Abstract
The effect of carbon content in the base metals of high-strength steel on the microstructure and impact toughness of simulated welding focusing on a coarse-grained heat-affected zone (CGHAZ) at different heat inputs was systematically investigated by using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and electron back-scattering diffraction (EBSD). The Charpy impact test confirmed that there was an optimal heat input, which caused the CGHAZ to obtain the highest impact toughness. The optimal heat input is ~20 kJ/cm and remains unchanged with an increase in carbon content from 0.04 to 0.12 wt.%. However, the impact toughness of the CGHAZ decreases with the increase in carbon content at each heat input. Microstructure characterization showed that a CGHAZ with 0.04 wt.% carbon gradually changed from lath bainite (LB) to granular bainite (GB) with an increase in heat input, while it changed from lath martensite (LM) to LB and then to GB for a CGHAZ with 0.12 wt.% carbon. Although the density of high-angle grain boundaries (HAGBs) obtained at 20 kJ/cm in the high-carbon sample is higher than that of the low-carbon sample, its impact toughness is lower, which is related to the parallel structure of the lath bundles and the morphology the austenite penetration.
1. Introduction
As a strengthening element, carbon is essential for the development of high-strength steel. It is advantageous in terms of cost reduction and availability when compared to other alloying elements. If the weldability permits, it should be employed as much as possible. For heavy steel plate, carbon can improve the hardenability by optimizing the variant selection to increase the density of high-angle grain boundaries (HAGBs, misorientation angle ≥ 45°) and, thus, increase the central hardness and toughness of the steel plate [1,2]. This is because it is difficult to increase the cooling rate in the center of heavy steel plate, but the hardenability of the center can be improved by increasing the carbon content. Moreover, another study [3] also indicated that increasing the carbon content would lower the martensite start temperature and driving force for martensitic transformation and increase the strength of the austenite matrix, which in turn contributes to producing more V1/V2 variant pairs to accommodate the transformation strain and enhance the impact toughness. However, it is generally believed that the increase in carbon content reduces the weldability of steel plate and increases the probability of brittle crack formation after welding, because high carbon content easily promotes the formation of martensite [4]. This requires either appropriate heat treatment to improve the transformation structure and proportion, or refinement of the transformation structure and improvement of its comprehensive properties by refining the austenite grain size, increasing deformation or adjusting the cooling rate [5,6,7]. While some studies [8] have shown that microstructure and properties of the heat-affected zone (HAZ) being welded can be improved by properly increasing the carbon content of the base metal, a small increase in the amount of carbon can increase twin-related variant pairs and the density of HAGBs, thus causing the coarse-grained heat-affected zone (CGHAZ) to obtain higher fracture toughness. Therefore, it seems that adjusting carbon content can ensure better comprehensive properties of base metals and welded zones simultaneously.
However, most investigations of the carbon effect on the transformation structure mainly focus on the single phase of martensite or bainite [1,8], and a large range of carbon content variation has not been systematically studied, especially regarding the influence of carbon content in the base metal on the structure and properties of the subsequent welding HAZ. In this study, high-strength steel with different carbon content (0.04 to 0.12 wt.%) was designed and welding simulation experiments of CGHAZs were carried out under different heat input conditions (10 to 50 kJ/cm). The aim is to investigate the influence of carbon content in the base metal on the microstructure and impact toughness of CGHAZs. The optimal matching conditions were found by adjusting carbon content and matching the welding process. Previous studies [9,10,11] have shown that the welding heat input determines the microstructure and properties of the CGHAZ, and the carbon content of the base metal has a similar effect. However, the matching effect of the two factors has not been systematically studied. In this study, the visualization and quantification of microstructure from crystallography, combined with the visualization of brittle crack propagation paths, is used to clarify the coupling effect of composition and process parameters on the low-temperature impact toughness of CGHAZ and, thus, guides future innovation towards a synergy between strength and toughness before and after welding in high-strength steel.
