Growth of Surface Oxide Layers on Dendritic Cu Particles by Wet Treatment and Enhancement of Sinter-Bondability by Using Cu Paste Containing the Particles
Abstract
1. Introduction
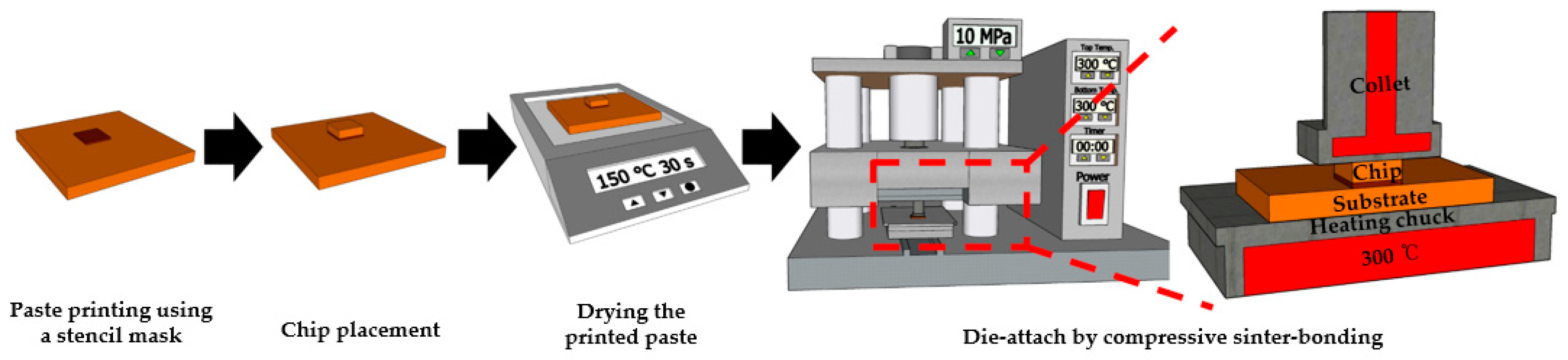
2. Materials and Methods
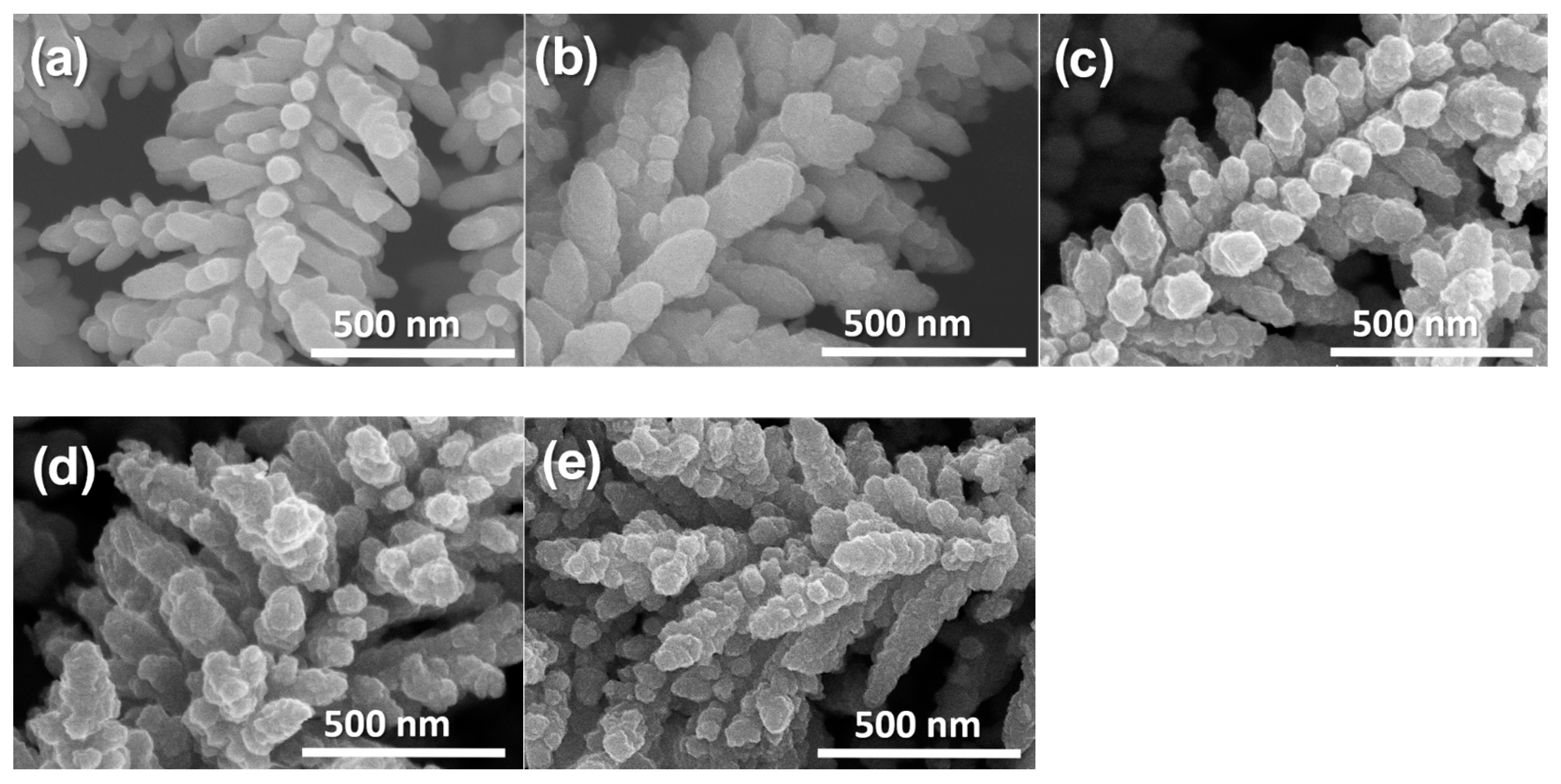
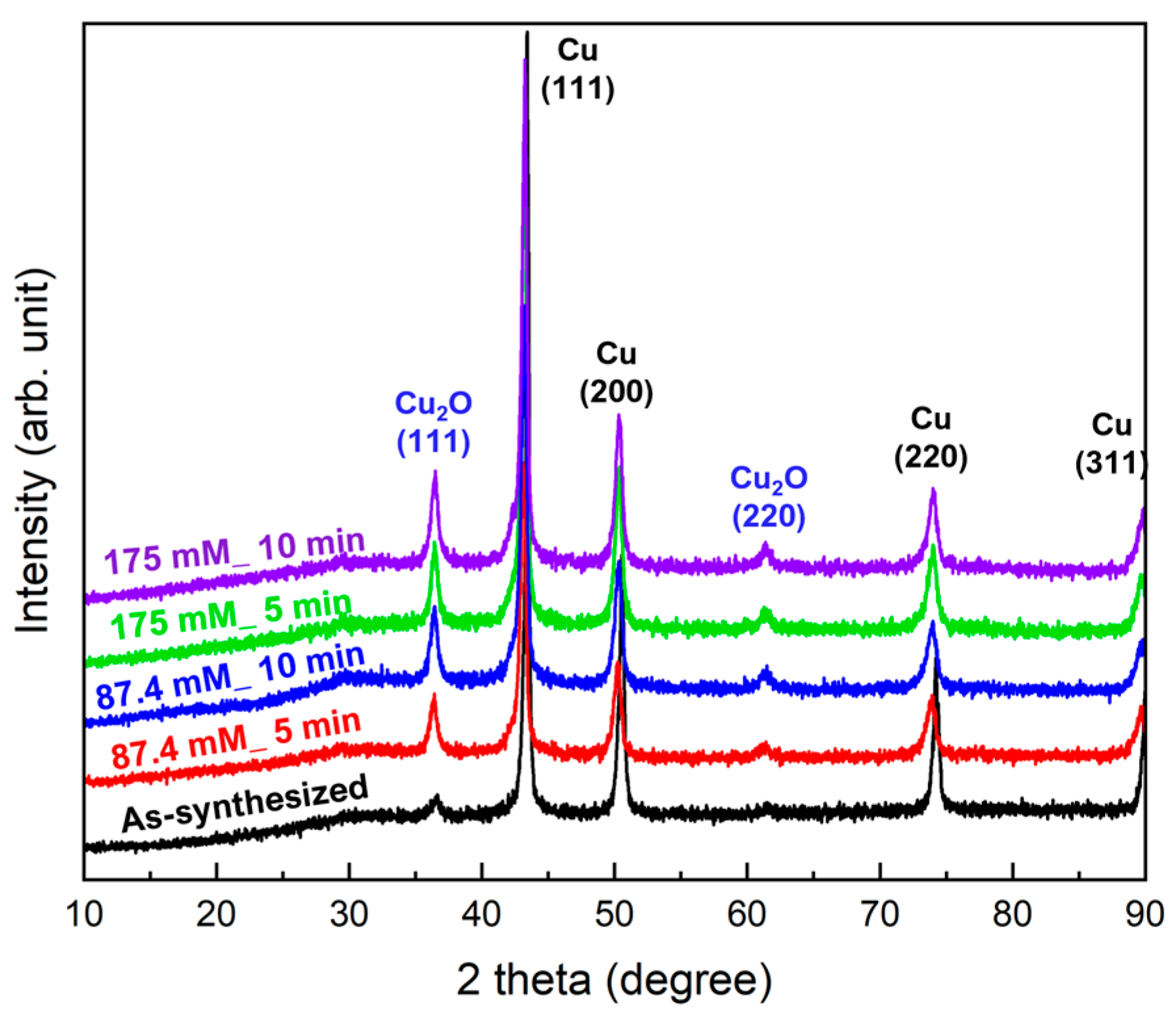
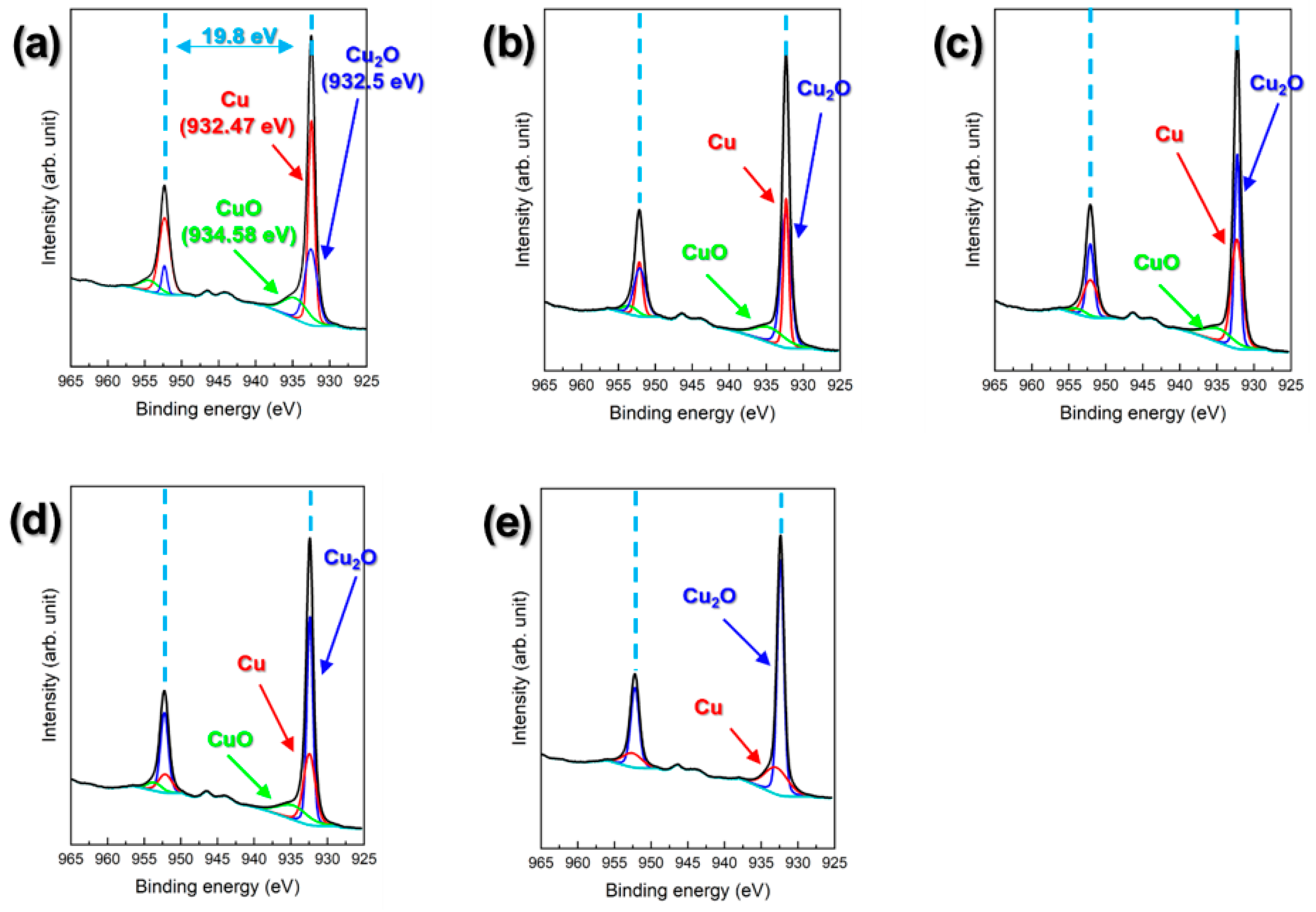
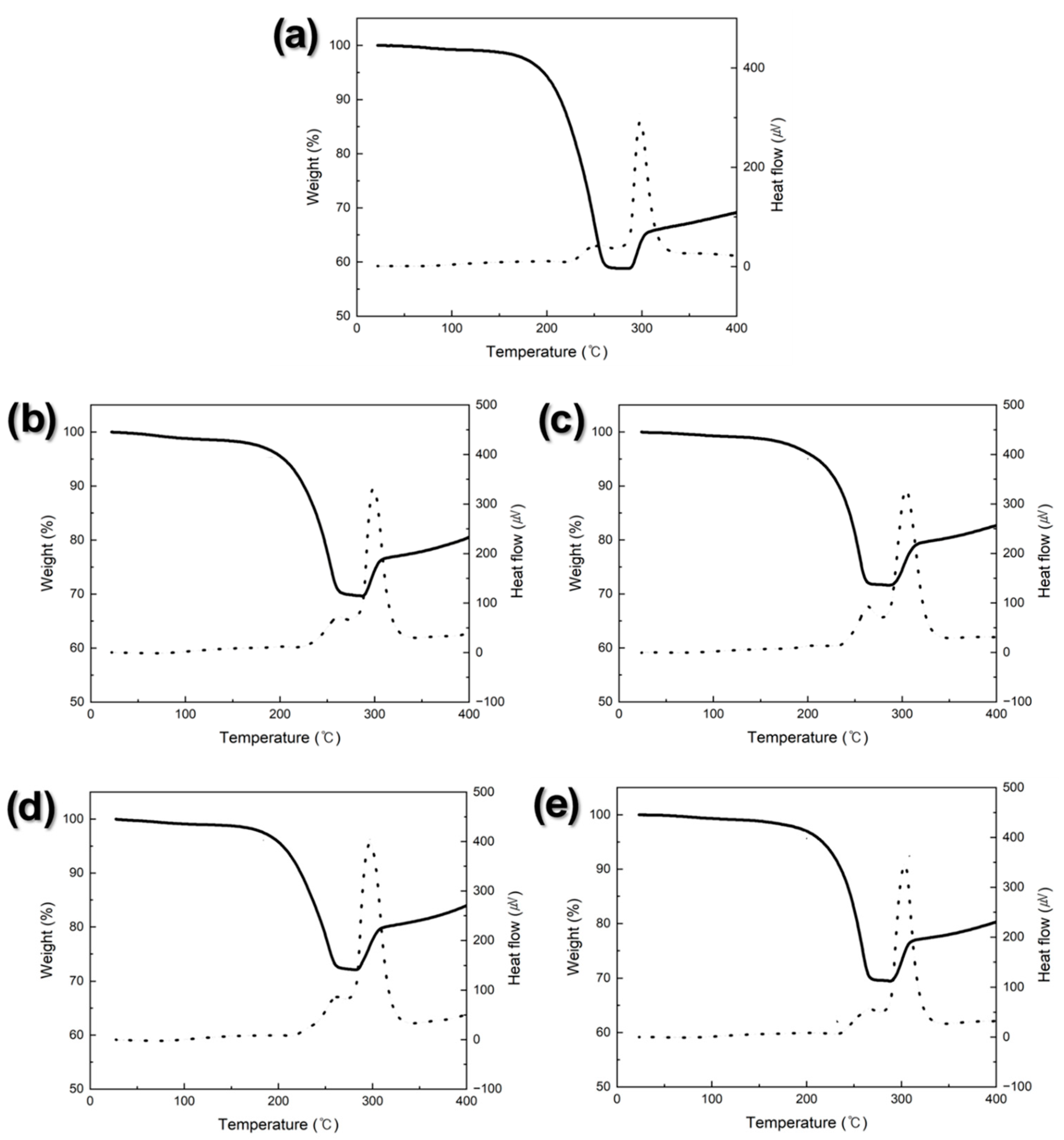
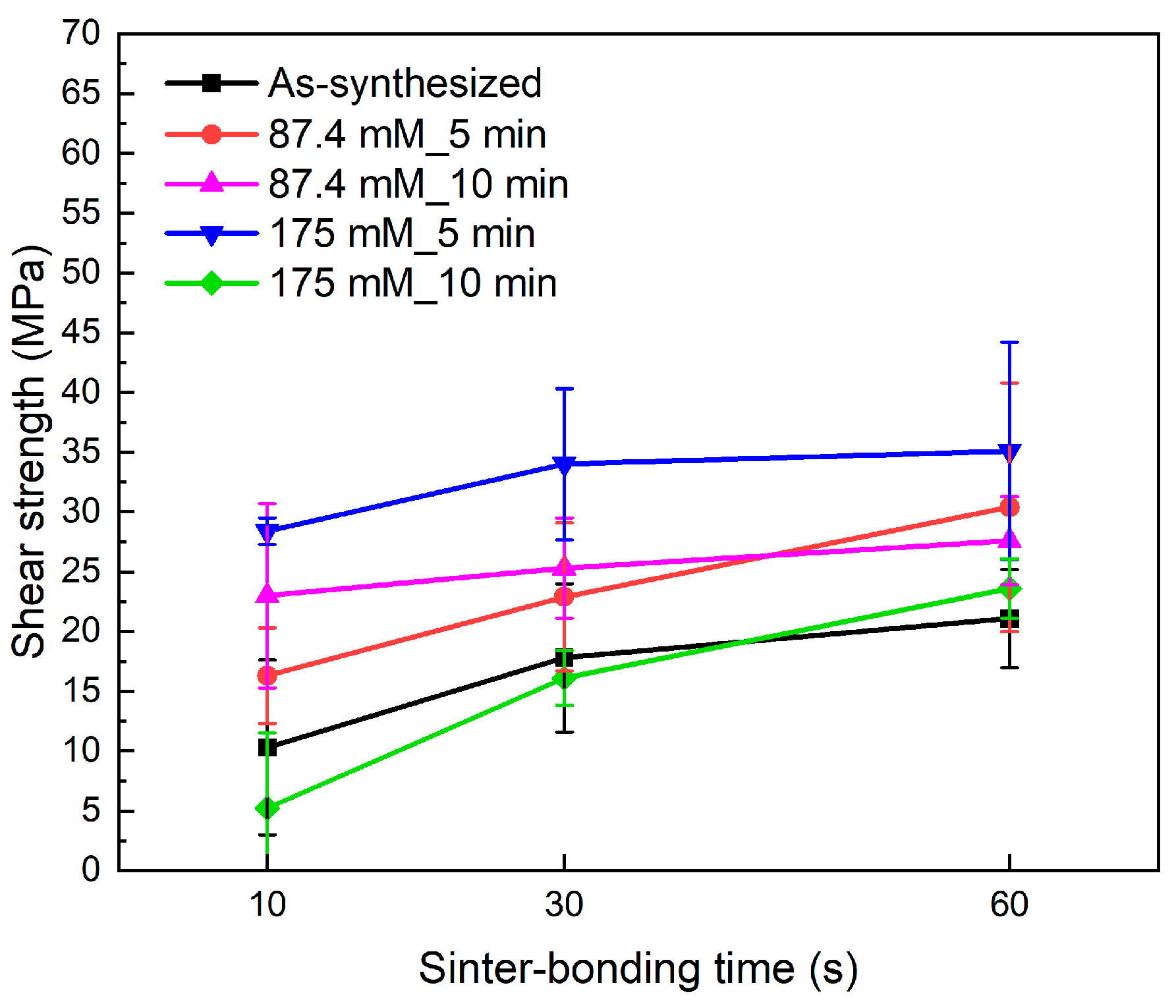
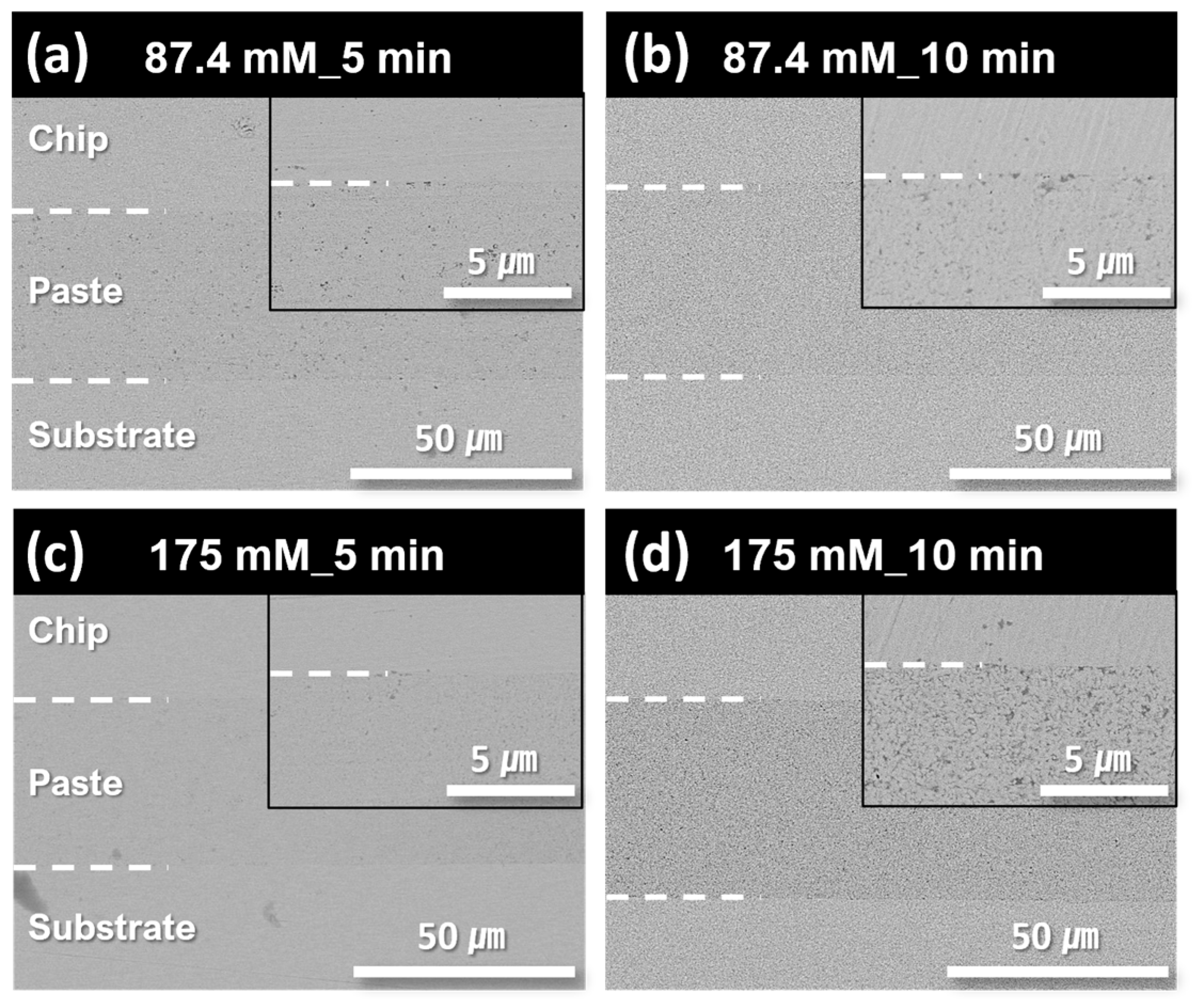
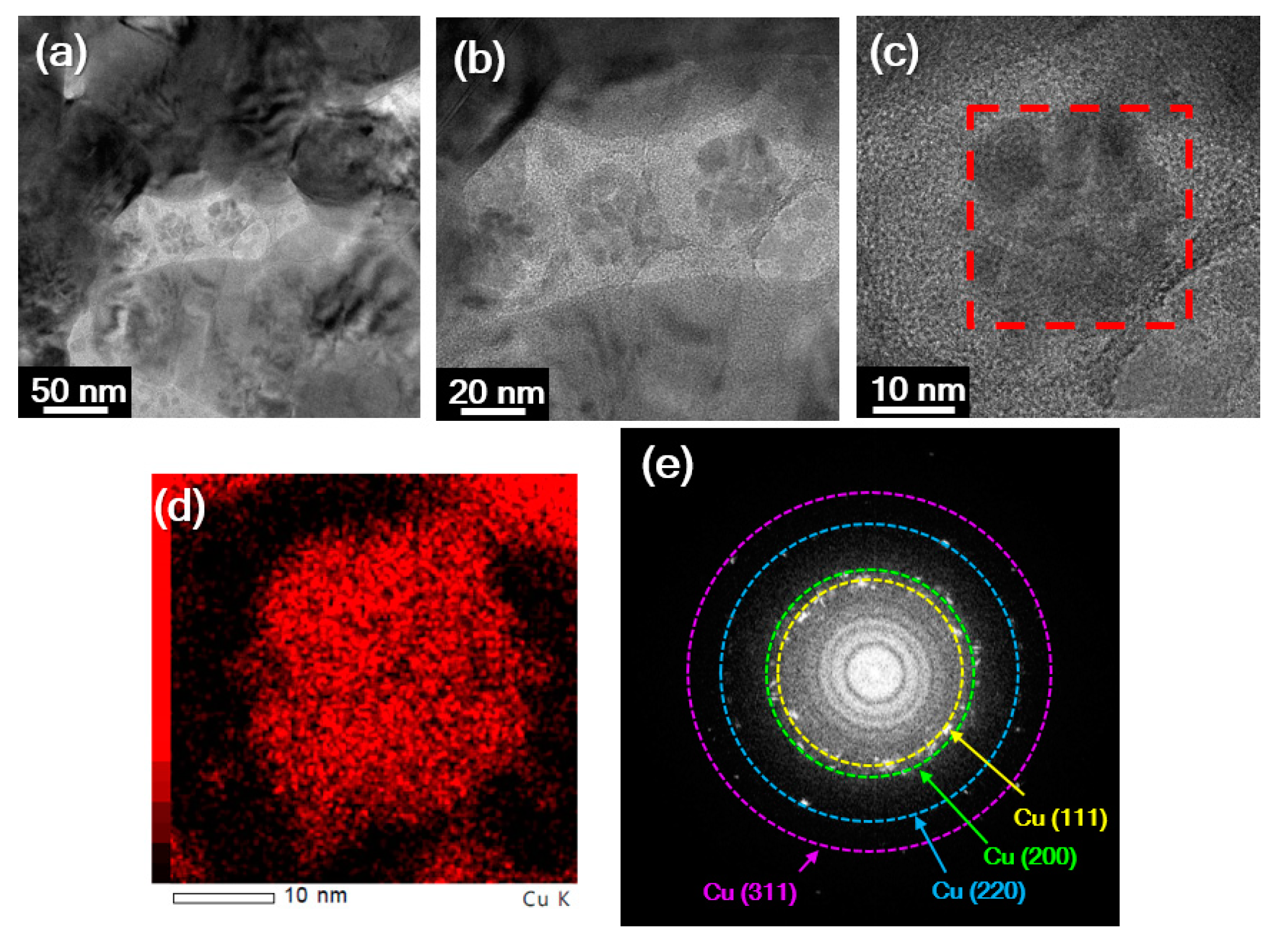
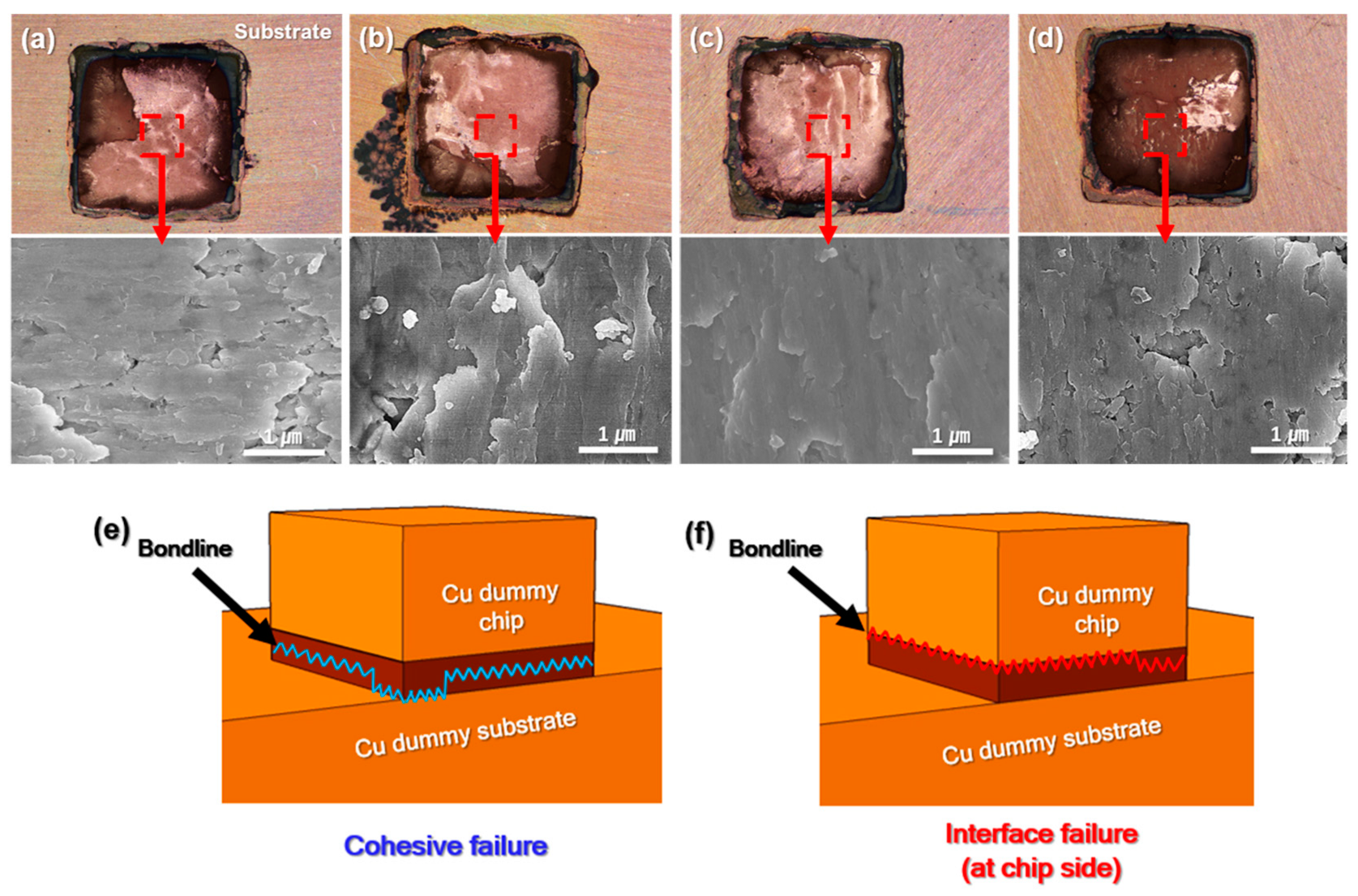
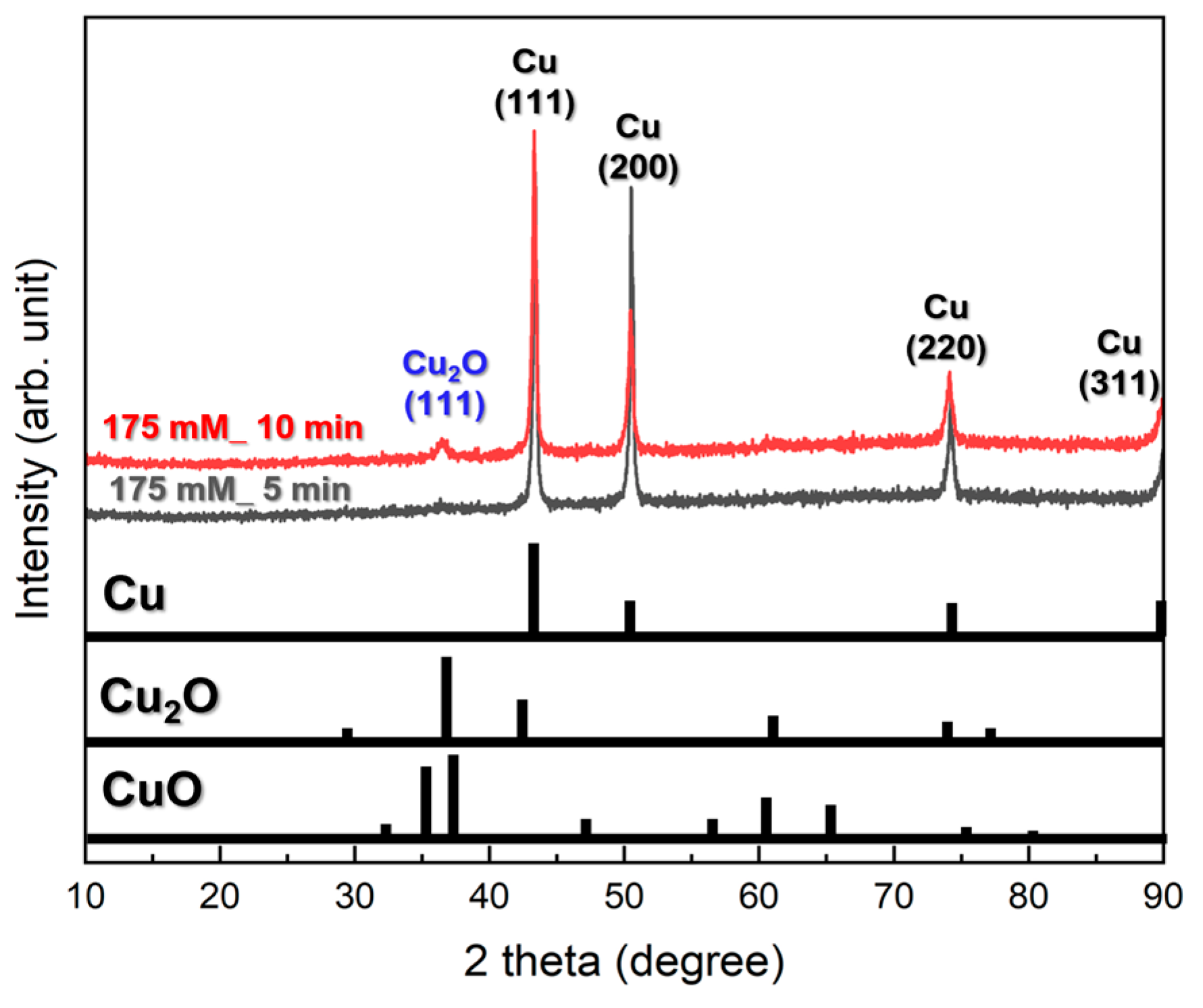
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shenai, K.; Dudley, M.; Davis, R.F. Current status and emerging trends in wide bandgap (WBG) semiconductor power switching devices. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 2013, 2, N3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminski, N.; Hilt, O. SiC and GaN devices–wide bandgap is not all the same. IET Circuits Devices Syst. 2014, 8, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Luo, F.; Kang, Y. A review of SiC power module packaging: Layout, material system and integration. CPSS Trans. Power Electron. Appl. 2017, 2, 