Abstract
Single-layer steel reticulated shell structures have a long history and are widely distributed. As their service life increases, corrosion in these structures becomes an increasingly prominent problem. However, currently, there is nearly no research available on the static behavior of corroded steel reticulated shell structures. Therefore, taking the single-layer steel reticulated shell structure as the research object, an accelerated corrosion test was first carried out on Q345, a commonly used steel for this structure, and an equivalent conversion calculation method was proposed. Then, a Python program (version 3.5.0) for single-layer reticulated shells considering component dimensions, joint stiffness, and random corrosion was written, and numerical simulation analysis was carried out on the static behavior of single-layer steel reticulated shell structures after corrosion. Finally, based on parametric analysis, the random corrosion influence coefficient and joint stiffness influence coefficient were derived, and a calculation method for the elastic–plastic ultimate bearing capacity of the structure was established, which could enhance the current design methods for steel reticulated shells by taking corrosion effects into account. The research results will provide specific and programmed references for the damage identification and safety assessment of single-layer steel reticulated shell structures during their service life in strongly corrosive environments along the coast and offshore, holding important engineering significance and scientific value.
1. Introduction
As commonly used spatial steel grid structures, single-layer steel reticulated shells are characterized by reasonable stress, simple construction, and environmental protection, so their use is favored, especially in coastal and offshore projects. However, the bearing performance of these structures is inevitably threatened by various corrosion factors [1,2,3], causing serious economic losses and casualties. At present, most studies on the degradation laws of mechanical properties after corrosion are carried out at the steel material and component levels [4,5,6,7,8,9]. The analysis of the mechanical properties of the overall steel reticulated shell structure is mainly based on finite-element numerical simulation and primarily concentrates on the influence of factors such as geometric defects and component sizes. In contrast, the influence of corrosion effects is rarely considered.
Gou et al. [10] conducted a full numerical simulation analysis on the collapse mechanism of single-layer steel reticulated shell structures under the influence of temperature and impact loads, then providing the basic principles, followed by the distribution of failure parts of reticulated shell structures. Meanwhile, Ge et al. [11] established a finite-element model of a single-layer steel reticulated shell structure composed of double-web plate members and semi-rigid joints and analyzed the impact of joint bending stiffness and geometric defects on the structural stability. Instead, Mashrah et al. [12] proposed a numerical simulation method for studying the static performance of single-layer steel reticulated shell structures with H-shaped beams and discussed the influence of purlins and roof panels on the static stability of the overall structure. Zuo et al. [13] proposed a complete computer-aided workflow for the optimal design of joint parts in steel reticulated shell structures and studied the impact of the optimized joints on the overall performance of the structure through finite-element simulation analysis. Malek et al. [14] evaluated the influence of different grid shapes, grid spacings, and span–depth ratios on the failure load of steel reticulated shell structures through finite-element analysis and put forward a design guide to maximize the overall service efficiency of these structures. Ma et al. [15,16] conducted dynamic finite-element analysis on single-layer steel reticulated shell structures with semi-rigid joints, analyzed the impact of factors such as joint stiffness and initial geometric defects, and then proposed corresponding seismic design methods. Ge et al. [17] proposed a new steel reticulated shell structure composed of plates and analyzed the impact of factors such as material nonlinearity, geometric dimensions, and geometric defects on the structural stability through finite-element simulation analysis. Liu et al. [18] employed the finite-element method to study the influence of mass-detuning modes on the natural frequencies and modal shapes of steel reticulated shell structures, while Li et al. [19] established a numerical simulation method for steel reticulated shell structures subjected to oblique impact loads and deeply studied the influence of different impactor masses, velocities, and initial kinetic energies on the failure modes of reticulated shell structures under oblique impacts.
From the research presented above, it is evident that existing studies have performed comprehensive parameter analyses on the static and seismic performance of single-layer steel reticulated shells, taking into account various geometric dimensions and defects. These studies yielded significant results. However, there has been no prior research addressing the effects of corrosion on steel reticulated shells. Consequently, it is not possible to establish relevant calculation methods or safety evaluation criteria for these structures post corrosion. Additionally, this gap in research hinders the ability to provide effective recommendations for current design specifications concerning corrosion issues in steel reticulated shells.
Based on this, in this paper, a qualitative analysis and quantitative evaluation are conducted on the degradation law of static mechanical properties of single-layer steel reticulated shells after corrosion. Firstly, artificial atmosphere-accelerated corrosion tests and calibration tests are carried out on commonly used Q345 structural steel, lasting up to 320 days. Then, a modeling method for corroded single-layer steel reticulated shells based on ABAQUS Python secondary development is proposed. Subsequently, the static behavior after corrosion of single-layer steel reticulated shells under constant static load conditions is analyzed based on the corrosion test results. Finally, a calculation method for the elastic–plastic ultimate bearing capacity of single-layer steel reticulated shells is constructed to provide a scientific basis for applying, promoting, detecting, and evaluating single-layer steel reticulated shell structures in coastal and offshore energy projects.
2. Steel Corrosion Test
2.1. Experimental Design
According to “GB/T 10125-2012: Corrosion Tests in Artificial Atmospheres—Salt Spray Tests” [20], the offshore corrosion environment was simulated by the artificial atmosphere-accelerated corrosion test (AASS) [21]. The model of the environmental chamber was AB-120B. The corrosion salt solution contained 50 ± 5 g/L NaCl and was adjusted to a pH of 3.1–3.3 with acetic acid. The salt solution was turned into mist by compressed air and blown into the inner cavity. The humidity in the inner cavity was controlled at 95%, and the temperature was set to 35 ± 2 °C. Then, commonly used Q355B steel for steel structures was selected to carry out accelerated corrosion test research, and the corrosion periods were 100, 131, 157, 283, and 320 days, respectively. At the same time, Q235B steel was selected for the calibration tests, and the calibration periods were 4, 6, 7, 10, and 20 days, respectively [22], which were used to estimate the acceleration and correlation of this accelerated corrosion test.
The specimen sizes of both Q235B steel and Q345B steel were designed to be 100 × 50 × 6 mm3 [22], as shown in Figure 1. The specimens were mechanically polished to a 1200 grit size with different grades of silicon carbide paper [23], rinsed with absolute ethanol, and dried. Finally, the initial weight of the specimens was measured with a balance. The specimens were placed on an L-shaped wooden bracket so that they would be located at 60° in the vertical direction [24], as shown in Figure 2. Three parallel specimens were designed for each corrosion period (/calibration period), with a total of 30 specimens. After the specimens reached the predetermined time, they were taken out, and the rust was removed by dilute hydrochloric acid added with hexamethylenetetramine inhibitor [25]. After rust removal, all specimens were cleaned with absolute ethanol, dried, and weighed to measure the mass loss.
