Effect of Zr Content on the Ignition Conditions and Flame Propagation of Ti100−xZrx Alloys
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
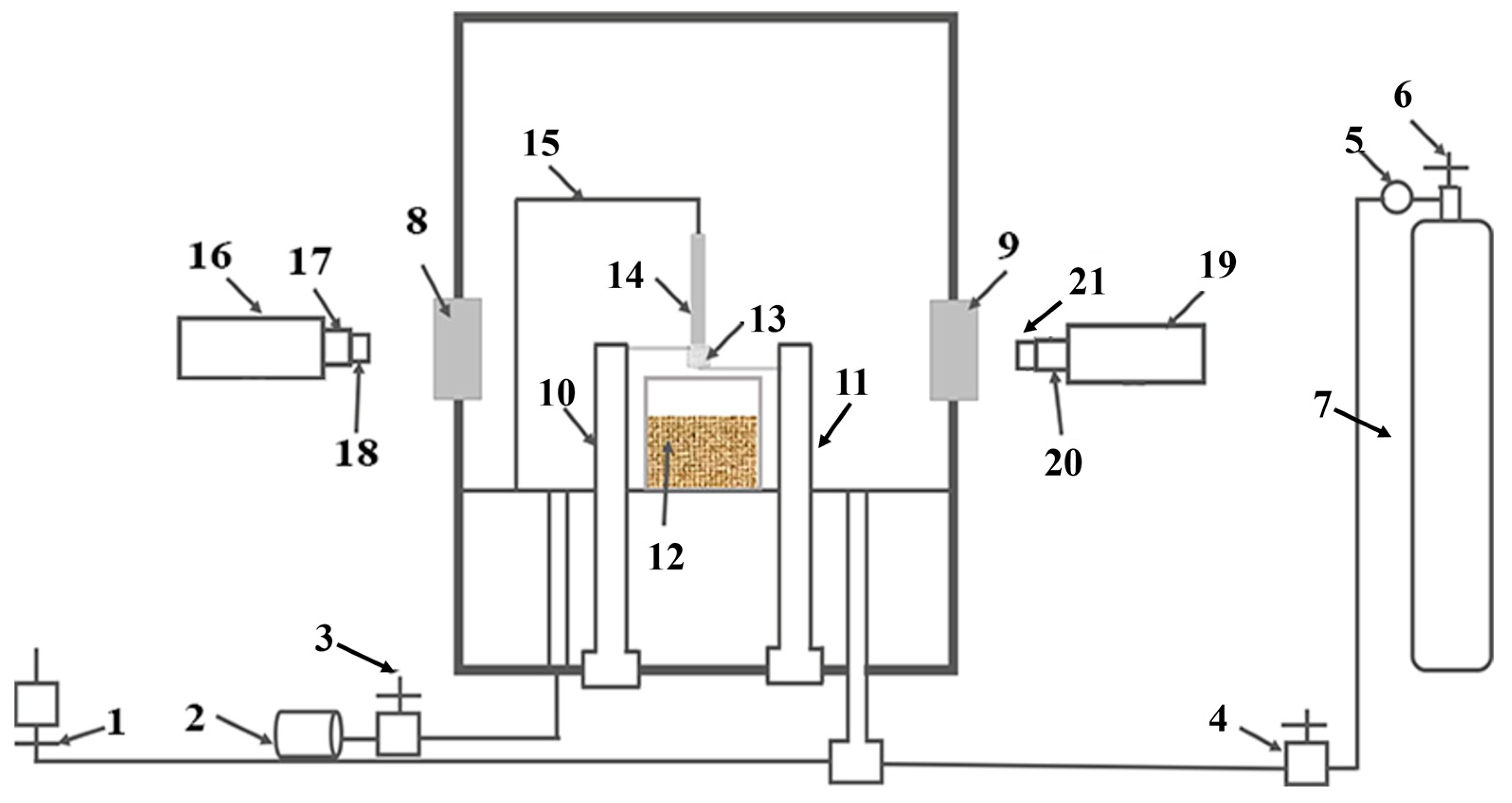
