Eutectoid Transformation Kinetics of FeO under N2 and Air Atmospheres
Abstract
1. Introduction
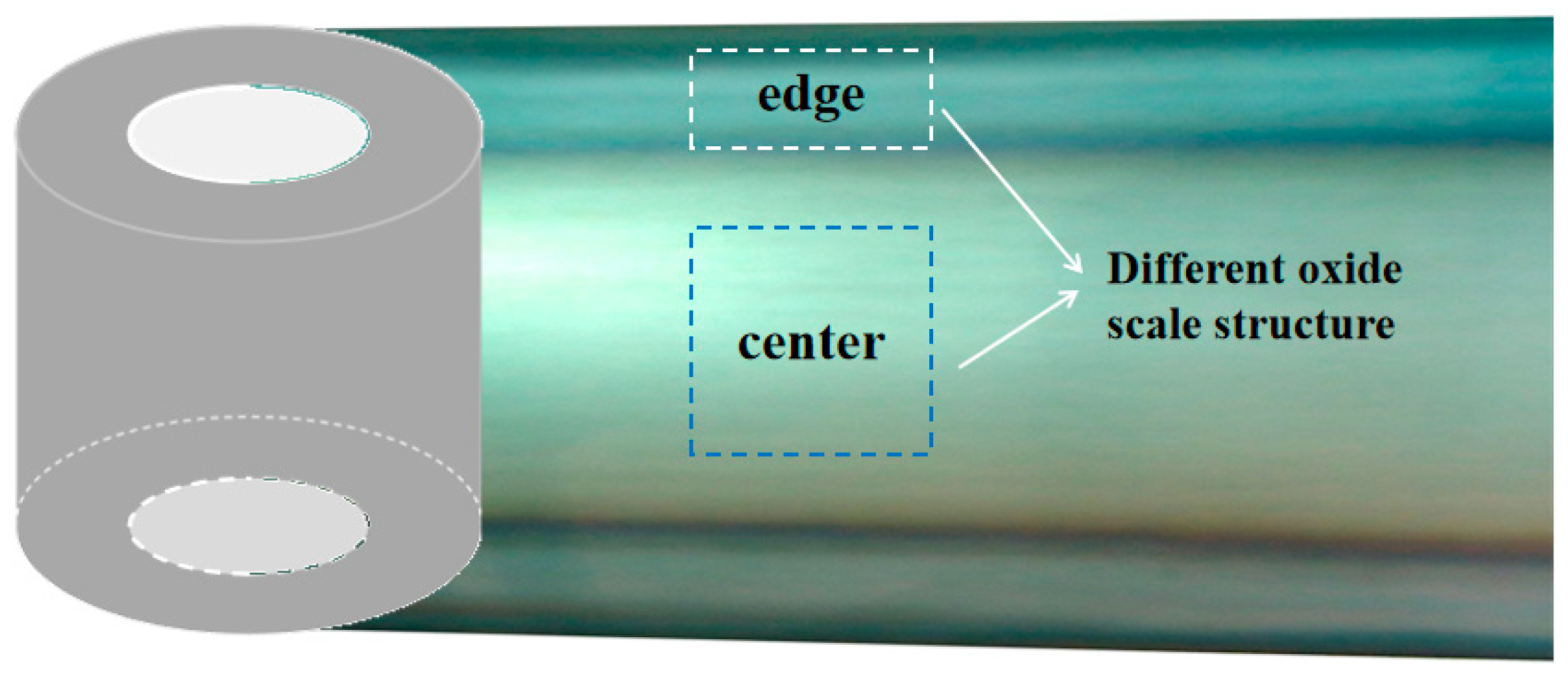
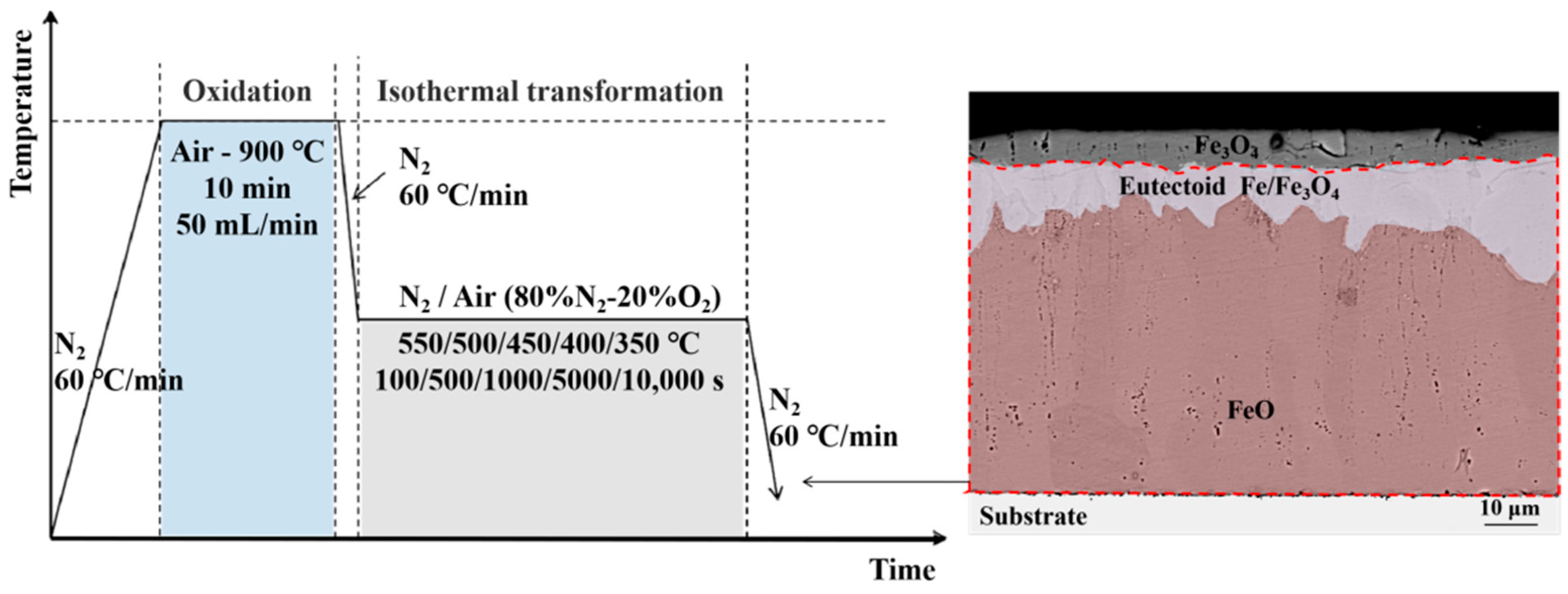