2. Materials and Methods
Three kinds of high-strength steels with different carbon content in wt.% (referred to as 0.04C, 0.08C and 0.12C steel) and with yield strengths of 853, 1022 and 1052 MPa, respectively, were used in this study. This kind of high-strength steel is mainly used in architectural structures and offshore engineering [3]. The chemical compositions are shown in Table 1, together with the carbon equivalent (Ceq). The chemical composition of the three steels is consistent in design, except for the change in carbon content. However, due to actual smelting and other reasons, other elements such as Mn and Si have slight changes, but this did not affect the impact toughness of carbon as the main influencing factor to determine the phase transformation in CGHAZs. In order to study the influence of carbon content on the microstructure and impact toughness of CGHAZ, thermal simulation experiments under different heat inputs (10, 14, 20, 30 and 50 kJ/cm) were performed on a Gleeble-3500 with an average heating rate of 130 °C/s and a peak temperature of 1350 °C. After thermal simulation, standard impact specimens with the size of 10 mm × 10 mm × 55 mm were prepared to evaluate Charpy V-Notch (CVN) impact toughness at −20 °C.

Table 1.
Chemical composition of high-strength steels (wt.%).
Thermal simulated samples were cut from the heat treatment region and then were mounted, mechanically polished and etched with 4% nital for scanning electron microscopy (SEM, TESCAN, Brno, Czech Republic) observation firstly. Fracture surfaces of the samples after Charpy impact tests were also characterized by SEM. To obtain the crystallographic information of transformation structure, electron back-scattering diffraction (EBSD, Oxford Instruments, Oxford, UK) analysis was carried out after mechanical and electrolytic polishing using TESCAN CLARA field emission SEM at an acceleration voltage of 20 kV, with a step size of 0.16 μm. HKL Channel 5 software and programs developed by MATLAB software (version 2021, MathWorks, Natick, MA, United States)were employed to achieve an analysis of visualization and digitization of crystallographic features. Meanwhile, the correlation between crystallographic structure and crack propagation behavior in simulated CGHAZs was analyzed by using EBSD, aiming to reveal the difference in impact toughness obtained under different conditions from the aspects of crack propagation and microstructure transformation mechanisms.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Impact Toughness and Fractographs
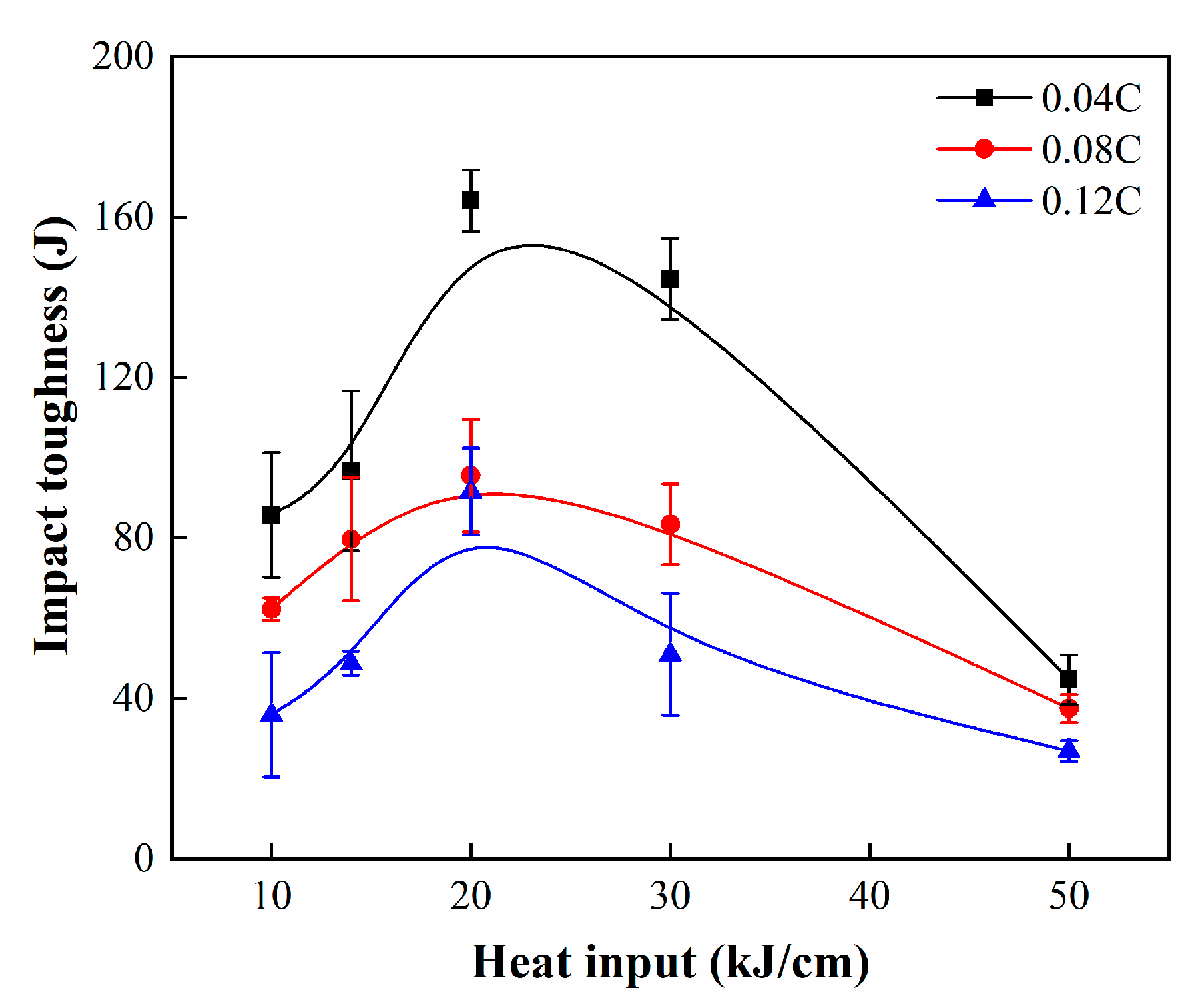
Figure 1 displays the variation in impact toughness of simulated CGHAZs with an increase in heat input from 10 to 50 kJ/cm. It can be clearly seen that the impact toughness of high-carbon samples is lower than that of low-carbon samples under various heat input conditions. The average impact toughness of the 0.08C sample is between those of the 0.04C and 0.12C samples. Moreover, it can be seen that the impact toughness of the CGHAZ with three kinds of carbon content first increases and then decreases with an increase in heat input, and the peak value mainly appears near the heat input of 20 kJ/cm. This is inconsistent with our expectation that the peak of impact toughness of high-carbon CGHAZs should correlate with high heat input. This indicates that within the range of carbon content variation in this study, the optimal welding process windows of the three studied steels are basically the same, i.e., 20 kJ/cm. It is difficult to obtain high impact toughness when the heat input is too high or too low. This can also be confirmed by the observation of impact fracture morphology, as shown in Figure 2.
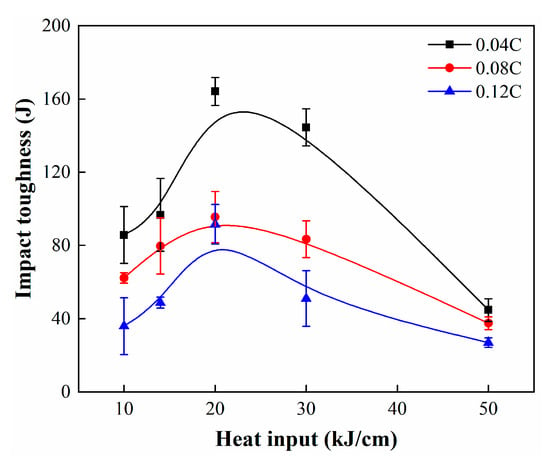
Figure 1.
Charpy impact toughness of the simulated samples.

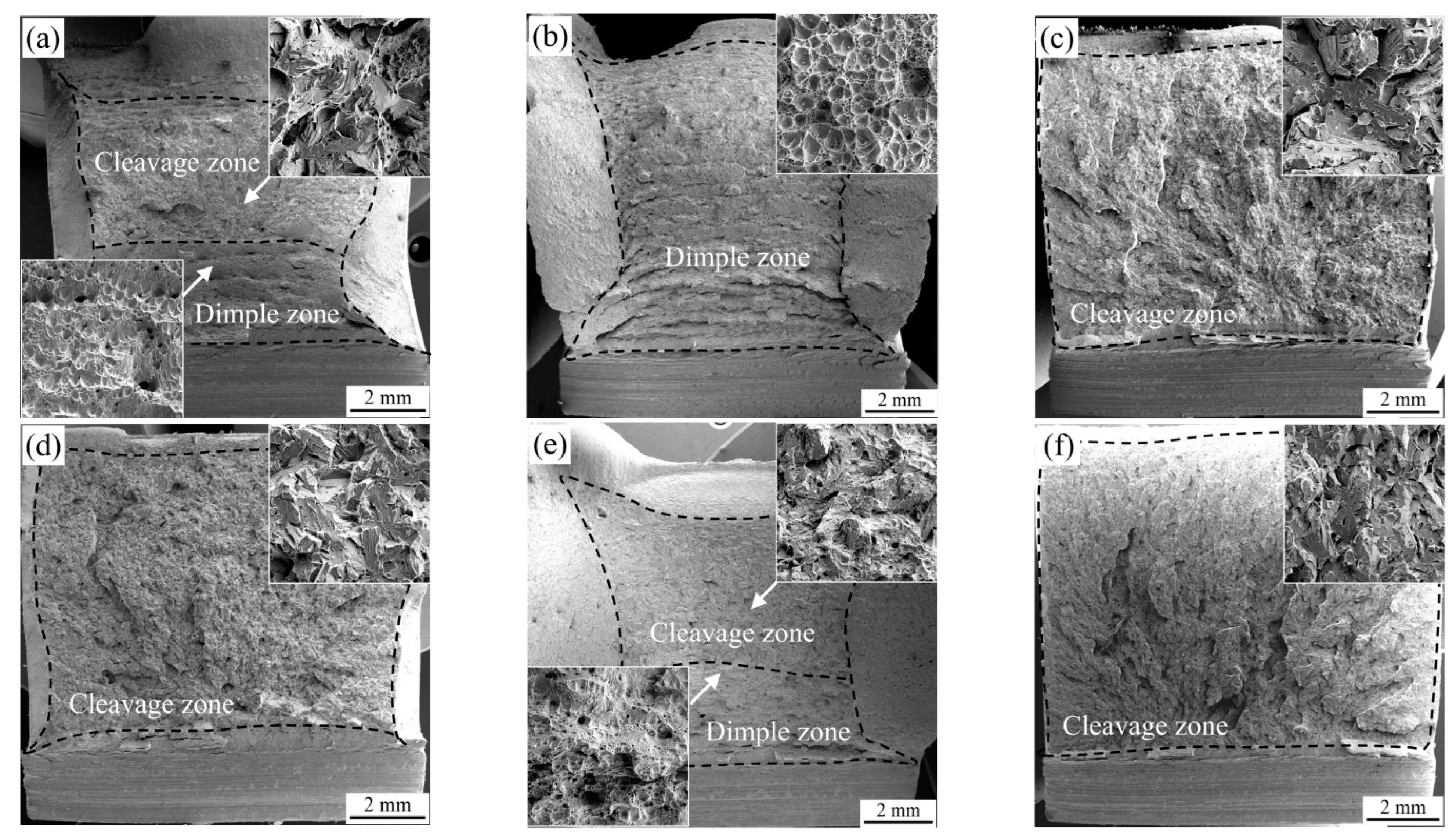
Figure 2.
SEM micrographs showing the fracture surface after Charpy impact tests for the simulated samples with 0.04 wt.% C (a–c) and 0.12 wt.% C (d–f) under the different heat inputs: (a,d) 10 kJ/cm, (b,e) 20 kJ/cm and (e,f) 50 kJ/cm.