2.2. Promoted Ignition-Combustion (PIC) Tests
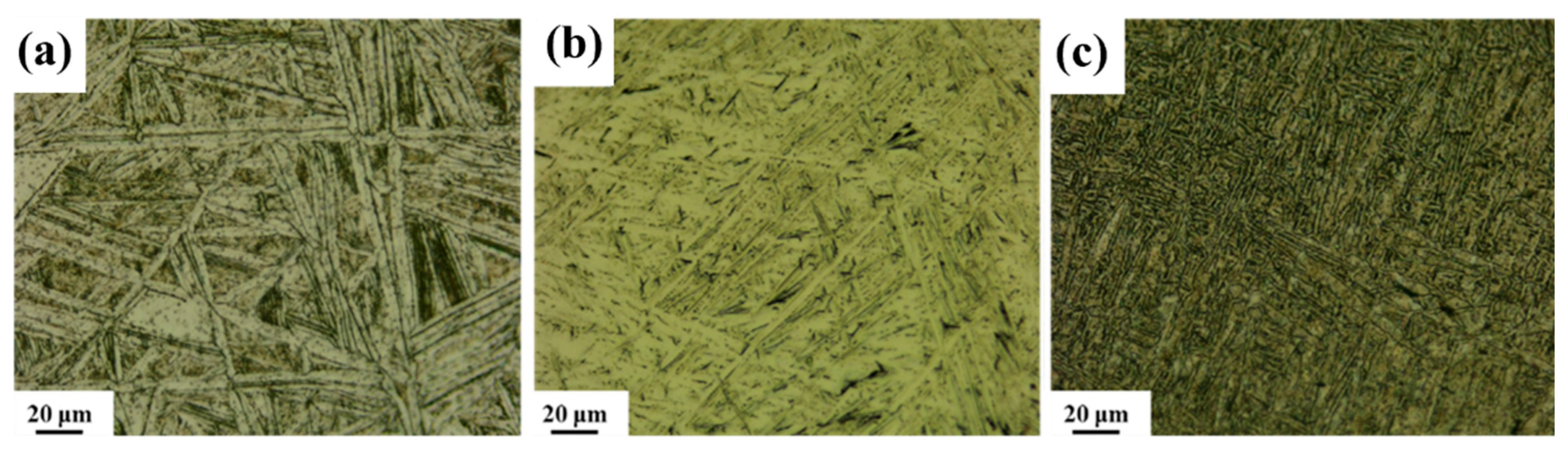
2.3. Microstructure Characterization
3. Results
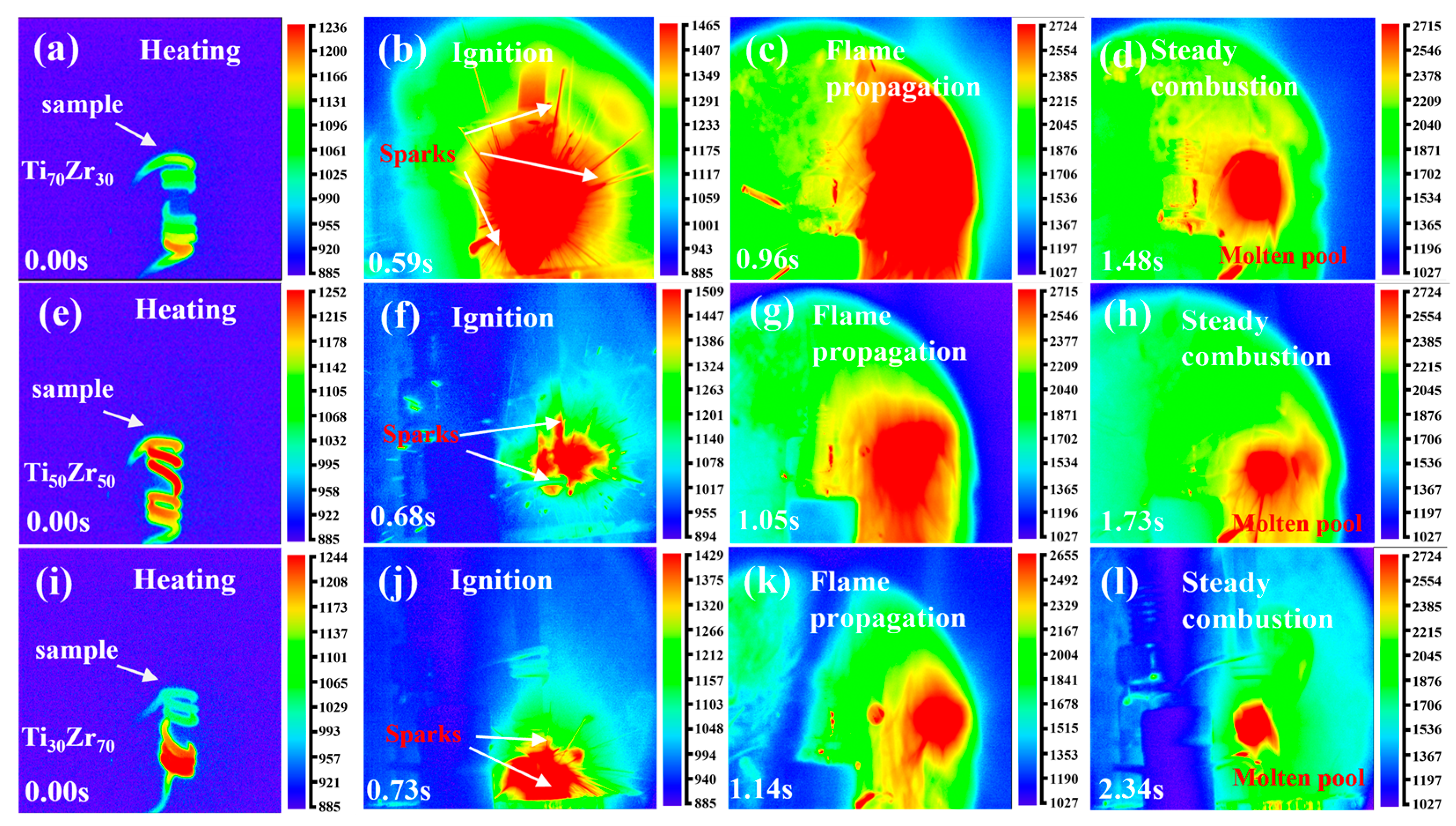
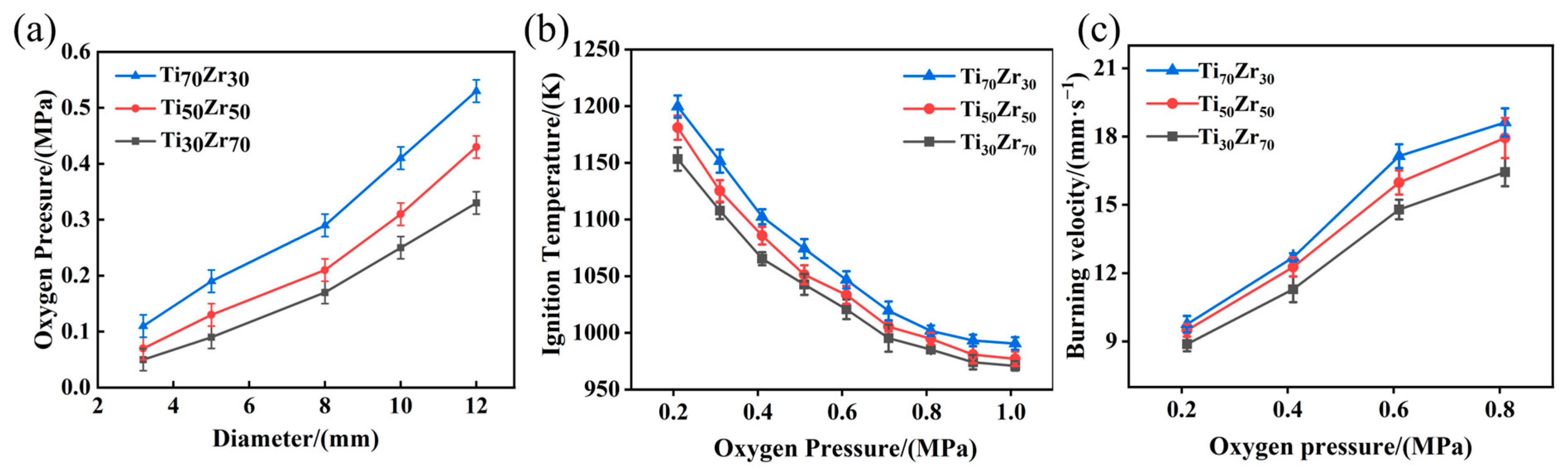
