Crystal Chemistry and Physical Properties of A Quaternary Intermetallic Compound, θ-(Al0.8718Cu0.0256Si0.1026)13Fe4
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Si Solution in θ-Al76Cu2Fe24
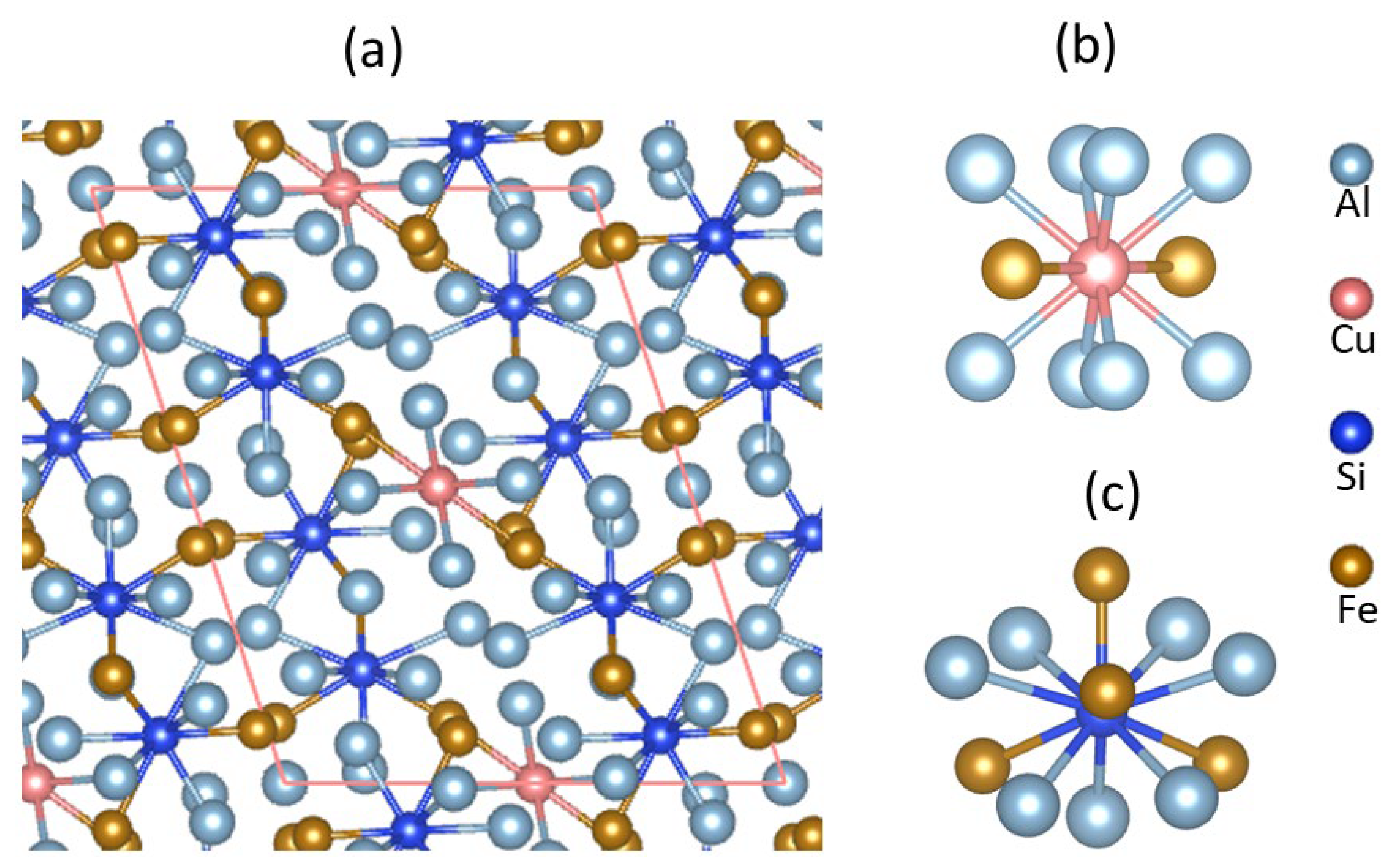
3.2. Crystal Chemistry of θ-Al68Cu2Si8Fe24
3.3. Electronic Properties of θ-Al68Cu2Si8Fe24
- (1)
- Al atoms have few electrons around them, corresponding to their metallic nature, as such metals are composed of free electrons and ions. Bader’s charge analysis showed the Al atoms are positively charged with a loss of 1.1 e/Al to 1.5 e/Al (Table 2).
