Abstract
Mg-based alloy anodes suffer from severe corrosion in alkaline electrolytes, which substantially impedes their cycle life and thereby limits their suitability as anode materials for nickel–metal hydride (Ni-MH) batteries. This work modifies the conventional 6 M KOH electrolyte by adding 0.1 M Al2(SO4)3·18H2O. The electrochemical hydrogen storage properties of Mg0.45Ti0.05Ni0.50 alloy in this electrolyte and its microstructural evolution during cycling are studied. In the 6 M KOH + 0.1 M Al2(SO4)3·18H2O electrolyte, a protective layer consisting of Mg2Al(OH)7 is formed on the surface of the Mg0.45Ti0.05Ni0.50 alloy anode during charge/discharge cycling instead of Mg(OH)2, effectively preventing further corrosion and improving its cycle life. The Mg0.45Ti0.05Ni0.50 alloy anode delivers a maximum discharge capacity of 479.0 mAh g−1 and maintains 318.4 mAh g−1 after 30 cycles in the 6 M KOH + 0.1 M Al2(SO4)3·18H2O electrolyte, which is significantly superior to that achieved in the 6 M KOH electrolyte (471.1 mAh g−1 and 201.8 mAh g−1, respectively). This work provides a new strategy for improving the cycle stability of Mg-based alloy anodes.
1. Introduction
Developing environmentally friendly electric vehicles (EVs), fuel-efficient hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs), and distributed energy storage stations represents a suitable strategy for alleviating environmental burdens and conserving energy resources. In this context, reliable batteries play a pivotal role as crucial devices for energy conversion and storage [1,2,3,4,5]. Owing to their excellent activation ability, ecological safety, wide temperature performance, and tolerance to overcharge and overdischarge, Ni-MH batteries have been extensively utilized in hybrid electric vehicles [1,2,3]. However, Ni-MH batteries employing AB5-type or RE-Mg-Ni-based alloys as negative electrodes face challenges in meeting the increasing energy density requirements of electrochemical power sources. Therefore, developing a high-capacity hydrogen storage alloy negative electrode is necessary to enhance the energy density of Ni-MH batteries. Mg-based hydrogen storage alloys are promising candidates for negative electrode material in Ni-MH batteries due to their lower cost and higher theoretical electrochemical capacity (2200 and 999 mAh g−1 for MgH2 and Mg2NiH4, respectively) [6,7,8]. Thus, Mg-based alloys have been intensively investigated since Lei et al. [9] found that amorphous Mg50Ni50 alloy prepared by ball milling has a high initial discharge capacity of around 500 mAh g−1 at room temperature. For example, Mg2Ni-Ni composites prepared by ball milling Mg2Ni with Ni achieved a high discharge capacity of more than 1000 mAh g−1 (Mg2Ni) [10,11,12,13]. A similar result was reported in that a Mg2NiH4-Ni composite prepared by ball milling a mixture of Mg2NiH4 powder and nano-nickel powder delivers a maximum discharge capacity of 896 mAh g−1 (Mg2NiH4) [14].
Although high discharge capacity can be achieved in Mg-Ni alloys prepared by the ball milling method, their cyclic behavior is very poor, and the discharge capacity typically decays to 100 mAh g−1 after just a few cycles [14,15,16,17]. Previous studies have suggested that the rapid capacity decay of milled Mg-Ni alloy anodes is attributed to the ready corrosion of Mg in KOH solution, primarily due to its extremely low corrosion potential (−2.37 V, vs. Hg/HgO). Additionally, the relatively loose Mg(OH)2 layer on the alloy surface fails to provide adequate protection against further corrosion and instead hinders charge transfer and hydrogen atom transfer. With the aim of improving the cycle stability of Mg-based alloy anodes, a number of approaches to prevent the corrosion of Mg-based alloys have been conducted, including alloying addition [18,19,20,21,22,23,24], composite with other materials [25,26,27,28], surface modification [29,30,31], powder sieving and control of the charge condition [32], electrolyte modification [33,34,35], etc. Among these approaches, partial substitution of Mg or Ni by transition metal element Ti is an effective way to extend the cycle life of Mg-based alloy anodes. For instance, as demonstrated in Table 1, a ball-milled Mg0.7Ti0.3Ni1.0 alloy exhibits a maximum discharge capacity of 325 mAh g−1 and retains 92% capacity after 20 cycles [18], ball-milled MgTi0.5Ni0.5 alloy demonstrates the highest discharge capacity of 536 mAh g−1 with an average capacity decay of 8 mAh g−1 per cycle [23]. Naturally, the improved cycling stability observed in Ti-containing alloys is attributed to the formation of a titanium oxide layer that can prevent further corrosion of Mg. Anyway, the improved cycle stability of Mg-based alloy anodes is rather limited, and it is still not satisfactory for marketing yet.

