The Study on Forming Property at High Temperature and Processing Map of 2219 Aluminum Alloy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiment and Result Analysis
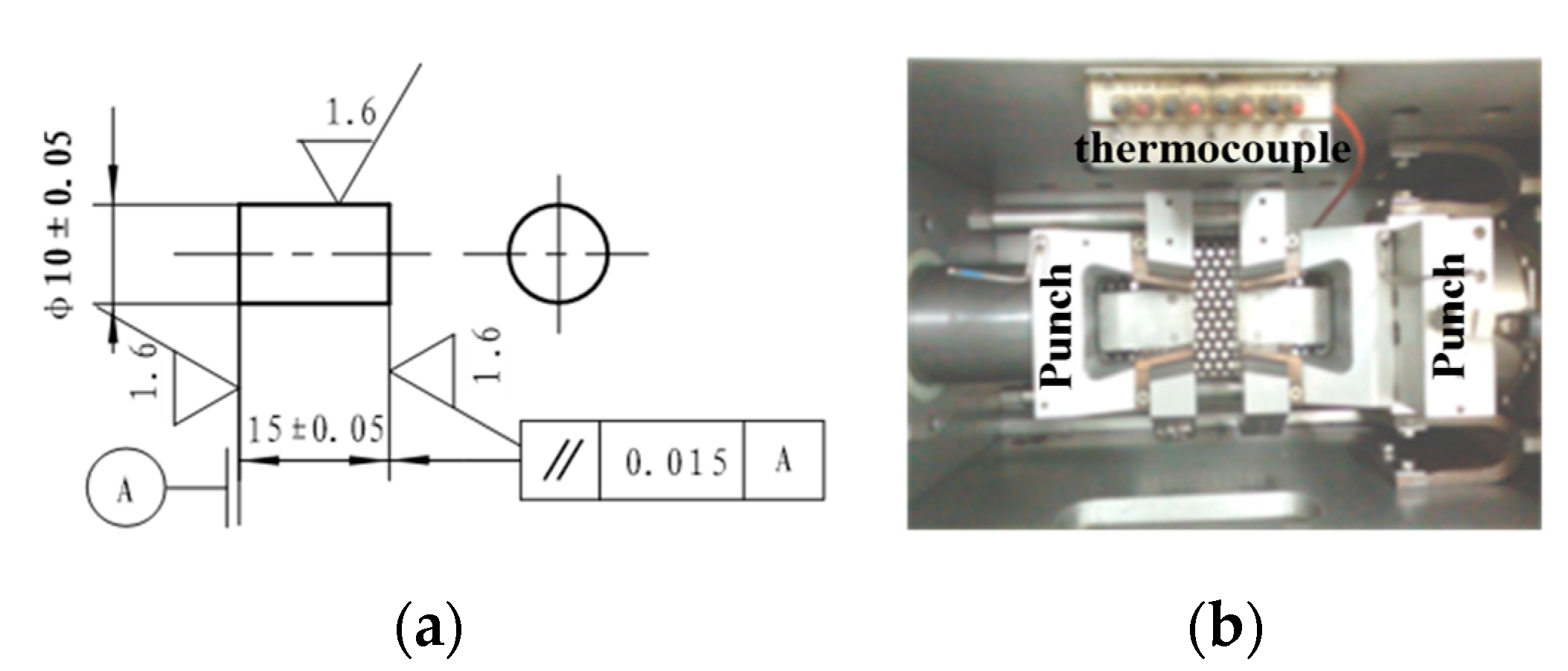
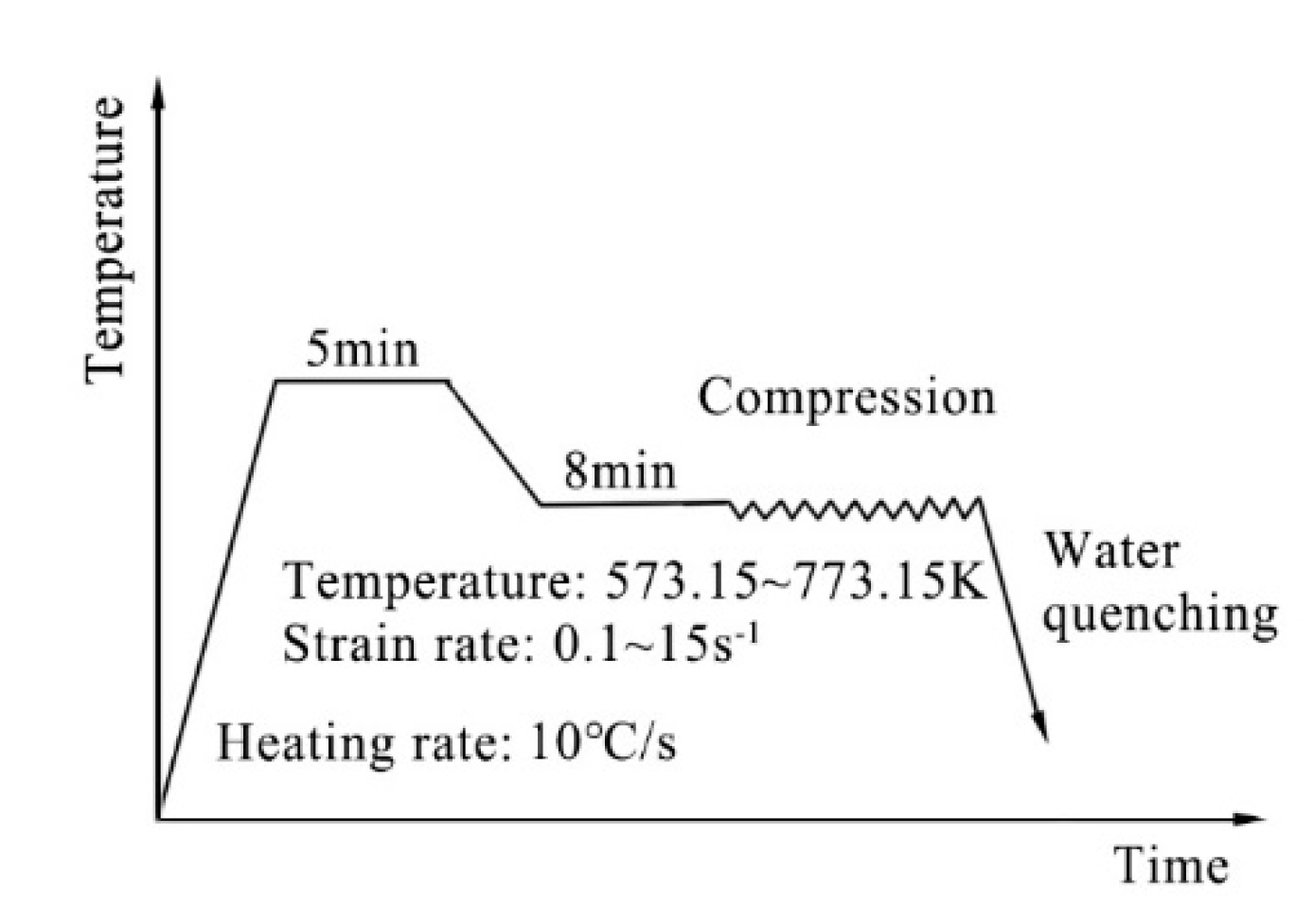
2.1. Experiment
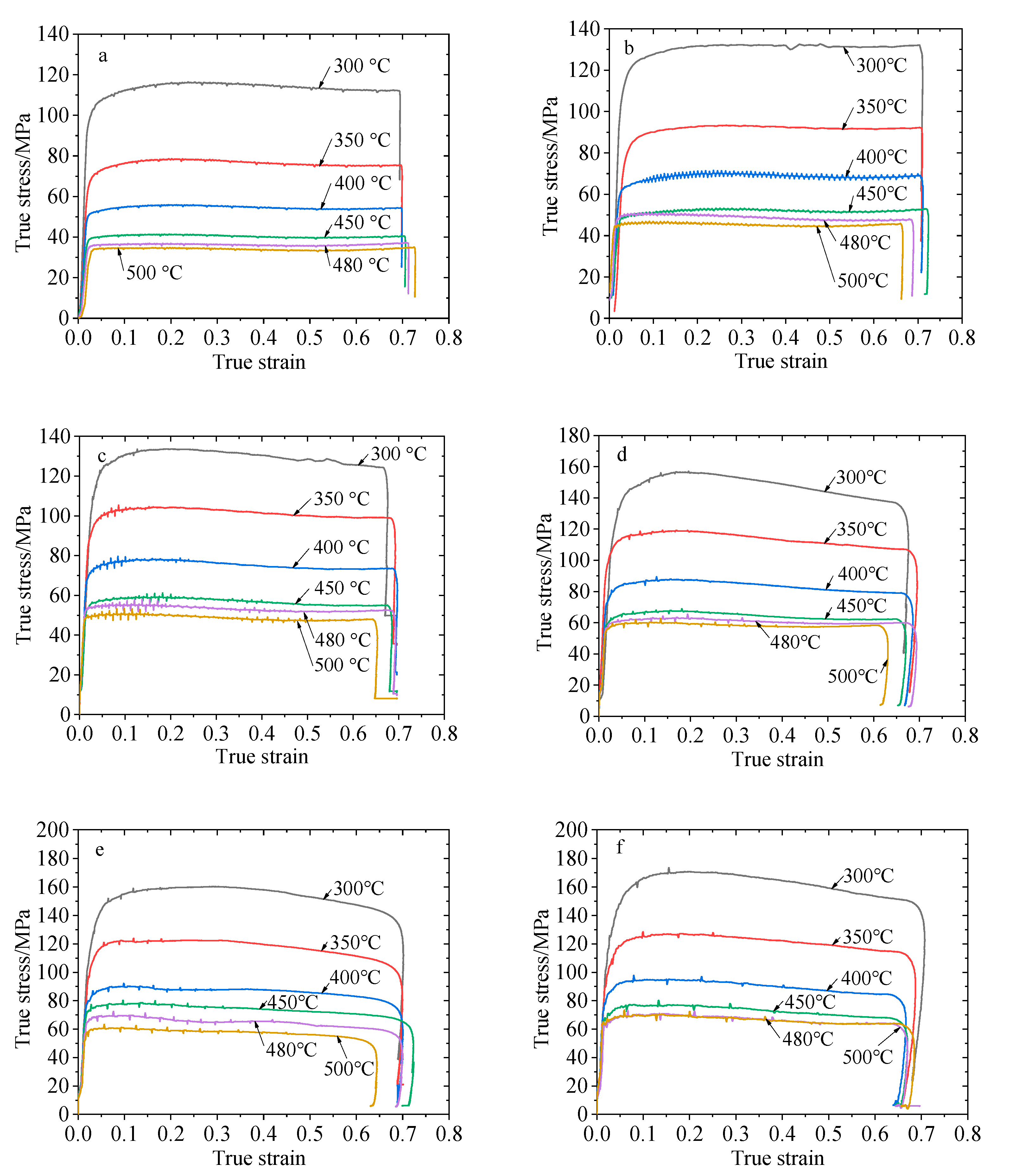
2.2. True Stress–Strain Curve