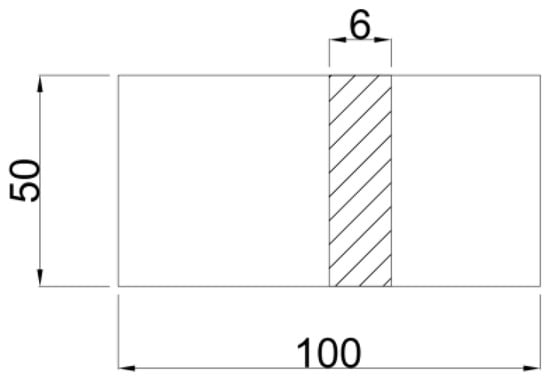
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the dimensions of the standard specimen (mm).
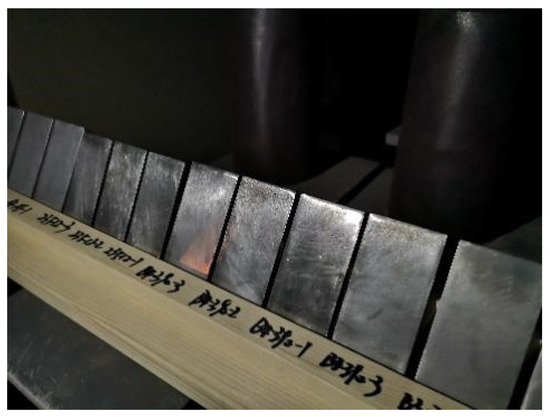

Figure 2.
Schematic diagram of the placement of specimens.
2.2. Results and Discussions
The corrosion degrees of Q235B steel and Q345B steel under different corrosion periods (/calibration periods) were represented by two parameters: mass loss rate ηC (%) and equivalent uniform corrosion depth dC (mm). The calculation methods used are those shown in Equations (1) and (2), and the calculation results are shown in Table 1 and Table 2. It should be noted that the data in the table are the average value of the corrosion degree of three parallel specimens in each group, represented by and .
where m0 represents the mass before corrosion (g); mC represents the mass after corrosion (g); ρ represents the density of the metal material (0.00785 g/mm3 for structural steel); and SA represents the total corrosion area of the metal material exposed to salt spray (mm2).

Table 1.
Test results of corrosion degree of Q235B steel under different calibration periods.

Table 2.
Test results of corrosion degree of Q345B steel under different corrosion periods.
According to the power function formula in Reference [26] and the calibration test results of Q235B steel in Table 1, the acceleration equation of the salt spray chamber (Equation (3)) was fitted, and the fitting correlation coefficient was R2 = 0.99849. Reference [27] provides the corrosion kinetic equation (Equation (4)) obtained by exposing structural steel of this grade in Qionghai, Hainan, a typical industrial marine atmospheric environment in China, for 16 years. The meteorological data for the atmospheric environment in Qionghai are as follows: an average temperature of 24.5 °C, an average humidity of 86%, a wetting time of 6314 h per year, annual rainfall of 1881 mm, and an illumination time of 2116 h per year. The corrosive factors of the atmospheric environment are as follows: a daily average chloride (Cl−) deposition of 0.199 mg/cm2, a daily average sulfur dioxide (SO2) deposition of 0.150 mg/cm2, a nitrogen dioxide (NO2) content of 0.008 mg/m3, a hydrogen sulfide (H2S) content of 0.029 mg/m3, a pH of 6.9, a chloride (Cl−) content of 1873 mg/m3 in rain, and a sulfate (SO42−) content of 9625 mg/m3.
where dC represents the equivalent uniform corrosion depth (mm), t represents the calibrated corrosion duration of the salt spray chamber (days), and ty represents the duration (years) of the natural exposure corrosion test.
Comparing these two equations and taking the equivalent uniform corrosion depth dC as the benchmark, the acceleration of the salt spray chamber-accelerated corrosion test relative to Qionghai, Hainan was calculated, as shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
Calculation results of the acceleration of the artificial atmosphere corrosion test.
The test period of 320 days was roughly equivalent to 40 years of exposure in the Qionghai environment. The correlation between the accelerated corrosion test and the actual environment was further studied based on the acceleration analysis. The corrosion test was divided into two groups: one was the calibration test result of acetate salt spray, and the other was the atmospheric exposure test result of the same material in the natural environment. The gray correlation method was used for analysis [28], which is a quantitative technique used to identify the correlation between sequences of random factors. Its fundamental concept involves assessing the degree of correlation in the developmental trends of gray processes by analyzing the similarity of the sequence curve sets. The specific calculation process is outlined below.
(1) According to the sampling time sequence, the corrosion amount of Q235B steel in the accelerated corrosion test conducted in an artificial atmosphere was organized into a corrosion depth sequence (in mm) of X1 = (0.0159, 0.0245, 0.0279, 0.0410, 0.0763).
(2) The corresponding sampling time series for the corrosion quantity sequence was (4 d, 6 d, 7 d, 10 d, 20 d).
(3) The corrosion depth sequence for the Qionghai natural environment atmospheric exposure test was calculated in relation to the time series of the artificial atmosphere-accelerated corrosion test. The time series for the Qionghai natural environment atmospheric exposure test was: (4 y, 6 y, 7 y, 10 y, 20 y). Based on Reference [27], the corresponding corrosion depth sequence for Qionghai was Y1 = (0.094316, 0.144372, 0.169737, 0.246844, 0.511098).
(4) Dimensionless processing was performed on the corrosion depth sequence.
Although the time series for the artificial atmosphere-accelerated corrosion test and the natural environment atmospheric exposure test shared the same proportion, their corresponding time axes were not uniform. Consequently, dimensionless processing was applied to all depth sequences to eliminate scaling coefficients between the time axes. By dividing each item in the sequence by the first item in the corresponding sequence, the following results were obtained: the artificial atmosphere-accelerated corrosion test results were X1 = (1, 1.540881, 1.754717, 2.578616, 4.798742), while those under the Qionghai atmospheric environment were Y1 = (1, 1.530726, 1.799663, 2.617202, 5.418996).
Using the corrosion depth sequence corresponding to Qionghai as the parent series and the corrosion depth sequence from the accelerated corrosion test under an artificial atmosphere as the sub-series, we calculated the absolute value of the difference between each item in the parent series and the sub-series.
Δ1 = (0, 0.010155, 0.044946, 0.038586, 0.620254)
According to the literature [28], the gray correlation degree r was calculated using the following formula:
Based on the gray correlation method, the calculation results of the gray correlation degree are shown in Table 4. It can be seen from the table that it is appropriate to use the artificial atmosphere-accelerated corrosion test in this paper to simulate the hot and humid coastal atmospheric environment.

Table 4.
Calculation results of the gray correlation degree of the artificial atmosphere corrosion test.
