; Hellawell, A. The mechanism of silicon modification in aluminum-silicon alloys: Impurity induced twinning. Metall. Trans. A 1987, 18, 1721–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexopoulos, N.D.; Tiryakioğlu, M.; Vasilakos, A.N.; Kourkoulis, S.K. The effect of Cu, Ag, Sm and Sr additions on the statistical distributions of Si particles and tensile properties in A357–T6 alloy castings. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 604, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Hong, Y.; Cho, H. The effects of Sc on the microstructure and mechanical properties of hypo-eutectic Al−Si alloys. Met. Mater. Int. 2004, 10, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, R.S.; Mahoney, M.; McFadden, S.; Mara, N.; Mukherjee, A. High strain rate superplasticity in a friction stir processed 7075 Al alloy. Scr. Mater. 1999, 42, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, R.S.; Mahoney, M.W. Friction stir processing: A new grain refinement technique to achieve high strain rate superplasticity in commercial alloys. In Proceedings of the Materials Science Forum, Kloster Banz, Germany, 10 October 2001; pp. 507–514. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, R.S.; Ma, Z.Y. Friction stir welding and processing. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2005, 50, 1–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jana, S.; Mishra, R.S.; Grant, G. Friction Stir Casting Modification for Enhanced Structural Efficiency: A Volume in the Friction Stir Welding and Processing Book Series; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Z.Y. Friction Stir Processing Technology: A Review. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2008, 39, 642–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, D.; Bauri, R. Effect of friction stir processing on microstructure and mechanical properties of aluminium. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 539, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netto, N.; Tiryakioğlu, M.; Eason, P. Characterization of Microstructural Refinement and Hardness Profile Resulting from Friction Stir Processing of 6061-T6 Aluminum Alloy Extrusions. Metals 2018, 8, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.; Apelian, D. Defect Elimination in Cast Al Components via Friction Stir Processing. In Proceedings of the TMS 2012 141st Annual Meeting and Exhibition, Materials Properties, Characterization, and Modeling, Orlando, FL, USA, 11–15 March 2012; p. 411. [Google Scholar]
- Santella, M.L.; Engstrom, T.; Storjohann, D.; Pan, T.Y. Effects of friction stir processing on mechanical properties of the cast aluminum alloys A319 and A356. Scr. Mater. 2005, 53, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.Y.; Sharma, S.R.; Mishra, R.S. Effect of friction stir processing on the microstructure of cast A356 aluminum. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 433, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, R.; Rao, V.S.H.; Mishra, R.S.; Baumann, J.A.; Grant, G. Probabilistic fatigue life prediction model for alloys with defects: Applied to A206. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 3447–3462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.R.; Ma, Z.Y.; Mishra, R.S. Effect of friction stir processing on fatigue behavior of A356 alloy. Scr. Mater. 2004, 51, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.R.; Mishra, R.S. Fatigue crack growth behavior of friction stir processed aluminum alloy. Scr. Mater. 2008, 59, 395–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammar, H.R.; Samuel, A.M.; Samuel, F.H. Porosity and the fatigue behavior of hypoeutectic and hypereutectic aluminum–silicon casting alloys. Int. J. Fatigue 2008, 30, 1024–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jana, S.; Mishra, R.S.; Baumann, J.B.; Grant, G. Effect of friction stir processing on fatigue behavior of an investment cast Al–7Si–0.6 Mg alloy. Acta Mater. 2010, 58, 989–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jana, S.; Mishra, R.S.; Baumann, J.B.; Grant, G. Effect of stress ratio on the fatigue behavior of a friction stir processed cast Al–Si–Mg alloy. Scr. Mater. 2009, 61, 992–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netto, N.; Tiryakioğlu, M.; Eason, P.D. On the Size, Shape and Spatial Distribution of Si Particles in A356 Castings After Single and Multiple Passes of Friction Stir Processing: The Effect of As-Cast Microstructures. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2021, 52, 5096–5106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM E8/E8M-22; Standard Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2024.
