Influence of Sand Fines Transport Velocity on Erosion-Corrosion Phenomena of Carbon Steel 90-Degree Elbow
Abstract
1. Introduction
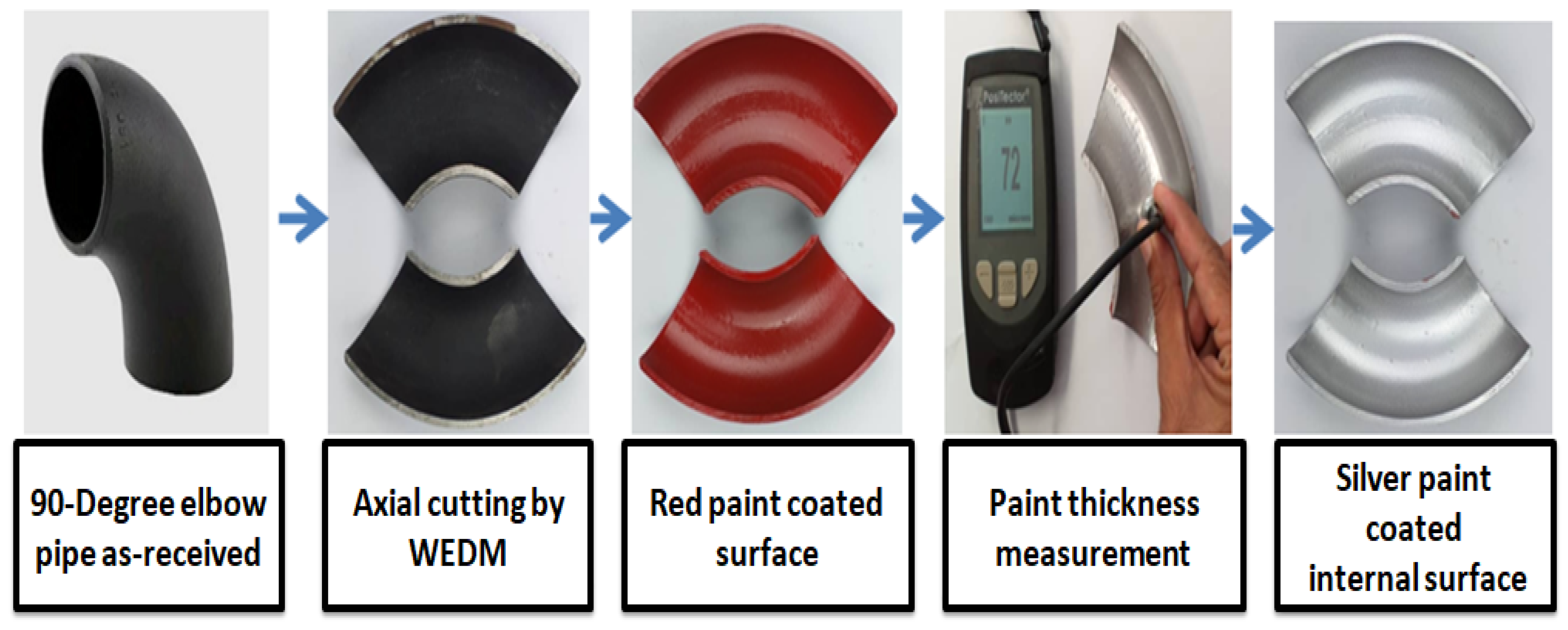
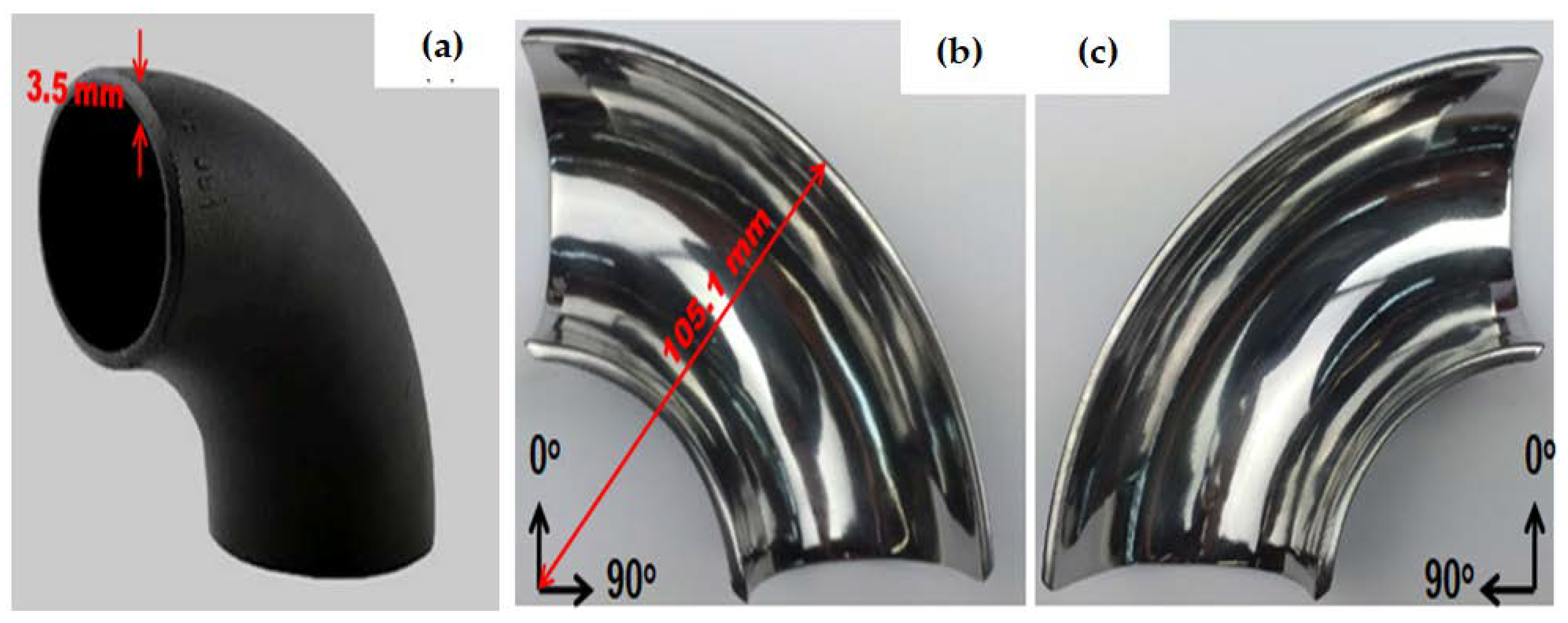
2. Experimental Methods and Materials
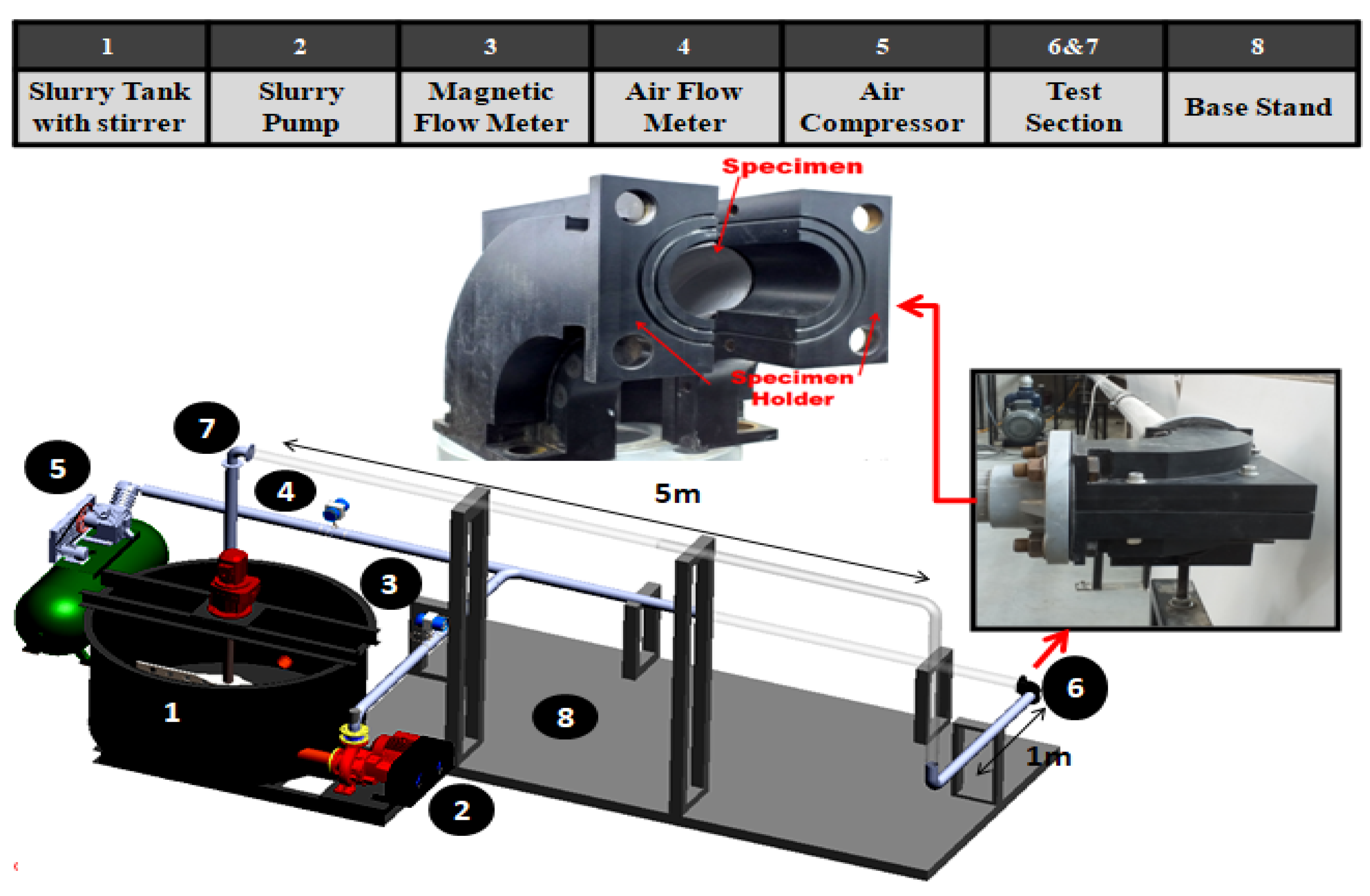