2.3. Influence of Temperature on Steady Flow Stress
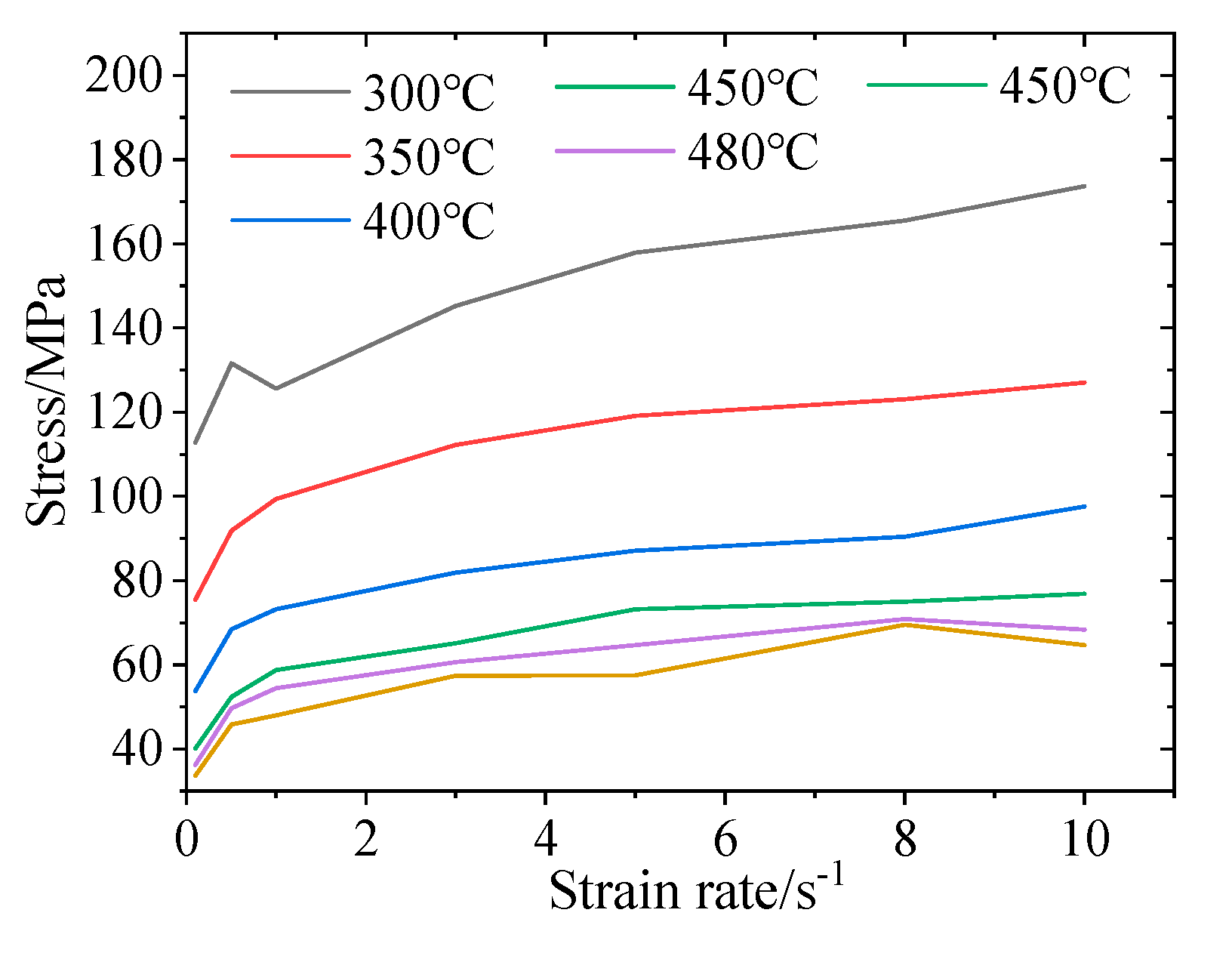
2.4. Influence of Deformation Rate on Steady Flow Stress
3. Constitutive Model
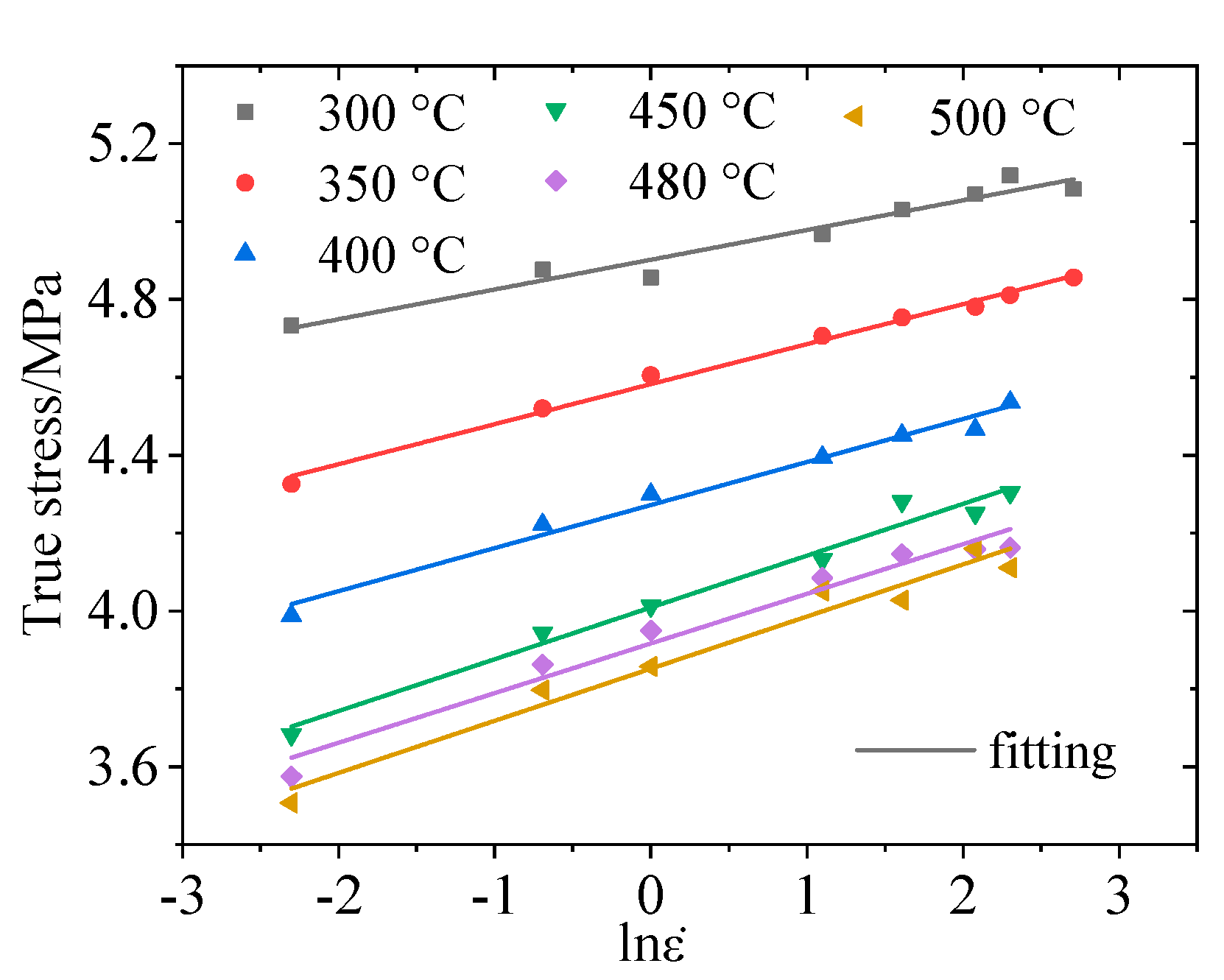
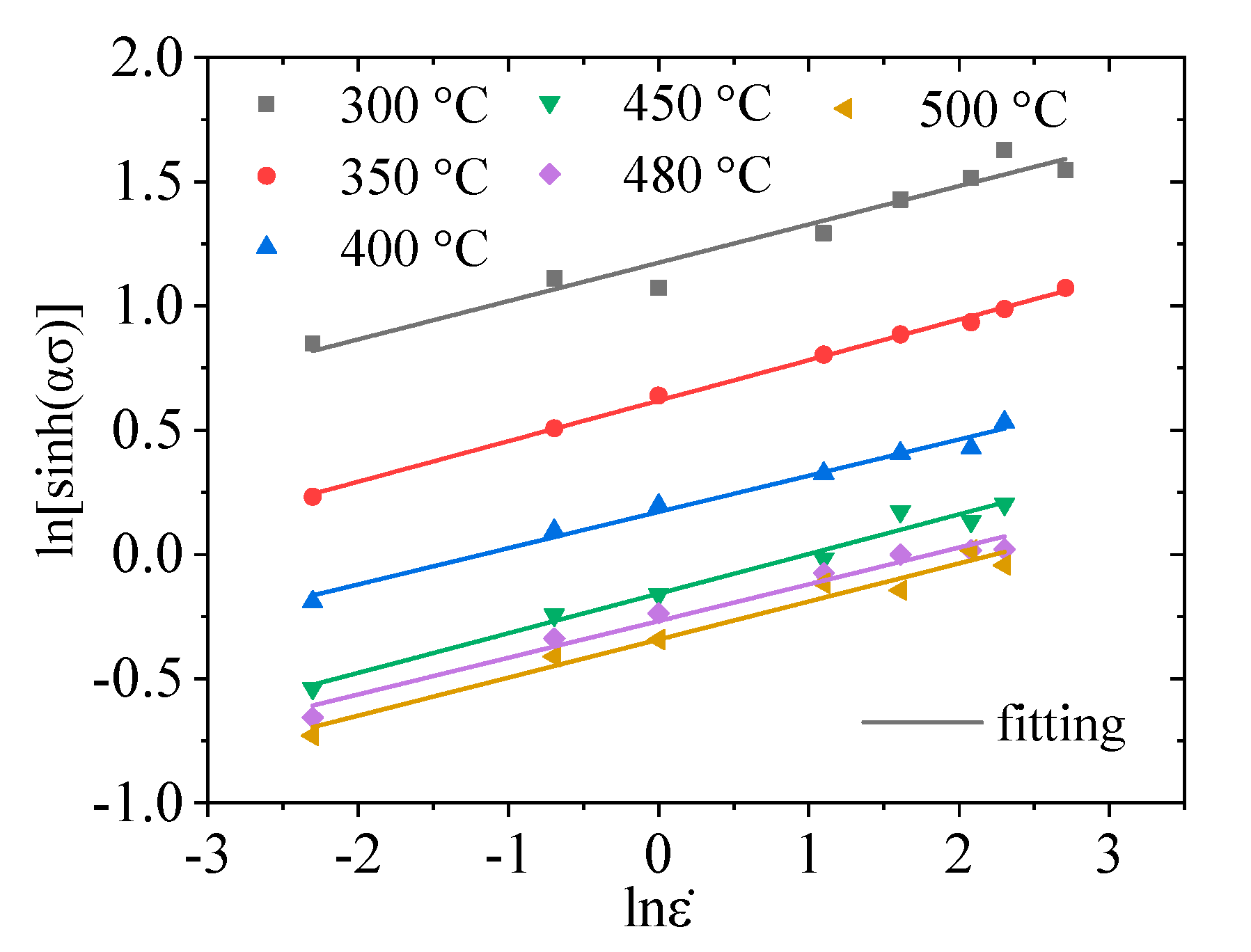
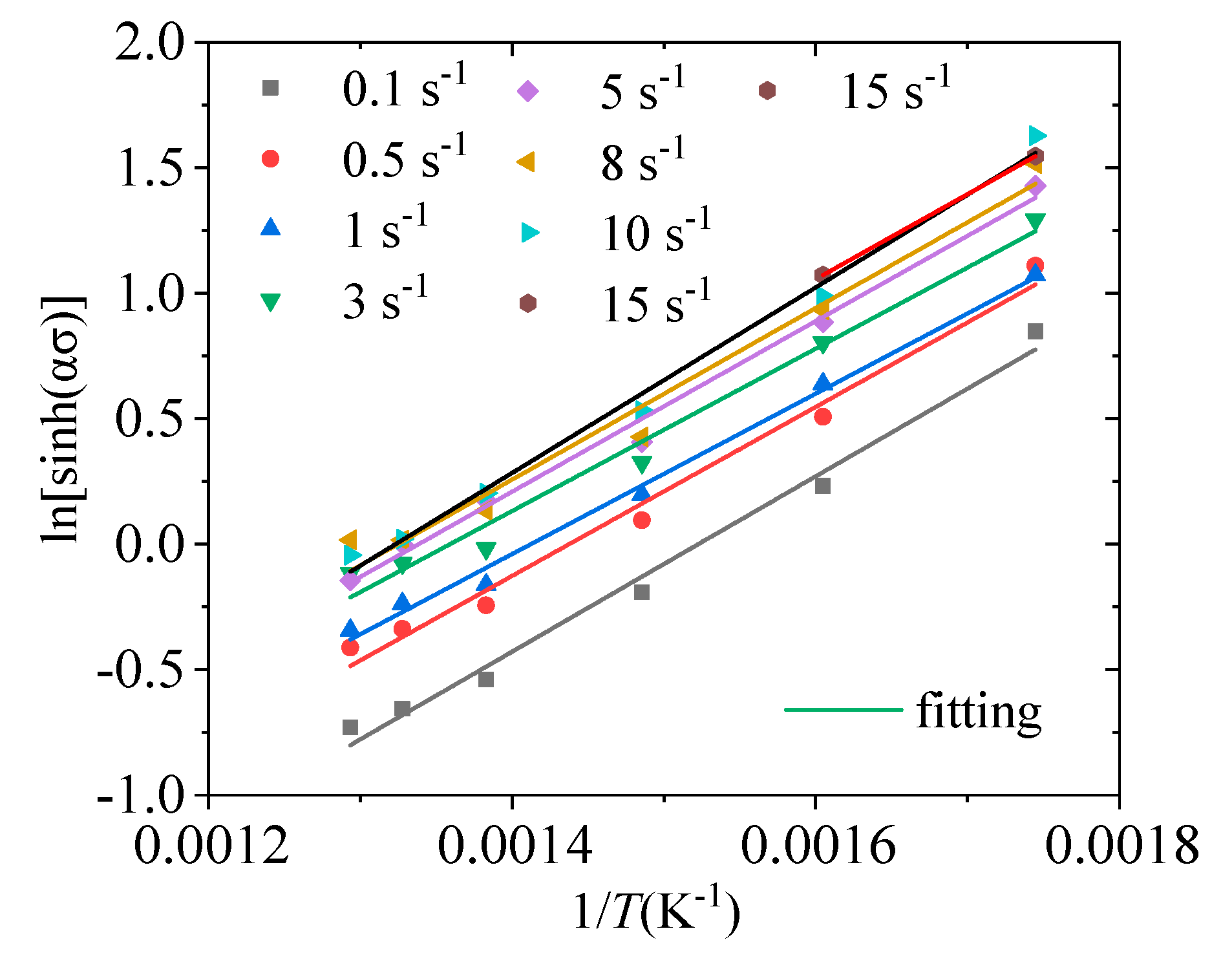
3.1. Arrhenius Constitutive Model
3.2. Exponential Constitutive Model