2. Experimental Procedure
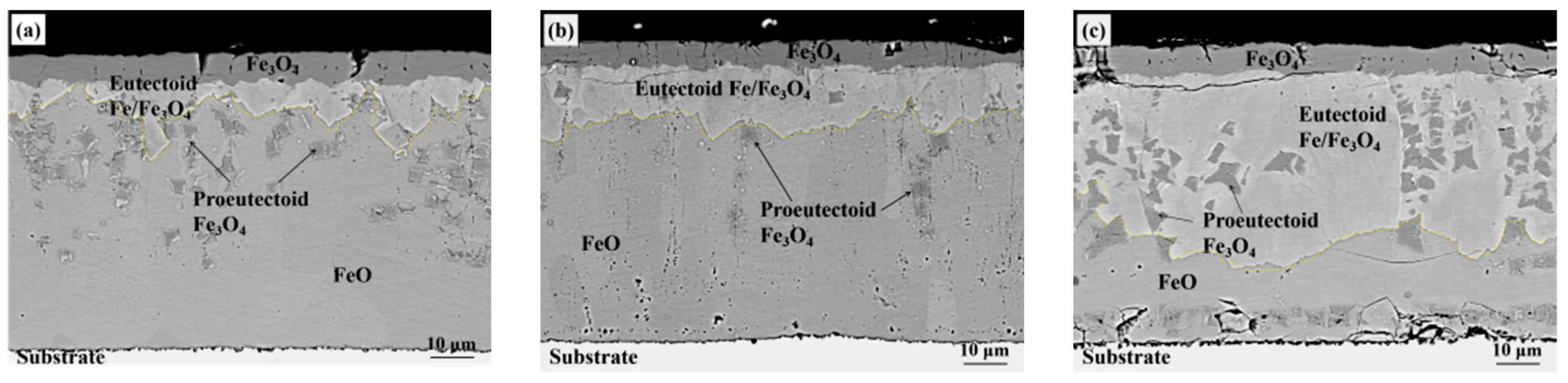
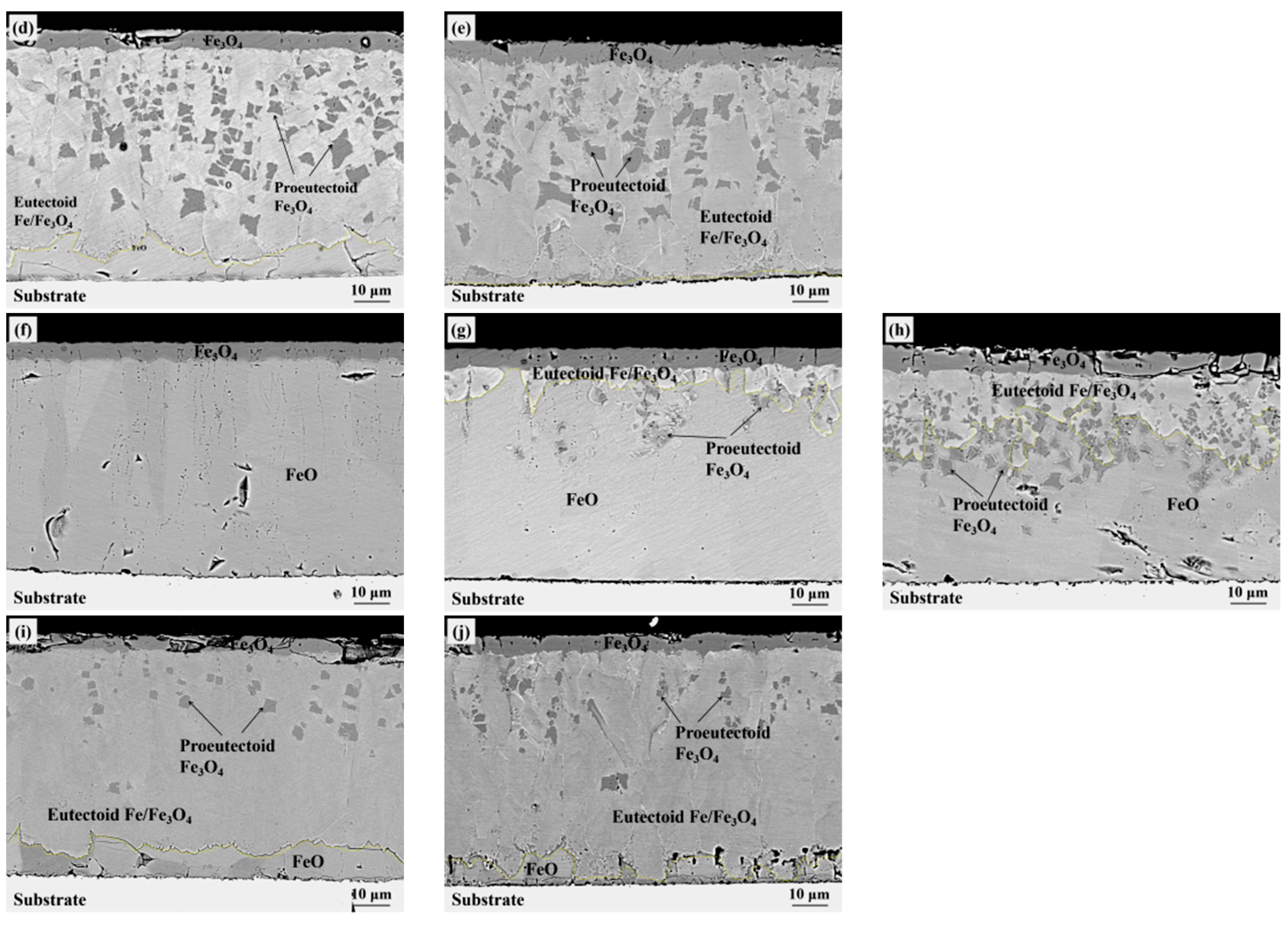
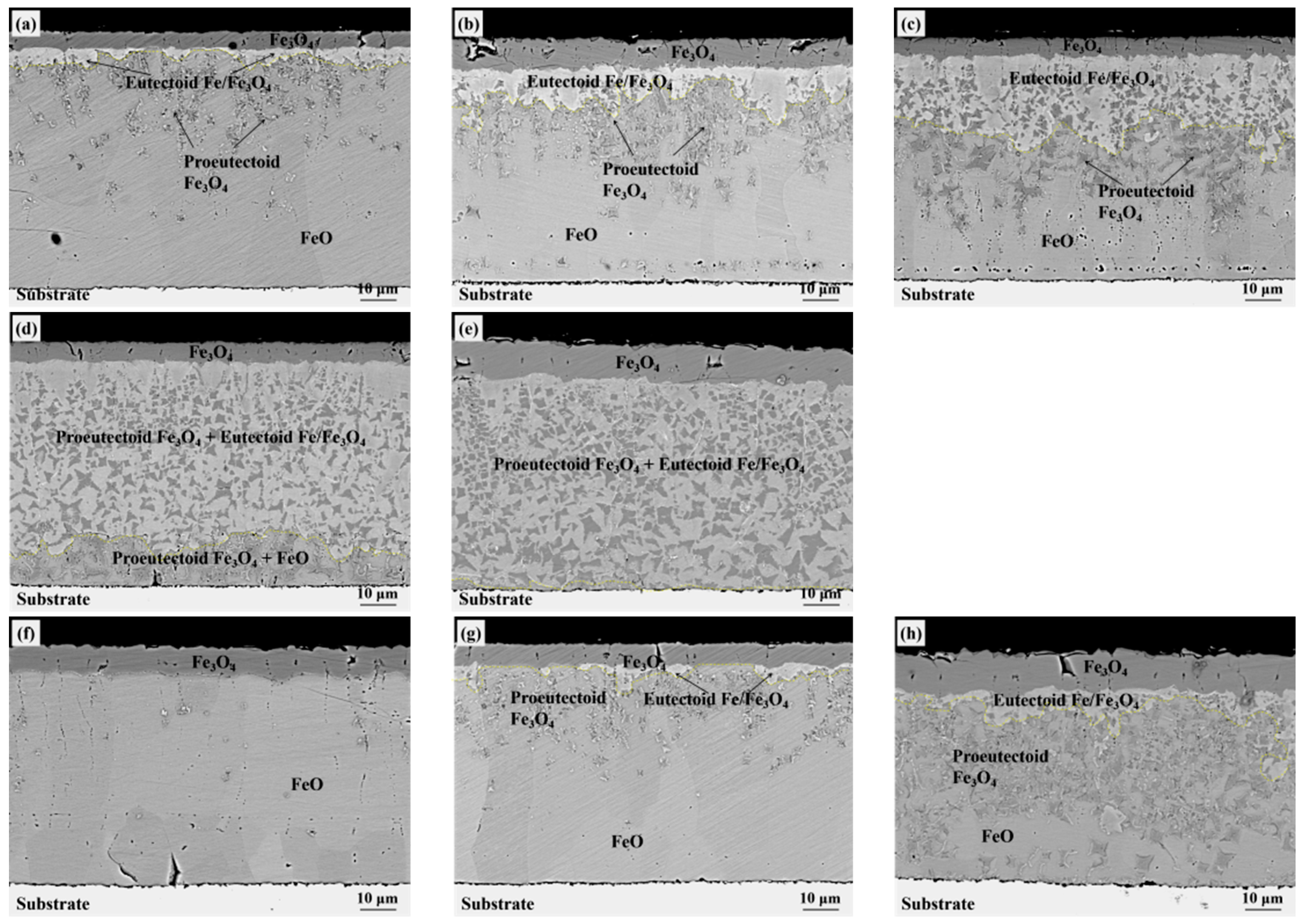
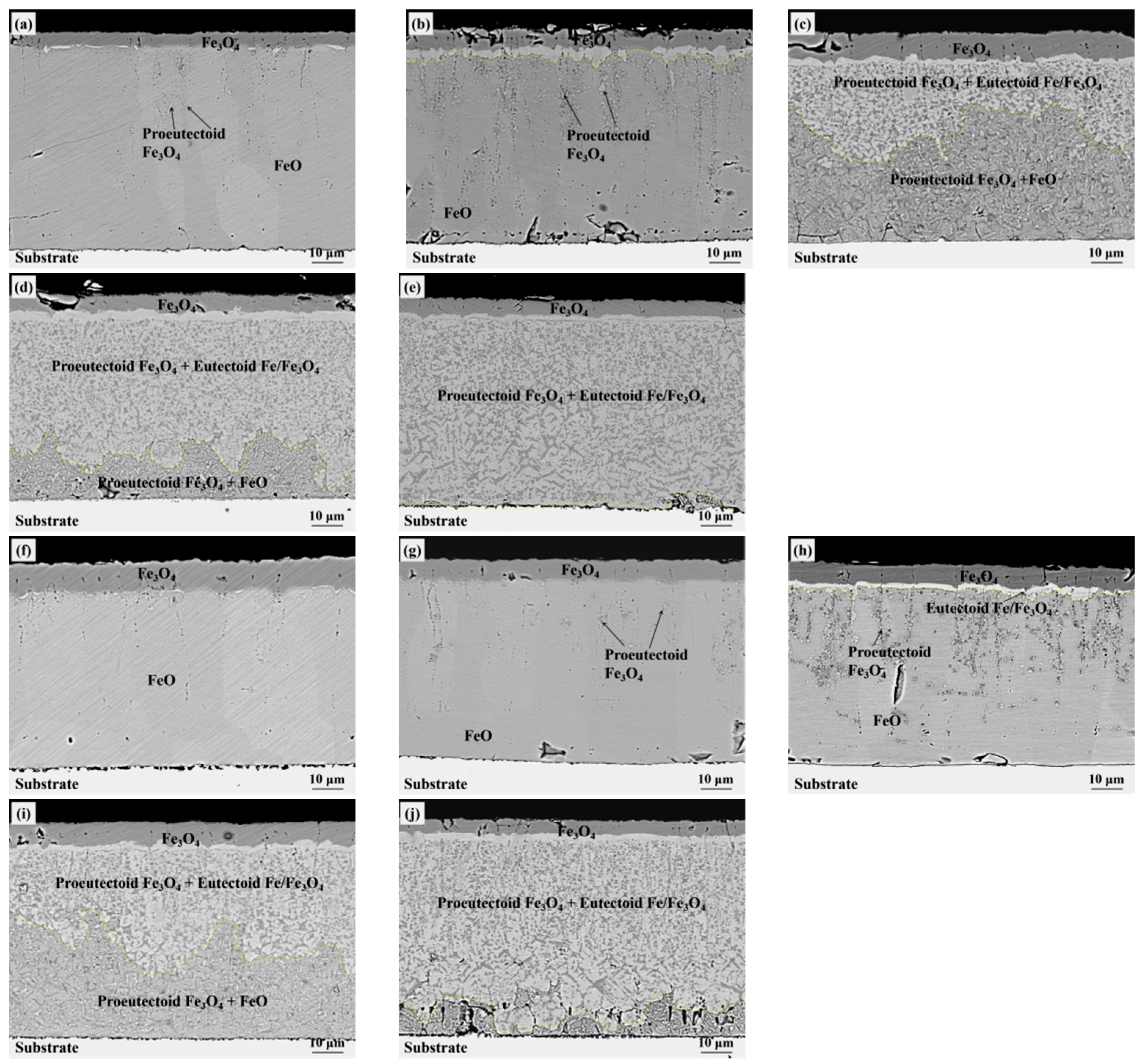