Multiphase Flow Loop Apparatus and Medium
3. Numerical Simulation
3.1. Carrier and Dispersed Phase Model
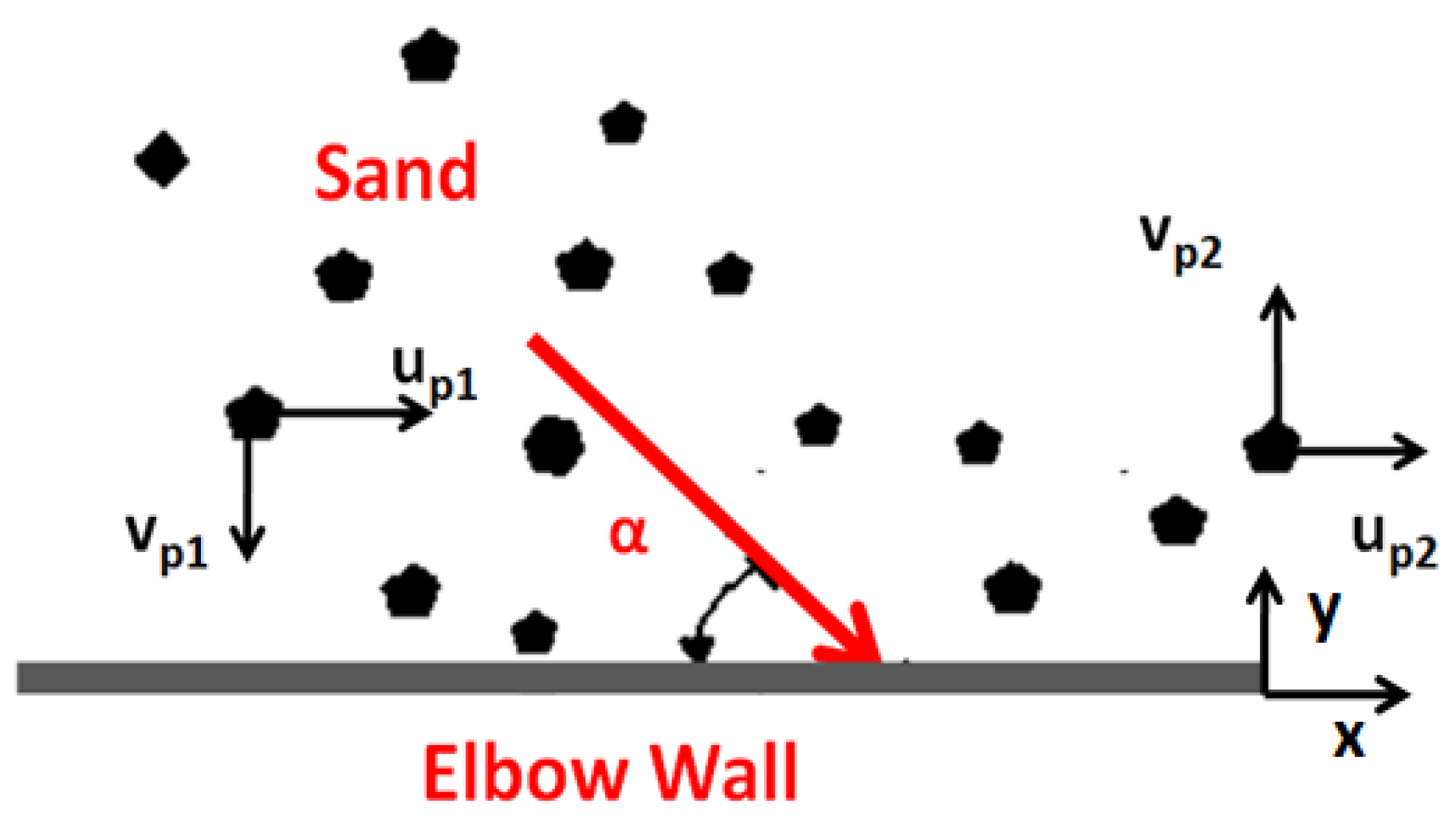
3.2. Erosion Model and Erodent Particle Rebound Equation
3.3. Turbulence Model
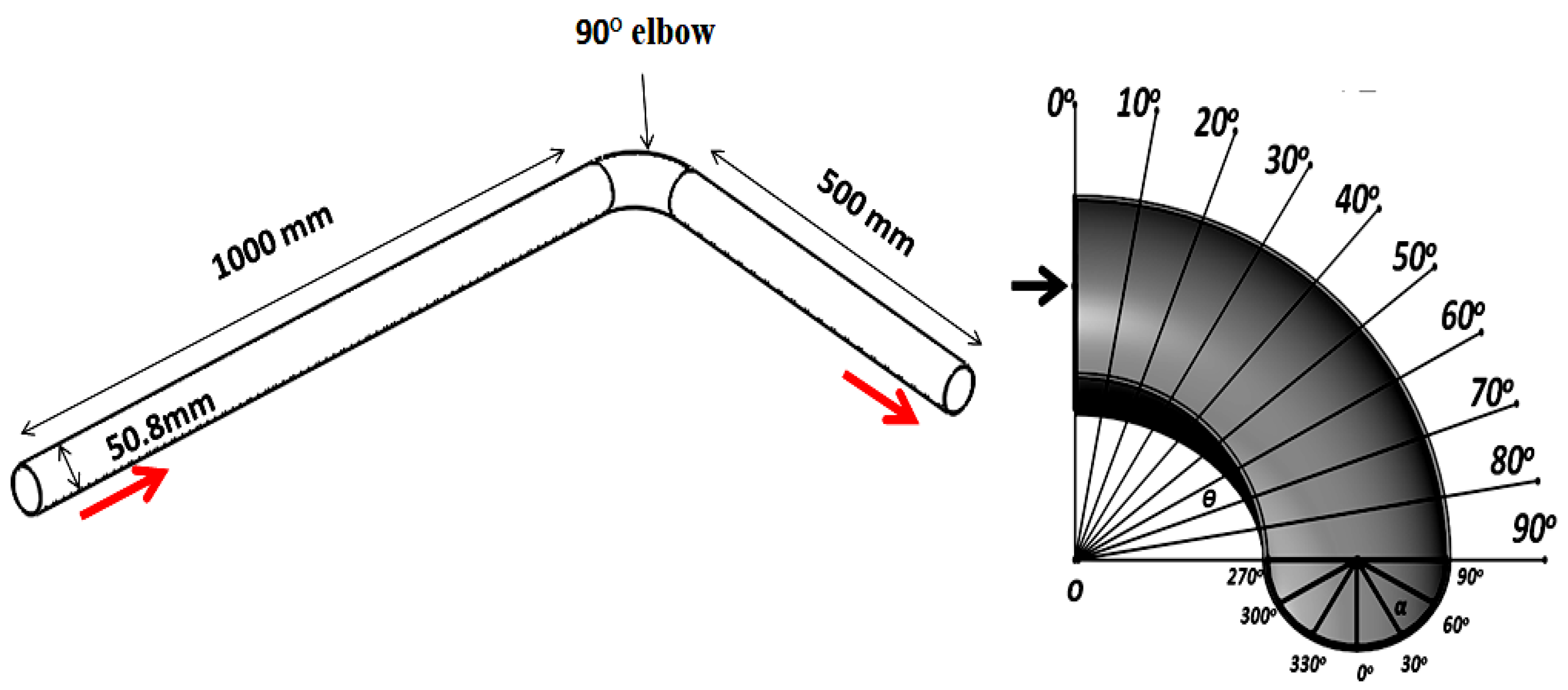
3.4. CFD Modeling