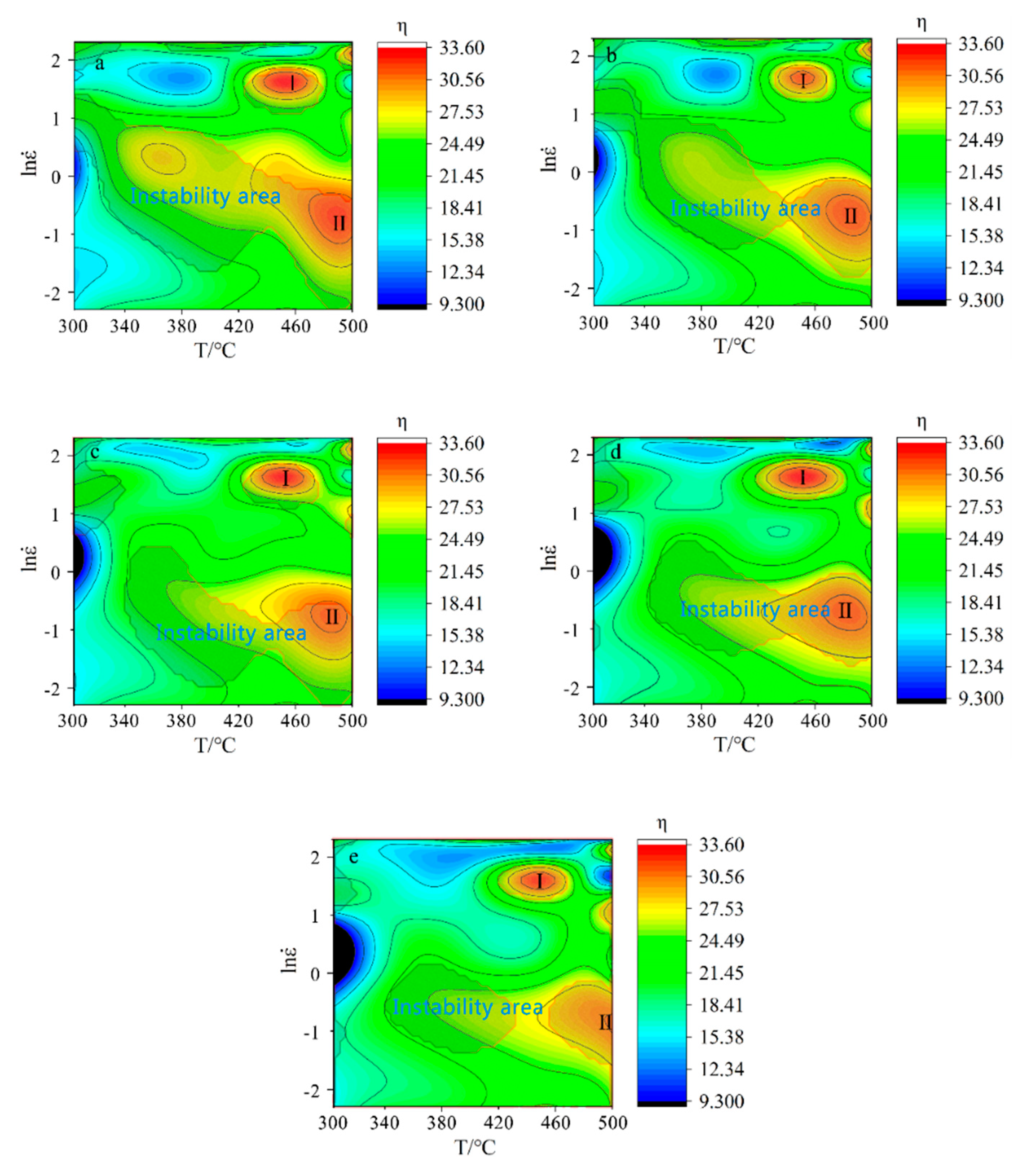
4. Processing Map
5. Conclusions
- The deformation behavior of 2219 aluminum alloy in high temperatures is greatly influenced by the deformation temperature and deformation velocity. The rheological stress is the result of the interaction of three mechanisms, namely, high-temperature softening, strain hardening and deformation rate hardening. At the same deformation rate, the softening effect is enhanced with the increase of the deformation temperature. At the same deformation temperature, with the increase of the deformation rate, the rheological stress gradually increases, and the 2219 aluminum alloy is a positive strain rate sensitive material.
