Influence of Heat Treatment and Deformation on the Structure, Phase Transformation, and Mechanical Behavior of Bulk TiNi-Based Alloys
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
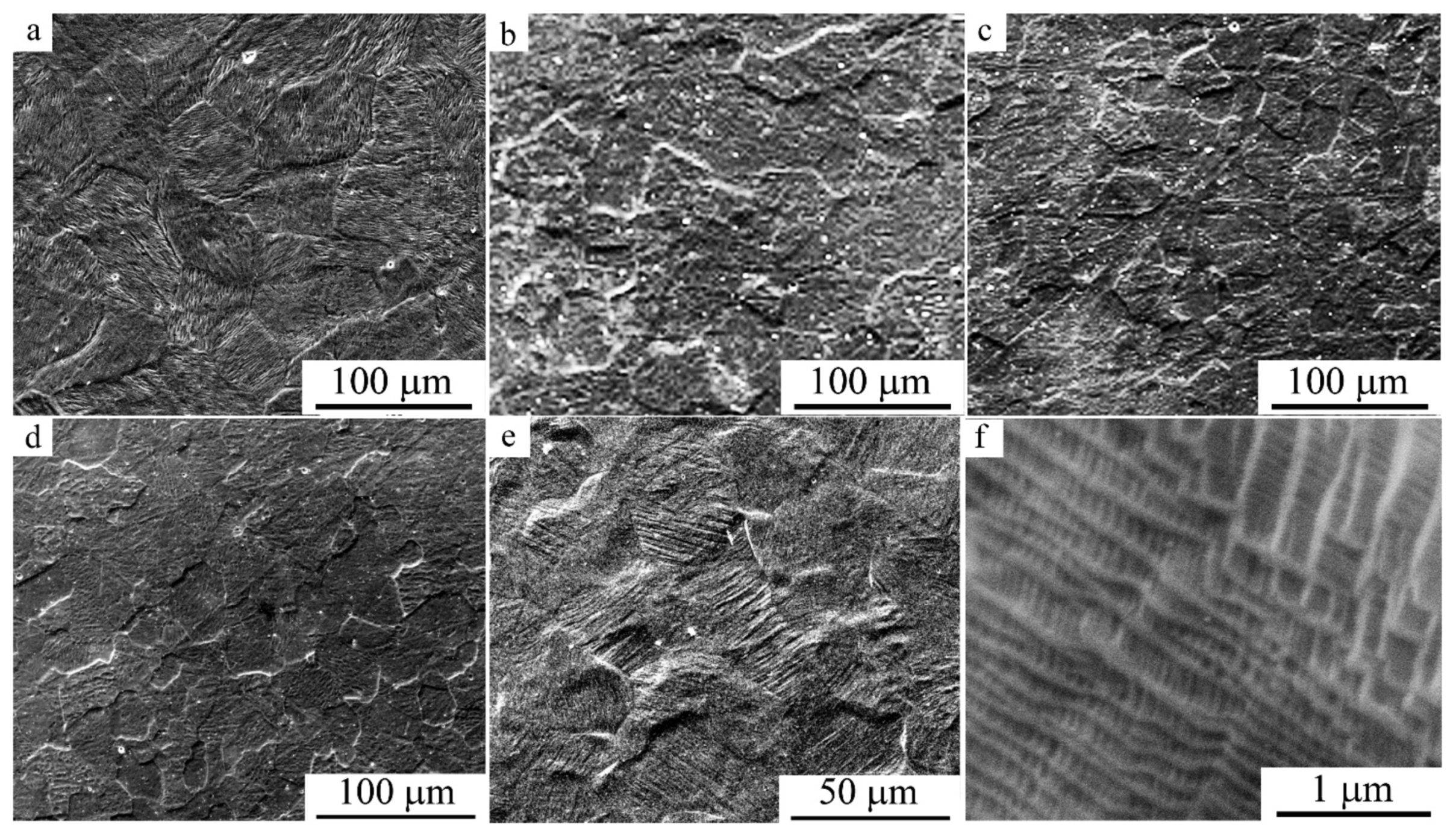
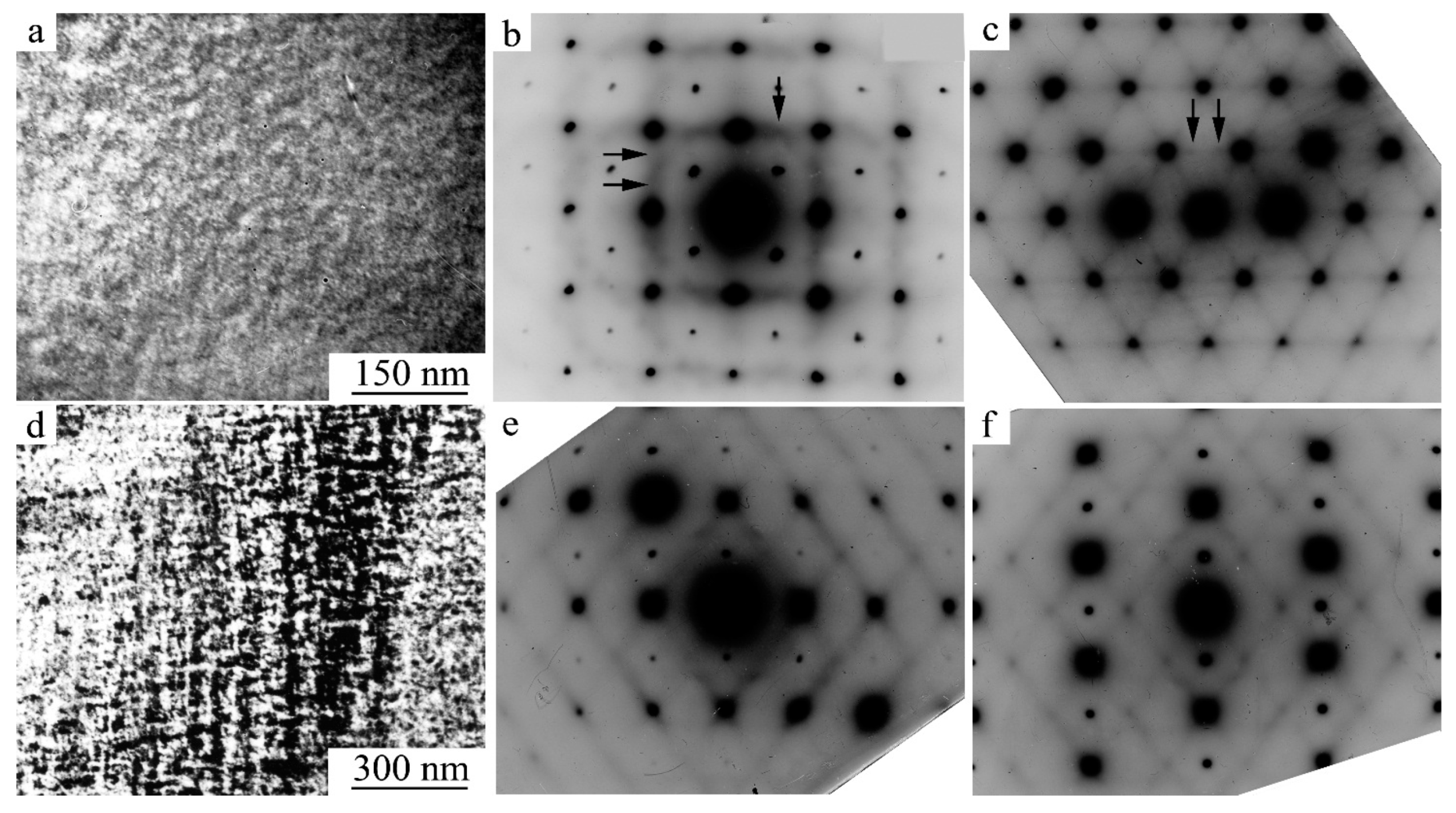
3.1. Initial Microstructure and Phase Transformations in Alloys during Cooling
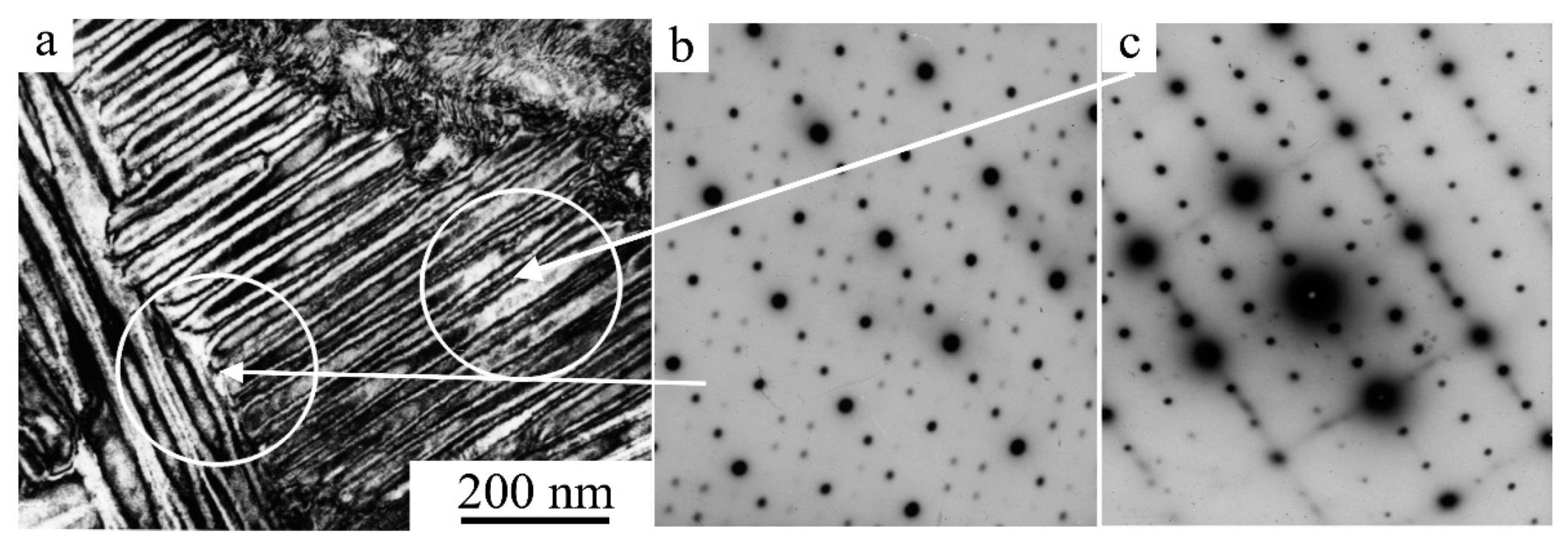
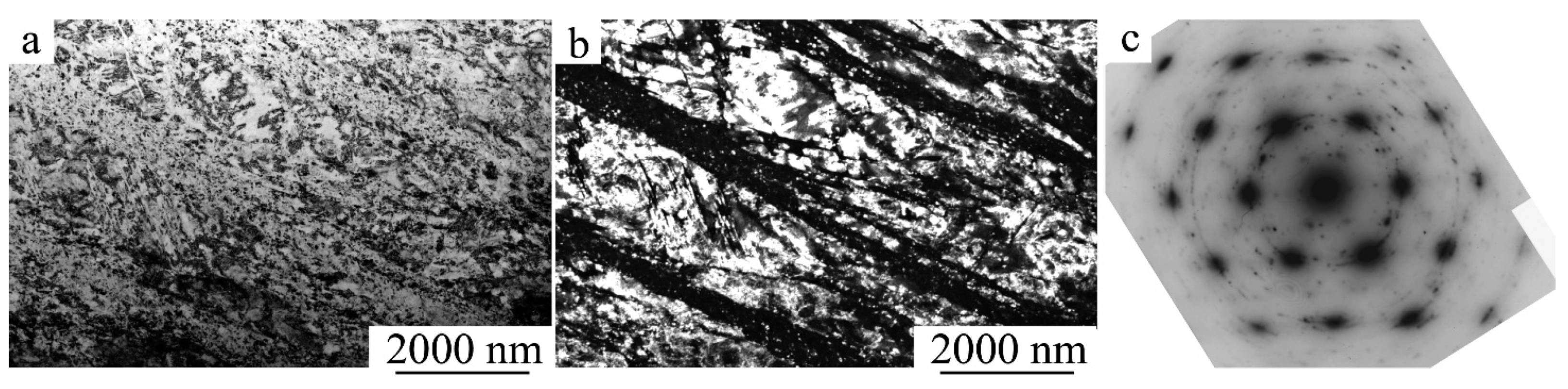
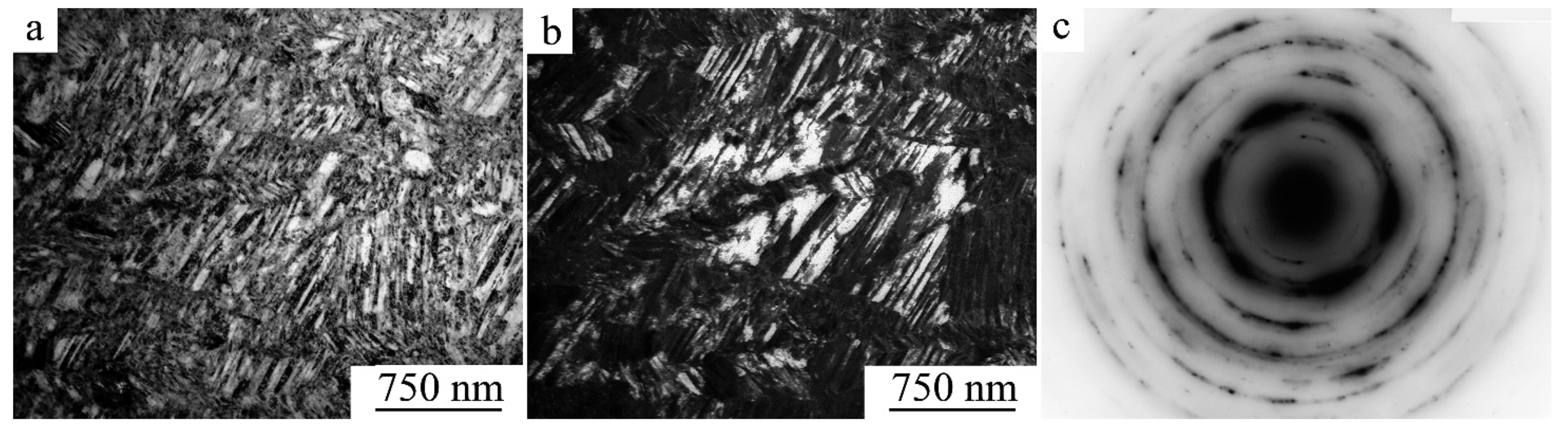
3.2. Influence of ECAP and HPT on the Structure and Mechanical Properties of Alloys
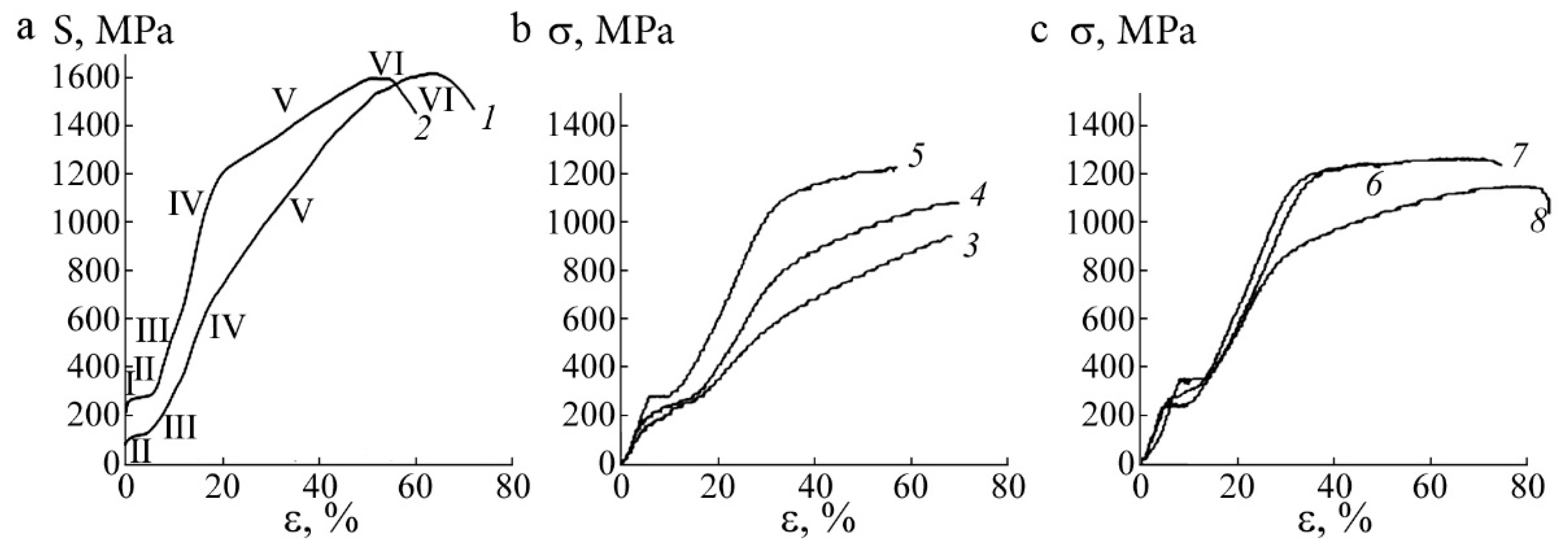
3.2.1. ECAP of SM Ti49.4Ni50.6 Alloy
3.2.2. ECAP of SM Ti49.8Ni50.2 Alloy
3.2.3. Microstructural Changes of the SME Ti49.4Ni50.6 Alloy upon Tensile Tests
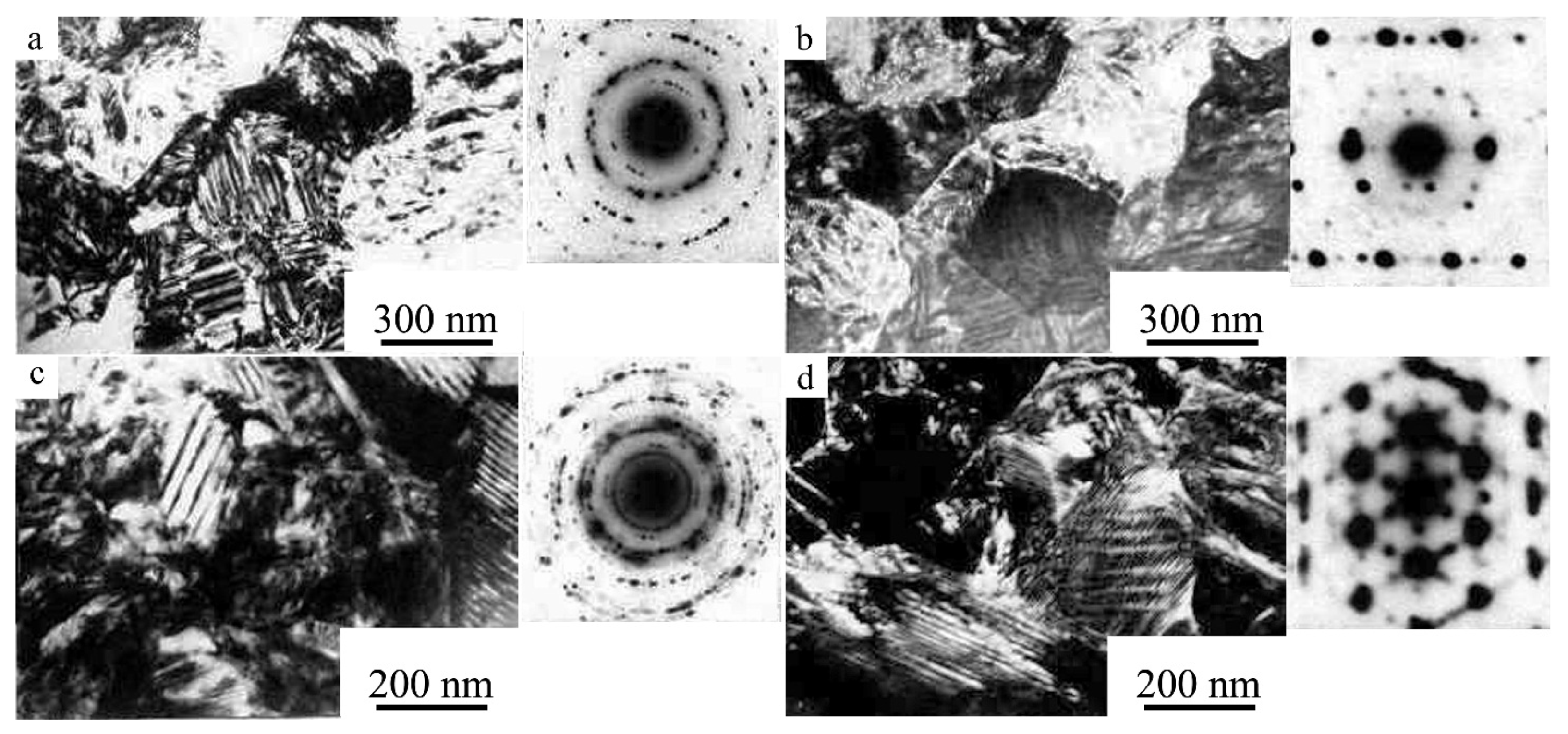
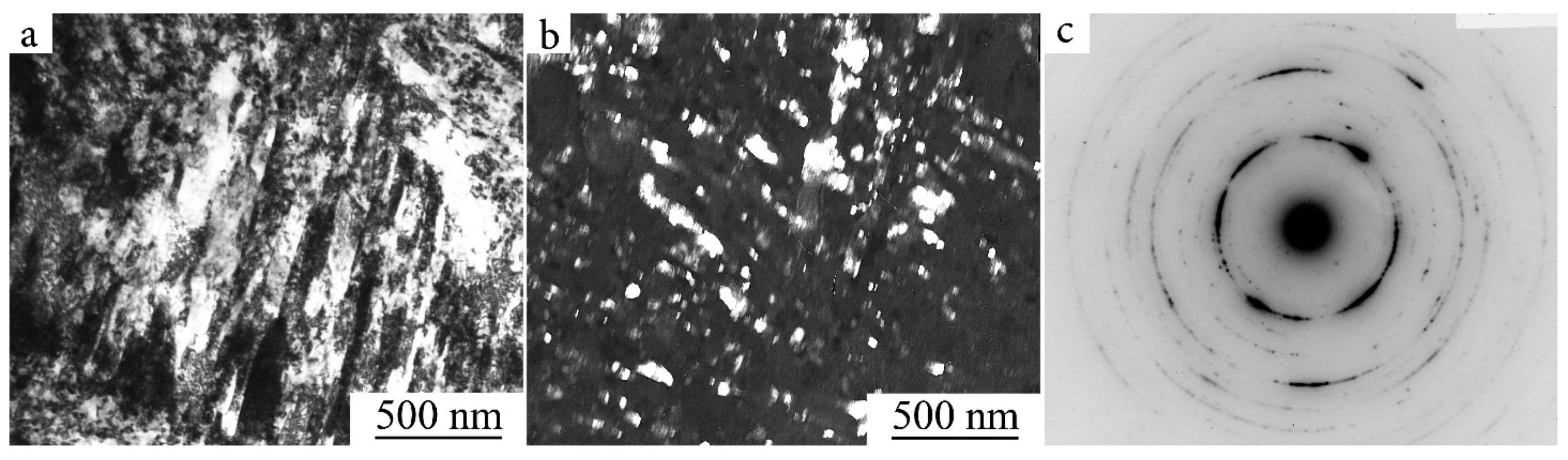
3.2.4. The Effect of HPT on the Structure and Mechanical Properties of the SME Alloy Ti49.4Ni50.6
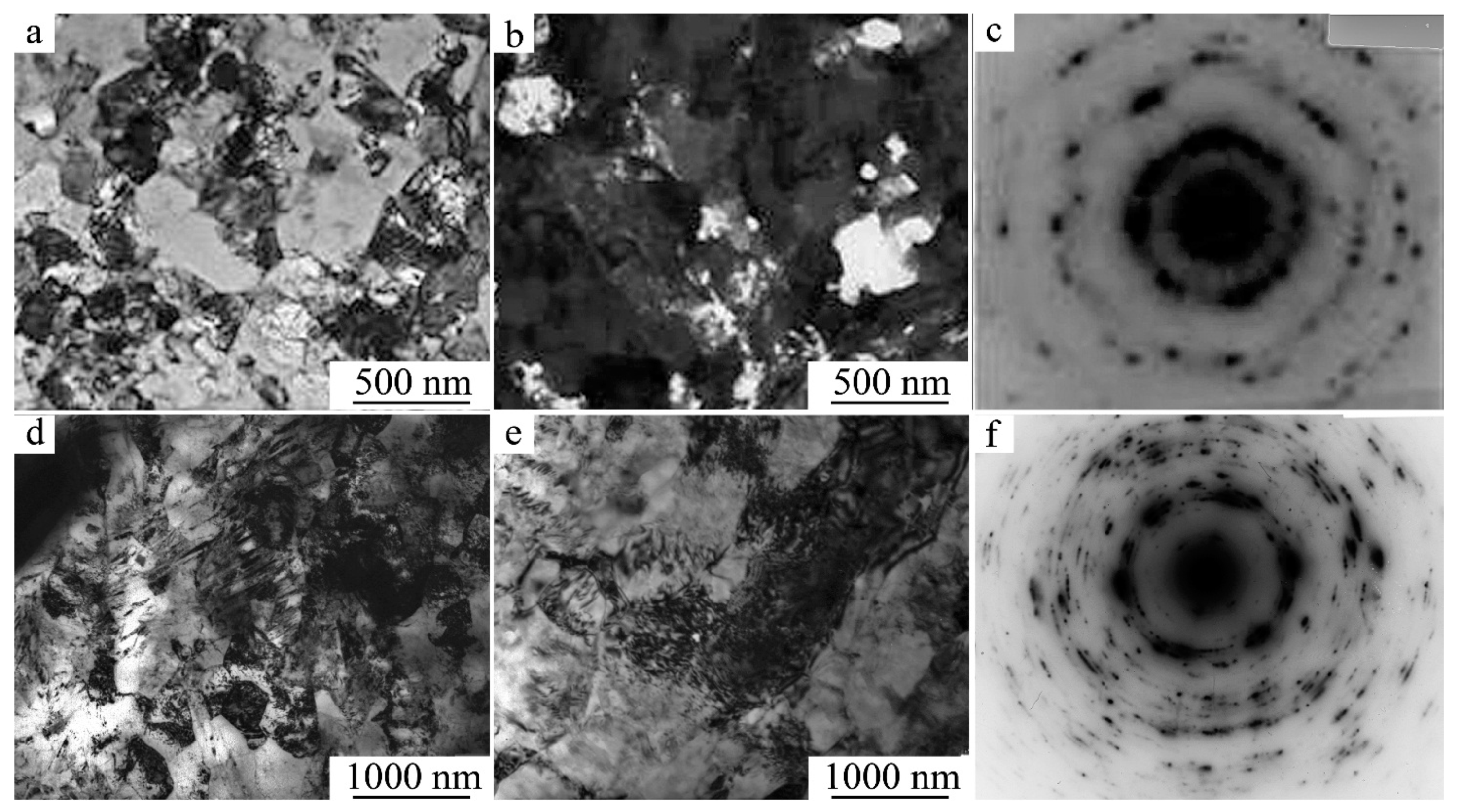
3.3. The Effect of HT, MPR, and PDHT on the Structure and Mechanical Properties of Bulk Alloys
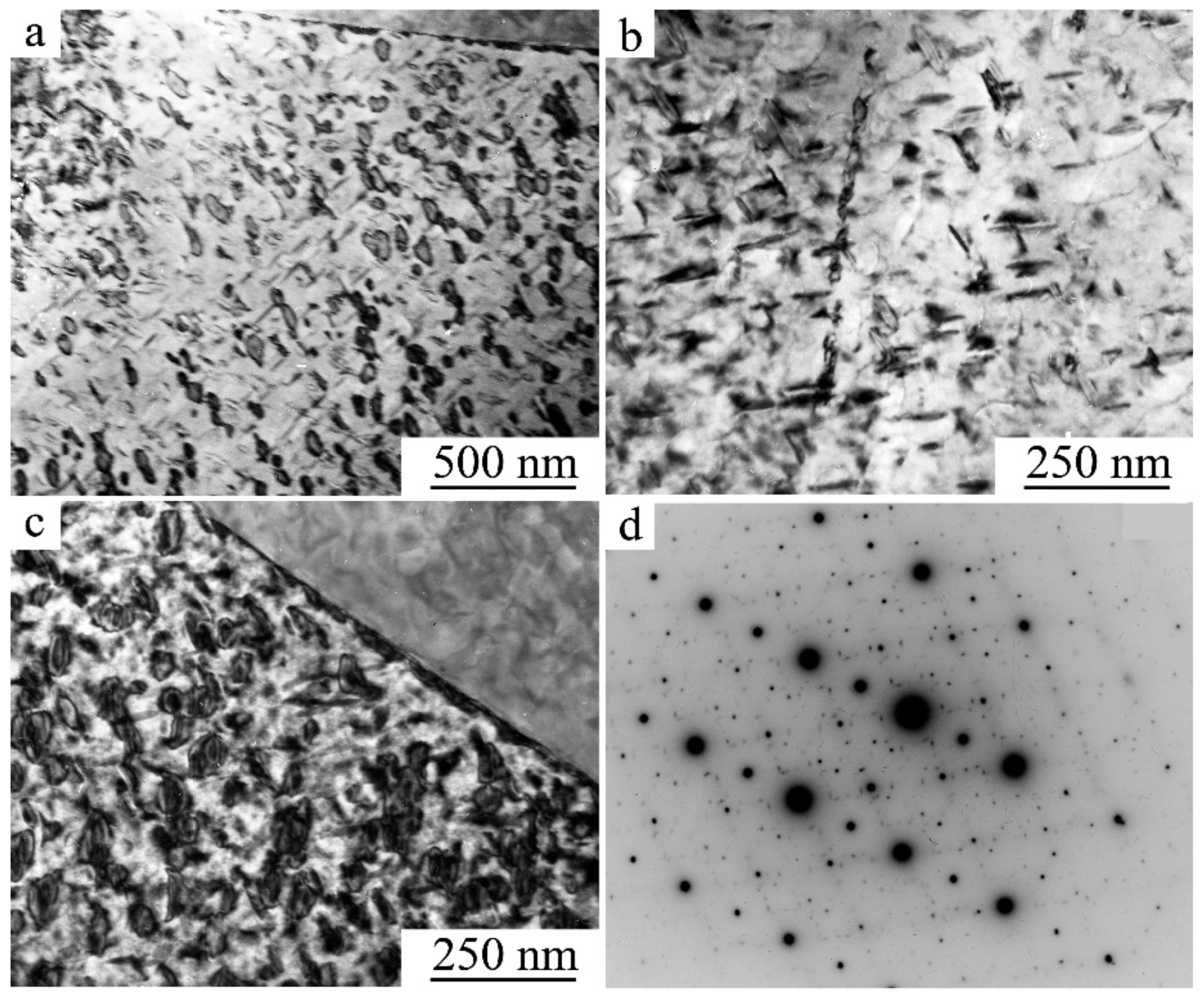
3.3.1. Features of the Decomposition of Supersaturated B2 SME Ti-Ni Alloys at HT
3.3.2. The Effect of the MPR and PDHT on the Structure and Mechanical Properties of the SME Ti49.5Ni50.5 Alloy
3.3.3. The Effect of Cold MPR and PDHT on the Structure and Mechanical Properties of the SME Ti49Ni51 Alloy