- Campbell, J. Complete Casting Handbook: Metal Casting Processes, Metallurgy, Techniques and Design, 2nd ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Rømming, C.; Hansen, V.; Gjønnes, J. Crystal structure of β-Al4. 5FeSi. Struct. Sci. 1994, 50, 307–312. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, V.; Hauback, B.; Sundberg, M.; Rømming, C.; Gjønnes, J. β-Al4. 5FeSi: A combined synchrotron powder diffraction, electron diffraction, high-resolution electron microscopy and single-crystal X-ray diffraction study of a faulted structure. Struct. Sci. 1998, 54, 351–357. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, X.; Campbell, J. The nucleation of Fe-Rich phases on oxide films in Al-11.5Si-0.4Mg cast alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2003, 34, 1409–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Campbell, J. Morphology of β-Al5FeSi Phase in Al-Si Cast Alloys. Mater. Trans. 2006, 47, 1303–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferdian, D.; Josse, C.; Nguyen, P.; Gey, N.; Ratel-Ramond, N.; de Parseval, P.; Thebault, Y.; Malard, B.; Lacaze, J.; Salvo, L. Chinese Script vs Plate-Like Precipitation of Beta-Al9Fe2Si2 Phase in an Al-6.5Si-1Fe Alloy. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2015, 46, 2814–2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Saunders, N.; Campbell, J. Effect of iron and manganese contents on convection-free precipitation and sedimentation of primary α-Al(FeMn)Si phase in liquid Al-11.5Si-0.4Mg alloy. J. Mater. Sci. 2004, 39, 