Red Tourism and Youth Education: A Systematic Review of the Literature
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- What is the role of RT in the socialization of youth regarding the understanding and assimilation of revolutionary history and red ideology in China?
- (2)
- What are the main concepts and foundations of RT?
- (3)
- How can the design of RT be optimized to enrich the educational experience of students and maximize its educational potential?
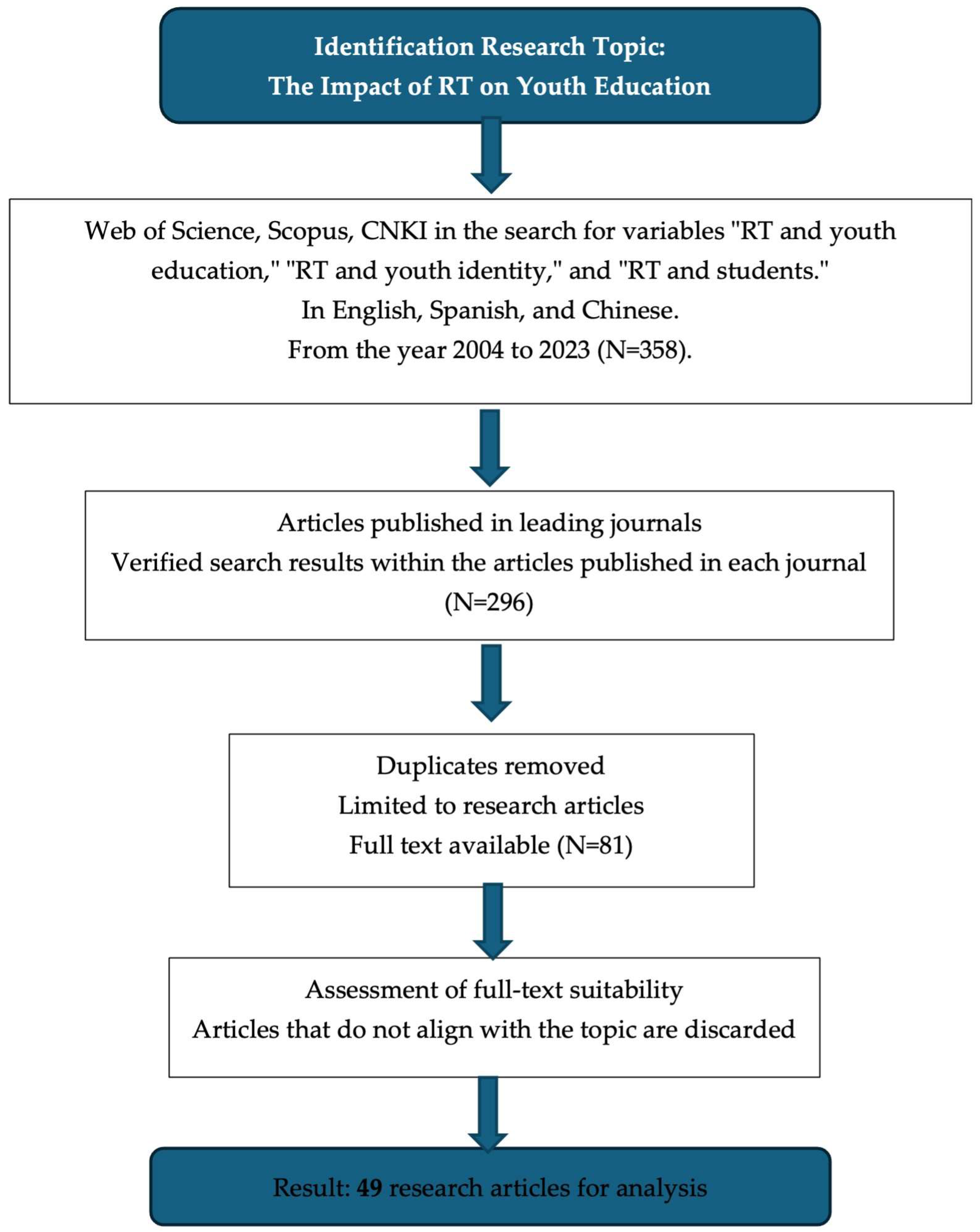
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
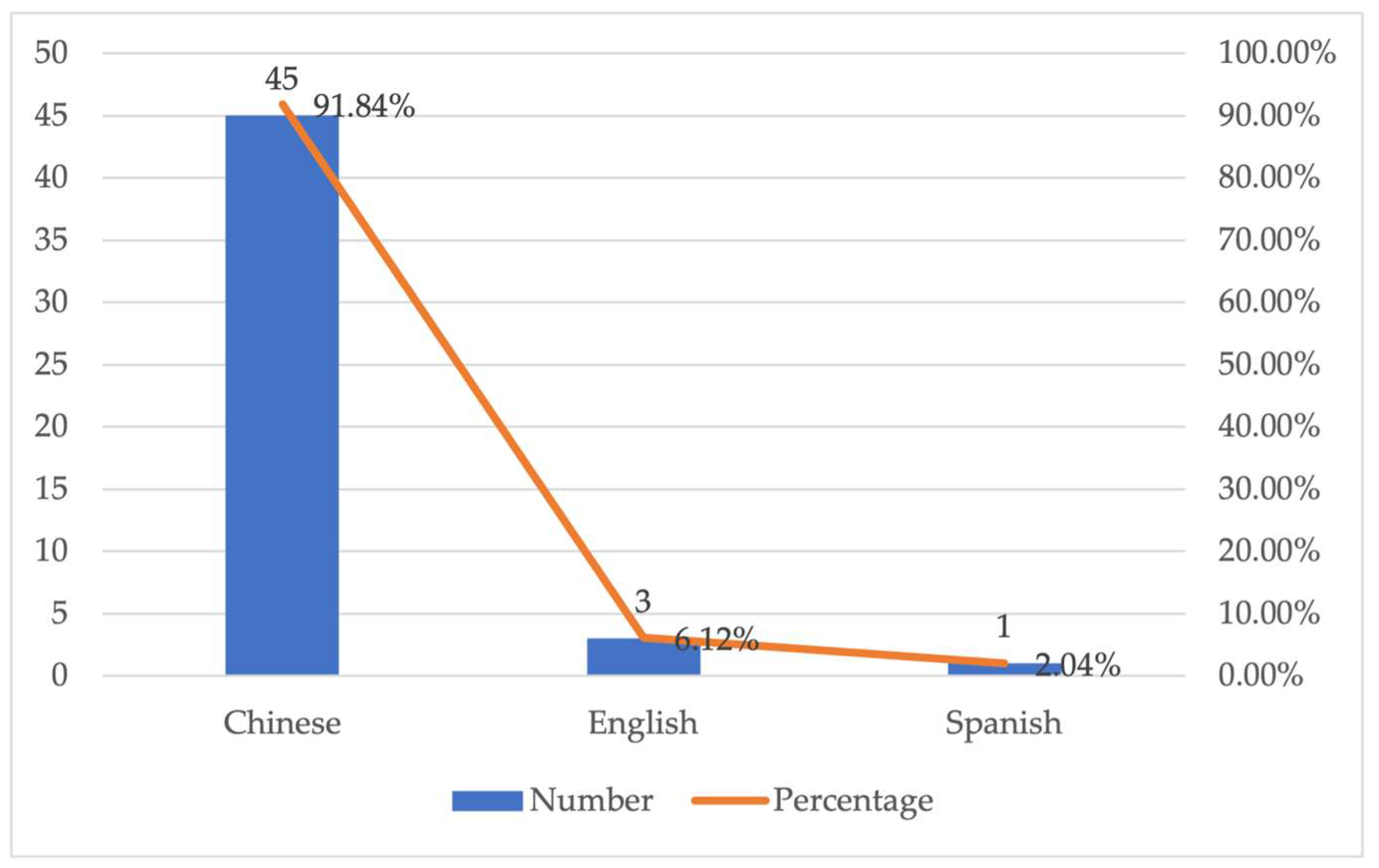
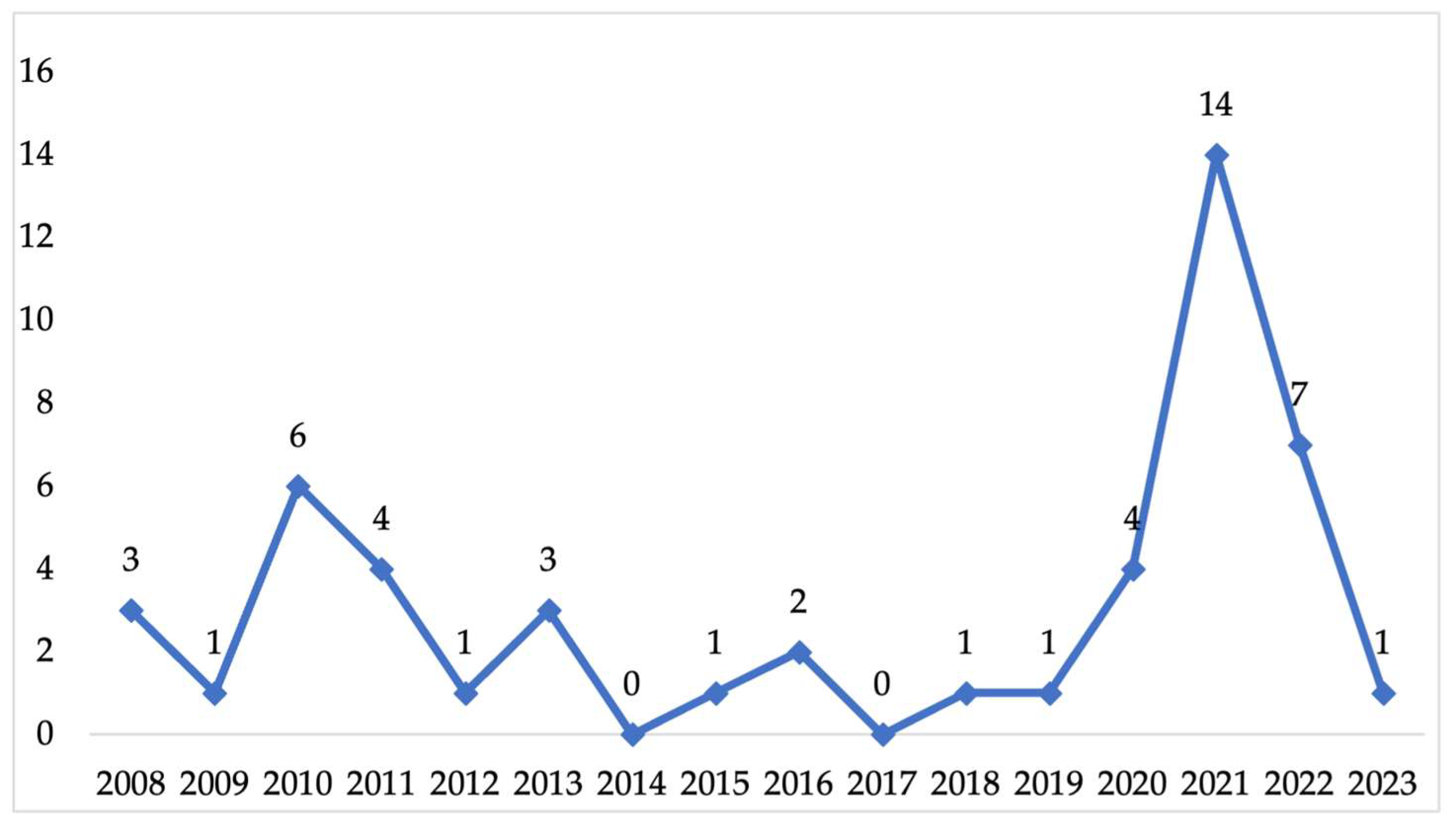
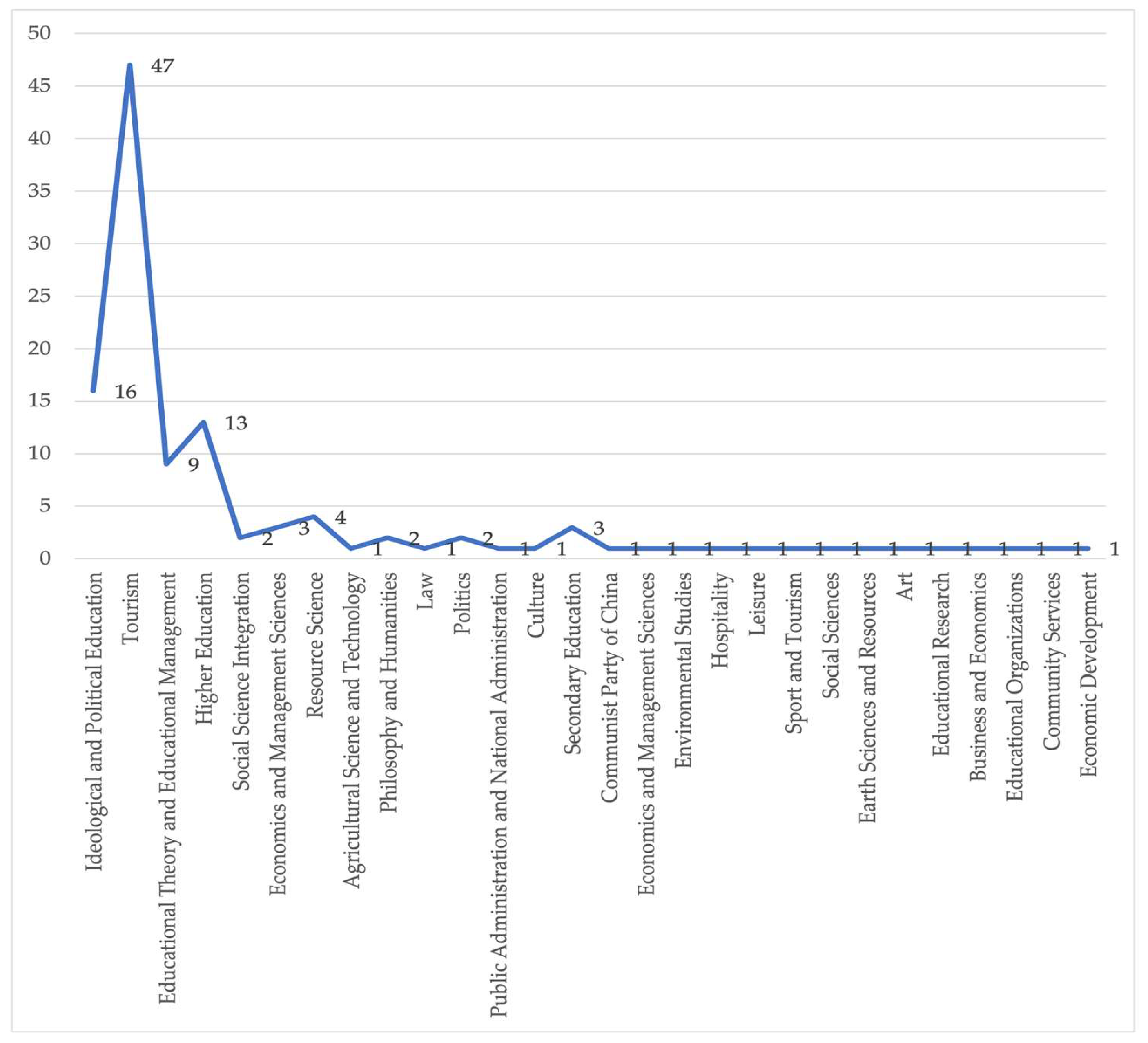
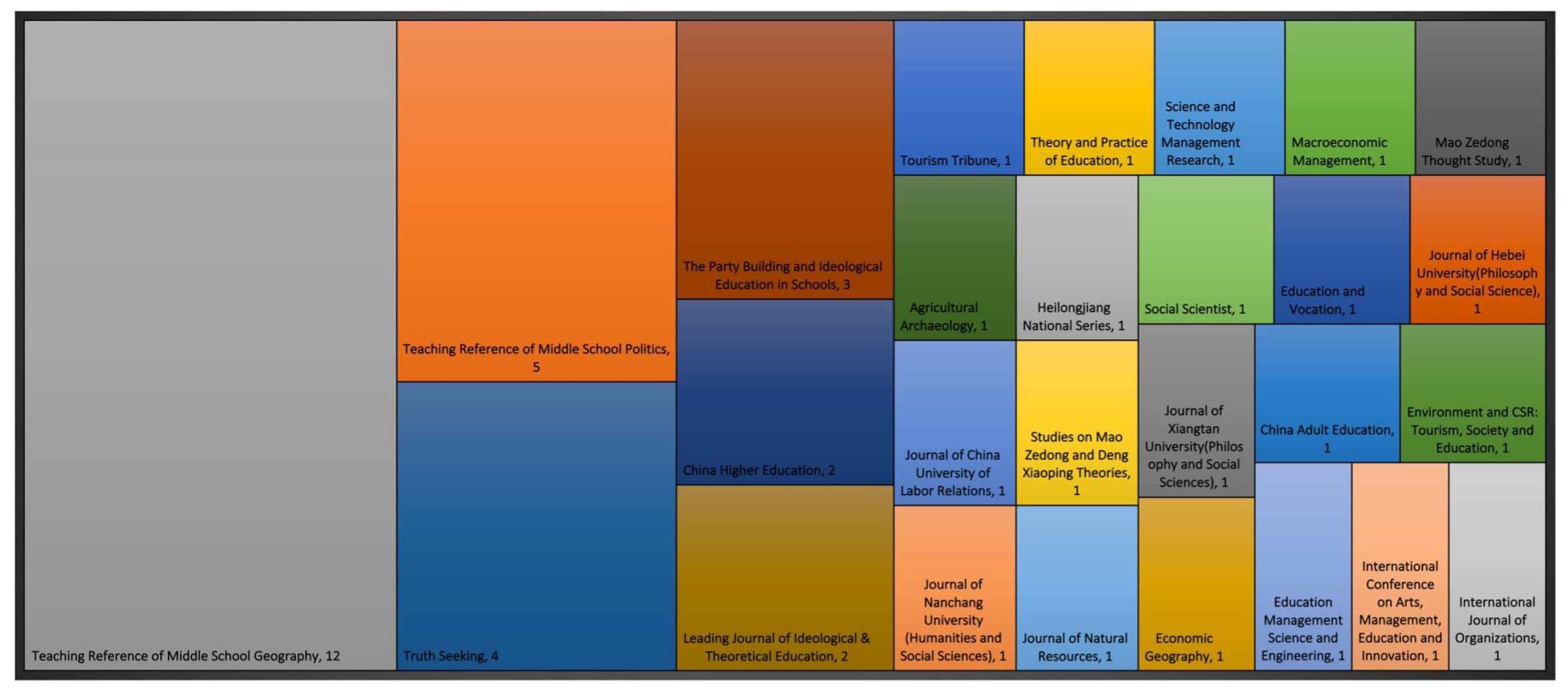
3.1. Linguistic, Temporal, and Disciplinary Distribution of RT Publications
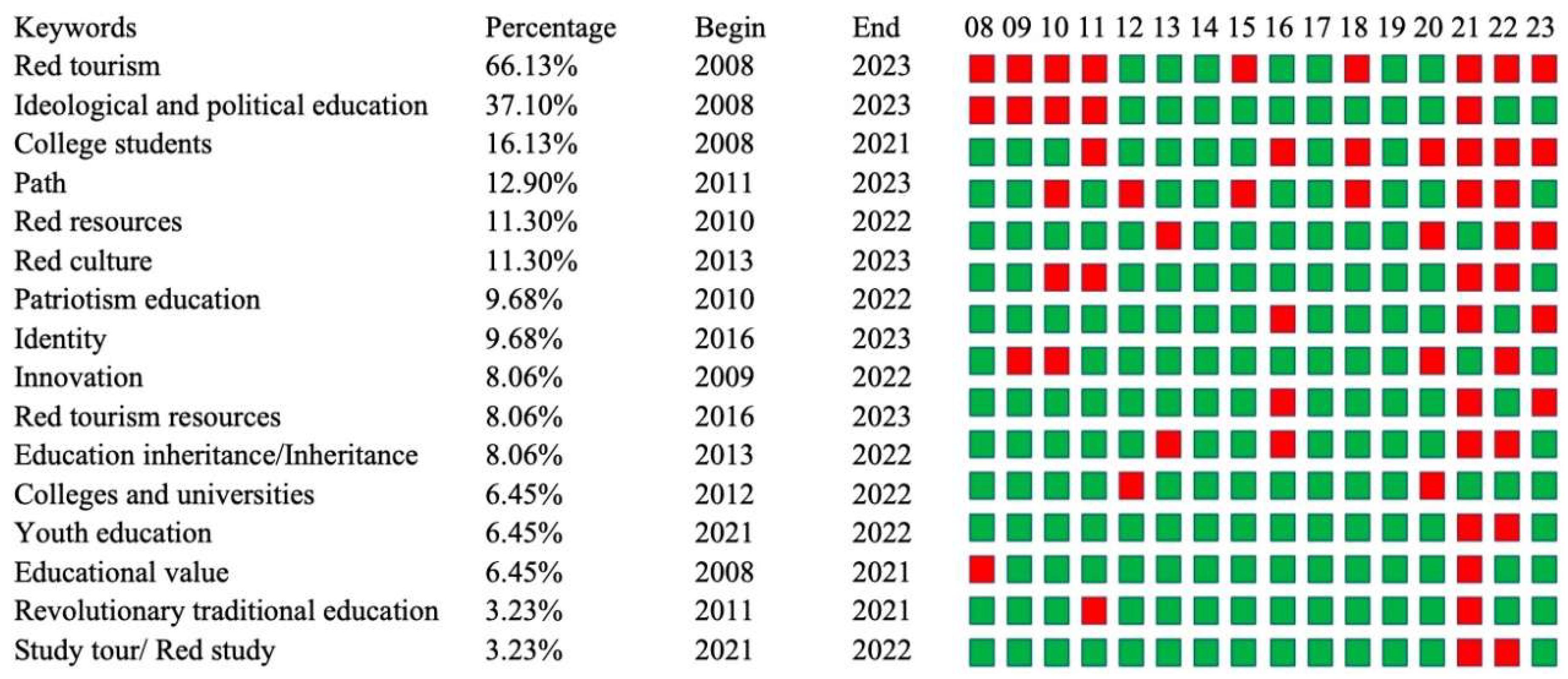
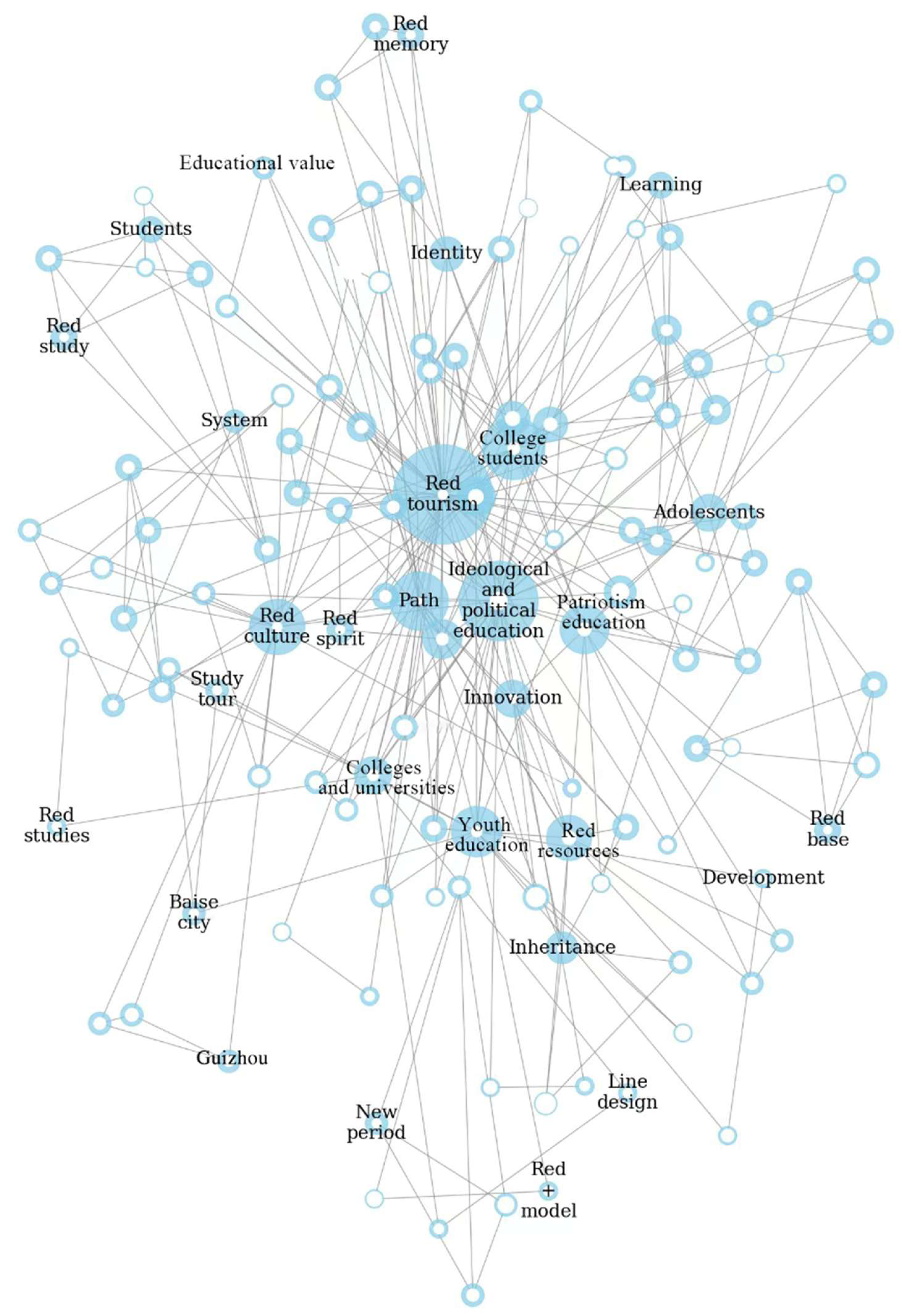
3.2. Keyword Analysis
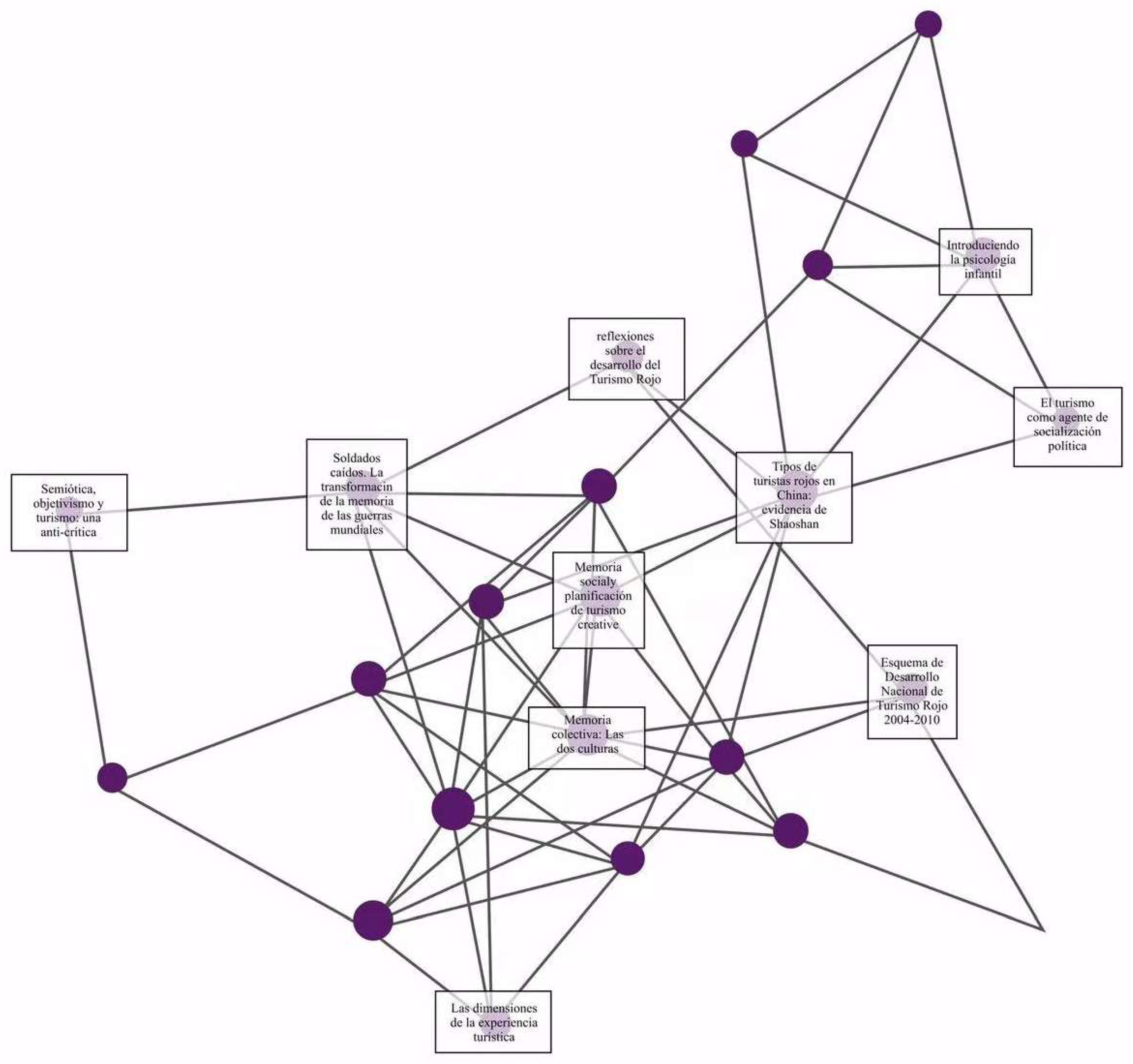
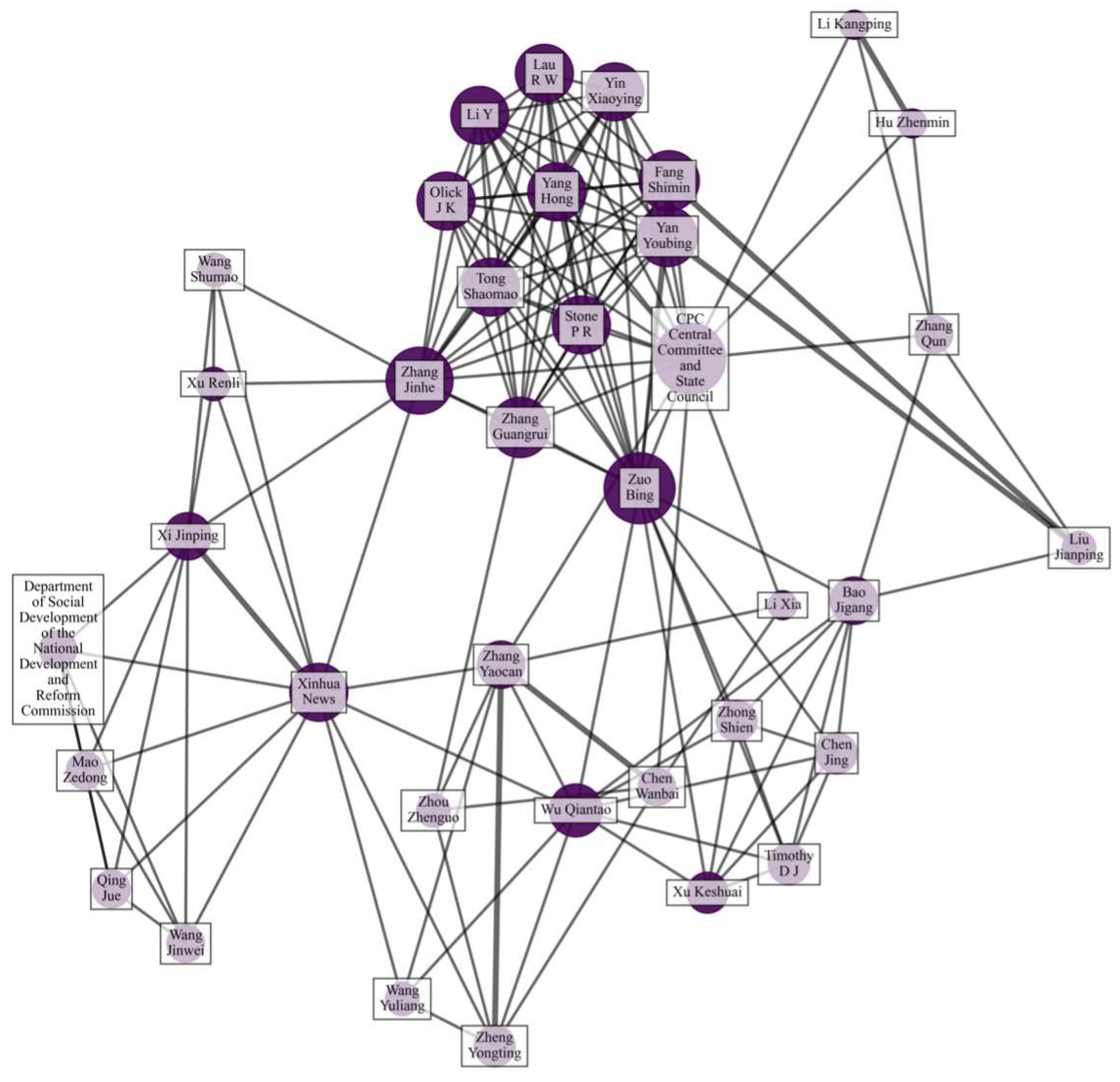
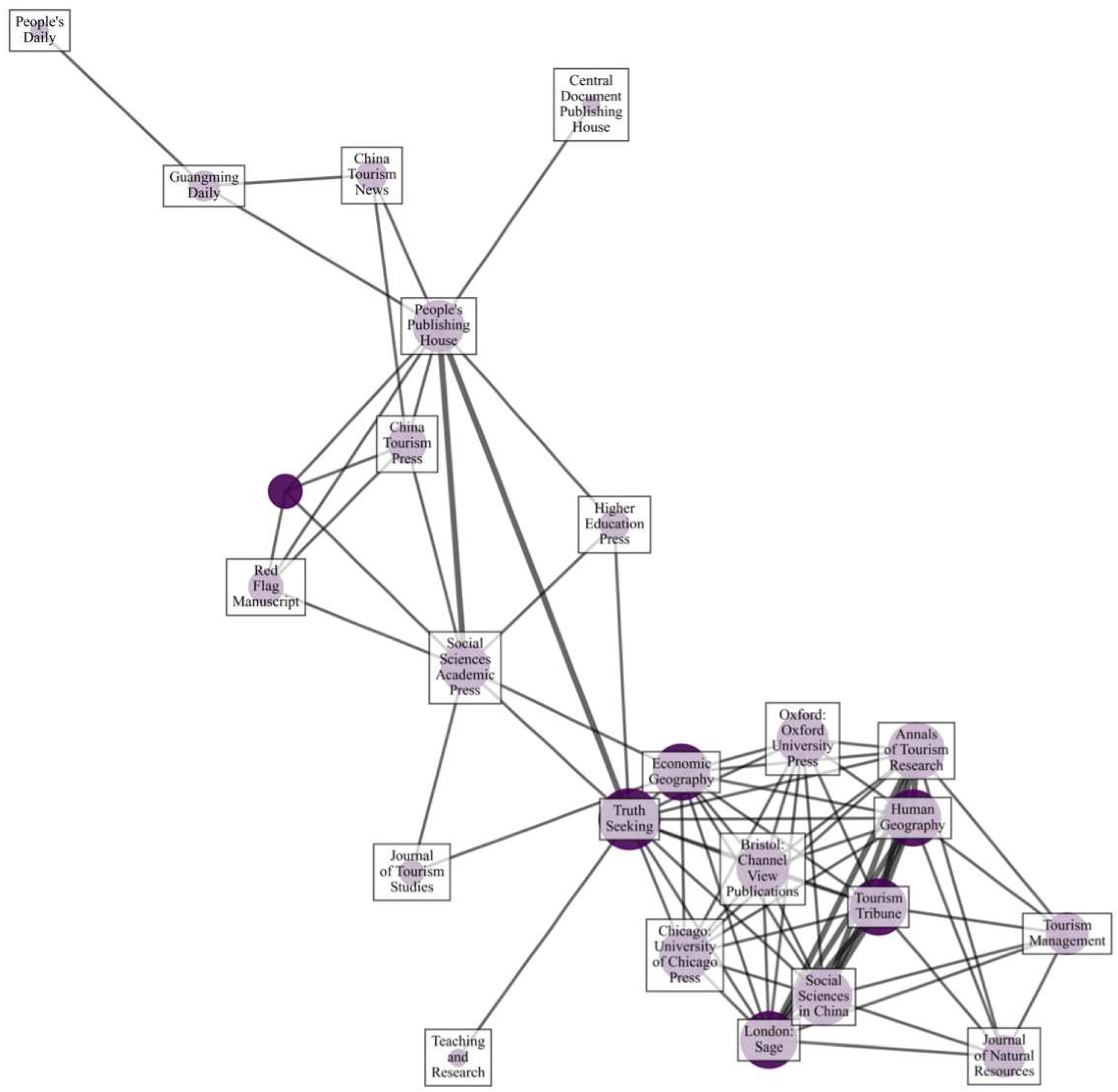
3.3. Co-Citation Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RT | red tourism |
| SLR | systematic literature review |
| CPC | Communist Party of China |
Appendix A
| No. | Author | Year | Title | Keywords | Language | Discipline | Academic Bases | Journal |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Xu Keshuai [50] | 2016 | RT and social memory | RT; red memory; Identity; symbol system; Sense of Sacredness | Chinese | Ideological and political education; tourism | CNKI | Tourism Tribune |
| 2 | Shi Huijun [2] | 2022 | The significance and path of integrating RT into ideological and political education | RT; ideological and political education; path; youth education | Chinese | Educational theory and educational management; tourism | CNKI | Teaching Reference of Middle School Politics |
| 3 | Qi Linna [3] | 2021 | The realization of ideological and political education function in RT | RT; ideological and political education; educational function; youth education | Chinese | Ideological and political education; tourism | CNKI | Teaching Reference of Middle School Geography |
| 4 | Zhang Li [4] | 2021 | Research on the value and application of Shanxi RT resources to the ideological and political education of college students | Shanxi RT; college students; ideological and political education; theoretical value; practical value; curriculum civics | Chinese | Higher education; social science integration; tourism | CNKI | Theory and Practice of Education |
| 5 | Zhu Xiaojie [6] | 2021 | The application of RT resources in ideological and political education in colleges and universities | RT; college students; sense of identity; red spirit; educational value | Chinese | Higher education; social science integration; tourism | CNKI | Teaching Reference of Middle School Geography |
| 6 | Jiao Xiaoying [23] | 2021 | Research on the path to improve the ideological and political functions of Guangdong’s RT resources | RT resources; ideological and political education resources; revolutionary culture; inheritance | Chinese | Educational theory and educational management; tourism | CNKI | Teaching Reference of Middle School Geography |
| 7 | Zhu Hong [8] | 2021 | The ideological and political education function of RT and its implementation path | RT; historical resources; ideological and political education; inheritance significance | Chinese | Educational theory and educational management; tourism | CNKI | Teaching Reference of Middle School Geography |
| 8 | Wang Yang [9] | 2021 | Research on the ideological and political education value of RT resources | Ideological and political education; educational carrier; RT resources; educational value; path | Chinese | Educational theory and educational management; tourism | CNKI | Teaching Reference of Middle School Geography |
| 9 | Li Qingyuan [10] | 2021 | Utilizing RT resources to expand ideological and political education for college students | Colleges and universities; ideological and political education; college students; spiritual life; RT | Chinese | Higher education; tourism | CNKI | Teaching Reference of Middle School Geography |
| 10 | Wei Dan [16] | 2021 | The development of red culture in the ideological and political social practice of colleges and universities in the new era. Take “Research on the Integration of RT Education Elements into Ideological and Political Education in Colleges and Universities in the New Media Era” as an example | Ideological and political education; college teaching; RT; college students; cultural identity | Chinese | Higher education; tourism | CNKI | Science and Technology Management Research |
| 11 | Shi Peixin [17] | 2020 | Improvement of RT education function and innovation of sustainable development mechanism | RT; sustainable tourism; tourism education function | Chinese | Ideological and political education; tourism | CNKI | Macroeconomic Management |