3.1. Combustion Behavior
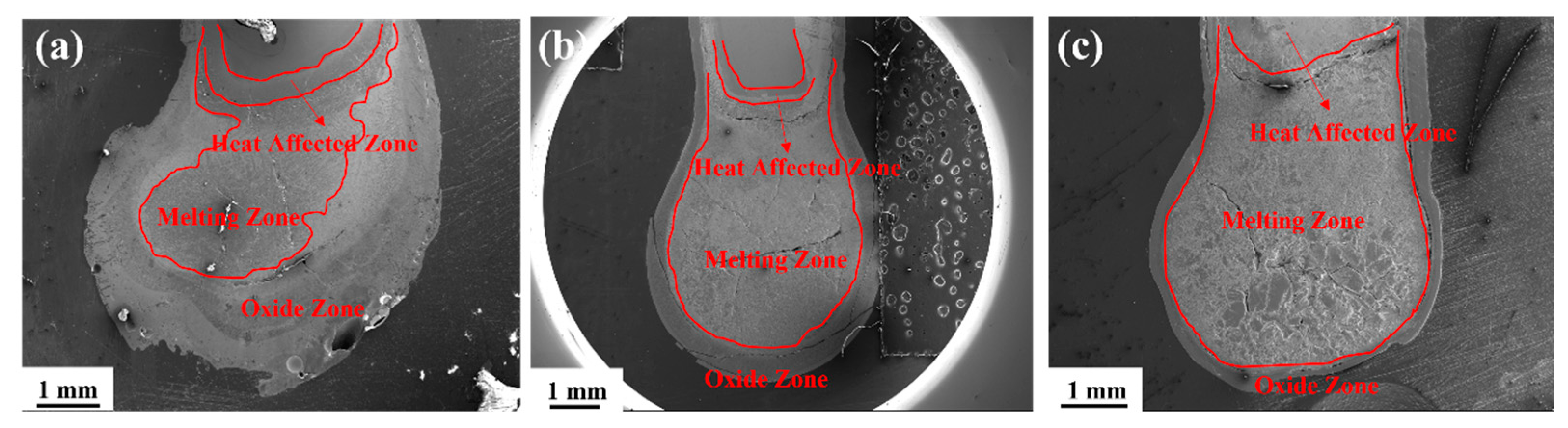
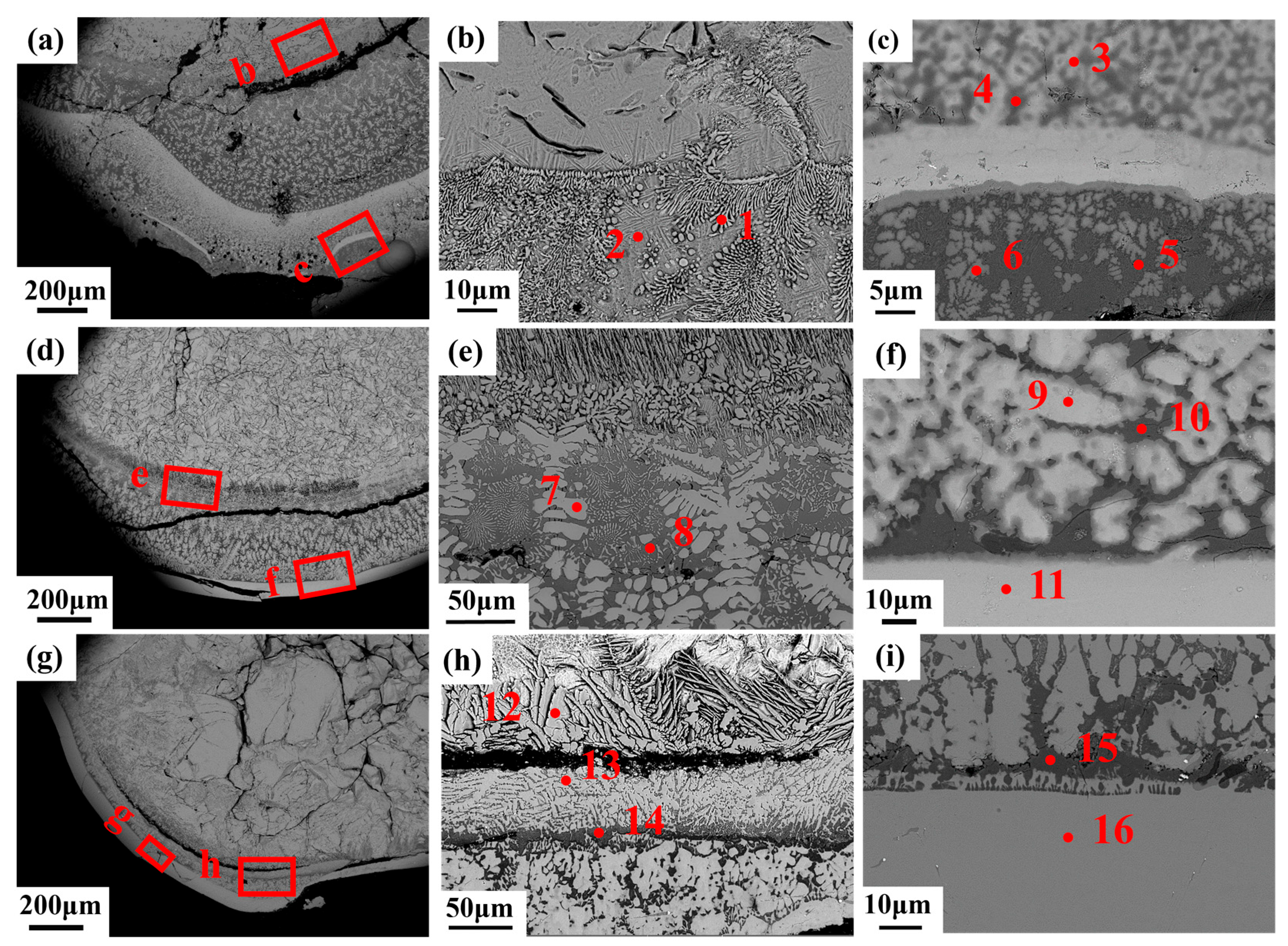
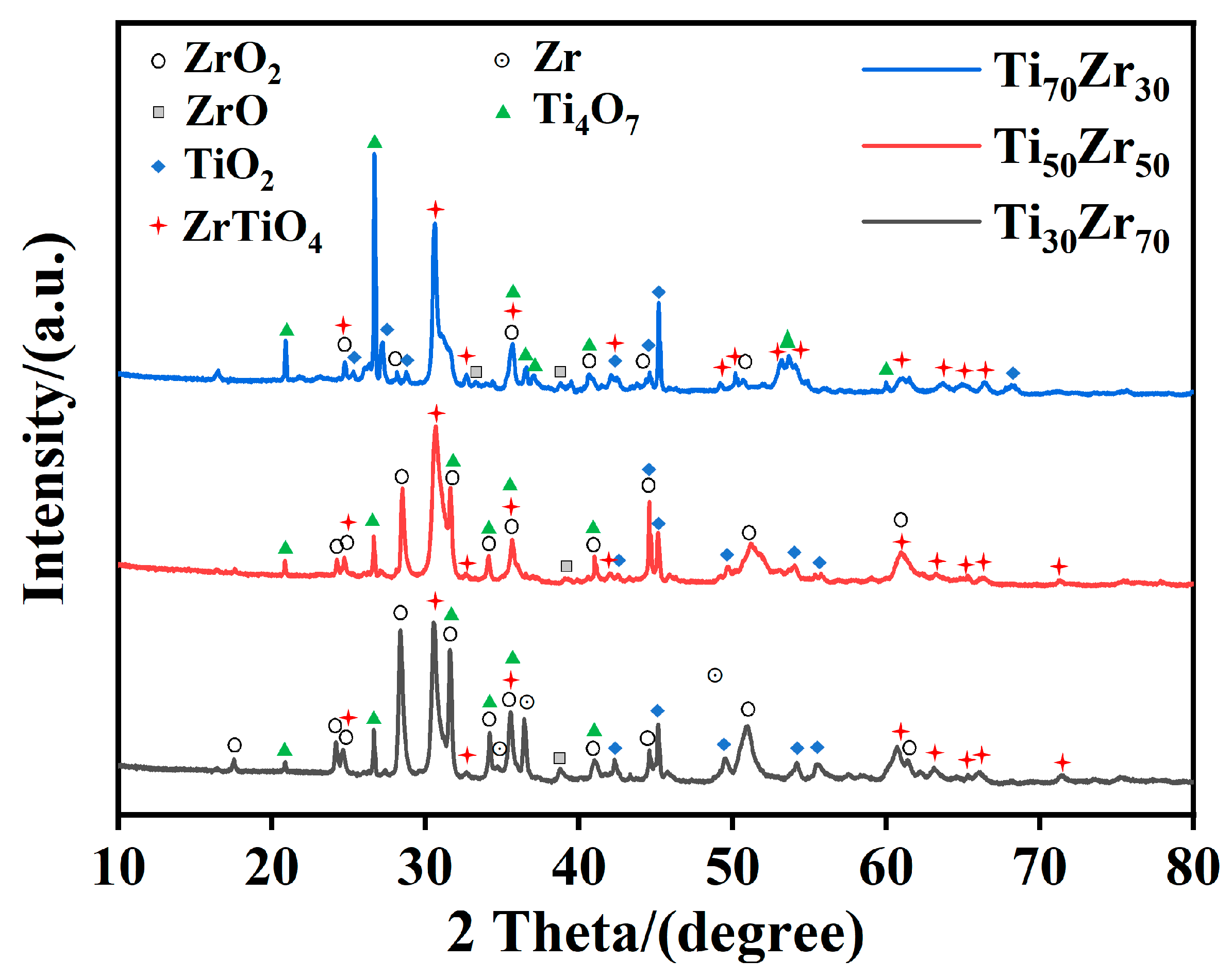
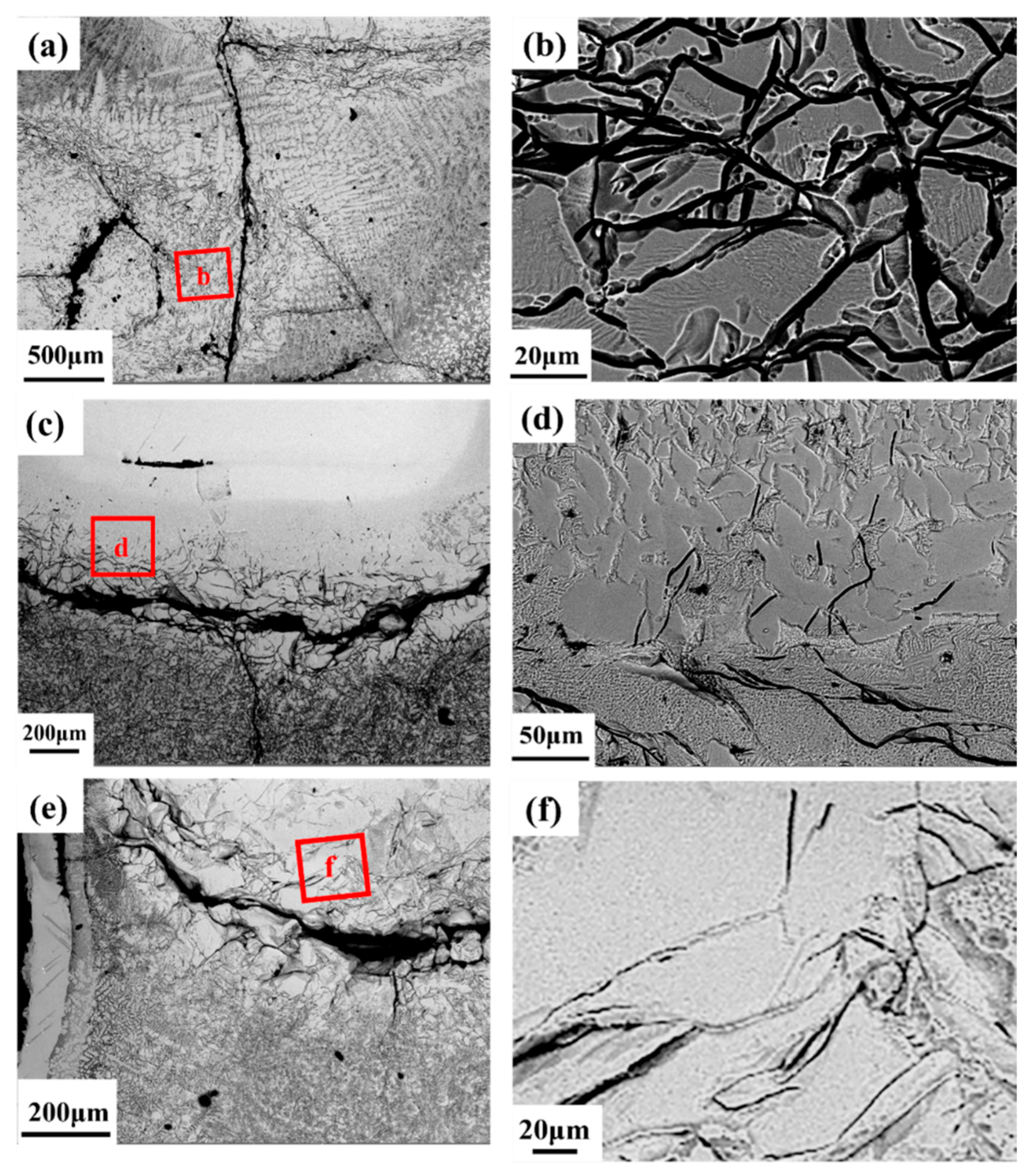
3.2. Microstructural Characteristics After Combustion
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison of Thermodynamic Parameters for Ignition of Ti100−xZrx
4.2. Flame Propagation Mechanism of Ti100−xZrx Alloy
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- An increase in zirconium content leads to decreases in critical oxygen pressure, ignition temperature, and burning velocity under identical conditions.