2303–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, A.; Samuel, F.; Doty, H. Observations on the formation of β-Al5FeSi phase in 319 type Al-Si alloys. J. Mater. Sci. 1996, 31, 5529–5539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Cao, X.-j.; Chen, X.-G. Precipitation of iron-rich intermetallic phases in Al-4.6 Cu-0.5 Fe-0.5 Mn cast alloy. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 47, 4290–4298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, S.; Riddle, Y.W.; Makhlouf, M.M. Eutectic solidification of aluminum-silicon alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2004, 35, 3038–3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, S.; Riddle, Y.W.; Makhlouf, M.M. Nucleation mechanism of the eutectic phases in aluminum–silicon hypoeutectic alloys. Acta Mater. 2004, 52, 4447–4460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiryakioğlu, M.; Shuey, R.T. Quench sensitivity of an Al-7 pct Si-0.6 pct Mg alloy: Characterization and modeling. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2007, 38, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurz, W.; Fisher, D.J. Fundamentals of Solidification; Trans Tech publications: Aedermannsdorf, Switzerland, 1986; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Kirkwood, D. A simple model for dendrite arm coarsening during solidification. Mater. Sci. Eng. 1985, 73, L1–L4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, A.; Samuel, F. Effect of alloying elements and dendrite arm spacing on the microstructure and hardness of an