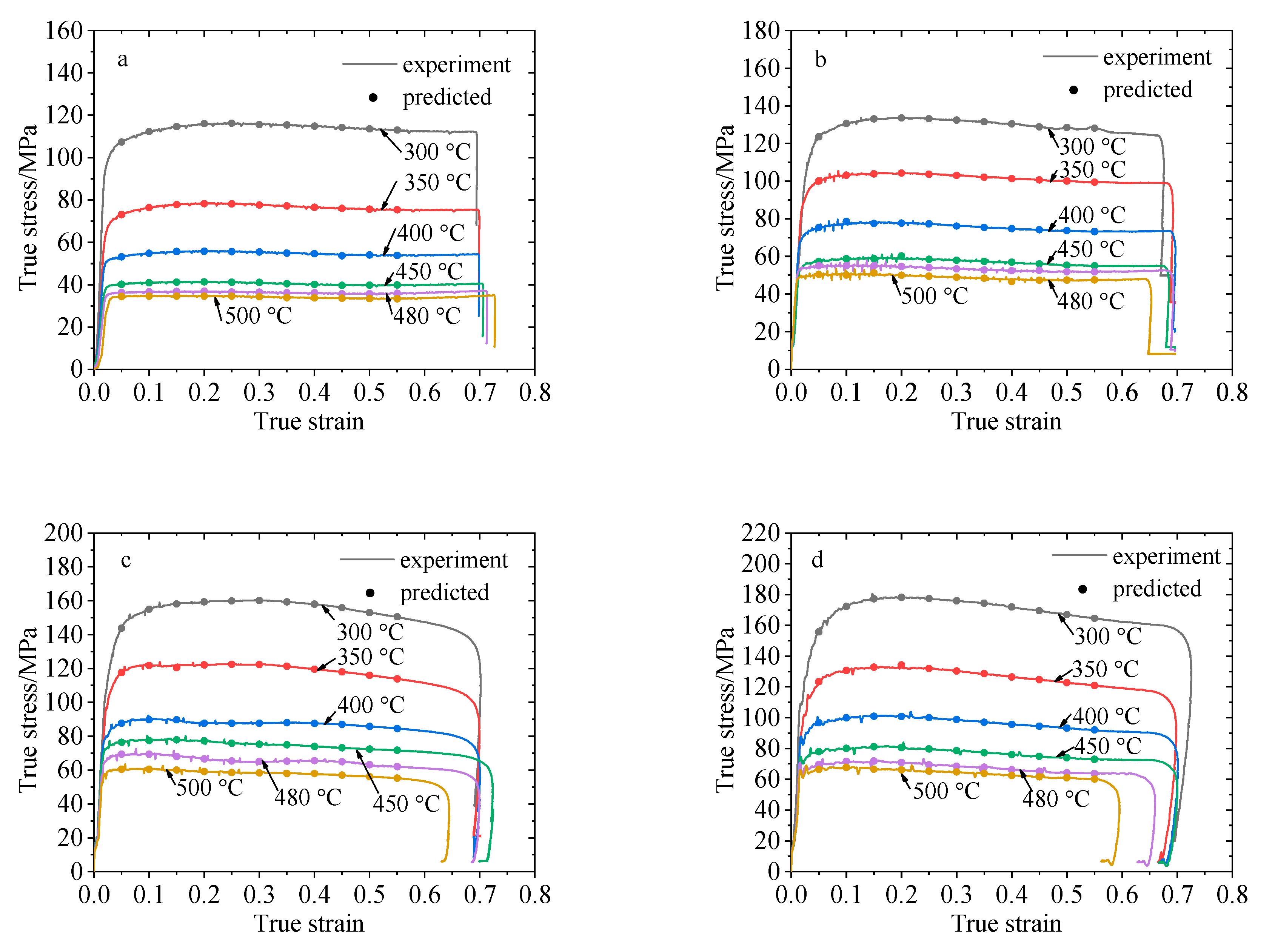
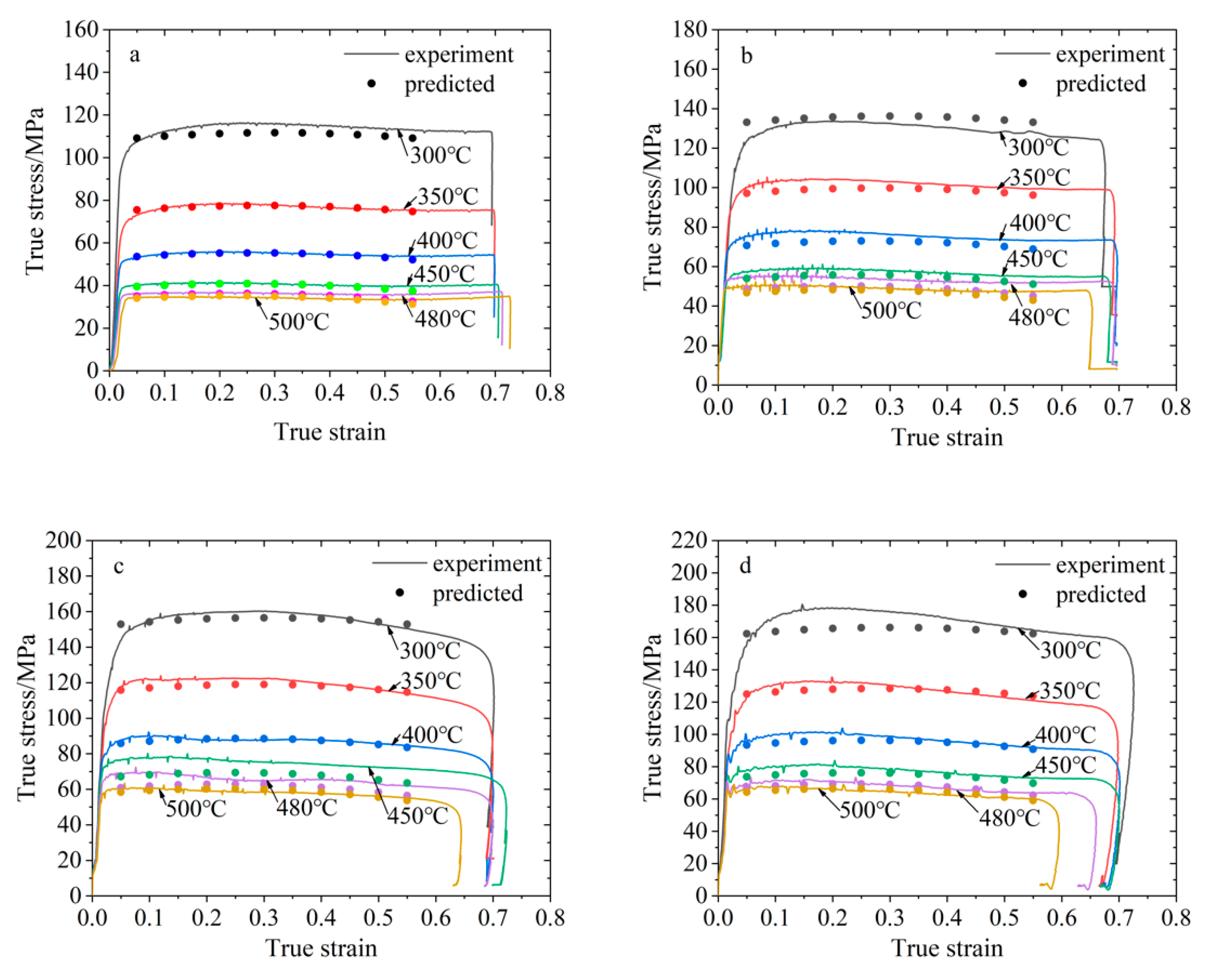
- The Arrhenius-type constitutive model of 2219 aluminum alloy was established. Through a comparison with the experimental data, the correlation coefficient between the predicted results of the Arrhenius-type constitutive model and the experimental results is R = 0.995, and the average relative error AARE = 3.542%.
- The exponential constitutive model considering the influence of temperature and strain rate was established. The correlation coefficient between the predicted results and the test results is R = 0.996 and the average relative error AARE = 3.789%.
- According to the dynamic material model proposed by Prasad, the processing map of 2219 aluminum alloy was established. During thermal deformation, the two peak zones of energy dissipation of 2219 aluminum alloy coincide with the plastic instability zone. Under the condition of high temperature plastic deformation, the area of the plastic instability zone decreases gradually with the increase of strain. Under the same deformation temperature, the lower the strain rate, the less possibility of plastic instability. The optimal thermal deformation conditions of 2219 aluminum alloy are as follows: deformation temperature range is 420 °C to 460 °C, strain rate is not greater than 0.3 s−1.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- An, L.-H.; Cai, Y.; Liu, W.; Yuan, S.-J.; Zhu, S.-Q.; Meng, F.-C. Effect of pre-deformation on microstructure and mechanical properties of 2219 aluminum alloy sheet by thermomechanical treatment. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2012, 22, s370–s375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.J.; Zhang, H.J.; Huang, Y.X.; Yu, L. Mechanical properties of underwater friction stir welded 2219 aluminum alloy. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2010, 20, 1387–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Wu, J.; Zhang, Y.-D.; Gao, H.-J.; Hui, D. Analysis and homogenization of residual stress in aerospace ring rolling process of 2219 aluminum alloy using thermal stress relief method. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2019, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, W.Q.; Song, M.Y.; Yao, J.S.; Zhao, H.Y. Effect of Temperature and Heat Treatment Status on the Ductile Fracture Toughness of 2219 Aluminum Alloy. Mater. Sci. Forum 2011, 689, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Li, F.; Liu, Q.; Chen, K.; Huang, L. Effect of Post-aging Heat Treatment on Strength and Local Corrosion Behavior of Ultrafine-Grained 2219 Al Alloy. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2020, 29, 3420–3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, B.; Baoxiang, Z. Effect of initial microstructure on the hot compression deformation behavior of a 2219 aluminum alloy. Mater. Des. 2012, 34, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wu, Y.-X.; Gong, H.; Wang, K. Modification of constitutive model and evolution of activation energy on 2219 aluminum alloy during warm deformation process. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2019, 29, 448–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, R.; Venugopal, A.; Rao, G.S.; Narayanan, P.R.; Pant, B.; Cherian, R.M. Effect of Temper Condition on the Corrosion and Fatigue Performance of AA2219 Aluminum Alloy. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2018, 27, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olasumboye, A.; Owolabi, G.; Odeshi, A.; Zeytinci, A.; Yilmaz, N. Dynamic Response and Microstructure Evolution of AA2219-T4 and AA2219-T6 Aluminum Alloys. J. Dyn. Behav. Mater. 2018, 4, 162–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Yi, Y.P.; Huang, S.Q.; He, H.L.; Guo, W.F. Influence of Pre-tensile Deformation on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of 2219 Aluminum Alloy Forgings. Mater. Rep. 2019, 33, 3062–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Li, W.; Li, R.; Zhou, D. Effects of pre-deformation on the microstructures and corrosion behavior of 2219 aluminum alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 723, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiang, R.; Yang, Y.; Li, R.; Chen, P.; Li, X.; Zhang, L. Hot Deformation Behavior and Microstructure Mechanisms of As-Cast 2219 Al Alloy. JOM 2020, 72, 1638–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, R. Development of a possessing map for use in warm forming and hot forming processes. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 1981, 12, 1089–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, K.; Lu, S.; Gao, X.Y.; Zhou, F. Hot deformation behavior and processing map of Zr-4 alloy. J. Nucl. Mater. 2020, 531, 151993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Wnag, K.L.; Lu, S.Q.; Xu, Q.X. Hot Deformation Behavior and Forging Process Optimization of MoLa Alloy Based on Polar Reciprocity Model. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2018, 47, 279–285. [Google Scholar]
- Prasad, Y.V.R.K.; Gegel, H.L.; Doraivelu, S.M.; Malas, J.C.; Morgan, J.T.; Lark, K.A.; Barker, D.R. Modeling of dynamic material behavior in hot deformation: Forging of Ti-6242. Met. Mater. Trans. A 1984, 15, 1883–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murty, S.; Rao, B. On the development of instability criteria during hotworking with reference to IN 718. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1998, 254, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Hui, S.; Tong, K.; Yu, Y.; Ye, W.; Song, S.-Y. Investigation of high temperature behavior and processing map of Ti-6Al-4V-0.11Ru titanium alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 787, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.-H.; Liu, B.; Liu, Y.-X.; Liu, Y. Processing map and hot deformation behavior of Ta-particle reinforced TiAl composite. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2020, 30, 657–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayana, P.L.; Li, C.-L.; Hong, J.-K.; Choi, S.-W.; Park, C.H.; Kim, S.-W.; Kim, S.E.; Reddy, N.S.; Yeom, J.