- (2)
- The thermodynamic parameters of Ti100−xZrx alloys were obtained based on the ignition thermodynamic model. Increased Zr content lowers the activation energy (from 108.37 kJ/mol to 94.26 kJ/mol) for ignition and increases the heat release (from 986.34 kJ/mol to 1049.84 kJ/mol), thereby decreasing the ignition conditions.
- (3)
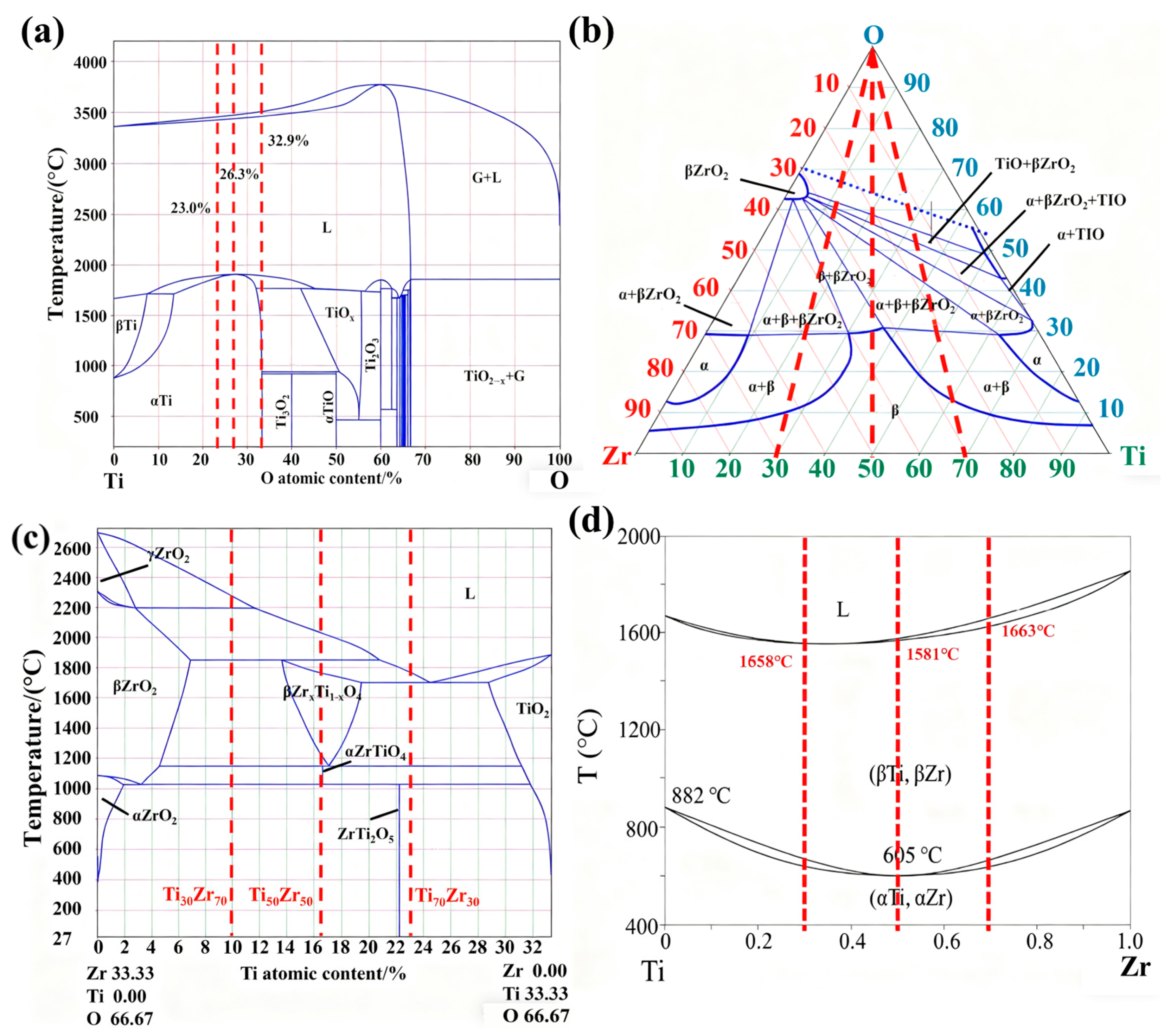
- Increasing Zr promotes the formation of a dense Zr oxide layer in the oxide zone, impeding oxygen diffusion into the matrix. This reduces the oxidation zone area and lowers oxygen content in the melting zone (from 32.9 at% to 23.0 at%). The decreased oxygen content inhibits reactions in the oxide zone, alters the peritectic reaction mechanism in the melting zone, reduces heat release, and ultimately leads to a lower burning velocity.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, D. One Generation of New Material, One generation of new type engine: Development trend of aero-engine and Its requirements for materials. J. Mater. Eng. 2017, 45, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.C.; Starke, E.A., Jr. Progress in structural materials for aerospace systems. Acta Mater. 2003, 51, 5775–5799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filonenko, A.K. Spin combustion of titanium at reduced pressure. Combust. Explos. Shock. Waves 1991, 27, 685–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Li, S.; Pei, H. Progress in titanium fire resistant technology for aero-engine. J. Aerosp. Power 2012, 27, 2763–2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Mi, G.; Li, P.; Sui, N.; Cao, J. Influence of airflow velocity on friction ignition behavior of Ti3Al-based alloy. J. Mater. Eng. 2024, 52, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Wang, G.; Ma, X.; Zheng, L.; Wang, R. Simulation of flame spread of titanium-alloy sheet under effect of titanium droplet. Acta Aeronaut. Astronaut. Sin. 2022, 43, 425652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; He, G.; Huang, J.; Zhang, C. Ignition and flame propagation behaviors of titanium alloys in oxygen-enriched atmospheres. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2025, 34, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Dong, Y.; Tong, Y.Q.; Liu, M.J.; Yang, G.J. Critical firing conditions for titanium alloys by molten droplet ignition. Corros. Commun. 2023, 11, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Xie, G.; Li, H.; Lu, W.; Liu, X.; Yu, J.; Huang, J. Combustion behavior and mechanism of Ti14 titanium alloy. Materials 2020, 13, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Xie, G.; Liu, X.; Wu, Y.; Tan, Q.; Xie, L.; Xin, S.; Hao, F.; Yu, J.; Xue, W.; et al. Combustion behavior and mechanism of Ti-25V-15Cr compared to Ti-6Al-4V alloy. Corros. Sci. 2002, 194, 109957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Liu, J.; Sun, T.; Jia, L.; Liang, Y.; Peng, H.; Lin, J. Flame-retardant mechanism of TiAl alloy by frictional ignition method. Mater. Des. 2024, 241, 112878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, G.; Huang, X.; Cao, J.; Cao, C. Ignition resistance performance and its theoretical analysis of Ti-V-Cr type fireproof titanium alloys. Acta Metall. Sin. 2014, 50, 575–586. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, W.; Bo, A.; Zhan, H.