Effects of L-PBF Scanning Strategy and Sloping Angle on the Process Properties of TC11 Titanium Alloy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.2. Experimental Equipment
2.3. Experimental Method
3. Results and Analysis
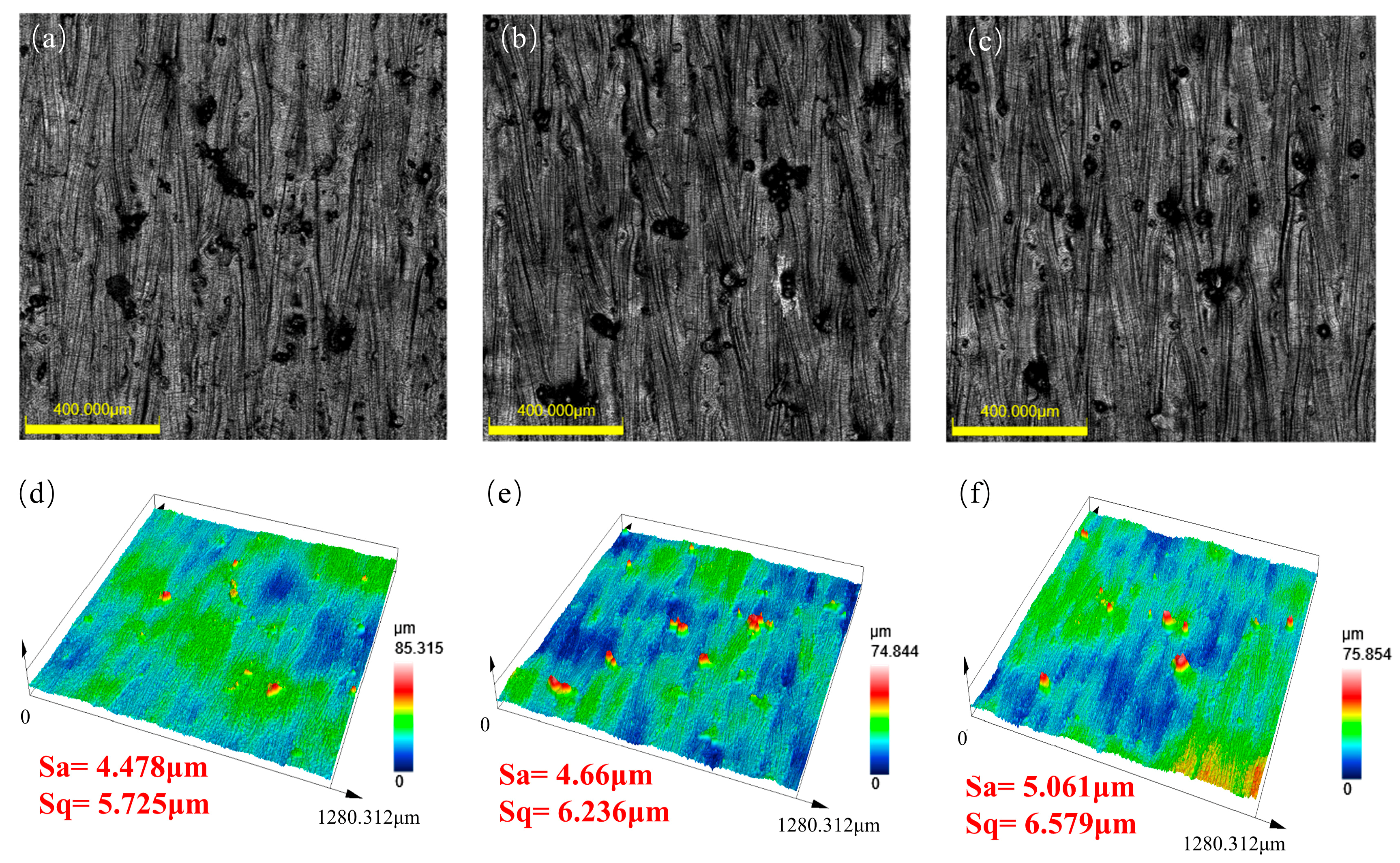
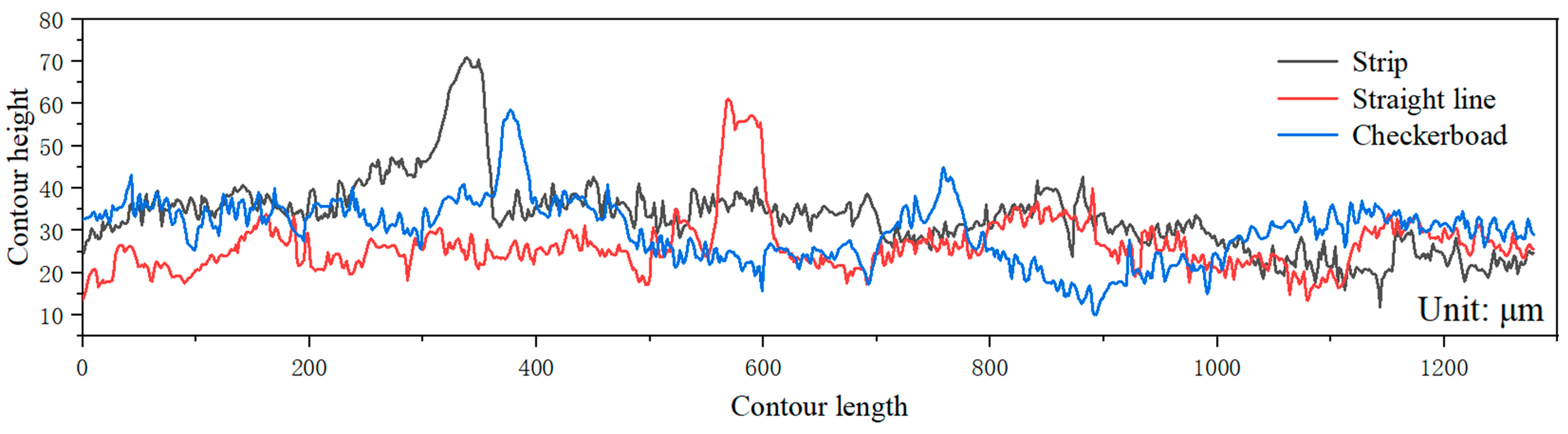
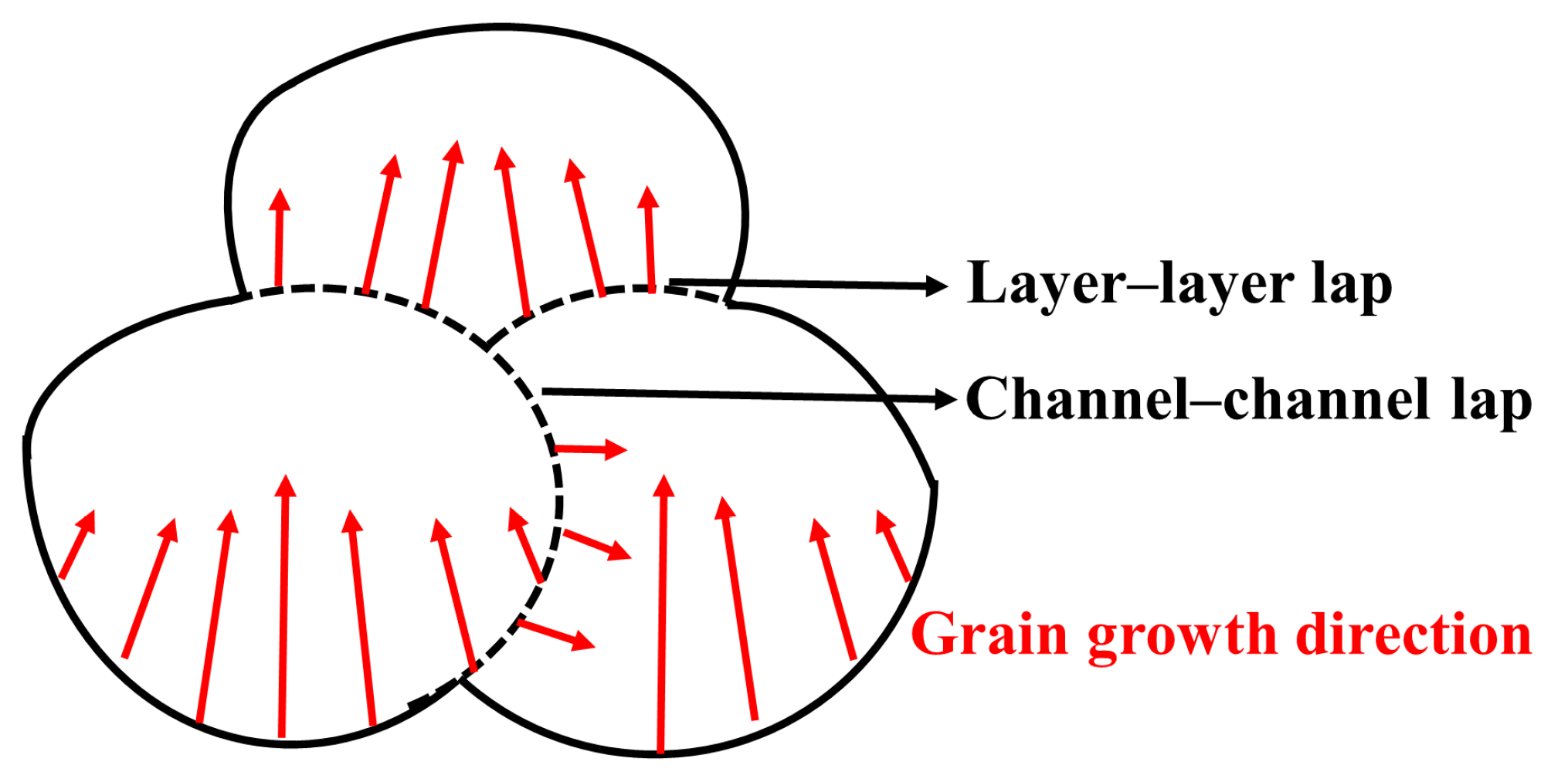
3.1. Effect of Scanning Strategy on Surface Morphology and Roughness
3.2. Effect of Scanning Strategy on Microhardness
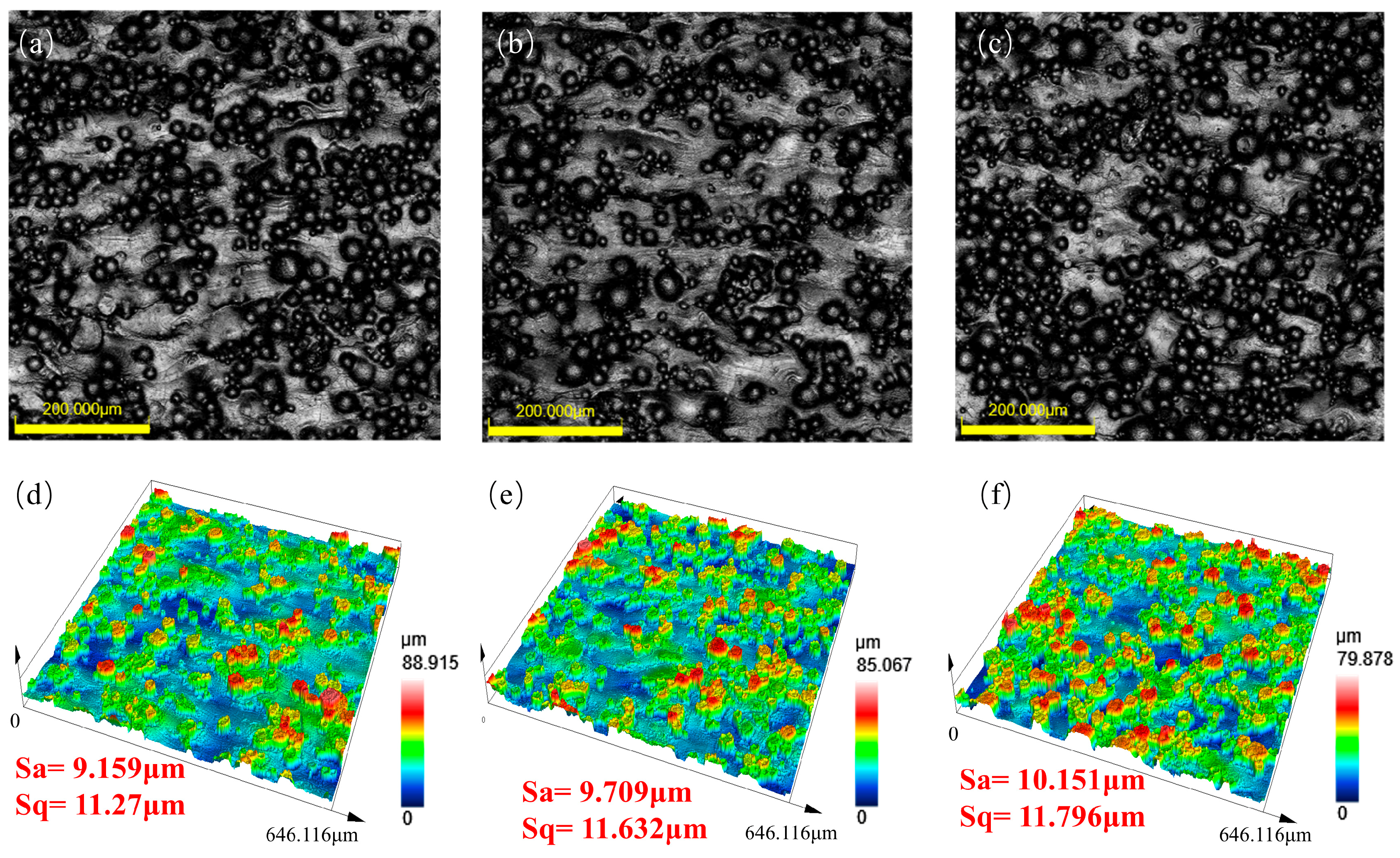
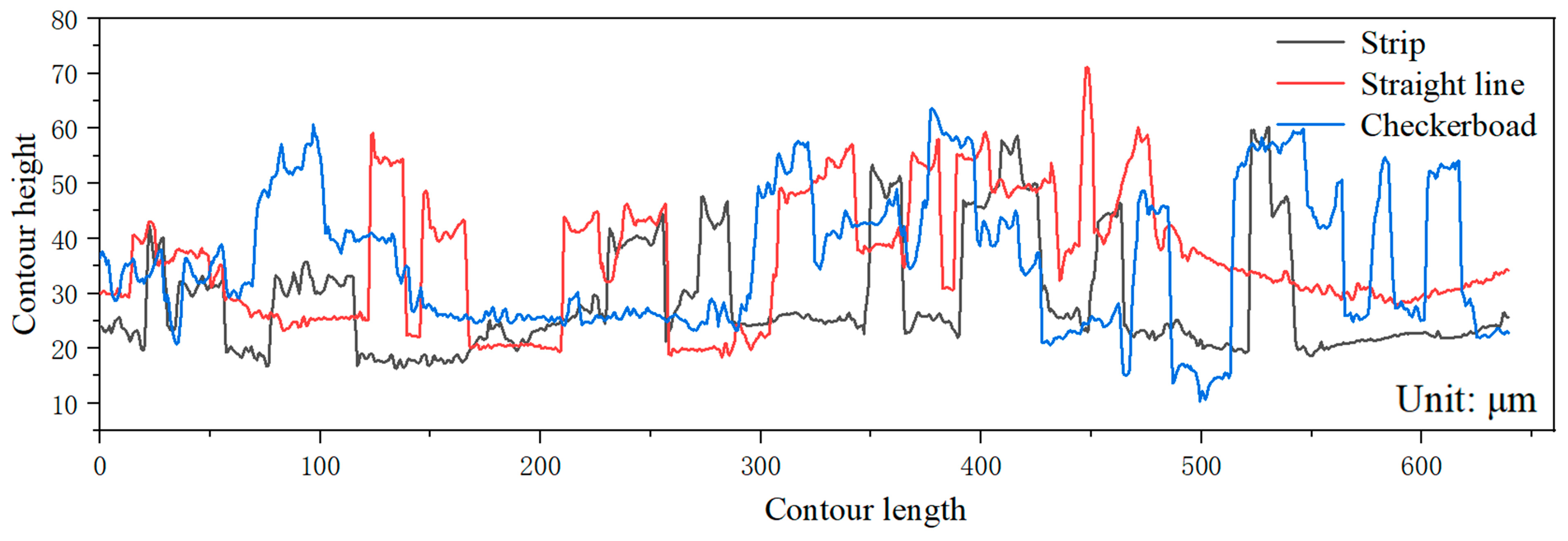
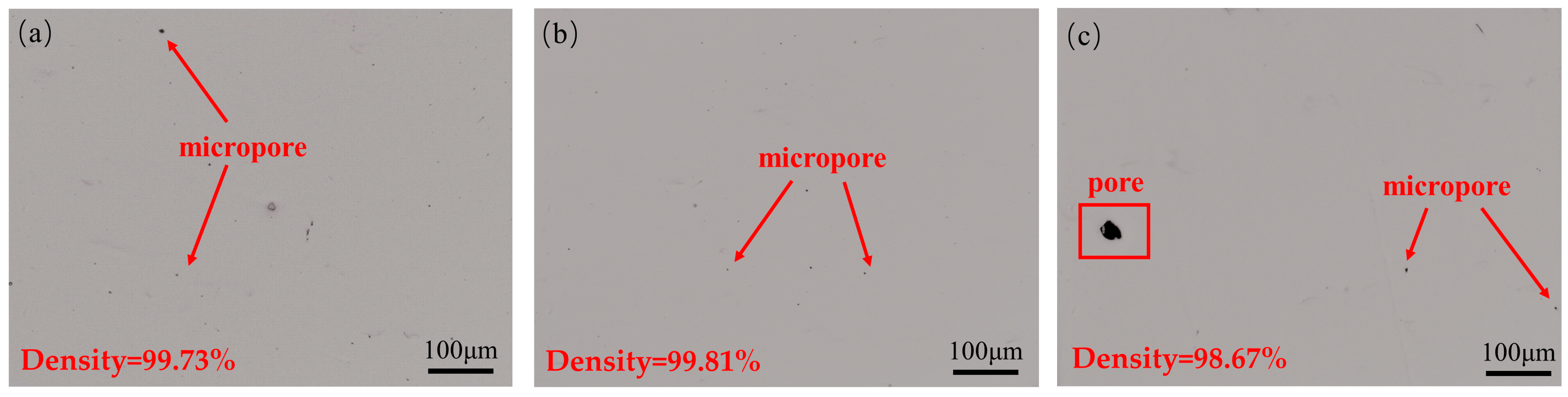
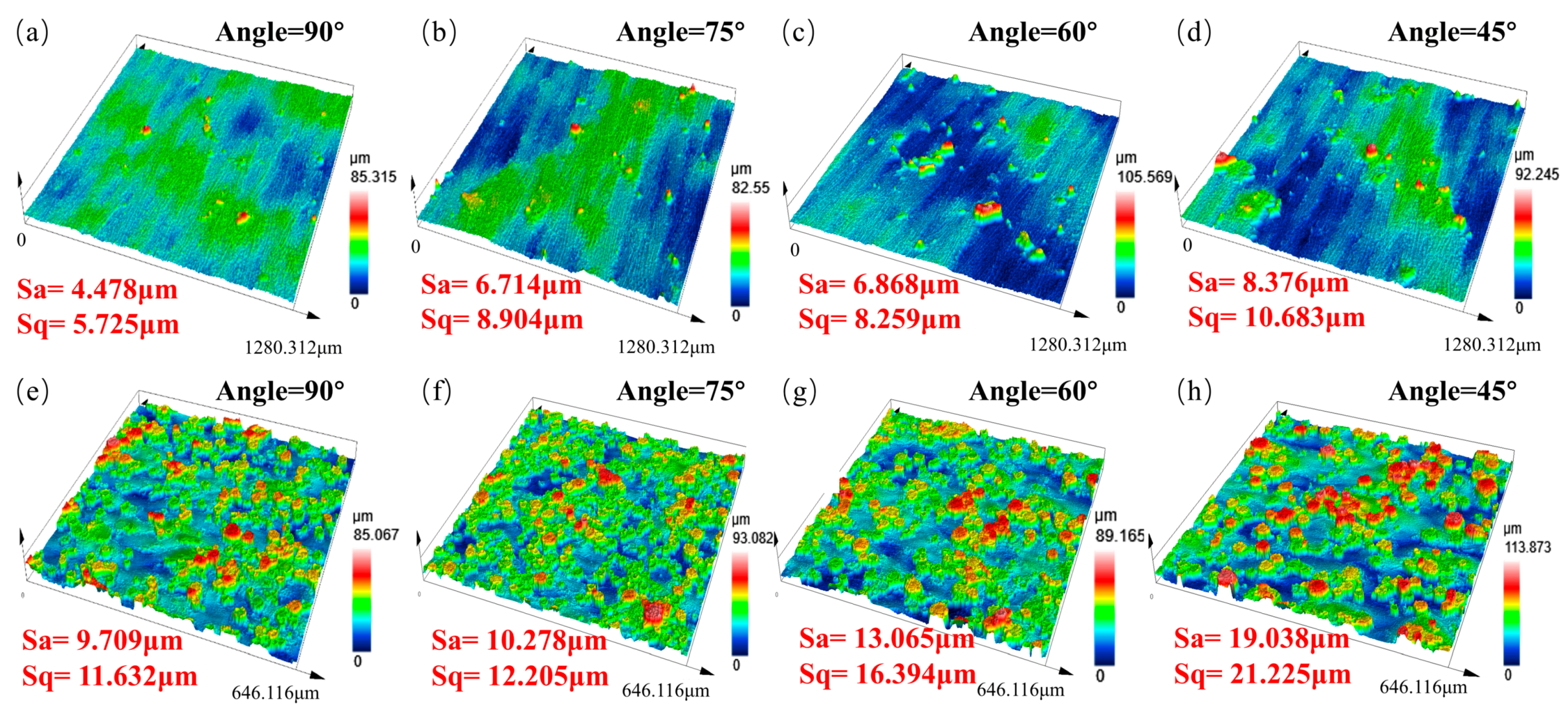
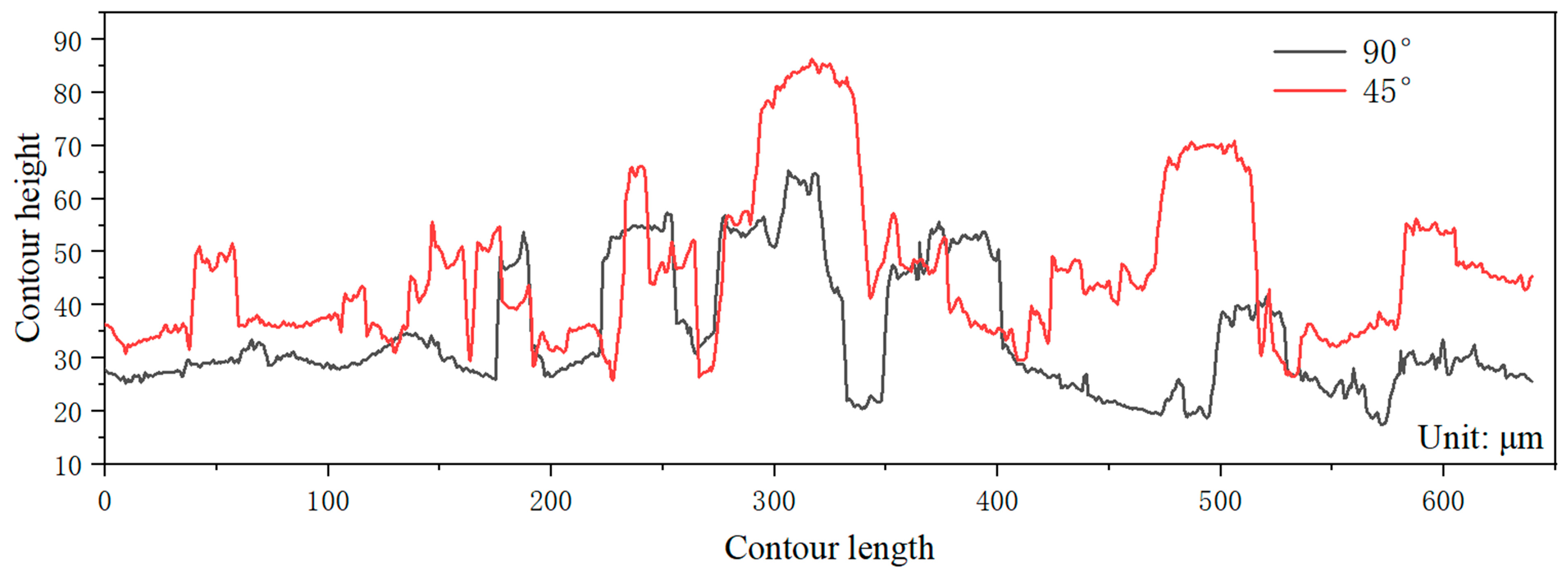
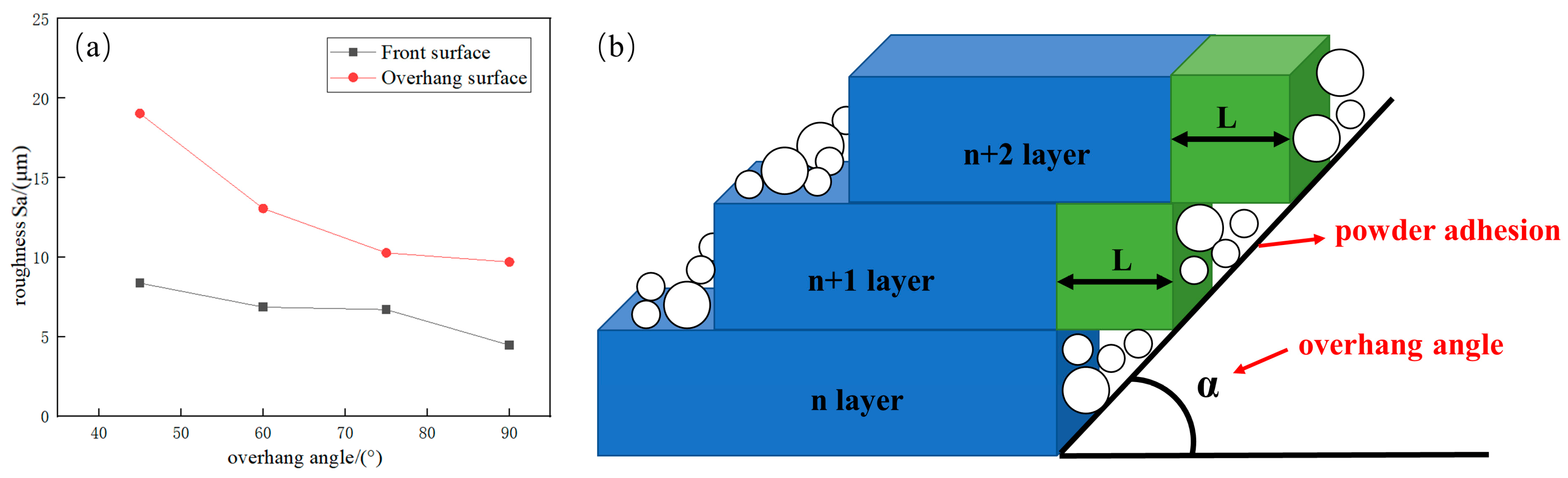
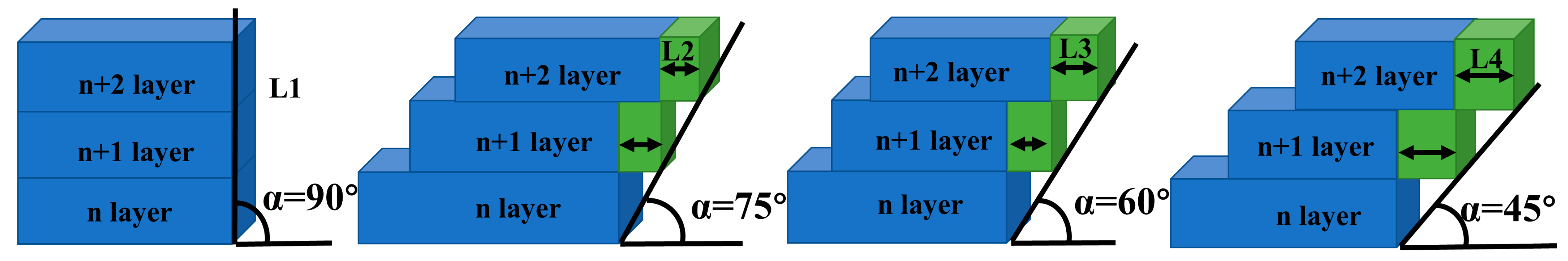
3.3. Effect of Forming Angle
3.4. Effect of Sloping Angle on Microhardness of Sample
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, N.; Huang, S.; Zhang, G.; Qin, R.; Liu, W.; Xiong, H.; Shi, G.; Blackburn, J. Progress in Additive Manufacturing on New Materials: A Review. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2019, 35, 242–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Han, J.; Yu, H.; Yin, J.; Gao, M.; Wang, Z.; Zeng, X. Role of molten pool mode on formability, microstructure and mechanical properties of selective laser melted Ti-6Al-4V