Figure 2 shows SEM images of the typical fracture surfaces obtained at heat inputs of 10, 20 and 50 kJ/cm in 0.04C and 0.12C simulated samples. For the 0.04C sample, the fracture surface contains ductile and brittle manners, i.e., dimple and cleavage patterns under the heat input of 10 kJ/cm (Figure 2a). With an increase in heat input to 20 kJ/cm, the fracture surface is occupied entirely by a dimple pattern (Figure 2b). However, when the heat input further increases to 50 kJ/cm, the fracture surface presents complete cleavage morphology (Figure 2c). For the 0.12C sample, the fracture surface obtained at the heat input of 10 and 50 kJ/cm is dominated by cleavage fractures, while under the heat input of 20 kJ/cm, the fracture surface features the coexistence of dimple and cleavage features. The fracture morphology of the 0.12C sample at 20 kJ/cm is similar to that of the 0.04C sample at 10 kJ/cm, so the impact toughness of both samples is basically the same. This is consistent with the impact toughness results shown in Figure 1, which is discussed in the viewpoint of microstructure evolution in further sections.
3.2. Microstructure Evolution
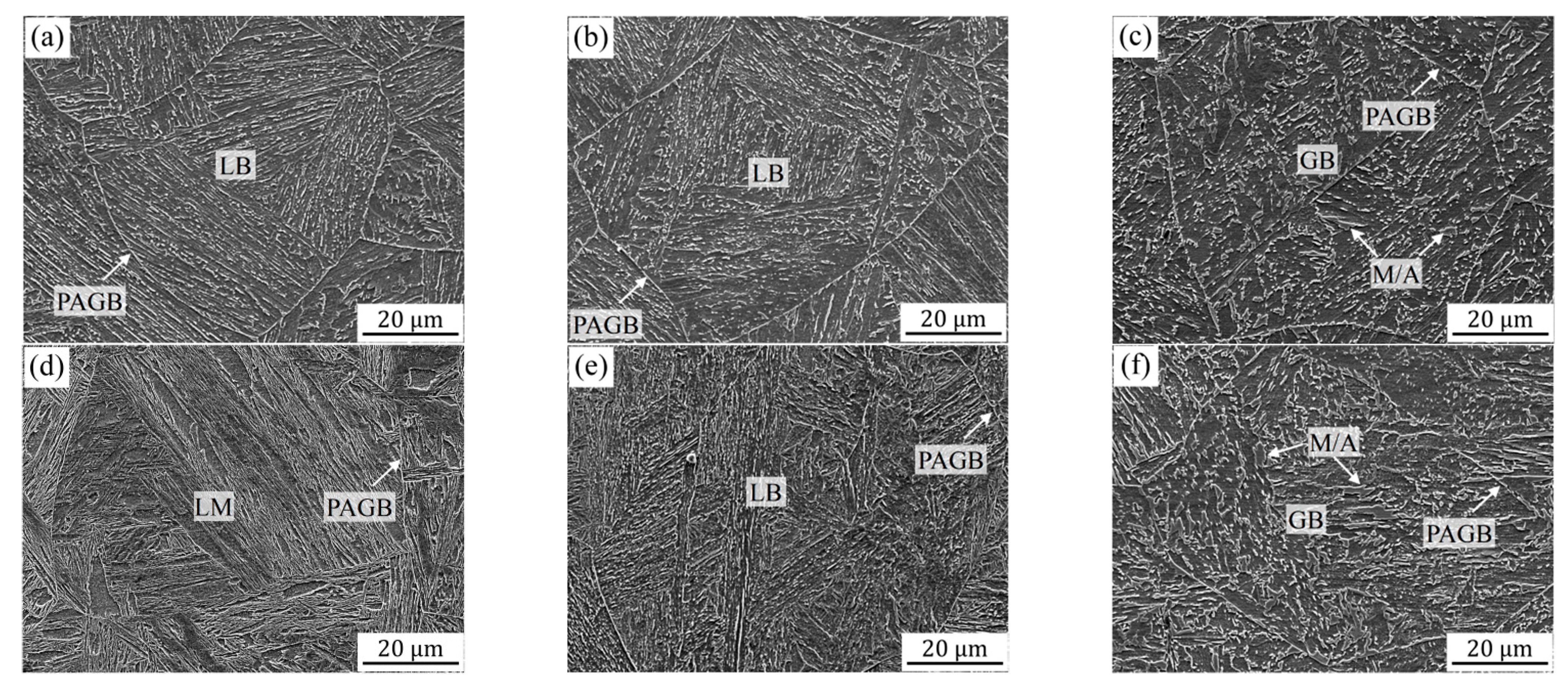
Shown in Figure 3 are the typical microstructures of the simulated CGHAZs with carbon contents of 0.04 and 0.12 wt.%, which display the characteristics of martensitic and bainitic structures, i.e., lath martensite (LM), lath bainite (LB) and granular bainite (GB). Based on the observation of microstructure, it is found that the microstructure of the 0.08C sample is similar to those of 0.04C and 0.12C samples under various heat input conditions. This study focuses on the analysis of these two groups of samples. It can be seen that the microstructures of the 0.04C sample changes from LB to GB with an increase in heat input from 10 to 50 kJ/cm. Although LB can be obtained at the heat input of 10 and 20 kJ/cm, the lower heat input induces a higher cooling rate and a decrease in the bainite transformation temperature [11]. From a comparison of Figure 3a,b, it can be found that the lath bundles obtained under the lower heat input have a parallel structure and the coarse packet structure penetrates the entire austenite grain. However, the bainite obtained at 20 kJ/cm shows an approximate staggered arrangement. The above difference should be the main reason for the variation in impact toughness, which also produces better evidence regarding the crystallographic structure. However, at the lowest heat input, the microstructure obtained in the 0.12C sample is mainly composed of LM (Figure 3d). Furthermore, with the increase in heat input, the microstructure gradually changes into LB and GB, in which fine carbides and coarse martensite/austenite (M/A) constituents can be clearly seen, respectively (Figure 3e,f). Many previous studies [12,13,14] have confirmed that it is difficult to obtain high impact toughness in GB structures with coarse M/A, which is also the essential reason for the lower impact energy obtained at the heat input of 50 kJ/cm.
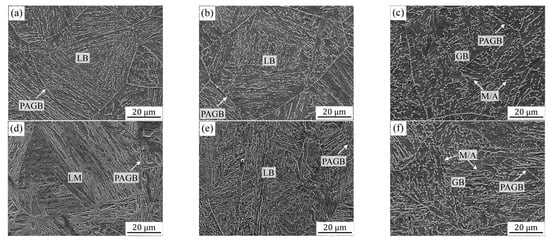
Figure 3.
SEM images showing the microstructure of the simulated samples with 0.04 wt.% C (a–c) and 0.12 wt.% C (d–f) under the different heat inputs: (a,d) 10 kJ/cm, (b,e) 20 kJ/cm and (e,f) 50 kJ/cm. (PAGB: prior austenite grain boundary).