Al-Si-Cu-Mg-Fe-Mn (380) aluminium die-casting alloy. J. Mater. Sci. 1995, 30, 1698–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorren, O.; Evensen, J.; Pedersen, T. Microstructure and mechanical properties of AlSi (Mg) casting alloys. AFS Trans. 1984, 92, 459–466. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, X.; Campbell, J. Oxide inclusion defects in Al-Si-Mg cast alloys. Can. Metall. Q. 2005, 44, 435–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeHoff, R. A geometrically general theory of diffusion controlled coarsening. Acta Metall. Et Mater. 1991, 39, 2349–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, P.P.; Ardell, A.J. Average nearest-neighbor distances between uniformly distributed finite particles. Metallography 1972, 5, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoharan, M.; Lewandowski, J.J.; Hunt, W.H. Fracture characteristics of an Al–Si–Mg model composite system. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1993, 172, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexopoulos, N.D.; Tiryakioğlu, M. On the uniform elongation of cast Al–7%Si–0.6%Mg (A357) alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2009, 507, 236–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olofsson, J.; Bogdanoff, T.; Tiryakioğlu, M. On revealing hidden entrainment damage during in situ tensile testing of cast aluminum alloy components. Mater. Charact. 2024, 208, 113647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olofsson, J.; Bogdanoff, T.; Tiryakioğlu, M.; Bramann, H.; Sturm, J. The Effect of Hidden Damage on Local Process Variability in Al-10 Pct Si Alloy High-Pressure Die Castings. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2024, 56, 595–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erzi, E.; Tiryakioğlu, M. A simple procedure to determine incoming quality of aluminum alloy ingots and its application to A356 alloy ingots. Int. J. Met. 2020, 14, 999–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiryakioğlu, M.; Yousefian, P.; Eason, P.D. Quantification of Entrainment Damage in A356 Aluminum Alloy Castings. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2018, 49, 5815–5822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghiabadi, R.; Rostamabadi, A.; Tasvibi, S.; Shaeri, M.H. Increasing the recycling percent in liquid-state recycling of Al machining chips by friction stir processing. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 243, 122627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiryakioğlu, M.; Campbell, J. Quality index for aluminum alloy castings. Int. J. Met. 2014, 8, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiryakioǧlu, M.; Campbell, J.; Staley, J.T. The influence of structural integrity on the tensile deformation of cast Al–7wt.%Si–0.6wt.%Mg alloys. Scr. Mater. 2003, 49, 873–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meenia, S.; Khan, F.; Babu, S.; Immanuel, R.; Panigrahi, S.; Ram, G.J. Particle refinement and fine-grain formation leading to enhanced mechanical behaviour in a hypo-eutectic Al–Si alloy subjected to multi-pass friction stir processing. Mater. Charact. 2016, 113, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocks, U. Laws for work-hardening and low-temperature creep. J. Eng. Mater. Technol. 1976, 98, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mecking, H.; Kocks, U. Kinetics of flow and strain-hardening. Acta Metall. 1981, 29, 1865–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocks, U.; Mecking, H. Physics and phenomenology of strain hardening: The FCC case. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2003, 48, 171–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiryakioğlu, M.; Campbell, J.; Alexopoulos, N.D. Quality indices for aluminum alloy castings: A critical review. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2009, 40, 802–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiryakioğlu, M.; Alexopoulos, N.D. The Effect of Artificial Aging on Tensile Work Hardening Characteristics of a Cast Al-7 Pct Si-0.55 Pct Mg (A357) Alloy. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2008, 39, 2772–2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiryakioğlu, M.; Campbell, J.; Staley, J.T. Evaluating structural integrity of cast Al–7% Si–Mg alloys via work hardening characteristics: 1. Concept of target properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 368, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiryakioğlu, M.; Staley, J.T.; Campbell, J. The effect of structural integrity on the tensile deformation characteristics of A206-T71 alloy castings. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 487, 383–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisaabadi, B.G.; Tiryakioğlu, M.; Davami, P.; Kim, S.-K.; Yoon, Y.O.; Yeom, G.-Y.; Kim, N.-S. The effect of remelting on the melt and casting quality in Al–7%Si–Mg castings. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 605, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, G.; Ni, D.; Ma, Z.; Li, S. Effects of friction stir processing parameters and in situ passes on microstructure and tensile properties of Al-Si-Mg casting. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2014, 45, 5318–5331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

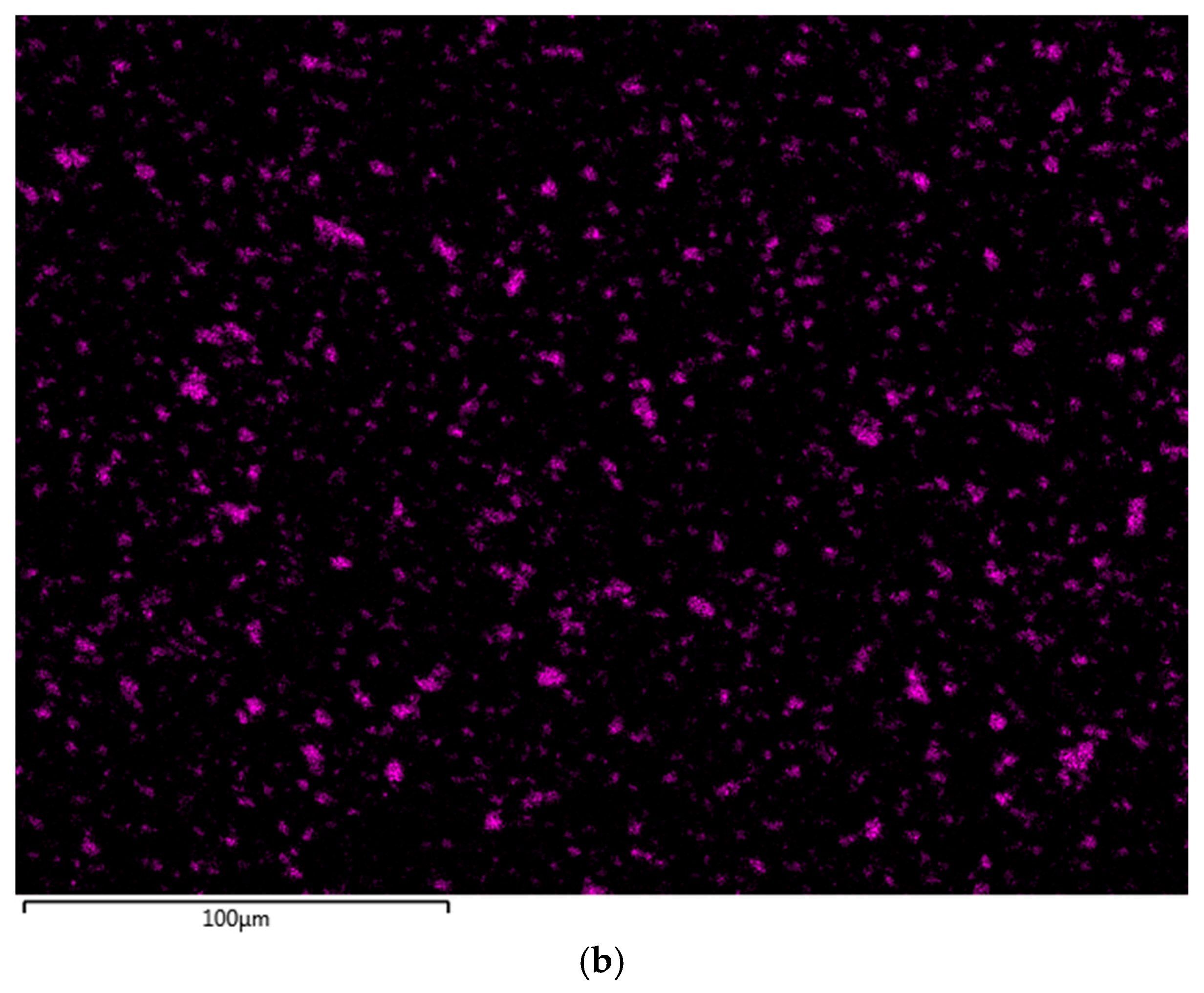
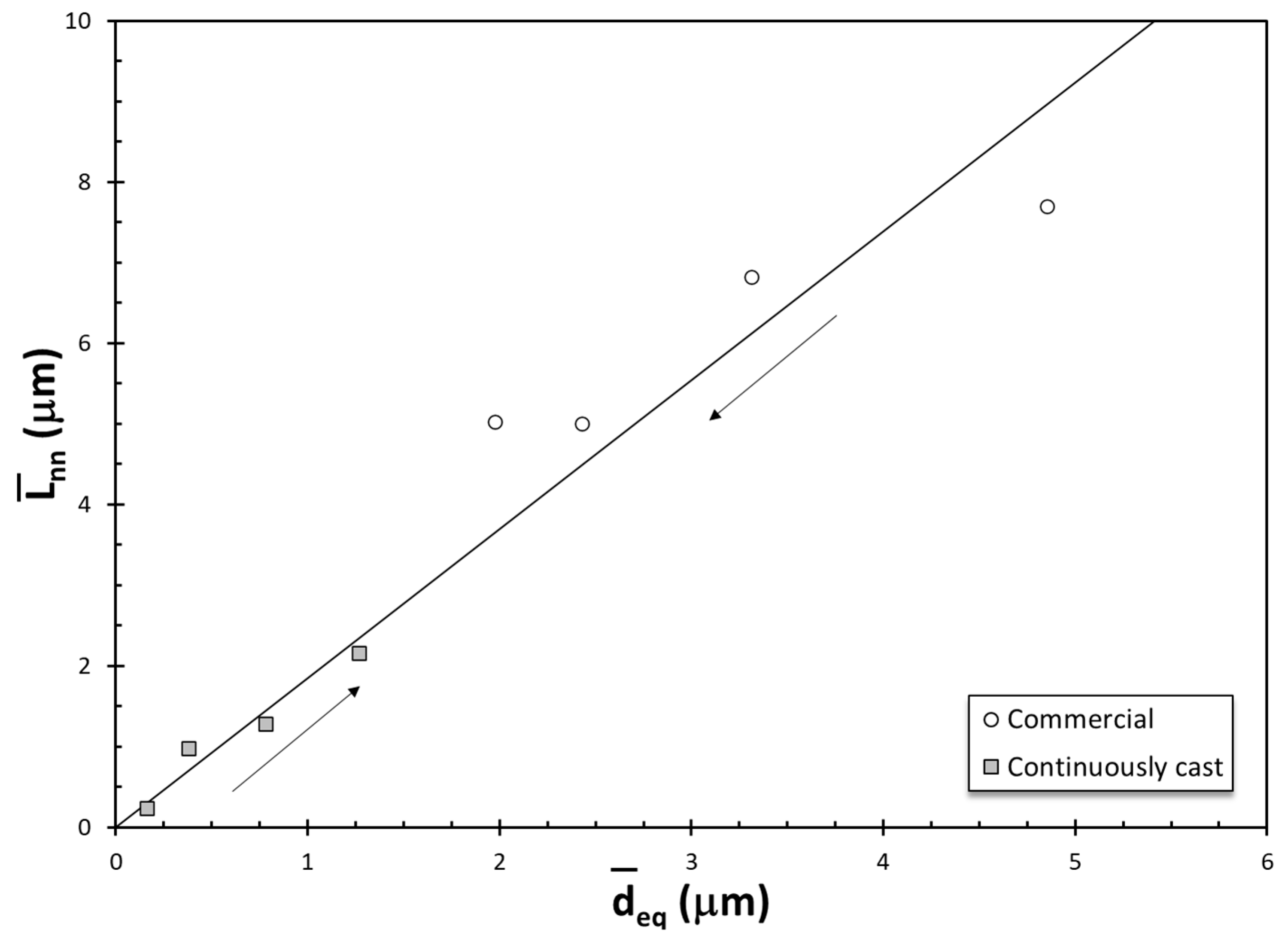

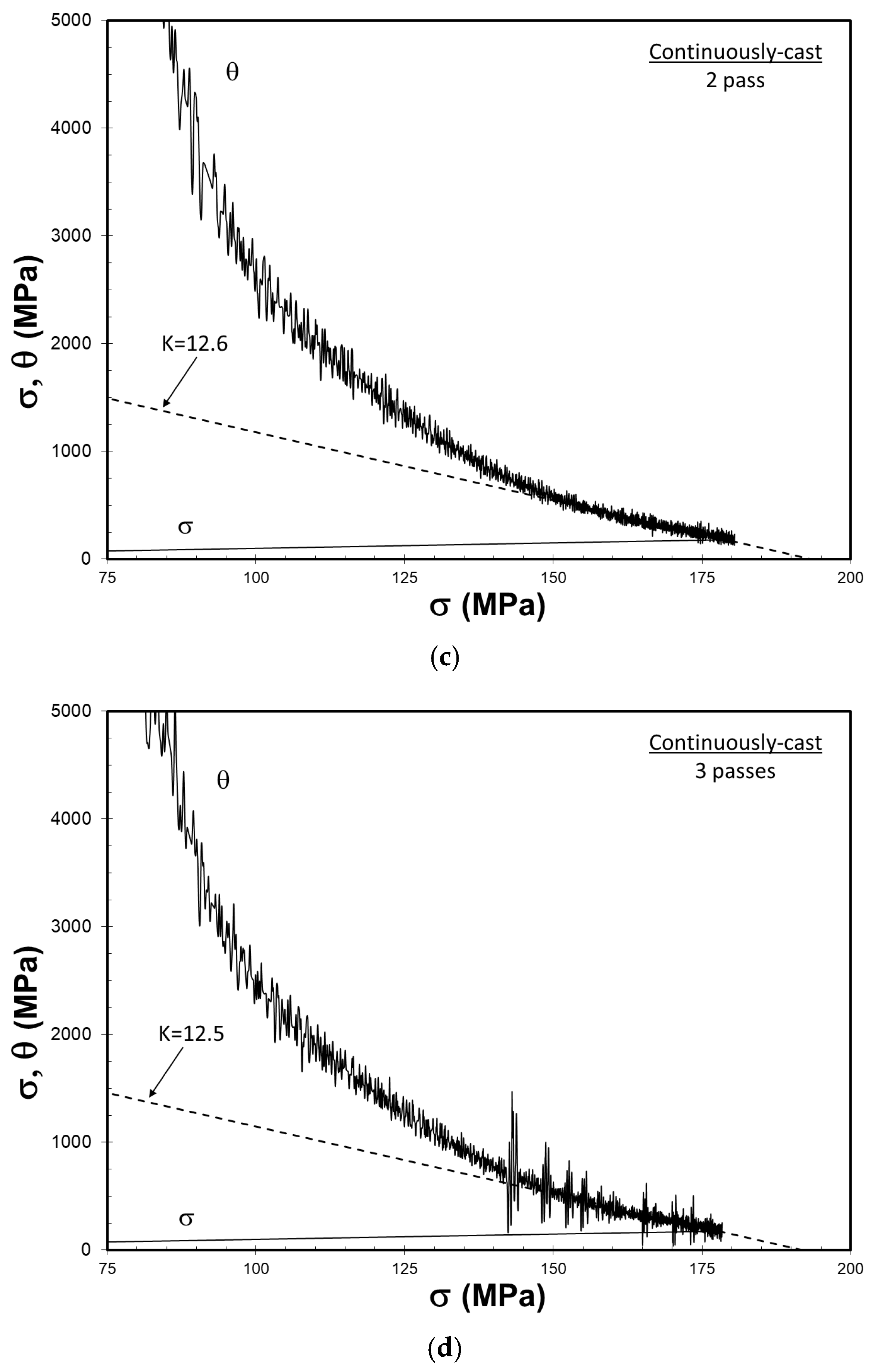
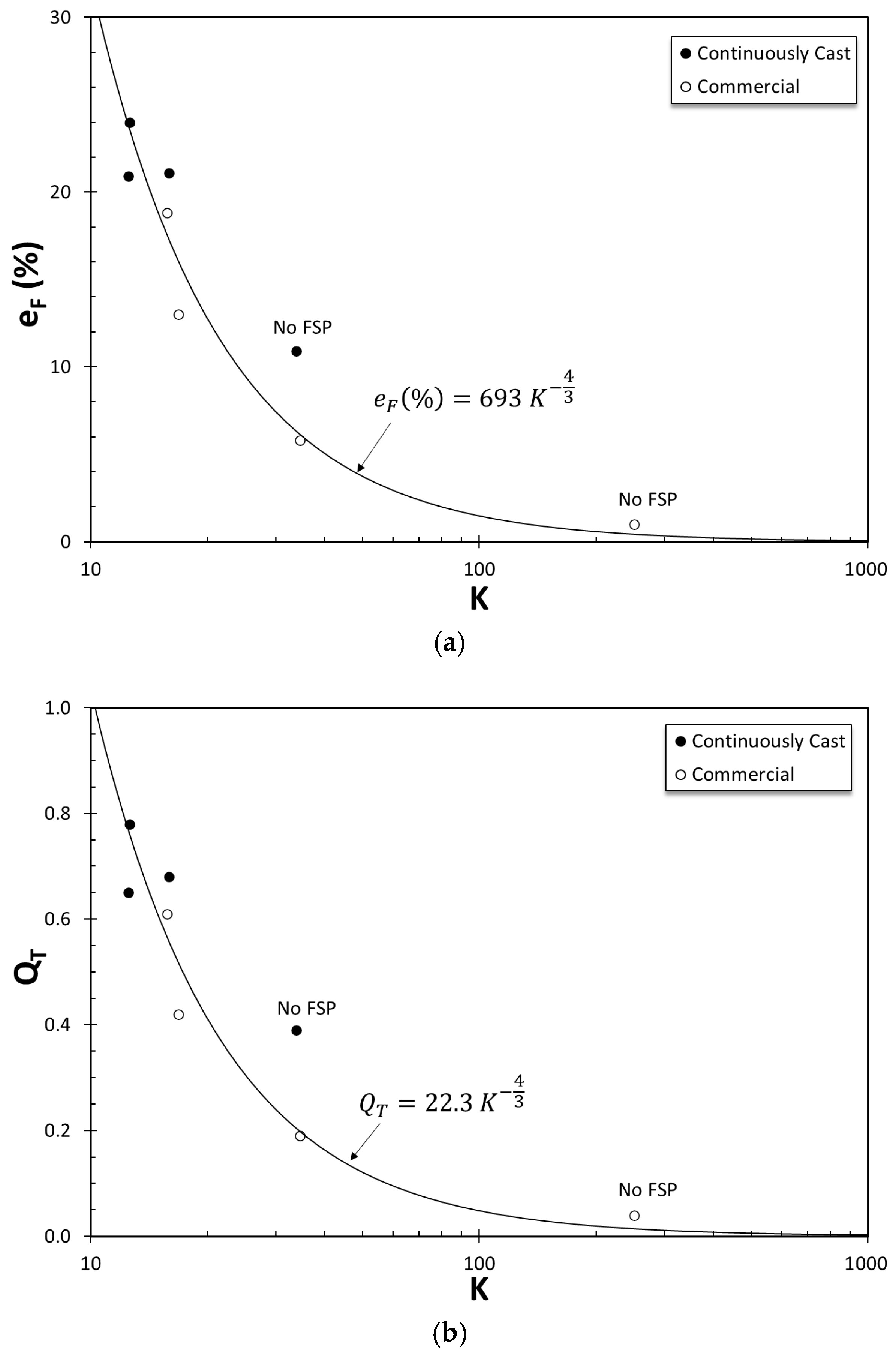
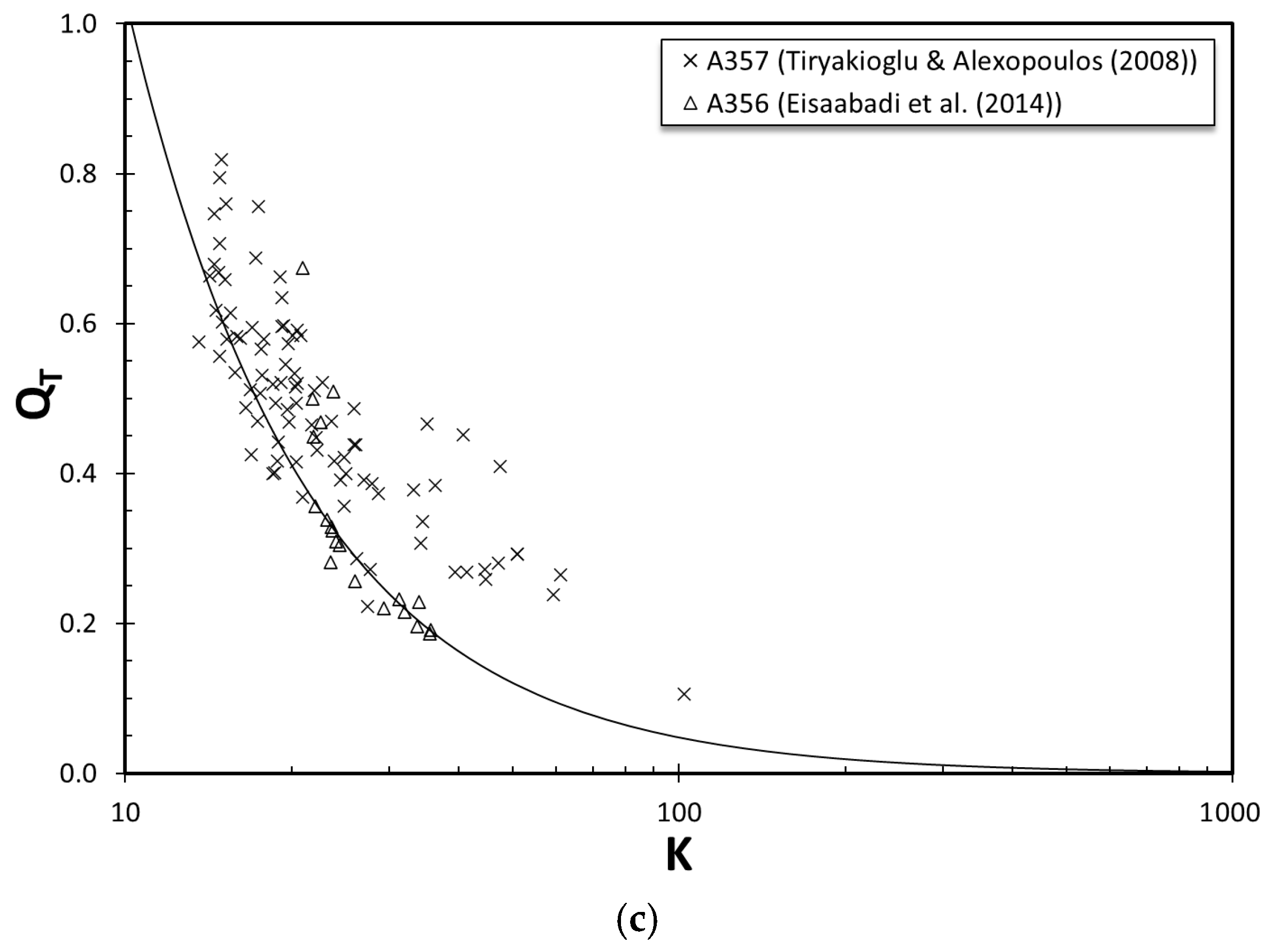
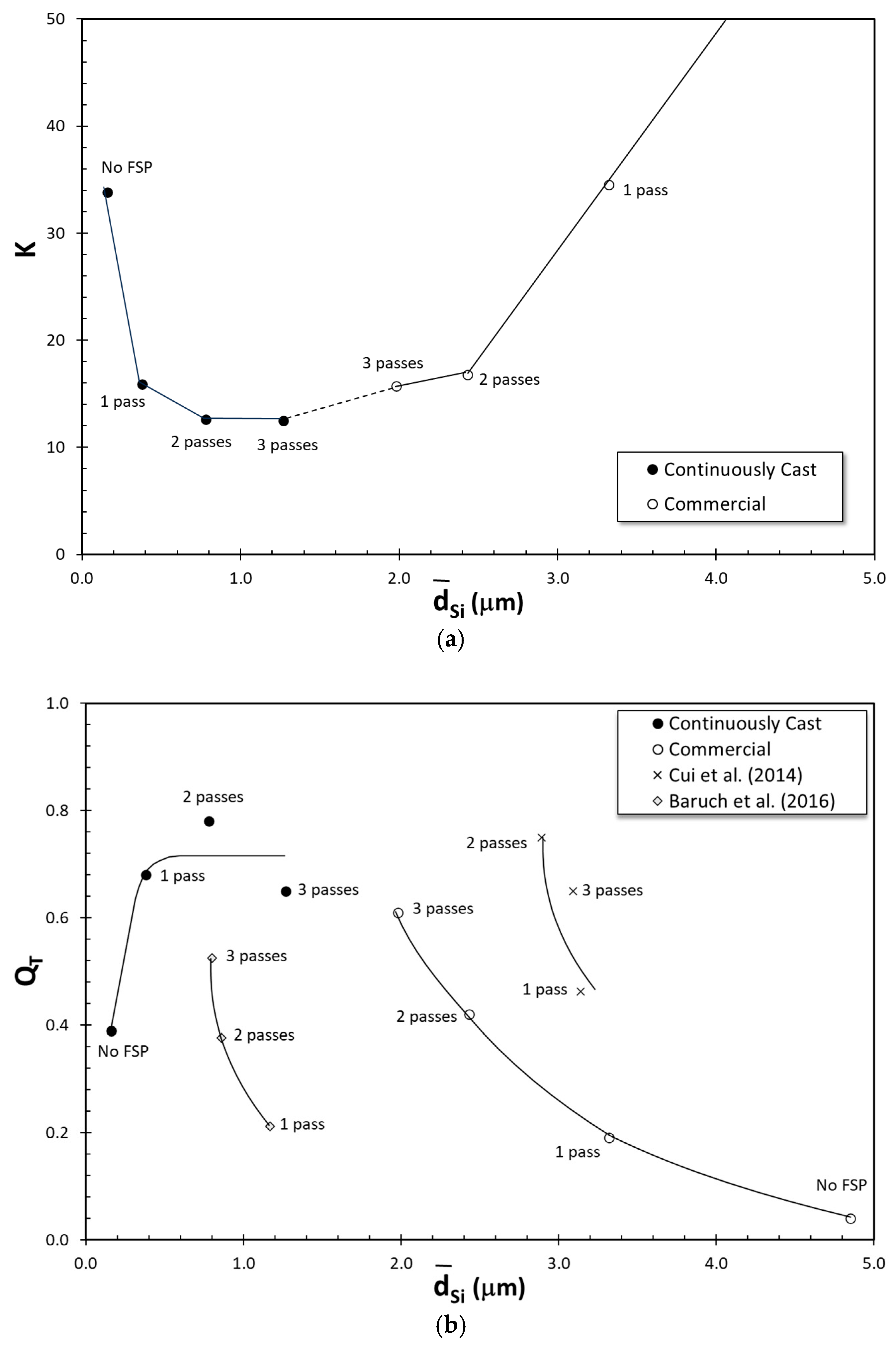
| Commercial | Continuously Cast | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FSP Passes | ||||
| 0 | 4.852 | 7.703 | 0.161 | 0.244 |
| 1 | 3.314 | 6.826 | 0.379 | 0.980 |
| 2 | 2.427 | 5.007 | 0.781 | 1.284 |
| 3 | 1.973 | 5.030 | 1.267 | 2.157 |
| Material | FSP Pass | σy (MPa) | ST (MPa) | eF (%) | QT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Commercial | 0 | 153.7 | 175.3 | 1.0 | 0.04 |
| 1 | 91.1 | 141.4 | 5.8 | 0.19 | |
| 2 | 78.2 | 152.8 | 13.0 | 0.42 | |
| 3 | 81.9 | 154.4 | 18.8 | 0.61 | |
| Continuously cast | 0 | 121.0 | 221.0 | 10.9 | 0.39 |
| 1 | 79.5 | 153.7 | 21.1 | 0.68 | |
| 2 | 75.5 | 157.0 | 24.0 | 0.78 | |