3. Experiment Results
4. Discussion
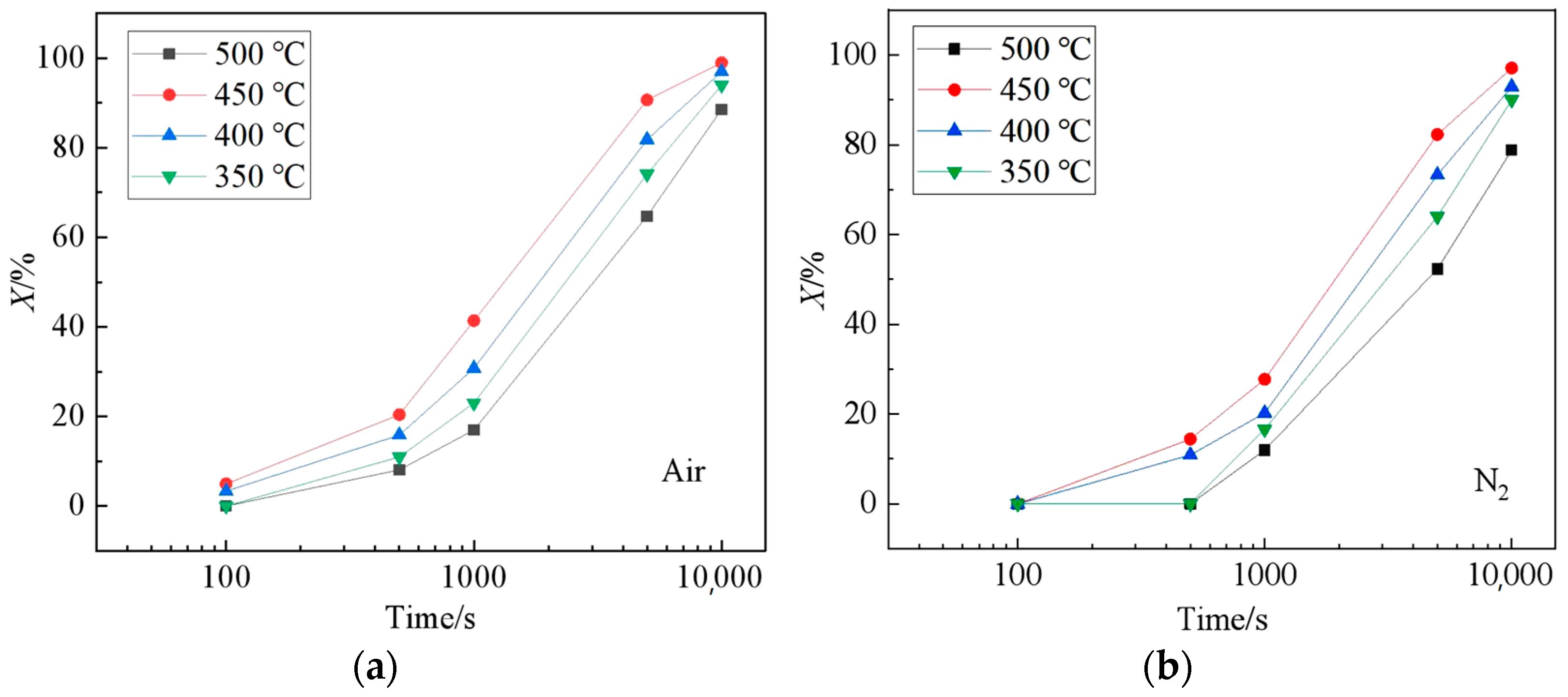
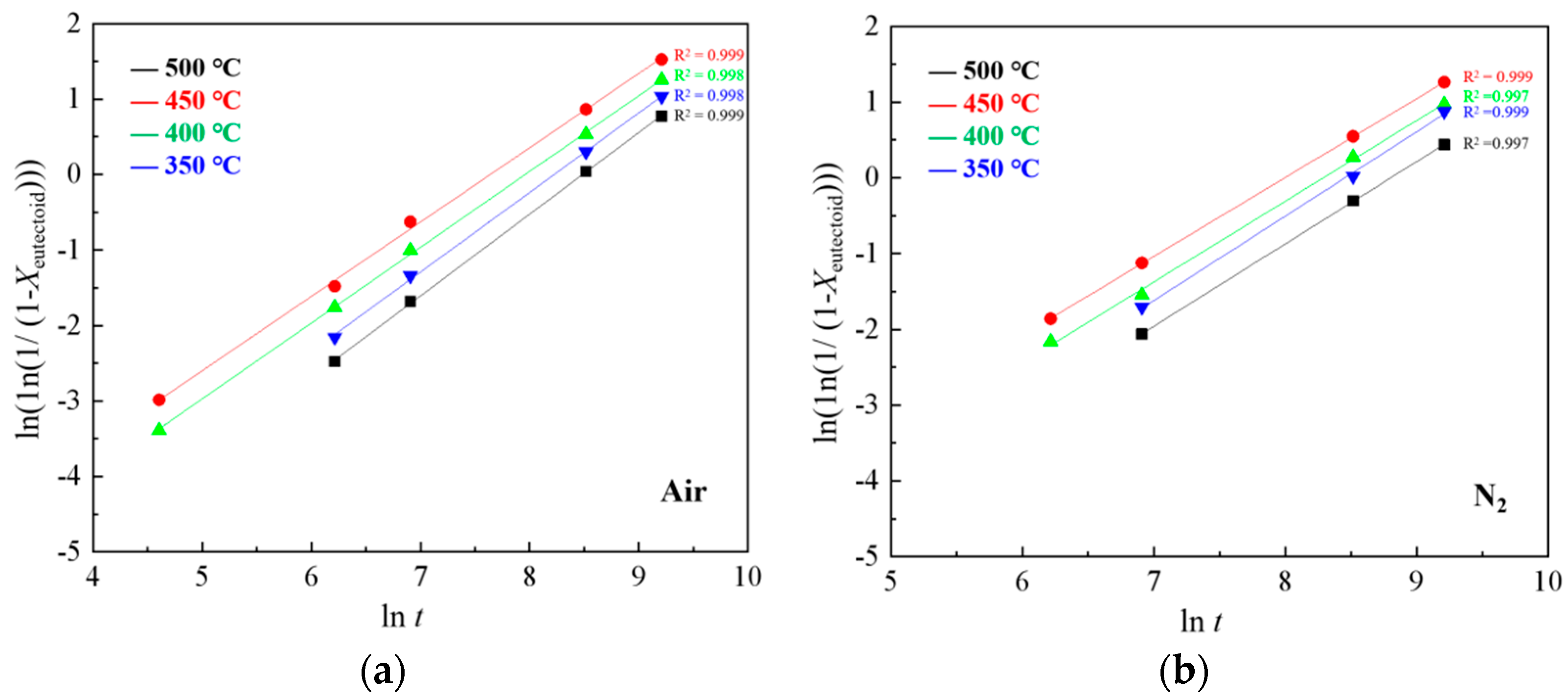
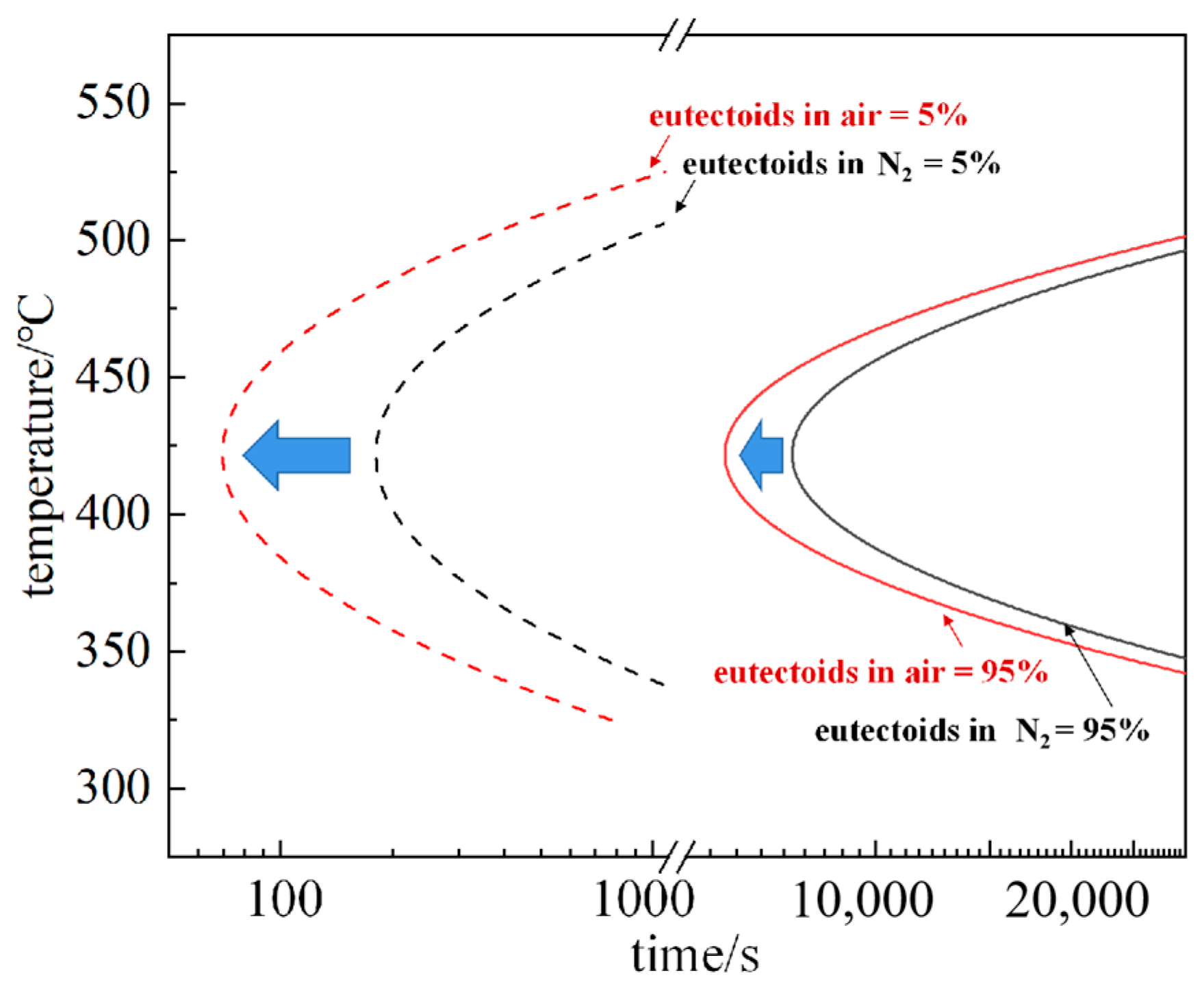
4.1. Eutectoid Transformation Kinetics