Table 1.
Electrochemical properties of some Mg-based alloy electrodes.
Recently, Huang et al. [36] revealed that hydrogenation-induced crystallization results in irreversible electrochemical dehydrogenation also being a dominating reason for the capacity decay of the milled Mg-Ni alloys in addition to corrosion. Then, Huang et al. [37] found that the addition of Ti can enhance the stability of the amorphous phase in milled Mg-Ni alloys, thereby improving the cycle stability of the alloy anodes. Moreover, Ti addition leads to the formation of a TiNi phase, resulting in improved electrochemical reaction kinetics and significantly enhanced rate capability of the alloys. However, the anode still suffers from capacity decay because Ti addition does not prevent it from corrosion.
Electrolyte modification is an effective approach to reduce the corrosion of Mg-based alloy electrodes, and extensive research has been conducted in this area [33,34,35]. For instance, the addition of KF into a 6 M KOH electrolyte enhanced the cyclic stability of the Mg-based alloy electrode by forming a protective layer of stable MgF2, thereby preventing the formation of Mg(OH)2 [33]. Yan et al. [35] investigated the influence of Cs2CO3 additives in KOH electrolyte. They found that a carbon-containing fluffy layer formed on the surface of the alloy particles after cycling in Cs2CO3-containing KOH electrolyte, which was considered to improve the corrosion resistance of the alloy electrodes.
To inhibit the corrosion of Mg-based alloy anodes, this study aims to modify the conventional 6 M KOH solution by incorporating a small amount of Al2(SO4)3·18H2O. By adding 0.1 M Al2(SO4)3·18H2O into 6 M KOH electrolyte, a protective Mg2Al(OH)7 layer can be formed on the surface of a Mg0.45Ti0.05Ni0.50 alloy anode during the charge/discharge cycles instead of Mg(OH)2. This protective layer effectively prevents further corrosion and improves the cycle life of the alloy anode. After 30 cycles, the reversible electrochemical capacity of the Mg0.45Ti0.05Ni0.50 alloy anode in Al2(SO4)3·18H2O-containing electrolyte reaches 318.4 mAh g−1, which is higher than that achieved in 6 M KOH electrolyte (201.8 mAh g−1).
2. Experimental
2.1. Electrode Materials and Electrolyte
In this study, Mg0.45Ti0.05Ni0.50 alloy was chosen as the active material for the anode, prepared by milling the mixture of commercial Mg powder (99.5%, AR, M109153, Aladdin, Shanghai, China), commercial Ti powder (99.5%, 200-mesh, T130070, Aladdin, Shanghai, China), and commercial Ni powder (99.5%, 200-mesh, N105828, Aladdin, Shanghai, China) in a planetary mill under an argon atmosphere. The ball-to-powder weight ratio was 60:1; the milling speed was 450 rpm. The milling process operates in an alternating manner, with a forward rotation lasting for 30 min followed by an equal duration of reverse rotation; the total milling time was 60 h. Mg0.45Ti0.05Ni0.50 alloy was prepared multiple times to ensure the repeatability and reproducibility of the experiments. As for the cathode material, Ni(OH)2 powder was used. For electrolyte preparation, a 6 M KOH solution was prepared by dissolving a specific amount of KOH (AR, P112284, Aladdin, Shanghai, China) in ultrapure water. A 6 M KOH + 0.1 M Al2(SO4)3·18H2O solution was obtained by dissolving a specific amount of Al2(SO4)3·18H2O (99%, A489714, Aladdin, Shanghai, China) in 6 M KOH solution.