3. Programmed Modeling Method for Corroded Single-Layer Steel Reticulated Shells
3.1. Construction Process of the Overall Model of Single-Layer Steel Reticulated Shells
According to different shapes, reticulated shell structures can be divided into spherical reticulated shells, cylindrical reticulated shells, hyperboloid reticulated shells, etc. Among them, the spherical reticulated shell is also known as a dome and is currently one of the most commonly used forms. Based on different grid division methods, there are mainly the following forms: ribbed annular spherical reticulated shell, ribbed ring diagonal rod spherical reticulated shell, three-way grid spherical reticulated shell, Kiewitt spherical reticulated shell, etc. The Kiewitt reticulated shell is a reticulated shell structure formed using n radial members to divide the spherical surface into n symmetrical curved surfaces and then forming a relatively well-proportioned triangular grid with ring members and diagonal members. It has the combined advantages of the rotary division method and the equal division triangular division method. The grid size is well proportioned and the internal force distribution is uniform, so it is one of the most widely used reticulated shell structure forms in engineering practice. In addition, according to the different numbers of radial members, the Kiewitt reticulated shell structure is divided into two types: K6 and K8. Among them, the K6-type reticulated shell with six radial members is the most widely used. Therefore, in this paper, taking the K6 Kiewitt reticulated shell as a typical representative of the spatial grid structure, an analysis model is established and used as the basis for analyzing the changes in mechanical properties and disaster resistance of single-layer steel reticulated shells after corrosion. The overall model is constructed by performing the secondary development of Python on ABAQUS. The model construction process is shown in Figure 3. Welded hollow spherical joints are used for connecting joints, while circular steel tubes are used for connecting members.
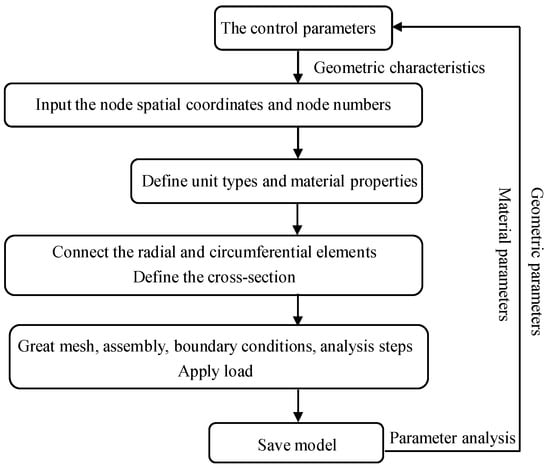
Figure 3.
Flow chart of Python parametric modeling of single-layer reticulated shell.
3.2. Simplified Simulation Method for Single-Layer Steel Reticulated Shell After Corrosion
The author’s previous studies [29,30] and studies in the literature [31] found that the corrosion morphology on the surface of welded hollow spherical joints and circular steel tubes had little influence on the mechanical behavior of connecting joints and members, and the remaining mechanical properties of joints and members during actual service were mainly controlled by the equivalent uniform corrosion depth. The literature [32] found that short rods of the same length can be divided according to the diameter of the welded spherical joint at both ends of the steel tube, and the cross-sectional area and moment of inertia of the short rod can be set according to the principle of equivalent stiffness of the joint and the short rod, thus considering the semi-rigidity of the joint. The calculation method for the cross-sectional dimensions of the equivalent short bars is as follows:
Assuming that the outer diameter and inner diameter of the short rod j corresponding to joint i are Dji and dji, respectively, Equations (6) and (7) can be combined to determine the values of the outer diameter and inner diameter required for the equivalent short rod.
KNi and KMi represent the axial stiffness and bending stiffness of joint i, respectively, measured in N/m and N·m/rad. The calculation formulas are provided in Equations (8) and (9). Here, E denotes the elastic modulus of the steel, while di and Di refer to the wall thickness of the welded hollow spherical joint i, the outer diameter of the steel pipe, and the outer diameter of the hollow sphere, respectively. Additionally, Aji and Iji represent the cross-sectional area and moment of inertia of the short rod after joint i has been transformed into short rod j.
Based on the actual diameter, wall thickness, and connected steel pipe diameter of the specified joints in Table 5 of this article, the inner and outer diameters of various equivalent short rods required for the model can be calculated. Additionally, different short rod sections can be assigned values by modifying the Python script. The schematic diagram of the end-node domain of the finite-element model, after introducing equivalent short rods, is shown in Figure 4.

Table 5.
Geometric parameter allocation of K6 Kiewitt reticulated shell.
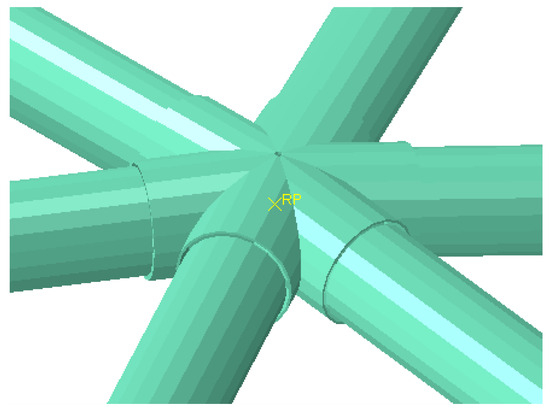
Figure 4.
Rod end-node domain after introducing equivalent short rods.
Therefore, based on the simplified assumptions of weakening the wall thickness of members and the equivalent short rod of joints based on the equivalent uniform corrosion depth, the geometric dimensions of joints and members are modified by writing Python code to realize the numerical simulation of single-layer steel reticulated shells after corrosion. The detailed Python parametric modeling idea is shown in Figure 5. If different corrosion conditions are considered, only the assignment statement for the member section in the command stream and the scope of action of the random function in the loop need to be changed. The suggestions in Technical Specification for Spatial Frame Structures (JGJ7-2010) [33] are taken to regard the lowest-order buckling mode of the structure as the shape of the initial geometric defect, and the maximum calculated value of the initial defect can be taken as 1/300 of the span of the reticulated shell. If it needs to only analyze the mechanical performance response under the constant static load condition of the rust-damaged reticulated shell structure, only the static risk analysis step in Figure 5 needs to be changed to the static general analysis step, and then the displacement, stress, strain, and support reaction force after the corrosion of the corresponding key parts can be exported.

Figure 5.
Simplified simulation method of single-layer reticulated shell after corrosion.
4. Static Behavior After the Corrosion of Single-Layer Steel Reticulated Shells Under Constant Static Load Conditions
The K6 Kiewitt single-layer spherical reticulated shell model with a span of 40 m, a rise of 8 m, and six ring rods was selected, as shown in Figure 6. Circular steel tubes were used for long rods. The section of the main rib rod and ring rod was Φ121 × 3.5, and the section of the diagonal rod was Φ114 × 3, with a unit of mm [34]. The diameter of the welded hollow spherical joint was 300 mm, and the wall thickness was 8 mm (when modeling, considering the “equivalent short rod method”, the equivalent sections were Φ133.21 × 2.88 and Φ125.67 × 2.88, respectively). The geometric dimensions of the structure and the cross-section of the members were preliminarily checked by structural design software, which could ensure that there was considerable bearing capacity and that they would not be damaged under normal use. The model element was the B31 beam element. The steel was Q345, with a yield strength of 370 MPa, an ultimate strength of 510 MPa, and an elastic modulus of 206 GPa. Then, the influence of mesh division on the static mechanical performance analysis results of the rust-damaged single-layer reticulated shell structure was studied in detail, and the modeling scheme of taking the number of meshes in the circular steel tube part as 6 and the number of meshes in the equivalent short rod part as 1 was determined. Moreover, ABAQUS was used to automatically calculate the self-weight of the member bar. The dead load on the roof was taken as 0.5 kN/m2, and the live load was taken as 0.5 kN/m2; it was supported by a three-way hinged rigid support fully distributed around. Finally, it was assumed that there would be an ideal working condition where both joints and circular steel tubes would undergo equivalent uniform corrosion to simulate the entire corrosion process of the structure. The equivalent uniform corrosion depth results obtained in Table 2 were used to uniformly weaken all joints and all long rod sections on the reticulated shell structure, respectively, and carry out the mechanical performance analysis of the corroded single-layer steel reticulated shell under the constant static load condition.