3.4. The Effect of SIMT on the Phenomena of the Thermomechanical Shape Memory and Super-Elasticity of Bulk Alloys
4. Summary and Conclusions
- The special mechanical behavior of the studied alloys, which is responsible for the complex of their abnormally high effects of shape memory and superelasticity, strength, plasticity, and deformation hardening, is physically caused by their low elasticity moduli and their isotropy not only in the pre-martensitic state of B2 austenite, but also in the state of B19′ martensite.
- As a consequence, during mechanical tests (or during practical use in actuators in superelasticity modes), a specific mechanism of superelastic stress-induced martensitic transformation (SIMT effect) is first implemented. At stresses above the dislocation-assisted fluidity limit (i.e., yield stress), the homogeneous planar dislocation sliding and mechanical twinning are effectively realized with the progressive formation of a developed band substructure with a high number density of the dislocations and mechanical nanotwins uniformly distributed in nanograins, where all the latter ultimately determine the effect of superplasticity by strain-assisted martensitic transformation (SAMT).
- This combined mechanism of the deforming and strengthening simultaneously provides both the high deformation hardening homogeneous alloy volume and the effective relaxation of peak stresses, preventing by itself (i) the transition to premature localization of deformation in the alloy and (ii) its destruction during a long period of accumulation of the degree of deformation.
- In alloys that are metastable with respect to martensitic transformations, an important independent process of the hardening and concurrent relaxation of excess stresses is the deformation-induced size refinement of the grain and subgrain structure—under various mechanically activated external effects—in both B2 austenite and B19′ martensite at the stage of developed plastic deformation, up to the formation of UFG, nanostructured, or even amorphous states in them (for example, during mechanical tests).
- The studied UFG titanium nickelide alloys, obtained by various technological schemes and depending on the chemical composition, demonstrate an attractive set of mechanical properties, including strength, plasticity, shape memory effects, superelasticity, high damping, and other characteristics.
- It is shown that in Ti49.8Ni50.2 and Ti49.4Ni50.6 UFG alloys, which are not subject to homogeneous aging, the use of multi-pass ECAP (including that with PDHT in combination) leads to a high-strength (σu up to 1200 MPa) and ductile (δ up to 60–70%) condition of the materials.