-T. Characterization of Hot Deformation Behavior and Processing Maps of Ti–19Al–22Mo Alloy. Met. Mater. Int. 2019, 25, 1063–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liao, Q.; Niu, Y.; Jia, Y.; Le, Q.; Ning, S.; Hu, C.; Hu, K.; Yu, F. Comparison study of hot deformation behavior and processing map of AZ80 magnesium alloy casted with and without ultrasonic vibration. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 803, 585–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Guan, Y.P.; Duan, Y.C.; Qu, X.Y. Hot Tensile Deformation Behavior and Processing Map of Rolled ME20M Magnesium Alloy. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2020, 49, 1715–1721. [Google Scholar]
- Qunying, Y.; Wenyi, L.; Zhiqing, Z.; Guangjie, H.; Xiaoyong, L. Hot Deformation Behavior and Processing Maps of AA7085 Aluminum Alloy. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2018, 47, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhao, G.; Gong, J.; Chen, X.; Chen, M. Hot Deformation Behaviors and Processing Maps of 2024 Aluminum Alloy in As-cast and Homogenized States. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2015, 24, 5002–5012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, B.; Ye, L.; Tang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Lin, H.; Dong, Y.; Liu, X. Hot deformation behavior and 3D processing maps of AA7020 aluminum alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 845, 156113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolovsky, V.; Stepanov, N.; Zherebtsov, S.; Nochovnaya, N.; Panin, P.; Zhilyakova, M.; Popov, A.; Salishchev, G. Hot deformation behavior and processing maps of B and Gd containing β-solidified TiAl based alloy. Intermetallics 2018, 94, 138–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zherebtsov, S.; Ozerov, M.; Klimova, M.; Moskovskikh, D.; Stepanov, N.; Salishchev, G. Mechanical Behavior and Microstructure Evolution of a Ti-15Mo/TiB Titanium–Matrix Composite during Hot Deformation. Metals 2019, 9, 1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, W.; Qiang, L.; Ping, L. Hot Deformation Behavior and Microstructure Evolution of 2219/TiB2 Al-matrix Composite. Mater. Res. 2020, 23, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Heating Temperature | Heating Rate | Deformation Temperature | Cooling Rate | Hold Time | Strain Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 °C | 10 °C/s | 300 °C | 5 °C/s | 5 min | 0.1 s−1 0.5 s−1 1 s−1 3 s−1 5 s−1 8 s−1 10 s−1 |
| 350 °C | |||||
| 400 °C | |||||
| 450 °C | |||||
| 480 °C | |||||
| 500 °C |
| Parameters | 300 °C | 350 °C | 400 °C | 450 °C | 480 °C | 500 °C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n1 | 12.047 | 9.603 | 8.890 | 7.361 | 7.6051 | 7.222 |
| β | 0.08582 | 0.09832 | 0.12423 | 0.13081 | 0.15510 | 0.15271 |
| α | 0.007127 | 0.01024 | 0.01397 | 0.01777 | 0.02039 | 0.02115 |
| Parameters | 300 °C | 350 °C | 400 °C | 450 °C | 480 °C | 500 °C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | 6.491 | 6.618 | 7.098 | 6.348 | 6.777 | 6.484 |