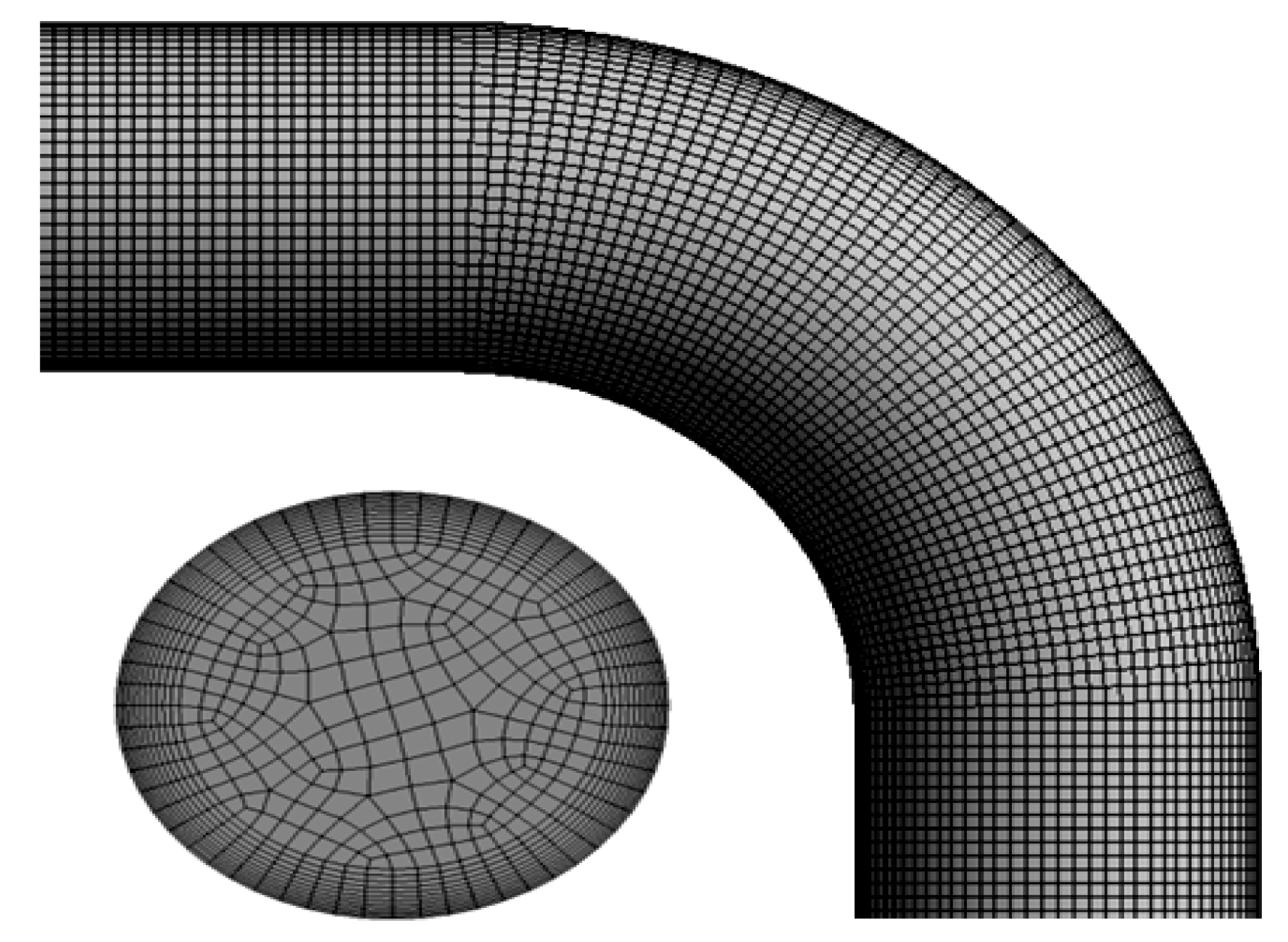
3.5. Mesh Independence
4. Results and Discussion
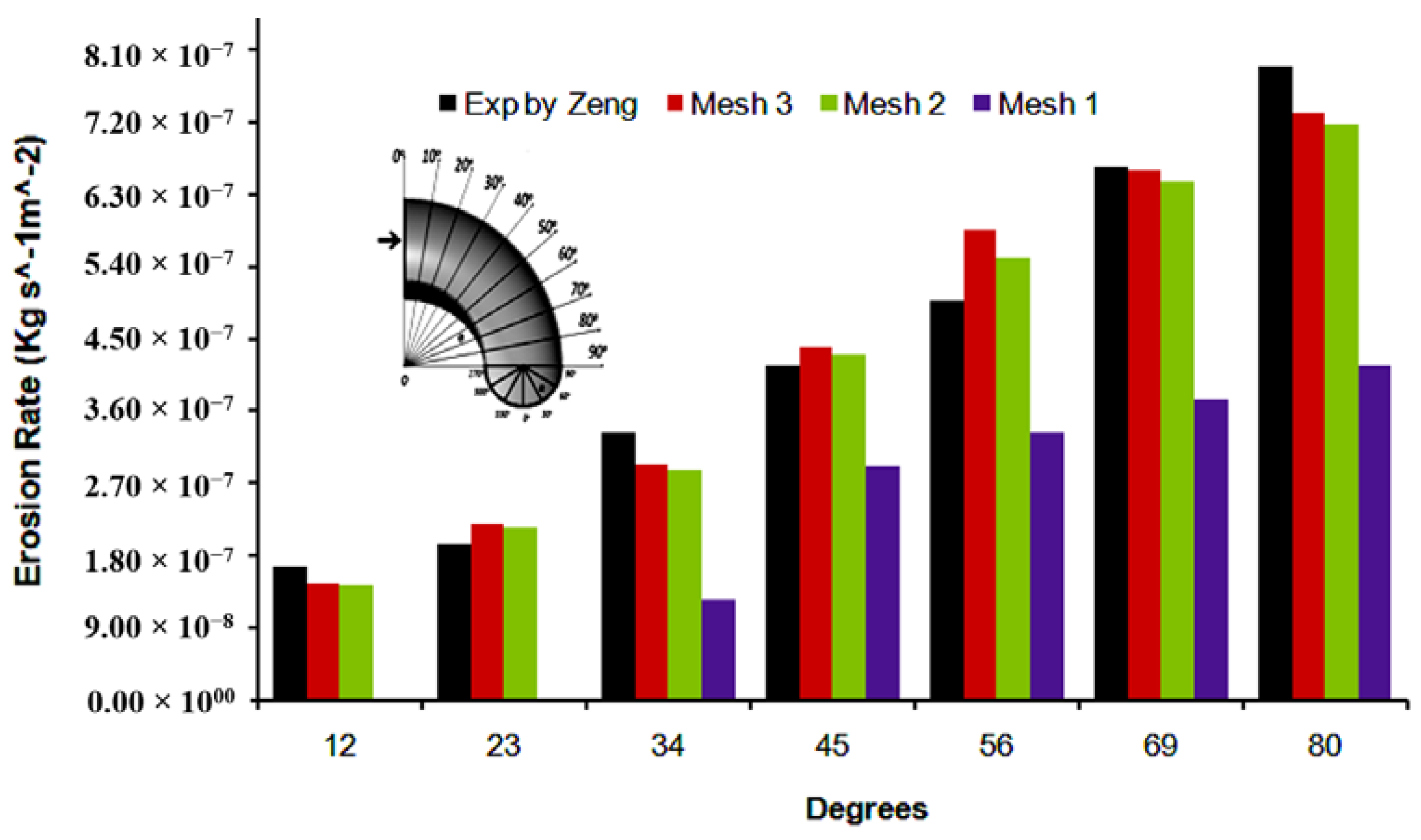
4.1. Validation
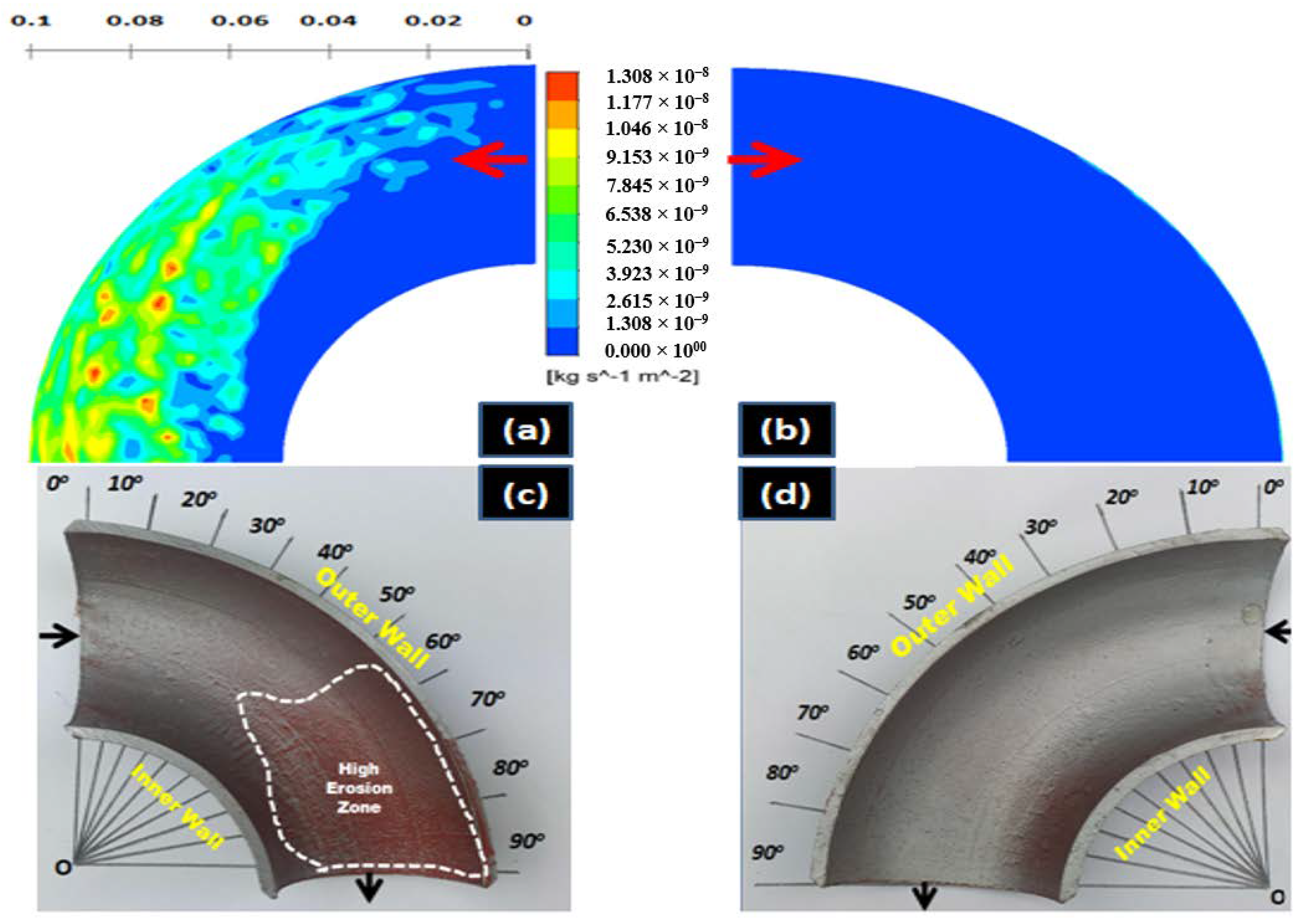
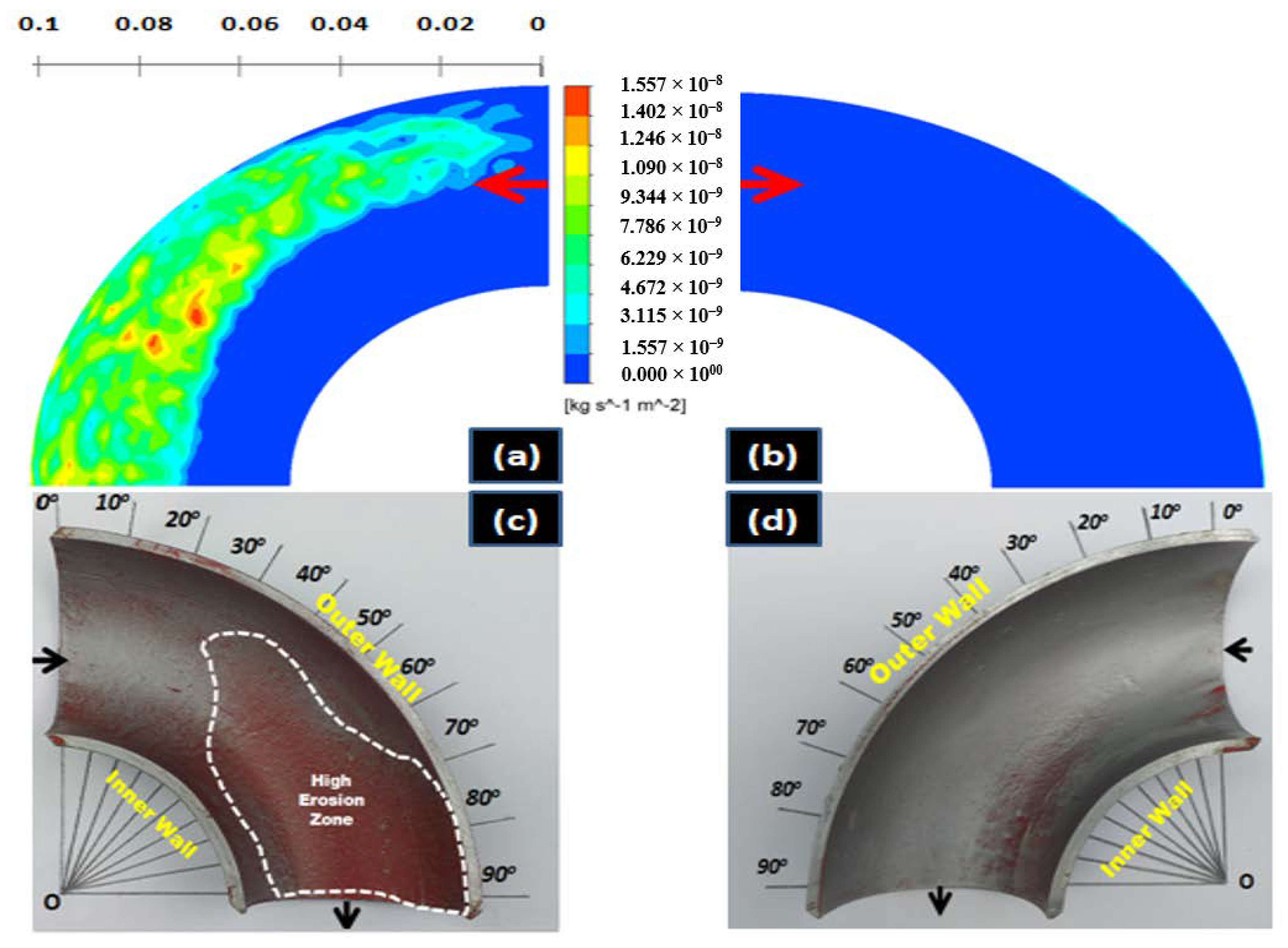
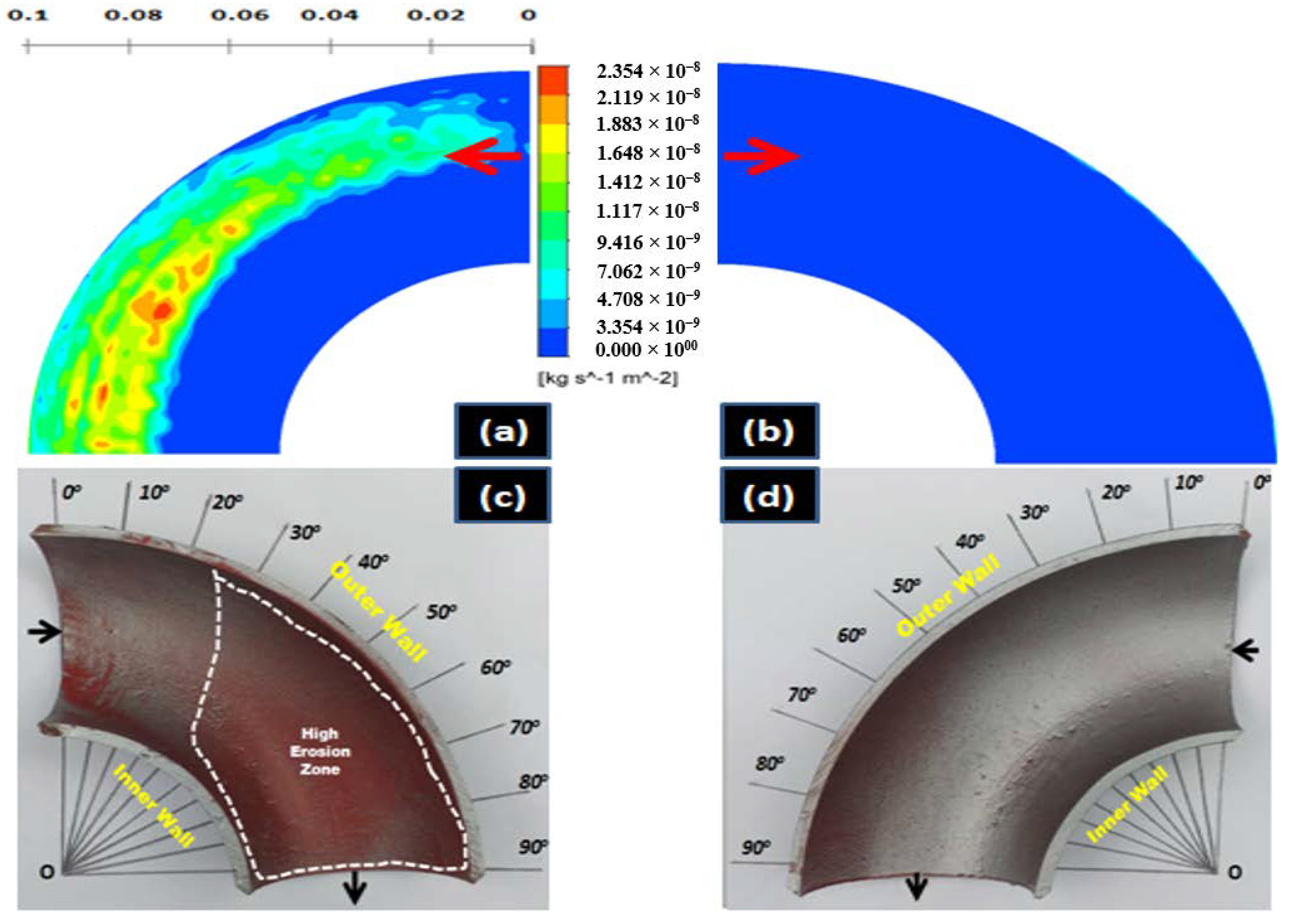
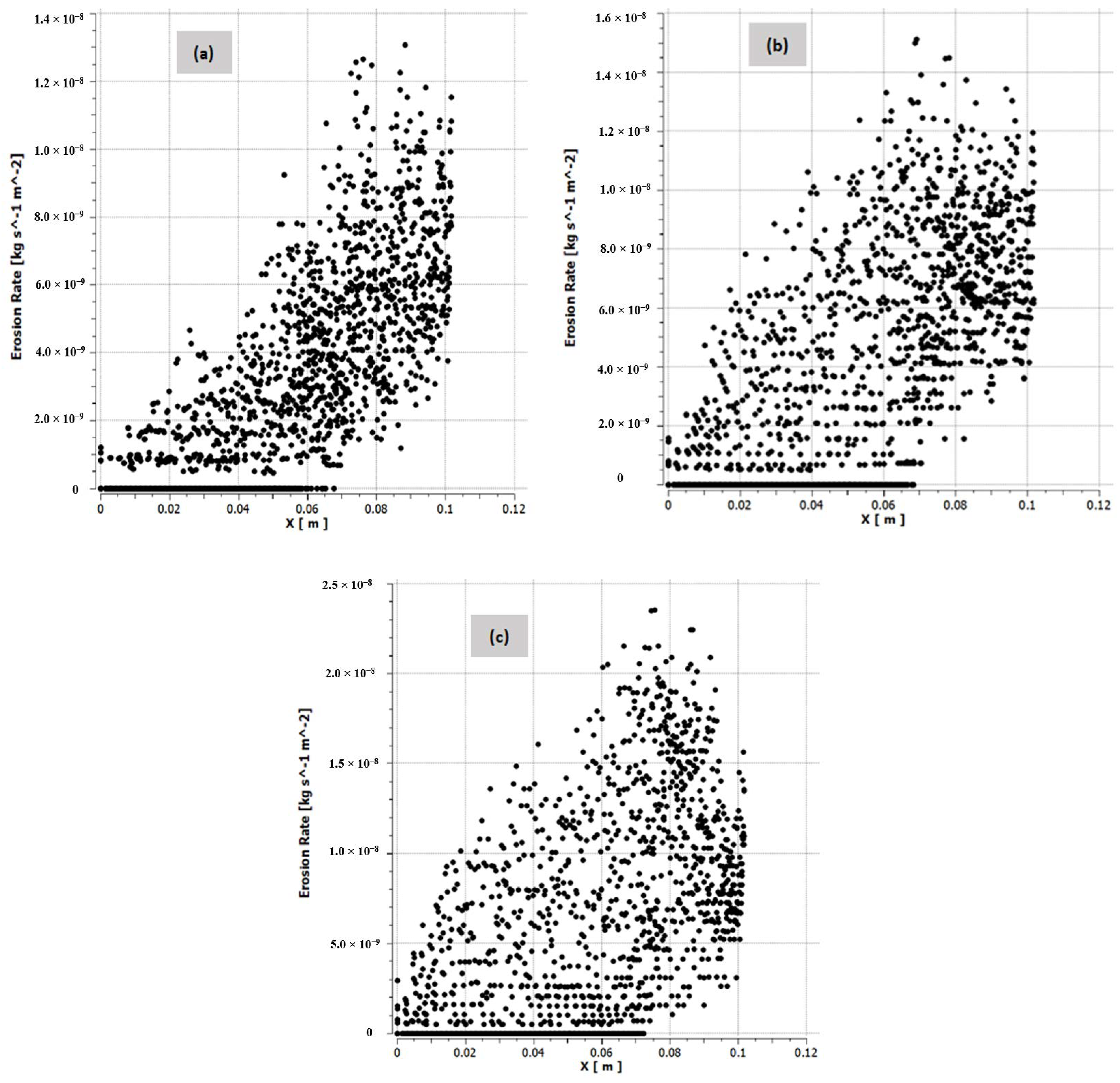