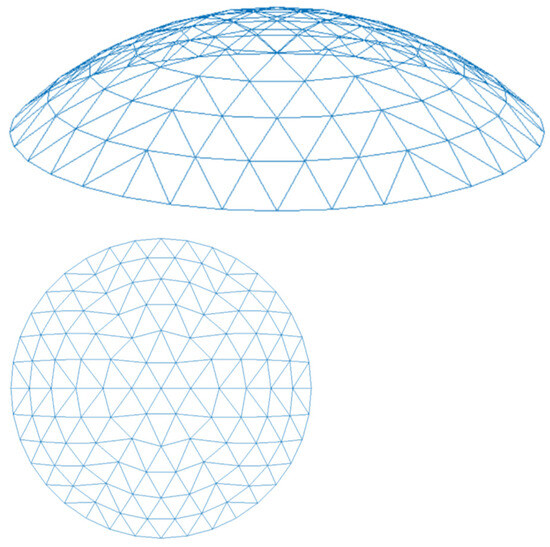
Figure 6.
K6-type Kiewitt single-layer spherical reticulated shell.
4.1. Displacement Response
Figure 7 shows the displacement change history over time of the central joint of the reticulated shell and typical joints (N1-N7) on each ring of ring rods and the joint with the maximum displacement (Nmax). As the outermost ring joints are support joints and there will always be no displacement, they are not shown in Figure 7. It should be noted that the displacement values in Figure 7 are positive when pointing to the inside of the reticulated shell.
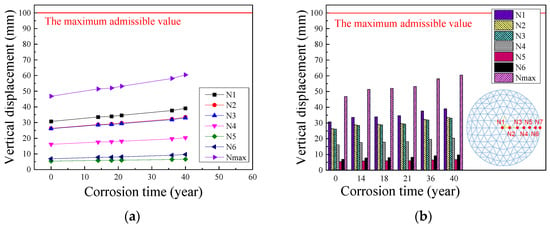
Figure 7.
Variation law of vertical displacement of each joint of reticulated shell under different service years in Qionghai: (a) line chart and (b) column chart.
The analysis found that, as the service life increased, the vertical displacements of each typical joint of the reticulated shell gradually increased, showing an approximately linear pattern. Meanwhile, the growth rate of the maximum displacement value Nmax was slightly faster than that of other typical joints. However, the structure did not experience an overall buckling failure characterized by sudden displacement changes. After 40 years of equivalent service in Qionghai, the maximum joint displacement was 60.47 mm, still meeting the requirement as it did not exceed 1/400 of the span in Technical Specification for Spatial Frame Structures (JGJ7-2010) [33]. This indicates that, when corrosion is uniformly distributed throughout the reticulated shell, the single-layer reticulated shell has good corrosion resistance and is not likely to be suddenly damaged during service. Therefore, it is greatly possible to continue its service after regular inspection, assessment, repair, and reinforcement.
In addition, it should also be noted that, when an abnormal joint with extremely severe local corrosion is found during detection, it is necessary to modify the cross-sectional assignment of the equivalent short rod of the joint in the abnormal part in the Python script and then complete the modeling and submit the analysis to carry out the specific analysis of the static mechanical performance of the single-layer reticulated shell after corrosion in specific projects.
4.2. Stress Response
The analysis found that, as the corrosion degree of the structure continuously increased, the location of the most dangerous member of the reticulated shell remained unchanged and was always located on the diagonal rod in the middle of the symmetrical area of the second ring near the support (Figure 8), while the stress value almost increased linearly (Figure 9). When the service time was 40 years, the maximum stress value was 90.01 MPa. Compared to the uncorroded structure, the maximum stress value increased by 17.26 MPa, but it was still far less than the yield strength of the steel selected for the model. Therefore, it can be considered that, for the reticulated shell structure, considering the joint volume, stiffness, and uniform corrosion, each member meets the requirements of stability and strength-bearing capacity during its basic service process. Under a normal service life and the service environment in Qionghai, the uniform corrosion of the full model had little influence on the stress distribution form and the change in extreme stress values of the member bars. Each member bar was in an elastic state throughout the corrosion process.
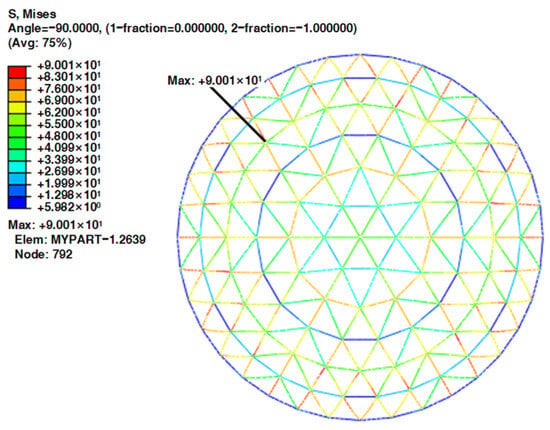
Figure 8.
Mises stress distribution of reticulated shell members after 40 years of service in Qionghai.
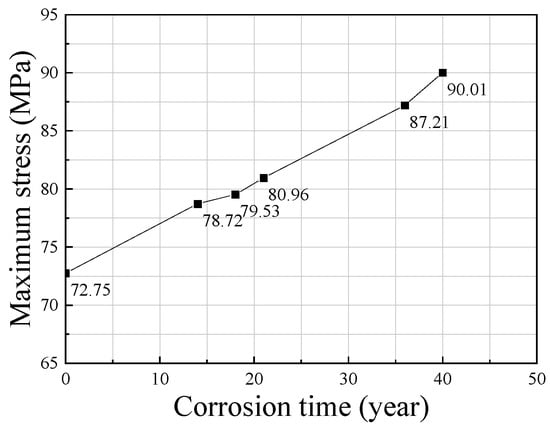
Figure 9.
Variation law of maximum Mises stress of member sections at different service years in Qionghai.
4.3. Support Reaction Response
Representative support joints were selected according to the symmetry of the structure (Figure 10), and the broken line chart of the change law of the three-way support reaction force with service time (/steel uniform corrosion degree) and the histogram of the absolute value of the support reaction force were drawn, respectively, as shown in Figure 11. It should be noted that the vertical support reaction force is positive when it is vertically upward, the radial support reaction force is positive when it goes from the center to the edge, and the circumferential support reaction force is positive in the counterclockwise direction. The reaction force of the reticulated shell support joint did not change significantly during the entire corrosion process, and the support joint at the main rib was most likely to be damaged. Although under the conditions of this model the change with corrosion was not obvious, full attention and a detailed analysis should be given in the corrosion assessment of the reticulated shell structure for the case of the non-uniform corrosion of joints, especially when the support joint at the main rib is extremely severely corroded.