- It was found that in the aging-prone UFG alloys (namely, the alloy Ti49.5Ni50.5 is prone to heterogeneous decomposition and the alloy Ti49Ni51 is prone to the homogeneous type), the use of multi-pass rolling in combination with PDHT provides for high strength (σu up to 1400–1500 MPa) and increased plasticity (δ 25–30%) due to operation of the combined mechanism of recrystallization and decomposition, with the precipitation of disperse X-Ni4Ti3 nanoparticles.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kaufman, L.; Kohen, M. Thermodynamics and Kinetics of Martensite Transformations. In Progress Metal Physics. V. 7; Pergamon Press: London, UK; New York, NY, USA; Paris, France; Los Angeles, CA, USA, 1958. [Google Scholar]
- Kurdyumov, G.V.; Utevsky, L.M.; Entin, R.I. Transformations in Iron and Steel; Nauka: Moscow, Russia, 1977. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Perkins, J. (Ed.) Shape Memory Effects in Alloys; Plenum: London, UK, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Otsuka, K.; Shimizu, K.; Suzuki, Y.; Sekiguchi, Y.; Tadaki, C.; Honma, T.; Miyazaki, S. Shape Memory Alloys; Funakubo, H., Ed.; Funakubo: Kyoto, Japan, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Duering, T.W.; Melton, K.L.; Stockel, D.; Wayman, C.M. (Eds.) Engineering Aspects of Shape Memory Alloys; Butterworth-Heineman: London, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Khachin, V.N.; Pushin, V.G.; Kondratyev, V.V. Titanium Nickelide: Structure and Properties; Nauka: Moscow, Russia, 1992. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Pushin, V.G.; Kondratyev, V.V.; Khachin, V.N. Pretransition Phenomena and Martensitic Transformations; UrO RAN: Yekaterinburg, Russia, 1998. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Otsuka, K.; Wayman, C.M. Shape Memory Materials; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez, C.; Brown, L.C. The thermal effect due to stress-induced martensite formation in β-CuAlNi single crystals. Metall. Mater. Trans. 1980, 11, 147–150. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, S.; Geng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Pillsbury, T.E.; Hada, Y.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Fujimoto, K.; Hwang, Y.; Radermacher, R.; Cui, J.; et al. Elastocaloric effect in CuAlZn and CuAlMn shape memory alloys under compression. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. 2016, 374, 20150309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mañosa, L.; González-Alonso, D.; Planes, A.; Bonnot, E.; Barrio, M.; Tamarit, J.-L.; Aksoy, S.; Acet, M. Giant solid-state barocaloric effect in the Ni-Mn-In magnetic shape-memory alloy. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 478–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnot, E.; Romero, R.; Mañosa, L.; Vives, E.; Planes, A. Elastocaloric effect associated with the martensitic transition in shape-memory alloys. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 100, 125901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bechtold, C.; Chluba, C.; De Miranda, R.L.; Quandt, E. High cyclic stability of the elastocaloric effect in sputtered TiNiCu shape memory films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 101, 091903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Wu, Y.; Muehlbauer, J.; Hwang, Y.; Radermacher, R.; Fackler, S.; Wuttig, M.; Takeuchi, I. Demonstration of high efficiency elastocaloric cooling with large δT using NiTi wires. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 101, 073904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mañosa, L.; Jarque-Farnos, S.; Vives, E.; Planes, A. Large temperature span and giant refrigerant capacity in elastocaloric Cu-Zn-Al shape memory alloys. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 103, 211904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gschneidner, K.A., Jr.; Pecharsky, V.; Tsokol, A. Recent developments in magnetocaloric materials. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2005, 68, 1479–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planes, A.; Mañosa, L.; Acet, M. Magnetocaloric effect and its relation to shape memory properties in ferromagnetic Heusler alloys. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 2009, 21, 233201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moya, X.; Stern-Taulats, E.; Crossley, S.; González-Alonso, D.; Kar-Narayan, S.; Planes, A.; Mañosa, L.; Mathur, N.D. Giant electrocaloric strength in single-crystal BaTiO3. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 1360–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.; Bahl, C.R.; Bjørk, R.; Engelbrecht, K.; Nielsen, K.K.; Pryds, N. Materials challenges for high performance magnetocaloric refrigeration devices. Adv. Energy Mater. 2012, 2, 1288–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mischenko, A.; Zhang, Q.; Scott, J.; Whatmore, R.; Mathur, N. Giant electrocaloric effect in thin-film PbZr0.95Ti0.05O3. Science 2006, 311, 1270–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razov, A.I. Application of titanium nickelide-based alloys in engineering. Phys. Met. Metallogr. 2004, 97, S97–S126. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Z.; Lee, Q.; Onuki, Y.; Sun, Q. Multifunctional nanostructured NiTi alloys with Invar, Evinvar and Rinvar properties. J. Alloys Comp. 2022, 909, 164682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, J.; Weselowsky, M. Shape Memory Alloys for Seismic Response Modification: A State-of-the-Art Review. Earth. Spectra 2005, 21, 569–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Cai, C.; O’Keil, A. Overview of Potential and Existing Applications of Shape Memory Alloys in Bridges. J. Bridg. Eng. 2011, 16, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J. Shape memory alloys and their applications in power generation and refrigeration. In Mesoscopic Phenomena in Multifunctional Materials; Saxena, A., Planes, A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 289–307. [Google Scholar]
