Optimization of the First-Step Drawing Parameters for Platinum-Clad Nickel Bar Based on FEM Simulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
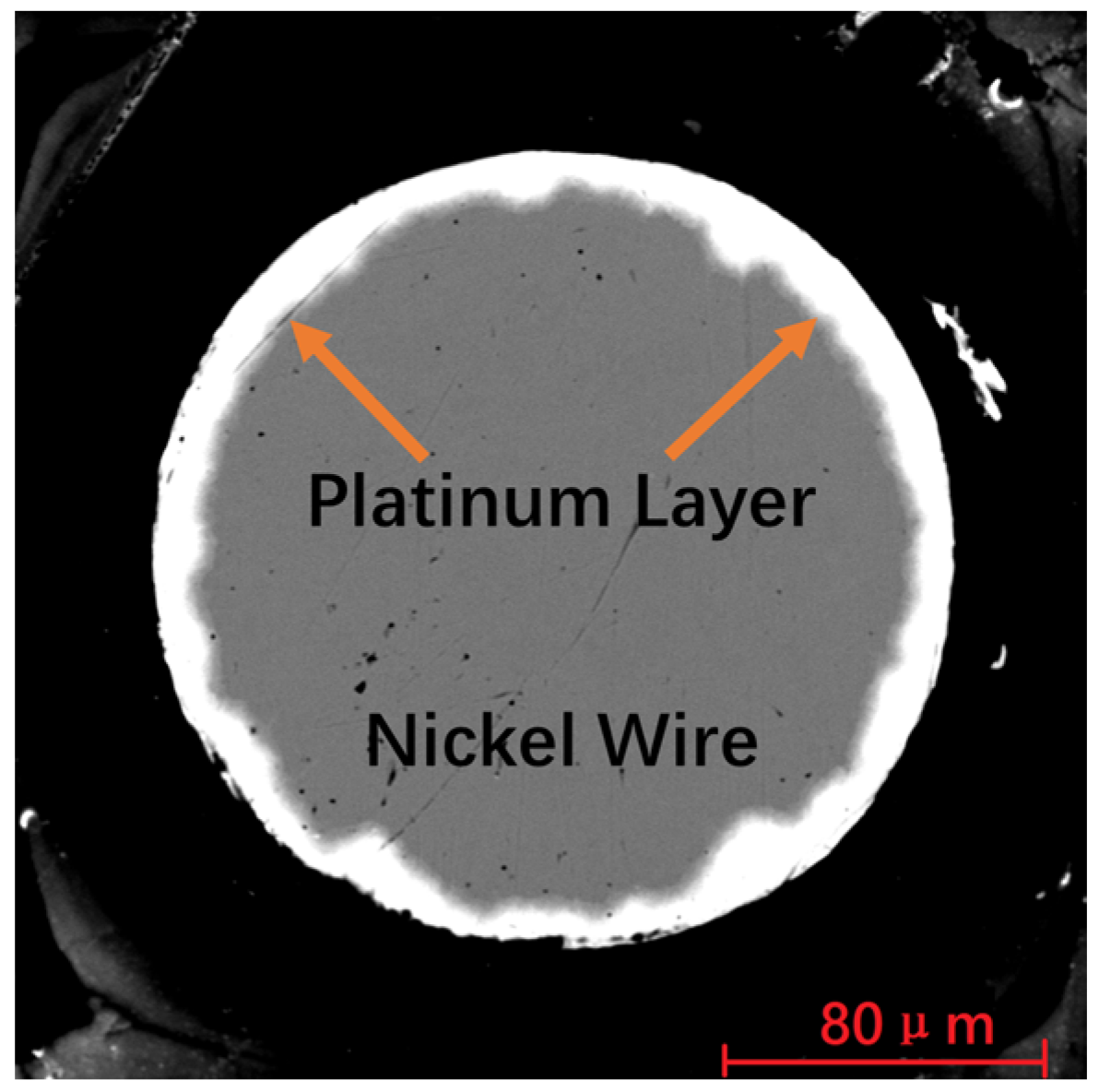
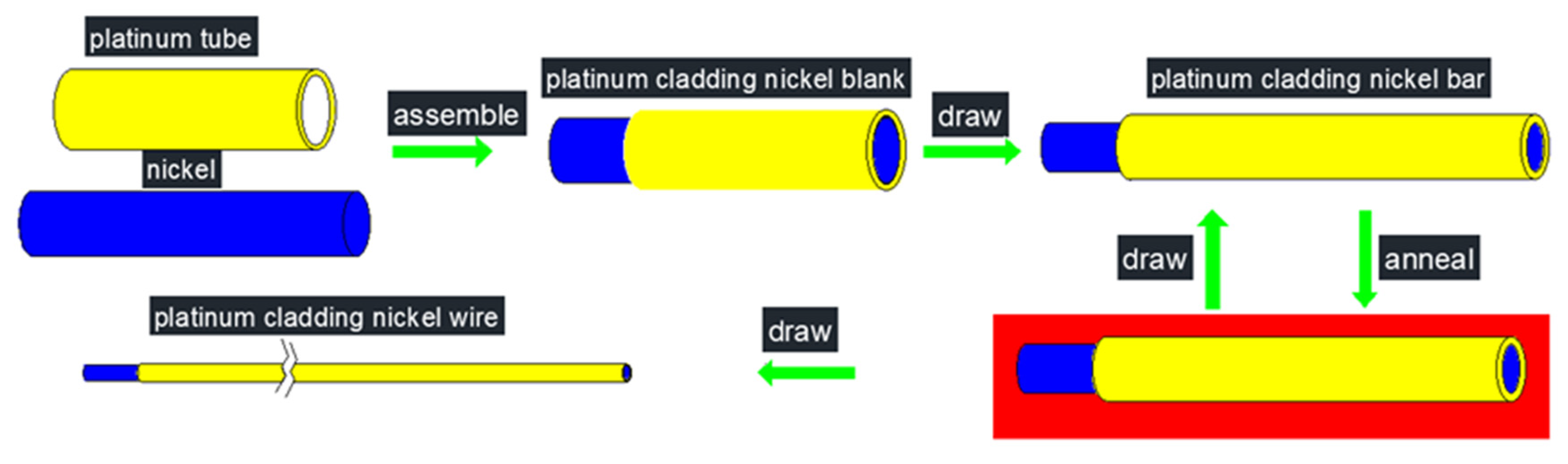
2. Materials and Model
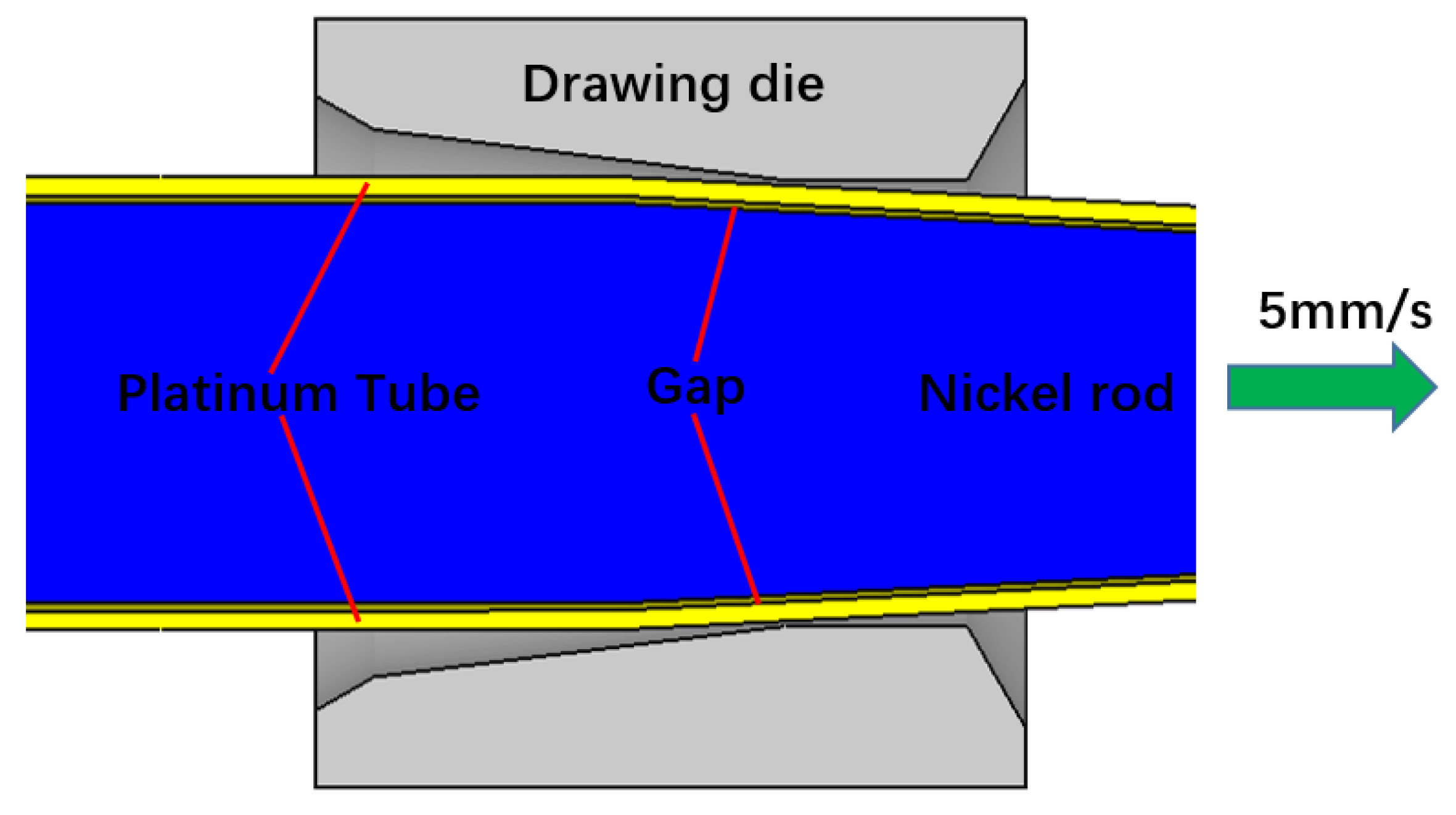
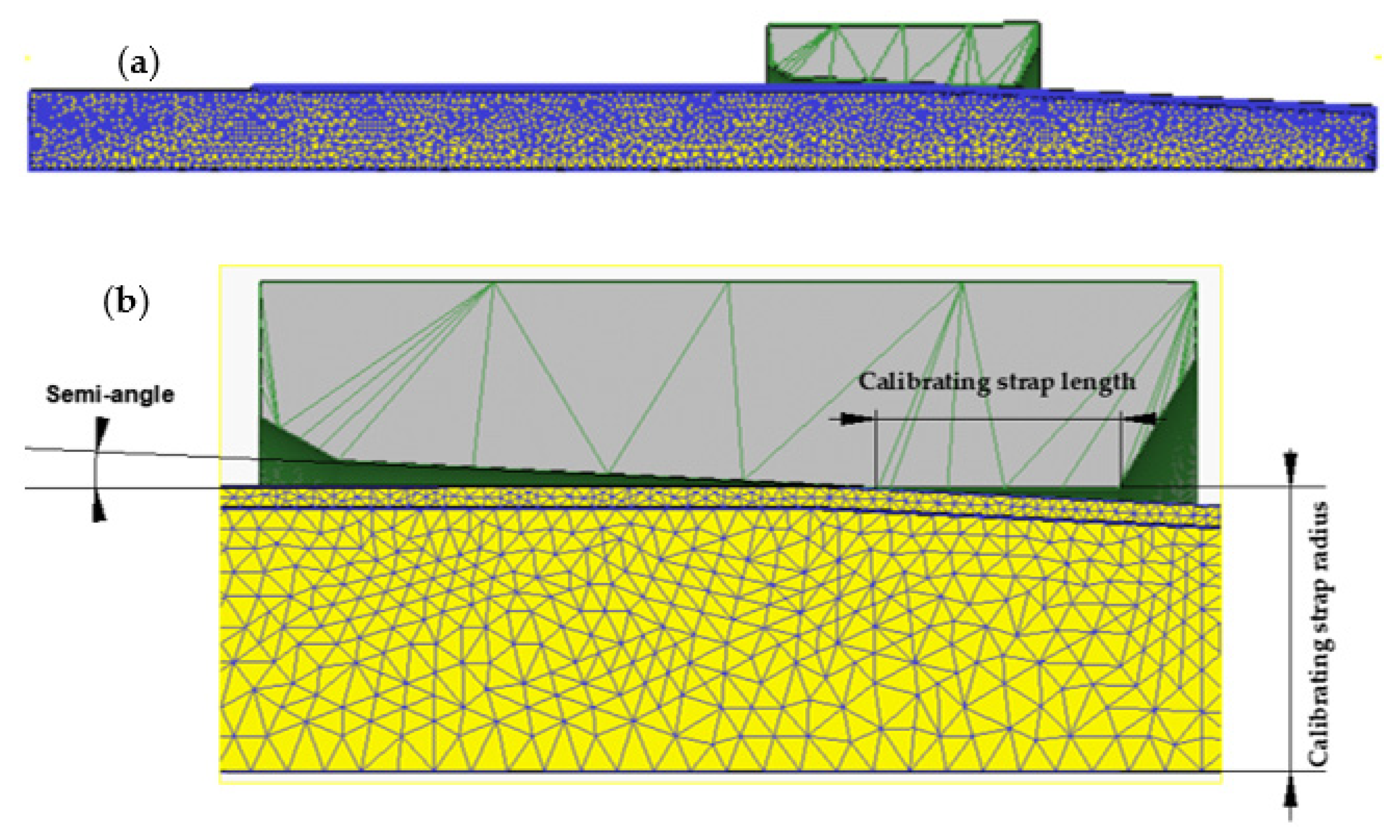
2.1. Simplification and Assumption of Finite Element Model
- 1.
- Without considering the eccentricity and thickness deviation of platinum tube.
- 2.
- Regardless of frictional heat and deformation work.
- 3.
- The platinum and nickel are homogeneous and isotropic, and their intrinsic parameters such as density, elastic modulus and Poisson’s ratio do not change with temperature.
- 4.
- The drawing die is simplified into four areas: the lubrication cone, work cone, calibrating strap and exit cone.
- 5.
- The platinum-clad nickel bar is simplified to select 1/4 of the longitudinal section of the platinum tube, nickel rod and wire drawing die to establish a model for analysis.