alloy. Mater. Des. 2016, 110, 558–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahrubudin, N.; Chuan, L.T.; Ramlan, R. An Overview on 3D Printing Technology: Technological, Materials, and Applications. Procedia Manuf. 2019, 35, 1286–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, D.D.; Zhang, H.M.; Chen, H.Y.; Zhang, H.; Xi, L. Laser Additive Manufacturing of High-Performance Metallic Aerospace Components. Chin. J. Lasers 2020, 47, 32–55. [Google Scholar]
- Morsi, K. Review: Titanium-titanium boride composites. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 6753–6771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tshephe, T.S.; Akinwamide, S.O.; Olevsky, E.; Olubambi, P.A. Additive manufacturing of titanium-based alloys- A review of methods, properties, challenges, and prospects. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahulan, N.; Sharma, S.S.; Rakesh, N.; Sambhu, R. A short review on mechanical properties of SLM titanium alloys based on recent research works. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 56, A7–A12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.L.; Jia, D.C.; Yang, Z.H.; Duan, X.M.; Cai, D.L.; Zhou, Y. Research progress on selective laser melting 3D printing of titanium alloys and titanium matrix composites. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2019, 27, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Pasang, T.; Budiman, A.S.; Wang, J.C.; Jiang, C.P.; Boyer, R.; Williams, J.; Misiolek, W.Z. Additive manufacturing of titanium alloys—Enabling re-manufacturing of aerospace and biomedical components. Microelectron. Eng. 2023, 270, 111935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo-Pulgarín, J.C.; Biffi, C.A.; Vedani, M.; Celentano, D.; Sánchez-Egea, A.; Boccardo, A.D.; Ponthot, J.P. Beta Titanium Alloys Processed By Laser Powder Bed Fusion: A Review. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2021, 30, 6365–6388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liang, Z.; Sun, Z.; Chen, X. Study on the matching of TC4 alloy powder and SLM process parameters. Inf. Rec. Mater. 2022, 23, 10–13. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Xie, X.; Wu, H.; Ji, X.; Shen, H.; Xue, M.; Wu, H.; Chao, Q.; Fan, G.; Liu, Q. In-situ control of residual stress and its distribution in a titanium alloy additively manufactured by laser powder bed fusion. Mater. Charact. 2023, 28, 112953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chekotu, J.C.; Goodall, R.; Kinahan, D.; Brabazon, D. Control of Ni-Ti Phase Structure, Solid-State Transformation Temperatures and Enthalpies via Control of L-PBF Process Parameters. Mater. Des. 2022, 218, 