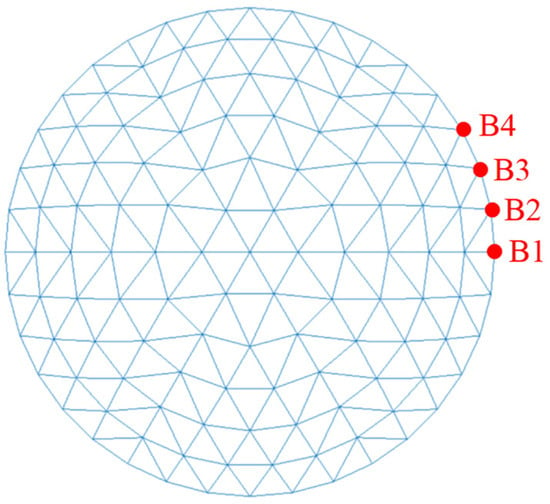
Figure 10.
Selection of support joints.
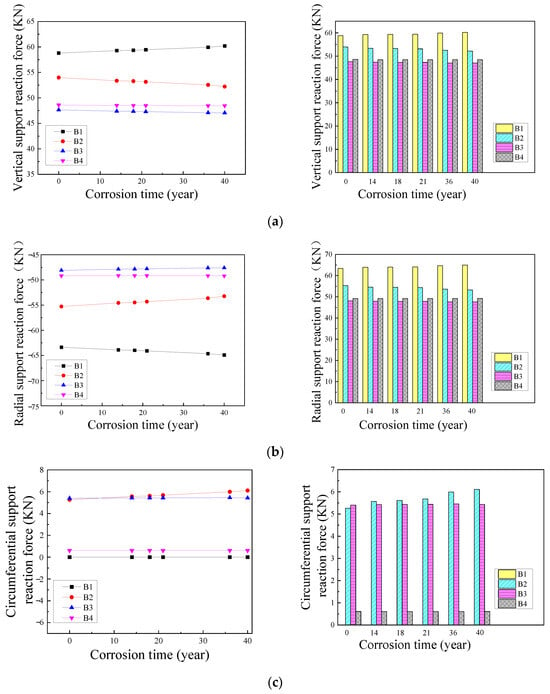
Figure 11.
Comparison of the variation laws of reaction forces of typical support joints under different service years in Qionghai: (a) vertical reaction force; (b) radial reaction force; and (c) circumferential reaction force.
5. Calculation Method of the Elastic–Plastic Ultimate Bearing Capacity of Single-Layer Steel Reticulated Shells After Corrosion
Based on Figure 5, a parametric analysis was carried out on the elastic–plastic ultimate bearing capacity of the single-layer reticulated shell structure after corrosion. Based on Technical Specification for Spatial Frame Structures (JGJ7-2010) [33] and Welded Hollow Spherical Node of Space Grid Structures (JG11-2009) [35], parameters were selected as shown in Table 5 and Table 6. Figure 12 shows three different corrosion modes of the reticulated shells.

Table 6.
Model calculation parameters.
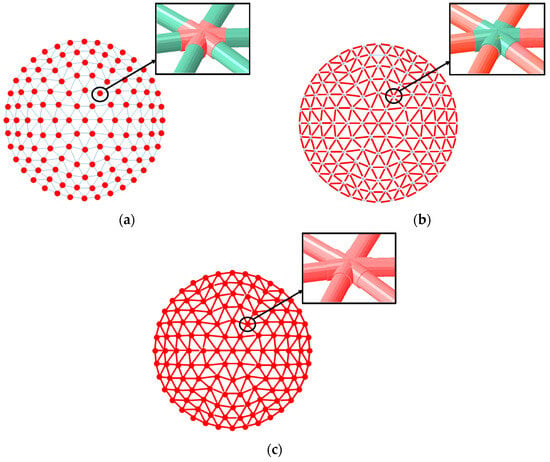
Figure 12.
Three different corrosion modes of the reticulated shells (red represents the corroded area): (a) overall corrosion of joint area/only hollow sphere corrosion; (b) only steel tube corrosion; and (c) uniform corrosion of the entire component.
5.1. Analysis of Factors Influencing the Elastic–Plastic Ultimate Bearing Capacity
- (1)
- Influence of Corrosion Degree
By referring to the cross-sectional data in Table 6, Figure 13 takes the corrosion rate of the main rib rods and the ring rods (referred to as the corrosion rate of main rib and ring rods) and the corrosion rate of the diagonal rods as independent variables, while the reduction coefficient of the elastic–plastic ultimate bearing capacity of the structure is the dependent variable. It is found that the reduction coefficient of the elastic–plastic ultimate bearing capacity linearly decreases with the increase in the degree of uniform corrosion. When taking the corrosion rate of the weak section (diagonal rod section) as the independent variable, the impact of uniform corrosion on the reduction coefficient of the elastic–plastic ultimate bearing capacity of the structure is independent of both the cross-sectional size and the structural span. Under the premise of uniform corrosion of the entire component, the corrosion rate of weak section components is the dominant factor influencing the weakening of the elastic–plastic ultimate bearing capacity of the structure.
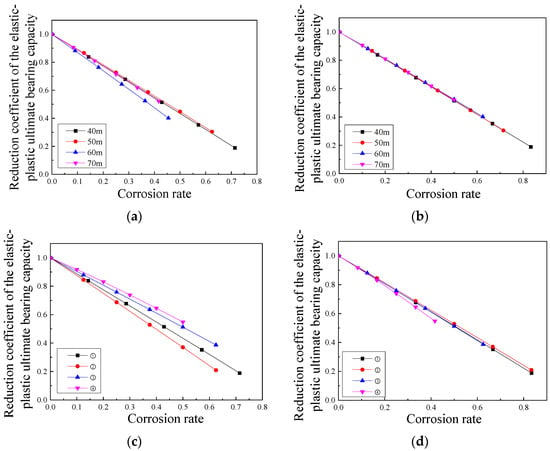
Figure 13.
Influence of corrosion rate on the reduction coefficient of the elastic–plastic ultimate bearing capacity: (a) corrosion rate of main rib rod and ring rod at different spans; (b) corrosion rate of diagonal rod at different spans; (c) corrosion rate of main rib rod and ring rod in different sections; and (d) corrosion rate of diagonal rod in different sections.