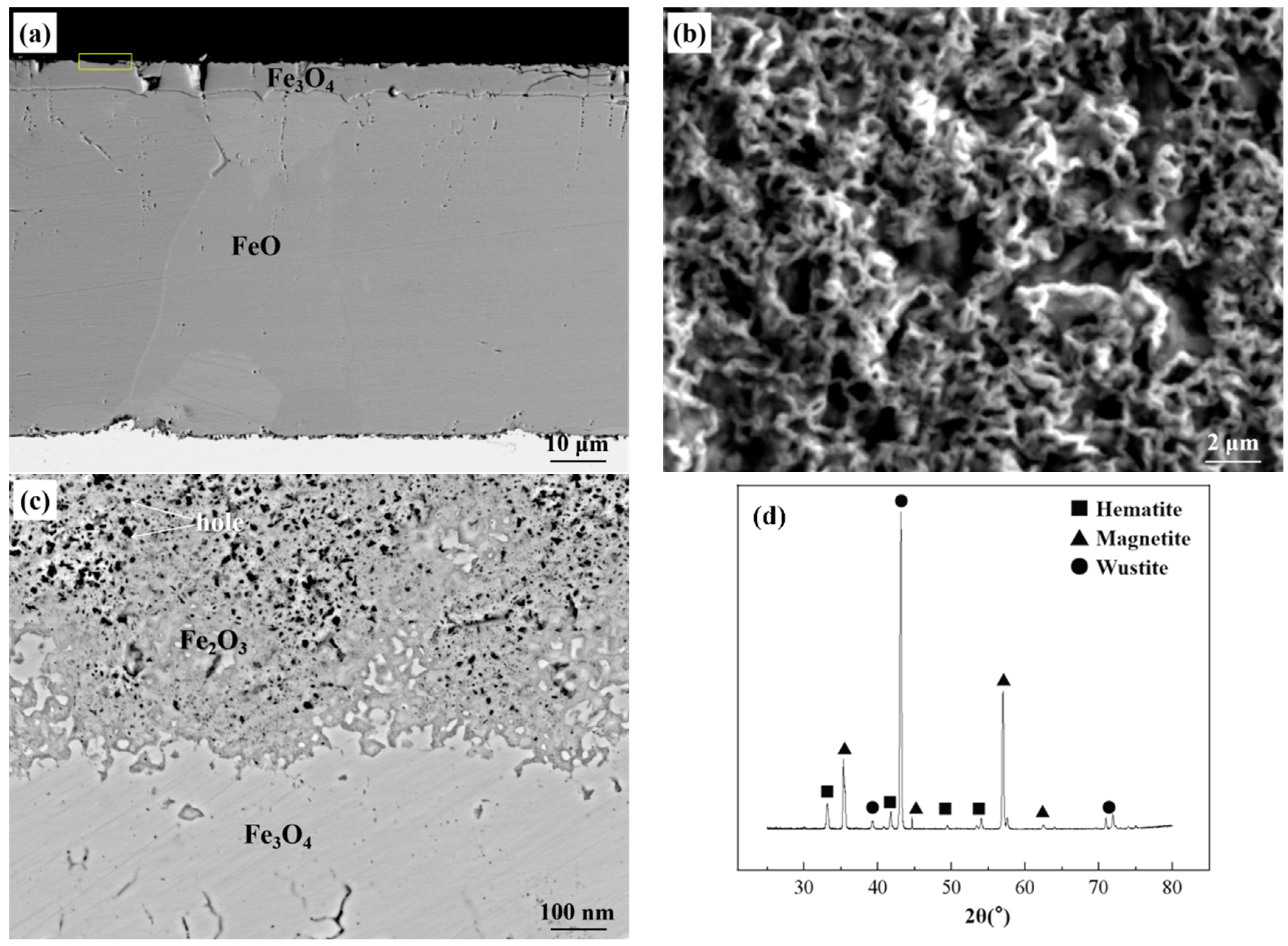
4.2. Oxide after High Temperature Oxidation and Fe3O4 Seam
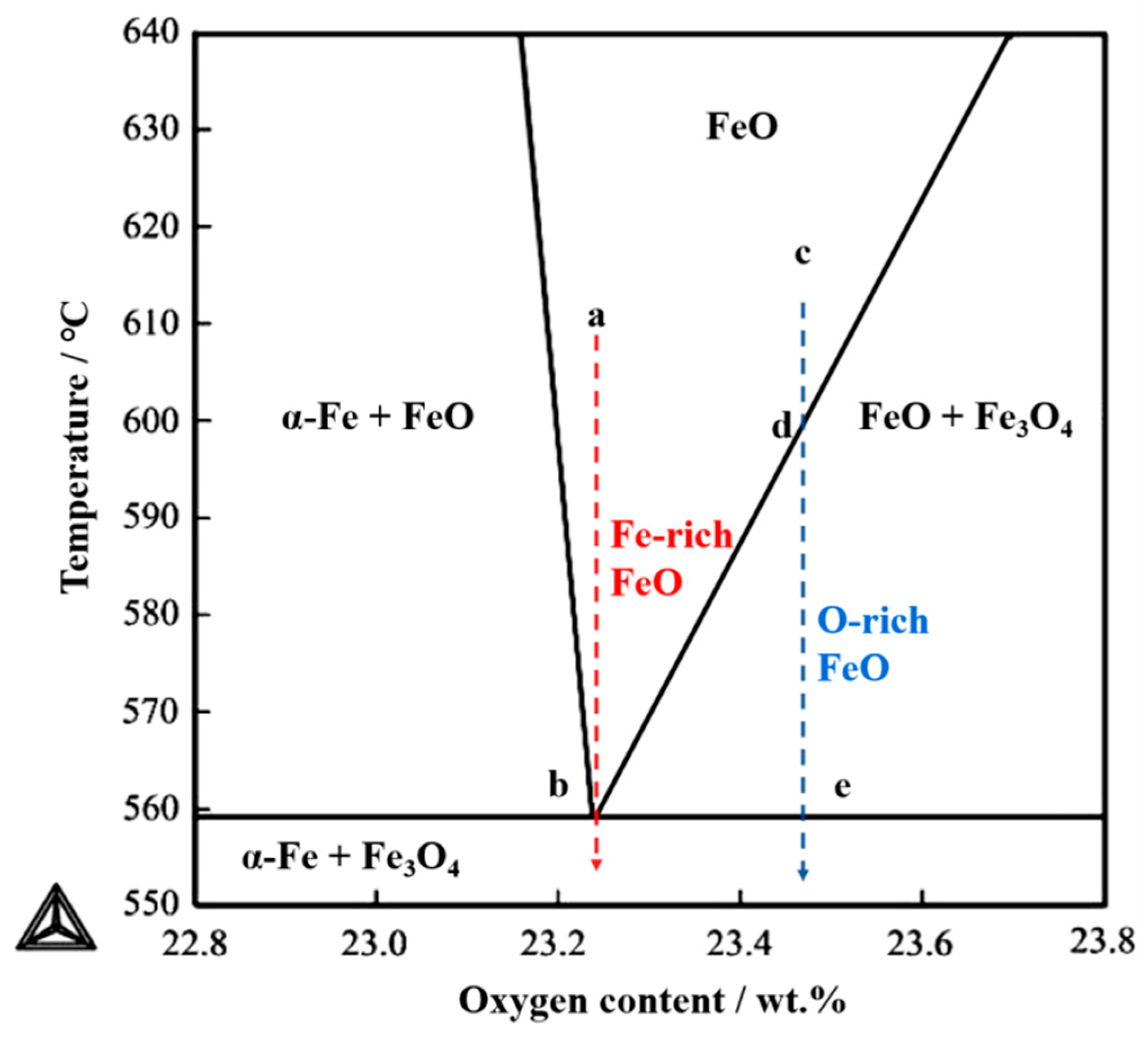
4.3. Eutectoid Transformation
5. Conclusions
- Model of FeO eutectoid transformation is established based on the JMAK equation, and the time of eutectoid structure in air is earlier than that of N2.
- Fe3O4 seams formed at the interface of the FeO-substrate after the eutectoid reaction began, which means they are not a necessary condition of the eutectoid reaction. The eutectoids are more affected by local ion concentration changes in this experiment.
- The isothermal temperature affects the concentration of Fe ions in FeO, which directly determines the nucleation and growth of proeutectoid in FeO.