| 12 | Wei Zhen; Tan Juan [18] | 2021 | Exploring the ideological and political education value of red cultural tourism | Red cultural tourism; revolutionary traditional education; patriotism education; adolescents; ideological and political education | Chinese | Educational theory and educational management; tourism | CNKI | Teaching Reference of Middle School Politics |
| 13 | Xuan Shanwen [24] | 2020 | RT: opening up new ways of ideological and political education in colleges and universities | RT; ideological and political education; innovation | Chinese | Ideological and political education; tourism | CNKI | China Higher Education |
| 14 | Li Zhihui [29] | 2018 | On the value transformation of red resources in the ideological and political education of college students | Red resources; ideological and political education; value transformation; path | Chinese | Ideological and political education; tourism | CNKI | The Party Building and Ideological Education in Schools |
| 15 | Yan Jun; Yin Hang [47] | 2015 | The development of red resources and the coordinated realization of its ideological and political education functions—taking Sichuan Garze Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture as an example | Red resources; ideological and political education function; collaborative realization | Chinese | Ideological and political education; tourism | CNKI | Mao Zedong Thought Study |
| 16 | Sun Ying [20] | 2013 | An analysis of innovative carriers of moral education in colleges and universities based on the perspective of RT | RT; universities; moral education carriers | Chinese | Higher education; tourism | CNKI | Leading Journal of Ideological & Theoretical Education |
| 17 | Yang Zhaohui [79] | 2011 | The development path of RT’s integrated ideological permeability | RT; ideological and political education; integration; path | Chinese | Economics and management sciences; ideological and political education; tourism | CNKI | Truth Seeking |
| 18 | Hu Xiaojia; Liao Yunsheng [40] | 2011 | Ideological and political education and red resource development | Red resource; benefit distribution; ideological and political education | Chinese | Ideological and political education; resource science; tourism | CNKI | Truth Seeking |
| 19 | Jin Lingyun; Hu Zhenyu [71] | 2010 | Thoughts on the ideological and political education of college students using red resources | Ideological and political education; Jiangxi red resources; development and utilization | Chinese | Agricultural science and technology; philosophy and humanities; education and social sciences integration; higher education; tourism | CNKI | Agricultural Archaeology |
| 20 | Cheng Yangguo; Huang Xijia; Wang Ge [41] | 2010 | Innovation of RT methods based on ideological and political education | RT; ideological and political education; innovation | Chinese | Ideological and political education; resource science; tourism | CNKI | Truth Seeking |
| 21 | Lyu Li [72] | 2010 | An analysis of RT and the ideological and political education of contemporary college students | RT; college students; ideological and political education | Chinese | Education and social sciences integration; higher education; tourism | CNKI | Journal of China University of Labor Relations |
| 22 | Zhou Meng [49] | 2010 | RT: a pioneering work in traditional education of patriotism and revolution | Revolutionary education; patriotism; RT; Jinggangshan spirit | Chinese | Ideological and political education; law; tourism | CNKI | Truth Seeking |
| 23 | Xu Renli [27] | 2009 | On the ideological and political education function of RT and its realization | RT; ideological and political education function; innovation | Chinese | Politics; ideological and political education; tourism | CNKI | The Party Building and Ideological Education in Schools |
| 24 | Liao Yunsheng; Chen Bo [48] | 2008 | On the realization of the ideological and political education value of RT in Jinggangshan | Jinggangshan spirit; RT; ideological and political education; educational value | Chinese | Politics; ideological and political education; tourism | CNKI | Journal of Nanchang University(Humanities and Social Sciences) |
| 25 | Zhou Rui [54] | 2022 | Give full play to the ideological and political education value of RT resources | Ideological and political education; patriotism education; RT; innovation | Chinese | Resource science; educational theory and educational management; tourism | CNKI | Teaching Reference of Middle School Politics |
| 26 | Wang Wei; Tu Dengshenggen [25] | 2022 | Research on the “Red+” model to build a strong sense of community for the Chinese nation in ethnic areas | Chinese nation’s community; red resources; Red+ model | Chinese | Public administration and national administration; tourism | CNKI | Heilongjiang National Series |