2.2. Establishment of Geometric Model
2.3. Taguchi Experimental Design
3. Simulation Results and Analysis
3.1. Range Analysis of Simulation Results
3.2. Simulation and of Optimization Scheme
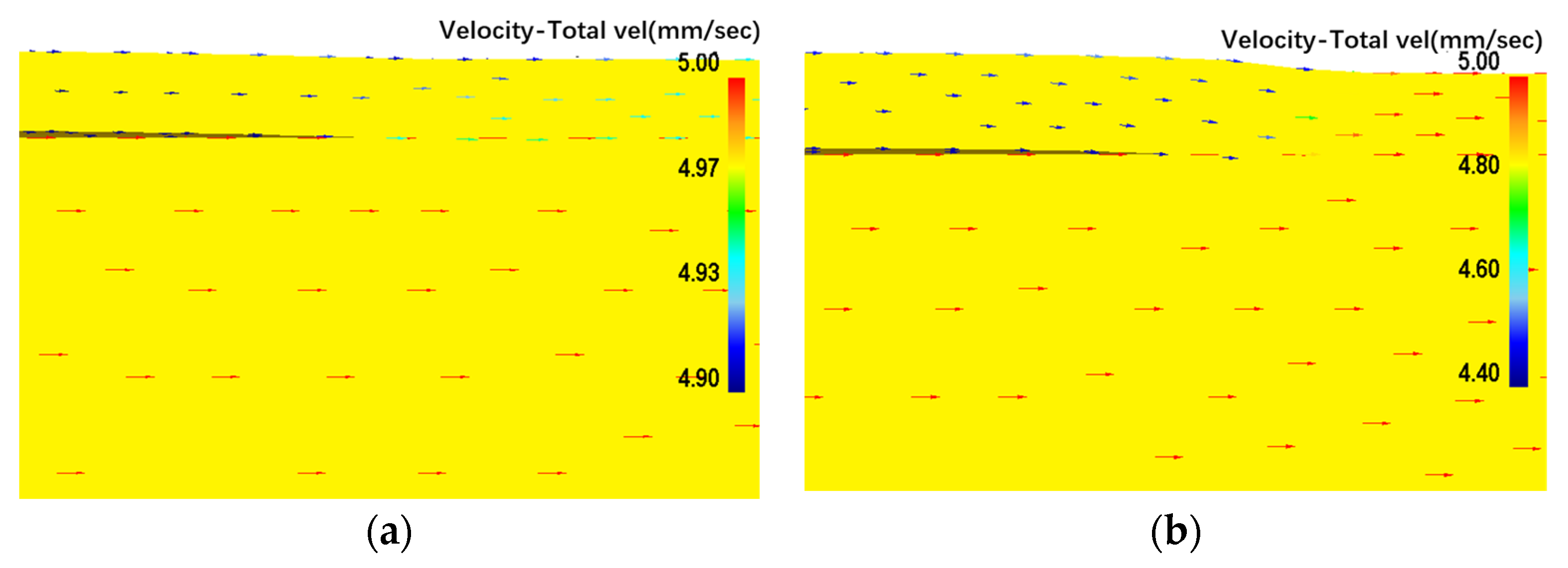
3.3. Analysis of Deformation Behavior
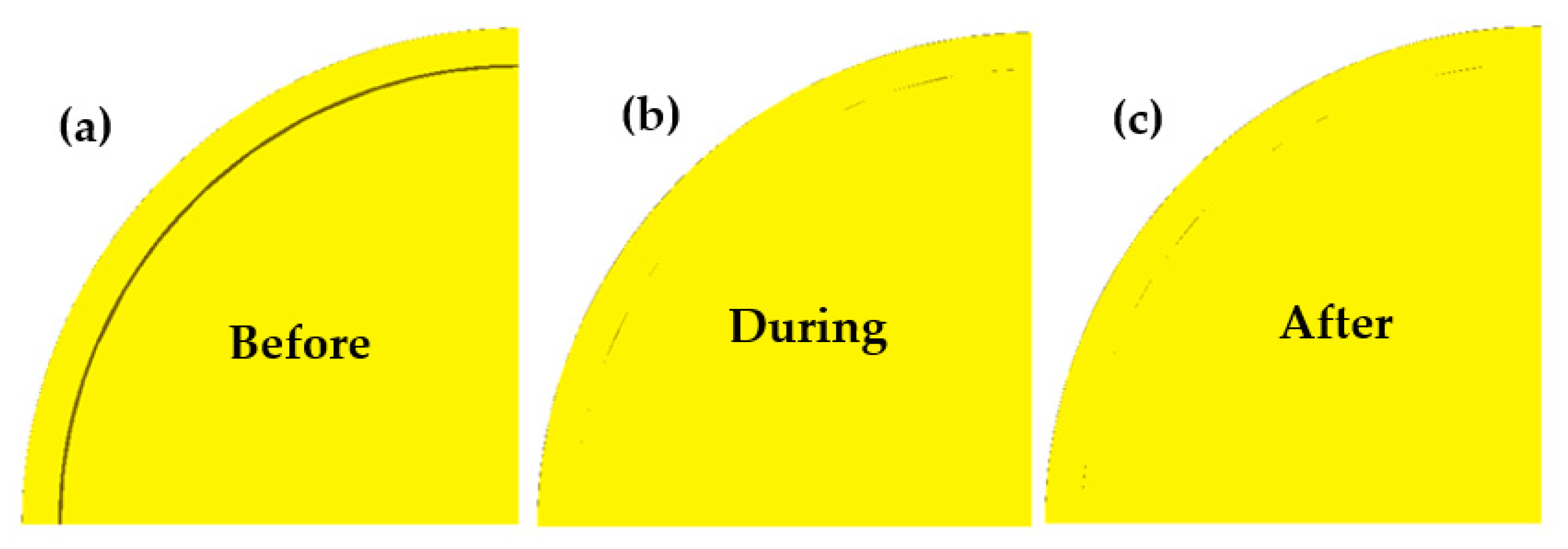