- In air conditions, there is a high concentration enrichment of Fe ions at the Fe3O4-FeO interface because of the oxygen in the environment, which gives priority to the formation of Fe-rich FeO and makes the eutectoid phase transition time earlier than N2 conditions.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, R.Y.; Yuen, W.Y.D. Oxide-Scale Structures Formed on Commercial Hot-Rolled Steel Strip and Their Formation Mechanisms. Oxid. Met. 2001, 56, 89–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleeson, B.; Hadavi, S.M.M.; Young, D.J. Isothermal transformation behavior of thermally-grown wüstite. Mater. High Temp. 2000, 17, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.N.; Hung, G.C.; Wu, M.T.; Wang, W.L.; Hsieh, K.C.S. Crucial Mechanism to the Eutectoid Transformation of Wüstite Scale on Low Carbon Steel. Steel. Res. Int. 2017, 88, 1700045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.Q.; Jia, T.; Li, Z.F.; Cao, G.M.; Liu, Z.Y.; Li, J. Hot-dip Galvanizing of Carbon Steel after Cold Rolling with Oxide Scale and Hydrogen Descaling. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2014, 21, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.J.; Cao, G.M.; He, Y.Q.; Yang, M.; Liu, Z.Y. Reduction of Oxide Scale with Hydrogen. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2014, 21, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.F.; He, Y.Q.; Cao, G.M.; Tang, J.J.; Zhang, X.J.; Liu, Z.Y. Effects of Al contents on microstructure and properties of hot-dip Zn-Al alloy coatings on hydrogen reduced hot-rolled steel without acid pickling. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2017, 24, 1032–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.Y.; Cao, G.M. Studies on Oxidation Behavior of Steels during Hot Rolling and Development and Application of the Scale Control Techologies; Metallurgical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Young, D.J. High Temperature Oxidation and Corrosion of Metals, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Tanei, H.; Kondo, Y. Effects of Initial Scale Structure on Transformation Behavior of Wüstite. ISIJ Int. 2012, 52, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.F.; Cao, G.M.; Lin, F.; Cui, C.Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, Z.Y. Phase Transformation Behavior of Oxide Scale on Plain Carbon Steel Containing 0.4 wt.% Cr during Continuous Cooling. ISIJ Int. 2018, 58, 2338–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, M.; Kushida, H.; Onishi, T.; Toyama, M.; Koizumi, F.; Fujimoto, S. Influence of Oxidation Temperature and Cr Content on the Adhesion and Microstructure of Scale on Low Cr Steels. Oxid. Met. 2010, 73, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, S.; Yamanouchi, Y.; Hayashi, K.; Hidaka, Y.; Sato, M. Stress measurement in the iron oxide scale formed on pure Fe during isothermal transformation by in situ high-temperature X-ray diffraction. Cor. Sci. 2021, 187, 109482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, S.; Mizumoto, K.; Yoneda, S.; Kondo, Y.; Tanei, H.; Ukai, S. The Mechanism of Phase Transformation in Thermally-Grown FeO Scale Formed on Pure-Fe in Air. Oxid. Met. 2014, 81, 357–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, S.; Yoneda, S.; Kondo, Y.; Tanei, H. Phase Transformation of Thermally Grown FeO Formed on High-Purity Fe at Low Oxygen Potential. Oxid. Met. 2020, 94, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shizukawa, Y.; Hayashi, S.; Yoneda, S.; Kondo, Y.; Tanei, H.; Ukai, S. Mechanism of Magnetite Seam Formation and its Role for FeO Scale Transformation. Oxid. Met. 2016, 86, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoneda, S.; Hayashi, S.; Kondo, Y.; Tanei, H.; Ukai, S. Effect of Mn on Isothermal Transformation of Thermally Grown FeO Scale Formed on Fe–Mn Alloys. Oxid. Met. 2017, 87, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.F.; Cao, G.M.; Lin, F.; Wang, H.; Liu, Z.Y. Characterization of Oxide Scales Formed on Plain Carbon Steels in Dry and Wet Atmospheres and Their Eutectoid Transformation from FeO in Inert Atmosphere. Oxid. Met. 2018, 90, 337–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, W.A.; Mehl, R.F. Reaction kinetics in process of nucleation and growth. Trans. Am. Inst. Min. Metall. Eng. 1939, 135, 416–458. [Google Scholar]
- Avrami, M. Kinetics of phase change I. General theory. J. Chem. Phys. 1939, 7, 1103–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolmogorov, A.N. On the statistical theory of metal crystallization. Bull. Acad. Sci. USSR 1937, 3, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwenk, W.; Rahmel, A. Theoretical considerations on phase boundary reactions and mass transfer during the oxidation of iron. Oxid. Met. 1986, 25, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engell, H.; Eisenhuttenwesen, J. Untersuchungen über Thermodynamik und Zusammensetzung des Wüstits. Arch. Eisenhüttenwesen 1957, 28, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.L.; Jiang, Z.Y.; Zhao, J.W.; Wei, D.B.; Zhou, C.L.; Huang, Q.X. Microstructure and microtexture evolutions of deformed oxide layers on a hot-rolled microalloyed steel. Cor. Sci. 2015, 90, 140–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Temperature /°C | Air | N2 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 °C | 450 °C | 400 °C | 350 °C | 500 °C | 450 °C | 400 °C | 350 °C | |
| n | 1.08 | 1.00 | 1.01 | 1.05 | 1.08 | 1.04 | 1.06 | 1.11 |
| ln k | −9.18 | −7.69 | −7.79 | −8.87 | −9.98 | −8.50 | −8.65 | −9.68 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Cao, G.; Li, S.; Zhao, W.; Liu, Z. Eutectoid Transformation Kinetics of FeO under N2 and Air Atmospheres. Metals 2023, 13, 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13020220
Wang H, Cao G, Li S, Zhao W, Liu Z. Eutectoid Transformation Kinetics of FeO under N2 and Air Atmospheres. Metals. 2023; 13(2):220. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13020220
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Hao, Guangming Cao, Silin Li, Wencong Zhao, and Zhenyu Liu. 2023. "Eutectoid Transformation Kinetics of FeO under N2 and Air Atmospheres" Metals 13, no. 2: 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13020220
APA StyleWang, H., Cao, G., Li, S., Zhao, W., & Liu, Z. (2023). Eutectoid Transformation Kinetics of FeO under N2 and Air Atmospheres. Metals, 13(2), 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13020220