2.2. Materials Characterization
The microstructure was characterized using an X-ray diffractometer (XRD, Empyrean, PANalytical, Almelo, Netherlands, Cu Kα, 45 kV × 40 mA). The corrosion rate of the cycled electrodes was measured by thermogravimetric analysis (TGA, 209F3 Tarsus, Netzsch, Bayern, Germany) in an argon atmosphere from 30 to 500 °C at a rate of 5 °C/min. The cycled electrodes were sequentially cleaned with distilled water and absolute ethanol before being dried at a temperature of 60 °C for 24 h under a high-purity argon atmosphere provided by a tube furnace.
2.3. Electrochemical Measurements
For the electrochemical tests, the Mg0.45Ti0.05Ni0.50 alloy powder was homogenously mixed with Ni powder (99.5%, 200-mesh, N105828, Aladdin, Shanghai, China) at a mass ratio of 1:4. Then, the tested electrodes were fabricated by cold pressing the mixture into a circular pellet of ø10 mm under 30 MPa pressure. Nickel foam was applied on both sides of the electrode disc and connected to the pole ear at a pressure of 6 MPa. The electrochemical tests were carried out in a three-electrode glass electrolytic cell with Ni(OH)2/NiOOH as the counter electrode and Hg/HgO as the reference electrode. The electrolyte used was either 6 M KOH + 0.1 M Al2(SO4)3·18H2O or pure 6 M KOH for comparison. The cycle stability testing was performed using a LAND-CT2001A battery system, where the electrodes were charged at a current density of 200 mA g−1 for 2.5 h, followed by resting for 5 min and discharging to −0.6 V (vs. Hg/HgO) at a current density of 50 mA g−1. The corrosion behavior of the alloy electrode was characterized using a Tafel polarization curve on a Gamry Interface 1000 workstation, employing a scanning rate of 1 mV s−1 from −0.4 V to −1.2 V (vs. Hg/HgO). The testing temperature was set at 25 °C. All the electrochemical tests were conducted more than twice to ensure repeatability and reproducibility.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Structural Analysis
The XRD pattern of Mg0.45Ti0.05Ni0.50 after 60 h of ball milling is presented in Figure 1. It is evident from the XRD curves of the milled alloy that only a broad diffraction halo is observed, indicating the presence of amorphous phases and/or nanocrystalline alloys. According to Ref. [37], the alloy exists in an amorphous state, accompanied by a minor fraction of TiNi nanocrystalline phase.
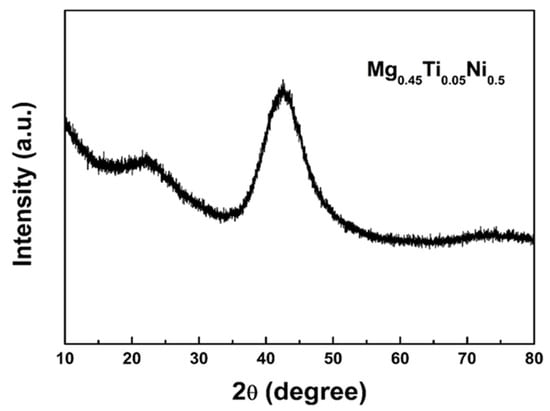
Figure 1.
The XRD patterns of the milled Mg0.45Ti0.05Ni0.50 alloy.