| 3 | 77.9 | 155.2 | 20.9 | 0.65 |
| Ingot | FSP Passes | K | θ0 (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Commercial | 0 | 250.0 * | 47413 * |
| 1 | 34.5 | 5523 | |
| 2 | 16.8 | 3034 | |
| 3 | 15.7 | 2872 | |
| Continuously Cast | 0 | 33.8 | 8129 |
| 1 | 15.9 | 2888 | |
| 2 | 12.6 | 2438 | |
| 3 | 12.5 | 2396 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tiryakioğlu, M.; Netto, N.; Eason, P.D. On the Effect of Multi-Pass Friction Stir Processing on Microstructure-Tensile Deformation Behavior Relationships in Cast Al-7%Si-0.4%Mg Specimens. Metals 2025, 15, 1309. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15121309
Tiryakioğlu M, Netto N, Eason PD. On the Effect of Multi-Pass Friction Stir Processing on Microstructure-Tensile Deformation Behavior Relationships in Cast Al-7%Si-0.4%Mg Specimens. Metals. 2025; 15(12):1309. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15121309
Chicago/Turabian StyleTiryakioğlu, Murat, Nelson Netto, and Paul D. Eason. 2025. "On the Effect of Multi-Pass Friction Stir Processing on Microstructure-Tensile Deformation Behavior Relationships in Cast Al-7%Si-0.4%Mg Specimens" Metals 15, no. 12: 1309. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15121309
APA StyleTiryakioğlu, M., Netto, N., & Eason, P. D. (2025). On the Effect of Multi-Pass Friction Stir Processing on Microstructure-Tensile Deformation Behavior Relationships in Cast Al-7%Si-0.4%Mg Specimens. Metals, 15(12), 1309. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15121309