- (2)
- Influence of Corrosion Location
The location of corrosion often has a significant impact on structural performance [36]. Finite-element analysis was carried out by taking the reticulated shell structure with a span of 40 m, a rise–span ratio of 1/5, and a section of ① as an example, and the results are shown in Figure 14. It should be noted that, for the horizontal coordinate corrosion rate, Figure 14b shows the cases of only steel pipe corrosion and uniform corrosion of the entire component, and it takes the wall thickness loss rate of the diagonal rod (weak section rod) as the corrosion rate; for the cases of overall corrosion of the joint area and only hollow sphere corrosion, it takes the wall thickness loss rate of the joint (WS3008) as the corrosion rate. Observations show that the ultimate bearing capacity of the structure in the case of only steel pipe corrosion and uniform corrosion of the entire component decreases linearly with the increase in the corrosion rate of weak rods, while the ultimate bearing capacity of the structure in the case of only joint corrosion decreases nonlinearly with the increase in the joint corrosion rate, and the rate of decline gradually accelerates. In addition, under the same corrosion depth, the corrosion of only the joint part has much less influence on the ultimate bearing capacity of the structure than the corrosion of the steel pipe. Therefore, when detecting and evaluating existing structures, it is recommended to pay more attention to the corrosion of weak section members, especially the corrosion of members at the ball–tube connection. When conducting parametric analysis of numerical simulations, the assumption recommending to consider the uniform corrosion of the entire component is safer.
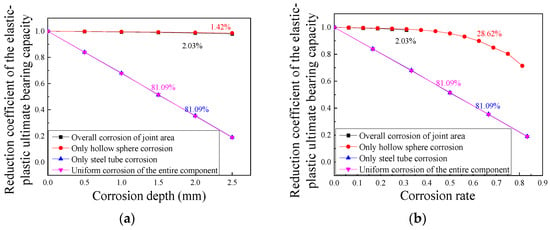
Figure 14.
Influence of corrosion location on the reduction coefficient of the elastic–plastic ultimate bearing capacity: (a) corrosion depth and (b) corrosion rate of weak rod section.
- (3)
- Influence of Random Corrosion
The model effect of introducing the random corrosion function is defined as asymmetric corrosion, and the uniform corrosion of the entire component is defined as symmetric corrosion. Then, the two are compared. The median value of the random corrosion function is defined as the same as the uniform corrosion value of the entire component. The lower and upper limits of the random function correspond to the previous and next corrosion gradients of the uniform corrosion value in Table 6, respectively. Assuming that the calculation times of the random corrosion model are 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, and 40 times, respectively, then it is found that the relevant parameters of normal distribution change slightly after the calculation times are over 10. Therefore, according to the calculation times (10), a random corrosion analysis is performed on all cross-sectional dimensions, structural spans, and rise–span ratios in Table 5 and Table 6, and the influence of joint stiffness and size is considered, with a total of 400 models. The random corrosion reduction coefficient is defined as qc,r/qc. Then, qc is the ultimate bearing capacity calculated by the uniform corrosion of the entire component corresponding to the median value of the corrosion interval, while qc,r is the calculation result of the random corrosion of the entire component. To eliminate the influence of corrosion depth on the cross-sectional dimension, the variation law of the random corrosion reduction coefficient is analyzed by taking the wall thickness reduction rate (corrosion rate) of the weak section member as an independent variable, as shown in Figure 15. The analysis finds that the random corrosion reduction coefficient decreases as the corrosion rate of the weak section rod increases, and, as the corrosion rate increases, the distribution of the random corrosion reduction coefficient tends to be discrete under the influence of other geometric parameters. In addition, the influence of random corrosion on the elastic–plastic ultimate bearing capacity of the structure is still correlated with the cross-sectional dimension and structural span. The bearing capacity of the structure under random corrosion decreases as the structure’s rise–span ratio, structural span, and cross-sectional dimension decrease. For convenient application in practical engineering, all random corrosion reduction coefficients are summarized as shown in Figure 16.
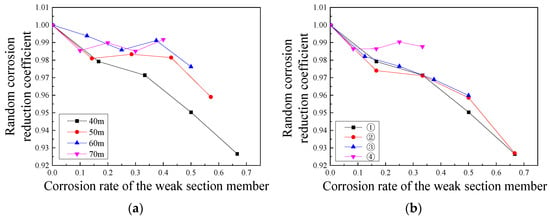
Figure 15.
Summary of random corrosion reduction coefficients of K6 reticulated shells: (a) different spans and (b) different sections.
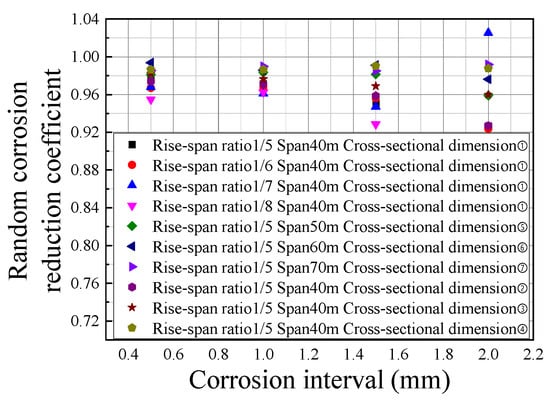
Figure 16.
Summary of random corrosion reduction coefficients of K6 reticulated shells.
Based on all the parametric analysis results (Figure 16), the mean value (0.96907) and variance (0.0005597956) of the random corrosion reduction coefficient of the K6 Kiewitt reticulated shell structure within the span of 40–70 m, the rise–span ratio of 1/5–1/8, the cross-section of common components, and the corrosion interval of 0–2.5 mm were calculated. Considering a guaranteed rate of 95%, the engineering-recommended random corrosion reduction coefficient αc,r was finally obtained, as shown in Equation (10). Or, for safety considerations, the minimum value of 0.901 of all the data results simulated in this section could also be taken as αc,r.
- (4)
- Influence of Joint Stiffness
The joint stiffness influence coefficient is defined as αJ = qc/qc,G, where qc,G is the model calculation result without considering the joint volume and stiffness. The variation law of the joint stiffness influence coefficient and other parameters is shown in Figure 17. It is observed that, under different rise–span ratios, spans, and cross-sectional dimensions, the influence of joint stiffness and volume on the elastic–plastic ultimate bearing capacity of the structure does not exceed 3%, and the joint stiffness influence coefficient qc/qc,G is between 1.000 and 1.027. In addition, the joint stiffness influence coefficient gradually increases as the corrosion degree increases: the greater the corrosion degree, the more discrete the distribution of the joint stiffness influence coefficient. Moreover, under the same degree of corrosion, there is no obvious correlation between the joint stiffness influence coefficient and various geometric parameters of the structure. It is speculated that this is because the gap in the degree of section weakening at the point of connection between members, considering and not considering joints, gradually increases as the degree of corrosion increases, so the joint stiffness influence coefficient gradually increases as well. The instability process of a reticulated shell structure is a continuous redistribution process of internal forces. Different degrees of corrosion may create different finite-element models that are closest to the optimal force-bearing structure. Therefore, there is no obvious correlation between the joint stiffness influence coefficient and geometric parameters.
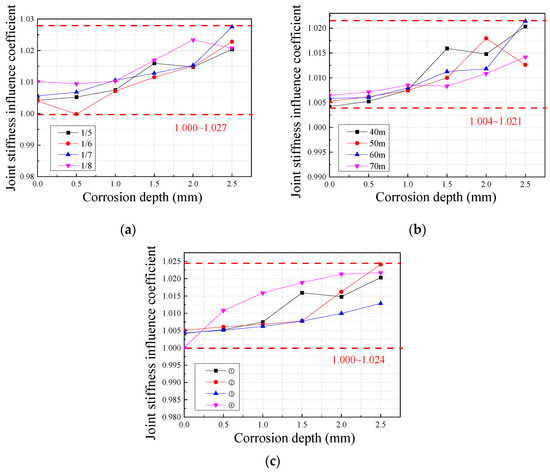
Figure 17.