3.2. Electrochemical Performances
Electrochemical performances were evaluated to assess the electrochemical properties of the Mg0.45Ti0.05Ni0.50 alloy anode in different electrolytes. The first charge/discharge curves of the Mg0.45Ti0.05Ni0.5 alloy electrode are depicted (Figure 2a), revealing similar charging and discharging platform pressures as well as discharge capacities in both 6 M KOH and 6 M KOH + 0.1 M Al2(SO4)3·18H2O electrolytes, and the largest Mg0.45Ti0.05Ni0.5 alloy electrode discharge capacity in 6 M KOH and 6 M KOH + 0.1 M Al2(SO4)3·18H2O are 471.1 mAh g−1 and 479.0 mAh g−1, respectively. The cycle stability of the Mg0.45Ti0.05Ni0.5 alloy electrode in 6 M KOH and 6 M KOH + 0.1 M Al2(SO4)3·18H2O is shown in Figure 2b. Indeed, the Mg0.45Ti0.05Ni0.50 alloy electrode exhibits significantly improved cycling stability when utilizing the 6 M KOH + 0.1 M Al2(SO4)3·18H2O electrolyte compared to solely using pure 6 M KOH solution. After 30 cycles, the reversible electrochemical capacity of the Mg0.45Ti0.05Ni0.50 alloy anode in 6 M KOH + 0.1 M Al2(SO4)3·18H2O and 6 M KOH is 318.4 and 201.8 mAh g−1, respectively, corresponding to capacity retention rate of 66.5% and 4.8%, respectively.
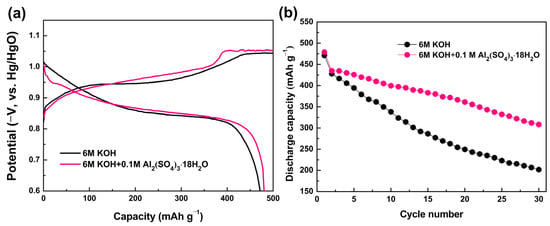
Figure 2.
Charge/discharge curves (a) and cycle stability (b) of Mg0.45Ti0.05Ni0.50 alloy electrode.
3.3. The Mechanism for Improved Electrochemical Performances
To reveal the effect of adding Al2(SO4)3·18H2O to 6 M KOH electrolyte on the cycle stability of Mg0.45Ti0.05Ni0.50 alloy, the structural variation in the charge/discharge process was further investigated by XRD after different cycles. Commercial Ni powder was intentionally excluded as a conductive agent in order to accurately observe the structural variations in the alloy throughout cycling. Figure 3a,b illustrates the XRD patterns of the Mg0.45Ti0.05Ni0.50 alloy electrode after 15 and 30 cycles in both 6 M KOH and 6 M KOH + 0.1 M Al2(SO4)3·18H2O electrolytes. Distinct diffraction peaks corresponding to Mg(OH)2 are observed in the 6 M KOH, with their intensity increasing as the number of cycles progresses, indicating progressive corrosion of Mg within the Mg0.45Ti0.05Ni0.50 alloy during charge/discharge cycling. However, the weakened diffraction peaks attributed to Mg2Al(OH)7, instead of Mg(OH)2, were found in the XRD pattern of the Mg0.45Ti0.05Ni0.50 alloy anode after different cycles in 6 M KOH + 0.1 M Al2(SO4)3·18H2O. Furthermore, these diffraction peaks associated with Mg2Al(OH)7 do not exhibit significant changes as cycling proceeds, confirming that the formation of Mg2Al(OH)7 can effectively inhibit further corrosion of Mg within the Mg0.45Ti0.05Ni0.50 alloy anode. The formation of Mg2Al(OH)7 can be attributed to the in situ formation of an Al coating on the surface of the Mg0.45Ti0.05Ni0.50 electrode during the charging process, facilitated by the addition of 0.1 M Al2(SO4)3·18H2O in 6 M KOH electrolyte solution. Subsequently, Mg combines with Al and oxidizes to form Mg2Al(OH)7 during the discharging process.
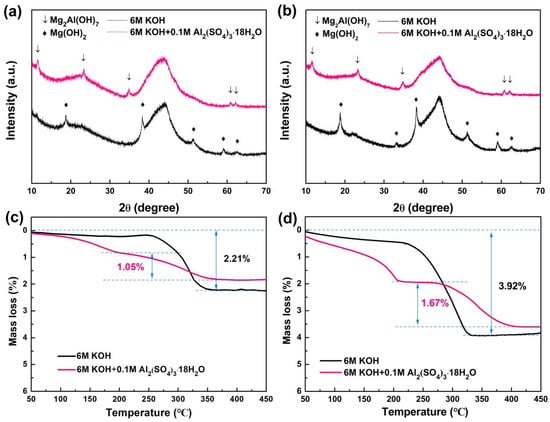
Figure 3.