170–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roccaforte, F.; Fiorenza, P.; Greco, G.; Nigro, R.L.; Giannazzo, F.; Lucolano, F.; Saggio, M. Emerging trends in wide band gap semiconductors (SiC and GaN) technology for power devices. Microelectron. Eng. 2018, 187–188, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadlapalli, R.T.; Kotapati, A.; Kandipati, R.; Balusu, S.R.; Koritala, C.S. Advancements in energy efficient GaN power devices and power modules for electric vehicle applications: A review. Int. J. Energy Res. 2021, 45.9, 12638–12664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suganuma, K.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, K.S. High-temperature lead-free solders: Properties and possibilities. JOM 2009, 61, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, H.S.; Cheong, K.Y.; Ismail, A.B. A review on die attach materials for SiC-based high-temperature power devices. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2010, 41, 824–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, S.; Nagao, S.; Suganuma, K. Thermal fatigue of Ag flake sintering die-attachment for Si/SiC power devices. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2013, 24, 2593–2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.C.; Lee, C.C.; Hsieh, C.P.; Hung, S.C.; Cheng, R.S. Electrical characteristics and reliability performance of IGBT power device packaging by chip embedding technology. Microelectron. Reliab. 2015, 55, 2582–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.S.; Ko, Y.H.; Bang, J.H.; Lee, C.W.; Yoo, S.; Kim, J.K.; Yoon, J.W. Interfacial reactions and mechanical strength of Sn-3.0 Ag-0.5 Cu/Ni/Cu and Au-20Sn/Ni/Cu solder joints for power electronics applications. Microelectron. Reliab. 2017, 71, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, C.; Chen, C.; Noh, S.; Suganuma, K. Thermal shock performance of DBA/AMB substrates plated by Ni and Ni–P layers for high-temperature applications of power device modules. Materials 2018, 11, 2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, W.; Bai, H.; Zou, G.; Liu, L.; Peng, P.; Guo, W. Microstructural and mechanical evolution of silver sintering die attach for SiC power devices during high temperature applications. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 774, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Zou, G.; Wu, A.P.; Ren, J.; Yan, J.; Hu, A.; Zhou, Y. Pressureless bonding process using Ag nanoparticle paste for flexible electronics packaging. Scr. Mater. 