Variation law of joint stiffness influence coefficient: (a) different rise–span ratios; (b) different spans; and (c) different sections.
In conclusion, when there are no particularly high requirements regarding analytical accuracy, the beam element model can be conservatively used for direct analysis and calculation without considering the volume and stiffness of the welded hollow spherical joint. However, if the influence of joints needs to be considered in a refined way, the joint stiffness influence coefficients obtained from different geometric parameters under the same degree of corrosion can be averaged, and then polynomial fitting can be performed with the corrosion depth as the independent variable. The fitting result is shown in Equation (11), and R2 = 0.998, indicating a good fitting effect. In the formula, dC is the equivalent uniform corrosion depth of the entire component (mm).
5.2. Calculation Method of Elastic–Plastic Ultimate Bearing Capacity
Finally, based on the parametric analysis results and the formula for calculating the stable bearing capacity of reticulated shell structures in the current Technical Specification for Spatial Frame Structures (JGJ7-2010) [33], the influence of corrosion damage and joint stiffness is introduced to obtain a simplified calculation method for the elastic–plastic ultimate bearing capacity of corroded single-layer reticulated shell structures (Equation (12)).
Here, qc,r,J is the elastic–plastic ultimate bearing capacity (KN), Be,c is the equivalent membrane stiffness (KN/m) of the corroded reticulated shell, and De,c is the equivalent flexural stiffness (KN·m) of the corroded reticulated shell. For Be,c and De,c, the cross-sectional dimensions after corrosion are directly taken to calculate the cross-sectional area and moment of inertia of the member, and they are calculated by referring to the formula in Appendix C of Technical Specification for Spatial Frame Structures (JGJ7-2010) [33] for calculation. Meanwhile, r is the radius of curvature (m) of the spherical surface of the reticulated shell; Ke is the coefficient obtained by regression analysis after a large number of elastic numerical calculations, with Ke = 1.05; cp is the plastic reduction coefficient, and the specification suggests taking cp = 0.47 for reticulated shell structures when considering a guarantee rate of 95%; αc,r is the random corrosion influence coefficient, measuring 0.9 for safety by referring to Equation (10); and αJ is the joint stiffness influence coefficient, measuring 1.0 for safety by referring to Equation (11).
In the actual application process, the concept of safety factor K also needs to be introduced. According to the current technical specification for grid structures, the safety factor is generally taken as 2 for the elastic–plastic ultimate bearing capacity. That is, the corroded elastic–plastic allowable bearing capacity [qc,r,J] of the reticulated shell structure considering joint stiffness and random corrosion is taken according to Equation (13).
It should be noted that the above calculation method is a fitting result obtained by finite-element analysis based on the parameters within the range of Table 5 and Table 6. Therefore, its application range is also limited to the K6 Kiewitt rigidly supported reticulated shell structure with a rise–span ratio of 1/5 to 1/8, a span of 40 to 70 m, common component sections, and a corrosion interval of 0 to 2.5 mm. As for other support methods and reticulated shell forms, the Python program in Figure 3 needs to be adjusted, and corresponding calculation methods need to be proposed based on a similar parametric analysis.
6. Conclusions
A research was carried out on the static behavior and calculation method of the elastic–plastic ultimate bearing capacity of single-layer steel reticulated shell structures after corrosion based on the results and analysis of the accelerated corrosion test of Q345 steel in an artificial atmosphere. Based on this study, the following conclusions were drawn.
(1) An equivalent conversion calculation method between the accelerated corrosion test under an artificial atmosphere (AASS) and the actual atmospheric environment is hereby proposed. A total of 320 days of testing time are roughly equivalent to 40 years of exposure in the atmospheric environment of Qionghai. Based on the calculation of the gray correlation degree, it was verified that the accelerated corrosion test in artificial atmosphere (AASS) is suitable for simulating the hot and humid coastal atmospheric environment.
(2) A parametric modeling process for the overall model of single-layer steel reticulated shells is put forward, and a simplified calculation and simulation method for the dimension and stiffness of joints is established. A single-layer reticulated shell Python program considering the size and stiffness of welded spherical joints and different corrosion conditions for the ABAQUS finite-element software (version 6.14-4) is established and applied to analyze the static behavior after corrosion and the elastic–plastic ultimate bearing capacity of single-layer steel reticulated shell structures under static load conditions.
(3) Under static load conditions, normal service life, and service environment in Qionghai, uniform corrosion of the entire component has little impact on the displacement distribution form of joints, the extreme value change in stress in members, and the change in reaction force. After corrosion, each component is still in an elastic state. Single-layer steel reticulated shells have good corrosion resistance and are not likely to be suddenly damaged during service. There is a great possibility that they could continue to serve after regular inspection, evaluation, repair, and reinforcement. However, during the inspection process, special attention should be paid to the abnormal local corrosion of the second circle of diagonal members near the support and the support joints at the main ribs.
(4) The reduction coefficient of the elastic–plastic ultimate bearing capacity decreases with the increase in the component corrosion rate. When taking the corrosion rate of weak section members (diagonal members) as the independent variable, the impact of uniform corrosion of the entire component on the reduction coefficient of the structure’s elastic–plastic ultimate bearing capacity is independent of the cross-sectional dimension and structural span. The influence of joint corrosion on the ultimate bearing capacity of single-layer reticulated shell structures is much smaller than that of member corrosion. Therefore, when inspecting reticulated shell structures, attention should be paid to the corrosion degree of weak section members. When conducting simulations and evaluations, it is recommended to apply the uniform corrosion model of the entire component more conservatively.
(5) The reduction coefficient of random corrosion decreases with the increase in the corrosion rate of weak section members. The influence of random corrosion on the structure’s elastic–plastic ultimate bearing capacity is still correlated with the cross-sectional dimension and structural span. Under random corrosion, the bearing capacity of the structure decreases with the decrease in the structure’s rise–span ratio, structural span, and cross-sectional dimension. The influence of joint stiffness on the structure’s bearing capacity increases with the increase in the degree of corrosion and has no obvious correlation with geometric parameters.
(6) The uniform corrosion of the entire component is taken as a section transformation and directly introduced into the theoretical formula. Meanwhile, based on the parametric analysis results, the random corrosion influence coefficient and the joint stiffness influence coefficient are introduced, and a calculation method for the elastic–plastic ultimate bearing capacity of single-layer steel reticulated shell structures is proposed, providing a scientific basis for applying, promoting, detecting, and evaluating single-layer steel reticulated shell structures in coastal and offshore energy projects.