XRD patterns of the Mg0.45Ti0.05Ni0.50 alloy electrode after 15 (a) and 30 (b) cycles in 6 M KOH and 6 M KOH + 0.1 M Al2(SO4)3, and corresponding TG curves (c,d).
To characterize the corrosion rate of the corresponding alloys, thermogravimetric analysis was employed, and the results are presented in Figure 3c,d. It can be seen that a weight loss at approximately 310 °C appeared in the TG curves of Mg0.45Ti0.05Ni0.50 alloy anodes in 6 M KOH, which characterized the decomposition of Mg(OH)2 [34,35]. The weight loss of Mg0.45Ti0.05Ni0.50 alloy anodes after 15 and 30 cycles in 6 M KOH is 2.21% and 3.92%, respectively, with corresponding Mg losses in the alloys being 12.2% and 22.3% after 15 and 30 cycles, respectively. For Mg0.45Ti0.05Ni0.50 alloy anodes in 6 M KOH + 0.1 M Al2(SO4)3·18H2O electrolyte, two weight losses appeared at about 180 and 310 °C on the curves, respectively. These corresponded to the decomposition of Mg2Al(OH)7 into Al2O3 and MgO [38]. The corrosion rate of the Mg in Mg0.45Ti0.05Ni0.50 alloy anodes after 15 and 30 cycles in 6 M KOH + 0.1 M Al2(SO4)3·18H2O electrolyte calculated from the thermogravimetric analysis are 5.6% and 9.3%, respectively. In other words, the Mg0.45Ti0.05Ni0.50 alloy anode has a lower corrosion rate in 6 M KOH + 0.1 M Al2(SO4)3·18H2O than that in 6 M KOH during the electrochemical charging/discharging process, which is the key reason for the better cyclic stability of the Mg0.45Ti0.05Ni0.50 alloy in 6 M KOH + 0.1 M Al2(SO4)3·18H2O electrolyte.
The corrosion behavior of the Mg0.45Ti0.05Ni0.50 alloy anode in 6 M KOH and 6 M KOH + 0.1 M Al2(SO4)3·18H2O electrolytes was further characterized by the change in corrosion potential. As shown in the Tafel curves in Figure 4, the corrosion potential of Mg0.45Ti0.05Ni0.50 alloy anode shifts positively after adding Al2(SO4)3·18H2O to 6 M KOH electrolyte. In addition, the difference value of the corrosion potential of Mg0.45Ti0.05Ni0.50 alloy anode in those two electrolytes increases as the cycle number increases. The corrosion potential of the Mg0.45Ti0.05Ni0.50 alloy anodes after 15 cycles in 6 M KOH and 6 M KOH + 0.1 M Al2(SO4)3·18H2O electrolytes is −1.037 V and −1.030 V (vs. Hg/HgO), respectively, while the values are −1.033 V and −1.021 V (vs. Hg/HgO) after 30 cycles, suggesting that the formed layer of Mg2Al(OH)7 effectively inhibited further corrosion of Mg in Mg0.45Ti0.05Ni0.50 alloy anode.
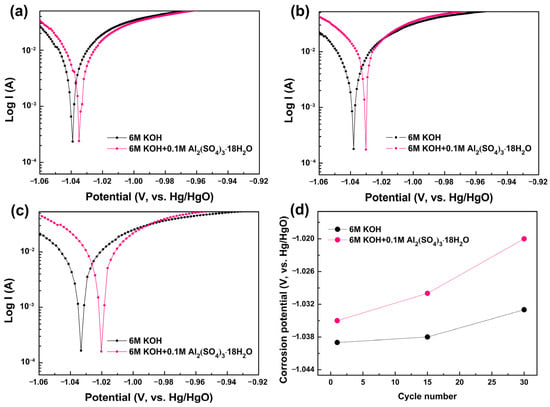
Figure 4.