110715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Jin, X.; Bai, Y.; Yang, Y.; Ni, C.; Lu, W.F.; Wang, H. Microstructure and anisotropic mechanical properties of selective laser melted Ti6Al4V alloy under different scanning strategies. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 831, 142236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadali, M.F.; Hassan, M.Z.; Ahmad, F.; Yahaya, H.; Rasid, Z.A. Influence of selective laser melting scanning speed parameter on the surface morphology, surface roughness, and micropores for manufactured Ti6Al4V parts. J. Mater. Res. 2020, 35, 2025–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Li, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Wen, P.; Shi, Z. Study on the Influence of Process Parameters on the Densification and Surface Hardness of TC4 Titanium Alloy Formed Parts by Selective Laser Melting. Appl. Laser 2022, 42, 55–62. [Google Scholar]
- Wo’zniak, A.; Adamiak, M.; Ziębowicz, B. The surface morphology and electrochemical properties of pure titanium obtained by selective laser melting method. Solid State Phenom. 2020, 308, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, S.; Gutzeit, K.; Hotz, H.; Kirsch, B.; Aurich, J.C. Selective laser melting (SLM) of AISI 316L-impact of laser power, layer thickness, and hatch spacing on roughness, density, and microhardness at constant input energy density. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 108, 1551–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Liu, K.; Sun, J.; Gu, D. Effects of Laser Scan Strategies on Densification, Residual Stress, and Mechanical Properties of W-Ti Heavy Alloy Fabricated by Laser Powder Bed Fusion. Chin. J. Lasers 2023, 50, 29–39. [Google Scholar]
- Pushp, P.; Dasharath, S.M.; Arati, C. Classification and applications of titanium and its alloys. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 54, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, L.L.; Cheng, K.W.; Wang, F.; Shi, J.W. Application of Selective Laser Melting Technology Based on Titanium Alloy in Aerospace Products. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 740, 012056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Wang, J.; Ren, J.; Hong, Q. Effects of scanning strategies on microstructure and properties of selective laser melted cobalt-chromium alloy. Laser J. 2020, 41, 133–136. [Google Scholar]
- Zong, X.; Wang, L.; Gao, Q.; Liu, W.; Zhou, H. The Effect of Laser Scanning Angle on the Structure and Properties of SLM Forming 316L Stainless Steel. Appl. Laser 2021, 41, 421–430. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.-J.; Yang, H.-C.; Wang, X.-B.; Kuang, C.