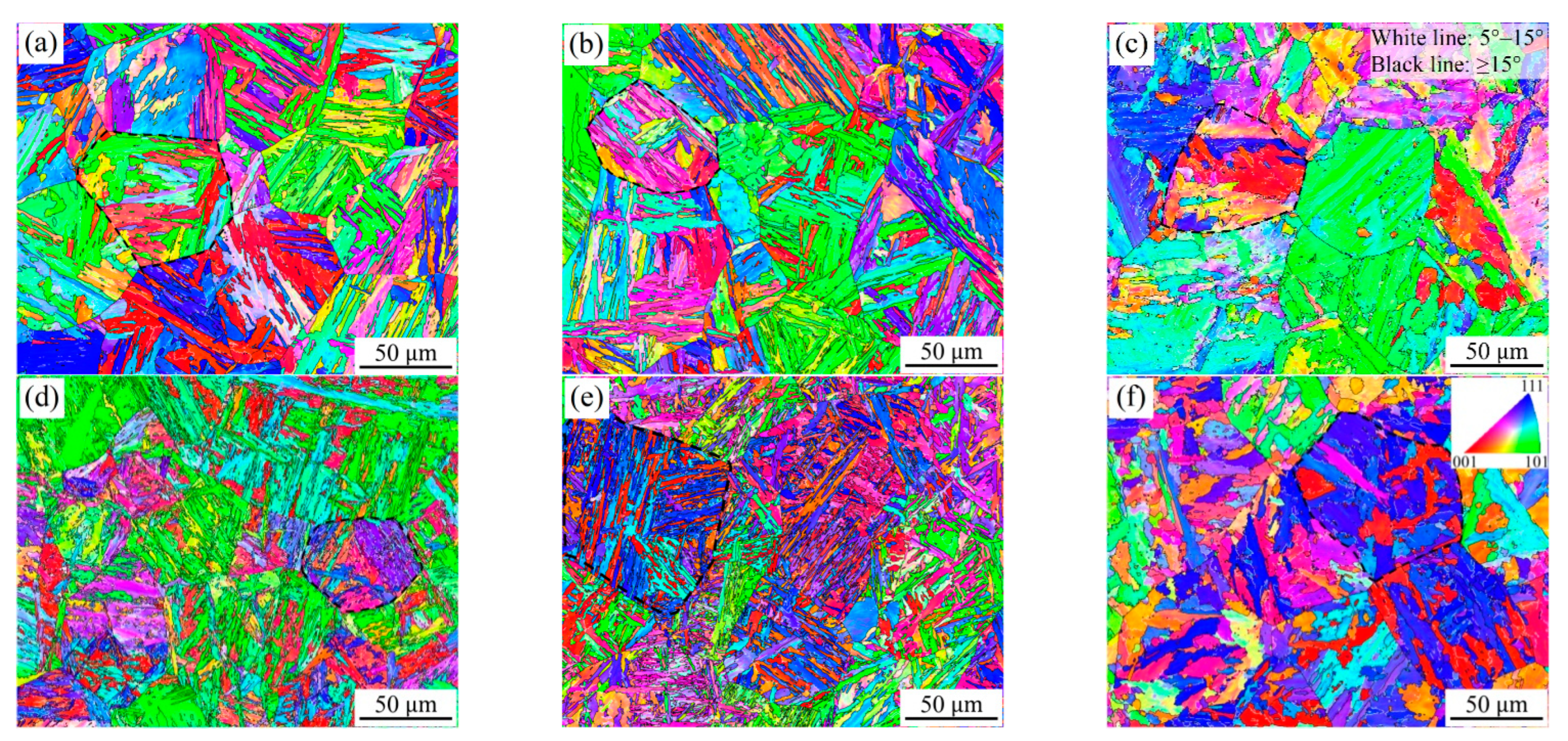
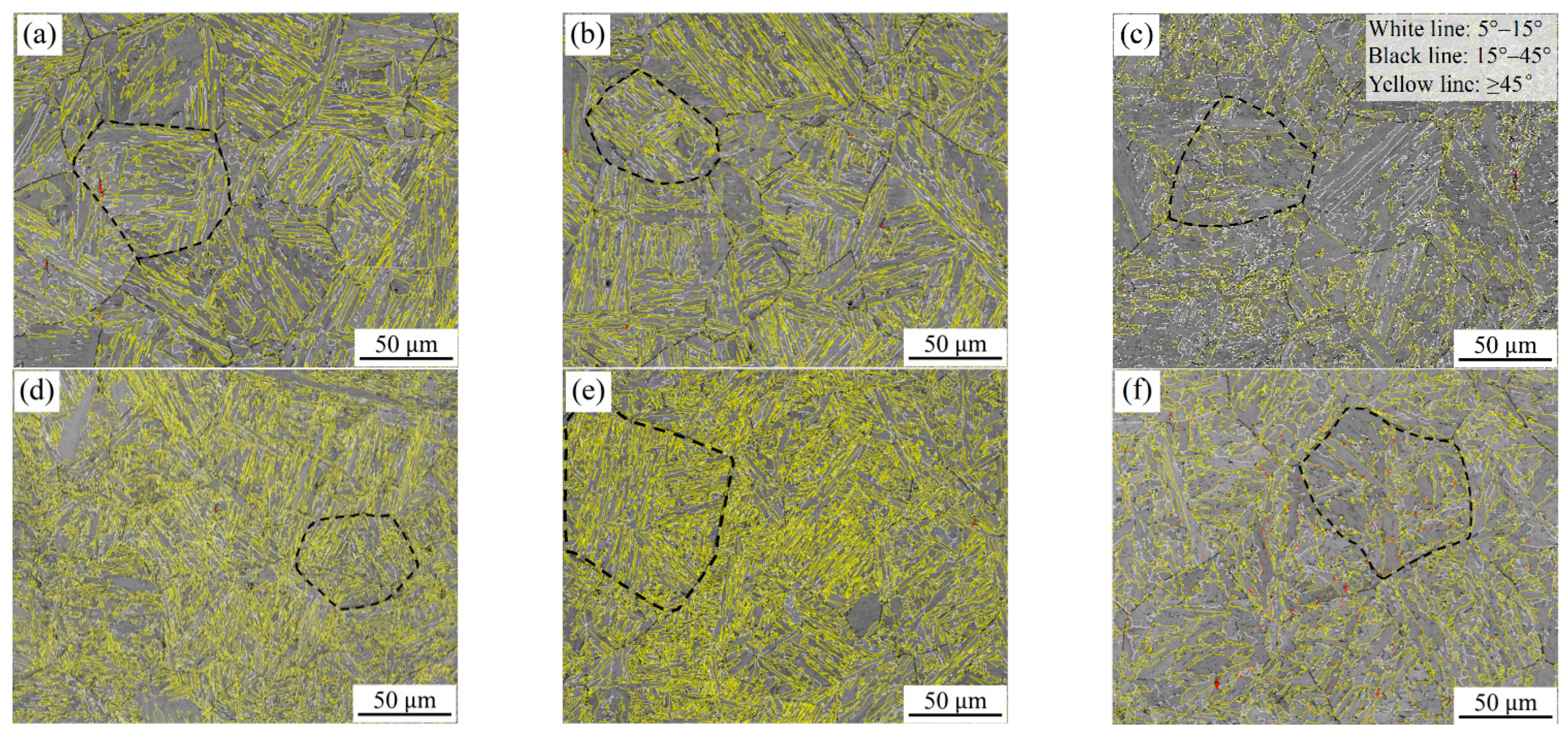
In order to further analyze the microstructure differences under different conditions from the perspective of crystallography, inverse pole figures (IPF) and grain boundary distribution maps are shown in Figure 4 and Figure 5, respectively. It can be found that the microstructures obtained at the heat input of 20 kJ/cm have a high HAGB density, and the corresponding crystallographic structures are also finer. On the contrary, if the heat input is too high or too low, the density of HAGBs decreases, especially for high heat inputs. Of course, it is also found that the increase in carbon content is helpful for improving the density of HAGBs. A previous study [15] indicated that the misorientation of the high-angle boundary able to arrest brittle cracks is mainly above 45° and always shows specific misorientation in the same prior austenite grain. However, the high-carbon samples in this study have high HAGB density, but their impact toughness is lower than that of the low-carbon samples. Therefore, further discussion is needed regarding the aspect of phase transformation mechanisms, because the impact toughness is not only determined by the grain boundary density, but is also related to the arrangement of variants [13]. Ghosh et al. [16] confirmed that the crack path is related to the crystallographic misorientation between the neighboring grains when brittle cracks go through boundaries. In some particular cases, HAGBs seem unable to deflect or arrest the crack propagation.

Figure 4.
Inverse pole figures (IPF) showing the microstructure of the simulated samples with 0.04 wt.% C (a–c) and 0.12 wt.% C (d–f) under the different heat inputs: (a,d) 10 kJ/cm, (b,e) 20 kJ/cm and (e,f) 50 kJ/cm.
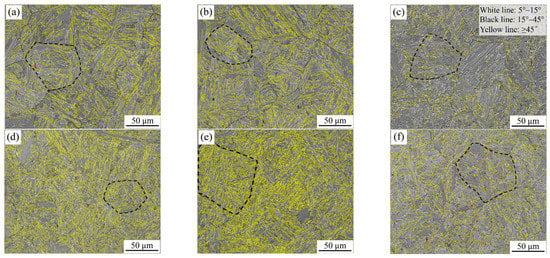
Figure 5.
Boundary distributions of the simulated samples with 0.04 wt.% C (a–c) and 0.12 wt.% C (d–f) under the different heat inputs: (a,d) 10 kJ/cm, (b,e) 20 kJ/cm and (e,f) 50 kJ/cm.