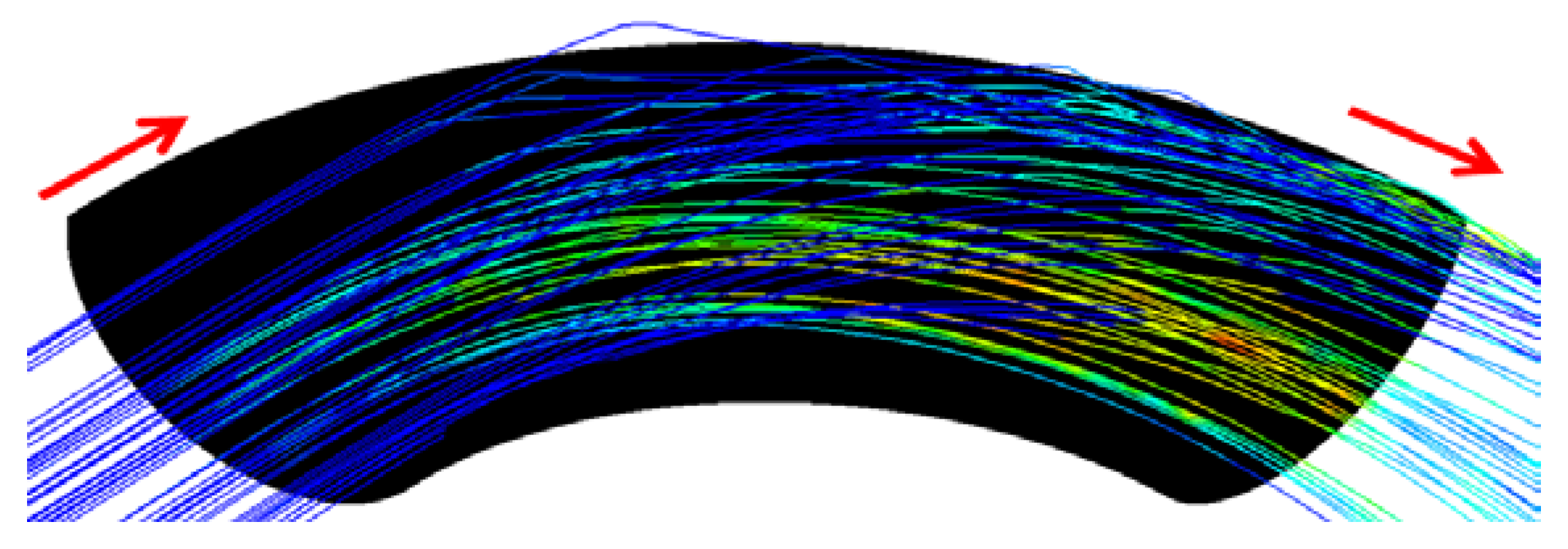
4.2. Influence of the Slurry Speed on the Erosion Profile and Erosion Rate
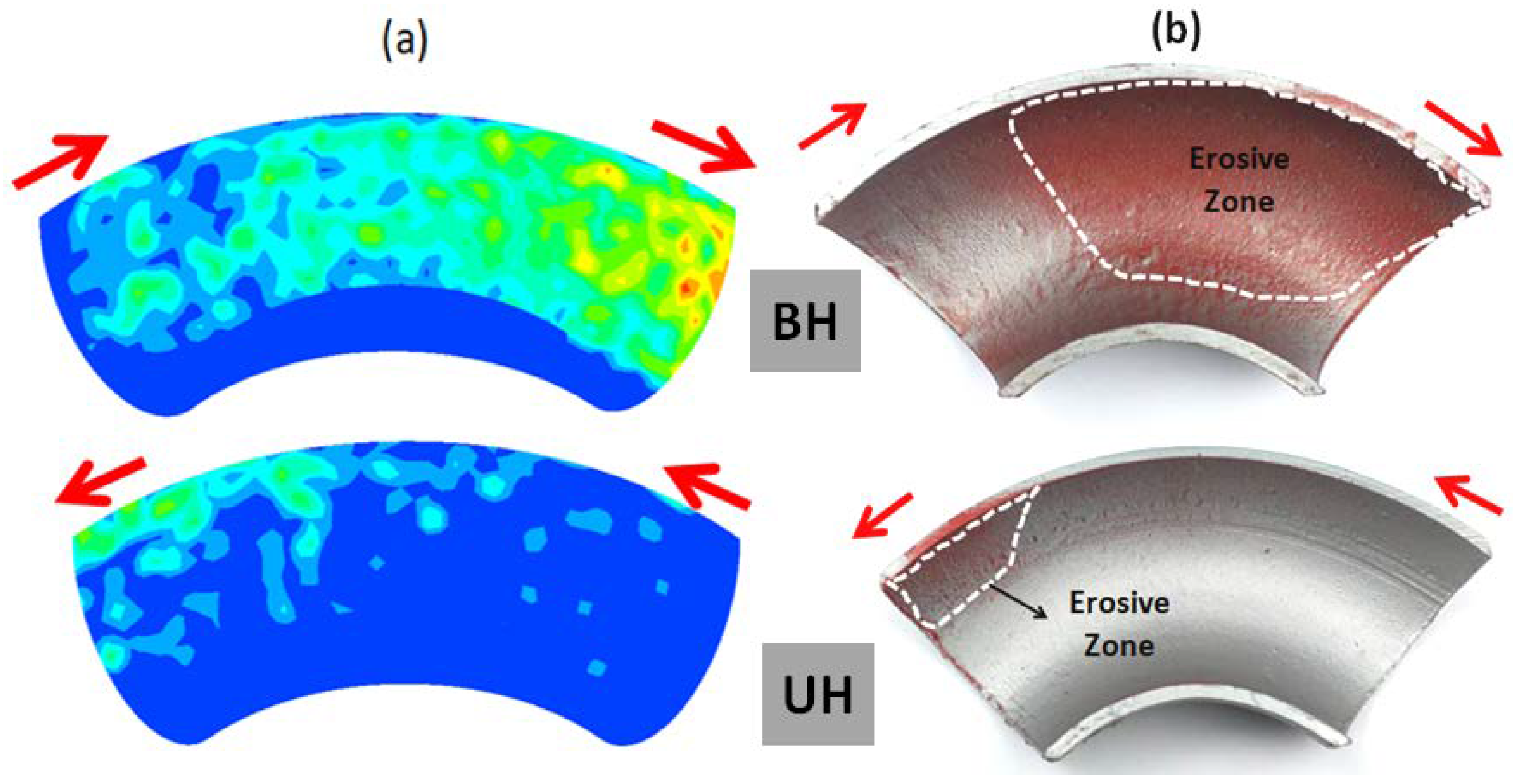
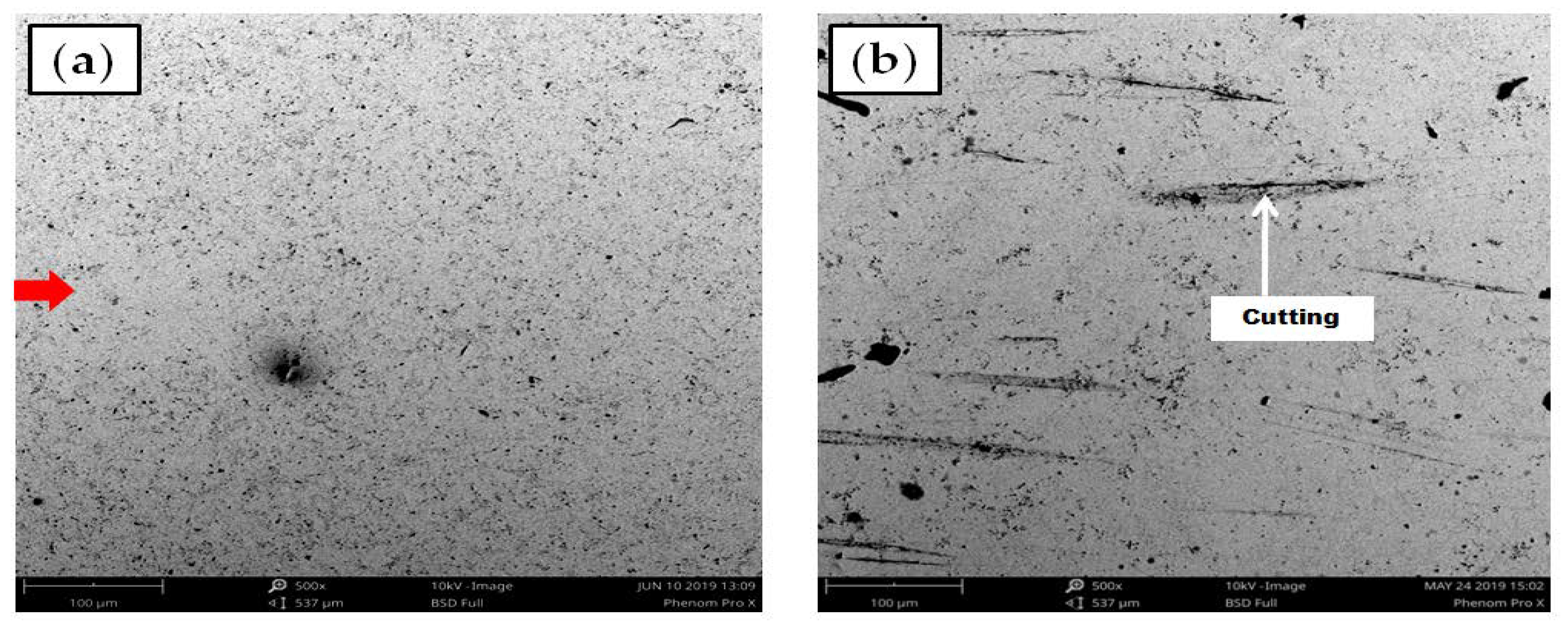
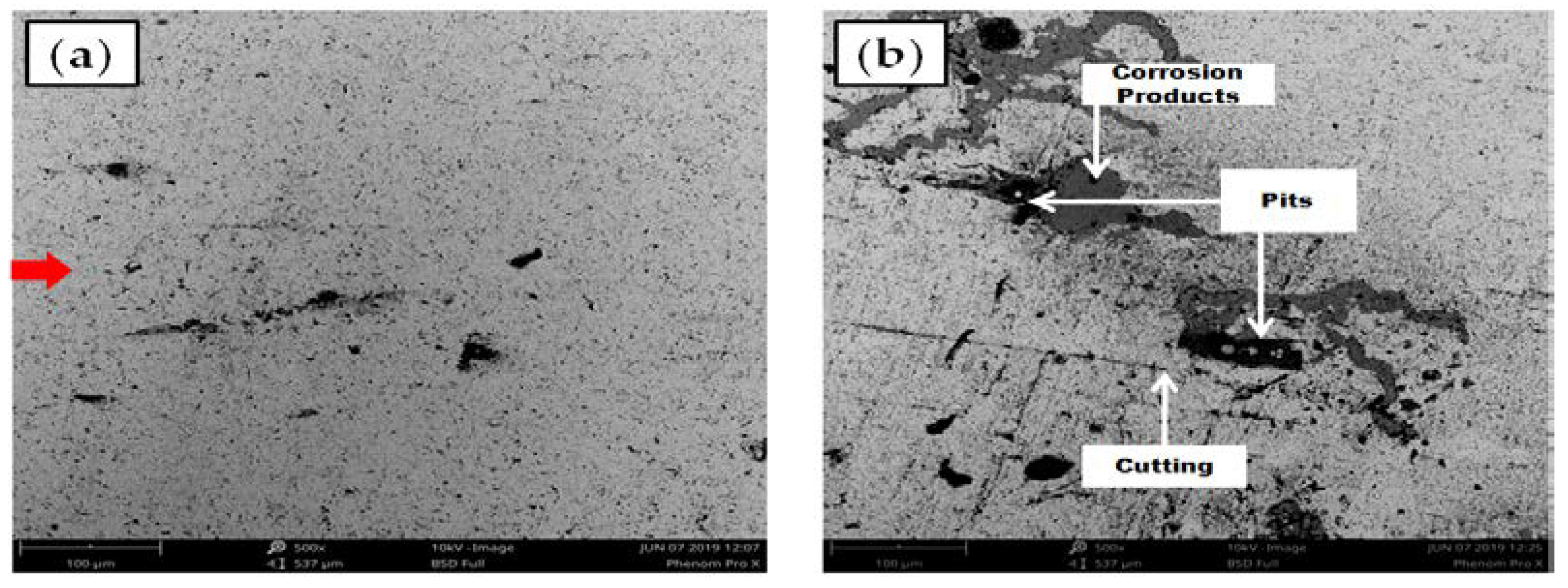
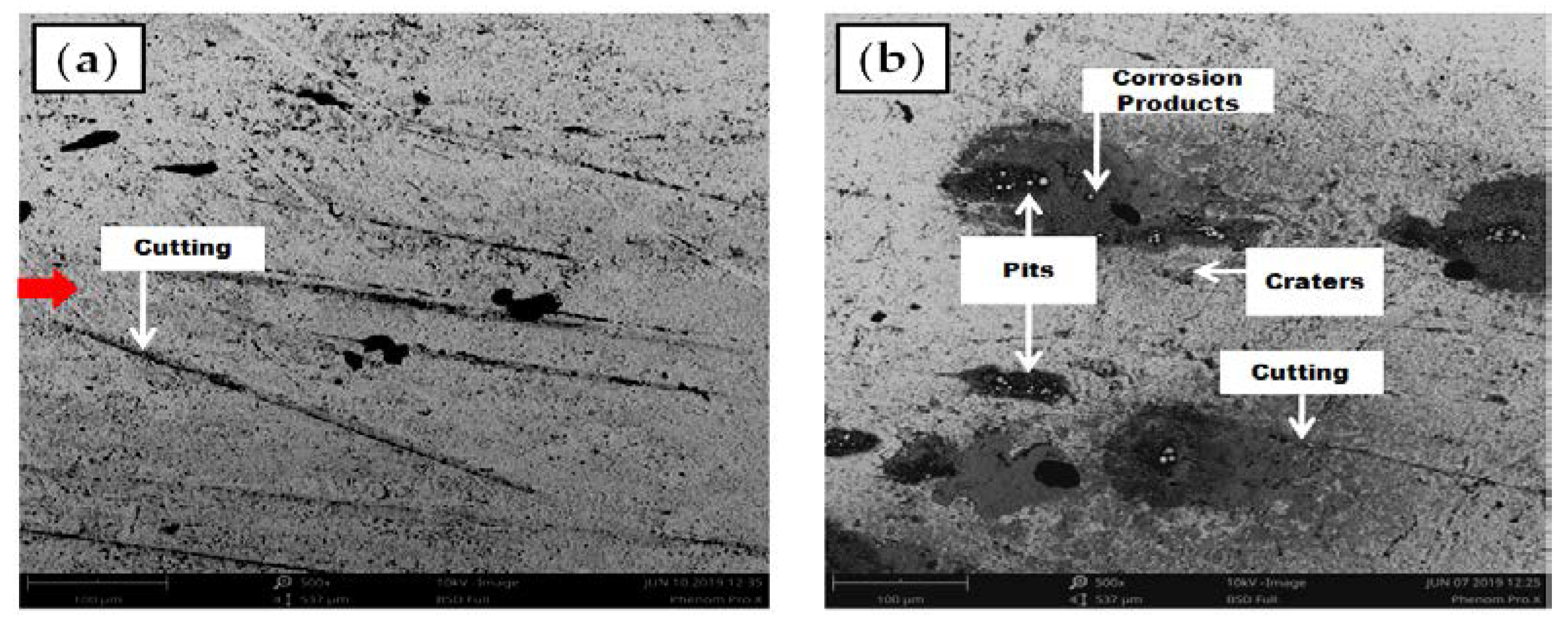