-J.; Han, W. Effects of laser parameters and scanning strategy on the forming properties of selective laser melting TC11 alloy. Powder Metall. Ind. 2018, 28, 18–24. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Sun, J.; Bi, X.; Chen, J.; Chen, W.; Ren, Y.; Niu, Y.; Li, C.; Qiu, W.; Yuan, T. Effect of scanning strategies on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti–15Mo alloy fabricated by selective laser melting. Vacuum 2022, 205, 111454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.J.; Wei, Z.X. Influences of the scanning strategy on surface roughness in selective laser melting. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 2020, 236, 095440542097811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorasani, A.; Gibson, I.; Awan, U.S.; Ghaderi, A. The Effect of SLM Process Parameters on Density, Hardness, Tensile Strength and Surface Quality of Ti-6Al-4V. Addit. Manuf. 2018, 25, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Wang, P.; Liu, Y.; Han, G. Process Strategy of Selected Laser Melting Forming Non-Horizontal Suspension Structure Experiment of Nicochrome Steel. Chin. J. Rare Met. 2019, 43, 486–493. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, G.; Liu, T.; Zhang, C.; Liao, W. Research on Forming Quality of Overhanging Structure by Selective Laser Melting. China Mech. Eng. 2016, 27, 1810–1815. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, G. Research on Laser Selective Melting Forming Process of Metal Hanging Feature Structure; Nanjing University of Science and Technology: Nanjing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, W.-Y.; Xiao, Z.-Y.; Cheng, Y.-W.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Gao, C.-F.; Zhang, W.-W. Effect of sloping angle on forming of CoCrMoW alloy by selective laser melting. Chin. J. Nonferrous Met. 2017, 27, 2251–2259. [Google Scholar]
- Weiyong, Y.; Zhiyu, X.; Yingying, C.; Chuanshou, H.; Quanli, Z. Powder Characteristics and Selective Laser Melting Forming Properties of CoCrMoW Alloy. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2019, 48, 973–980. [Google Scholar]
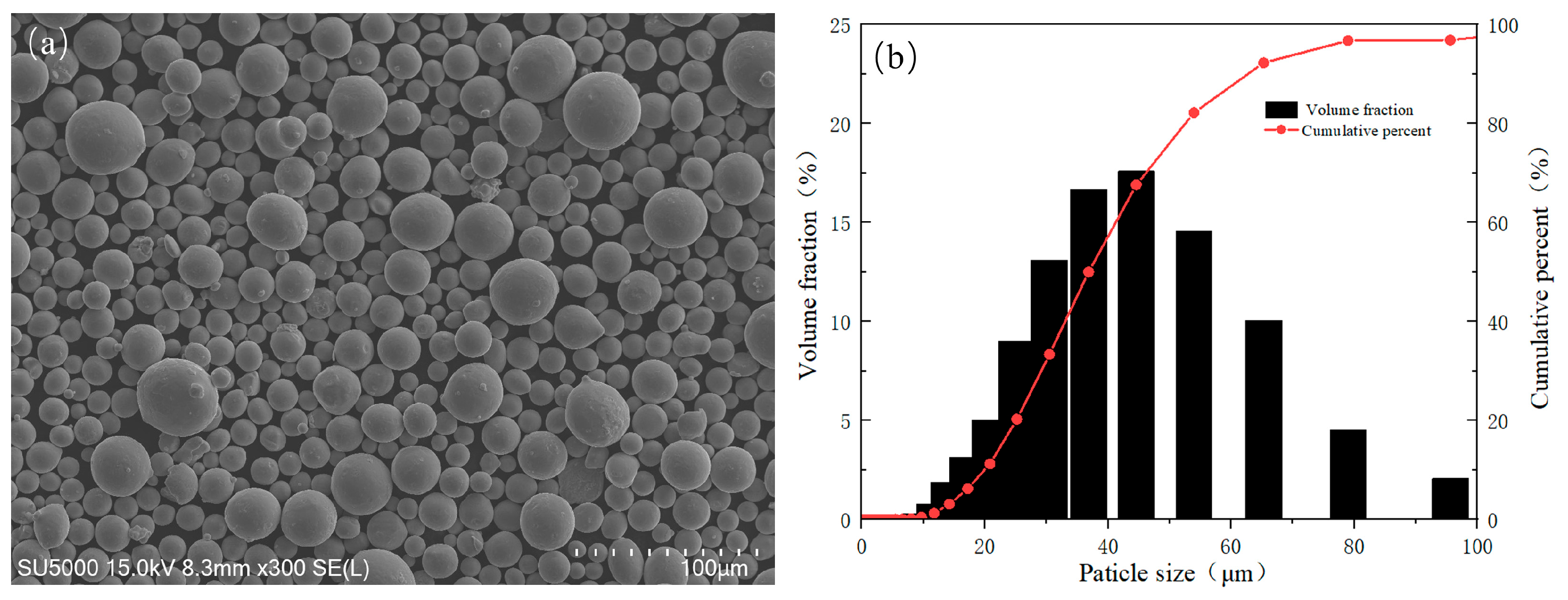
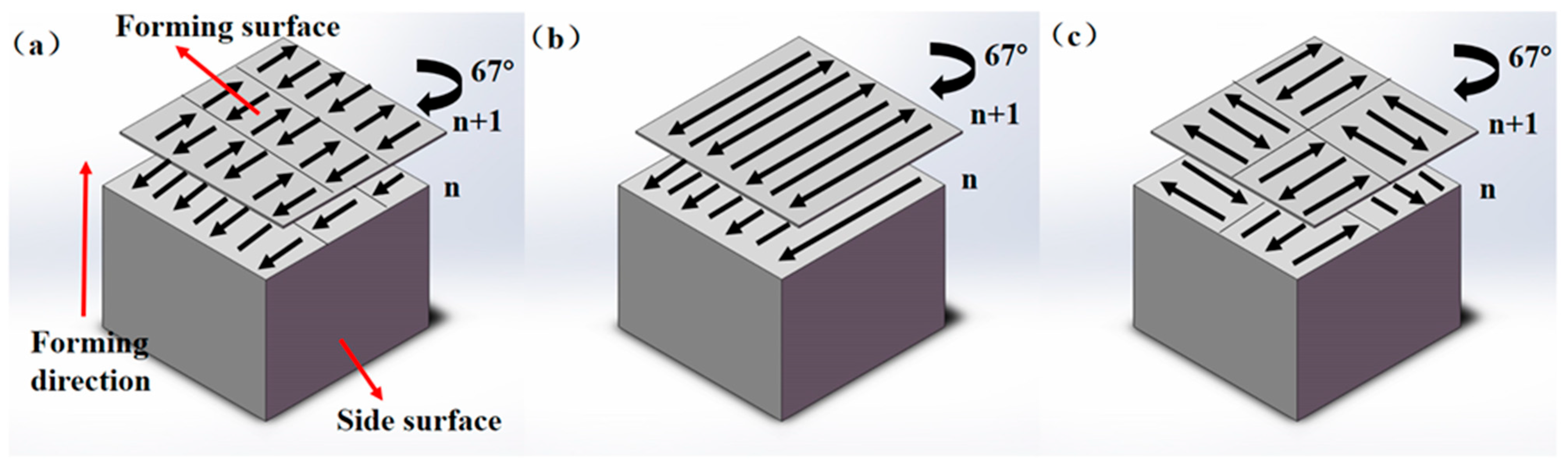
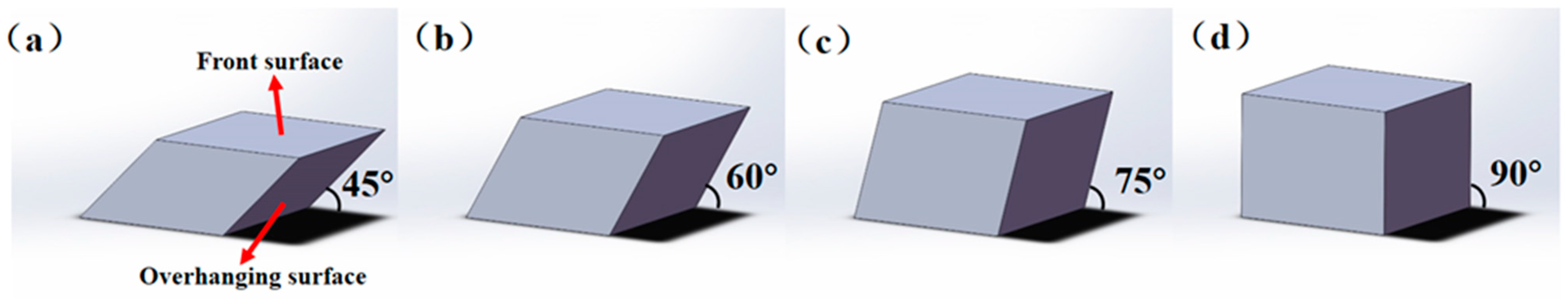
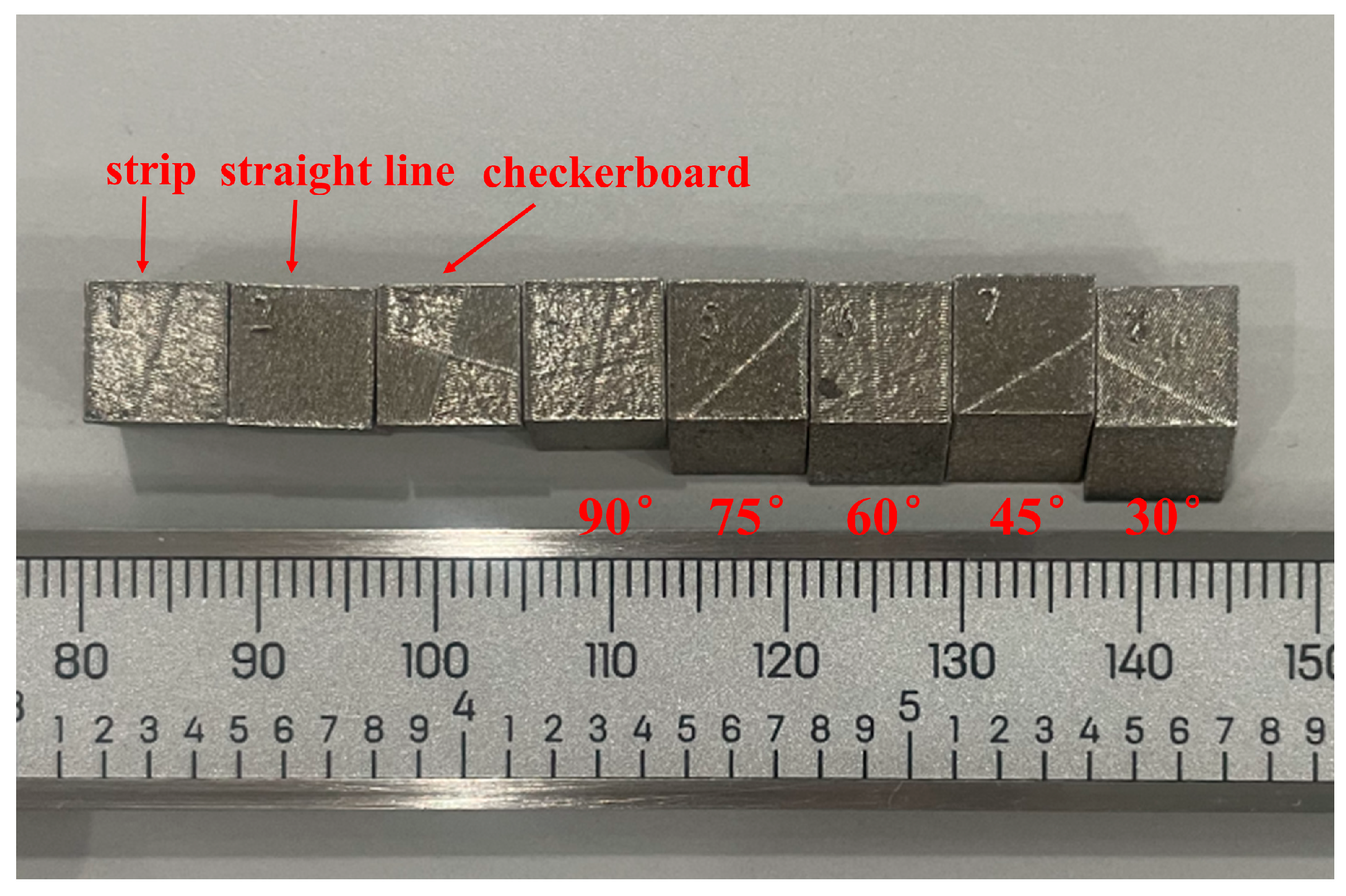

| Element | Ti | Zr | Al | Fe | Mo | Si | C | H | N | O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mass fraction (%) | 88.05 | 1.43 | 6.44 | 0.182 | 3.52 | 0.255 | 0.014 | 0.0033 | 0.001 | 0.096 |
| Scanning Strategy | Microhardness (HV) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | Average Value | |
| Strip scanning | 365.7 | 374.8 | 370.7 | 364.9 | 377.2 | 370.7 ± 23.54 |