3.3. Phase Transformation Mechanism and Correlation with Impact Toughness
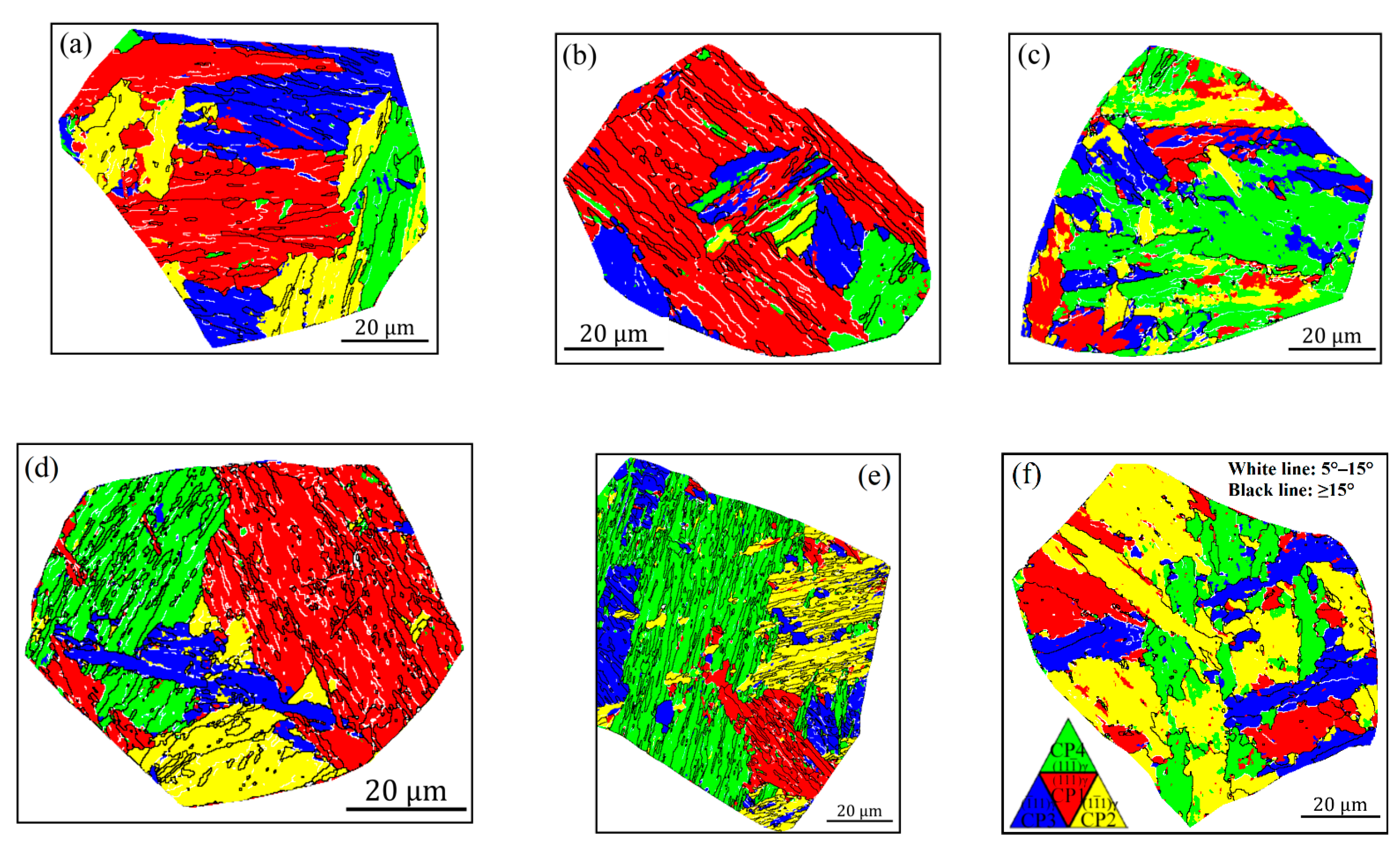
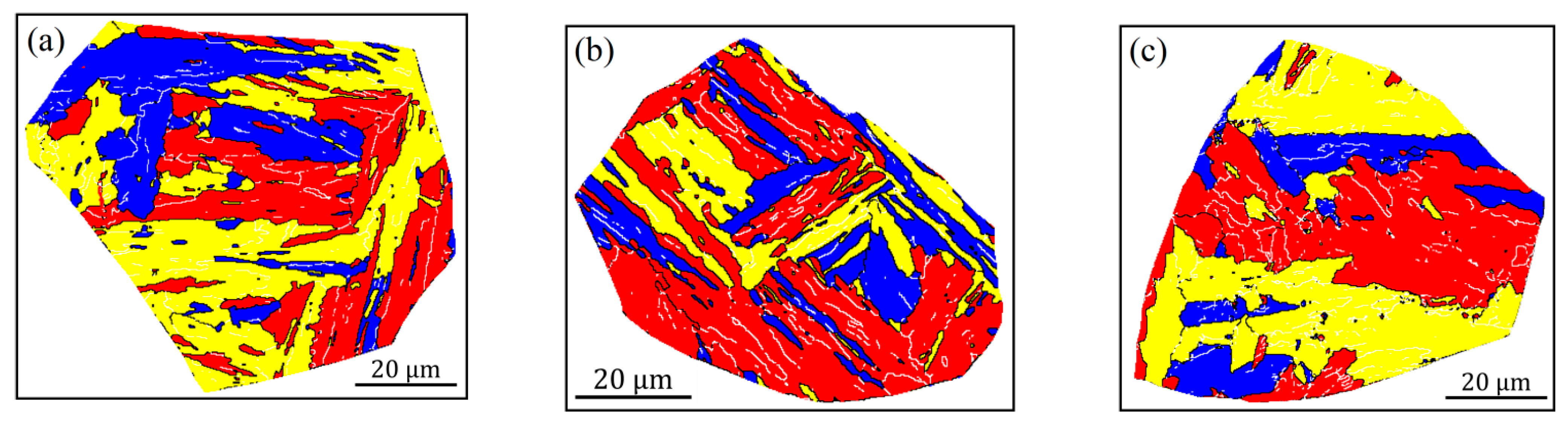
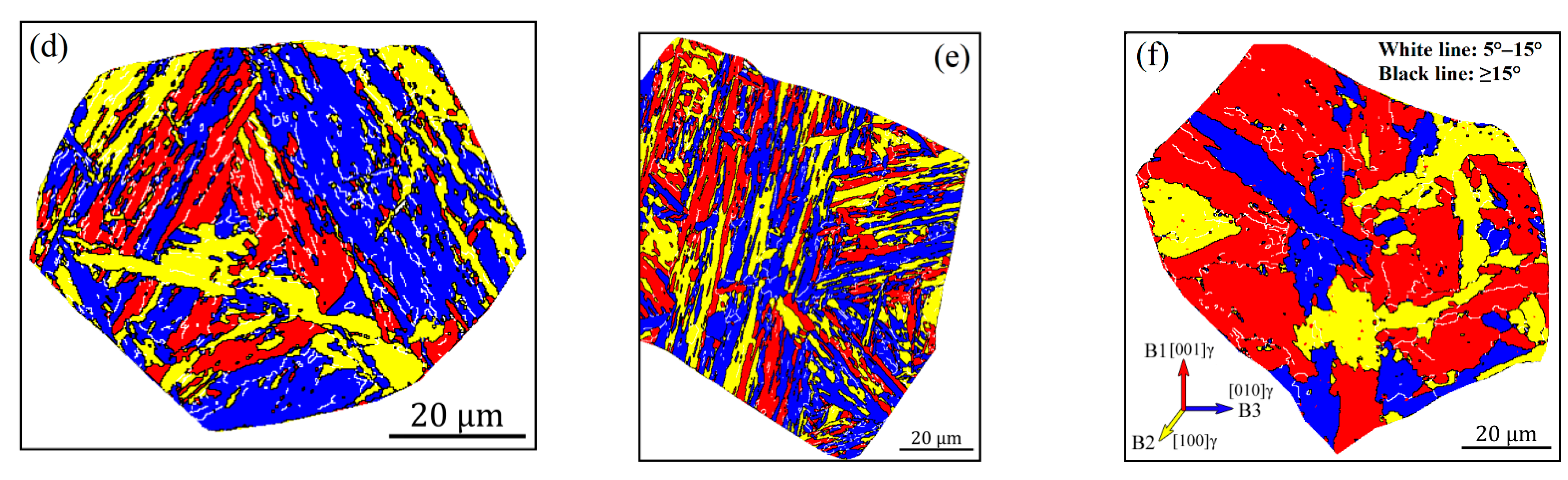
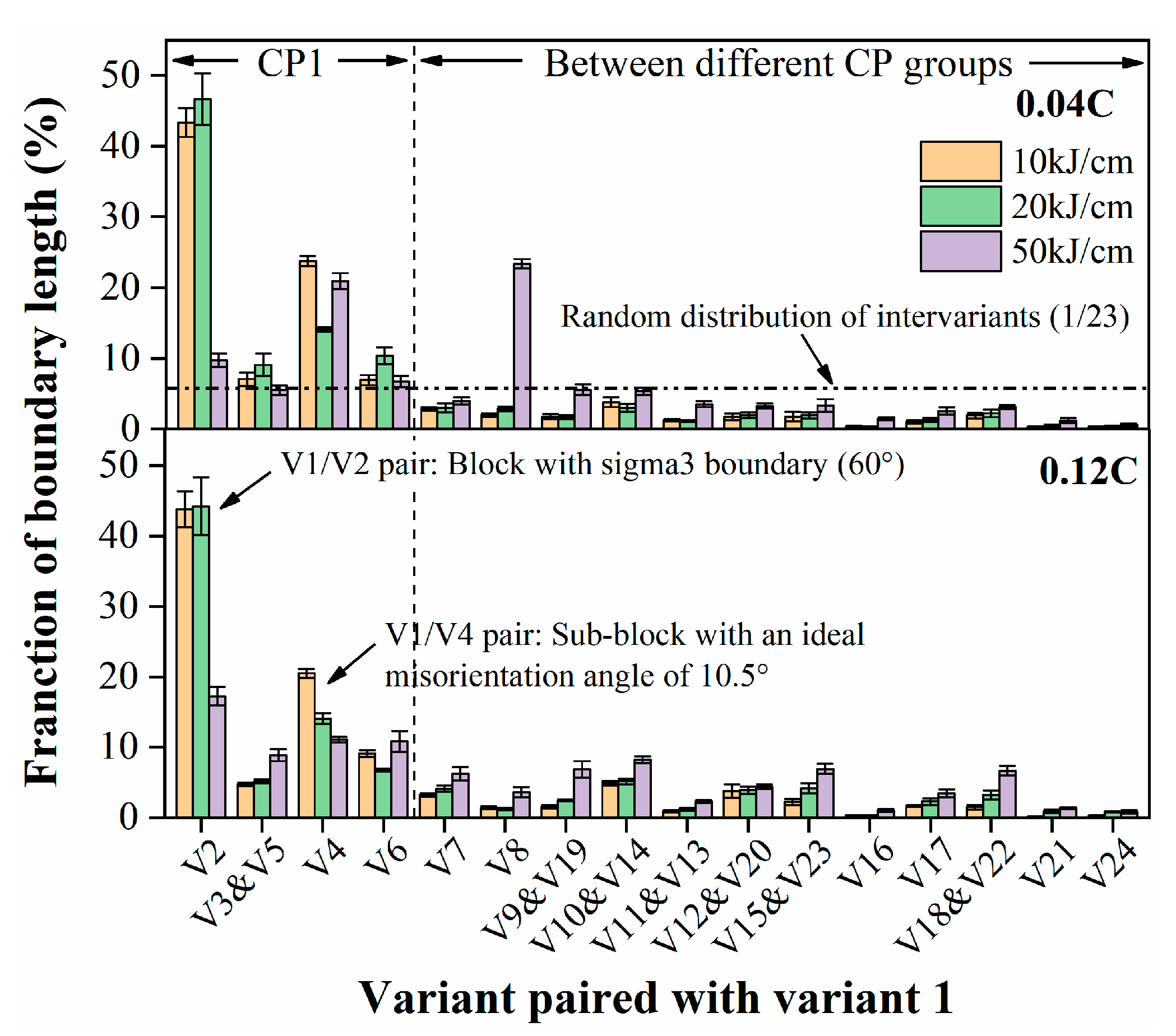
To display the effects of carbon content and heat input on the crystallographic structure more clearly, the crystallographic packet and Bain zone on representative grains marked in Figure 4 and Figure 5 are visualized in Figure 6 and Figure 7, by highlighting with four (red, yellow, blue and green) and three (red, yellow and blue) colors, which correspond to four CP groups (close-packed groups, CP1–CP4) and three Bain groups (B1–B3), respectively. Moreover, the corresponding results from quantitative calculation of the length fraction of intervariant boundaries between V1 and the other variants in each sample are shown in Figure 8. It can be seen from the packet map (Figure 6) that the regular packets interactively split the entire austenite grains for LM and LB structures, while for GB structures, the packets present serrated morphology, reflecting the characteristics of high-temperature transformation products. Compared with the Bain group map (Figure 7), it is also found that different Bain groups in a packet of LM or LB structures are arranged interactively, while the dominant coarse Bain group is formed in GB structures, resulting in a significant reduction in the density of HAGBs. This can also be seen from the quantization result in Figure 8.

Figure 6.
Reconstructed crystallographic packets of the simulated samples with 0.04 wt.% C (a–c) and 0.12 wt.% C (d–f) under the different heat inputs: (a,d) 10 kJ/cm, (b,e) 20 kJ/cm and (e,f) 50 kJ/cm.