- (2)
- (3)
- Fe atoms also exhibit irregularly shaped clouds of high densities, indicating interactions between Fe 3d states with neighboring atoms, including Si, Cu and Al. Bader charge analysis showed more significant electron gains for the Fe atoms with charges ranging between −2.82 e/Fe and −3.54 e/Fe, corresponding to its electronegativity value being larger than Al. Correspondingly, the Fe atoms are non-spin-polarized in the compounds.
- (4)
- Si atoms have high electron density around them, and they connect to Fe atoms, forming Si-Fe and Si-Fe-Cu clusters. They are negatively charged with −0.9 e/Si8 to −1.2 e/Si9 from the neighboring Al atoms.
- (5)
- The number of charge transfers between the atoms, Al, Cu, and Si also indicate the covalent nature of θ-Al68Cu2Si8Fe24.
3.4. Stability and Mechanical Properties of the θ-Phases
3.5. Formation Range and Stability of θ-(Al76-nSinCu2)Fe24 at Casting Temperature
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mondolfo, L.F. Aluminum Alloys: Structure and Properties; Butterworths: London, UK, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.F.; Gao, J.W.; Nana, L.; Damoah, W.; Robertson, D.G. Removal of iron aluminum: A review. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 2012, 33, 99–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glazoff, M.V.; Khvan, A.V.; Zolotorevsky, V.S.; Belov, N.A.; Dinsdale, A.T. Casting Aluminum Alloys, Their Physical and Mechanical Metallurgy; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK; Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Stefániay, V.; Griger, A.; Turmezey, T. Intermetallic phases in the aluminium-side corner or the AlFeSi-alloy system. J. Mater. Sci. 1987, 22, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabestari, S.G. The effect of iron and manganese on the formation of intermetallic compounds in aluminum-silicon alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 383, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marker, M.C.J.; Skolyszewska-Kühberger, B.; Effenberger, H.S.; Schmetterer, C.; Richter, K.W. Phase equilibria and structural investigations in the system Al-Fe-Si. Intermetallics 2011, 19, 1919–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Que, Z.P.; Mendis, C.L. Formation of θ-Al13Fe4 and the multi-step phase transformations to α-Al8Fe2Si, β-Al5FeSi and δ-Al4FeSi2 in Al-20Si-0.7Fe alloy. Intermetallics 2020, 127, 106960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Que, Z.; Wang, Y.; Fan, Z. Formation of the Fe-Containing Intermetallic Compounds during Solidification of Al-5Mg-2Si-0.7Mn-1.1Fe Alloy. Met. Mater. Trans. A 2018, 49, 2173–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taylor, J. Iron-Containing Intermetallic Phases in Al-Si Based Casting Alloys. Procedia Mater. Sci. 2012, 1, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khalifa, W.; Samuel, F.H.; Gruzleski, J.E. Iron intermetallic phases in the Al corner of the Al-Si-Fe system. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2003, 34, 807–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krendelsberger, N.; Weitzer, F.; Schuster, J.C. On the Reaction Scheme and Liquidus Surface in the Ternary System Al-Fe-Si. Met. Mater. Trans. A 2007, 38, 1681–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlesinger, M.E. Aluminum Recycling; Taylor & Francis Group: Oxfordshire, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Gesing, A.; Berry, L.; Dalton, R.; Wolanski, R. Assuring continued recyclability of automotive aluminum alloys: Grouping of wrought alloys by color, X-ray adsorption and chemical composition-based sorting. In Proceedings of the TMS 2002 Annual Meeting: Automotive Alloys and Aluminum Sheet and Plate Rolling and Finishing Technology Symposia, Seattle, WA, USA, 17–21 February 2002; pp. 3–17. [Google Scholar]
- Raabe, D.; Ponge, D.; Uggowitzer, P.J.; Roscher, M.; Paolantonio, M.; Liu, C.L.; Antreckowitsch, H.; Kozenschnik, E.; Seidmann, D.; Gault, B.; et al. Making sustainable aluminum by recycling scrap: The science of “dirtyȍ alloys”. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2022, 128, 100947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.-C.; Gao, F.; Ji, S.-X. Formation and sedimention of Fe-rich intermetallics in Al-Si-Cu-Fe alloy. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2015, 25, 1704–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sundman, B.; Ohnuma, I.; Dupin, N.; Kattner, U.R.; Fries, S.G. An assessment of the entire Al–Fe system including D03 ordering. Acta Mater. 2009, 57, 2896–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zienert, T.; Fabrichnaya, O. Experimental investigation and thermodynamic assessment of the Al-Fe system. J. Alloy. Compd. 2018, 743, 795–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.L.; Scherf, A.; Heilmaier, M.; Stein, F. The Al-rich part of the Fe-Al phase diagram. JPEDAV 2016, 37, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grin, J.; Burkhard, U.; Ellner, M.; Peters, K. Refinement of the Fe4Al13 structure and its relationship to the quasihomogical homeotypical structures. Z. Kristal. 1994, 209, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitoh, K.; Yokosawa, T.; Tanaka, M.; Tsai, A.P. Structural studied of monoclinic approximants of Al13Fe4 and τ2-inflated Al13Co4 by the high-angle annular dark-field method. J. Electron Microsc. 1999, 48, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popčević, P.; Smontara, A.; Ivkov, J.; Wencka, M.; Komelj, M.; Jeglič, P.; Vrtnik, S.; Bohnar, M.; Jagličić, Z.; Baer, B.; et al. Anisotropic physical properties of the Al13Fe4 complex intermetallic and its ternary derivative Al13(Fe, Ni)4. Phys. Rev. B 2010, 81, 184203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeglič, P.; Vrtnik, S.; Bobnar, M.; Klanjšek, M.; Bauer, B.; Gille, P.; Grin, Y.; Haarmann, F.; Dolinšek, J. M-Al-M groups trapped in cages of Al13M4 (M = Co, Fe, Ni, Ru) complex intermetallic phases as seen via NMR. Phys. Rev. B 2010, 82, 104201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafaye, P.; Oishi, K.; Bourdon, M.; Harvey, J.-P. Crystal chemistry and thermodynamic modelling of the Al13(Fe,TM)4 solid solutions (TM = Co, Cr, Ni, Pt). J. Alloy. Compd. 2022, 920, 165779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freiburg, C.; Grushko, B. An Al13Fe4 phase in the Al-Cu-Fe alloy system. J. Alloys Compd. 1994, 210, 149–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genba, M.; Sugiyama, K.; Hiraga, K.; Yokoyama, Y. Crystalline structure of a Cu-substituted λ-Al13Fe4 phase by means of the anomalous X-ray scattering. J. Alloy. Compd. 