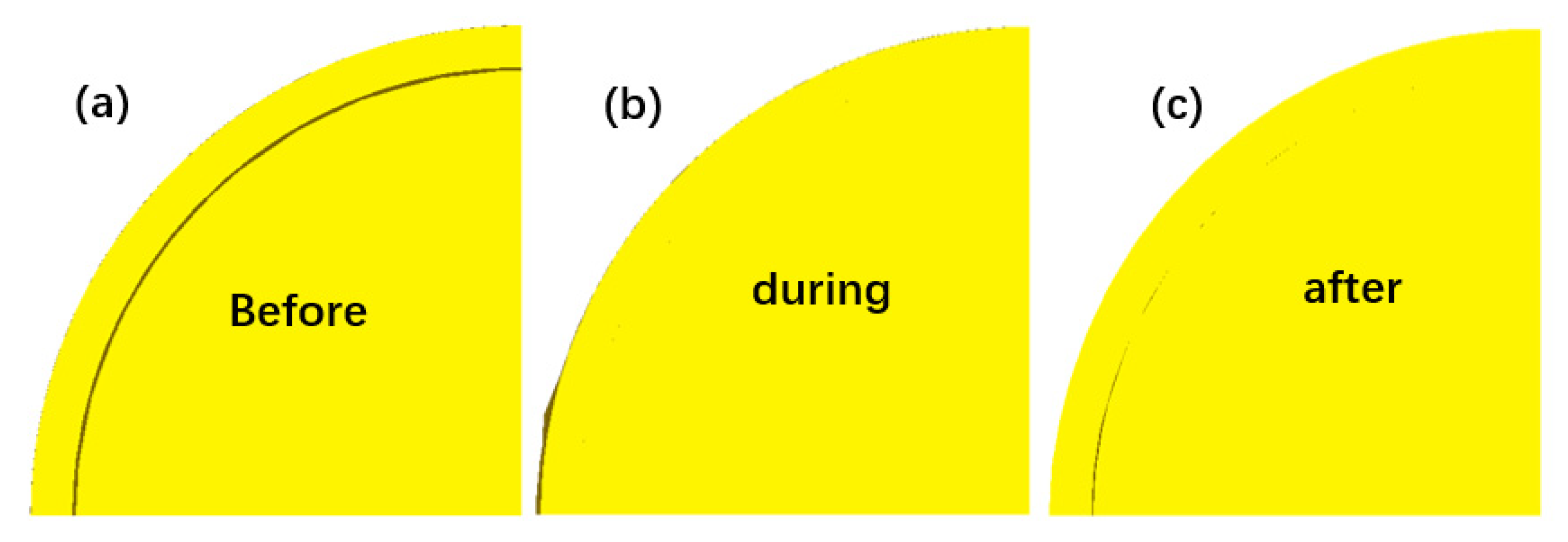
3.4. Analysis of Cladding Behavior
3.5. Analysis of Effective Stress
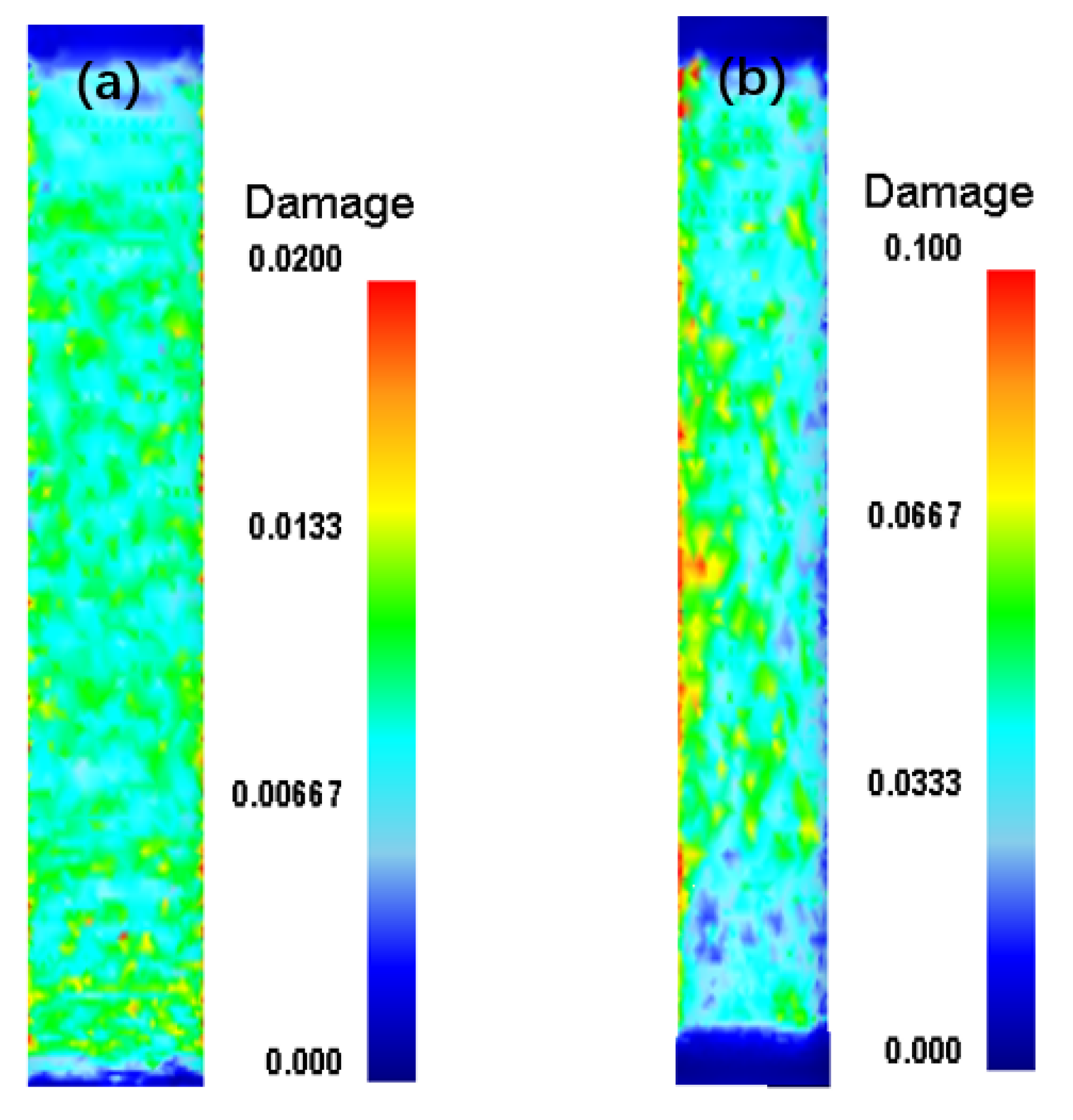
3.6. Analysis of Damage
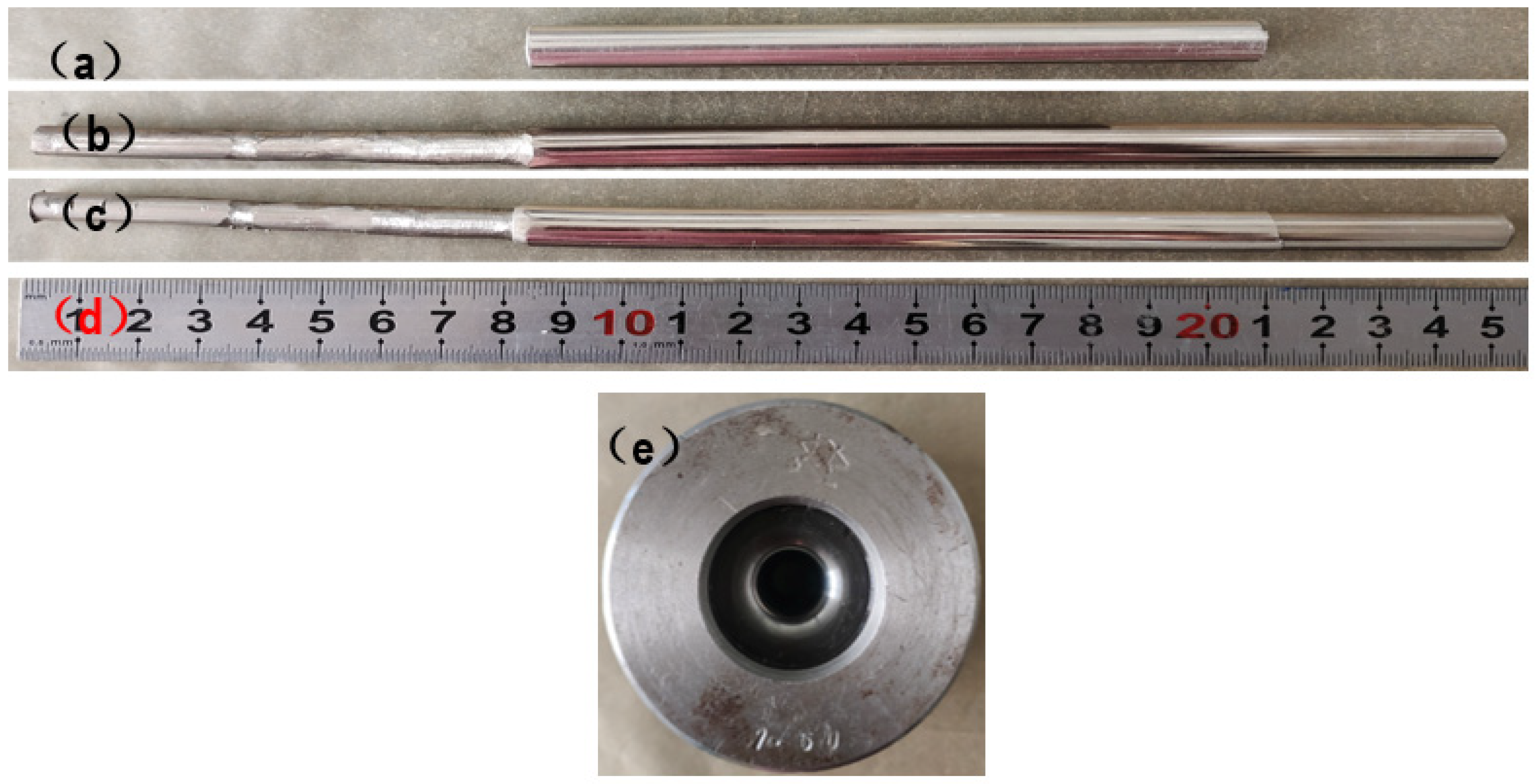
4. Confirmation Experiment
5. Conclusions
- 1.
- The optimal combination of parameters is A1B2C3D1 (α = 3°, µ1 = 0.2, µ2 = 0.3, D = 7.55 mm). The influence rank of parameters to the effective stress is listed as: outer diameter of the original platinum tube > semi-angle of drawing die > friction coefficient between platinum tube and nickel bar > friction coefficient between platinum tube and drawing die.
- 2.