| 27 | Wen Fengping; Hu Xueqin [67] | 2022 | Research on red study tours from the perspective of regional geography—taking Baise City, Guangxi, as an example | Regional geography; study tour; red resources; Baise City | Chinese | Education and social sciences integration; philosophy and humanities; culture; tourism | CNKI | Teaching Reference of Middle School Geography |
| 28 | Zhang Qingxue [68] | 2022 | The value and exploration of red research resources in border areas | Red studies; resource mining; youth education | Chinese | Educational theory and education management; tourism | CNKI | Teaching Reference of Middle School Geography |
| 29 | Zhang Zhen; Liu Qian; Wang Yun [69] | 2022 | Research on the design and implementation of red study tour routes in Northern Shaanxi | Red research; line design; youth education | Chinese | Secondary education; tourism | CNKI | Teaching Reference of Middle School Geography |
| 30 | Zhao Hong [78] | 2022 | The inheritance of red culture in subject education | Red culture; subject education; red education; cultural inheritance | Chinese | Educational theory and educational management; tourism | CNKI | Teaching Reference of Middle School Politics |
| 31 | Wang Hongchun; Xu Qun; Zhao Donglai [56] | 2021 | The development and utilization of red resources must adhere to the education standard—an analysis of several adverse phenomena | Red resources; development; education-oriented | Chinese | Resource science; Communist Party of China; tourism | CNKI | Studies on Mao Zedong and Deng Xiaoping Theories |
| 32 | Yuan Zhiling [35] | 2021 | The design and implementation of red study tour activities from the perspective of core literacy | Core competencies; red study; design of activities; political education; students | Chinese | Secondary education; tourism | CNKI | Teaching Reference of Middle School Geography |
| 33 | Peng Jinfu [80] | 2021 | RT and ideological and political education | Patriotism education; red cultural dissemination; RT; college students; identity | Chinese | Ideological and political education; tourism | CNKI | Teaching Reference of Middle School Geography |
| 34 | Fan Weihong; Li Jiguang [82] | 2021 | Research on the ideological and political education function of RT | Youth groups; mainstream values; ideological and political education; RT; strengthening awareness | Chinese | Secondary education; tourism | CNKI | Teaching Reference of Middle School Geography |
| 35 | Zhong Shi’en; Lu Wenjing; Peng Hongsong; Dai Shuqi [38] | 2021 | Red scarf children’s understanding of RT resources and patriotism—empirical evidence and inspiration from the case of Yuhuatai Martyrs Cemetery | Children’s tourism; RT resources; patriotism education; educational value | Chinese | Ideological and political education; tourism | CNKI | Journal of Natural Resources |
| 36 | Wang Xiaoju; Xu Lilan [42] | 2020 | The integration and mutual promotion of RT and political ethics education in the new era | RT; political ethics education; realistic basis; institutional guarantee; path | Chinese | Ideological and political education; tourism | CNKI | Social Scientist |
| 37 | Gai Yanqiu; Li Jianfeng [83] | 2020 | The educational function of RT resources | Spiritual needs; RT; revolutionary history; learning; educational function | Chinese | Higher education; tourism | CNKI | Teaching Reference of Middle School Politics |
| 38 | Yang Kai [30] | 2016 | Analysis of RT resources and innovation paths for cultural inheritance in universities | RT resources; university culture; inheritance; innovation; path | Chinese | Higher education; tourism | CNKI | The Party Building and Ideological Education in Schools |
| 39 | Zhang Shaorong [39] | 2013 | On the construction of the red cultural education inheritance system | Red culture; education inheritance; system; construction | Chinese | Higher education; tourism | CNKI | Leading Journal of Ideological & Theoretical Education |
| 40 | Liu Huazheng [37] | 2012 | The educational form of red resources in extracurricular practice of ideological and political theory in colleges and universities | Colleges and universities; ideological and political theory; extracurricular practice; red resources | Chinese | Higher education; tourism | CNKI | Education and Vocation |
| 41 | Wang Wanyi [81] | 2011 | Carry out RT and promote patriotism education in colleges and universities | Patriotism education; RT; revolutionary traditional education; college students | Chinese | Higher education; tourism | CNKI | China Higher Education |
| 42 | Zhou Yan; Xing Huibin [53] | 2011 | Using RT to improve college students’ ideological and moral cultivation | RT; educational function; college students | Chinese | Higher education; tourism | CNKI | Journal of Hebei University (Philosophy and Social Science) |