- Nakanishi, N. Elastic Constants as They Relate to Lattice Properties and Martensitic Formation. Prog. Mater. Sci. 1980, 24, 143–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushin, V.G.; Kondratyev, V.V.; Khachin, V.N. Pretransition Phenomena and Martensitic Transformations in Alloys Based on Titanium Nickel. Izvestiya VUZov. Phys. 1985, 27, 5–8. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kondratyev, V.V.; Pushin, V.G. Pretransitional state in Metals, Their Alloys and Compounds: Experimental Results, Structure Models, Classification. Phys. Met. Metallogr. 1985, 60, 629–650. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Khachin, V.N.; Muslov, S.A.; Pushin, V.G.; Chumlyakov, Y.I. Anomalies of the Elastic Properties of Single Crystals of TiNi-TiFe. DAN SSSR 1987, 295, 606–609. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kuznetsov, A.V.; Muslov, S.A.; Lotkov, A.I.; Pushin, V.G.; Khachin, V.N.; Grishkov, V.N. Elastic Constants Near the TiNi Martensitic Transformations. Izvestia VUZov. Phys. 1987, 30, 98–99. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Muslov, S.A.; Kuznetsov, A.V.; Khachin, V.N.; Lotkov, A.I.; Grishkov, V.N.; Pushin, V.G. Anomalies of the Elastic Constants of Single Crystals Ti50Ni48Fe2 Near Martensitic Transformations. Izvestiya VUZov. Phys. 1987, 30, 104–105. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Khachin, V.N.; Muslov, S.A.; Pushin, V.G.; Kondratyev, V.V. Special elastic properties of B2-compounds of titanium with unstable lattice. Metallophysics 1988, 10, 102–104. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Pushin, V.G.; Khachin, V.N.; Kondratyev, V.V.; Muslov, S.A.; Pavlova, S.P.; Yurchenko, L.I. Structure and Properties of B2 Compounds of Titanium. I. Pre-Martensitic Phenomena. Phys. Met. Metallogr. 1988, 66, 350–358. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kondratyev, V.V.; Muslov, S.A.; Pushin, V.G.; Khachin, V.N. Structure and Properties of Titanium B2 Compounds. II. Premartensitic Instability of the BCC (B2) Lattice. Phys. Met. Metallogr. 1988, 66, 359–369. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Pushin, V.G.; Kondratyev, V.V. Pretransition Phenomena and Martensitic Transformations. Phys. Met. Metallogr. 1994, 78, 40–61. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Pushin, V.G.; Khachin, V.N.; Yurchenko, L.I.; Muslov, S.A.; Ivanova, L.Y.; Sokolova, A.Y. Microstructure and Physical Properties of Ti50Ni50-xFex Alloys with Memory Effects. II. Elastic Properties. Phys. Met. Metallogr. 1995, 79, 70–76. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Worgull, J.; Petti, E.; Trivisonno, J. Behavior of the elastic properties near an intermediate phase transition in Ni2MnGa. Phys. Rev. B 1996, 54, 15695–15699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushin, V.G. Alloys with a Thermo-Mechanical Memory: Structure, Properties, and Application. Phys. Met. Metallogr. 2000, 90, S68–S95. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, X.; Miura, N.; Zhang, J.; Otsuka, K.; Tanake, K.; Koiwa, M.; Suzuki, N.; Chumlykov, Y.I. A Comparative Study of Elastic Constants of Ti-Ni-based Alloys Prior to Martensitic Transformation. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2001, 312, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedlak, P.; Seiner, H.; Landa, M.; Novák, V.; Šittner, P.; Manosa, L.I. Elastic Constants of bcc Austenite and 2H Orthorhombic Martensite in CuAlNi Shape Memory Alloy. Acta Mater. 2005, 53, 3643–3661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobodyuk, V.A.; Koval’, Y.N.; Pushin, V.G. Crystal-Structural Features of Pretransition Phenomena and Thermoelastic Martensitic Transformations in Alloys of Nonferrous Metals. Phys. Met. Metallogr. 2011, 111, 165–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushin, V.; Kuranova, N.; Marchenkova, E.; Pushin, A. Design and Development of Ti–Ni, Ni–Mn–Ga and Cu–Al–Ni-based Alloys with High and Low Temperature Shape Memory Effects. Materials 2019, 12, 2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svirid, A.E.; Pushin, V.G.; Kuranova, N.N.; Makarov, V.V.; Ustyugov, Y.M. Structural and Phase Transformations and Physical and Mechanical Properties of Cu-Al-Ni Shape Memory Alloys Subjected to Severe Plastic Deformation and Annealing. Materials 2021, 14, 4394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushin, V.; Kuranova, N.; Svirid, A.; Ustyugov, Y. Mechanical behavior and structure characterization of a Cu-Al-Ni-based shape memory alloys subjected to isothermal uniaxial mega-plastic compression. Materials 2022, 15, 3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushin, V.G.; Kuranova, N.N.; Svirid, A.E.; Uksusnikov, A.N.; Ustyugov, Y.M. Design and development of high-strength and ductile ternary and multicomponent eutectoid Cu-based shape memory alloys: Problems and perspectives. Metals 2022, 12, 1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesare, R.; Pons, J.; Santamarta, R.; Segui, C.; Chernenko, V.A. Ferromagnetic Shape Memory Alloys: An Overview. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2004, 49, 779–789. [Google Scholar]