2002, 342, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, H.; Bulut, N.; Kortus, J.; Leineweber, A. β-Al4.5FeSi: Hierarchical crystal and defect structure: Reconciling experimental and theoretical evidence including the influence of Al vs. Si ordering on the crystal structure. J. Alloy. Compd. 2022, 911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.M.; Que, Z.P.; Fan, Z. Crystal chemistry and electronic structure of the β-AlFeSi phase from first-principles. Solid State Chem. 2021, 299, 122199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zienert, T.; Leineweber, A.; Fabrichnaya, O. Heat capacity of Fe-Al intermetallics: B2-FeAl, FeAl2, Fe2Al5 and Fe4Al13. J. Alloy. Compd. 2017, 725, 848–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.K.; Krajčí, M.; Sarkar, S.; Bala, M.; Barman, S.; Sadhukhan, P.; Gloskovskii, A.; Feuerbacher, M.; Barman, S.R. Electronic structure of β-Al3Mg2 and Al13Fe4 complex metallic alloys. Phys. Rev. B 2022, 105, 205107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Alboom, A.; Lemmens, B.; Breitbach, B.; De Grave, E.; Cottenier, S.; Verbeken, K. Multi-method identification and characterization of the intermetallic surface layers of hot-dip Al-coated steel: FeAl 3 or Fe 4 Al 13 and Fe 2 Al 5 or Fe 2 Al 5+x. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 324, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledieu, J.; Gaudry, Ė.; Loli, L.N.; Villaseca, S.A.; de Weerd, M.C.; Hahne, M.; Gille, P.; Dubois, J.M.; Fournée, V. Structural investigation of the (010) surface of the Al13Fe4 catalyst. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 110, 076102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Armbrüster, M.; Kovnir, K.; Friedrich, M.; Teschner, D.; Wowsnick, G.; Hahne, M.; Gille, P.; Szentmiklósi, L.; Feuerbacher, M.; Heggen, M.; et al. Al13Fe4 as a low-cost alternative for palladium in heterogeneous hydrogenation. Nat. Mater. 2012, 11, 690–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, C.M.; Dinsdale, A.T.; Que, Z.P.; Fan, Z. Intrinsic defects in and electronic properties of θ-Al13Fe4: An ab initio DFT study. J. Phys. Mater. 2019, 2, 015004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinsdale, A.; Fang, C.; Que, Z.; Fan, Z. Understanding the Thermodynamics and Crystal Structure of Complex Fe Containing Intermetallic Phases Formed on Solidification of Aluminium Alloys. JOM 2019, 71, 1731–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Que, Z.; Dinsdale, A.; Fan, Z. Si solution in θ-Al13Fe4 from first-principles. Intermetallics 2020, 126, 106939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Souissi, M.; Que, Z.; Fan, Z. Crystal Chemistry and Electronic Properties of the Al-Rich Compounds, Al2Cu, ω-Al7Cu2Fe and θ-Al13Fe4 with Cu Solution. Metals 2022, 12, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresse, G.; Hafner, J. Ab initio molecular-dynamics simulation of the liquid-metal-amorphous-semiconductor transition in germanium. Phys. Rev. B 1994, 49, 14251–14269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kresse, G.; Furthmüller, J. Efficiency of ab-initio total energy calculations for metals and semiconductors using a plane-wave basis set. Comput. Mater. Sci. 1996, 6, 15–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdew, J.P.; Burke, K.; Ernzerhof, M. Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 3865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blöchl, P.E. Projector augmented-wave method. Phys. Rev. B Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 1994, 50, 17953–17979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, C.M.; van Huis, M.A.; Sluiter, M.H.F.; Zandbergen, H.W. Stability, structure and electronic properties of γ-Fe23C6 from first-principles. Acta Mater. 2010, 58, 2968–2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.M.; Sluiter, M.H.F.; van Huis, M.A.; Ande, C.K.; Zandbergen, H.W. Origin of Predominance of Cementite among Iron Carbides in Steel at Elevated Temperature. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 105, 055503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hubbard, J. Electron correlations in narrow energy bands. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Sci. 1963, 276, 238–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liechtenstein, A.I.; Anisimov, V.; Zaanen, J. Density-functional theory and strong interactions: Orbital ordering in Mott-Hubbard insulators. Phys. Rev. B 1995, 52, R5467–R5470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souissi, M.; Fang, C.M.; Sahara, R.; Fan, Z. Formation energies of θ-Al2Cu phase and precursor Al-Cu compounds: Importance of on-site Coulomb repulsion. Comp. Mater. Sci. 2021, 194, 110461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monkhorst, H.J.; Pack, J.D. Special points for Brillouin-zone integrations. Phys. Rev. B 1976, 13, 5188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyckoff, R.W.G. The Structure of Crystals; Reinhold Publishing Corporation: New York, NY, USA, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Arblaster, J. Selected Values of the Crystallographic Properties of the Elements; ASM International: Materials Park, OH, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bader, R.F.W. A Bond Path: A Universal Indicator of Bonded Interactions. J. Phys. Chem. A 1998, 102, 7314–7323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murnaghan, F.D. The Compressibility of Media under Extreme Pressures. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1944, 30, 244–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tyuterev, V.G.; Vast, N. Murnaghan’s equation of state for the electronic ground energy. Comp. Mater. Sci. 2006, 38, 250–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Que, Z.; Wang, Y.; Mendis, C.L.; Fang, C.; Xia, J.; Zhou, X.; Fan, Z. Understanding Fe-Containing Intermetallic Compounds in Al Alloys: An Overview of Recent Advances from the LiME Research Hub. Metals 2022, 12, 1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Que, Z.; Fang, C.; Mendis, C.L.; Wang, Y.; Fan, Z. Effects of Si solution in θ-Al13Fe4 on phase transformation between Fe-containing intermetallic compounds in Al alloys. J. Alloy. Compd. 2023, 932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Si-Sites | Local Sym. | Lattice Parameters and Volume a(Å), b(Å), c(Å), β(°); V(Å3) | CNN(Si) | q(e/Si) | ΔE (eV/Cell) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| θ-Al76Cu2Fe24 | - | 15.501, 7.928, 12.459, 108.15; 1455.08 | - | - | 0.00 |