| 43 | Zhu Dongguo [31] | 2010 | RT consumption behavior and marketing strategies of college students | RT; college students; consumer behavior; marketing strategy | Chinese | Education and social sciences integration; tourism | CNKI | Journal of Xiangtan University (Philosophy and Social Sciences) |
| 44 | Tan Shuhui; Yu Caixia; Zhang Heqing [36] | 2008 | In-depth development of RT and interactive development of outdoor sports for college students—taking Changsha–Zhuzhoutan as an example | RT; college students; extracurricular practice; Interactive development; Changsha–Zhuzhou–Tantan | Chinese | Economics and management sciences; ideological and political education; tourism | CNKI | Economic Geography |
| 45 | Wang Jingping; Xie Meijun [55] | 2008 | An analysis of the educational function of RT culture | RT; RT culture; educational function; | Chinese | Economics and management sciences; tourism | CNKI | China Adult Education |
| 46 | Cao Xiaoyong; Zhang, Y [34] | 2013 | A Research on RT and ideological education of Chinese universities students | RT; university students; ideological and political education | English | Environmental studies; hospitality, leisure, sport, and tourism; social sciences | Web of Science | Environment and CSR: Tourism, Society and Education |
| 47 | Sun Ying [26] | 2010 | Research on educational functions of special interest tourism for university students in China | Special interest tourism; educational functions; patriotism education | English | Earth sciences and resources; tourism | Web of Science | Education Management Science and Engineering |
| 48 | Chen Xiaoyan; Gao, J [52] | 2019 | Research on the promotion of tourism attraction of red research tourism products in Shaanxi Province | RT products; research tourism; tourism attraction | English | Art; educational research; business and economics; management | Web of Science | International Conference on Arts, Management, Education and Innovation |
| 49 | Fengyi Wang; Victoria Sanagustín Fons; Violante Martínez Quintana [84] | 2023 | Innovations in educational organizations: the case of RT in China | RT; service-learning; solidarity initiatives; logistical support; economic development | Spanish | Educational organizations; community services; economic development | Web of Science | International Journal of Organizations |
Appendix B
| Section and Topic | Item # | Checklist Item | Location Where Item Is Reported |
|---|---|---|---|
| TITLE | |||
| Title | 1 | Identify the report as a systematic review. | 1 |
| ABSTRACT | |||
| Abstract | 2 | See the PRISMA 2020 for the abstracts checklist. | 19 |
| INTRODUCTION | |||
| Rationale | 3 | Describe the rationale for the review in the context of existing knowledge. | 1–3 |
| Objectives | 4 | Provide an explicit statement of the objective(s) or question(s) the review addresses. | 3 |
| METHODS | |||
| Eligibility criteria | 5 | Specify the inclusion and exclusion criteria for the review and how studies were grouped for the syntheses. | 4 |
| Information sources | 6 | Specify all databases, registers, websites, organisations, reference lists, and other sources searched or consulted to identify studies. Specify the date when each source was last searched or consulted. | 4 |
| Search strategy | 7 | Present the full search strategies for all databases, registers and websites, including any filters and limits used. | 4 |
| Selection process | 8 | Specify the methods used to decide whether a study met the inclusion criteria of the review, including how many reviewers screened each record and each report retrieved, whether they worked independently, and if applicable, details of automation tools used in the process. | 4–5 |
| Data collection process | 9 | Specify the methods used to collect data from reports, including how many reviewers collected data from each report, whether they worked independently, any processes for obtaining or confirming data from study investigators, and if applicable, details of automation tools used in the process. | 4–5 |
| Data items | 10a | List and define all outcomes for which data were sought. Specify whether all results that were compatible with each outcome domain in each study were sought (e.g., for all measures, time points, and analyses), and if not, the methods used to decide which results to collect. | 4 |
| 10b | List and define all other variables for which data were sought (e.g., participant and intervention characteristics and funding sources). Describe any assumptions made about any missing or unclear information. | 4 | |
| Study risk of bias assessment | 11 | Specify the methods used to assess risk of bias in the included studies, including details of the tool(s) used, how many reviewers assessed each study and whether they worked independently, and if applicable, details of automation tools used in the process. | 4–5 |
| Effect measures | 12 | Specify for each outcome the effect measure(s) (e.g., risk ratio and mean difference) used in the synthesis or presentation of results. | 3–5 |