4.3. Identification of the Erosion-Corrosion Regions Using SEM
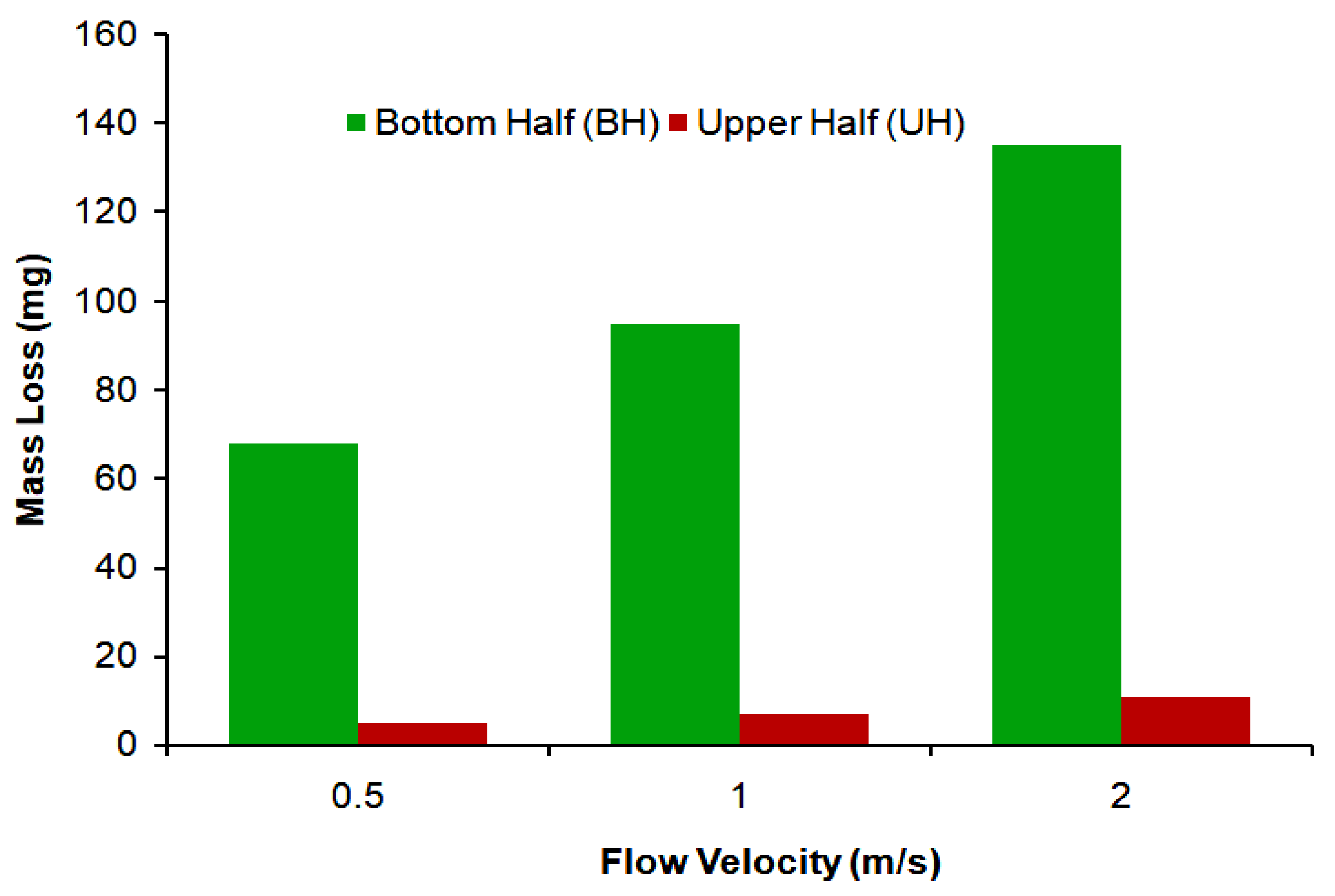
4.4. Mass Loss
5. Conclusions
- The eroded pattern of 90-degree elbows indicates that the erosion-corrosion mechanism alters with flow field conditions. The pitting and cutting action increased at high transport velocity, showing an ascent in kinetic energy of the dispersed phase. The results also indicate the signs of low and high angle particle impaction at 2 m/s flow velocity which may contribute to the development of elongated and circular pits on elbow internal surface.