| Straight line scanning | 378.8 | 390.4 | 381.6 | 379.7 | 388.5 | 383.8 ± 22.46 |
| Checkerboard scanning | 370.5 | 362.4 | 364.8 | 355.6 | 368.7 | 364.4 ± 27.46 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, X.; Shu, C.; Zheng, Z.; Shu, X.; Chen, S.; Essa, K.; Li, Z.; Xu, H. Effects of L-PBF Scanning Strategy and Sloping Angle on the Process Properties of TC11 Titanium Alloy. Metals 2023, 13, 983. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13050983
Lu X, Shu C, Zheng Z, Shu X, Chen S, Essa K, Li Z, Xu H. Effects of L-PBF Scanning Strategy and Sloping Angle on the Process Properties of TC11 Titanium Alloy. Metals. 2023; 13(5):983. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13050983
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Xuben, Chang Shu, Zhiyu Zheng, Xuedao Shu, Siyuan Chen, Khamis Essa, Zixuan Li, and Haijie Xu. 2023. "Effects of L-PBF Scanning Strategy and Sloping Angle on the Process Properties of TC11 Titanium Alloy" Metals 13, no. 5: 983. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13050983
APA StyleLu, X., Shu, C., Zheng, Z., Shu, X., Chen, S., Essa, K., Li, Z., & Xu, H. (2023). Effects of L-PBF Scanning Strategy and Sloping Angle on the Process Properties of TC11 Titanium Alloy. Metals, 13(5), 983. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13050983