| Synthesis methods | 13a | Describe the processes used to decide which studies were eligible for each synthesis (e.g., tabulating the study intervention characteristics and comparing against the planned groups for each synthesis (item #5)). | 3–5 |
| 13b | Describe any methods required to prepare the data for presentation or synthesis, such as handling of missing summary statistics, or data conversions. | 3–5 | |
| 13c | Describe any methods used to tabulate or visually display results of individual studies and syntheses. | 3–5 | |
| 13d | Describe any methods used to synthesize results and provide a rationale for the choice(s). If meta-analysis was performed, describe the model(s), method(s) to identify the presence and extent of statistical heterogeneity, and software package(s) used. | 3–5 | |
| 13e | Describe any methods used to explore possible causes of heterogeneity among study results (e.g., subgroup analysis and meta-regression). | 3–5 | |
| 13f | Describe any sensitivity analyses conducted to assess robustness of the synthesized results. | 3–5 | |
| Reporting bias assessment | 14 | Describe any methods used to assess risk of bias due to missing results in a synthesis (arising from reporting biases). | 3–5 |
| Certainty assessment | 15 | Describe any methods used to assess certainty (or confidence) in the body of evidence for an outcome. | 3–5 |
| RESULTS | |||
| Study selection | 16a | Describe the results of the search and selection process, from the number of records identified in the search to the number of studies included in the review, ideally using a flow diagram. | 5–13 |
| 16b | Cite studies that might appear to meet the inclusion criteria, but which were excluded, and explain why they were excluded. | 5–13 | |
| Study characteristics | 17 | Cite each included study and present its characteristics. | 5–13 |
| Risk of bias in studies | 18 | Present assessments of risk of bias for each included study. | 5–13 |
| Results of individual studies | 19 | For all outcomes, present the following results for each study: (a) summary statistics for each group (where appropriate) and (b) an effect estimate and its precision (e.g., confidence/credible interval), ideally using structured tables or plots. | 5–13 |
| Results of syntheses | 20a | For each synthesis, briefly summarize the characteristics and risk of bias among contributing studies. | 5–13 |
| 20b | Present results of all statistical syntheses conducted. If meta-analysis was performed, present for each the summary estimate and its precision (e.g., confidence/credible interval) and measures of statistical heterogeneity. If comparing groups, describe the direction of the effect. | 5–13 | |
| 20c | Present results of all investigations of possible causes of heterogeneity among study results. | 5–13 | |
| 20d | Present results of all sensitivity analyses conducted to assess the robustness of the synthesized results. | 5–13 | |
| Reporting biases | 21 | Present assessments of risk of bias due to missing results (arising from reporting biases) for each synthesis assessed. | 5–13 |
| Certainty of evidence | 22 | Present assessments of certainty (or confidence) in the body of evidence for each outcome assessed. | 5–13 |
| DISCUSSION | |||
| Discussion | 23a | Provide a general interpretation of the results in the context of other evidence. | 13–14 |
| 23b | Discuss any limitations of the evidence included in the review. | 13–14 | |
| 23c | Discuss any limitations of the review processes used. | 14 | |
| 23d | Discuss implications of the results for practice, policy, and future research. | 14 | |
| OTHER INFORMATION | |||
| Registration and protocol | 24a | Provide registration information for the review, including register name and registration number, or state that the review was not registered. | 14 |
| 24b | Indicate where the review protocol can be accessed, or state that a protocol was not prepared. | 14 | |
| 24c | Describe and explain any amendments to information provided at registration or in the protocol. | 14 | |
| Support | 25 | Describe sources of financial or non-financial support for the review and the role of the funders or sponsors in the review. | 14 |
| Competing interests | 26 | Declare any competing interests of review authors. | 15 |
| Availability of data, code and other materials | 27 | Report which of the following are publicly available and where they can be found: template data collection forms; data extracted from included studies; data used for all analyses; analytic code; any other materials used in the review. | 15 |
References