| lnA | 32.453 | 30.902 | 29.307 | 29.382 | 30.746 | 30.825 |
| Parameter | 0.1 s−1 | 0.5 s−1 | 1 s−1 | 3 s−1 | 5 s−1 | 8 s−1 | 10 s−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q | 184,768.621 | 175,816.573 | 166,608.899 | 167,040.577 | 174,916.781 | 175,370.157 | 189,337.170 |
| Strain | Q | n | LnA | α |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.05 | 144,588.970 | 5.938 | 24.815 | 0.01333 |
| 0.1 | 149,660.592 | 6.010 | 26.588 | 0.01152 |
| 015 | 154,130.135 | 6.078 | 27.419 | 0.01135 |
| 0.2 | 157,414.723 | 6.118 | 27.992 | 0.01135 |
| 0.25 | 162,739.484 | 6.310 | 29.118 | 0.01116 |
| 0.3 | 164,977.358 | 6.352 | 29.413 | 0.01138 |
| 0.35 | 167,103.495 | 6.363 | 29.661 | 0.01167 |
| 0.4 | 170,307.342 | 6.439 | 30.138 | 0.01191 |
| 0.45 | 171,912.108 | 6.486 | 30.329 | 0.01216 |
| 0.5 | 176,265.540 | 6.636 | 30.980 | 0.01242 |
| 0.55 | 180,006.288 | 6.743 | 31.402 | 0.01284 |
| Parameter | 300 °C | 350 °C | 400 °C | 450 °C | 480 °C | 500 °C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
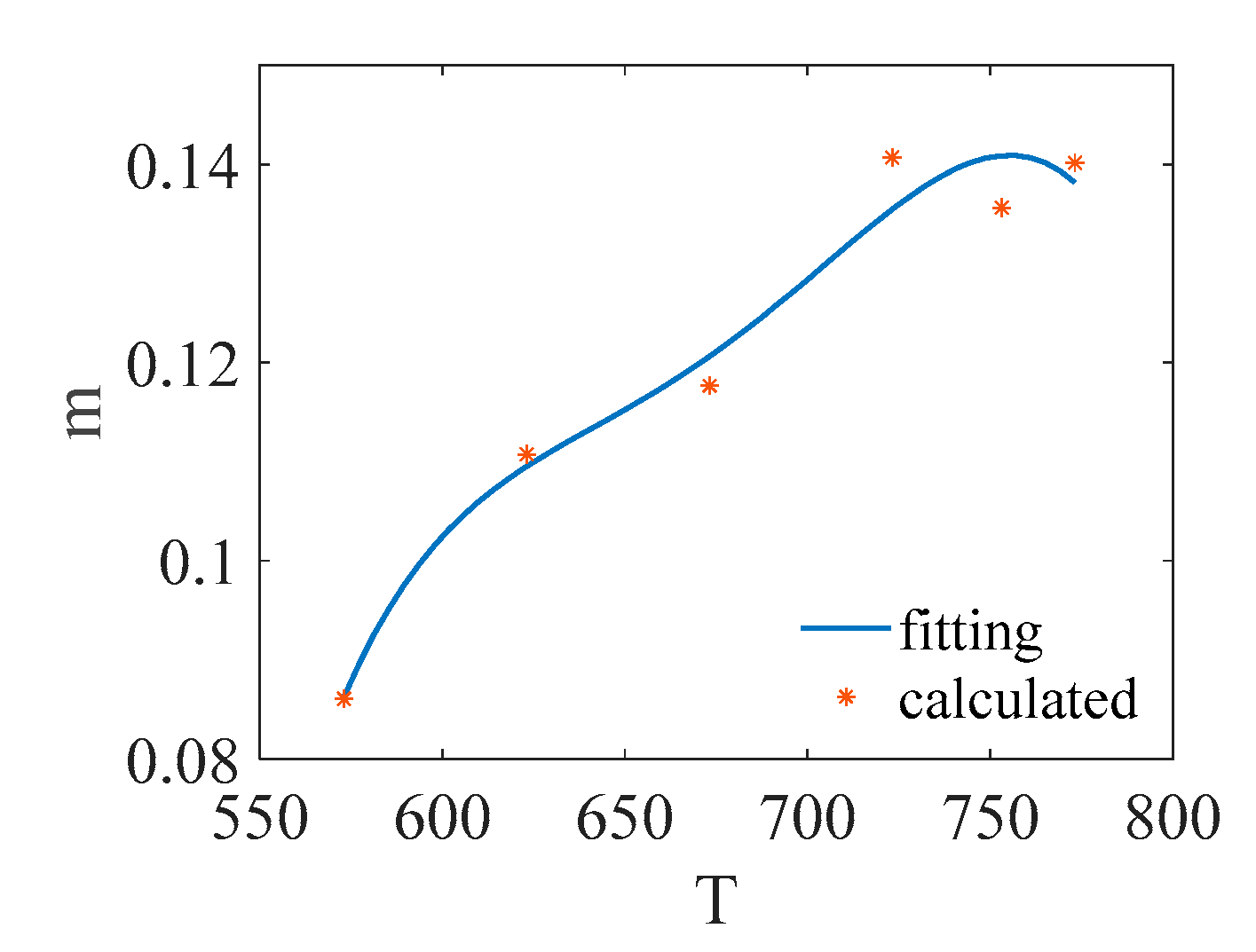
| m | 0.0863 | 0.1095 | 0.1206 | 0.1355 | 0.1409 | 0.1382 |
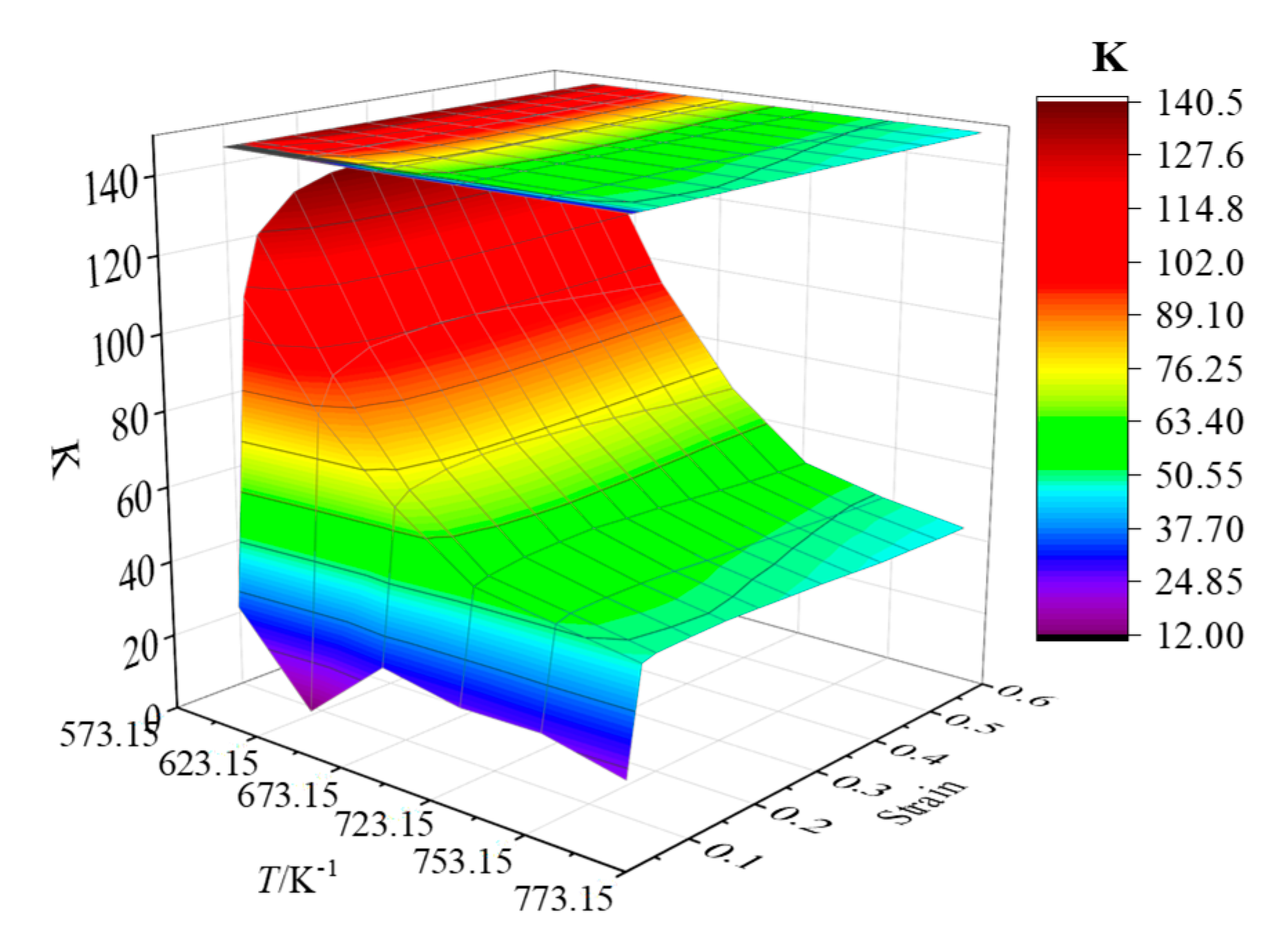
| K | 300 °C | 350 °C | 400 °C | 450 °C | 480 °C | 500 °C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.05 | 127.0776 | 95.9248 | 72.1167 | 56.1892 | 52.8729 | 49.4418 |
| 0.1 | 135.9259 | 100.5428 | 74.3353 | 57.5801 | 53.2324 | 49.7229 |
| 015 | 138.9989 | 101.5581 | 75.1788 | 58.1093 | 53.2363 | 49.8727 |
| 0.2 | 140.1107 | 102.2098 | 75.1821 | 58.3904 | 52.9354 | 49.4976 |
| 0.25 | 140.0622 | 101.9647 | 74.7446 | 57.8259 | 52.3553 | 49.0345 |
| 0.3 | 139.3609 | 101.2364 | 74.3031 | 57.4266 | 52.0183 | 48.6364 |
| 0.35 | 138.5305 | 100.3752 | 73.6435 | 56.7040 | 51.5590 | 48.0543 |
| 0.4 | 137.4246 | 99.4421 | 72.9850 | 56.0861 | 51.1284 | 47.4691 |
| 0.45 | 136.1900 | 98.5891 | 72.0760 | 55.4743 | 50.7142 | 47.3152 |
| 0.5 | 134.8083 | 97.7991 | 71.6639 | 55.0985 | 50.2306 | 47.0829 |
| 0.55 | 133.6564 | 97.0464 | 71.1797 | 54.7661 | 50.0956 | 47.0190 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jia, X.-D.; Wang, Y.-N.; Zhou, Y.; Cao, M.-Y. The Study on Forming Property at High Temperature and Processing Map of 2219 Aluminum Alloy. Metals 2021, 11, 77. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11010077
Jia X-D, Wang Y-N, Zhou Y, Cao M-Y. The Study on Forming Property at High Temperature and Processing Map of 2219 Aluminum Alloy. Metals. 2021; 11(1):77. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11010077
Chicago/Turabian StyleJia, Xiang-Dong, Yi-Ning Wang, Ying Zhou, and Miao-Yan Cao. 2021. "The Study on Forming Property at High Temperature and Processing Map of 2219 Aluminum Alloy" Metals 11, no. 1: 77. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11010077
APA StyleJia, X.-D., Wang, Y.-N., Zhou, Y., & Cao, M.-Y. (2021). The Study on Forming Property at High Temperature and Processing Map of 2219 Aluminum Alloy. Metals, 11(1), 77. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11010077