- During the first-step drawing process, the nickel bar does not deform. Only the platinum tube deforms. The experimental results are in general agreement with the simulation results.
- 3.
- It is beneficial for a better coating to increase the friction coefficient between the platinum tube and nickel rod and reduce the original diameter of the platinum tube.
- 4.
- The larger the thickness of platinum tube, the greater deformation as well as the greater the effective stress on. The dangerous section occurs at the beginning of the bearing zone of drawing die.
- 5.
- Large and uniformly distributed effective stress can easily cause local damage to platinum tubes.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sharifian, A.F.; Jamal, H.S.; Jamshidi, A.H.; Roohollah, J. Fabrication of a novel high-strength and high-conductivity copper-clad aluminum composite wire. CIRP J. Manuf. Sci. Technol. 2023, 41, 144–159. [Google Scholar]
- Kocich, R.; Kunčická, L.; Král, P.; Strunz, P. Characterization of innovative rotary swaged Cu-Al clad composite wire conductors. Mater. Des. 2018, 160, 828–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.L.; Li, X.; Pan, H.L.; Luan, H.Y.; Zhao, Z.J. Magneto-impedance effect of composite wires prepared by chemical plating under DC current. Nano-Micro Lett. 2014, 6, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Zhang, F.W.; Han, S.L.; Chen, X.H.; Gao, P.F.; Zheng, K.H. Analysis of microstructure and properties in cold rotary swaged copper-clad magnesium wires. Metals 2023, 13, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, S.H.; Xu, J.Y.; Li, J.X.; Qiu, Y.C.; Yang, X.F.; Zhang, D.F. Study on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Cu-12%Nb composite wire during annealing. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2023, 52, 763–769. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, Y.; Huang, L.J.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, R.; An, Q.; Zhang, C.W.; Geng, L.; Ma, X.X. A novel Ti cored cire developed for wire-feed arc deposition of TiB/Ti composite coating. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 83, 145–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Mi, X.J.; Feng, X.; Xie, H.F.; Peng, L.J.; Huang, G.J.; Li, Y.F.; Yin, X.Q. Interface evolution of Cu-Ni-Si/Al-Mg-Si clad composite wires after annealing. Rare Met. 2020, 39, 1419–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.H.; Ning, Y.T. Platinum alloys and composites used for the glass manufacturing industry. Precious Met. 2013, 34, 88–94. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Yang, E.Q.; Wang, Y.H. Preparation and high temperature oxidation performance of platinum-aluminum coating on CMSX-4 single crystal superalloy. Liaoning Chem. Ind. 2022, 51, 325–328. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, C.F.; Liu, X.Q.; Shao, Z.C. A study on the platinum plating on molybdenum wire surface. Electroplat. Pollut. Control 2013, 33, 26–28. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Y.J.; Chen, G.C.; Wu, C.; Pan, X.C.; Lin, F.; Xu, L.D.; Zhao, F.X.; He, Y.P.; He, G.H.; Chen, Q.N.; et al. Thin-film platinum resistance temperature detector with a SiCN/Yttria-stabilized zirconia protective layer by direct ink writing for high-temperature applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 15, 2172–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.K.; Yan, X.F.; Huang, G.L.; Bo, X.P. Manufacturing of platinum-nickel 30/70 compound wires. Electr. Mater. 2006, 1, 6–9+13. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.G.; Kuan, A.L.; Hu, Z.; Liu, Z.P.; Pan, C.G. Resistance lead. Chinese Patent CN207731673U, 14 August 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Guan, R.G.; Zhang, Y.; Su, N.; Ji, L.Z.; Li, Y.D.; Chen, T.J. Microstructure evolution and properties of Al/Al–Mg–Si alloy clad wire during heat treatment. Appl. Phys. A 2016, 122, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, Y. Interface compatibility During different-temperature Cu/NbTi cladding extrusion: Simulation and experiment. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2023, 52, 441–447. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.K.; Lee, S.P.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, S.; Jo, I.; Bae, D.S. Change of microstructure and hardness of duo-casted Al3003/Al4004 clad material during extrusion process. Metals 2020, 10, 1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhnke, S.; Gensch, F.; Nitschke, R.; Sanabria, V.; Mueller, S. Influence of die surface topography and lubrication on the product quality during indirect extrusion of copper-clad aluminum rods. Metals 2020, 10, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.Y.; Liang, H.; Yu, W.H. Orthogonal tests of copper-clad aluminum bimetal continuous casting by nitrogen pressure core-filling. China Foundry 2013, 10, 385–390. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, X.K.; Liu, X.H.; Xie, G.L. Interfacial microstructure and properties copper cladding aluminum alloy composites. Chin. J. Rare Met. 2022, 46, 862–872. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, B.B.; Liu, X.H.; Xie, J.X.; Xie, M. Preparation process for silver clad aluminum bars by vertical continuous casting composite forming. Chin. J. Eng. 2019, 41, 633–645. [Google Scholar]