- Otsuka, K.; Yamada, H.; Maruyama, T.; Tanahashi, H.; Matsuda, S.; Murakami, M. Effect of alloying additions on Fe-Mn-Si shape memory alloys. ISIJ. Int. 1990, 30, 674–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.Z.; Kajiwara, S.; Kikuchi, T.; Sawaguchi, T. Effect of pre-deformation at room temperature on shape memory properties of stainless type Fe-15Mn-9Cr-5Ni-(0.5-1.0)NbC alloys. Acta Mater. 2005, 3, 4009–4018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagaradze, V.V.; Belozerov, Y.V.; Pecherkina, N.L.; Mukhin, M.L.; Zaynutdinov, Y.R. The shape memory effect in high-strength precipitation-hardening austenitic steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2006, 438, 812–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagaradze, V.V.; Afanas’ev, S.V.; Kataeva, N.V. Shape Memory Effect in Corrosion-Resistant Steels Hardened by Various Carbides. Phys. Met. Metallogr. 2018, 119, 764–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuravlev, V.N.; Pushin, V.G. Alloys with Thermomechanical Shape Memory and Their Application in Medicine; UrO RAN: Yekaterinburg, Russia, 2000. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Yoneyama, T.; Miyazaki, S. Shape Memory Alloys for Medical Applications; Wordhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Prokoshkin, S.D.; Pushin, V.G.; Ryklina, E.P.; Khmelevskaya, I.Y. Application of Titanium Nickelide–based Alloys in Medicine. Phys. Met. Metallogr. 2004, 97, 56–96. [Google Scholar]
- Brailovski, V.; Khmelevskaya, I.Y.; Prokoshkin, S.D.; Pushin, V.G.; Ryklina, E.P.; Valiev, R.Z. Foundation of Heat and Thermomechanical Treatments and Their on the Structure and Properties of Titanium Nickelide-Based Alloys. Phys. Met. Metallogr. 2004, 97, S3–S55. [Google Scholar]
- Valiev, R.Z.; Alexandrov, I.V. Nanostructured Materials Produced by Severe Plastic Deformation; Logos: Moscow, Russia, 2000. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Valiev, R.Z.; Aleksandrov, I.V. Bulk Nanostructured Metallic Materials; Academkniga: Moscow, Russia, 2007. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Valiev, R.Z.; Pushin, V.G. Bulk Nanostructured Metallic Materials: Production, Structure, Properties and Functioning. Phys. Met. Metallogr. 2002, 94, S1–S4. [Google Scholar]
- Pushin, V.G.; Stolyarov, V.V.; Valiev, R.Z.; Kourov, N.I.; Kuranova, N.N.; Prokofiev, E.A.; Yurchenko, L.I. Features of Structure and Phase Transformations in Shape Memory TiNi-Based Alloys after Severe Plastic Deformation. Ann. Chim. Sci. Mat. 2002, 27, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushin, V.G.; Stolyarov, V.V.; Valiev, R.Z.; Kourov, N.I.; Kuranova, N.N.; Prokofiev, E.A.; Yurchenko, L.I. Development of Methods of Severe Plastic Deformation for the Production of High-Strength Alloys Based on Titanium Nickelide with a Shape Memory Effect. Phys. Met. Metallogr. 2002, 94, S54–S68. [Google Scholar]
- Pushin, V.G.; Valiev, R.Z. The Nanostructured TiNi Shape-Memory Alloys: New Properties and Applications. Solid State Phenom. 2003, 94, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sergueeva, A.V.; Song, C.; Valiev, R.Z.; Mukherjee, A.K. Structure and properties of amorphous and nanocrystalline NiTi prepared by severe plastic deformation and annealing. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2003, 339, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushin, V.G. Structure, properties and application of nanostructured shape memory TiNi-based alloys. In Nanomaterials by Severe Plastic Deformation; Zehetbauer, M., Valiev, R., Eds.; Willey-VCH Verlag GmbH and Co, KgaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2004; pp. 822–828. [Google Scholar]
- Valiev, R.Z.; Pushin, V.G.; Gunderov, D.V.; Popov, A.G. The use of severe deformations for preparing bulk nanocrystalline materials from amorphous alloys. Dokl. Phys. 2004, 49, 519–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiev, R.Z.; Gunderov, D.V.; Pushin, V.G. Metastable nanostructured SPD Ti-Ni alloys with unique properties. J. Met. Nanocryst. Mater. 2005, 24, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolyarov, V.V.; Prokof’ev, E.A.; Prokoshkin, S.D.; Dobatkin, S.B.; Trubitsyna, I.B.; Khmelevskaya, I.Y.; Pushin, V.G.; Valiev, R.Z. Structural features, mechanical properties, and the shape memory effect in TiNi alloys subjected to equal-channel angular pressing. Phys. Met. Metallogr. 2005, 100, 608–618. [Google Scholar]
- Pushin, V.G.; Valiev, R.Z.; Zhu, Y.T.; Gunderov, D.V.; Korolev, A.V.; Kourov, N.I.; Kuntsevich, T.E.; Valiev, E.Z.; Yurchenko, L.I. Severe Plastic Deformation of Melt-Spun Shape Memory Ti2NiCu and Ni2MnGa Alloys. Mater. Trans. 2006, 47, 546–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pushin, V.G.; Korolev, A.V.; Kourov, N.I.; Gunderov, D.V.; Valiev, R.Z.; Koledov, V.V.; Shavrov, V.G. SPD-Induced Nanocrystallization of Shape Memory Ni2MnGa-Based and NiTi-Based Alloys Quenched from Liquid State. Mater. Sci. Forum 2006, 503–504, 545–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiev, R.Z.; Gunderov, D.V.; Pushin, V.G. The New SPD Processing Routes to Fabricate Bulk Nanostructured Materials. Ultrafine Grained Materials IV; Zhu, Y.T., Langdon, T.G., Horita, Z., Zehetbauer, M.J., Semiatin, S.L., Lowe, T.C., Eds.; TMS (The Minerals, Metals and Materials Society): Warrendale, PA, USA, 2006; pp. 105–112. [Google Scholar]
- Pushin, V.G.; Valiev, R.Z.; Zhu, Y.T.; Prockoshkin, S.; Gunderov, D.V.; Yurchenko, L.I. Effect of Equal Channel Angular Pressing and Repeated Rolling on Structure, Phase Transformation and Properties of TiNi Shape Memory Alloys. Mater. Sci. Forum 2006, 503–504, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiev, R.; Gunderov, D.; Prokofiev, E.; Pushin, V.; Zhu, Y. Nanostructuring of TiNi alloy by SPD processing for advanced properties. Mater. Trans. 2008, 49, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchiya, K.; Hada, Y.; Koyano, T.; Nakajima, K.; Ohnuma, M.; Koike, T.; Todaka, Y.; Umimota, M. Production of TiNi Amorphous/Nanocrystalline Wires with High-Strength and Elastic Modulus by Severe Cold Drawing. Scr. Mater. 2009, 60, 749–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushin, V.G.; Lotkov, A.I.; Kolobov, Y.R.; Valiev, R.Z.; Dudarev, E.F.; Kuranova, N.N.; Dyupin, A.P.; Gunderov, D.V.; Bakach, G.P. On the nature of anomalously high plasticity of high-strength titanium nickelide alloys with shape memory effects: I. Initial structure and mechanical properties. Phys. Met. Metallogr. 