- Soro, J.L. La Memoria Histórica Como Atractivo Turístico. El Diario.es, Aragón 2017. Available online: https://www.eldiario.es/aragon/sociedad/memoria-historica-atractivo-turistico_1_2977086.html (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- Shi, H. The Significance and Path of Integrating RT into Ideological and Political Education. Teach. Ref. Middle Sch. Politics 2022, 32, 111. Available online: https://www.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFD&dbname=CJFDLAST2022&filename=ZXZZ202232015&uniplatform=OVERSEA&v=IxCQ18NPtIi9XRIYZMma-Xk35uQ7a_p8Fw5-qIcG6b5Ud5bNG90vJ6TPLGidPX9t (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- Qi, L. The Realization of Ideological and Political Education Function in RT. Teach. Ref. Middle Sch. Geogr. 2021, 17, I0010. Available online: https://www.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFD&dbname=CJFDLAST2023&filename=ZDCK202117034&uniplatform=OVERSEA&v=Kfwxy7P2BfHZndwV32I1mtwcHoW1ky6WBduh5Hmi_TmNt0NuOHiN5wioyBIVzt9A (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- Zhang, L. Research on the Value and Application of Shanxi RT Resources to the Ideological and Political Education of College Students. Theory Pract. Educ. 2021, 41, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Shi, X. Informal institutions and corporate innovation: A Perspective from Red Culture. Heliyon 2024, 10, e32049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X. The Application of RT Resources in Ideological and Political Education in Colleges and Universities. Teach. Ref. Middle Sch. Geogr. 2021, 16, 99. [Google Scholar]
- People’s Education Press. Outline of Chinese and Foreign History (Part 1); People’s Education Press: Beijing, China, 2019; ISBN 9787517837558. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H. The Ideological and Political Education Function of RT and Its Implementation Path. Teach. Ref. Middle Sch. Geogr. 2021, 14, 97. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y. Research on the Ideological and Political Educational Value of Red Tourism Resources. Teach. Ref. Middle Sch. Geogr. 2021, 14, 103–104. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q. Utilizing RT Resources to Expand Ideological and Political Education for College Students. Teach. Ref. Middle Sch. Geogr. 2021, 14, 98–99. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=wUXT8w3WHHosx4EZp0AVZCbu9L4-FQ7Pl8q5-57J_UAtq7ZyxthGAgqiYLGfXbuVy4WzimLG7cNXafyJayPw2_0r9OguJB5GrMVyEZ_m_JFjqlFuMFpGZmg3usH3WbwFntO_McgdcKjOvnUqmUvZgkZGcxwvu5G05hF691Xu98ynTop_W0xGIJ4x02jxtMH4&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- Poria, Y.; Butler, R.; Airey, D. Revisiting Mieczkowski’s conceptualization of tourism. Tour. Geogr. 2003, 5, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuxin, F.; Yunxia, T.; Xiaoyu, L. The network characteristics of classic red tourist attractions in Shaanxi province, China. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0299286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heung, V.C.S.; Leong, J.S.L. Travel demand and behavior of university students in Hong Kong. Asia Pac. J. Tour. Res. 2006, 11, 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.N.; Timothy, D.J. Tourists’ consumption and perceptions of red heritage. Ann. Tour. Res. 2017, 63, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wall, G.; Zhao, N.R. China’s red tourism: Communist heritage, politics, and identity in a party-state. Int. J. Tour. Cities 2017, 3, 305–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D. The Development of Red Culture in the Ideological and Political Social Practice of Colleges and Universities in the New Era. Take “Research on the Integration of RT Education Elements into Ideological and Political Education in Colleges and Universities in the New Media Era” as an Example. Sci. Tech. Manag. Res. 2021, 41, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P. Improvement of RT Education Function and Innovation of Sustainable Development Mechanism. Macroecon. Manag. 2020, 5, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Tan, J. Exploring the Ideological and Political Education Value of Red Cultural Tourism. Red Cult. Tourism Teach. Ref. Middle Sch. Politics 2020. Available online: https://www.zhangqiaokeyan.com/academic-journal-cn_detail_thesis/02012102168424.html (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- Ministry of Culture and Tourism. Utilizing Red Resources to Cultivate the New People of the Era: Action Plan for RT to Promote Moral Education (2023–2025); Ministry of Culture and Tourism: Beijing, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y. An Analysis of Innovative Carriers of Moral Education in Colleges and Universities Based on the Perspective of RT. Lead. J. Ideol. Theor. Educ. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. Available online: https://www.bmj.com/content/372/bmj.n71 (accessed on 12 December 2024). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavlou, E.-S.; Garmpis, A. Enhancing Social Skills in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder Through Natural Musical Instruments and Innovative Digital Musical Instruments: A Literature Review. Societies 2025, 15, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, X. Research on the Path to Enhance the Ideological and Political Functions of Guangdong’s RT Resources. Teach. Ref. Middle Sch. Geogr. 2021, 15, 87. [Google Scholar]