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Wan, M.; Gu, Y. Underlying burning resistant mechanisms for titanium alloy. Mater. Des. 2018, 156, 588–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhou, L.; Ju, D. Effects of the alloying element Cr on the burning behavior of titanium alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 1999, 284, 190–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Xie, G.; Liu, X.; Wu, Y.; Yu, J.; Feng, K.; Xue, W. The effect of Cu content and Ti2Cu precipitation on the combustion behavior and mechanism of Ti-xCu alloys. Corros. Sci. 2021, 190, 109641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Wang, Y.; Xie, G.; Li, H.; Xiong, J.; Yu, J.; He, G.; Huang, J. Combustion Mechanism of Alloying Elements Cr in Ti-Cr-V Alloys. Materials 2019, 12, 3206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, G.B.; Huang, X.; Cao, J.X.; Wang, B.; Cao, C.X. Microstructure characteristics of burning products of Ti-V-Cr fireproof titanium alloy by frictional ignition. Acta Phys. Sin. 2016, 65, 056103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Li, Z.; Yu, J.; Yang, G.; Zhang, C.; Zou, Y.; Huang, J. Combustion behavior and mechanisms of Ti2AlNb compared to an α + β Ti alloy. Corros. Sci. 2021, 192, 109868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Wang, B. Combustion Characteristics of Titanium Alloy TC11. Gas Turb. Exp. Res. 2012, 25, 40–43. [Google Scholar]
- Mi, G.; Cao, C.; Huang, X.; Cao, J.; Wang, B. Ignition Resistance Performance and Its Mechanism of TC11 Titanium Alloy for Aero-Engine. J. Aeronaut. Mater. 2014, 34, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Jia, L.; Guo, H.; Peng, H. Analysis of ignition resistance performance and mechanism of TA7 andTC11 titanium alloys under impact-grinding conditions. J. Aeronaut. Mater. 2024, 44, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, N.; Mi, G.; Cao, J.; Huang, X.; Cao, C. Characteristics and formation mechanism of near α type high temperature titanium alloy combustion microstructure under oxygen enriched conditions. Rare Metal. Mat. Eng. 2022, 51, 3263–3275. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.D.; Gu, W.S.; Pei, Z.L.; Gong, J.; Sun, C. Combustion behavior and mechanism of TC25 alloy. Mater. Lett. 2023, 351, 135002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Xie, G.; Liu, X.; Wu, Y.; Yu, J.; Hao, Z.; Lu, W.; Liu, X. Combustion behaviour and mechanism of TC4 and TC11 alloys. Corros. Sci. 2020, 168, 108564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushp, P.; Dasharath, S.M.; Arati, C. Classification and applications of titanium and its alloys. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 54, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veiga, C.; Davim, J.P.; Loureiro, A.J.R. Properties and applications of titanium alloys: A brief review. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2012, 32, 133–148. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Y.; Chen, W.; Dai, J.; Wu, J.; Mei, J.; Tang, B. Effect of Mo and Zr addition on the microstructure and mechanical properties of a novel α + β titanium alloy. Foundry Technol. 2025, 46, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Zhao, Y.; Zeng, W. Effect of Zr Addition on the Mechanical Properties and Superplasticity of a Forged SP700 Titanium Alloy. Materials 2021, 14, 906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.S.; Shiu, S.J.; Tsai, P.H.; Liao, Y.C.; Jang, J.S.C.; Wu, H.J.; Chang, S.Y.; Chen, C.Y.; Tsao, I.Y. Remarkable Enhanced Mechanical Properties of TiAlCrNbV Medium-Entropy Alloy with Zr Additions. Materials 2022, 15, 6324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, A.L.R.; Junior, R.C.; Cardoso, F.F.; Filho, R.B.F.; Vaz, L.G. Mechanical, physical, and chemical characterization of Ti-35Nb-5Zr and Ti-35Nb-10Zr casting alloys. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2009, 20, 1629–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM G124-18; Standard Test Method for Determining the Burning Behavior of Metallic Materials in Oxygen-Enriched Atmospheres. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2010.