2008, 106, 520–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudarev, E.F.; Valiev, R.Z.; Kolobov, Y.R.; Lotkov, A.I.; Pushin, V.G.; Bakach, G.P.; Gunderov, D.V.; Dyupin, A.P.; Kuranova, N.N. On the nature of anomalously high plasticity of high-strength titanium nickelide alloys with shape memory effects: II. Phys. Met. Metallogr. 2009, 107, 298–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunderov, D.V.; Kuranova, N.N.; Luk’yanov, A.V.; Uksusnikov, A.N.; Prokof’ev, E.A.; Yurchenko, L.I.; Valiev, R.Z.; Pushin, V.G. Application of Severe Plastic Deformation by Torsion to form amorphous and nanocrystalline states in large-size TiNi alloy sample. Phys. Met. Metallogr. 2009, 108, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuranova, N.N.; Gunderov, D.V.; Uksusnikov, A.N.; Luk’yanov, A.V.; Yurchenko, L.I.; Prokof’ev, E.A.; Pushin, V.G.; Valiev, R.Z. Effect of heat treatment on the structural and phase transformations and mechanical properties of TiNi alloy subjected to severe plastic deformation by Torsion. Phys. Met. Metallogr. 2009, 108, 556–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuranova, N.N.; Makarov, V.V.; Pushin, V.G.; Uksusnikov, A.N.; Valiev, R.Z.; Gunderov, D.V.; Lukyanov, A.V.; Prokofiev, E.A. Amorphization of bulk TiNi-based alloys by severe plastic deformation under high pressure torsion. Bull. Russ. Acad. Sci. Physics 2009, 73, 1117–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuranova, N.N.; Pushin, V.G.; Uksusnikov, A.N.; Yurchenko, L.I.; Gunderov, D.V.; Valiev, R.Z. Effect of severe plastic deformation on the phase and structural transformations and mechanical properties of metastable austenitic Ti-Ni alloys. Russ. Metall. 2010, 2010, 296–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunderov, D.; Kuranova, N.; Lukyanov, A.; Makarov, V.; Prokofiev, E.; Pushin, A. Structure and Properties of Ageing and Nonageing Alloys Ti49.4Ni50.6 and Ti50.2Ni49.8 Subjected to High Pressure Torsion. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2010, 25, 58–66. [Google Scholar]
- Prokoshkin, S.; Brailivski, V.; Korotitskiy, A.; Inaekyan, K.; Dubinsky, S.; Filonov, M.; Petrzhic, M. Formation of Nanostructures in Thermo-Mechanically-Treated Ti-Ni and Ti-Nb-(Zr, Ta) SMAs and Their Roles in Martensite Crystal Lattice Changes and Mechanical Behavior. Alloy. Comp. 2011, 509, 2066–2075. [Google Scholar]
- Pushin, V.G.; Kuranova, N.N.; Kourov, N.I.; Valiev, R.Z.; Valiev, E.Z.; Makarov, V.V.; Pushin, A.V.; Uksusnikov, A.N. Baroelastic shape memory effects in titanium nickelide alloys subjected to plastic deformation under high pressure. Tech. Phys. 2012, 57, 1106–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiang, S.; Hu, L.; Liang, Y. Deformation Mechanism of NiTi Shape Memory Alloy Subjected to Severe Plastic Deformation at Low Temperature. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 559, 606–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushin, V.G.; Valiev, R.Z.; Valiev, E.Z.; Kourov, N.I.; Kuranova, N.N.; Makarov, V.V.; Pushin, A.V.; Uksusnikov, A.N. Phase and structural transformations in the Ti49.5Ni50.5 alloy with a shape memory effect during torsion under high pressure. Phys. Met. Metallogr. 2012, 113, 256–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushin, V.G.; Kuranova, N.N.; Kourov, N.I.; Valiev, R.Z.; Korolev, A.V.; Makarov, V.V.; Pushin, A.V.; Uksusnikov, A.N. Effect of Heat Treatment on Structural and Phase Transformations in the Ti49.5Ni50.5 Alloy Amorphized by High-Pressure Torsion. Phys. Met. Metallogr. 2013, 114, 488–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dye, D.; Azeem, M.A. In Situ Evaluation of the Transformation Behaviour of NiTi-based High Temperature Shape Memory Alloys. Intermetallics 2014, 46, 222–230. [Google Scholar]
- Shahmir, H.; Nili-Ahmadabadi, M.; Huang, Y.; Jung, J.M.; Kim, H.S.; Langdon, T.G. Shape Memory Effect in Nanocrystalline NiTi Alloy Processed by High Pressure Torsion. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 626, 203–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokoshkin, S.; Dubinsky, S.; Brailivski, V.; Korotitskiy, A.; Konopatsky, A.; Sheremetyev, V.; Blinova, E. Nanostructures and Stress-Induced Phase Transformation Mechanism in Titanium Nickelide annealed after Moderate Cold Deformation. Mater. Lett. 2017, 192, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulic, S.; Kerber, M.; Matsuda, M.; Waitz, T. Phase Transformations of Severely Plastically Deformed Ti-Ni-Pd High-Temperature Shape Memory Alloys. Funct. Mater. Lett. 2017, 10, 1740012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokoshkin, S.; Dubinsky, S.; Korotitskiy, A.; Konopatsky, A.; Sheremetyev, V.; Schetitin, I.; Gleser, A.; Brailivski, V. Nanostructure Features and Stress-Induced Transformation Mechanisms in Extremely Fine-Grained Titanium Nickelide. J. Alloy. Comp. 2019, 770, 667–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushin, V.G. (Ed.) Shape Memory Alloys of Titanium Nickelide: Structure, Phase Transformations and Properties; UrO RAN: Yekatirinburg, Russia, 2006. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Satija, S.K.; Shapiro, S.M.; Salamon, M.B.; Wayman, C.M. Phonon Softening in Ni46.8Ti50Fe3.2. Phys. Rev. B 1984, 29, 6031–6035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moine, P.; Allain, J.; Renker, B. Observation of a soft-phonon mode and a premartensitic phase in the intermetallic compound Ti50Ni47Fe3 studied by inelastic neutron scattering. J. Phys. F Met. Phys. 1984, 14, 2517–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tietzet, H.; Miillner, M.; Renker, B. Dynamical properties of premartensitic NiTi. J. Phys. C Solid State Phys. 1984, 17, L520–L532. [Google Scholar]