| 4Si at Al1 | 4i, m | 15.446, 7.978, 12.346, 108.24; 1444.98 | 3Fe,7Al | −0.79 | +0.48 |
| 4Si at Al2 | 4i, m | 15.449, 7.909, 12.540, 108.18; 1455.64 | 2Fe, 10Al | −0.27 | +0.95 |
| 4Si at Al3 | 4i, m | 15.373, 7.995, 12.541, 109.31; 1454.38 | 2Fe, 10Al | −0.59 | +1.25 |
| 4Si at Al4 | 4i, m | 15.412, 7.930, 12.403, 107.90; 1442.54 | 4Fe, 1Si, 6Al | −0.77 | +0.17 |
| 4Si at Al5 | 4i, m | 15.228, 7.992, 12.532, 107.60; 1453.68 | 2Fe, 10Al | −0.64 | +1.45 |
| 4Si at Al6 | 4i, m | 15.446, 7.967, 12.356, 108.37; 1443.11 | 3Fe, 7Al | −0.66 | −0.22 |
| 4Si at Al8 | 4i, m | 15.454, 7.906, 12.385, 107.97; 1439.44 | 4Fe, 7Al | −0.88 | −0.63 |
| 4Si at Al9 | 4i, m | 15.454, 7.926, 12.395, 108.27; 1441.69 | 4Fe, 7Al | −1.18 | −0.45 |
| 8Si at Al10 | 8j, 1 | 15.421, 7.959, 12.385, 109.18; 1435.65 | 3Fe, 9Al | −0.88 | +1.41 |
| 8Si at Al11 | 8j, 1 | 15.419, 7.958, 12.289, 107.70; 1436.54 | 3Fe, 9Al | −0.85 | +1.41 |
| 8Si at Al12 | 8j, 1 | 15.275, 7.943, 12.376, 107.01; 1436.02 | 3Fe, 9Al | −0.70 | +1.45 |
| 8Si at Al13 | 8j, 1 | 15.249, 7.955, 12.518, 108.78; 1437.56 | 3Fe, 1Cu, 8Al | −0.52 | +1.41 |
| 8Si at Al14 | 8j, 1 | 15.461, 7.957, 12.295, 108.21; 1436.78 | 2Fe, 1Si, 9Al | −0.79 | +0.92 |
| 4Si at Al15 | 4g, 2 | 15.422, 7.891, 12.481, 108.09; 1443.70 | 4Fe, 8Al | −0.46 | +0.50 |
| Label Sites | Coordinates of Atoms x, y, z | Interatomic Distances (Å) | q(e/atom) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Al1, 4i | 0.0657, 0.0000, 0.1709 | Al1-3Fe: 2.47, 2.50, 2.53; -1Si: 2.48; -6Al: 2.79(×2); 2.81(×2); 2.84(×2) | +1.24 |
| Al2, 4i | 0.3212, 0.0000, 0.2759 | Al2-2Fe: 2.41(×2); -10Al: 2.85(×2), 2.92(×2), 2.98(×2); 3.03(×2); 3.09(×2) | +1.17 |
| Al3, 4i | 0.2320, 0.0000, 0.5323 | Al3-4Fe: 2.41, 2.55, 3.13(×2); -1Si: 2.81 -9Al: 2.66, 2.76(×2), 2.85(×2), 2.88(×2); 2.90(×2) | +1.07 |
| Al4, 4i | 0.0740, 0.0000, 0.5784 | Al4-4Fe: 2.51, 2.56(×2), 2.57; -1Si: 2.48 -6Al: 2.49, 2.66(×3), 2.76(×2) | +1.33 |
| Al5, 4i | 0.2378, 0.0000, 0.9503 | Al5-4Fe: 2.39, 2.41, 3.05(×2); -2Si: 2.66, 2.74; -8Al: 2.74(×2), 2.76(×2), 2.87(×2), 2.90(×2) | +1.49 |
| Al6, 4i | 0.4801, 0.0000, 0.8323 | Al6-3Fe: 2.41, 2.49(×2); -1Si: 2.51; -6Al: 2.79(×2), 2.80(×2), 2.84(×2) | +1.34 |
| Cu7, 2c | 0.5000, 0.0000, 0.5000 | Cu7-2Fe: 2.64(×2); -8Al: 2.57(×4), 2.66(×4) | −1.00 |
| Si8, 4i | 0.3089, 0.0000, 0.7716 | Si8-4Fe: 2.42(×2), 2.46, 2.49; -7Al: 2.51, 2.62(×2), 2.66(×2), 2.74, 2.81 | −0.91 |
| Si9, 4i | 0.0800, 0.0000, 0.7823 | Si9-4Fe: 2.38, 2.44(×2), 2.61; -7Al: 2.48(×2), 2.63(×2), 2.66, 2.67(×2) | −1.19 |
| Al10, 8j | 0.1849, 0.2172, 0.1094 | Al10-3Fe: 2.49(×2), 2.64; -1Si: 2.66; -8Al: 2.61, 2.74, 2.76, 2.79, 2.82(×2), 2.90, 2.98 | +1.23 |
| Al11, 8j | 0.3684, 0.2131, 0.1090 | Al11-3Fe: 2.47, 2.49, 2.68; -1Si: 2.63; -8Al: 2.61, 2.76, 2.77, 2.79, 2.82, 2.83, 2.87, 2.92 | +1.26 |
| Al12, 8j | 0.1767, 0.2206, 0.3352 | Al12-3Fe: 2.46, 2.55, 2.61; -1Si: 2.62; -8Al: 2.68, 2.81, 2.82, 2.85, 2.90(×3), 3.09 | +1.22 |
| Al13, 8j | 0.4906, 0.2221, 0.3344 | Al13-3Fe:2.45,2.55, 2.61; -1Cu:2.66; -1Si:2.67 -7Al: 2.68, 2.76, 2.83, 2.84, 2.90, 2.96,3.03 | +1.34 |