- Xuan, S. RT: Opening Up New Ways of Ideological and Political Education in Colleges and Universities. China High. Educ. 2020, 2, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Tu, D. Research on the “Red+” Model to Build a Strong Sense of Community for the Chinese Nation in Ethnic Areas. Heilongjiang Natl. Ser. 2022, 4, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y. Research on Educational Functions of Special Interest Tourism for University Students in China. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Education and Management Science, Shenzhen, China, 21–22 January 2010; pp. 896–900, ISBN 978-0-98-6854-6-6. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, R.L. Research on the Integration and Innovation of RT in China; Editorial China: Yanshi, China, 2020; ISBN 9787517133278. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, K.S. Types of red tourists in China: Evidence from Shaoshan. Ann. Tour. Res. 2015, 51, 57–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.H. On the Transformation of the Value of Red Resources in the Ideological and Political Education of University Students. Party Build. Ideol. Educ. Sch. 2018, 8, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, K. Analysis of RT Resources and Innovation Paths for Cultural Inheritance in Universities. Party Build. Ideol. Educ. Sch. 2016, 3, 80–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D. RT Consumption Behavior and Marketing Strategies of College Students. J. Xiangtan Univ. (Philos. Soc. Sci.) 2010, 34, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, X. Review and Perspective on Research on RT for Youth in China in the New Era. Travel Overv. (Second. Half Mon.) 2016, 12, 286. [Google Scholar]
- Heck, R.H. Studying Educational and Social Policy: Theoretical Concepts and Research Methods; Routledge: London, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Zhang, Y. A Research on Red Tourism and Ideological Education of Chinese University Students. In Proceedings of the 9th Euro-Asia Conference on Environment and CSR: Tourism, Society and Education, Tokyo, Japan, 29–30 June 2013; pp. 187–192, ISBN 978-3-86573-751-9. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Z. The Design and Implementation of Red Study Tour Activities from the Perspective of Core Literacy. Teach. Ref. Middle Sch. Geogr. 2021, 21, 90–91. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, S.; Yu, C.; Zhang, H. In-depth Development of Red Tourism and Interactive Development of Outdoor Sports for College Students—Taking Changsha−Zhuzhoutan as an Example. Econ. Geogr. 2008, 28, 4. Available online: https://xueshu.baidu.com/usercenter/paper/show?paperid=6e6b019f251003b1fe1daf2dfb916bfa&site=xueshu_se (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- Liu, H. The Educational Form of Red Resources in Extracurricular Practice of Ideological and Political Theory in Colleges and Universities. Educ. Vocat. 2012, 29, 173–174. Available online: https://xueshu.baidu.com/usercenter/paper/show?paperid=97ec44176750565281a8556d419bf128&site=xueshu_se (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- Zhong, S.; Lu, W.; Peng, H.; Dai, S. Red Scarf Children’s Understanding of RT Resources and Patriotism—Empirical Evidence and Inspiration from the Case of Yuhuatai Martyrs Cemetery. J. Nat. Resour. 2021, 36, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S. On the Construction of the Red Cultural Education Inheritance System. Leading J. Ideol. Theor. Educ. 2013, 5, 116–118. Available online: https://xueshu.baidu.com/usercenter/paper/show?paperid=948961408fd4be201c7b27a6b088d755&site=xueshu_se&hitarticle=1 (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- Hu, X.; Liao, Y. Ideological and Political Education and Red Resource Development. Truth Seeking 2011, 3, 94–96. Available online: https://xueshu.baidu.com/usercenter/paper/show?paperid=6f45548cc67b39363844e7b78407dc76&site=xueshu_se&hitarticle=1 (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- Cheng, Y.; Huang, X.; Wang, G. Innovation of RT Methods Based on Ideological and Political Education. Truth Seeking 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xu, L. The Integration and Mutual Promotion of RT and Political Ethics Education in the New Era. Soc. Sci. 2020, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, W. Rethinking authenticity in tourism experience. In The Political Nature of Cultural Heritage and Tourism; Routledge: London, UK, 2017; pp. 469–490. ISBN 9781315237749. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, T.H. Emotional Experiences in RT: An Affective Practice Approach. 2024. Available online: https://theses.lib.polyu.edu.hk/handle/200/13006 (accessed on 3 March 2025).