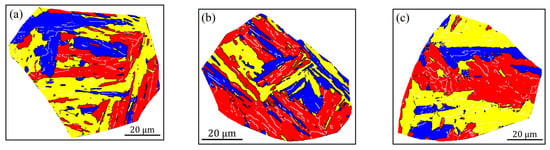
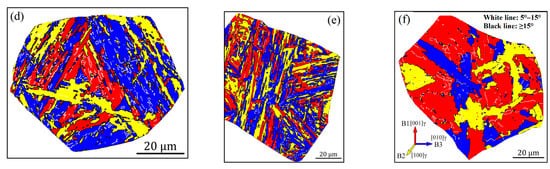
Figure 7.
Reconstructed crystallographic Bain groups of the simulated samples with 0.04 wt.% C (a–c) and 0.12 wt.% C (d–f) under the different heat inputs: (a,d) 10 kJ/cm, (b,e) 20 kJ/cm and (e,f) 50 kJ/cm.

Figure 8.
Average length fraction of intervariant boundaries between V1 and other variants in simulated samples with 0.04 wt.% C and 0.12 wt.% C under the different heat inputs.
From Figure 8, it can be found that LM and LB structures are more likely to facilitate the formation of V1/V2 pairs dominated by high misorientation angles, while GB structures are more likely to facilitate the formation of V1/V4 and V1/V8 pairs with low misorientation angles. The essence of the above differences can be attributed to the differences in variant selection mechanism caused by the driving force of phase transformation. High heat input leads to lower cooling rates and lower driving forces, which induces higher transformation temperatures and Bain grouping-dominated mechanisms [11,12]. This strengthens the selection of variants, and decreases the number of different variant formations inside the austenite, while lower heat input can provide a greater driving force for more variants from different Bain groups (block) formed in single packets or austenite, aiming to accommodate greater transformation strain by initiating the formation of different variants in the neighbors [17]. This further confirms that the block is the most important crystallographic structural unit that can contribute to the impact toughness, consistent with previous studies [8,12].