- In liquid-solid flow, the erosion-corrosion rate weighs more in the bottom half section as compared to the top of the 90-degree elbow. The experimental analysis indicates that slurry transport at 2 m/s through 90-degree elbow aggravates material disintegration up to 2 times in comparison to the low transport velocity. The weight loss analysis and CFD-DPM contours show particle wall impaction was maximum in the bottom section towards downstream adjacent to elbow outlet.
- The highest erosive wear originated from a combination of the cutting and pitting adjacent to the elbow outlet. Sand fines tended to redirect the path at the downstream; facilitating erosion scars and pits development in the region. A closer descry at the worn surface manifests that in addition to the pitting, the contiguous impact craters materialized which are evidence of plastic deformation due to the sand fines impactions. The cumulative effect of pitting and cutting escalates erosion-corrosion in the flow direction.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, P.G.; Smith, B.R.J.; Vedapuri, D.; Subramani, H.J.; Rhyne, L.D. Sand Fines Erosion in Gas Pipelines–Experiments and CFD Modeling, Proceedings of the CORROSION 2014, San Antonio, TX, USA, 9–13 March 2014; NACE International: Houston, TX, USA, 2014; p. 12. [Google Scholar]
- Elemuren, R.; Evitts, R.; Oguocha, I.; Kennell, G.; Gerspacher, R.; Odeshi, A. Slurry erosion-corrosion of 90° AISI 1018 steel elbow in saturated potash brine containing abrasive silica particles. Wear 2018, 410–411, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyagari, A.; Hasannaeimi, V.; Grewal, H.S.; Arora, H.; Mukherjee, S. Corrosion, Erosion and Wear Behavior of Complex Concentrated Alloys: A Review. Metals 2018, 8, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toor, I.U.; Irshad, H.M.; Badr, H.M.; Samad, M.A. The Effect of Impingement Velocity and Angle Variation on the Erosion Corrosion Performance of API 5L-X65 Carbon Steel in a Flow Loop. Metals 2018, 8, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Wang, D.; Wang, T.; Feng, Q.; Yang, X. Analysis and Comparison of Long-Distance Pipeline Failures. J. Pet. Eng. 2017, 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, C.A.R.; de Souza, F.J.; dos Santos, V.F. Mitigating elbow erosion with a vortex chamber. Powder Technol. 2016, 288, 6–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnie, I. Erosion of surfaces by solid particles. Wear 1960, 3, 87–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, R.E.; Kesana, N.R.; McLaury, B.S.; Shirazi, S.A.; Torres, C.F.; Schleicher, E.; Hampel, U. Experimental investigation of the effect of 90° standard elbow on horizontal gas–liquid stratified and annular flow characteristics using dual wire-mesh sensors. Exp. Therm Fluid Sci. 2014, 59, 72–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawancy, H.M.; Al-Hadhrami, L.M.; Al-Yousef, F.K. Analysis of corroded elbow section of carbon steel piping system of an oil–gas separator vessel. Case Stud. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2013, 1, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.A.; Alam, T.; Farhat, Z.N.; Mohamed, A.; Alfantazi, A. Effect of microstructure on the erosion behavior of carbon steel. Wear 2015, 332–333, 1080–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Kang, J.; Fan, J.; Gao, J. Study on erosion wear of fracturing pipeline under the action of multiphase flow in oil & gas industry. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2016, 32, 334–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, N.; Arabnejad, H.; Shirazi, S.A.; McLaury, B.S.; Lan, H. Experimental study of particle size, shape and particle flow rate on Erosion of stainless steel. Powder Technol. 2018, 336, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, T.; Farhat, Z.N. Slurry erosion surface damage under normal impact for pipeline steels. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2018, 90, 116–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; BaKeDaShi, W.; Li, Z.; Xu, Y.; Ji, W.; Zhang, C.; Cui, G.; Zhang, R. Effect of flow velocity on erosion–corrosion of 90-degree horizontal elbow. Wear 2017, 376–377, 516–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Zhang, G.A.; Guo, X.P. Erosion–corrosion at different locations of X65 carbon steel elbow. Corros. Sci. 2014, 85, 318–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; He, R.; Han, S.; Chen, Y. Erosion prediction of liquid-particle two-phase flow in pipeline elbows via CFD–DEM coupling method. Powder Technol. 2015, 275, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansouri, A.; Arabnejad, H.; Karimi, S.; Shirazi, S.A.; McLaury, B.S. Improved CFD modeling and validation of erosion damage due to fine sand particles. Wear 2015, 338–339, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, J.; Lui, A.; Zhang, Q.; Xiong, T.; Jiang, P.; Wei, W. Numerical investigation of the maximum erosion zone in elbows for liquid-particle flow. Powder Technol. 2018, 333, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.R.; Ya, H.H.; Pao, W.; Majid, M.A.A. Numerical Investigation of Sand Particle Erosion in Long Radius Elbow for Multiphase Flow; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 41–49. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, G.C.; de Souza, F.J.; de Moro Martins, D.A. Numerical prediction of the erosion due to particles in elbows. Powder Technol. 2014, 261, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.; Ya, H.H.; Pao, W. An Experimental Study on the Erosion-Corrosion Performance of AISI 1018 Carbon Steel and AISI 304L Stainless Steel 90-Degree Elbow Pipe. Metals 2019, 9, 1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.; Ya, H.H.; Pao, W.; Khan, A. Erosion–Corrosion of 30°, 60° and 90° Carbon Steel Elbows in a Multiphase Flow Containing Sand Particles. Materials 2019, 12, 3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oka, Y.I.; Yoshida, T. Practical estimation of erosion damage caused by solid particle impact: Part 2: Mechanical properties of materials directly associated with erosion damage. Wear 2005, 259, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, G.; Tabakoff, W. Erosion Prediction in Turbomachinery Resulting from Environmental Solid Particles. J. Aircr. 1975, 12, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Liu, H. Numerical simulation of solid particle erosion in a 90 degree bend for gas flow. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Offshore Mechanics and Arctic Engineering—OMAE, San Francisco, CA, USA, 8–13 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, L.; Shuang, S.; Guo, X.P.; Zhang, G.A. Erosion-corrosion of stainless steel at different locations of a 90° elbow. Corros. Sci. 2016, 111, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajahram, S.S.; Harvey, T.J.; Walker, J.C.; Wang, S.C.; Wood, R.J.K. Investigation of erosion–corrosion mechanisms of UNS S31603 using FIB and TEM. Tribol. Int. 2012, 46, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, C.; Frawley, P. Modelling of erosion–corrosion in practical geometries. Corr. Sci. 2009, 51, 769–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aminul Islam, M.; Farhat, Z.N.; Ahmed, E.M.; Alfantazi, A.M. Erosion enhanced corrosion and corrosion enhanced erosion of API X-70 pipeline steel. Wear 2013, 302, 1592–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Dou, Y.; Zhang, N.; Li, Z.; Wang, Z. A new method for predicting erosion damage of suddenly contracted pipe impacted by particle cluster via CFD-DEM. Materials 2018, 11, 1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
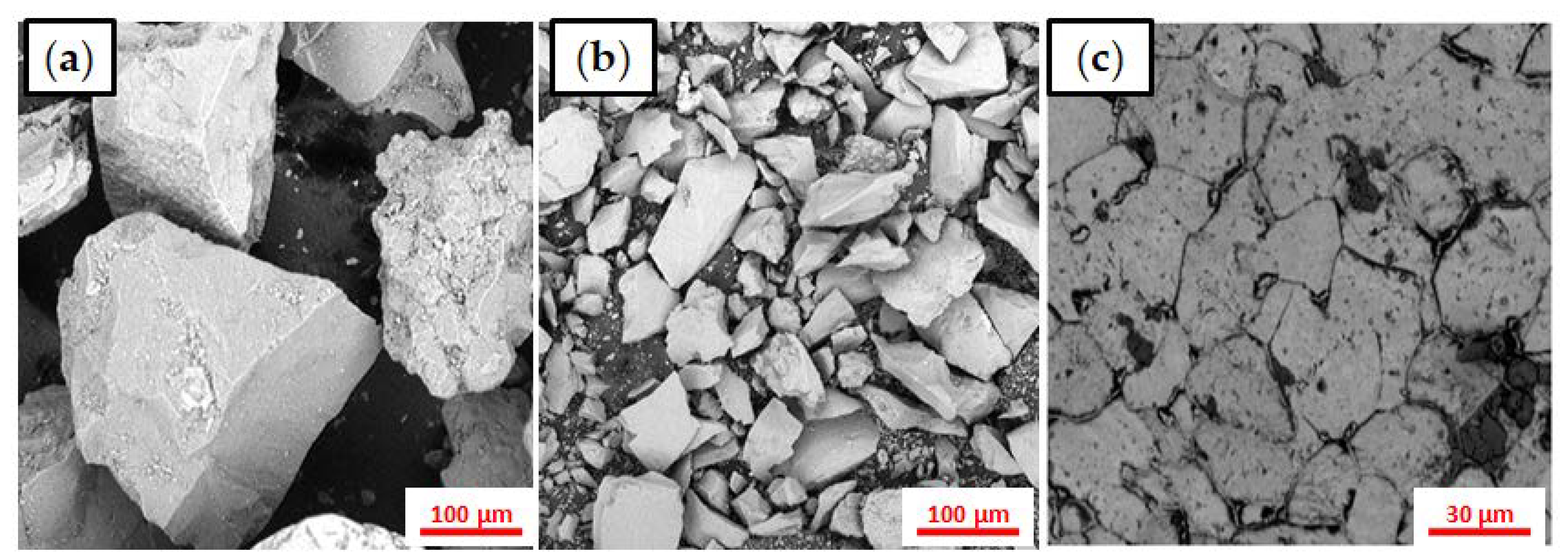



| 1018 CS | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Si | Cr | Cu | P | C | S | Ni | Mn | Fe |
| 0.26 | 0.21 | 0.25 | 0.045 | 0.2 | 0.035 | 0.3 | 0.52 | 98.18 |
| SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | Na2O | MgO | CaO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 98.08 | 1.17 | 0.28 | 0.03 | 0.22 | 0.22 |
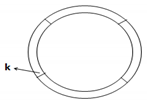
| Mesh Study | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Mesh | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| No of cells | 356912 | 524000 | 876313 |
| No of the node on k | 12 | 12 | 12 |
| Erosion rate (Maximum) (nm/s) | 0.053 | 0.092 | 0.093 |
 |  |  |  |
| Experimental Parameters from Zeng et al. [15] | |
|---|---|
| Target surface material | Carbon Steel |
| Erodent Particle | Sand |
| Erodent Diameter | 450 µm |
| Erodent Density | 2650 kg/m3 |
| Shape | Semi-round |
| Sand Concentration | 1.2 wt.% |
| Erodent Mass Flow Rate | 0.235 kg/s |
| Material Density | 7800 kg/m3 |
| Carrier Fluid | Water |
| Flow Velocity | 4 m/s |
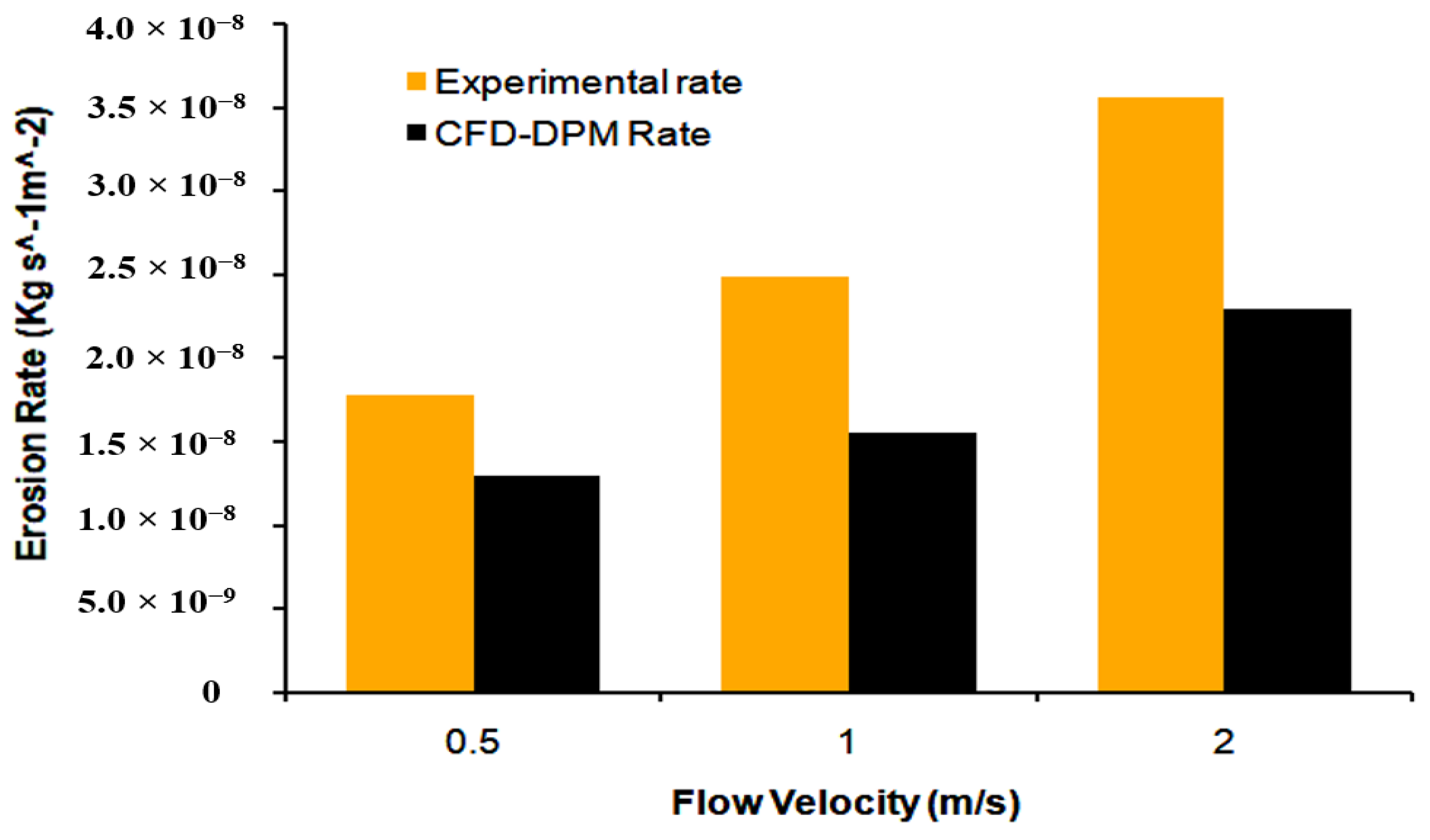
| Method | VL (m/s) | Mean Particle Size (µm) | Particle Concentration (Wt. %) | Mass Loss Rate (kg/m2·s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exp | 0.5 | 50 | 2 | 1.79 × 10−8 |
| Exp | 1 | 50 | 2 | 2.48 × 10−8 |
| Exp | 2 | 50 | 2 | 3.56 × 10−8 |
| CFD | 0.5 | 50 | 2 | 1.30 × 10−8 |
| CFD | 1 | 50 | 2 | 1.56 × 10−8 |
| CFD | 2 | 50 | 2 | 2.30 × 10−8 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khan, R.; H. Ya, H.; Pao, W.; bin Abdullah, M.Z.; Dzubir, F.A. Influence of Sand Fines Transport Velocity on Erosion-Corrosion Phenomena of Carbon Steel 90-Degree Elbow. Metals 2020, 10, 626. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10050626
Khan R, H. Ya H, Pao W, bin Abdullah MZ, Dzubir FA. Influence of Sand Fines Transport Velocity on Erosion-Corrosion Phenomena of Carbon Steel 90-Degree Elbow. Metals. 2020; 10(5):626. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10050626
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhan, Rehan, Hamdan H. Ya, William Pao, Mohamad Zaki bin Abdullah, and Faizul Azly Dzubir. 2020. "Influence of Sand Fines Transport Velocity on Erosion-Corrosion Phenomena of Carbon Steel 90-Degree Elbow" Metals 10, no. 5: 626. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10050626
APA StyleKhan, R., H. Ya, H., Pao, W., bin Abdullah, M. Z., & Dzubir, F. A. (2020). Influence of Sand Fines Transport Velocity on Erosion-Corrosion Phenomena of Carbon Steel 90-Degree Elbow. Metals, 10(5), 626. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10050626