2012, 66, 582–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Zhang, D.; Zou, G.; Liu, L.; Bai, H.; Wu, A.; Zhou, Y.N. Sintering bonding process with Ag nanoparticle paste and joint properties in high temperature environment. J. Nanomater. 2016, 2016, 5284048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.S.; Yoon, J.W. Die-attach for power devices using the Ag sintering process: Interfacial microstructure and mechanical strength. Met. Mater. Int. 2017, 23, 958–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paknejad, S.A.; Mannan, S.H. Review of silver nanoparticle based die attach materials for high power/temperature applications. Microelectron. Reliab. 2017, 70, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, W.S.; Kim, M.S.; Oh, C.; Joo, Y.; Kim, Y.; Hong, K.K. Pressureless silver sintering of silicon-carbide power modules for electric vehicles. JOM 2020, 72, 889–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, C.; Suetake, A.; Hsieh, M.C.; Suganuma, K. Reliability of Ag sinter-joining die attach under harsh thermal cycling and power cycling tests. J. Electron. Mater. 2021, 50, 6597–6606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J. A review of sintering-bonding technology using Ag nanoparticles for electronic packaging. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Park, B.H.; Hyun, S.K.; Nishikawa, H. The influence of porosity and pore shape on the thermal conductivity of silver sintered joint for die attach. Mater. Today Commun. 2021, 29, 102772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jianfeng, Y.; Guisheng, Z.; Anming, H.; Zhou, Y.N. Preparation of PVP coated Cu NPs and the application for low-temperature bonding. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 15981–15986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.S.; Cheong, K.Y. Mechanical properties of sintered Ag–Cu die-attach nanopaste for application on SiC device. Mater. Des. 2014, 64, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yu, X.; Shi, T.; Cheng, C.; Fan, J.; Cheng, S.; Liao, G.; Tang, Z. Low-temperature and low-pressure Cu–Cu bonding by highly sinterable Cu nanoparticle paste. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.W.; Back, J.H. Effect of sintering conditions on the mechanical strength of Cu-sintered joints for high-power applications. Materials 2018, 11, 2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liang, Q.; Shi, T.; Fan, J.; Gong, B.; Feng, C.; Tang, Z. Design of Cu nanoaggregates composed of ultra-small Cu nanoparticles for Cu-Cu thermocompression bonding. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 772, 793–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, B.U.; Jung, K.H.; Min, K.D.; Lee, C.J.; Jung, S.B. Pressureless Cu–Cu bonding using hybrid Cu–epoxy paste and its reliability. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2021, 32, 3054–3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.F.; Siow, K.S. Comparing the mechanical and thermal-electrical properties of sintered copper (Cu) and sintered silver (Ag) joints. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 866, 158783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Lee, J.-H. Suppression of Ag dewetting in submicron Cu@Ag particles in paste for improving sinter bondability through surface modification. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 30, 3558–3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, H.; Ji, H.; Li, M. Highly conductive Cu-Cu joint formation by low-temperature sintering of formic acid-treated Cu nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 33289–33298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, Y.; Cheng, H.; Peng, Y.; Chen, M. Fabrication of reliable Cu-Cu joints by low temperature bonding isopropanol stabilized Cu nanoparticles in air. Mater. Lett. 2018, 229, 353–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namgoong, D.; Kim, Y.; Siow, K.S.; Lee, J.-H. Superior sinterability of copper oxalate-coated Cu particles in a double reductant system and rapid compression sinter-bonding characteristics between Cu finishes. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 24, 2332–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y.; Carter-Searjeant, S.; Green, M.; Mills, L.; Mannan, S.H. High bond strength Cu joints fabricated by rapid and pressureless in situ reduction-sintering of Cu nanoparticles. Mater. Lett. 2020, 276, 128260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, E.B.; Lee, J.-H. Sub-1 min sinter-bonding technique in air using modified Cu dendritic particles for formation of a high-temperature sustainable bondline. Met. Mater. Int. 2021, 27, 5278–5284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, E.B.; Lee, J.-H. Tens-of-seconds solid-state sinter-bonding technique in air using in situ reduction of surface oxide layers on easily bendable dendritic Cu particles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 580, 152347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fievet, F.; Fievet-Vincent, F.; Lagier, J.; Dumont, B.; Figlarz, M. Controlled nucleation and growth of micrometre-size copper particles prepared by the polyol process. J. Mater. Chem. 1993, 3, 627–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, H.; Lee, J.-H. Growth of Surface Oxide Layers on Dendritic Cu Particles by Wet Treatment and Enhancement of Sinter-Bondability by Using Cu Paste Containing the Particles. Metals 2024, 14, 1254. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14111254
Kim H, Lee J-H. Growth of Surface Oxide Layers on Dendritic Cu Particles by Wet Treatment and Enhancement of Sinter-Bondability by Using Cu Paste Containing the Particles. Metals. 2024; 14(11):1254. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14111254
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Horyun, and Jong-Hyun Lee. 2024. "Growth of Surface Oxide Layers on Dendritic Cu Particles by Wet Treatment and Enhancement of Sinter-Bondability by Using Cu Paste Containing the Particles" Metals 14, no. 11: 1254. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14111254
APA StyleKim, H., & Lee, J.-H. (2024). Growth of Surface Oxide Layers on Dendritic Cu Particles by Wet Treatment and Enhancement of Sinter-Bondability by Using Cu Paste Containing the Particles. Metals, 14(11), 1254. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14111254