- Salamon, M.B.; Meichle, M.E.; Wayman, C.M. Premartensitic Phases of Ti50Ni47Fe3. Phys. Rev. B 1985, 31, 7306–7315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.M.; Wang, Y.U.; Ren, Y. Theory and experimental evidence of phonon domains and their roles in pre-martensitic phenomena. Comput. Mater. 2015, 1, 15002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Luo, J.; Lee, C.; Shen, Y.; Li, C.; Ma, X.; Lee, M. Mechanisms of stress-induces martensitic transformation and transformation-induced plasticity in NiTi shape memory alloy related to superelastic stability. Scripta Met. 2022, 217, 114775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








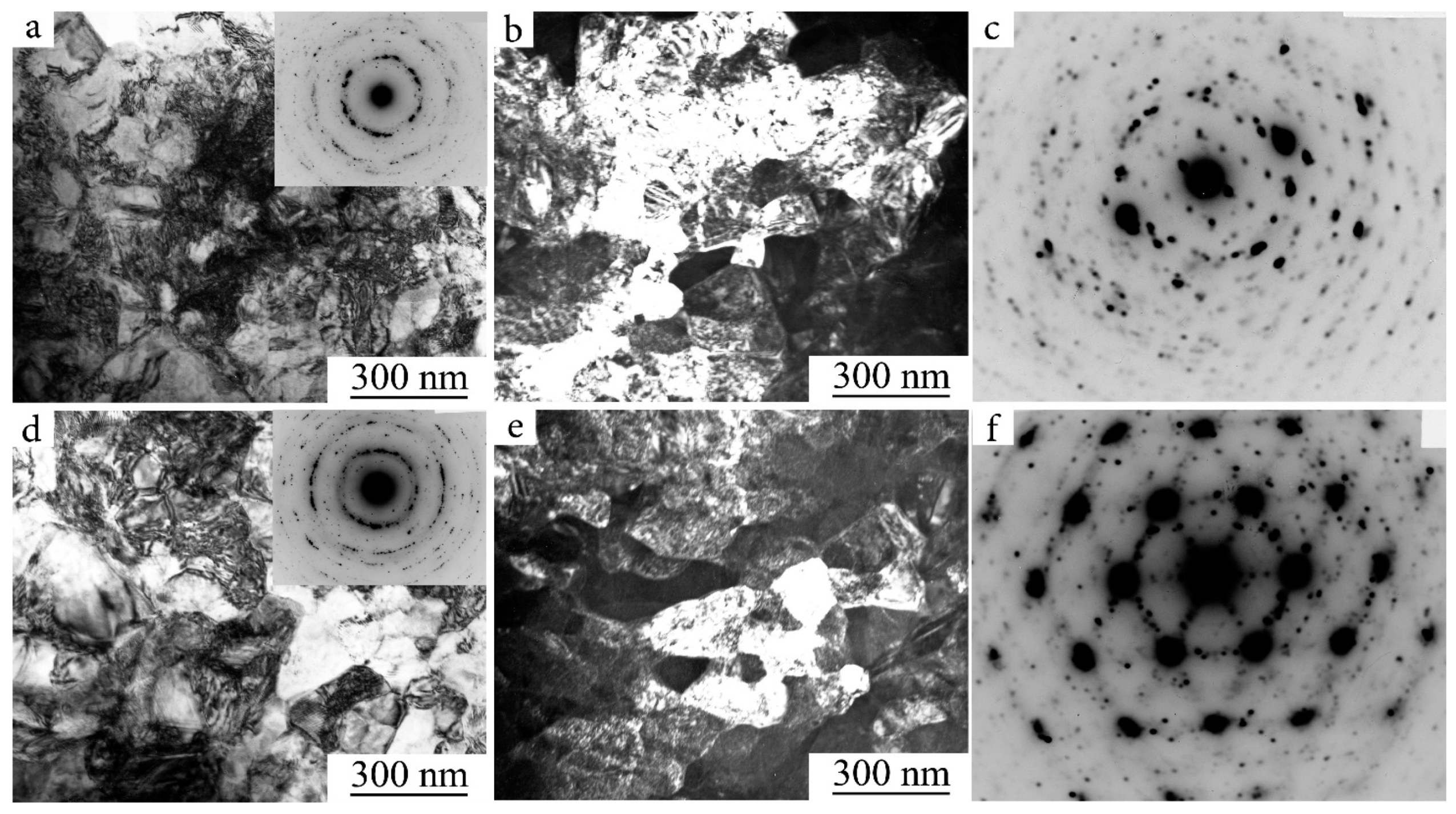
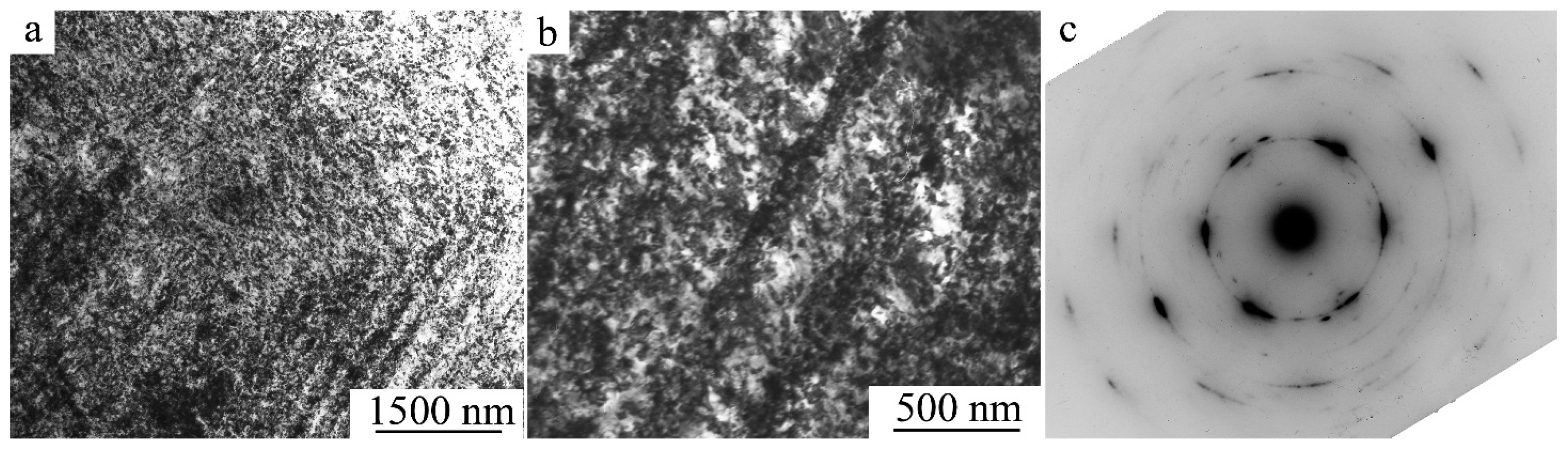
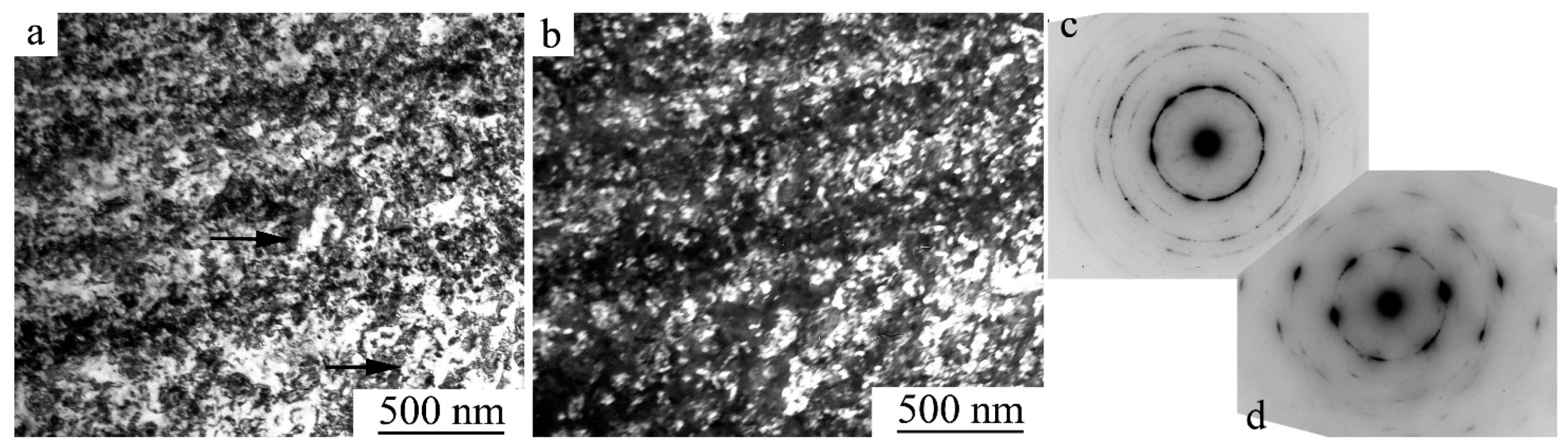
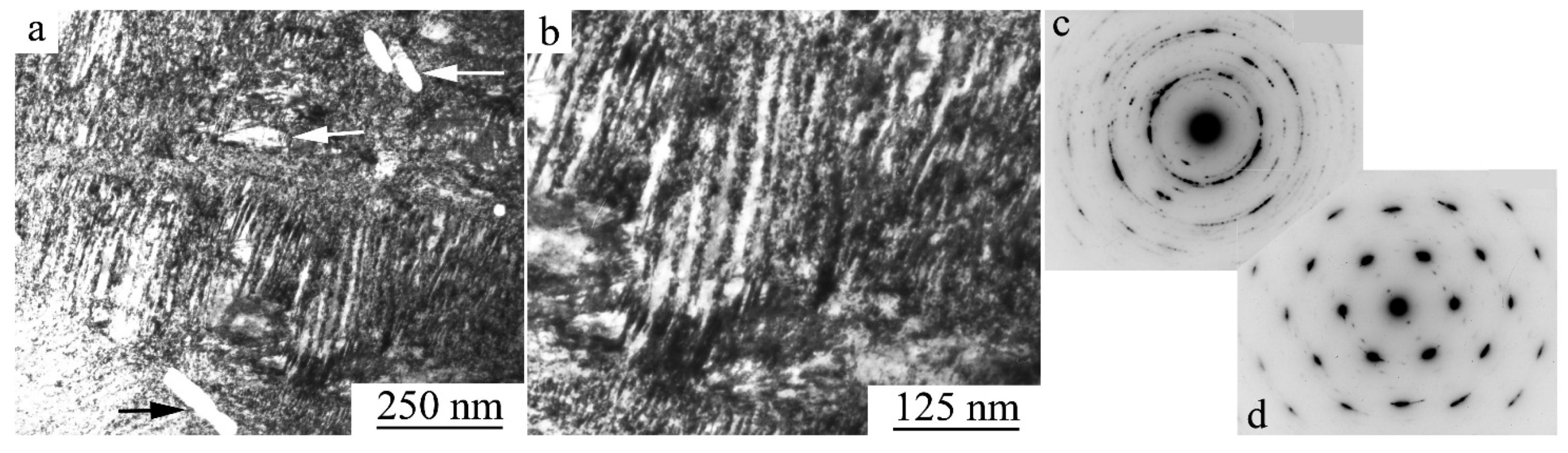
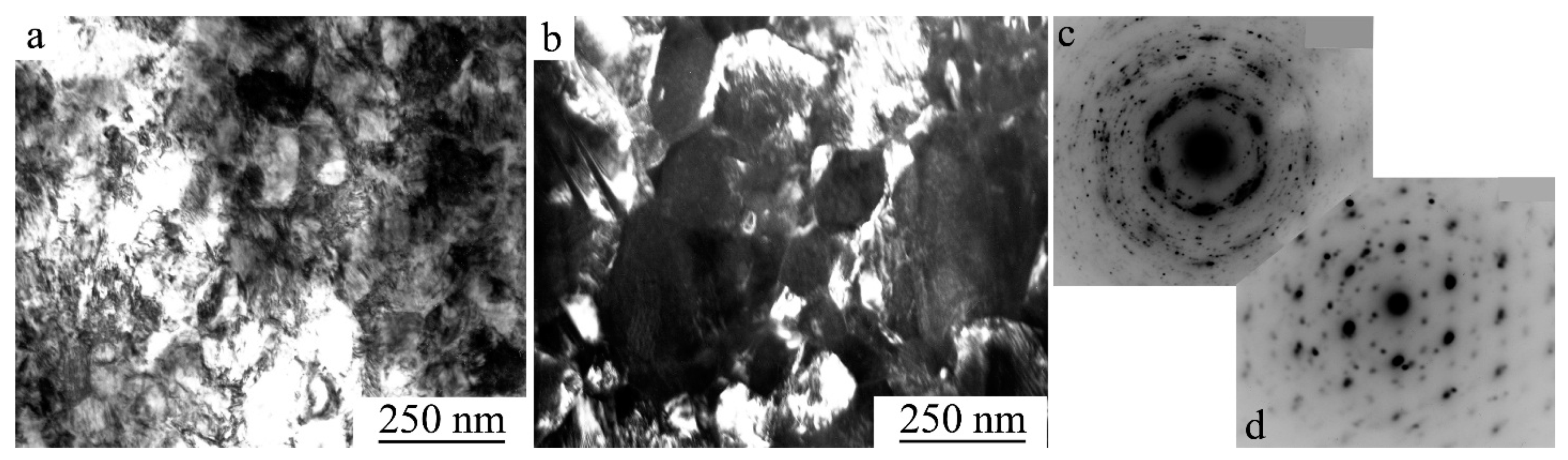
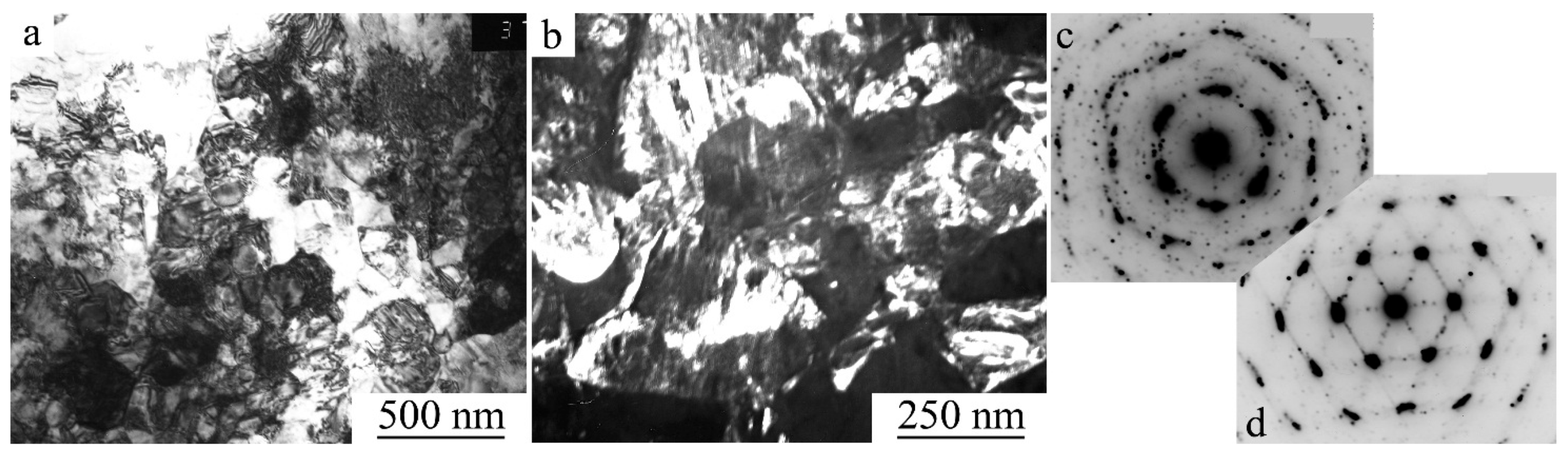



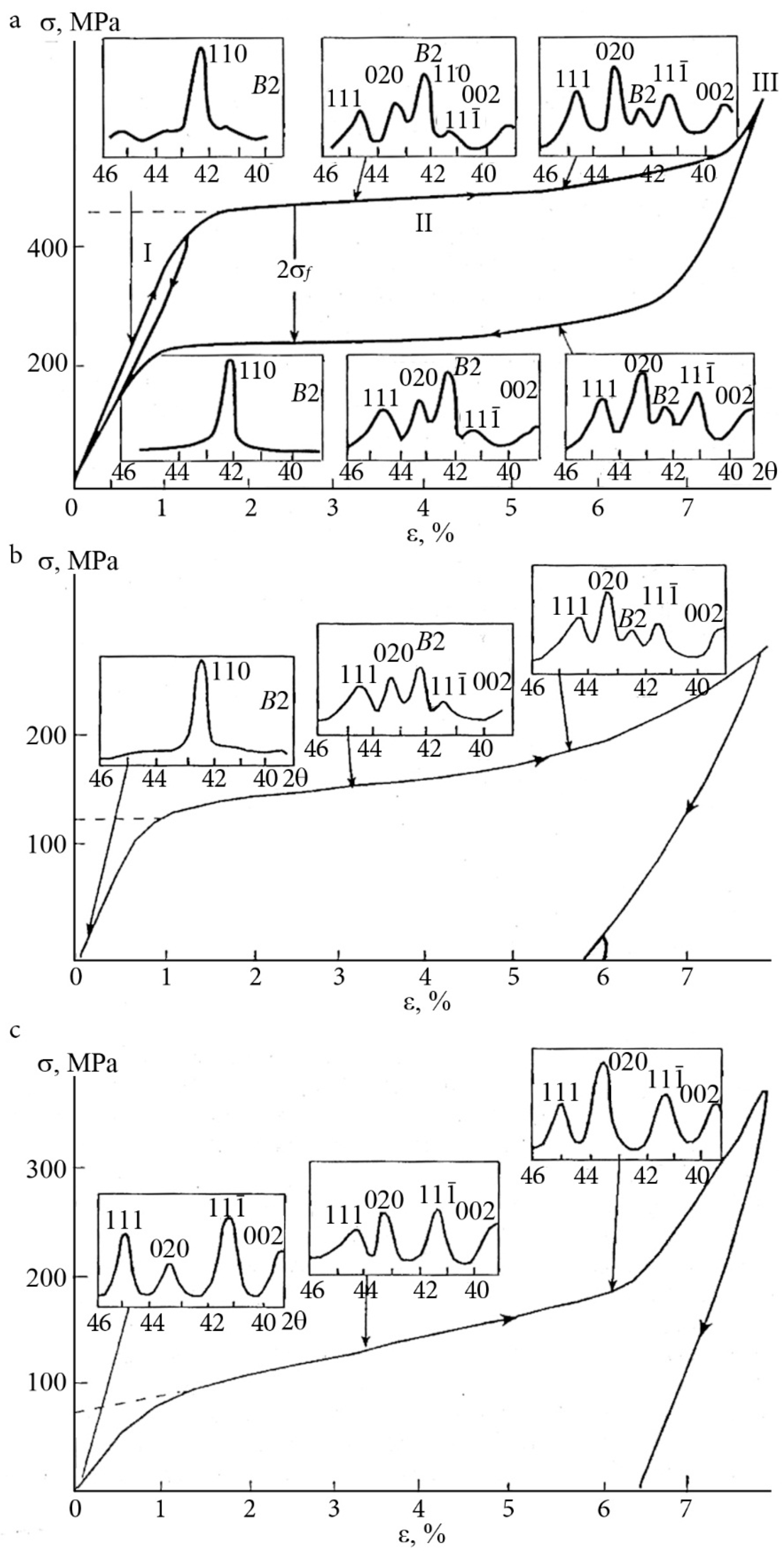
| Nominal Composition | Ti49.8Ni50.2 | Ti49.5Ni50.5 | Ti49.4Ni50.6 | Ti49Ni51 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Ti49.76Ni50.24 | Ti49.48Ni50.52 | Ti49.39Ni50.61 | Ti49.08Ni50.92 |
| O, wt.% | 0.070 | 0.070 | 0.017 | 0.070 |
| C, wt.% | 0.100 | 0.100 | 0.037 | 0.100 |
| d, μm | 80 | 50 | 40 | 40 |
| Ms, K | 320 | 290 | 290 | 220 |
| Mf, K | 290 | 260 | 270 | 180 |
| As, K | 330 | 305 | 300 | 240 |
| Af, K | 350 | 325 | 310 | 270 |
| ΔT *, K | 30 | 35 | 25 | 35 |
| Production | IMP, Ekaterinburg or Mateks, Moscow, Russia | IMP, Russia | Intrinsic Devices Inc., San Francisco, CA, USA | IMP, Russia |
| State | Sm, MPa | Sy, MPa | Su, MPa | Sr, MPa | εr, % | ψ, % | δu, % | δ, % | KIII, MPa | KIV, MPa | KV, MPa | d, μm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CG | 130 | 630 | 1630 | 500 | 5 | 62 | 63 | 72 | 3200 | 6600 | 3000 | 40 |
| UFG | 260 | 1180 | 1600 | 920 | 8 | 68 | 53 | 60 | 6000 | 11,500 | 1500 | 0.25 |
| Treatment | σm, MPa | σy, MPa | σu, MPa | σr, MPa | εr, % | δ, % | d, μm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quenching | 150 | 560 | 950 | 310 | 11 | 60 | 80 |
| 723 K, 1 pass | 200 | 750 | 1100 | 550 | 11 | 63 | 0.47 |
| 723 K, 4 passes | 280 | 1000 | 1220 | 720 | 5 | 50 | 0.45 |
| 723 K, 8 passes | 250 | 1120 | 1250 | 870 | 7 | 43 | 0.24 |
| 723 K, 12 passes | 300 | 1350 | 1410 | 1050 | 9 | 41 | 0.23 |
| 723 K, 8 passes + PDHT 773 K, 1 h | 350 | 1120 | 1260 | 810 | 5 | 65 | 0.28 |
| 723 K, 8 passes + PDHT 873 K, 1 h | 250 | 820 | 1150 | 620 | 6 | 78 | 3.40 |
| Treatment | σm, MPa | σy, MPa | σu, MPa | σr, MPa | εr, % | δ,% | d, μm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quenching | 160 | 500 | 1040 | 340 | 8 | 78 | 40 |
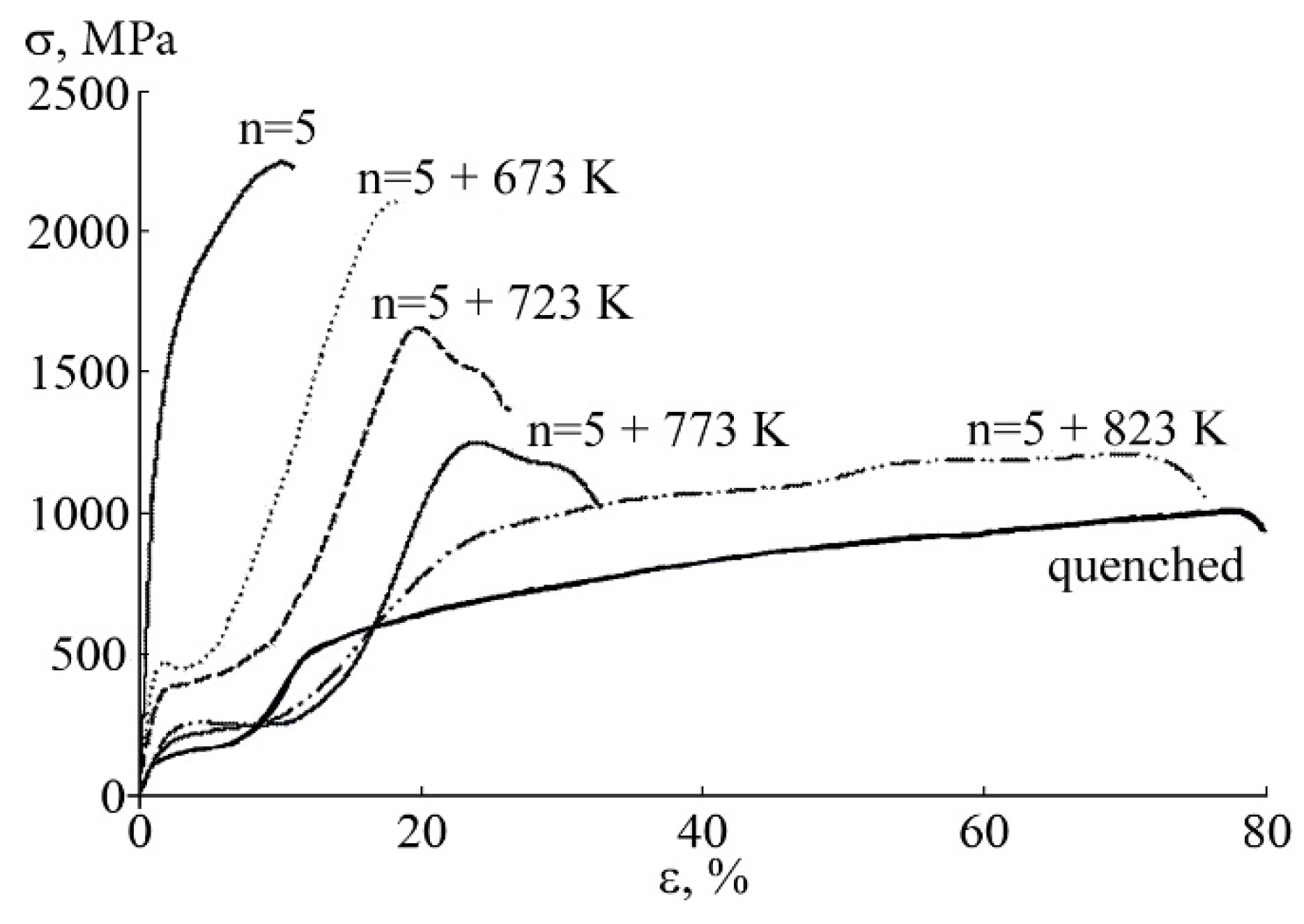
| n = 5 rev | - | 1500 | 2250 | - | 8 | A + NC | |
| n = 5 rev + PDHT 673 K, 1 h | 460 | 1800 | 2100 | 1340 | 5 | 15 | 0.03 |
| n = 5 rev + PDHT 723 K, 1 h | 370 | 1500 | 1670 | 1130 | 10 | 25 | 0.04 |
| n = 5 rev + PDHT 773 K, 1 h | 200 | 1120 | 1250 | 920 | 15 | 30 | 0.06 |
| n = 5 rev + PDHT 823 K, 1 h | 250 | 900 | 1210 | 650 | 12 | 75 | 0.6 |
| Treatment | σm, MPa | σy, MPa | σu, MPa | σr, MPa | δ, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| quenching | - | 550 | 940 | - | 42 |
| HT 373 K, 1 h | - | 530 | 920 | - | 43 |
| HT 473 K, 1 h | - | 520 | 870 | - | 31 |
| HT 573 K, 1 h | - | 530 | 850 | - | 21 |
| HT 673 K, 1 h | 350 | 800 | 1210 | 450 | 25 |
| HT 773 K, 1 h | 310 | 770 | 1180 | 460 | 36 |
| HT 873 K, 1 h | - | 510 | 970 | - | 44 |
| HT 973 K, 1 h | - | 530 | 870 | - | 41 |
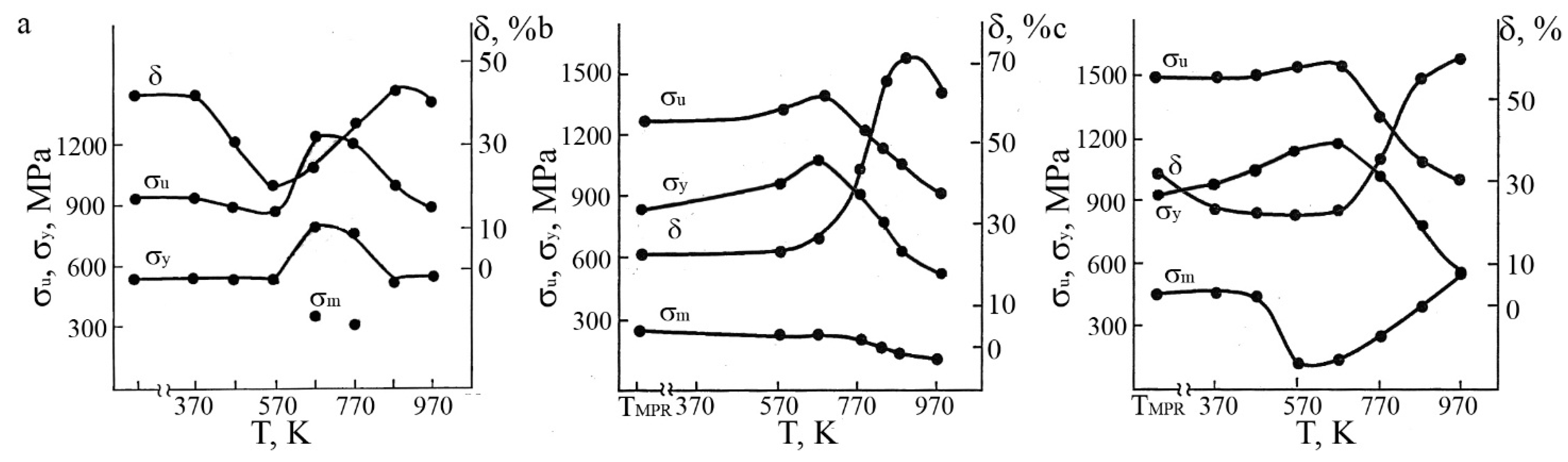
| Treatment | σm, MPa | σy, MPa | σu, MPa | σr, MPa | δ, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti49.8Ni50.2 | |||||
| quenching | 150 | 600 | 970 | 450 | 55 |
| MPR 30% | 240 | 830 | 1260 | 590 | 25 |
| MPR + PDHT 573 K | 200 | 900 | 1220 | 700 | 30 |
| MPR + PDHT 773 K | 180 | 790 | 1140 | 610 | 45 |
| MPR + PDHT 973 K | 140 | 610 | 980 | 470 | 50 |
| Ti49.5Ni50.5 | |||||
| quenching | 180 | 590 | 930 | 410 | 60 |
| MPR 30% | 250 | 840 | 1270 | 590 | 22 |
| MPR 30% + PDHT 573 K | 230 | 960 | 1320 | 730 | 25 |
| MPR 30% + PDHT 673 K | 235 | 1070 | 1390 | 835 | 30 |
| MPR 30% + PDHT 773 K | 210 | 900 | 1210 | 690 | 45 |
| MPR 30% + PDHT 823 K | 170 | 780 | 1130 | 610 | 65 |
| MPR 30% + PDHT 873 K | 140 | 620 | 1040 | 480 | 70 |
| MPR 30% + PDHT 973 K | 120 | 530 | 910 | 410 | 62 |
| Ti49Ni51 | |||||
| quenching | - | 550 | 940 | - | 42 |
| MPR 30% | 450 | 920 | 1490 | 470 | 30 |
| MPR + PDHT 373 K | 460 | 980 | 1500 | 520 | 25 |
| MPR + PDHT 473 K | 450 | 1050 | 1510 | 600 | 25 |
| MPR + PDHT 573 K | 130 | 1150 | 1550 | 1020 | 25 |
| MPR + PDHT 673 K | 150 | 1180 | 1550 | 1030 | 25 |
| MPR + PDHT 773 K | 260 | 1020 | 1320 | 760 | 35 |
| MPR + PDHT 873 K | 400 | 780 | 1100 | 380 | 55 |
| MPR + PDHT 973 K | - | 560 | 1010 | - | 60 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kuranova, N.N.; Makarov, V.V.; Pushin, V.G.; Ustyugov, Y.M. Influence of Heat Treatment and Deformation on the Structure, Phase Transformation, and Mechanical Behavior of Bulk TiNi-Based Alloys. Metals 2022, 12, 2188. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12122188
Kuranova NN, Makarov VV, Pushin VG, Ustyugov YM. Influence of Heat Treatment and Deformation on the Structure, Phase Transformation, and Mechanical Behavior of Bulk TiNi-Based Alloys. Metals. 2022; 12(12):2188. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12122188
Chicago/Turabian StyleKuranova, Nataliya N., Vladimir V. Makarov, Vladimir G. Pushin, and Yurii M. Ustyugov. 2022. "Influence of Heat Treatment and Deformation on the Structure, Phase Transformation, and Mechanical Behavior of Bulk TiNi-Based Alloys" Metals 12, no. 12: 2188. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12122188
APA StyleKuranova, N. N., Makarov, V. V., Pushin, V. G., & Ustyugov, Y. M. (2022). Influence of Heat Treatment and Deformation on the Structure, Phase Transformation, and Mechanical Behavior of Bulk TiNi-Based Alloys. Metals, 12(12), 2188. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12122188