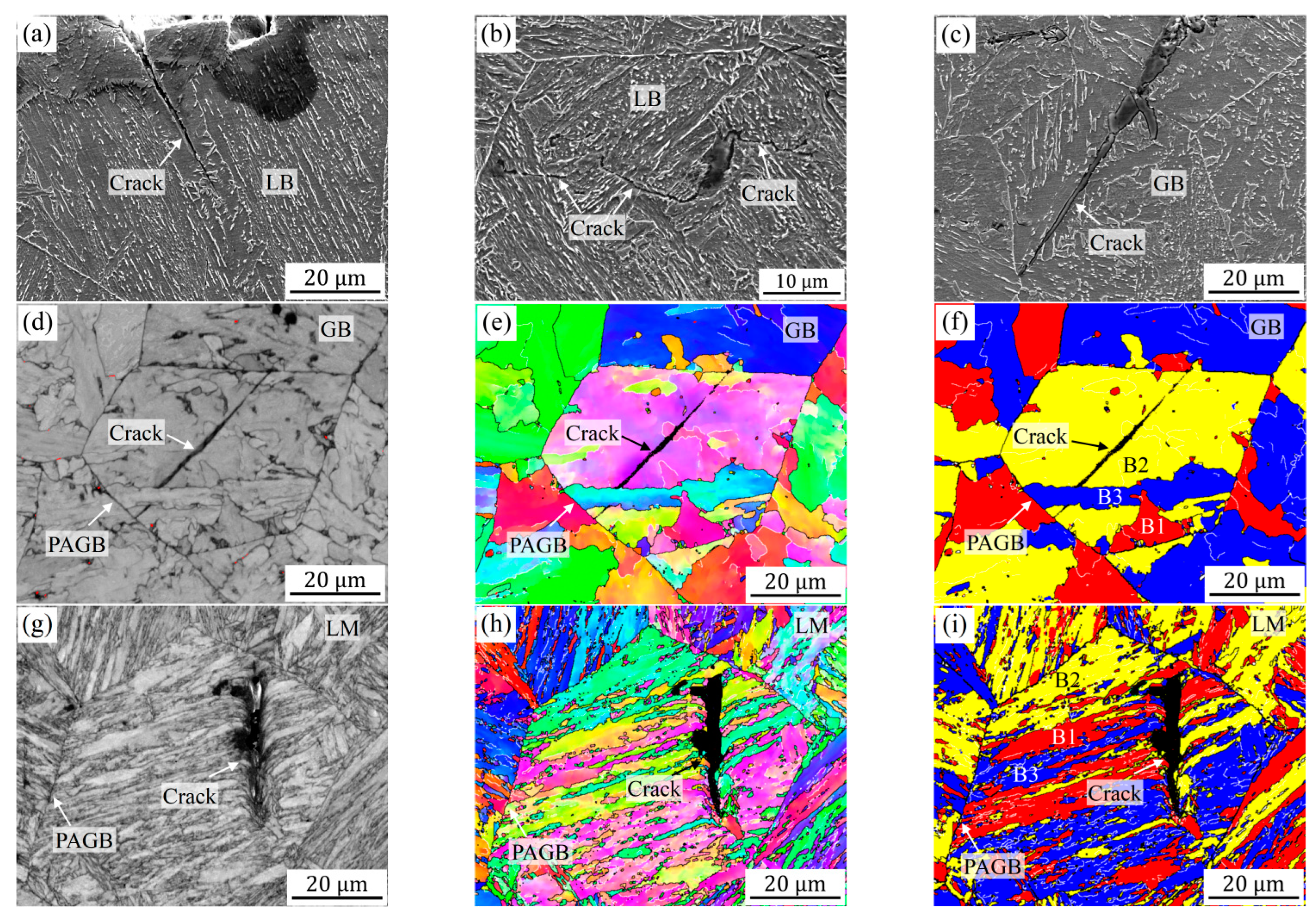
Although the increase in carbon content has a similar effect to the reduction in heat input, the penetration packet structure and narrow inter-spacing of block boundaries induced by high carbon content do not seem to be conducive to preventing brittle crack propagation. This can be concluded from the secondary crack observation, as shown in Figure 9. Under the condition of low heat input, brittle cracks can propagate parallel to the bainitic block with less resistance, and the cracks are straight without any deflection, as shown in Figure 9a. While for GB structures obtained at high heat input, brittle cracks can penetrate the entire austenite grain, and only stop when crack propagation meets the PAGB or different block boundaries (Figure 9c–f). The impact toughness obtained in both cases is low. In addition, it can be seen from the plastic deformation and micro-deflection in Figure 9g–i that different block boundaries of martensite can also play a certain role in hindering brittle crack propagation, although this role seems to be small and leads to the same low impact toughness. On the contrary, under the heat input of 20 kJ/cm, the LB structure presents an interactive arrangement, which promotes the continuous deflection of brittle crack propagation, thus generating greater propagation resistance and higher impact absorption energy. Wang et al. [8] also stated that when the inter-spacing of block boundaries is controlled below the critical Griffith crack length, micro-cracks can be arrested by these HAGBs, thereby suppressing brittle fracture initiation and increasing impact toughness. This is why the impact toughness of the high-carbon samples is lower than that of the low-carbon samples, although higher HAGB densities are obtained in the former.

Figure 9.
Secondary cracks observed on the fractured V-notch Charpy samples with 0.04 (a–f) and 0.12 (g–i) wt.% C by using SEM (a–c) and EBSD (d–i) under the different heat inputs: (a,g–i) 10 kJ/cm, (b) 20 kJ/cm and (c–f) 50 kJ/cm.
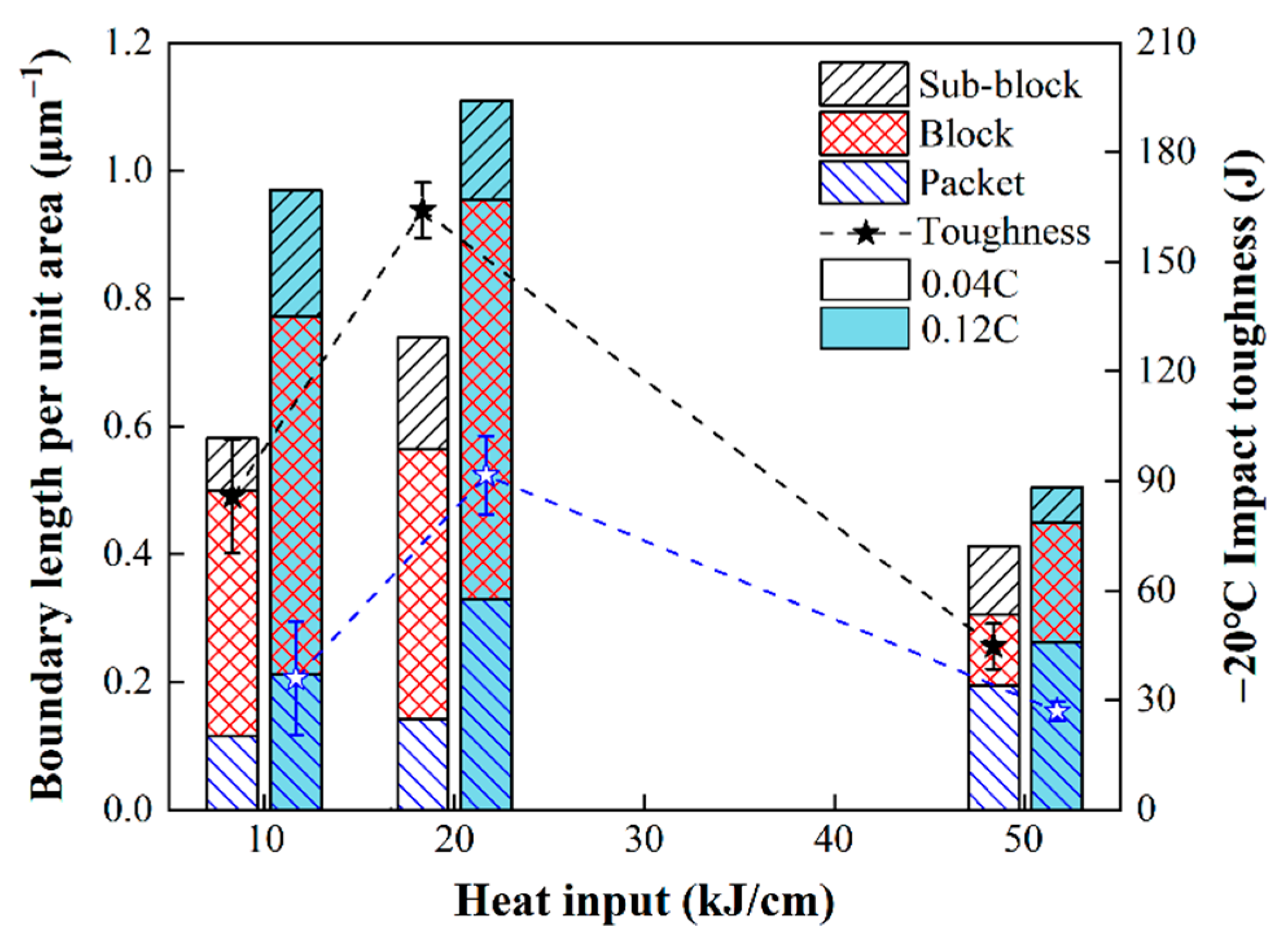
Figure 10 further shows the density of packet, block and sub-block boundaries, which are superposed onto the impact toughness. The density of packet and block boundaries in high-carbon samples is higher than that in low-carbon samples, but the impact toughness is opposite. This is because the increase in carbon content increases the hardenability of the samples, and the bainite or martensite transformation structure is more inclined to form a block or packet unit with a parallel structure, leading to a significant increase in the probability of brittle crack propagation parallel to the block during the impact test. Therefore, this leads to a decrease in the absorption energy of crack propagation, which ultimately reflects that although they have similar LB structure in morphology, the impact toughness is different due to the different structural arrangement in crystallography. Previous studies [18,19] have also indicated that the austenite grain size and the proportion of microstructure also affect the impact toughness. However, the density of the austenite grain boundary is usually low, and the austenite grain size obtained under the same peak temperature in this study is basically the same. Therefore, the influence of austenite grain size is excluded in this study. While the different proportions of microstructures do affect the impact toughness, especially for actual welded joints [20,21], this study focuses on the influence of different types of microstructures on impact toughness. Understanding the influence mechanism of various microstructures on crack propagation and impact toughness is helpful in guiding actual welding engineering. Thus, in order to obtain excellent comprehensive properties of base metals and welding HAZs at the same time, it is necessary to reasonably match the alloy composition and welding process.