| Al14, 8j | 0.3660, 0.2056, 0.4758 | Al14-2Fe: 2.46, 2.49; -1Cu: 2.57; -9Al: 2.66, 2.68(×2), 2.76, 2.85, 2.88, 2.90, 2.92, 2.96,(3.25) | +1.09 |
| Al15, 4g | 0.0000, 0.2505, 0.0000 | Al15-4Fe: 2.48(×4); -8Al: 2.76(×2), 2.77(×2), 2.80(×2), 2.84(×2) | +1.32 |
| Fe1, 4i | 0.0782, 0.0000, 0.3762 | Fe1-1Si: 2.61; -10Al: 2.46(×2), 2.47, 2.51, 2.55 (×3), 2.57,2.92(×2) | −2.91 |
| Fe2, 4i | 0.3937, 0.0000, 0.6322 | Fe2-1Cu: 2.64; -1Si: 2.46; -8Al: 2.41(×2), 2.45(×2), 2.46(×2), 2.55(×2) | −3.54 |
| Fe3, 4i | 0.0900, 0.0000, 0.9792 | Fe3-1Fe: 2.97; -1Si: 2.38; -9Al: 2.41, 2.48(×2), 2.49(×2), 2.50, 2.53, 2.68(×2) | −3.14 |
| Fe4, 4i | 0.3986, 0.0000, 0.9786 | Fe4-1Fe: 3.00; -1Si: 2.49; -9Al: 2.39, 2.47(×2),2.48(×2),2.49(×2),2.64(×2) | −3.42 |
| Fe5, 8j | 0.3185, 0.3048, 0.2738 | Fe5-1Fe: 3.09; -2Si: 2.42, 2.44; -9Al: 2.41, 2.49(×3), 2.56, 2.61(×2), 3.05, 3.13 | −2.82 |
| Site | θ-Al78Fe24 | θ-Al76Cu2Fe24 | θ-Al74Si4Fe24 | θ-Al68Cu2Si8Fe24 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M7, 2c | Al7-2Fe: 2.47(×2) -8Al: 2.69(×4),2.80(×4) | Cu7-2Fe: 2.61(×2) -8Al: 2.49(×4),2.80(×4) | Al7-2Fe: 2.46(×2) -8Al: 2.69(×4),2.79(×4) | Cu7-2Fe: 2.64(×2); -8Al: 2.57(×4), 2.66(×4) |
| M8, 4i | Al8-4Fe:2.47(×2), 2.61,2.70 -7Al: 2.56, 2.67(×4), 2.81(×2) | Al8-4Fe:2.47(×2),2.58,2.63 -7Al: 2.55, 2.66(×2), 2.67(×2), 2.79(×2) | Al8-4Fe:2.48(×2),2.59, 2.66 -7Al:2.54, 2.64(×2), 2.68(×2), 2.77, 2.84 | Si8-4Fe: 2.42(×2), 2.46, 2.49 -7Al: 2.51, 2.62(×2), 2.66(×2), 2.74, 2.81 |
| M9, 4i | Al9-4Fe:2.46,2.49(×2),2.86 -7Al: 2.53, 2.54,2.63(×2), 2.67(×3) | Al9-4Fe:2.49,2.50(×2),2.75 -7Al: 2.52 (×2), 2.52 (×2), 2.69, 2.70(×2) | Si9-4Fe: 2.37, 2.42(×2), 2.77 -7Al:2.51(×2),2.62(×2), 2.66 (×3) | Si9-4Fe: 2.38, 2.44(×2), 2.61 -7Al: 2.48(×2), 2.63(×2), 2.66,2.67(×2) |
| Composition | V0(Å3/Cell) | E0(eV/Cell) | B0(GPa) | B0′ | ΔEform (eV/cell) in () kJ/mol |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| θ-Al78Fe24 | 1466.4 | −523.54 | 121.8 | 4.3 | −33.52(−31.7) |
| θ-Al76Cu2Fe24 | 1457.2 | −521.10 | 122.5 | 4.3 | −33.84(−32.0) |
| θ-Al74Si4Fe24 | 1450.8 | −530.42 | 124.3 | 4.4 | −33.69(−31.9) |
| θ-Al72Cu2Si4Fe24 | 1439.6 | −528.45 | 127.3 | 4.2 | −34.24(−32.4) |
| θ-Al68Cu2Si8Fe24 | 1424.6 | −535.34 | 129.2 | 4.4 | −34.65(−32.8) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fang, C.; Que, Z.; Souissi, M.; Fan, Z. Crystal Chemistry and Physical Properties of A Quaternary Intermetallic Compound, θ-(Al0.8718Cu0.0256Si0.1026)13Fe4. Metals 2022, 12, 2112. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12122112
Fang C, Que Z, Souissi M, Fan Z. Crystal Chemistry and Physical Properties of A Quaternary Intermetallic Compound, θ-(Al0.8718Cu0.0256Si0.1026)13Fe4. Metals. 2022; 12(12):2112. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12122112
Chicago/Turabian StyleFang, Changming, Zhongping Que, Maaouia Souissi, and Zhongyun Fan. 2022. "Crystal Chemistry and Physical Properties of A Quaternary Intermetallic Compound, θ-(Al0.8718Cu0.0256Si0.1026)13Fe4" Metals 12, no. 12: 2112. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12122112
APA StyleFang, C., Que, Z., Souissi, M., & Fan, Z. (2022). Crystal Chemistry and Physical Properties of A Quaternary Intermetallic Compound, θ-(Al0.8718Cu0.0256Si0.1026)13Fe4. Metals, 12(12), 2112. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12122112