7. Future Work
When conducting random corrosion analysis on the structures discussed in this article, the division of the random corrosion interval was artificially assumed. The selected interval was defined as the corrosion depth ±0.5 mm, calculated based on the corrosion kinetics equation for the same period of steel. Although this interval range was relatively large compared to the annual atmospheric corrosion depth of structural steel, some extreme cases might still have been overlooked. In the future, plans will be made to conduct random corrosion analyses on shell structures in extreme scenarios where corrosion distribution is highly uneven. Additionally, efforts will be made to further enhance and refine the calculation method for the elastic–plastic ultimate bearing capacity of single-layer shell structures after corrosion.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.C.; methodology, H.C.; software, H.C.; validation, H.C. and H.Z.; formal analysis, H.C. and F.Q.; investigation, H.C., H.Z. and F.Q.; resources, H.C. and F.Q.; data curation, H.C., H.Z. and F.Q.; writing—original draft preparation, H.C.; writing—review and editing, F.Q.; visualization, H.C. and F.Q.; supervision, F.Q.; project administration, H.C.; and funding acquisition, H.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China grant number 52308187.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author due to privacy limitations.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Guo, Q.; Wu, Z.; Xing, Y.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Li, W. Corrosion evolution and mechanical property deterioration of Q355NH weathering steel in long-term neutral salt spray environment. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 411, 134193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, F.; Yuan, H.; Ai, D.; Xu, C. A Spiral Single-Layer Reticulated Shell Structure: Imperfection and Damage Tolerance Analysis and Stability Capacity Formulation for Conceptual Design. Buildings 2021, 11, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seghier, M.; Plevris, V.; Solorzano, G. Random forest-based algorithms for accurate evaluation of ultimate bending capacity of steel tubes. Structures 2022, 44, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Jia, C.; Zhao, O.; Guo, L. Local corrosion morphology analysis and simplification of low carbon steel plates. Ocean. Eng. 2023, 268, 113372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Lou, J.; He, H.; Wu, C.; Huang, Y.; Su, N.; Li, S. Effects of Carbon Content on the Properties of Novel Nitrogen-Free Austenitic Stainless Steel with High Hardness Prepared via Metal Injection Molding. Metals 2023, 13, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, P. Corrosion fatigue behavior and life prediction of butt-welded joint considering loading frequency. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2024, 219, 108744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.; Huo, H.; Wang, Y.; Fang, C. Influence of corrosion on ultra-low cycle fatigue performance of steel butt-welded joints with various welding methods. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2024, 215, 108561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Y.; Peng, J.; Xiao, L.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J. Fatigue Behavior of High-Performance Steel Beams Subjected to Different Corrosion Conditions. Int. J. Steel Struct. 2023, 23, 1105–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Kong, Z.; Xu, S. Hysteresis performance of steel beam-column welded T-joints corroded in steel industrial atmosphere. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2024, 159, 108118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, B.; Wang, X.L.; Wu, C.L. Experimental and numerical study on the behavior of single-layer spherical reticulated shells under the combined action of temperature and impact load. Thin-Walled Struct. 2023, 182, 110333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, H.B.; Wan, H.P.; Zheng, Y.; Luo, Y. Experimental and numerical study on stability behavior of reticulated shell composed of plate members. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2020, 171, 106102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashrah, W.; Rima, B.; Liu, H.; Chen, Z.; Fu, B. Static stability analysis of steel single-layer spherical latticed shells with and without roofing systems. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 77, 107141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, W.; Chen, M.-T.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, O.; Cheng, B.; Zhao, J. Additive manufacturing oriented parametric topology optimization design and numerical analysis of steel joints in grid shell structures. Thin-Walled Struct. 2023, 188, 110817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malek, S.; Wierzbicki, T.; Ochsendorf, J. Buckling of spherical cap grid shells: A numerical and analytical study revisiting the concept of the equivalent continuum. Eng. Struct. 2014, 75, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Fan, F.; Wen, P.; Zhang, H.; Shen, S. Experimental and numerical studies on a single-layer cylindrical reticulated shell with semi-rigid joints. Thin-Walled Struct. 2015, 86, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Shan, Z.; Fan, F. Dynamic behaviour and seismic design method of a single-layer reticulated shell with semi-rigid joints. Thin-Walled Struct. 2017, 119, 544–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, H.-B.; Wan, H.-P.; Luo, Y. Numerical investigation on stability of reticulated shell structures composed of built-up plate members. Thin-Walled Struct. 2023, 192, 111121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Lu, Z.; Gao, W.; Demartino, C.; Li, Y. Curve veering in spherical reticulated shells: Numerical simulations and mechanism analysis. Thin-Walled Struct. 2023, 191, 111026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Chen, G.; Lu, H.; Ke, L.; Wang, H.; Jian, B. Dynamic Responses of Single-Layer Reticulated Shells under Oblique Impact Loading. Buildings 2024, 14, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 10125-2012; Corrosion Tests in Artificial Atmospheres—Salt Spray Tests. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2012.
- Jiang, C.; Wu, C.; Jiang, X. Experimental study on fatigue performance of corroded high-strength steel wires used in bridges. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 187, 681–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 19292.4-2003; Corrosion of Metals and Alloys—Corrosivity of Atmospheres—Determination of Corrosion Rate of Standard Specimens for the Evaluation of Corrosivity. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2003.
- Yu, J.; Wang, H.; Yu, Y.; Luo, Z.; Liu, W.; Wang, C. Corrosion behavior of X65 pipeline steel: Comparison of wet–Dry cycle and full immersion. Corros. Sci. 2018, 133, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 14293-1998; Corrosion Tests in Artificial Atmospheres—General Requirement. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 1998.
- ISO 8407; Corrosion of Metals and Alloys—Removal of Corrosion Products from Corrosion Test Specimens. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009.
- ISO 9224; Corrosion of Metals and Alloys—Corrosivity of Atmospheres—Guiding Values for the Corrosivity Categories. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012.
- Liang, C.; Hou, W. Sixteen-year atmospheric corrosion exposure study of steels. J. Chin. Soc. Corros. Prot. 2005, 25, 1–6. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liang, J. Experimental Study on Fatigue Behavior of Corroded Weathering Steel Without Coating. Master’s Thesis, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China, 2017. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Liu, H.; Chen, Z.; Xiong, Y. Experimental investigation of ultimate bearing capacity of corroded welded hollow spherical joints. Structures 2023, 57, 105127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Liu, H.; Chen, Z. Residual behaviour of corroded welded hollow spherical joints subjected to eccentric loads. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2021, 182, 106661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z. Mechanical Properties and Bearing Capacity Evaluation Method of Corroded Circular Steel Tubes Under Axial Compression. Master’s Thesis, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, China, 2021. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J. Study on the Post-Fire Performance of Space Lattice Structures with Welded Hollow Spherical Joints. Ph.D. Thesis, Tianjin University, Tianjin, China, 2019. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- JGJ 7-2010; Technical Specification for Space Frame Structures. China Architecture Publishing & Media Co., Ltd.: Beijing, China, 2010. (In Chinese)
- Cao, Z. Elasto-Plastic Stability of Reticulated Shells; Harbin Institute of Technology: Harbin, China, 2007. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- JG11-2009; Welded Hollow Spherical Node of Space Grid Structures. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2009. (In Chinese)
- Simoncelli, M.; Angelo Aloisio, A.; Zucca, M.; Venturi, G.; Alaggio, R. Intensity and location of corrosion on the reliability of a steel bridge. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2023, 206, 107937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).