- Lin, C. RT in China: Propaganda, Space, Commodification. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Urbana, IL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.N.; Timothy, D.J. Governance of red tourism in China: Perspectives on power and guanxi. Tour. Manag. 2015, 46, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Yin, H. The Development of Red Resources and the Coordinated Realization of Its Ideological and Political Education Functions—Taking Sichuan Garze Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture as an Example. Mao Zedong Thought Study 2015, 32, 146–150. Available online: https://www.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFD&dbname=CJFDLAST2015&filename=MSYJ201503029&uniplatform=OVERSEA&v=EW6kj3_-PP87uxeA9l34Bo1_uvGRNip6u21ljWdhGWKDKhsNYN9N_CIV_e076zRb (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- Liao, Y.; Chen, B. On the Realization of the Ideological and Political Education Value of Red Tourism in Jinggangshan. J. Nanchang Univ. (Humanit. Soc. Sci.) 2008, 39, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M. Red Tourism: A Pioneering Work in Traditional Education of Patriotism and Revolution. Truth Seeking 2010, 1, 50–51. Available online: https://xueshu.baidu.com/usercenter/paper/show?paperid=ecc3a3b1b5c435e5fdd2a3cb039c8801&site=xueshu_se (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- Xu, K.S. RT and social memory. Tour. Trib. 2016, 31, 35–42. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez Quintana, M.V.; Sanagustín Fons, M.V.; Blanco Gregory, R. Paisajes culturales como imágenes de destino: Percepción y valoración como producto turístico. Rev. Tur. Patrim. Cult. 2018, 16, 873–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.Y. Research on the Promotion of Tourism Attraction of Red Research Tourism Products in Shaanxi Province. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Arts, Management, Education and Innovation (ICAMEI 2019), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 12–14 January 2019; pp. 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Xing, H.B. Using TR to Improve the Ideological and Moral Cultivation of University Students. J. Hebei Univ. (Philos. Soc. Sci.) 2011, 36, 159–160. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, R. Give Full Play to the Ideological and Political Education Value of Red Tourism Resources. Teach. Ref. Middle Sch. Politics 2022, 113–114. Available online: https://www.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFD&dbname=CJFDLAST2022&filename=ZXZZ202236016&uniplatform=OVERSEA&v=IxCQ18NPtIjvhFkt2ceeUxaatIPxNtZbdJAtmwgob9at9STiUEfxfAWgBI3COrPg (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- Wang, J.; Xie, M. An Analysis of the Educational Function of Red Tourism Culture. China Adult Educ. 2008, 13, 62–63. Available online: https://www.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFD&dbname=CJFD2008&filename=ZCRY200813038&uniplatform=OVERSEA&v=cup-ArEKp2k_6EAreD768g8rq41ci3ahge1uH7HLfj0Rd9Q_HlL78jQmnQ7QduTX (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- Wang, H.; Xu, Q.; Zhao, D.L. The Development and Utilization of Red Resources Must Adhere to the Education Principle: Analysis of Several Adverse Phenomena. Stud. Theor. Mao Zedong Deng Xiaoping 2021, 11, 7. [Google Scholar]
- University College Dublin. Education Theory: Constructivism and Social Constructivism in the Classroom: General Overview; Open Educational Resources of UCD Teaching and Learning; University College Dublin: Dublin, Ireland, 2016; Available online: https://www.ucd.ie/t4cms/ucdtlt0019.pdf (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- Zhao, L.H.; Ren, Y. Heuristic Teaching Methods and Constructivist Learning Theory. Educ. Geol. China 2009, 1, 140–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, D.L. Research on the Integration of Red Resources and Civic and Political Education in Colleges and Universities Based on Constructivist Theory. J. Jiangsu Univ. Technol. 2021, 27, 116–122. [Google Scholar]
- Damşa, C. Knowledge Co-Construction and Object-Oriented Collaboration: A Study of Learning Through Collaborative Construction of Knowledge Objects in Higher Education. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Oslo, Oslo, Norway, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Petticrew, M.; Roberts, H. Systematic Reviews in the Social Sciences: A Practical Guide; Black Publishing: Malden, MA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Chin, J.M.; Growns, B.; Sebastian, J.; Page, M.J.; Nakagawa, S. The Transparency and Reproducibility of Systematic Reviews in Forensic Science. Forensic Sci. Int. 2022, 340, 111472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lame, G. Systematic literature reviews: An introduction. In Proceedings of the Design Society: International Conference on Engineering Design; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2019; Volume 1, pp. 1633–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, C.; Byrne, J. The Benefits of Publishing Systematic Quantitative Literature Reviews for PhD Candidates and Other Early-Career Researchers. High. Educ. Res. Dev. 2013, 33, 534–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, E.; Khoo-Lattimore, C.; Arcodia, C. A systematic literature review of risk and gender research in tourism. Tour. Manag. 2017, 58, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seuring, S.; Müller, M. From a literature review to a conceptual framework for sustainable supply chain management. J. Clean. Prod. 2008, 16, 1699–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, F.; Hu, X. Research on Red Study Tours from the Perspective of Regional Geography—Taking Baise City, Guangxi, as an Example. Teach. Ref. Middle Sch. Geogr. 2022, 3, 91–93. Available online: https://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/periodical/zxdljxck202214031 (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- Zhang, Q. The Value and Exploration of Red Research Resources in Border Areas. Teach. Ref. Middle Sch. Geogr. 2022, 5, 41–42, 45. Available online: https://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/periodical/zxdljxck202210013 (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Y. Research on the Design and Implementation of Red Study Tour Routes in Northern Shaanxi. Teach. Ref. Middle Sch. Geogr. 2022, 4, 90–91, 94. Available online: https://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/periodical/zxdljxck202208030 (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- Zhao, S. Production, Transmission, and Consumption of Red Tourism in China: A Model of the Circuit of Red Heritage and Tourism; Arizona State University: Tempe, AZ, USA, 2014; Available online: https://www.proquest.com/openview/331b4cd42c92bdedda7962054df9fc88/1?pq-origsite=gscholar&cbl=18750 (accessed on 3 March 2025).
- Jin, L.; Hu, Z. Thoughts on the Ideological and Political Education of College Students Using Red Resources. Agric. Archaeol. 2010, 6, 286–288. Available online: https://xueshu.baidu.com/usercenter/paper/show?paperid=dd195b3734a38fd03e92714b521e65d2&site=xueshu_se&hitarticle=1 (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- Lyu, L. An Analysis of Red Tourism and the Ideological and Political Education of Contemporary College Students. J. China Univ. Labor Relat. 2010, 24, 107–110. Available online: https://xueshu.baidu.com/usercenter/paper/show?paperid=94016fbf594d8fcf3a7e4c813f700a5c&site=xueshu_se (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- Yang, H.; Zou, J.H.; Zhu, H.Y. Study on the Optimization Strategy of RT in Hunan Province. Econ. Geogr. 2010, 30, 2109–2115. [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, B. RT and communist party identity in China: An empirical study based on Jinggangshan Scenic Area. Tour. Trib. 2014, 29, 60–72. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.C. New Ideas to Expand the Function of Ideological and Political Education; People Press: Beijing, China, 2006; ISBN 9787010055343. [Google Scholar]
- Olick, J. The Politics of Regret: On Collective Memory and Historical Responsibility; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2013; ISBN 9780415956833. [Google Scholar]
- Stone, P. Dark tourism and significant other death: Towards a model of mortality mediation. Ann. Tour. Res. 2012, 39, 1565–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H. The Inheritance of Red Culture in Subject Education. Teach. Ref. Middle Sch. Polit. 2022, 11, 5–6. Available online: https://xueshu.baidu.com/usercenter/paper/show?paperid=1u5n0jk0p5100cu0tk0j0vb0r6125697&site=xueshu_se&hitarticle=1 (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- Yang, Z. The Development Path of Red Tourism’s Integrated Ideological Permeability. Truth Seeking. 2011, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J. Red Tourism and Ideological and Political Education. Teach. Ref. Middle Sch. Geogr. 2021. Available online: https://www.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFD&dbname=CJFDLAST2023&filename=ZDCK202113032&uniplatform=OVERSEA&v=Kfwxy7P2BfFj4rPqKnLa21aTAavTNcqOffXpSFPCoszfBNAm8vKJGlyRZ02u-4U8 (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- Wang, W. Carrying Out Red Tourism and Promoting Patriotism Education in Colleges and Universities. China High. Educ. 2011, 22, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, W.; Li, J. Research on the Ideological and Political Education Function of Red Tourism. Teach. Ref. Middle Sch. Geogr. 2021. Available online: https://www.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFD&dbname=CJFDLAST2023&filename=ZDCK202113027&uniplatform=OVERSEA&v=Kfwxy7P2BfHHJGuBzRAiny9KlYUEwLUQois9KOaEXuUpu_vzR8MW17y7FycT0e-h (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- Gai, Y.; Li, J. The Educational Function of Red Tourism Resources. Teach. Ref. Middle Sch. Politics. 2020. Available online: https://www.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFD&dbname=CJFDLAST2021&filename=ZXZZ202016037&uniplatform=OVERSEA&v=6CZZ8QhX3f-5ydI7xkjxlj2eWvt4-h30gBELHsBqfTLdK1C6CDECCelKmDi8C8fb (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- Wang, F.; Sanagustín Fons, V.; Martínez Quintana, V. Innovations in Educational Organizations: The Case of Red Tourism in China. Int. J. Org. 2023, 141–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yorgun, İ.; Mladenova, Z. The Transformative and Political Power of Tourism for World Peace: From Past to Present. Univ. Libr. Sci. Inf. Technol. 2024, 26, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, F.; Sanagustín-Fons, V.; Martínez-Quintana, V. Red Tourism and Youth Education: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Societies 2025, 15, 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/soc15030069
Wang F, Sanagustín-Fons V, Martínez-Quintana V. Red Tourism and Youth Education: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Societies. 2025; 15(3):69. https://doi.org/10.3390/soc15030069
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Fengyi, Victoria Sanagustín-Fons, and Violante Martínez-Quintana. 2025. "Red Tourism and Youth Education: A Systematic Review of the Literature" Societies 15, no. 3: 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/soc15030069
APA StyleWang, F., Sanagustín-Fons, V., & Martínez-Quintana, V. (2025). Red Tourism and Youth Education: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Societies, 15(3), 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/soc15030069