Tafel curves of Mg0.45Ti0.05Ni0.50 alloy electrode after 1 (a), 15 (b), and 30 (c) cycles in 6 M KOH and 6 M KOH + 0.1 M Al2(SO4)3·18H2O, and corresponding corrosion potential (d).
The effect of incorporating Al2(SO4)3·18H2O into the conventional 6 M KOH electrolyte is clear. In 6 M KOH + 0.1 M Al2(SO4)3·18H2O electrolyte, a protective Mg2Al(OH)7 layer can be formed on the surface of Mg0.45Ti0.05Ni0.50 alloy anode during the charge/discharge cycles, effectively preventing further corrosion and enhancing the cycle life of the alloy anode. It is important to note that there is still a decline in discharge capacity observed in the milled Mg0.45Ti0.05Ni0.50 alloy anode, highlighting the need for additional efforts to protect alloys from corrosion. Furthermore, it is crucial to explore higher-capacity Mg-based alloys to meet the increasing energy density requirements in Ni-MH batteries.
4. Conclusions
In summary, a conventional 6 M KOH electrolyte was modified by incorporating a small amount of Al2(SO4)3·18H2O, which enables the Mg-based alloy to exhibit improved cycle stability as an anode for Ni-MH batteries. By adding 0.1 M Al2(SO4)3·18 H2O into a 6 M KOH solution, the maximum discharge capacities remained unchanged for the Mg0.45Ti0.05Ni0.50 alloy electrode, which were 479.0 mAh g−1 and 471.1 mAh g−1, respectively. However, after 30 cycles, the discharge capacity of the Mg0.45Ti0.05Ni0.50 alloy electrode in 6 M KOH + 0.1 M Al2(SO4)3·18H2O electrolyte was 318.4 mAh g−1, higher than that of in 6 M KOH solution, being 201.8 mAh g−1. In the Al2(SO4)3·18H2O-containing electrolyte, a Mg2Al(OH)7 layer can be formed on the surface of the Mg0.45Ti0.05Ni0.50 alloy anode instead of Mg(OH)2 during the charge/discharge cycle, which can protect to the alloy anode from further corrosion, thus improving its cycle life.
Author Contributions
Methodology, J.L. and J.H.; Validation, J.L. and J.H.; Investigation, J.L. and Y.C.; Resources, J.H., S.Z. and D.C.; Data curation, J.L. and Y.C.; Writing—original draft, J.L.; Writing—review and editing, J.H.; Visualization, S.Z., and D.C.; Supervision, J.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (52101244), the Guangxi Special Program for Yong Talents (GuiKeAD21220111), the Fund Project of the Key Lab of Guangxi Key Laboratory of Automobile Components and Vehicle Technology under grant no. 2022GKLACVTZZ04, and the 21C Innovation Laboratory, Contemporary Amperex Technology Ltd. under project no. 21C-OP-202214.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Liu, Y.F.; Pan, H.G.; Gao, M.X.; Wang, Q.D. Advanced hydrogen storage alloys for Ni/MH rechargeable batteries. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 4743–4755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tliha, M.; Khaldi, C.; Boussami, S.; Fenineche, N.; El-Kedim, O.; Mathlouthi, H.; Lamloumi, J. Kinetic and thermodynamic studies of hydrogen storage alloys as negative electrode materials for Ni/MH batteries: A review. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2014, 18, 577–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, L.Z.; Huang, J.L.; Wang, H.; Liu, J.W.; Zhu, M. Progress of hydrogen storage alloys for Ni-MH rechargeable power batteries in electric vehicles: A review. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2017, 200, 164–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyanusamy, P.; Tharani, D.S.; Alphonse, R.; Minakshi, M.; Sivasubramanian, R. Synthesis of amorphous nickel-cobalt hydroxides for Ni-Zn rechargeable aqueous battery. Chem. Eur. J. 2024, e202402325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasudevan, S.; Tharani, D.S.; Manickam, M.; Sivasubramanian, R. A sol-gel derived LaCoO3 perovskite as an electrocatalyst for Al-air batteries. Dalton Trans. 2024, 53, 3713–3721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orimo, S.; Fujii, H. Materials science of Mg-Ni-based new hydrides. Appl. Phys. A 2001, 72, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakintuna, B.; Lamari-Darkrim, F.; Hirscher, M. Metal hydride materials for solid hydrogen storage: A review. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2007, 32, 1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, I.P.; Lal, C.; Jain, A. Hydrogen storage in Mg: A most promising material. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2010, 35, 5133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.Q.; Wu, Y.M.; Yang, Q.M.; Wu, J.; Wang, Q.D. Electrochemical behavior of some mechanically alloyed Mg-Ni-based amorphous hydrogen storage alloys. Z. Phys. Chem. 1994, 183, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohno, T.; Tsuruta, S.; Kanda, M. The hydrogen storage properties of new Mg2Ni alloy. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1996, 143, L198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohno, T.; Yamamoto, M.; Kanda, M. Electrochemical properties of mechanically ground Mg Ni alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 1999, 293–295, 643–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwakura, C.; Inoue, H.; Zhang, S.G.; Nohara, S. Hydriding and electrochemical characteristics of a homogeneous amorphous Mg2Ni-Ni composite. J. Alloys Compd. 1998, 270, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nohara, S.; Fujita, N.; Zhang, S.G.; Inoue, H.; Iwakura, C. Electrochemical characteristics of a homogeneous amorphous alloy prepared by ball-milling Mg2Ni with Ni. J. Alloys Compd. 1998, 267, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.H.; Zhu, Y.F.; Yang, C.; Zhang, J.G.; Chen, W.; Li, L.Q. Enhanced electrochemical hydrogen storage properties of Mg2NiH4 by coating with nano-nickel. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2015, 40, 13949–13956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Ren, H.P.; Li, B.W.; Guo, S.H.; Pang, Z.G.; Wang, X.L. Electrochemical hydrogen storage characteristics of nanocrystalline and amorphous Mg20Ni10-xCox (x = 0–4) alloys prepared by melt spinning. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2009, 34, 8144–8151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggeri, S.; Roue, L.; Huot, J.; Schulz, R.; Aymard, L.; Tarascon, J.M. Properties of mechanically alloyed Mg-Ni-Ti ternary hydrogen storage alloys for Ni-MH batteries. J. Power Sources 2002, 112, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorkounov, B.; Gebert, A.; Mickel, C.; Schultz, L. Improving the performance of hydrogen storage electrodes based on mechanically alloyed Mg61Ni30Y9. J. Alloys Compd. 2008, 458, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.C.; Lee, P.S.; Lee, J.Y.; Züttel, A.; Schlapbach, L. Effects of Ti on the cycle life of amorphous MgNi-based alloy prepared by ball milling. J. Alloys Compd. 2000, 306, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Lei, Y.Q.; Chen, L.S.; Zhang, H. Electrochemical characteristics of amorphous Mg0.9M0.1Ni (M = Ni, Ti, Zr, Co and Si) ternary alloys prepared by mechanical alloying. J. Alloys Compd. 2000, 311, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.Z.; Sun, L.X.; Tan, Z.C.; Xu, F.; Yuan, H.T.; Zhang, T. The effects of partial substitution of Cr for Ni on the electrochemical properties of Mg1.75Al0.25Ni1−xCrx (0 ≤ x ≤ 0.3) electrode alloys. J. Power Sources 2006, 159, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anik, M.; Özdemir, G.; Kücükdeveci, N.; Baksan, B.; Al, E.O. Ti and Zr additive elements on the electrochemical hydrogen storage performance of MgNi alloy. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 1568–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Q.F.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, L.X.; Xu, F.; Tan, Z.C.; Yuan, H.T.; Zhang, T. Effects of Pd substitution on the electrochemical properties of Mg0.9-xTi0.1PdxNi (x = 0.04-0.1) hydrogen storage alloys. J. Power Sources 2006, 158, 1463–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousselot, S.; Guay, D.; Roué, L. Comparative study on the structure and electrochemical hydriding properties of MgTi, Mg0.5Ni0.5Ti and MgTi0.5Ni0.5 alloys prepared by high energy ball milling. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 1561–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikkuni, F.R.; Santos, S.F.; Ticianelli, E.A. Microstructures and electrochemical properties of Mg49Ti6Ni(45-x)Mx (M = Pd and Pt) alloy electrodes. Int. J. Energy Res. 2013, 37, 706–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delchev, P.; Himitliiska, T.; Spassov, T. Microstructure and hydriding properties of ball-milled Mg–10at.% MmNi5 (Mm = La, Ce-rich mischmetal) composites. J. Alloys Compd. 2006, 417, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.; Jiao, L.F.; Yuan, H.T.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.J. Preparation and electrochemical properties of MgNi-MB (M = Co, Ti) composite alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2008, 450, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Zhu, Y.F.; Li, L.Q. Hydrogen storage properties of Mg–30 wt.% LaNi5 composite prepared by hydriding combustion synthesis followed by mechanical milling (HCS+MM). Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2009, 34, 1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.X.; Huang, K.L.; Chen, D.Y.; Liu, S.Q.; Zhuang, S.X. The electrochemical properties of MgNi-xwt% TiNi0.56Co0.44 (x = 0, 5, 10, 30, 50) composite alloys. J. Mater. Sci. 2010, 45, 1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwakura, C.; Nohara, S.; Inoue, H.; Fukumoto, Y. Surface modification of MgNi alloy with graphite by ball-milling for use in nickel-metal hydride batteries. Chem. Commun. 1996, 1, 1831–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, T.; Inoue, S.; Mu, D.B.; Hatano, Y.J.; Watanabe, K. Electrochemical studies of the effect of surface modification of amorphous MgNi electrodes by carbon or Ni. J. Alloys Compd. 2003, 349, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.C.; Li, L.; Liang, G.Y.; Guo, Y.L.; Wu, H.B. Improved electrochemical properties of amorphous Mg65Ni27La8 electrodes: Surface modification using graphite. J. Power Sources 2009, 189, 1251–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rongeat, C.; Grosjean, M.H.; Ruggeri, S.; Dehmas, M.; Bourlot, S.; Marcotte, S.; Roué, L. Evaluation of different approaches for improving the cycle life of MgNi-based electrodes for Ni-MH batteries. J. Power Sources 2006, 158, 747–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Lee, C.R.; Choi, J.W.; Kang, S.G. Effects of F-treatment on degradation of Mg2Ni electrode fabricated by mechanical alloying. J. Power Sources 2002, 104, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.L.; Ng, K.Y.S.; Young, K.-H. Effects of salt additives to the KOH electrolyte used in Ni/MH batteries. Batteries 2015, 1, 54–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.L.; Nei, J.; Li, P.F.; Young, K.H.; Ng, K.Y.S. Effects of Cs2CO3 additive in KOH electrolyte used in Ni/MH batteries. Batteries 2017, 3, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.L.; Ouyang, L.Z.; Wang, H.; Liu, J.W.; Zhu, M.; Fang, F.; Sun, D.L. Hydrogenation and crystallization of amorphous phase: A new mechanism for the electrochemical capacity and its decay in milled Mg-Ni alloys. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 305, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.L.; Wang, H.; Ouyang, L.Z.; Liu, J.W.; Zhu, M. Reducing the electrochemical capacity decay of milled Mg–Ni alloys: The role of stabilizing amorphous phase by Ti-substitution. J. Power Sources 2019, 438, 226984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahyaoui, R.; Jimenez, P.E.S.; Maqueda, L.A.P.; Nahdi, K.; Luque, J.M.C. Synthesis, characterization and combined kinetic analysis of thermal decomposition of hydrotalcite (Mg6Al2(OH)16CO3·4H2O). Thermochim. Acta 2018, 667, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).