- Onodera, M.; Shinma, Y.; Meguro, K.; Tanka, J.; Kasai, J. Wire bonding using Pd plated Cu wire. J. Jpn. Inst. Electron. Packag. 2008, 11, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moisy, F.; Gueydan, A.; Sauvage, X.; Guillet, A.; Keller, C.; Guilmeau, E.; Hug, E. Influence of intermetallic compounds on the electrical resistivity of architectured copper clad aluminum composites elaborated by a restacking drawing method. Mater. Des. 2018, 155, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, M.X.; Liu, X.H.; Jiang, Y.B.; Xie, J.X.; Xie, M. Rotary swaging-drawing formation, microstructure, and properties of copper-clad aluminum composite micro-wires. Chin. J. Eng. 2018, 40, 1358–1372. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, J.F.; Zhao, F.; Liu, X.H. Microstructure and properties of copper-clad beryllium copper wire fabricated by rotary swaging. Chin. J. Nonferrous Met. 2023, 33, 729–740. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.H.; Zou, W.J.; Fu, H.D.; Liu, X.F.; Xie, J.X. Cu/Ti bimetal composite pipe fabricated by heating rotary swaging forming and its Interface, microstructure and properties. Chin. J. Rare Met. 2017, 41, 364–370. [Google Scholar]
- Chai, U.C.; Tzou, Y.Y.; Tiong, I.K. Drawing force optimization research on forming parameters of drawing wire rod with rotating die under coulomb friction. Mater. Sci. Forum 2018, 920, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sas-Boca, I.M.; Tintelecan, M.; Pop, M.; Ilutiu-Varvara, D.A.; Mihu, A.D. The wire drawing process simulation and the optimization of geometry dies. Procedia Eng. 2017, 181, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bella, P.; P Buček, P.; Ridzoň, M.; Mojžiš, M.; Parilák, L. Numerical simulation of multi-rifled tube drawing-finding proper feedstock dimensions and tool geometry. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2017; Volume 179. [Google Scholar]
- Béland, J.F.; Fafard, M.; Rahem, A.; D’Amours, G.; Côté, T. Optimization on the cold drawing process of 6063 Aluminium tubes. Appl. Math. Model. 2011, 35, 5302–5313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Shan, X.B.; Cao, H.Q.; Xie, T. Finite element analysis on ultrasonic drawing process of fine titanium wire. Metals 2020, 10, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, Y.T.; Yang, Z.F.; Wen, F. Platinum; Metallurgical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, G.H.; Xiao, H.F.; Sui, F.L. Flow stress model of pure Al/Ni for cold deformation and its application. J. Anhui Univ. Technol. (Nat. Sci.) 2011, 28, 205–209. [Google Scholar]


| Parameters | Platinum Tube | Nickel Bar | Drawing Die |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material | Platinum | Nickel | AISI H13 |
| Object type | Plastic | Plastic | Rigid |
| Young’s modulus, E [GPa] | 169 | 207 | - |
| Poisson’s ratio, | 0.334 | 0.31 | - |
| Power law [MPa] | [31] | [32] | - |
| Number of elements | 80,000 | 50,000 | - |
| Factor Level | A | B | C | D | Response Variable MPa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α (°) | μ1 | μ2 | D (mm) | ||
| Level 1 | 3 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 7.55 | effective stress |
| Level 2 | 5 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 7.60 | |
| Level 3 | 7 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 7.65 |
| Simulations No | A (α) | B (μ1) | C (μ2) | D (D) | Effective Stress (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 7.55 | 141.6 |
| 2 | 3 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 7.60 | 207.4 |
| 3 | 3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 7.65 | 253.8 |
| 4 | 5 | 0.12 | 0.2 | 7.65 | 274.4 |
| 5 | 5 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 7.55 | 146.8 |
| 6 | 5 | 0.3 | 0.12 | 7.60 | 226.5 |
| 7 | 7 | 0.12 | 0.3 | 7.60 | 227.3 |
| 8 | 7 | 0.2 | 0.12 | 7.65 | 282.4 |
| 9 | 7 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 7.55 | 159.9 |
| Factor Level | A (α) | B (μ1) | C (μ2) | D (D) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Level 1 | 200.9 | 214.4 | 216.8 | 149.4 |
| Level 2 | 215.9 | 212.2 | 213.9 | 220.4 |
| Level 3 | 223.2 | 213.4 | 209.3 | 270.2 |
| Range | 22.3 | 2.3 | 7.6 | 120.8 |
| Rank | 2 | 4 | 3 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; Chong, X.; Zhao, S.; Yang, Y.; Li, A.; Fang, J.; Hu, J.; Xie, M. Optimization of the First-Step Drawing Parameters for Platinum-Clad Nickel Bar Based on FEM Simulation. Metals 2023, 13, 1201. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13071201
Chen Y, Chong X, Zhao S, Yang Y, Li A, Fang J, Hu J, Xie M. Optimization of the First-Step Drawing Parameters for Platinum-Clad Nickel Bar Based on FEM Simulation. Metals. 2023; 13(7):1201. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13071201
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yongtai, Xiaoyu Chong, Shangqiang Zhao, Youcai Yang, Aikun Li, Jiheng Fang, Jieqiong Hu, and Ming Xie. 2023. "Optimization of the First-Step Drawing Parameters for Platinum-Clad Nickel Bar Based on FEM Simulation" Metals 13, no. 7: 1201. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13071201
APA StyleChen, Y., Chong, X., Zhao, S., Yang, Y., Li, A., Fang, J., Hu, J., & Xie, M. (2023). Optimization of the First-Step Drawing Parameters for Platinum-Clad Nickel Bar Based on FEM Simulation. Metals, 13(7), 1201. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13071201