Figure 10.
Relationship between boundary density and impact toughness of the simulated samples at the heat input of 10, 20 and 50 kJ/cm.
4. Conclusions
The following conclusions are made:
(1) When the carbon content changes from 0.04 to 0.12 wt.%, there is an optimal heat input window (~20 kJ/cm), which makes CGHAZs obtain high impact toughness. Under this heat input, fine crystallographic structures and high densities of high-angle grain boundaries, especially block boundaries, which can effectively prevent brittle crack propagation, can be obtained;
(2) With the increase in carbon content, the impact toughness of CGHAZs shows a decreasing trend, although high carbon content induces the formation of high densities of high-angle grain boundaries. The reason is that high carbon content increases the formation probability of bainite composed of parallel crystallographic structure and reduces the resistance to brittle crack propagation;
(3) Prior austenite grain boundaries and Bain group (block) boundaries are effective boundaries for inhibiting brittle crack propagation. However, brittle cracks can propagate in parallel block structures and coarse block units with low resistance and show a straight morphology. It is possible to effectively optimize the crystallographic structure arrangement of transformation microstructures by weakening variant selection through the regulation of heat input or carbon content, thus obtaining higher impact toughness.
Author Contributions
X.W. contributed primarily to the writing and compilation of the manuscript and data analysis; Z.X. was heavily involved in the project’s conceptualization, administration and planning; W.S. contributed primarily to carrying out the main experiments and data collection; C.S. was in charge of reviewing and editing the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 52001023) and the Special Fund for Science and Technology Project of Guangdong Province (No. SDZX2020008).
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Wu, B.B.; Wang, Z.Q.; Wang, X.L.; Xu, W.S.; Shang, C.J.; Misra, R.D.K. Toughening of martensite matrix in high strength low alloy steel: Regulation of variant pairs. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 759, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.B.; Wang, Z.Q.; Yu, Y.S.; Wang, X.L.; Shang, C.J.; Misra, R.D.K. Thermo dynamic basis of twin-related variant pair in high strength low alloy steel. Scr. Mater. 2019, 170, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.S.; Wang, Z.Q.; Wu, B.B.; Zhao, J.X.; Wang, X.L.; Guo, H.; Shang, C.J. Tailoring variant pairing to enhance impact toughness in high-strength low-alloy steels via trace carbon addition. Acta Metall. Sin-Engl. 2021, 34, 755–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Yu, J.H.; Park, S.H.; Shim, D.S.; Choi, Y.S. Effect of carbon content in steel powder feedstock on impact toughness and microstructure of additively manufactured cast iron by directed energy deposition. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 15, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koczurkiewicz, B. The effect of time and temperature variations during isothermal annealing on the mechanical properties of high carbon bainitic steel. Mater. Sci. Forum. 2012, 706–709, 2158–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyja, H.; Koczurkiewicz, B.; Knapiński, M. The analyze of phase transformation in ultra fine grained construction steel. Mater. Sci. Forum. 2010, 638–642, 2610–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo, J.; Santofimia, M.J. Effect of prior austenite grain size refinement by thermal cycling on the microstructural features of as-quenched lath martensite. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2016, 47, 5288–5301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.L.; Ma, X.P.; Wang, Z.Q.; Subramanian, S.V.; Xie, Z.J.; Shang, C.J.; Li, X.C. Carbon microalloying effect of base material on variant selection in coarse grained heat affected zone of X80 pipeline steel. Mater. Charact. 2019, 149, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Kasyap, P.; Pandey, C.; Basu, B.; Nath, S.K. Role of heat inputs on microstructure and mechanical properties in coarse-grained heat-affected zone of bainitic steel. CIRP J. Manuf. Sci. Tec. 2021, 35, 724–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.N.; Huan, P.C.; Wang, X.N.; Liu, Z.G.; Shen, X.J.; Gao, Y.; Di, H.S. Effect of root welding heat input on microstructure evolution and fracture mechanism in intercritically reheat-coarse grained heat-affected zone of X80 pipeline steel. Mater. Today. Commun. 2022, 31, 103413. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.L.; Xie, Z.J.; Wang, Z.Q.; Yu, Y.S.; Wu, L.Q.; Shang, C.J. Crystallographic study on microstructure and impact toughness of coarse grained heat affected zone of ultra-high strength steel. Mater. Lett. 2022, 323, 132552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.L.; Wang, Z.Q.; Dong, L.L.; Shang, C.J.; Ma, X.P.; Subramanian, S.V. New insights in to the mechanism of cooling rate on the impact toughness of coarse grained heat affected zone from the aspect of variant selection. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 704, 448–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Y.; Shang, C.J.; Nie, W.J.; Subramanian, S.V. Investigation on the microstructure and toughness of coarse grained heat affected zone in X-100 multi-phase pipeline steel with high Nb content. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 558, 692–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, L.Y.; Kong, X.W.; Qiu, C.L. Characterization of coarse bainite transformation in low carbon steel during simulated welding thermal cycles. Mater. Charact. 2015, 105, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourgues, A.-F.; Flower, H.M.; Lindley, T.C. Electron backscattering diffraction study of acicular ferrite, bainite, and martensite steel microstructures. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2000, 16, 26–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.; Kundu, S.; Chakrabarti, D. Effect of crystallographic texture on the cleavage fracture mechanism and effective grain size of ferritic steel. Scr. Mater. 2014, 81, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takayama, N.; Miyamoto, G.; Furuhara, T. Effects of transformation temperature on variant pairing of bainitic ferrite in low carbon steel. Acta Mater. 2012, 60, 2387–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarti, D.; Strangwood, M.; Davis, C.L. Effect of bimodal grain size distribution on scatter in toughness. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2009, 40, 780–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhajed, B.; Mishra, K.; Singh, K.; Singh, A. Effect of prior austenite grain size on the tensile properties and fracture toughness of nano-structured bainite. Mater. Charact. 2022, 192, 112214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.D.; Ma, X.P.; Subramanian, S.V.; Misra, R.D.K.; Shang, C.J. Structure-property-fracture mechanism correlation in heat-affected zone of X100 ferrite-bainite pipeline steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. E 2015, 2E, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.P.; Li, X.C.; Shang, C.J.; Wang, Q.C.; Sun, W.H.; Li, G.B.; Guo, F.J.; Xia, D.X. Study on microstructure and impact toughness of laser hybrid welding joints. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2023, 39, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).