- Zha, X.; Feng, K.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zeng, X.-Y.; Zhang, C. Comparative Study on the Combustion Behavior and Mechanisms of Ti150 and TC11 Alloys in Oxygen-Enriched Environments. Materials 2025, 18, 4446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; LI, J.; LI, Y.; Jin, P.; Yu, S.; Wu, Y.; He, G.; Huang, J.; Zhang, C. Effect of grain boundary on the ignition and flame propagation mechanisms of TC11 alloy in oxygen-enriched environment. Corros. Sci. 2024, 237, 112291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chase, W.; Davies, C.A.; Downey, R.; Frurip, D.J.; Syverund, A.N. JANAF thermochemical tables, third edition. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 1975, 64, 502A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiedemann, U.; Rösner-Kuhn, M.; Drewes, K.; Kuppermann, G.; Frohberg, M.G. Mixing enthalpy measurements of liquid Ti-Zr, Fe-Ti-Zr and Fe-Ni-Zr alloys. Steel Res. 1999, 70, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Predel, F. Phase Equilibria, Crystallographic and Thermodynamic Data of Binary Alloys; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; p. 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunting, E.N. Phase equilibria in the systems TiO2, TiO2-SiO2 and TiO2-Al2O3. Bur. Stand. J. Res. 1933, 11, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, X.; Zuo, Y. Formation Reason and Optimization Measures of Non-martensitic Structure in Carburized Layer. Heat Treat Technol. Equip. 2014, 35, 6–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hari Kumar, K.S.; Wollants, P.; Delaey, L. Thermodynamic Assessment of the Ti100−xZrx System and Calculation of the Nb-Ti100−xZrx Phase Diagram. J. Alloys Compd. 1994, 206, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Ti | Zr | |
|---|---|---|
| Ti70Zr30 | 70.53 | 29.47 |
| Ti50Zr50 | 50.96 | 49.04 |
| Ti30Zr70 | 31.07 | 68.93 |
| Ti | Zr | O | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Point 1 | 2.6 | 31.4 | 65.9 |
| Point 2 | 54.1 | 15.4 | 30.4 |
| Point 3 | 8.3 | 35.0 | 56.7 |
| Point 4 | 50.3 | 0.0 | 49.7 |
| Point 5 | 32.0 | 9.3 | 58.7 |
| Point 6 | 30.1 | 15.6 | 54.3 |
| Point 7 | 0.8 | 35.4 | 63.7 |
| Point 8 | 41.6 | 10.7 | 47.5 |
| Point 9 | 16.0 | 58.0 | 25.9 |
| Point 10 | 42.0 | 4.0 | 54.0 |
| Point 11 | 4.9 | 38.7 | 56.4 |
| Point 12 | 0.0 | 36.6 | 63.3 |
| Point 13 | 1.3 | 35.1 | 63.6 |
| Point 14 | 45.0 | 11.0 | 43.9 |
| Point 15 | 47.7 | 0.3 | 52.0 |
| Point 16 | 3.6 | 43.1 | 53.4 |
| Melting Zone | Ti | Zr | O |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ti70Zr30 | 46.8 | 18.2 | 32.9 |
| Ti50Zr50 | 40.4 | 33.3 | 26.3 |
| Ti30Zr70 | 21.5 | 55.4 | 23.0 |
| Heat-Affected Zone | Ti | Zr | O |
|---|---|---|---|
| Point 1 | 54.4 | 22.7 | 22.7 |
| Point 2 | 58.7 | 24.2 | 17.0 |
| Point 3 | 45.2 | 39.0 | 15.6 |
| Point 4 | 43.6 | 37.4 | 18.9 |
| Point 5 | 27.1 | 64.8 | 8.1 |
| Point 6 | 26.8 | 62.8 | 10.4 |
|
Heat Release
(kJ/mol) | Reaction Order n |
Activation Energy E
(kJ/mol) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ti30Zr70 | 1049.84 | 1.23 | 94.26 |
| Ti50Zr50 | 1018.09 | 1.32 | 96.55 |
| Ti70Zr30 | 986.34 | 1.58 | 108.37 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zha, X.; Ran, Q.; Feng, K.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zeng, X.; Zhang, C. Effect of Zr Content on the Ignition Conditions and Flame Propagation of Ti100−xZrx Alloys. Metals 2025, 15, 1182. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15111182
Zha X, Ran Q, Feng K, Wang Y, Yang Y, Zeng X, Zhang C. Effect of Zr Content on the Ignition Conditions and Flame Propagation of Ti100−xZrx Alloys. Metals. 2025; 15(11):1182. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15111182
Chicago/Turabian StyleZha, Xiaohui, Qiwei Ran, Kaikai Feng, Yang Wang, Yuchen Yang, Xinyun Zeng, and Cheng Zhang. 2025. "Effect of Zr Content on the Ignition Conditions and Flame Propagation of Ti100−xZrx Alloys" Metals 15, no. 11: 1182. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15111182
APA StyleZha, X., Ran, Q., Feng, K., Wang, Y., Yang, Y., Zeng, X., & Zhang, C. (2025). Effect of Zr Content on the Ignition Conditions and Flame Propagation of Ti100−xZrx Alloys. Metals, 15(11), 1182. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15111182






